喉罩全身麻醉联合“圈麻”阻滞用于结肠癌手术的麻醉效果
2024-07-07傅志海陈再治马丽君曲轶涛林梅媛陈林辉
傅志海 陈再治 马丽君 曲轶涛 林梅媛 陈林辉

[摘要] 目的 观察喉罩全身麻醉联合腹部“圈麻”阻滞用于腹腔镜下结肠癌切除手术的麻醉效果。方法 选取2022年1月至2023年3月于厦门市第三医院行腹腔镜下结肠癌切除手术的患者60例,根据随机数字表法将其分为L组(喉罩全身麻醉,30例)和U组(喉罩全身麻醉联合腹部“圈麻”阻滞,30例)。记录并比较两组患者麻醉维持的丙泊酚和瑞芬太尼用量、手术完成时间、意识清醒后视觉模拟评分法(visual analogue scale,VAS)评分和舒芬太尼用量。比较两组患者术后12h的镇痛满意度。结果 两组患者的性别、年龄、体质量、身高、手术时间比较差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。U组患者的瑞芬太尼和丙泊酚总用量均显著少于L组(P<0.001);U组患者麻醉恢复室内的VAS评分显著低于L组,舒芬太尼用量显著少于L组(P<0.001)。U组患者的镇痛满意度显著高于L组(c2=6.772,P=0.031)。结论 与单一喉罩全身麻醉相比,喉罩全身麻醉联合腹部“圈麻”阻滞可减少腹腔镜下结肠癌切除手术中麻醉维持药物和麻醉恢复室内舒芬太尼的用量,改善术后镇痛满意度。
[关键词] 喉罩;腹直肌鞘阻滞;腰方肌阻滞;腹横肌平面阻滞;腹腔镜下结肠癌切除术
[中图分类号] R614 [文献标识码] A [DOI] 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9701.2024.16.010
Efficacy of laryngeal mask general anesthesia combined with“loop anesthesia” block for colon cancer surgery
FU Zhihai, CHEN Zaizhi, MA Lijun, QU Yitao, LIN Meiyuan, CHEN Linhui
Department of Anesthesiology, the Third Hospital of Xiamen, Xiamen 361100, Fujian, China
[Abstract] Objective To observe the anesthetic effect of laryngeal mask general anesthesia combined with abdominal “loop anesthesia” block in laparoscopic resection of colon cancer. Methods A total of 60 patients who underwent laparoscopic resection of colon cancer in the Third Hospital of Xiamen from January 2022 to March 2023 were selected. According to random number table method, they were divided into L group (laryngeal mask general anesthesia, 30 cases) and U group (laryngeal mask general anesthesia combined with abdominal “loop anesthesia” block, 30 cases). The dosage of propofol and remifentanil for anesthesia maintenance, time to completion of surgery, visual analogue scale (VAS) score after consciousness and sufentanil dosage were recorded and compared between two groups. The satisfaction of analgesia 12h after surgery was compared between two groups. Results There were no significant differences in gender, age, body mass, height and operation time between two groups (P>0.05). The total dosage of remifentanil and propofol in U group was significantly lower than that in L group (P<0.001). The VAS score in the anesthesia recovery room of U group was significantly lower than that of L group, and the dosage of sufentanil was significantly lower than that of L group (P<0.001). The satisfaction of analgesia in U group was significantly higher than that in L group (c2=6.772, P=0.031). Conclusion Compared with laryngeal mask general anesthesia, laryngeal mask general anesthesia combined with abdominal “loop anesthesia” block can reduce the amount of anesthesia maintenance drugs in laparoscopic colon cancer resection, reduce the amount of sufentanil in the anesthesia recovery room, and improve the satisfaction of postoperative analgesia.
[Key words] Laryngeal mask; Sheath of rectus abdominis block; Quadratus lumborum block; Transversus abdominis plane block; Laparoscopic resection of colon cancer
腹腔镜手术具有微创化、精准化等特点,目前腹腔镜下结肠癌切除手术已成为治疗结肠癌的主要方案[1-2]。传统开腹手术多采用全身麻醉联合胸段硬膜外镇痛。但硬膜外镇痛存在硬膜外血肿、肌力减退、血压降低等风险,故联合神经阻滞逐渐成为麻醉镇痛的主流[3-4]。有关腹部“圈麻”阻滞(即超声引导腹直肌鞘阻滞+双侧腰方肌阻滞+双侧肋缘下腹横肌平面阻滞)在腹腔镜下结肠癌切除手术中的研究较少。本研究拟观察喉罩全身麻醉联合腹部“圈麻”阻滞用于腹腔镜下结肠癌切除手术的麻醉效果,为腹腔镜下结肠癌切除手术提供一种全新的麻醉思路。
1 资料与方法
1.1 研究对象
选取2022年1月至2023年3月于厦门市第三医院行腹腔镜下结肠癌切除手术的患者60例。纳入标准:①美国麻醉医师协会(American Society of Anesthesiologists,ASA)分级Ⅱ~Ⅲ级;②年龄35~85岁;③常规5孔腹腔镜穿刺口。排除标准:①对局部麻醉药(罗哌卡因)过敏者;②体质量指数>28 kg/m2;③凝血功能不良者;④穿刺部位皮肤感染者;⑤长期使用镇痛药物者。根据随机数字表法将纳入患者分为U组(喉罩全身麻醉联合腹部“圈麻”阻滞)和L组(喉罩全身麻醉),每组各30例。本研究经厦门市第三医院伦理委员会批准(伦理审批号:20220901),所有患者均签署知情同意书。
1.2 麻醉方法
患者进入手术间后,静脉滴注乳酸林格液,监护生命体征:脑电双频指数(bispectral index,BIS),心电图,无创血压,心率,脉搏血氧饱和度。局部麻醉药:1%盐酸罗哌卡因(批准文号:国药准字H20227129,生产单位:瑞阳制药股份有限公司,规格:10ml∶75mg)。
L组患者麻醉诱导方案:依次注射瑞马唑仑(批准文号:国药准字H20200006,生产单位:宜昌人福药业有限责任公司,规格:25mg)0.01mg/kg,舒芬太尼(批准文号:国药准字H20205068,生产单位:宜昌人福药业有限责任公司,规格:1ml∶50μg)0.15μg/㎏,丙泊酚(批准文号:国药准字HJ20150654,生产单位:Fresenius Kabi Austria GmbH,规格:20ml∶200mg)2mg/kg,待患者睫毛反射消失后,注射罗库溴铵(批准文号:国药准字H20183106,生产单位:福安药业集团庆余堂制药有限公司,规格:5ml∶50mg)0.6mg/kg。麻醉诱导完成后置入喉罩,采用瑞芬太尼(批准文号:国药准字H20030197,生产单位:宜昌人福药业有限责任公司,规格:1mg)和丙泊酚联合静脉麻醉,维持BIS值在40~60。U组患者麻醉诱导方案同L组,诱导完成后,采用LOGIQe便携式超声(美国通用医疗公司),线阵探头6~13MHz,实施腹部“圈麻”阻滞。首先,在脐孔上、下方1cm处超声扫描找到腹直肌(前、后鞘),采用一次性神经阻滞针于超声引导下针尖到达后鞘处,注射10ml 0.25%罗哌卡因[5]。超声探头移至髂前上嵴外侧,扫描腹外斜肌、腹内斜肌、腹横肌、腰方肌和背阔肌结合处,在腰方肌外侧注射15ml 0.25%罗哌卡因[6]。最后,将超声探头移至近肋缘处,扫描腹直肌和腹横肌,在其交界处注射15ml 0.25%罗哌卡因[7]。U组患者完成“圈麻”阻滞后,麻醉维持同L组。两组患者术后于麻醉恢复室进行麻醉复苏,意识清醒后,按照视觉模拟评分法(visual analogue scale,VAS)评估切口疼痛程度,VAS评分≥3分者静脉注射舒芬太尼5~10μg。
由一名高年资麻醉医生实施喉罩麻醉和“圈麻”阻滞,在麻醉恢复室内,由另一名麻醉医生进行VAS评分和数据记录。
1.3 观察指标及数据收集
记录两组患者的丙泊酚、瑞芬太尼、舒芬太尼用量,比较两组患者的术后VAS评分和术后12h镇痛满意度。
1.4 统计学方法
采用SPSS 24.0软件对数据进行统计分析。符合正态分布的计量资料以均数±标准差(![]() )表示,比较采用t检验。计数资料以例数(百分率)[n(%)]表示,比较采用χ2检验或Fisher确切概率法。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
)表示,比较采用t检验。计数资料以例数(百分率)[n(%)]表示,比较采用χ2检验或Fisher确切概率法。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 两组患者的一般资料比较
两组患者均完成手术,两组患者的性别、年龄、体质量、身高、手术时间比较差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05),见表1。
2.2 两组患者的瑞芬太尼、丙泊酚用量比较
U组患者的瑞芬太尼总用量[(2835±404)μg vs. (3336±631)μg,t=–4.729,P<0.001]、丙泊酚总用量[(1528±279)mg vs. (2236±587)mg,t=–7.177,P<0.001]均显著少于L组。
2.3 两组患者的舒芬太尼用量和VAS评分比较
U组患者麻醉恢复室内的VAS评分显著低于L组[(0.8±0.2)分 vs. (2.9±0.5)分,t=–8.226,P<0.001],舒芬太尼用量显著少于L组[(1.3±0.4)μg vs. (7.5±2.8)μg,t=–9.950,P<0.001]。
2.4 两组患者的镇痛满意度比较
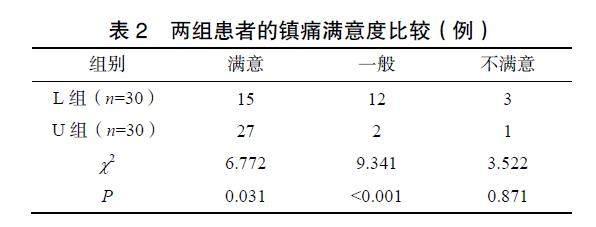
U组患者的镇痛满意度显著高于L组(c2=6.772,P=0.031),见表2。
3 讨论
与气管导管相比,喉罩对患者气道刺激小,是展现麻醉科机械通气“舒适化”的重要手段。近年来随着腹腔镜技术在基层医院的推广,开腹手术日益减少,喉罩全身麻醉联合神经阻滞是腹部手术常用的麻醉方案[8-9]。超声引导下下肢“圈麻”阻滞技术早期为危重症患者下肢手术提供麻醉方案,即超声引导下股神经、股外侧皮神经、闭孔神经、坐骨神经、股后皮神经联合阻滞。本研究在腹腔镜结肠癌切除术引入超声引导下腹部“圈麻”阻滞技术,即腹壁多处联合神经阻滞,包括腹横肌平面阻滞、腰方肌阻滞、腹直肌鞘阻滞。
本研究结果显示,U组患者麻醉维持的用量(丙泊酚和瑞芬太尼)显著少于L组。腹腔镜下结肠癌切除手术通常有5个孔,主孔多位于脐部,其余4个操作孔位于左、右侧腋前线肋缘下2cm处,左、右腹直肌外缘平脐部下5cm处。超声引导下腹部“圈麻”阻滞完全覆盖上述5孔的疼痛信号传导,即腹直肌鞘阻滞可阻断脐部和腹直肌外缘处3个孔的疼痛传导,肋缘下腹横肌平面阻滞可阻断腋前线肋缘下2个孔的疼痛传导,而腰方肌阻滞可阻断腹腔内外操作的疼痛传导,阻断疼痛传递是减少麻醉药物用量的关键所在。本研究中喉罩全身麻醉使用丙泊酚和瑞芬太尼维持,静脉维持麻醉深度使用BIS监测,维持麻醉深度相对稳定,从而保证两组患者麻醉用药的可对比性[10-11]。
多种联合神经阻滞的局部麻醉药用量常不确定,既往腹腔镜下结直肠癌手术中腹横肌平面阻滞镇痛的局部麻醉药用量多为20ml[12-13]。Cao等[14]使用腰方肌阻滞,局部麻醉药用量为25ml。多数研究在腹直肌鞘阻滞中局部麻醉药用量为10~ 20ml[15-16]。参考上述研究结果,本研究中腹直肌鞘阻滞使用0.25%罗哌卡因20ml,腰方肌阻滞使用0.25%罗哌卡因15ml,肋缘下腹横肌平面阻滞使用0.25%罗哌卡因15ml。能否减少麻醉药物剂量,还有待进一步研究。
本研究结果显示,U组患者的舒芬太尼用量显著小于L组,VAS评分显著低于L组,可能与实施腹部“圈麻”阻滞相关。腹部“圈麻”阻滞可完全覆盖腹部手术的疼痛信号传导,一般情况下神经阻滞的镇痛维持时间较镇痛药物长。全身麻醉诱导后外科切皮前实施神经阻滞可阻断痛觉等有害刺激信号传递,从而有利于术中、术后镇痛,最终减少阿片类镇痛药物的使用。不同种类的神经阻滞对腹部手术术后镇痛效果仍存在争议,阿片类镇痛药物伴有恶心、呕吐等不良反应,一定程度上影响患者对术后镇痛的满意度[17-20]。
综上所述,与单一喉罩全身麻醉相比,喉罩全身麻醉联合腹部“圈麻”阻滞可减少腹腔镜下结肠癌切除手术中静脉维持麻醉药物和麻醉恢复室内舒芬太尼的用量,提高术后镇痛满意度。
利益冲突:所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突。
[参考文献]
[1] DOWLI A, FICHERA A, FLESHMAN J. Primary colorectal cancer[J]. Surg Oncol Clin N Am, 2023, 32(1): 153–168.
[2] GROSEK J, ALES KOSIR J, SEVER P, et al. Robotic versus laparoscopic surgery for colorectal cancer: A case-control study[J]. Radiol Oncol, 2021, 55(4): 433–438.
[3] WEISS R, POPPING D M. Is epidural analgesia still a viable option for enhanced recovery after abdominal surgery[J]. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol, 2018, 31(5): 622–629.
[4] Desai N, El-Boghdadly K, Albrecht E. Epidural vs. transversus abdominis plane block for abdominal surgery-A systematic review, Meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis[J]. Anaesthesia, 2021, 76(1): 101–117.
[5] KWON H J, KIM Y J, KIM Y, et al. Complications and technical consideration of ultrasound-guided rectus sheath blocks: A retrospective analysis of 4033 patients[J]. Anesth Analg, 2023, 136(2): 365–372.
[6] UESHIMA H, OTAKE H, LIN J A. Ultrasound-guided quadratus lumborum block: An updated review of anatomy and techniques[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2017, 2017: 2752876.
[7] TRAN D Q, BRAVO D, LEURCHARUSMEE P, et al. Transversus abdominis plane block: A narrative review[J]. Anesthesiology, 2019, 131(5): 1166–1190.
[8] BHUSHAN D, NANDKUMAR S, BUTANI M. The comparison between supreme laryngeal mask airway and endotracheal tube with respect to adequacy of ventilation in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy under general anesthesia-A prospective, randomized, double-blind study, and comparative study[J]. Asian J Anesthesiol, 2022, 60(1): 2.
[9] KARAASLAN E, AKBAS S, OZKAN A S, et al. A comparison of laryngeal mask airway-supreme and endotracheal tube use with respect to airway protection in patients undergoing septoplasty: A randomized, single-blind, controlled clinical trial[J]. BMC Anesthesiol, 2021, 21(1): 5.
[10] HEAVNER M S, GORMAN E F, LINN D D, et al. Systematic review and Meta-analysis of the correlation between bispectral index (BIS) and clinical sedation scales: Toward defining the role of BIS in critically ill patients[J]. Pharmacotherapy, 2022, 42(8): 667–676.
[11] CHEW W Z, TEOH W Y, SIVANESAN N, et al. Bispectral index (BIS) monitoring and postoperative delirium in elderly patients undergoing surgery: A systematic review and Meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis[J]. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth, 2022, 36(12): 4449–4459.
[12] ALSHARARI A F, ABUADAS F H, ALNASSRALLAH Y S, et al. Transversus abdominis plane block as a strategy for effective pain management in patients with pain during laparoscopic cholecystectomy: A systematic review[J]. J Clin Med, 2022, 11(23): 6896.
[13] ZHANG Z, HAO D. Optimal dose of dexmedetomidine for preemptive analgesia combined with transversus abdominis plane block after colon cancer surgery[J]. J Nippon Med Sch, 2022, 89(4): 399–404.
[14] CAO R, LI X, YANG J, et al. The minimum effective concentration (MEC90) of ropivacaine for ultrasound- guided quadratus lumborum block for analgesia after cesarean delivery: A dose finding study[J]. BMC Anesthesiol, 2022, 22(1): 410.
[15] KIM W J, MUN J Y, KIM H J, et al. Surgical rectus sheath block combined with multimodal pain management reduces postoperative pain and analgesic requirement after single-incision laparoscopic appendectomy: A retrospective study[J]. Int J Colorectal Dis, 2021, 36(1): 75–82.
[16] FU H, FU Y, XU X, et al. Ultrasound-guided rectus sheath block combined with butorphanol for single- incision laparoscopic cholecystectomy: What is the optimal dose of ropivacaine?[J]. J Pain Res, 2020, 13(10): 2609–2615.
[17] EL-BOGHDADLY K, DESAI N, HALPERN S, et al. Quadratus lumborum block vs. transversus abdominis plane block for caesarean delivery: A systematic review and network Meta-analysis[J]. Anaesthesia, 2021, 76(3): 393–403.
[18] LIU X, SONG T, CHEN X, et al. Quadratus lumborum block versus transversus abdominis plane block for postoperative analgesia in patients undergoing abdominal surgeries: A systematic review and Meta- analysis of randomized controlled trials[J]. BMC Anesthesiol, 2020, 20(1): 53.
[19] TANGGAARD K, HASSELAGER R P, HOLMICH E R, et al. Anterior quadratus lumborum block does not reduce postoperative opioid consumption following laparoscopic hemicolectomy: A randomized, double- blind, controlled trial in an ERAS setting[J]. Reg Anesth Pain Med, 2023, 48(1): 7–13.
[20] PRIYADARSHINI K, BEHERA B K, TRIPATHY B B, et al. Ultrasound-guided transverse abdominis plane block, ilioinguinal/iliohypogastric nerve block, and quadratus lumborum block for elective open inguinal hernia repair in children: A randomized controlled trial[J]. Reg Anesth Pain Med, 2022, 47(4): 217–221.
(收稿日期:2023–08–11)
(修回日期:2024–05–02)
