数字经济背景下服装企业创新能力评价研究
2024-06-17许菱张克王耀刚钟少君
许菱 张克 王耀刚 钟少君


Research on the evaluation of the innovation ability of garment enterprises under thebackground of digital economy
摘要:
随着传统产业与数字化融合的步伐逐渐加快,数字经济的发展为服装企业提供了新的创新机遇。文章基于2016—2022年中国服装上市公司面板数据,从创新投入、创新产出、经营绩效、环境因素和数字化水平5个维度构建创新能力评价指标体系,运用全局因子分析法综合评价服装上市公司创新能力,并对中国服装上市公司创新能力总体状况进行分析。研究认为,研发投入和专利产出是提高服装上市公司创新能力的关键要素;中国服装上市公司整体创新能力处于中下游水平;不同上市公司创新能力之间存在较大差异;上市公司整体数字化水平较好。最后,文章从企业和政府2个方面提出相应的对策建议。
关键词:
创新能力评价;服装上市公司;全局因子分析;影响因素;数字经济;数字化水平
中图分类号:
TS101.1; F424.3
文献标志码:
A
文章编号: 1001-7003(2024)06-0013-10
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7003.2024.06.002
收稿日期:
20231201;
修回日期:
20240429
基金项目:
江西省教育厅科学技术研究项目(GJJ2200833);赣州市同心圆智库2023年度第一批重点课题项目(TXYZK20230105)
作者简介:
许菱(1970),女,教授,主要从事产业经济、创新管理的研究。
在数字经济快速发展的背景下,以云计算、物联网、数字孪生等为代表的信息技术全面嵌入服装产业,服装产业正在实现从设计到售后的全产业链的快速重组。目前,中国服装行业作为劳动密集型产业,正面临成本优势逐渐减弱、市场收缩、高端产品开发和制造能力薄弱等困境。加快技术融合步伐,提升创新能力,推进产业链、价值链高端化以应对发展困境日益成为业界和学界共识,乃至政府决策关注的重点。
服装上市公司是中国服装行业的龙头企业,是行业技术进步和创新发展的重要力量,其发展水平会对产业发展程度有直接的影响。通过全面科学地评价服装上市公司的创新能力,不仅可以让企业了解自身的优势和不足,据此完善企业的发展战略,提高企业的核心竞争力,还可以对服装产业总体层面的创新能力有前瞻性的把握。因此,对服装上市公司创新能力进行合理的评价具有一定的理论意义和现实价值。
1 相关研究综述
Burns & Stalker于1961年首次提出创新能力的概念,随
后的文献大体上从企业、区域、国家三个层面对创新能力进行诠释[1]。具体到企业创新能力,其内涵经历了“能力—核心能力—吸收和动态能力—创新能力”的演进过程[2]。对于服装企业,其创新指实现一种服装行业未曾出现过的生产要素和生产条件的“新组合”,具体为开发新产品、使用新生产工艺、研发新面料、实行新组织形式等[3]。数字经济时代,在大数据、人工智能、工业互联网等数字技术的驱动下,服装企业的创新过程逐步从知识积累、研发设计延伸到生产应用、推广销售为一体的全流程模式[4]。许多消费者的新思想和新数据能够便捷地传递至研发部门[4],研发与生产、厂商与消费者的边界日益模糊,服装企业的创新过程逐渐融为一体[5]。因此,本文认为服装企业创新能力是一种综合能力,它能够有效整合内外部创新资源,实现服装企业的创新目标[6]。
目前国内外学者和从业者从多个视角建立企业创新能力评价指标体系,并使用不同方法开展评价。其中,创新内涵、创新过程和创新系统3种视角较为常见,如表1所示。
在评价方法的选择上,学者们主要选择因子分析法[14]、熵权法[15]、灰色关联分析[16]、数据包络分析[17]、TOPSIS模型[18]、层次分析法[19]等对企业数据进行处理。无论是主观的还是客观的单一评价方法,都有各自的优点和缺陷。如因子分析等是基于绝对量进行分析,易导致片面追求高产出的误区[20];数据包络分析基于客观数据,进行多投入及多产出的相对效率评价,但存在权重不唯一的问题[21]。很多学者为了得出更科学的结论,他们逐渐采用以一种评价方法为主、其他方法为辅的综合评价方法,如将层次分析法分别与神经网络[22]和熵权法[23]相结合、因子分析与聚类分析相结合[24]、熵权法与TOPSIS法相结合[12]等。
在研究对象上,近年来研究纺织服装企业创新能力的文献较少。魏巍[25]从内外部环境和投入产出4个角度构建评价指标体系,建立评价模型,并以浙江某纺织企业为例验证了有效性。薛岩松等[26]使用随机层次分析法对3家纺织企业技术创新能力进行了评估。以上研究成果为本文研究提供了有益参考,但仍存在权重设计主观性较强及样本量不足的问题。2016年中国服装产业进入深度转型升级的发展时期,服装企业已开始主动拥抱数字经济,创新过程逐渐发生变化。在新时期,服装企业的创新能力水平如何?在前人的研究中并没有回答这个问题。基于以上内容,本文构建服装上市公司创新能力评价指标体系,通过客观赋权法全局因子分析对25家样本服装企业展开综合评估,从整体上了解中国服装企业的创新能力水平,为提高服装企业创新能力提供支持。
2 建立评价指标体系和研究方法选择
2.1 评价指标体系构建
综合国内外学者的研究,结合服装企业的特征,依据科学性、客观性、可行性、真实性等原则,构建服装上市公司创新能力评价指标体系。指标体系由1个目标层、5个一级指标和15个二级指标组成,如表2所示。
2.1.1 创新投入
参考邵争艳等[27]的做法,将创新投入分为经费投入及人力投入的总量和比值。通过总量反映创新投入的总规模,通过比值反映企业创新投入的力度,在一定程度上避免了不同企业规模带来的差异性影响。
2.1.2 创新产出
专利授权数量是企业研发最直观的成果之一。同时,无形资产是企业核心竞争力的组成部分[28],是以知识技术形态存在的经济资源[29],是创造公司价值和绩效的重要资源。因此,参考郑通等[30]和倪洁等[24]的做法,选取当年授权专利数量和无形资产比率2个指标来衡量创新产出。
2.1.3 经营绩效
一方面,研发创新是企业资产不断提高的动力,而企业资产在一定程度上为创新的开展提供了物质基础。另一方面,良好的盈利能力保障了企业创新活动的可持续性。因此,参考肖淑芳等[28]和郑通等[30]的做法,使用总资产同比增减、营业收入同比增减和营业利润率3项指标衡量企业经营绩效。
2.1.4 环境要素
外部经营环境是对企业创新活动产生影响的客观因素。借鉴邵争艳等[27]的研究,选取政府补助、地区发展水平、地区开放程度和地区科研环境4个指标来衡量不同省市的经营环境。政府补助:将公司年报披露的政府补贴金额定义为政府补助;地区发展水平:用各省市人均GDP衡量公司所处地区的发展水平;地区开放程度:将企业所处省市进出口额与GDP的比值衡量地区开放程度;地区科研环境:用各省市科学技术支出衡量地区科研环境[27]。
2.1.5 数字化水平
数字经济时代下,产业数字化作为主阵地,在微观层面表现为企业数字化[31]。企业数字化指企业应用与融合各类数字技术的过程。刘树林等[32]以341家中国A股上市公司为研究对象,研究了企业数字化对创新能力的影响,发现其能够显著驱动创新能力的提升,而且该驱动作用具有持续性。以往学者大多将企业数字化水平作为创新能力的影响因素展开分析,较少用于创新能力评价中,因此本文将其应用于企业创新能力评价中,以此探究企业数字化水平对创新能力的支持作用[12]。本文在已有研究的基础上,从设备和人员2个角度衡量企业的数字化水平[33]。对于企业在设备方面的数字化水平,本文借鉴张永坤等[34]的做法,使用“数字化技术无形资产净额除以总资产”衡量。具体地,当上市公司财务报表附注披露的无形资产明细项中包含“软件、网络、智能平台”等与数字化技术相关的关键词及有关的专利时,将此项目界定为数字化技术无形资产,最后对同一公司相同年份多项数字化技术无形资产的期末净值进行加总[34]。对于企业在人员方面的数字化水平,本文借鉴谢绚丽等[35]的做法,使用“信息科技背景的高管在高管团队中占比”衡量。具体地,通过教育背景和工作经历展开判断。其中教育背景根据其简历中介绍的所学专业是否涉及信息、智能、软件、网络等进行判断;工作经历根据其简历中的任职经历是否包含信息科技公司任职,或分管研发中心等信息科技部门、担任信息总监进行判断[35]。
2.2 方法选择
本文选择的15项指标均为定量指标,适用客观赋权法开展分析,包括数据包络分析、熵权法、神经网络等。其中因子分析法将错综复杂的变量聚合为少数几个独立且不能直接测量的公因子,这些公因子可以反映15项变量的主要信息,各公因子按照所对应的方差贡献率比例确定权重。但因子分析法只能分析截面数据,不适用于面板数据。
全局因子分析是在因子分析的基础上,增加时间序列维度,能够对面板数据进行分析。企业开展创新活动一般需要较长的时间,使用多年的数据进行分析可以更准确地体现创新能力的真实水平。所以,本文使用全局因子分析法展开创新能力综合评估。根据得出的结果,可比较纺织服装上市公司创新能力的大小。
3 数据来源及计算结果分析
3.1 样本选取与数据来源
在样本选择方面,上市公司竞争力强、发展潜力大,是服装行业的成功代表,故选择上市公司作为研究对象。选择的样本企业是根据《国民经济行业分类》划分的,参考赵君丽等[36]的研究,选择前两位代码为18的公司,即“纺织服装与服饰业”。
从时间尺度上看,2016年纺织服装产业开始进行深度转型升级,故选择的样本时间为2016—2022年。
在数据选择上,排除期间有退市风险、年报未披露、终止上市的企业后,选择25家服装上市公司,4年总计100组样本数据。专利数据来自中国研究数据服务平台,地区发展水平、地区开放程度和地区科研环境指标数据来自各省市政府网站,企业数字化水平相关数据来自服装上市公司年报,剩余指标来自国泰安数据库。对于各省市科学技术支出和数字化技术无形资产净额中的缺失值,使用线性插值法进行补充。
3.2 KMO和Bartlett球形检验结果
进行KMO和巴特利特球形检验,其中KMO的值为0.583,大于0.500,表明各项指标之间有关联性,适合进行因子分析;同时,Bartlett检验的P值为0.000,小于0.005,数据呈球形分布,符合因子分析的条件。
3.3 计算结果分析
3.3.1 纺织服装企业创新能力影响因素分析
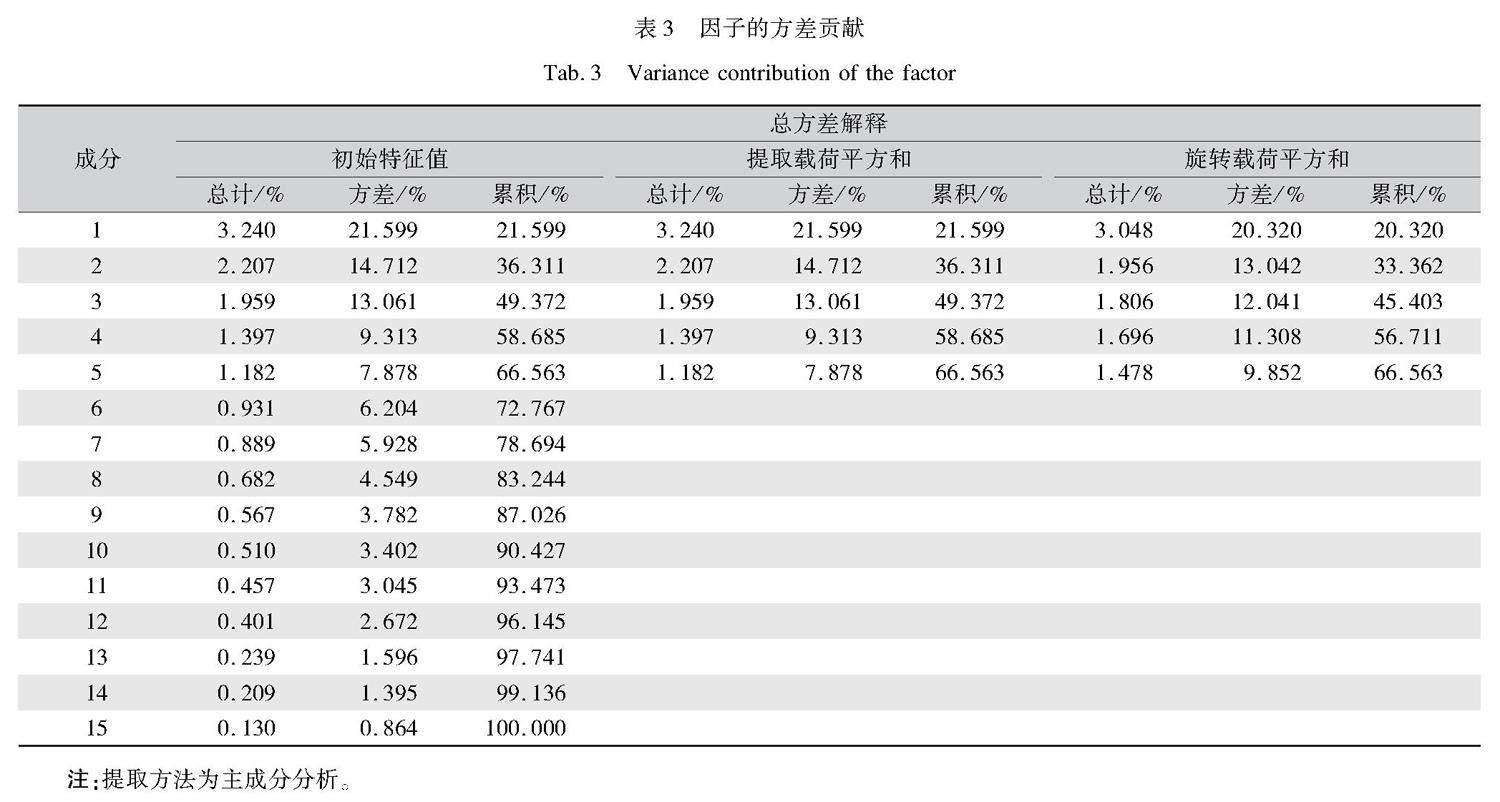
使用SPSS对15项指标数据展开全局因子分析,将特征值大于1为标准来选择公因子,得出对服装上市公司创新能力产生影响的主要因素,如表3所示。由表3可以看出,累积方差贡献率为66.563%。根据因子分析理论,只要主因子能够反映60%以上的方差贡献率即可[37],故这5个主因子是影响服装上市公司创新能力的主要因素。
通过旋转成分矩阵(表4)可得到15个指标在不同主因子上的分布状况。由表4可知,第一个因子与研发经费、研发人员数量、当年授权专利数量和政府补助相关性较高,命名为研发投入和专利产出因子(F1)。第二个因子在总资产同比增减、营业收入同比增减和营业利润率上载荷高,命名为企业成长因子(F2)。第三个因子与各省市进出口额与GDP的比值、各省市人均GDP和信息科技背景的高管在高管团队中占比相关性较高,命名为经营环境和数字化人才因子(F3)。第四个因子在研发经费占营业收入比例和研发人员占员工总数比例上载荷高,命名为研发投入强度因子(F4)。第五公因子与数字化技术无形资产净额除以总资产、无形资产比率和各省市科学技术支出相关性较高,命名为地区科研环境和设备数字化水平因子(F5)。由表4还可以得知,研发投入和专利产出因子的方差贡献率最高,表明其对创新能力的影响程度最高,且这些公因子的方差贡献率都大于0,说明其正向影响创新能力。
3.3.2 服装上市公司创新能力分析
使用SPSS软件进行全局因子分析会自动将变量数据标准化,且会得到5个公因子F1~F5的值。之后将5个公因子各自方差贡献率占5个公因子累积方差贡献率的比例作为权重,对这5个公因子进行加权平均,计算出企业创新能力综合得分,即可对中国服装上市公司创新能力进行综合评估,具体计算公式为:
F=0.305×F1+0.196×F2+0.181×F3+0.17×F4+0.148×F5(1)
25家样本公司2016—2022年各公因子和综合因子的平均得分和排名情况如表5所示。选择每家公司2016—2022年的平均值,可以体现公司在此时期内的创新能力大小。0代表平均水平,得分大于0说明创新能力高于平均水准。各公司综合因子平均得分越高,说明创新能力越强。
具体分析如下:
第1个公因子F1为研发投入和专利产出因子,25家服装上市公司中,F1大于0.000的有8家,说明该因子得分高于平均水平的有8家,占32%。排在前3名的分别是际华集团、森马服饰和伟星股份,在研发投入规模、专利数量等方面位于领先地位,说明这3家企业重视科技创新,专利产出能力强。
第2个公因子F2为企业成长因子,25家服装公司中,F2大于0.000的有12家,表明该因子得分高于平均水平的有12家,占48%。排在前3名的分别是比音勒芬、歌力思和锦泓集团,在营业收入同比增减、营业利润率等方面位于领先地位。其中比音勒芬的营业收入等一直处于增长态势,这表明该企业成长性强,具有强劲的经营韧性,成为坚持长期主义的模范企业。
第3个公因子F3为经营环境和数字化人才因子,25家服装公司中,F3大于0.000的有11家,表明该因子得分高于平均水平的有11家,占44%。其中嘉麟杰、际华集团和比音勒芬排名前3,这些企业在数字化管理、应用和技术人才建设方面取得了较好的成效。同时,这3家企业分别位于上海、北京和广东,说明这3个地区的发展水平和开放程度处于国内较高水平。
第4个公因子F4为研发投入强度因子,25家服装公司中,F4大于0.000的有13家,表明该因子得分高于平均水平的有13家,占52%。排在前3名的分别是森马服饰、探路者和锦泓集团,这3家企业的人员和经费投入力度较高,这也成为企业持续激发创新活力和增强创新能力的坚实保障。
第5个公因子F5为地区科研环境和设备数字化水平因子,25家服装公司中,F5大于0.000的有13家,表明该因子得分高于平均水平的有13家,占52%。排在前3名的分别是歌力思、锦泓集团和金发拉比,其中歌力思以2.536的得分远超其他企业,在数字科技创新、数据中台体系建设等方面卓有成效,设备数字化程度较高。同时,这3家企业位于广东和江苏,表明这2个省份的科学技术支出处于国内较高水平。
综合因子F得分为企业创新能力得分,由表5可知,际华集团的创新能力得分最高,为1.251,在代表创新投入、专利产出和数字化人才的因子上名列前茅,这说明该企业重视创新能力的培养,投入大量资源开展创新活动,对不同类型的数字化人才展开培训,同时样本期内每年至少有三百多项专利获授权,创新成果较多。排在前3名的分别为际华集团、歌力思和锦泓集团,这3家企业的研发经费、研发人员数量、数字化人才比重等位于前列,创新能力较强。综合因子F得分大于0.000的有8家,表明25家服装上市公司创新能力高于平均水平的有8家,占32%,可见中国多数服装上市公司创新能力的提升有较大空间。
3.3.3 各公因子和综合因子变化趋势分析
计算2016—2022年各公因子及综合因子得分平均值,分析因子变化趋势,探究25家服装上市公司整体状况,如表6所示。
由表6可知,样本期间综合因子平均得分逐渐减少到负数,可以看出样本服装企业整体创新能力呈现逐年下降的趋势,总体水平较低。从各公因子平均得分变化趋势来看,研发投入和专利产出因子在波动中呈现下降趋势,平均得分一直小于0.000,这表明服装上市公司整体的研发投入规模、专利产出等表现较差;企业成长因子和研发投入强度因子呈现持续下降的趋势,说明财务状况整体呈现低迷状态,经费和人员投入强度偏低;经营环境和数字化人才因子平均得分在波动中下降,但一直大于0.000,可以看出各省市人均GDP、开放程度和员工数字化程度整体水平较好;地区科研环境和设备数字化水平因子则呈现持续上升的趋势,这说明地区财政科学技术支出越来越高,服装上市公司在服装设计、制造等环节使用数字系统越来越频繁。
4 建 议
本文结合目前服装企业的发展状况,提出以下建议:
1) 在企业方面:第一,建议处于领头羊的企业需具备供应链核心企业的担当,除了在自身供应链生态圈中让链上各企业能够分享数字化应用的红利,同时肩负起将数字化技术全链推进的重担,让更多的企业分享数字化技术应用成果。第二,创新能力较弱的企业则可根据自身实际情况增加创新资源投入、完善创新激励机制,同时积极与供应商、客户、高校、行业协会、研究机构等开展数字化创新合作,利用外部资源提高创新效率,增强企业竞争力。最后,由于数字化技术在企业制造环节和管理方面的不断深入应用,势必推动企业组织架构的优化、业务流程的再造,这需要企业决策层具备创新的勇气。
2) 在政府方面:第一,不断完善鼓励企业科技创新的奖励机制,出台多元化扶持政策。如针对企业逐年增加研发投入、有效专利申请增加、在服装制造环节拓展数字化技术应用等方面给出具体的激励措施。第二,不断提升服装行业专利申请服务的水平,营造较好的创新氛围,尽快构建服装制造企业、服装装备企业、信息科技企业、专利服务咨询机构的多方协同平台。第三,依托行业协会和专业学会搭建行业内的数字化创新交流平台,让相关各方共享现有服装行业数字化创新的成就,共商全产业链数字化创新合作的可能。最后,加快推进服装行业中各类型专业市场、产业园区的信息技术基础设施建设,提供强有力的数字化应用硬件支撑。
5 结 论
本文基于2016—2022年25家中国服装上市公司面板数据,构建创新能力评价指标体系,运用全局因子分析法展开分析与评价,得出研究结论如下:
1) 研发投入和专利产出是影响服装上市公司创新能力的关键要素。大规模的研发投入可以确保企业有充足的人力物力开展创新活动,也将加快新产品和新技术的开发速度。同时专利的产出代表着新成果的出现,既能为企业带来商业收益,也能提高企业竞争力。另外企业成长等因素对创新能力也呈正向影响。当前数字化水平不足以成为影响创新能力的关键因素,但随着数字技术在创新活动中的应用程度不断提高,数字化水平对创新能力的影响作用也将进一步增强。
2) 25家服装上市公司整体创新能力还处于中下游水平,两极分化稍显严重;不同上市公司的创新能力之间具有较大差异,如锦泓集团的公因子得分几乎都位于前列,体现出领头羊企业的特征;但九牧王在整体上稍显逊色。部分企业数字化创新的侧重点在于产品研发方面,能够积极利用数字技术收集市场信息,快速推进新产品的研发工作,提高创新效率,如森马服饰具有完善的客户之声机制,积极收集消费者的问题反馈,并运用自有数字化研发技术,快速满足客户需求,而有些企业在该方面稍显滞后。在数字化设备和数字化人才建设方面,样本企业整体水平较好,可以看出这些企业在数字化转型过程中都有各自独特的组织架构与技术优化,能够快速响应市场的变化和消费者的需求。
本文从创新投入、创新产出、经营绩效、环境因素和数字化水平5个方面对服装上市公司的创新能力展开评价,发现创新能力受到研发投入、专利产出、企业成长、经营环境和数字化人才、地区科研环境和设备数字化水平的影响。后续研究可从更多角度测度设备数字化水平,如数字化固定资产加数字化无形资产再除以总资产等。
参考文献:
[1]张国良, 陈宏民. 关于组织创新性与创新能力的定义、度量及概念框架[J]. 研究与发展管理, 2007(1): 42-50.
ZHANG G L, CHEN H M. Organizational innovativeness and innovative capability: A research on definition, measurement, and conceptual framework[J]. R&D Management, 2007(1): 42-50.
[2]陈力田, 赵晓庆, 魏致善. 企业创新能力的内涵及其演变: 一个系统化的文献综述[J]. 科技进步与对策, 2012, 29(14): 154-160.
CHEN L T, ZHAO X Q, WEI Z S. The connotation and evolution of enterprise innovation capability: A systematic literature review[J]. Science & Technology Progress and Policy, 2012, 29(14): 154-160.
[3]彭纪生, 刘伯军. 技术创新理论探源及本质界定[J]. 科技进步与对策, 2002(12): 101-103.
PENG J S, LIU B J. Origin and essence definition of technological innovation theory[J]. Science & Technology Progress and Policy, 2002(12): 101-103.
[4]肖翔, 王晋梅, 董香书. 数字化转型如何影响制造业实质性创新? 基于“数字赋能”与“数字鸿沟”的视角[J]. 浙江大学学报(人文社会科学版), 2023, 53(10): 28-50.
XIAO X, WANG J M, DONG X S. How does digital transformation affect substantial innovation in manufacturing? Based on the perspectives of “digital empowerment” and “digital divide”[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Humanities and Social Sciences), 2023, 53(10): 28-50.
[5]NAMBISAN S, LYYTINEN K & MAJCHRZAK A, et al. Digital innovation management: Reinventing innovation management research in a digital world[J]. Mis Quarterly, 2017, 41(1): 223-238.
[6]王黎娜, 龚建立, 温瑞珺, 等. 创新模型选择与自主创新能力提升机理研究[J]. 科技进步与对策, 2006(7): 5-7.
WANG L N, GONG J L, WEN R J, et al. Research on the selection of innovation model and the improvement mechanism of independent innovation ability[J]Science & Technology Progress and Policy, 2006(7): 5-7.
[7]王胜兰, 魏凤, 牟乾辉. 企业技术创新能力评价新方法的研究[J]. 运筹与管理, 2021, 30(6): 198-204.
WANG S L, WEI F, MOU Q H. Research on new evaluation method of enterprises technology innovation ability[J]. Operations Research and Management Science, 2021, 30(6): 198-204.
[8]张玉娟, 汤湘希. 基于熵值-突变级数法的企业创新能力测度: 以创业板上市公司为例[J]. 山西财经大学学报, 2017, 39(8): 15-27.
ZHANG Y J, TANG X X. Research on the measurement of enterprise innovation capacity based on entropy and catastrophe progression methods: A case study of listed companies on gem[J]. Journal of Shanxi University of Finance and Economics, 2017, 39(8): 15-27.
[9]CASTELA B, FERREIRA F, FERREIRA J, et al. Assessing the innovation capability of small-and medium-sized enterprises using a non-parametric and integrative approach[J]. Management Decision, 2018, 56(6): 1365-1383.
[10]谢婼青, 朱平芳. 中国工业上市公司创新能力评价研究[J]. 社会科学, 2020(2): 40-51.
XIE R Q, ZHU P F. Research on the evaluation of Chinese industrial listed companies innovation ability based on a subjective and objective comprehensive weighting method[J]. Journal of Social Sciences, 2020(2): 40-51.
[11]GU W, SAATY T, WEI L. Evaluating and optimizing technological innovation efficiency of industrial enterprises based on both data and judgments[J]. International Journal of Information Technology and Decision Making, 2018, 17(1): 9-43.
[12]石薛桥, 齐晓秀. 山西上市公司技术创新能力评价: 基于改进熵权TOPSIS法[J]. 经济问题, 2016(9): 112-115.
SHI X Q, QI X X. Research on technological innovation capability evaluation of listed corporation in Shanxi province: Based on TOPSIS and the improved entropy method[J]. On Economic Problems, 2016(9): 112-115.
[13]肖叶黎, 刘纯阳. 农业上市企业创新能力评价及其区域差异研究: 基于我国56家农业上市企业的面板数据[J]. 科技管理研究, 2021, 41(21): 30-37.
XIAO Y L, LIU C Y. Evaluation of innovation ability of listed agricultural enterprises and study on its regional difference based on the panel data of 56 listed agricultural enterprises in China[J]. Science and Technology Management Research, 2021, 41(21): 30-37.
[14]张治河, 王艳伟, 阎亮, 等. 上市公司创新能力评价研究: 来自陕西省41家上市公司的数据[J]. 科研管理, 2016, 37(3): 81-92.
ZHANG Z H, WANG Y W, YAN L, et al. A research on the innovation ability of listed companies based on the data of 41 listed companies in Shaanxi[J]. Science Research Management, 2016, 37(3): 81-92.
[15]王影, 梁祺. 基于广义最大熵原理的上市公司技术创新能力评价[J]. 科技管理研究, 2006(10): 195-197.
WANG Y, LIANG Q. Evaluation of technological innovation capability of listed companies based on generalized maximum entropy principle[J]. Science and Technology Management Research, 2006(10): 195-197.
[16]李广凯, 曾森, 王杰峰, 等. 基于G2-GRA的电力企业创新竞争力评价模型及实证研究[J]. 科技管理研究, 2019, 39(15): 56-62.
LI G K, ZENG S, WANG J F, et al. Evaluation model and empirical research of innovative competitiveness of electric power enterprises based on G2-GRA[J]. Science and Technology Management Research, 2019, 39(15): 56-62.
[17]童泽望. 湖北省上市企业技术创新效率评价[J]. 统计与决策, 2019, 35(18): 185-188.
TONG Z W. Evaluation of technological innovation efficiency of listed companies in Hubei province[J]. Statistics & Decision, 2019, 35(18): 185-188.
[18]符峰华, 尹正江, 唐纯武. 基于CL-TOPSIS法的我国高技术企业技术创新能力评价研究[J]. 科学管理研究, 2018, 36(3): 68-71.
FU F H, YI Z J, TANG C W. Research on the evaluation of innovation capability of high-tech enterprise in China based on CL-TOPSIS[J]. Scientific Management Research, 2018, 36(3): 68-71.
[19]俞健飞, 石学彬. 基于层次分析法的农机装备企业创新能力评价研究[J]. 科学管理研究, 2022, 40(6): 100-106.
YU J F, SHI X B. Research on the evaluation of innovation ability of agricultural machinery equipment manufacturing enterprises based on AHP[J]. Scientific Management Research, 2022, 40(6): 100-106.
[20]苏屹, 刘艳雪. 国内外区域创新研究方法综述[J]. 科研管理, 2019, 40(9): 14-24.
SU Y, LIU Y X. A literature review on the regional innovation research methods[J]. Science Research Management, 2019, 40(9): 14-24.
[21]王庆, 郑彩玲, 刘学鹏. 统一组织管理下的单元效率排序研究: 一种基于DEA的方法[J]. 预测, 2015, 34(3): 65-69.
WANG Q, ZHENG C L, LIU X P. Ranking efficiency of units under a central organization: A modified DEA method[J]. Forecasting, 2015, 34(3): 65-69.
[22]李素英, 王贝贝, 冯雯. 基于AHP-BP的科技型中小企业创新能力评价研究: 以京津冀创业板上市公司数据为样本[J]. 会计之友, 2017(24): 60-64.
LI S Y, WANG B B, FENG W. Research on the evaluation of innovation ability of small and medium-sized technology-based enterprises based on AHP-BP: Taking the data of listed companies in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei GEM as samples[J]. Friends of Accounting, 2017(24): 60-64.
[23]夏文飞, 苏屹, 支鹏飞. 基于组合赋权法的高新技术企业创新能力评价研究[J]. 东南学术, 2020(3): 153-161.
XIA W F, SU Y, ZHI P F. A research on evaluation of innovation ability of high-tech enterprises based on combination weighting method[J]. Southeast Academic Research, 2020(3): 153-161.
[24]倪洁, 赵醒村. 科创版首批上市企业创新能力评价研究[J]. 科技管理研究, 2020, 40(17): 13-18.
NI J, ZHAO X C. A research on the evaluation of technological innovation ability of the first listed enterprises of the science and technology innovation board[J]. Science and Technology Management Research, 2020, 40(17): 13-18.
[25]魏巍. 纺织企业自主创新能力评价研究[J]. 科技管理研究, 2012, 32(3): 8-11.
WEI W. Research on independent innovation evaluation of spinning and weaving enterprises[J]. Science and Technology Management Research, 2012, 32(3): 8-11.
[26]薛岩松, 卢福强. 基于随机层次分析法的纺织企业技术创新能力评价[J]. 工业技术经济, 2012, 31(1): 113-119.
XUE Y S, LU F Q. SAHP based evaluation of technology innovation in textile enterprise[J]. Journal of Industrial Technological and Economy, 2012, 31(1): 113-119.
[27]邵争艳, 赵亚楠. 纺织服装企业三阶段DEA创新绩效评价及对策研究[J]. 北京服装学院学报(自然科学版), 2022, 42(1): 74-80.
SHAO Z Y, ZHAO Y N. Innovation performance evaluation and strategies of textile and garment enterprises based on three-stage DEA[J]. Journal of Beijing Institute of Fashion Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 42(1): 74-80.
[28]肖淑芳, 石琦, 张一鸣. 上市公司创新能力指数的构建[J]. 北京理工大学学报(社会科学版), 2020, 22(1): 57-69.
XIAO S F, SHI Q, ZHANG Y M. The construction of listed companies innovation capability index[J]. Journal of Beijing Institute of Technology (Social Sciences Edition), 2020, 22(1): 57-69.
[29]崔也光, 赵迎. 我国高新技术行业上市公司无形资产现状研究[J]. 会计研究, 2013(3): 59-64.
CUI Y G, ZHAO Y. Current situation of intangible assets of high-tech corporations in China[J]. Accounting Research, 2013(3): 59-64.
[30]郑通, 胡金玉, 张立杰. 纺织服装企业科技创新效率及影响因素研究[J]. 北京服装学院学报(自然科学版), 2023, 43(4): 106-112.
ZHENG T, HU J Y, ZHANG L J. Research on technological innovation efficiency and influencing factor of textile and clothing enterprise[J]. Journal of Beijing Institute of Fashion Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2023, 43(4): 106-112.
[31]陈小辉, 张红伟, 陈文. 企业数字化如何影响企业杠杆率?[J/OL]. 中国管理科学: 1-13. (2022-12-02)[2024-01-02]. https://doi.org/10.16381/j.cnki.issn1003-207x.2021.0936.
CHEN X H, ZHANG H W, CHEN W. How does enterprise digitalization affect enterprise leverage?[J/OL]. Chinese Journal of Management Science: 1-13. (2022-12-02)[2024-01-02]. https://doi.org/10.16381/j.cnki.issn1003-207x.2021.0936.
[32]刘树林, 李梦洁, 胡苏敏. 企业数字化对技术创新能力的影响机制[J]. 现代管理科学, 2022(3): 109-117.
LIU S L, LI M J, HU S M. The influence mechanism of enterprise digitization on technological innovation capability[J]. Modern Management Science, 2022(3): 109-117.
[33]王永进, 匡霞, 邵文波. 信息化、企业柔性与产能利用率[J]. 世界经济, 2017, 40(1): 67-90.
WANG Y J, KUANG X, SHAO W B. Information, firms flexibility and capacity utilization[J]. The Journal of World Economy, 2017, 40(1): 67-90.
[34]张永坤, 李小波, 邢铭强. 企业数字化转型与审计定价[J]. 审计研究, 2021(3): 6
ZHANG Y K, LI X B, XING M Q. Enterprise digital transformation and audit pricing[J]. Auditing Research, 2021(3): 62-71.
[35]谢绚丽, 王诗卉. 中国商业银行数字化转型: 测度、进程及影响[J]. 经济学(季刊), 2022, 22(6): 1937-1956.
XIE X L, WANG S H. Digital transformation of commercial banks in China: Measurement, progress and impact[J]. China Economic Quarterly, 2022, 22(6): 1937-1956.
[36]赵君丽, 王芳芳. 环境规制对中国纺织产业升级的影响研究[J]. 生态经济, 2017, 33(6): 78-84.
ZHAO J L, WANG F F. Impact of environmental regulation on the upgrading of Chinas textile industry[J]. Ecological Economy, 2017, 33(6): 78-84.
[37]曾凡付, 彭晨明, 吕朋悦, 等. 创新型企业成长性评价研究[J]. 新疆社会科学, 2016(1): 31-38.
ZENG F F, PENG C M, L P Y, et al. Research on the growth evaluation of innovative enterprises[J]. Social Science in Xinjiang, 2016(1): 31-38.
Research on the evaluation of the innovation ability of garment enterprises under thebackground of digital economy
ZHANG Chi, WANG Xiangrong
XU Ling1,2, ZHANG Ke1, WANG Yaogang1, ZHONG Shaojun1,2
(1.School of Economics and Management, Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, Ganzhou 341000, China;2.Ganzhou High-Quality Development Research Institute, Ganzhou 341000, China)
Abstract:
In the context of the rapid development of the digital economy, information technologies represented by cloud computing, Internet of Things, and digital twins are fully embedded in the garment industry. The garment industry is rapidly reorganizing the entire industrial chain from design to after-sales. At present, Chinas garment industry, as a labor-intensive industry, is facing the dilemma of gradually weakening cost advantages, market contraction, weak high-end product development and manufacturing capabilities. Accelerating the pace of technology integration and improving the innovation ability of garment enterprises to cope with the development dilemma has increasingly become the consensus of the industry and academia, and even the focus of government decision-making. By combing the literature, it is found that there is little literature on the evaluation of innovation ability of textile and garment enterprises, and there are problems of strong subjectivity in the evaluation process and insufficient sample size. At the same time, driven by digital technologies such as big data, artificial intelligence and industrial Internet, the innovation process of garment enterprises is gradually integrated, and a new index system needs to be constructed to evaluate their innovation ability.
To promote the technological progress and innovation development of clothing enterprises, this paper took Chinas listed clothing companies as the research object, analyzed the main factors affecting the innovation ability, measured the level of innovation ability, and evaluated the innovation ability. The research time interval is from 2016 to 2022. Through the analysis of the relevant literature in the field of textile and garment, this paper chose the listed companies in the textile and garment industry. After excluding the enterprises with delisting risk, undisclosed annual report and termination of listing during the sample period, this paper selected 25 sample enterprises that have survived. In terms of evaluation methods, global factor analysis has the advantage of objective results in dealing with multi-dimensional and multi-index index system, which meets the needs of research. Therefore, this paper introduced the dimension of digital level and constructed the evaluation index system of innovation ability of listed clothing companies, which contains 15 indicators in five dimensions: innovation input, innovation output, business performance, environmental factors and digital level. Based on the panel data of 25 listed Chinese clothing companies from 2016 to 2022, the global factor analysis method was used to aggregate 15 quantitative indicators into five common factors. The weights of these common factors were determined according to the corresponding variance contribution rate, and then the scores of each common factor were weighted and averaged to obtain the innovation ability score. After obtaining the score of enterprise innovation ability, the average scores of common factors and comprehensive factors of sample enterprises were calculated to explore the overall level of innovation ability. Three major conclusions were drawn. First, R&D investment and patent output, enterprise growth, business environment and digital talents, regional scientific research environment and equipment digitization level positively affected the innovation ability of listed clothing companies. Among them, R&D investment and patent output had the highest variance contribution rate of 20.32%, which was the key factor affecting innovation ability. Second, during the sample period, the average score of innovation ability continued to decrease from 0.003 to -0.011, indicating that the overall innovation ability of listed clothing companies was still at the middle and lower levels. Third, the average score of business environment and digital talent factor decreased from 0.024 to 0.020 in fluctuation, while the average score of regional scientific research environment and equipment digitization level factor continued to rise from -0.002 to 0.013, indicating that the overall level of digitization of sample enterprises was good. Finally, this paper put forward four major suggestions. First, the core enterprises of the supply chain need to enable the enterprises on the chain to share the dividends of digital applications, and also shoulder the burden of promoting the whole chain of digital technology. Second, enterprises with weak innovation ability should increase investment in innovation resources and actively carry out digital cooperative innovation. Third, the government should introduce diversified support policies, improve the level of patent application services in the garment industry, and accelerate the construction of information technology infrastructure. Fourth, it is necessary to rely on industry associations and professional societies to build a digital innovation exchange platform and share digital innovation achievements.
This paper evaluates the innovation ability of listed clothing companies from five aspects: innovation input, innovation output, business performance, environmental factors and digital level. It is found that innovation ability is affected by R&D investment, patent output, enterprise growth, business environment and digital talents, regional scientific research environment and equipment digital level. Follow-up research can measure the level of equipment digitization from more perspectives, such as digital fixed assets plus digital intangible assets divided by total assets.
Key words:
innovation ability evaluation; listed apparel company; global factor analysis; influencing factor; digital economy; digitization level