深度学习在地震监测预报中的应用进展
2024-05-29贾漯昭孟令媛闫睿
贾漯昭 孟令媛 闫睿


摘要:对深度学习的方法原理及主流的前馈神经网络、卷积神经网络、循环神经网络、Transformer网络、自编码器、生成对抗网络以及深度强化学习网络等进行了介绍,讨论了不同网络的适用领域。从震相拾取、震相关联、地震定位与事件检测,地震信号和地震事件的分类,地震预测预报等方面对近年来深度学习方法的应用技术进行了提炼总结,综述了深度学习方法的应用进展,讨论了当前常见深度学习方法在地震监测预报领域中的主要应用方式、优势特点及解决的主要问题。总结了现阶段深度学习方法在地震监测预报领域中存在的应用局限性以及后续发展方向。
关键词:深度学习;监测预报;地震检测;地震定位;地震预测
中图分类号:P315.72文献标识码:A文章编号:1000-0666(2024)03-0336-14
doi:10.20015/j.cnki.ISSN1000-0666.2024.0037
0引言
近年来,随着人工智能相关技术的高速发展,以深度学习为代表的机器学习相关技术在地震学领域的应用迅速增加。深度学习已被广泛应用于地震事件自动检测和识别(Lomax et al,2019;Perol et al,2018)、地震事件分类器(Chen et al,2020;Jia et al,2022;隗永刚等,2019;Aden-Antoniow et al,2022;Linville et al,2019)、地震预测(Jasperson et al,2021;Shreedharan et al,2021;Rouet-Leduc et al,2017;石耀霖等,2022;Ma et al,2022)等,并且取得了一定的成果。
事实证明,深度学习相关算法在地震学中的应用非常理想,一方面是长期的地震观测业务工作中积累了大量的标记数据集(Mousavi et al,2022b;Linville et al,2019),比如由专业的地震编目人员精心标注而成的地震目录,这些目录不仅包含准确的地震坐标,还包含地震事件类型等参数。这些数据为监督学习方法提供了前提条件,也为无监督学习方法提供了必要的测试要素。另一方面,许多地震数据都有明确的格式和组织方式,例如地震震相报告、地震事件波形、连续地震观测波形等。地震学的重要任务之一就是从这些数据中提取特征总结规律。特征提取的过程一般是计算密集型任务。深度学习算法中采用的反向传播算法,模型训练时常用的卷积操作等(Goodfellow et al,2016)都要耗费巨大的算力,这些计算密集型任务随着图形处理器(GPU)在计算领域的高速发展,使原本需要耗费大量时间和资源才能完成的计算任务变得简单。
Bergen 等(2019)的研究展示了机器学习在地球物理数据上的发展和应用潜力,认为机器学习可以用于地震数据自动化处理、建模和反演、发现地震数据固有规律等方面的研究,通过机器学习可以帮助研究者更好地理解地球动力学过程。Yu和Ma(2021)总结了深度学习在不同的地球物理任务中的应用,如地球物理勘探、地震数据处理、地震数据成像、地震资料解释与分析,指出使用半监督和无监督学习、迁移学习、多模态深度学习等深度学习方法在地震学中的应用具有潜力。近年来基于深度学习技术的地震学研究正在快速增长,Mousavi等(2022a)在《科学》杂志研究指出近几年深度学习在数据处理,正演问题,反演问题、数据分析等方面取得了巨大的进展,但作为科学发现的通用工具,深度学习仍处于起步阶段,基于物理且可解释的深度学习是未来的发展方向。
1方法概述
深度学习(Deep Learning,DL)是机器学习(Alpaydin,2020;Jordan,Mitchell,2015;Hinton,Salakhutdinov,2006)领域的一个分支,是一种能够从数据中自动学习任务表征的机器学习方法,按照其应用方法可以分为有监督学习和无监督学习两大类,有监督学习通过有标注的训练数据对模型进行指导解决具体问题,无监督学习则是在没有标注数据的情况下,通过寻找数据中内在结构和特征来学习数据规律。
深度学习方法核心原理是通过多层非线性变换来逐层提取数据的高级抽象特征,通过构建深层神经网络来学习数据的内在特征(LeCun et al,2015;Goodfellow et al,2016)。通常深度学习神经网络由多个层次的神经元组成,每个神经元接收来自上一层的输入,通过非线性的激活函数对输入进行变换,而后将变换后的结果传递给下一层。每一层神经元都可以学习到不同的特征表示,而深层网络可以通过组合这些特征来学习到更加復杂和抽象的特征,从而实现对复杂模式的建模和预测。
在深度学习训练过程中通常使用梯度下降算法来最小化预测结果与真实结果之间的误差。通过反向传播算法计算每个神经元对误差的贡献,并根据贡献的大小来更新神经元的权重,从而逐步优化网络的性能。
深度学习可以用于地震数据处理和分析。传统的地震数据处理方法通常需要人工干预和专业知识,而深度学习可以通过自动学习和特征提取减少人工干预,在一定程度上提高数据处理效率。深度学习的准确性受模型结构、训练数据、算法优化等因素的影响。在实际应用中,需根据具体问题选择合适的深度学习方法,并对模型进行调参和优化,以提高其准确性和鲁棒性。在应用深度学习时,地震专家仍然需要参与到数据的处理和分析过程中,以保证数据处理过程正确。深度学习与传统的机器学习方法,如逻辑回归、决策树、支持向量机等相比,具有特征提取不需要手动设计,处理大规模数据更容易,非线性拟合能力更强、扩展性更高等优点(Goodfellow et al,2009,2016)。
深度学习中常用的基本网络结构包括前馈神经网络(Feedforward Neural Network,FNN)、卷积神经网络(Convolutional Neural Network,CNN)、循环神经网络(Recurrent Neural Network,RNN)(图1)。此外,还有自编码器(Autoencoder,AE)、生成对抗网络(Generative Adversarial Network,GAN)、Transformer等网络结构,它们可以使用FNN、CNN、RNN等基本结构来构建。另外,强化学习(Deep Reinforcement Learning,DRL)也是一种与深度学习结合广泛的方法,以下分别介绍。
前馈神经网络(FNN)是深度学习方法的最初版本,由Rosenblatt(1958)提出,其网络从输入层直接映射到输出层,前一层的输入连接到下一层的每个单元,不进行反向反馈。只包含多个全连接层的前馈神经网络称为多层感知器(Multilayer Perceptron,MLP),是最常用的前馈神经网络类型。FNN常用于分类、回归等任务中。
卷积神经网络(CNN)早期主要用于处理图像和視频等数据(LeCun et al,2015),其包含卷积层、池化层和全连接层等,是深度学习使用最广泛的网络结构。CNN通过卷积操作在输入数据上提取特定的特征信息,池化操作减少数据维度,通过反向传播算法和梯度下降等优化方法以及最小化损失函数来学习模型参数。在这个过程中实现自动化提取数据中的特征和模式,实现分类、回归等任务。在地震监测中,CNN常用于处理地震波形数据,用以提取波形特征。其特点是可以通过卷积层对地震数据进行降维,自动提取特征,有效提升这类任务的效率和准确率。
循环神经网络(RNN)用于处理时序数据的神经网络(Elman,1990),在不同时间片段间传递信息,网络的输出或隐藏状态被用作循环中的输入,在语音识别和自然语言处理等领域应用广泛。作为循环神经网络的一种变体,长短时记忆网络也取得了较大的影响(Long Short-Term Memory,LSTM)(Hochreiter,Schmidhuber,1997),它是一种特殊的循环神经网络,能够在处理长序列时避免梯度消失和爆炸问题,使得模型能够更好地保留长期记忆。在地震学中,RNN可以用于处理地震事件序列数据,并建立时间上的关联性。
Transformer网络是针对数据序列建模的神经网络模型其主要特点是引入了自注意力机制(Self-Attention Mechanism)来建模输入序列中的长距离依赖关系,避免了传统的循环神经网络(RNN)中梯度消失等问题。近年来,Transformer在机器翻译、文本生成、自然语言处理等方面成果显著,如最近自然语言处理领域大获成功的ChatGPT(Brown et al,2020)。在地震学中,已经证明其可以应用于地震事件检测,震相提取等工作(Mousavi et al,2020a)。
自编码器(AE)是一种应用于无监督学习的神经网络模型(Hinton,Salakhutdinov,2006),通过对数据进行压缩和解压缩,学习数据中的主要特征,对数据降维后用于回归或者分类任务,常见于图像、音频和视频信号的降噪和压缩编码。可以用于降维和特征提取。在地震学中,AE可以用来对高维地震数据进行降维和特征提取。
生成对抗网络(GAN)是由一个生成器和一个判别器组成的神经网络模型(Goodfellow et al,2014),使用低维随机向量从生成器生成样本,然后由鉴别器将样本分类为真或假。一般用于生成逼真的虚拟数据,如图像、视频等,近年也用于提取特征,从而进行分类或者目标检测。在地震学中,GAN可以用于生成、合成地震波形数据或增加其他类型的样本数据。
深度强化学习(DRL)结合了深度学习和强化学习的方法,使用深度学习网络进行特征提取,加入奖励机制从而影响神经网络整体决策,在未知环境中实现端到端的学习和控制,常用于游戏、机器人控制等领域(Mnih et al,2015)。Google旗下DeepMind公司的Alpha Go(Silver et al,2016)和Alpha Zero(Silver et al,2017)在围棋领域取得突破,战胜人类顶尖围棋选手即使用类似技术。这一机制,在地震学中可用于地震预报等相关工作。
除了以上常见的深度学习网络结构以外,另外一些神经网络结构变体也在深度学习领域中取得了很好的应用效果。比如Variational Auto-Encoders(VAE)被应用于地震震源谱的生成方面(Ma et al,2022)。Graph Neural Networks(GNN)能够处理处理非规则化数据,在地震波形反演,地震事件分类识别方面都有进展(Bilal et al,2022;Zhang et al,2022)。不同种类的深度学习方法适用于不同的任务和数据类型,恰当的方法可进一步提高模型性能。
2应用与发展
目前我国地震监测预报工作包括地震速报编目和地震预报等。随着深度学习方法的有效实施,这些领域都取得了飞速发展。
2.1地震速报编目
在基于深度学习的地震监测工作流程中,通常先通过相关深度学习算法进行地震震相的识别检出,再通过震相关联算法把震相联合到一个地震事件上,对地震定位处理形成自动化的地震目录。在这个过程中,涉及震相拾取、震相关联、地震定位与事件检测、地震波形分类等工作。
(1)震相拾取
基于深度学习的地震初至波识别检测发展方法较多,深度学习到时拾取算法可以克服传统方法的一些缺点。这类方法通常首先检测出初至P波或S波,Mousavi等(2019b)、Withers 等(1998)、Yoon 等(2015)、Zhu和Beroza(2019)都提出了很好的初至波提取方案。
Zhao 等(2019)、Zhou 等(2019)在使用足够大训练集的条件下,已经实现比STA/LTA更高的准确性和分类精度。同时进行震相拾取和地震事件检测可以进一步提高两个任务的准确性(Mousavi et al,2020a;Zhou et al,2019)。其他学者如Perol等(2018)、Hu 等(2019)、Wang等(2021)、张逸伦等(2021)、李辉峰等(2006)的研究也取得了很好的应用效果。
Ross等(2018)开发了用于自动P波拾取和初动识别的卷积神经网络(CNN),并使用美国南加州地震台网(SCSN)2000—2017年的地震数据进行了检测(图2),震相识别精度达到了专业人员水平,这也是地震震相拾取的典型网络结构。
Zhu和Beroza(2019)基于U-Net神经网络提出了到时震相拾取方法PhaseNet,该方法使用三分量地震波形作为输入,输出为P、S波到时以及噪声概率。PhaseNet在设计和训练过程中以地震事件为中心,可以在单一地震波段完成震相到时拾取,但在连续波形上进行震相识别时需要进行窗口截取等操作。赵明等(2019)将PhaseNet震相拾取模型用于连续波形。尹欣欣等(2022)将PhaseNet模型应用于2013年岷县MS6.6余震检测中,在微震检测上对比了人工方法和深度学习方法,证明深度学习方法在中小地震事件检测中具有较强的鲁棒性。
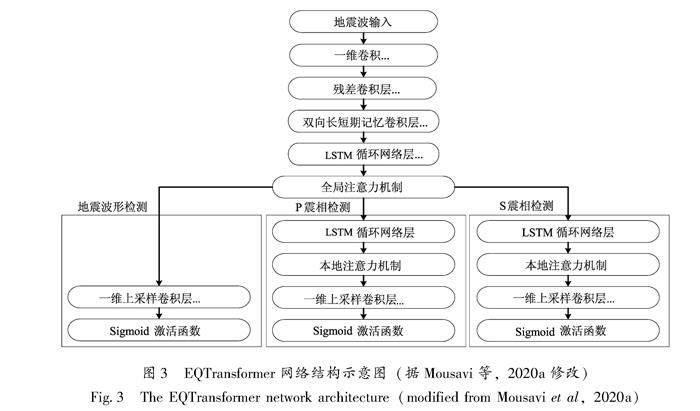
Wang 等(2019)基于残差网络设计了深度学习方法PickNet来自动拾取更多的局部地震的P波和S波到达时间,并给出了参考应用,说明其结果可以直接用于地震层析成像。对PickNet少量改动即可应用于其它震相(如PmP、SmS和PKiKP)的拾取。Mousavi等(2020a)提出了用于同时进行地震事件检测和震相拾取的全局深度学习模型EQTransformer,它由一个非常深的编码器和三个单独的解码器组成,通过使用分层注意力机制检测地震信号,并在近震(<300 km)记录中拾取首个P和S震相(图3)。它与PhaseNet,PickNet有相似的功能,在震相拾取方面各有千秋。
Zhou等(2019)将地震波形看作有前后关联的时间序列数据,利用循环神经网络(RNN)对时间序列不同阶段变化作出预测,并根据每段开始的时间拾取震相。李薇薇等(2021)通过U-Net深度神经网络,将震相拾取问题转换为二值分类问题。陈德武等(2020,2021)通过使用多个卷积块的残差连接替代跳跃连接的方式,改进U-Net网络结构,使用多道观测数据解决微弱信号在低信噪比中震相拾取准确率低的问题。郑晶等(2018)提出基于 S 变换和深度信念神经网络的地震波到时拾取方法,对原始数据进行 S 变换,提高小数据量样本的识别效率。周创等(2020)使用深度卷积对抗神经网络(DCGAN),选取初至时刻后含波峰的半波长数据作为初至特征加入训练,将噪声数据与含初至震相的数据输入生成器与判别器进行训练。Zheng 等(2018)提出基于深度递归神经网络的初至拾取算法,通过在原始数据集中加入随机噪声的方式达选择任务转换为序列标记任务。刘芳等(2020)基于U-Net网络提出了识别P波和S波的震相拾取方法(APP)应用于地震台阵。李健等(2020)使用震相拾取的多任务卷积神经网络结构,利用美国南加州地震台网的200万条震相和噪声数据进行训练,利用迁移学习和数据增强将训练模型应用于东北地区地震台网,震相识别率达84.5%。
(2)震相关联
震相关联是地震事件自动检测的关键流程,它将不同地震台站记录到的同一个地震的震相联系在一起从而确定地震事件,是形成地震目录的基础。Ross等(2019)基于递归神经网络(RNN)提出了一种无网格震相关联的深度学习方法(PhaseLink)。一旦确定震源,该方法就可以对附近的所有震相进行快速反向投影,从而关联到该事件的识别震相。在震相关联中使用深度学习方法可以高精度、高召回率地利用其特征提取能力,结合大量标记好的数据集,提高地震事件检测的准确性和效率(Draelos et al,2015;Yeck et al,2019;Zhang et al,2019;Zhu et al,2022a)。
(3)地震定位与事件检测
许多中小地震甚至微震事件,可能体现更多的地震活动规律,但传统的地震检测手段对微震事件检出率相对较低。使用深度学习方法,可以提高对小地震事件的检测能力。对历史地震连续波形使用深度学习方法地震事件检测可以为研究地震活动规律提供更多有价值的信息。
深度学习应用于地震事件的自动检测和定位,可减轻使用传统的人工地震定位方法(孔韩东等,2017)开展地震速报和编目的负担。近几年基于深度学习方法的地震定位方法发展较快,比如Perol等(2018)开发了卷积定位网络(ConvNetQuake),使用监督学习的方法将地震定位转化为分类问题,并在美国俄克拉荷马州进行地震定位以及地震活动性研究,其模型的地震事件检出准确率为74.5%。Lomax等(2019)改进了其方法(ConvNetQuake_INGV),使该卷积神经网络的地震事件检出准确率提升至87%。
一些学者利用深度学习方法对地震事件进行自动检测和定位,提高了检测和定位的准确性,如Wiszniowski等(2014)开发了一种使用递归神经网络(RNN)的实时地震检测算法。Perol等(2018)、Wu 等(2017,2018)、Zhu和Beroza(2019)使用深度学习的不同网络架构应用于自动地震事件检测和震相拾取。Mosher和Audet(2020)、Xiao等(2021)、Feng 等(2022)结合Transformer网络架构(Saad et al,2021),級联神经网络架构(DCNN)[KG0](Majstorovic et al,2021)及迁移学习(Lapins et al,2021)改进了深度学习地震监测方法,进一步提高了深度学习地震检测的鲁棒性和泛化能力,同时减少了需要的数据样本量。
Kriegerowski等(2019)直接使用多台站的三分量地震波形数据训练卷积神经网络,应用于地震定位。Kail等(2021)将循环神经网络与卷积神经网络相结合设计了地震定位的新方法应用于日本地区。Janbakhsh等(2019)将循环神经网络(RNN)、自编码器(AE)与卷积神经网络(CNN)相结合,提出 CNN+AE+RNN 的方法,完成了地震检测、震级预测和震中距测定工作。
Mousavi和Beroza和(2020a)提出了由两个深度贝叶斯神经网络组成的地震定位方法,其中一个网络用于预测P波走时和震中距,另一个网络用于预测反方位角,结果都取得了较高精度。
传统的地震定位很大程度上依赖于速度模型,容易受到震相拾取不准确的影响(孔韩东等,2017)。Zhang 等(2020)开发了一种方法,使用多个地震台站的全波形进行输入,适用于中小地震(ML<3.0)直接输出定位结果,该方法对信噪比要求较低。
赵明等(2021)应用震相识别和震相关联技术对2019年6月17日四川长宁MS6.0地震震中附近21个地震台站震前半个月的连续波形进行处理,获得的地震目录数量是人工地震目录的8倍以上,同时监测能力下限也提升至ML1.0左右,揭示了长宁 MS6.0主震所发生的区域震前异常频繁的微震活动以及与区域内盐矿注水井的关联性。
Mousavi等(2019c)基于深度神经网络的CNN和RNN的组合设计了地震检测器(CRED),使用卷积层和双向长短时记忆单元的组合结构,在残差结构中进行检测,其检测到的最小地震低至ML1.3。
Chen(2022)将深度学习震相检测器EQTransformer(Mousavi et al,2020a)应用于海底地震仪(OBS)的觀测数据,并使用快速地震关联和定位(REAL)算法关联检测到的震相(Zhang et al,2019),再通过反演(Klein,2002)和HypoDD程序完善震源位置(Waldhauser,Ellsworth,2000),发现了超过1 975次地震,从而对马里亚纳海沟最南端深处的构造结构有了新的认识。作者还对比了EQTransformer与PhaseNet(Zhu,Beroza,2019)在震相拾取上的优缺点。
Cianetti等(2021)和Münchmeyer等(2022)比较了Generalized Phase Detection(GPD)和EQTransformer等常见模型识别地震事件的能力,展现了不同场景下的算法表现,并特别测试了他们在训练集之外数据的泛化能力,给出了各种模型的应用要点。
Zhou等(2022)基于深度学习方法开发了一种地震检测和地震定位的方法(Phasepicking,Association,Location,and Matchedfilter,PALM),可直接快速生成高质量的地震目录。另外,深度学习还可以帮助单台信号估算地震位置和震级(Mousavi,Beroza,2020a,b)。Zhu等(2022b)开发了用于联合震相选择和关联的端到端架构识别P和S波到时,之后通过聚合多个测震站点提取到的波形特征关联和监测地震事件。其算法在斯坦福地震数据集(STEAD)和2019年加州里奇克雷斯特地震序列上进行了评估。
Yoon等(2015)、Bergen和Beroza(2018)、Rong 等(2018)采用无监督模式挖掘方法进行地震检测,使用快速相似性算法搜索连续波形数据中的相似或重复的地震信号。这类方法支持多个测震站点,并可处理长达10年的连续数据。苏金波等(2021)使用深度学习方法进行了高分辨率地震目录生成。Dahmen等(2022)基于深度学习网络提出了用于检测火星地震和去除噪声的检测器。他们的方法基于三分量地震数据进行自动事件检测和去噪,可以检测到大约60%手动编目未发现的地震事件。
(4)地震信号与事件分类
采用深度学习方法在地震信号和事件识别分类中也表现出优于经典方法的能力,包括从爆炸和其他来源中区分地震、从背景噪声中分离地震信号、地震事件聚类等等。
Magaa-Zook和Ruppert(2017)使用长短期记忆(LSTM)网络,区分自然地震活动与爆炸。Li等(2018)在地震预警系统中使用美国南加州和日本的30万个地震波形生成对抗网络(GAN)获取地震波的P波特征,在此基础上使用随机森林分类器将地震事件区分为地震信号或是噪声。Meier等(2019)使用深度卷积网络识别噪声与信号,精度可达99%以上。Mousavi等(2019b)开发了在强噪声环境下区分地震信号的方法。
陈润航等(2018)对原始地震波形划分窗口提取梅尔频率倒谱系数作为特征构建神经网络进行地震事件的分类识别。隗永刚等(2019)基于深度学习技术中的残差网络模型,提出了爆破识别方法。Chen等(2022)使用无监督模糊聚类方法将连续波形分为波形点和非波形点,证明了其方法在中等强度噪声的条件下优于长短期平均(STA/LTA)方法。Kim等(2021)对比了使用随机森林和卷积神经网络中有监督的分类方法和无监督分类的K-Medoids聚类方法在微震数据集的应用,达到了同级别的准确率。Linville等(2019)在三分量和单通道传感器90秒事件频谱图上使用RNN和CNN来区分工业爆破活动(例如采矿或采石爆炸)和天然构造地震,探讨了不同的特征提取方法对分类器性能的影响。Chen 等(2019)提出了高噪声环境下的CNN架构用于地震事件波形分类方法和一种将CNN与k-means聚类(CNN-KC)相结合的到时拾取方法,证明CNN模型的性能比MLP表现更好,而CNN-KC在到时拾取方面也优于k-means聚类,特别是对于噪声水平较高的微震数据。
Jia 等(2022)设计了3种深度学习分类器对地震事件进行实时分类(图4),将地震事件实时分类为地震、爆破、塌陷等。并详细对比了串联、并联以及残差深度学习网络在使用上的优缺点,其设计的深度学习分类器在中国区域地震台网实验精度均超过90%。
2.2地震预测
地震预测是地震监测预报领域的重要工作,也是深度学习方法在地震学中的重要应用领域。深度学习方法将不同类型的地球物理观测数据和地震活动联合分析,结合已知的地球物理约束,可以提高地震预测的准确性和可靠性,也可以帮助地震学家更好地理解和描述不同类型的地震事件的震源特征。Mignan和Broaardo(2020)指出,近年来在地震监测预报领域将深度学习网络应用于地震预测的研究逐渐大幅增加,并且用于地震预测的深度学习神经网络结构逐年愈加复杂。
目前我国的地震预测工作划分为长、中、短临不同的预测时段,短临阶段的地震预测减灾效果最大,地震短临异常也是地预测预报是否成功的关键(张肇诚,张炜,2016)。在1975年2月4日海城地震中,主震发生前几个月至几小时的前震活动,被认为是可信的测震学异常前兆(Wyss,1997)。
在地震预测方面,深度学习方法结合地震目录的完整时空结构,利用深度卷积的自动特征提取能力及其学习动态数据的潜力为地震可预测性提供新的认识,一些例子已经说明其方法有效性高于传统的经验方法。
在实验室地震预测方面,Fieseler等(2022)将无监督稀疏回归模型应用于对与不同开裂机制相关的声发射信号进行分类,并建议使用重建精度作为分类指标。通过将神经网络的注意力集中在具体特征、断裂载荷模式(Song et al,2022)和断裂饱和度(Nolte,Pyrak-Nolte,2022)方面,成功实现了实验室地震的预测(Jasperson et al,2021;Shreedharan et al,2021)。
Panakkat和Adeli(2007)在十幾年前就构建了一个人工神经网络(ANN)系统,根据地震活动性指标(如自上次事件以来经过的时间、过去事件释放的能量以及古登堡-里克特关系的参数)预测未来几个月的大地震事件。该系统在美国南加州和旧金山湾地区的地震活动中得到了一定程度的成功应用。
Panakkat和Adeli(2009)基于循环神经网络(RNN)的方法提出了预测震中位置和发震时刻的方法,其将研究地区细分为多个小区域,用记录到的地震事件数据训练循环神经网络,使得网络具备预测地震位置的能力。Mirrashid(2014)使用了3种ANFIS算法(网格划分、子活动聚类和模糊C-均值)来预测伊朗的地震并获得了大约0.95的相关系数,预报效能极高,但作者使用了1 958个数据样本进行模型训练,可能存在数据过拟合,泛化能力低的问题。Last等(2016)使用机器学习相关技术来预测最大地震事件的震级,使用ROC曲线进行评估,其AUC值为0.7。说明该方法在地震预测上具备一定的预测效能。
Asencio-Cortés等(2017a)使用主成分分析(PCA)来降低地震目录特征维度,并成功应用于地震预测。作者还对比了人工神经网络,朴素贝叶斯,支持向量机,决策树、随机森林、K近邻等方法,在实验中人工神经网络取得了最佳的预报效能。Asencio-Cortés等(2017b)又提出了一种基于人工神经网络的方法(EQP-ANN)的地震预测器,将地震震级预测转化为适合建立基于机器学习的比较的分类问题,并应用于预测东京中大型地震震级,这说明了基于神经网络的地震预测方法适合地震预报工作。
Field等(2017)基于概率预测提出了长短时间自洽的UCERF3地震预报模型,Shcherbakov等(2019)将贝叶斯网络与极值理论相结合,通过研究过去的地震活动来计算大震的预测分布,评估发震概率。石耀霖等(2022)运用机器学习方法中的长短时记忆神经网络(LSTM)对川滇地区进行了地震中期预报,准确率为70.2%。
Seydoux等(2020)使用无监督深度学习方法识别数据中的模式,并应用于地震波形数据,揭示了2017年格陵兰岛大规模破坏性滑坡和海啸之前的前兆信号。Ida和Ishida(2022)使用无监督学习的AI技术-自组织图(SOM)分析了地震活动的时间和空间分布,以日本北部、中部东北地区和关东地区适当划分的空间段的地震目录进行测试,从地震目录的分布中找出大地震和较小地震之间的关系,证明了此类机器学习方法是提取地震状态隐藏规律的有力工具,适用于地震预测。
DeVries等(2018)采用深度学习方法,使用超过13万个主、余震对,训练神经网络用于预测余震位置,预测效能达到0.849,且其方法具有较好的可解释性。Ma等(2022)使用深度变分自编码无监督机器学习方法,推导了来自3 675个MW>5.5全球地震的震源谱,表明深度变分自编码方法可能揭示大型和高维地震数据的隐藏特征。
Zhu等(2021)设计了一种用于强化学习的神经嵌入时空网络(NEST),对比了ETAS算法模型(Ogata,2017),并使用美国密苏里州新马德里发生的4次地震及其余震作为研究对象,说明了离散地震事件作为训练数据和模型生成数据之间的经验分布之间的差异。证明了基于强化学习的神经网络方法在捕捉空间信息,呈现复杂的空间相关性、可解释性和计算效率方面的优势。这些例子说明了以深度学习为代表的相关数据分析技术在地震预报领域中的潜力,也说明新一代的精细化地震目录为地震预报工作带来了新的转机。但使用机器学习相关方法预测地震需要考虑训练样本数据量以及当地地质结构特点。不能盲目迷信高准确度,避免陷入过拟合与低泛化或者无法泛化的陷阱中。
2.3其它应用
深度学习方法已经在地震监测预报各个方面都取得了较好的进展。有学者使用深度学习方法改进地壳接收函数计算效率等方面(Wang et al,2022;李志强等,2021;杨庭威等,2022;甘露等,2021)。在地震矩张量反演(Steinberg et al,2021)、层析成像(Araya-Polo et al,2018)中都取得了良好的效果。
3讨论与结论
本文介绍了深度学习方法背景和常见深度学习网络结构,概述了近年来利用深度学习方法在地震监测预报领域的发展及研究成果,讨论并总结了深度学习方法值得注意的方面与应用展望
(1)深度学习方法在地震监测预报领域的应用已经得到了广泛的关注和研究,已有的深度学习在地震监测预报方面的应用,为地震学家处理高维、海量、复杂的大规模地震观测数据提供了新的思路和方法。通过深度学习的高效计算和特征提取能力,也将帮助人们更好地理解地球内部结构和物理过程,并提高对自然灾害的预警和响应能力。
(2)随着深度学习方法与地震监测预报的深度融合,未来在地震信号识别、发震机理探索,地震预测预报、地震数据解釋等方面可能会取得进一步的发展。基于深度学习的地震学方法已被证明比传统方法更有效和准确(Qin et al,2022;Zou et al,2022)。
虽然深度学习已取得一定研究进度,但在地震监测预报领域仍然存在以下需要解决的问题:
(1)在数据过拟合方面,处理复杂地质结构和非线性效应时,深度学习模型可能会出现过拟合或欠拟合等问题(Li et al,2023)。尤其是深度学习网络过于庞大时,网络参数数量甚至远远大于训练样本数量,这将不可避免地带来模型过拟合,泛化能力差等问题(Jia et al,2022)。需要进一步研究和发展新的算法和技术来克服这些挑战。
(2)在数据方面,深度学习模型通常需要大量的训练数据进行拟合和优化,而通常有标注的地震数据有限,而且有些数据受到观测环境干扰,数据质量不达标。这就需要对地震数据进行精细化标注和数据预处理,这将耗费大量的人力物力。
(3)随着网络结构的增加,深度学习算法在训练和优化方面需要大量的数据和计算资源支持,这也是目前深度学习在地震学应用中受到限制的一个重要因素。深度学习通常需要多路并行的高性能图形处理单元,价格昂贵。科学家需要更好地利用现有资源,开发出更高效、更精确、更可靠的深度学习算法来解决这些问题。
展望未来,深度学习技术在地震监测预报领域将会得到更加广泛和深入的应用,产出更有实际价值的产品。但是,深度学习技术在地震监测预报领域仍处于初级阶段,尚存在许多亟待解决的问题,需要进一步完善和优化。地震工作者还需继续研究和探索深度学习技术方法,更好地为地震监测预报工作服务,为社会服务。
评审专家和本文编辑提出了诸多指导建议,对稿件质量提升帮助很大,在此表示感谢。
参考文献:
陈德武,杨午阳,魏新建,等.2020.基于混合网络 U-SegNet 的地震初至自动拾取[J].石油地球物理勘探,55(6):1188-1201.Chen D W,Yang W Y,Wei X J,et al.2020.Automatic picking of seismic first arrivals based on hybrid network U-SegNet[J].Oil Geophysical Prospecting,55(6):1188-1201.(in Chinese)
陈德武,杨午阳,魏新建,等.2021.一种基于改进的 U-Net 网络的初至自动拾取研究[J].地球物理学进展,36(4):1493-1503.Chen D W,Yang W Y,Wei X J,et al.2021.Research on first-break automatic picking based on an improved U-Net network[J].Progress in Geophysics,36(4):1493-1503.(in Chinese)
陈润航,黄汉明,柴慧敏.2018.地震和爆破事件源波形信号的卷积神经网络分类研究[J].地球物理学进展,33(4):1331-1338.Chen R H,Huang H M,Chai H M.2018.Study on the discrimination of seismic waveform signals between earthquake and explosion events by convolutional neural network[J].Progress in Geophysics,33(4):1331-1338.(in Chinese)
甘露,吴庆举,黄清华,等.2021.卷积神经网络快速挑选接收函数[J].地球物理学报,64(7):2394-2404.Gan L,Wu Q J,Huang Q H,et al.2021.Quick selection of receiver function based on convolutional neural network[J].Chinese Journal of Geophysics,64(7):2394-2404.(in Chinese)
孔韩东,边银菊,刘瑞丰,等.2017.地震定位方法研究进展[J].地震地磁观测与研究,38(4):81-92.Kong H D,Bian Y J,Liu R F,et al.2017.Review of seismic location study[J].38(4):81-92.(in Chinese)
李辉峰,邹强,金文昱.2006.基于边缘检测的初至波自动拾取方法[J].石油地球物理勘探,41(2):150-155,159.Li H F,Zou Q,Jin W Y.2006.Method of automatic first breaks pick-up based on edge detection[J].Oil Geophysical Prospecting,41(2):150-155,159.(in Chinese)
李健,王晓明,张英海,等.2020.基于深度卷积神经网络的地震震相拾取方法研究[J].地球物理学报,63(4):1591-1606.Li J,Wang X M,Zhang Y H,et al.2020.Research on the seismic phase picking method based on the deep convolution neural network[J].Chinese Journal of Geophysics,63(4):1591-1606.(in Chinese)
李薇薇,龚仁彬,周相广,等.2021.基于深度学习 UNet++网络的初至波拾取方法[J].地球物理学进展,36(1):187-194.Li W W,Gong R B,Zhou X G,et al.2021.UNet++:a deep-neural-network-based seismic arrival time picking method[J].Progress in Geophysics,36(1):187-194.(in Chinese)
李志強,田有,赵鹏飞,等.2021.基于深度学习的接收函数自动挑选方法[J].地球物理学报,64(5):1632-1642.Li Z Q,Tian Y,Zhao P F,et al.2021.Receiver functions auto-picking method on the basis of deep learning[J].Chinese Journal of Geophysics,64(5):1632-1642.(in Chinese)
刘芳,蒋一然,宁杰远,等.2020.结合台阵策略的震相拾取深度学习方法[J].科学通报,65(11):1016-1026.Liu F,Jiang Y R,Ning J Y,et al.2020.An array-assisted deep learning approach to seismic phase-picking[J].Chin Sci Bull,65(11):1016-1026.(in Chinese)
石耀霖,李林芳,程术.2022.运用LSTM神经网络对川滇地区的地震中期预报——回溯性预测2008年汶川MS8.0地震的探索[J].中国科学院大学学报,39(1):1-12.Shi Y L,Li L F,Cheng S,et al.2022.Application of LSTM neural network for intermediate-term earthquake prediction:retrospective prediction of 2008 Wenchuan MS8.0 Earthquake[J].Journal of University of Chinese Academy of Sciences,39(1):1-12.(in Chinese)
苏金波,刘敏,张云鹏,等.2021.基于深度学习构建2021年5月21日云南漾濞MS6.4地震序列高分辨率地震目录[J].地球物理学报,64(8):2647-2656.Su J B,Liu M,Zhang Y P,et al.2021.High resolution earthquake catalog building for the 21 May 2021 Yangbi,Yunnan,MS6.4 earthquake sequence using deep-learning phase picker.Chinese Journal of Geophysics[J].Chinese Journal of Geophysics,64(8):2647-2656.(in Chinese)
隗永刚,杨千里,王婷婷,等.2019.基于深度学习残差网络模型的地震和爆破识别[J].地震学报,41(5):646-657.Wei Y G,Yang Q L,Wang T T,et al.2019.Earthquake and explosion identification based on deep learning residual network model[J].Acta Seismologica Sinica,41(5):646-657.(in Chinese)
杨庭威,曹丹平,杜南樵,等.2022.基于深度学习的接收函数横波速度预测[J].地球物理学报,65(1):214-226.Yang T W,Cao D P,Du N Q,et al.2022.Prediction of shear-wave velocity using receiver functions based on the deep learning method[J].Chinese Journal of Geophysics,65(1):214-226.(in Chinese)
尹欣欣,杨晓鹏,蔡润,等.2022.基于PhaseNet的地震信号自动处理方法准确性分析[J].大地测量与地球动力学,42(8):870-873.Yi X X,Yang X P,Cai R,et al.2022.Accuracy analysis of automatic seismic signal processing method based on PhaseNet[J].Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics,42(8):870-873.(in Chinese)
张逸伦,喻志超,胡天跃,等.2021.基于 U-Net 的井中多道联合微地震震相识别和初至拾取方法[J].地球物理学报,64(6):2073-2085.Zhang Y L,Yu Z C,Hu T Y,et al.2021.Multi-trace joint downhole microseismic phase detection and arrival picking method based on U-Net[J].Chinese Journal of Geophysics,64(6):2073-2085.(in Chinese)
张肇诚,张炜.2016.地震预报可行性的科学与实践问题讨论[J].地震学报,38(4):564-579.Zhang Z C,Zhang W.2016.Discussion on scientific and practical problems of feasibility of earthquake prediction[J].Acta Seismologica Sinica,38(4):564-579.(in Chinese)
趙明,陈石,房立华,等.2019.基于U形卷积神经网络的震相识别与到时拾取方法研究[J].地球物理学报,62(8):3034-3042.Zhao M,Chen S,Fang L H,et al.2019.Earthquake phase arrival auto-picking based on U-shaped convolutional neural network[J].Chinese Journal of Geophysics,62(8):3034-3042.(in Chinese)
赵明,唐淋,陈石,等.2021.基于深度学习到时拾取自动构建长宁地震前震目录[J].地球物理学报,64(1):54-66.Zhao M,Tang L,Chen S,et al.2021.Machine learning based automatic foreshock catalog building for the 2019 MS6.0 Changning,Sichuan earthquake[J].Chinese Journal of Geophysics,64(1):54-66.(in Chinese)
郑晶,曹子原,姜天琪,等.2018.基于深度信念神经网络的微震波到时拾取方法[J].矿业科学学报,3(6):521-526.Zheng J,Cao Z Y,Jiang T Q,et al.2018.Deep belief neural network based arrival picking for microseismic data[J].Journal of Mining Science and Technology,3(6):521-526.(in Chinese)
周创,居兴国,李子昂,等.2020.基于深度卷积生成对抗网络的地震初至拾取[J].石油物探,59(5):795-803.Zhou C,Ju X G,Li Z A,et al.2020.A deep convolutional generative adversarial network for first-arrival pickup from seismic data[J].Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum,59(5):795-803.(in Chinese)
Aden-Antoniów F,Frank W B,Seydoux L.2022.An adaptable random forest model for the declustering of earthquake catalogs[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,127(2):e2021JB023254.
Alpaydin E.2020.Introduction to machine learning[M].Cambridge,MA:MIT Press.
Araya-Polo M,Jennings J,Adler A,et al.2018.Deep-learning tomography[J].The Leading Edge,37(1):58-66.
Asencio-Cortés G,Martínez-álvarez F,Morales-Esteban A,et al.2017a.Using principal component analysis to improve earthquake magnitude prediction in Japan[J].Logic Journal of the IGPL,25(6),949-966.
Asencio-Cortés G,Martínez-álvarez F,Troncoso A,et al.2017b.Medium-large earthquake magnitude prediction in Tokyo with artificial neural networks[J].Neural Computing and Applications,28(5):1043-1055.
Bergen K J,Beroza G C.2018.Detecting earthquakes over a seismic network using single-station similarity measures[J].Geophysical Journal International,213(3):1984-1998.
Bergen K J,Johnson P A,de Hoop M V,et al.2019.Machine learning for data-driven discovery in solid Earth geoscience[J].Science,363(6433):eaau0323.
Bilal M A,Ji Y,Wang Y,et al.2022.Early earthquake detection using Batch Normalization Graph Convolutional Neural Network(BNGCNN)[J].Applied Sciences,12(15):7548.
Brown T,Mann B,Ryder N,et al.2006.Language models are few-shot learners[C]//NIPS'20: Proceedings of the 34th international conference on neural information processing systems.New York:1877-1901.
Chen H,Yang H,Zhu G,et al.2022.Deep outer-rise faults in the southern mariana subduction zone indicated by a machine-learning-based high-resolution earthquake catalog[J].Geophysical Research Letters,49(12):e2022GL097779.
Chen Y,Zhang G,Bai M,et al.2019 Automatic waveform classification and arrival picking based on convolutional neural network[J].Earth and Space Science,6(7):1244-1261.
Chen Y.2020.Automatic microseismic event picking via unsupervised machine learning.Geophysical Journal International,222(3):1750-1764.
Cianetti S,Bruni R,Gaviano S,et al.2021.Comparison of deep learning techniques for the investigation of a seismic sequence:An application to the 2019,Mw 4.5 Mugello(Italy)earthquake[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,126(12):e2021JB023405.
Dahmen N L,Clinton J F,Meier M A,et al.2022.MarsQuakeNet:A more complete marsquake catalog obtained by deep learning techniques[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Planets,127(11):e2022JE007503.
DeVries P M R,Viégas F,Wattenberg M,et al.2018.Deep learning of aftershock patterns following large earthquakes[J].Nature,560(7720):632-634.
Draelos T J,Ballard S,Young C J,et al.2015.A new method for producing automated seismic Bulletins:Probabilistic event detection,association,and location[J].Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America,105(5):2453-2467.
Elman J L.1990.Finding structure in time[J].Cognitive science,14(2):179-211.
Feng T,Mohanna S,Meng L,et al.2022.Edgephase:A deep learning model for multi-station seismic phase picking[J].Geochemistry,Geophysics,Geosystems,23(11):e2022GC010453.
Field E H,Jordan T H,Page M T,et al.2017.A synoptic view of the third Uniform California Earthquake Rupture Forecast(UCERF3)[J].Seismological Research Letters,88(5):1259-1267.
Fieseler C,Mitchell C A,Pyrak-Nolte L J,et al.2022.Characterization of acoustic emissions from analogue rocks using sparse regression-DMDC[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,127(7):e2022JB024144.
Goodfellow I,Bengio Y,Courville A.2016.Deep learning[M].Cambridge,MA:MIT Press.
Goodfellow I J,Le Q V,Saxe A M,et al.2009.Measuring invariances in deep networks[C]// Curran Associates Inc.Proceedings of 23rd annual conference on neural information processing systems 2009:Advances in neural information processing systems 22.Vancouver:646-654.
Goodfellow I J,Pouget-Abadie J,Mirza M,et al.2014.Generative adversarial nets[C]// NIPS'14:Proceedings of the 27th international conference on neural information processing systems——Volume 2:Advances in neural information processing systems.Cambridge,MA:MIT Press,2672-2680.
Hinton G E,Salakhutdinov R R.2006.Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks[J].Science,313(5786):504-507.
Hochreiter S,Schmidhuber J.1997.Long short-term memory[J].Neural Computation,9(8):1735-1780.
Hu L,Zheng X,Duan Y,et al.2019.First-arrival picking with a U-net convolutional network[J].Geophysics,84(6):U45-U57.
Ida Y,Ishida M.2022.Analysis of seismic activity using self-organizing map:implications for earthquake prediction[J].Pure and Applied Geophysics,179(1):1-9.
Janbakhsh P,Pysklywec R,Shahnas M H.2019.Earthquake magnitude,distance,first motion polarity,and noise/event determination using AE,CNN1D,RNN Networks[C]//AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts.
Jasperson H,Bolton D C,Johnson P,et al.2021.Attention network forecasts time-to-failure in laboratory shear experiments[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,126(11):e2021JB022195.
Jia L Z,Chen H F,Xing K.2022.Rapid classification of local seismic events using machine learning[J].Journal of Seismology,26(5):897-912.
Jordan M I,Mitchell T M.2015.Machine learning:Trends,perspectives,and prospects[J].Science,349(6245):255-260.
Kail R,Burnaev E,Zaytsev A.2021.Recurrent convolutional neural networks help to predict location of earthquakes[J].IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters,19:1-5.
Kim S,Yoon B,Lim J T,et al.2021.Data-driven signal-noise classification for microseismic data using machine learning[J].Energies,14(5):1499.
Klein F W.2002.Users guide to HYPOINVERSE-2000,a Fortran program to solve for earthquake locations and magnitudes[R].US Geological Survey.
Kriegerowski M,Petersen G M,Vasyura-Bathke H,et al.2019.A deep convolutional neural network for localization of clustered earthquakes based on multistation full waveforms[J].Seismological Research Letters,90(2A):510-516.
Lapins S,Goitom B,Kendall J M,et al.2021.A little data goes a long way:Automating seismic phase arrival picking at Nabro volcano with transfer learning[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,126(7):e2021JB021910.
Last M,Rabinowitz N,Leonard G.2016.Predicting the maximum earthquake magnitude from seismic data in Israel and its neighboring countries[J].PloS One,11(1):e0146101.
LeCun Y,Bengio Y,Hinton G.2015.Deep learning[J].Nature,521(7553):436-444.
Li Y E,OMalley D,Beroza G,et al.2023.Machine Learning Developments and Applications in Solid-Earth Geosciences:Fad or Future?[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,128(1):e2022JB026310.
Li Z F,Meier M A,Hauksson E,et al.2018.Machine learning seismic wave discrimination:Application to earthquake early warning[J].Geophysical Research Letters,45(10):4773-4779.
Linville L,Pankow K,Draelos,et al.2019.Deep learning models augment analyst decisions for event discrimination[J].Geophysical Research Letters,46(7):3643-3651.
Lomax A,Michelini A,Jozinovi D.2019.An investigation of rapid earthquake characterization using single-station waveforms and a convolutional neural network[J].Seismological Research Letters,90(2A):517-529.
Ma S,Li Z,Wang W.2022.Machine learning of source spectra for large earthquakes[J].Geophysical Journal International,231(1):692-702.
Magaa-Zook S A,Ruppert S D.2017.Explosion monitoring with machine learning:A LSTM approach to seismic event discrimination[C]//AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts.S43A-0834.
MajstoroviAc'1 J,Giffard-Roisin S,Poli P.2021.Designing convolutional neural network pipeline for near-fault earthquake catalog extension using single-station waveforms[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,126(7):e2020JB021566.
Meier M A,Ross Z E,Ramachandran A,et al.2019.Reliable real-time seismic signal/noise discrimination with machine learning[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,124(1):788-800.
Mignan A,Broccardo M.2020.Neural network applications in earthquake prediction(1994-2019):Meta-analytic and statistical insights on their limitations[J].Seismological Research Letters,91(4):2330-2342.
Mirrashid M.2014.Earthquake magnitude prediction by adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system(ANFIS)based on fuzzy C-means algorithm[J].Natural Hazards,74(3):1577-1593.
Mnih V,Kavukcuoglu K,Silver,D,et al.2015.Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning[J].Nature,518(7540):529-533.
Mosher S G,Audet P.2020.Automatic detection and location of seismic events from time-delay projection mapping and neural network classification[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,125(10):e2020JB019426.
Mousavi S M,Beroza G C.2020b.A machine-learning approach for earthquake magnitude estimation[J].Geophysical Research Letters,47(1):e2019GL085976.
Mousavi S M,Beroza G C.2022a.Deep-learning seismology[J].Science,377(6607),doi:10.1126/science.abm4470.
Mousavi S M,Beroza G.2022b.A dataset of published journal papers using neural networks for seismological tasks[J/OL].(2022-03-26)[2023-02-15].https://explore.openaire.eu/search/dataset?
pid=10.5281%2Fzenodo.6386952.
Mousavi S M,Ellsworth W L,Zhu W,et al.2020a.Earthquake transformer-an attentive deep-learning model for simultaneous earthquake detection and phase picking[J].Nature Communications,11(1):3952.
Mousavi S M,Sheng Y,Zhu W,et al.2019a.Stanford earthquake dataset(STEAD):A global data set of seismic signals for AI[J].IEEE Access,7:179464-179476.
Mousavi S M,Zhu W,Ellsworth W,et al.2019b.Unsupervised clustering of seismic signals using deep convolutional autoencoders[J].IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters,16(11):1693-1697.
Mousavi S M,Zhu W,Sheng Y,et al.2019c.CRED:A deep residual network of convolutional and recurrent units for earthquake signal detection[J].Scientific Reports,9(1):1-14.
Mousavi S M,Beroza,G C.2020c.Bayesian-deep-learning estimation of earthquake location from single-station observations[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,58(11):8211-8224.
Münchmeyer J,Woollam J,Rietbrock A,et al.2022.Which picker fits my data? A quantitative evaluation of deep learning based seismic pickers[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,127(1):e2021JB023499.
Nolte D D,Pyrak-Nolte L J.2022.Monitoring fracture saturation with internal seismic sources and twin neural networks[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,127(2):e2021JB023005.
Ogata Y.2017.Statistics of earthquake activity:Models and methods for earthquake predictability studies[J].Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences,45:497-527.
Panakkat A,Adeli H.2007.Neural network models for earthquake magnitude prediction using multiple seismicity indicators[J].International Journal of Neural Systems,17:13-33.
Panakkat A,Adeli H.2009.Recurrent neural network for approximate earthquake time and location prediction using multiple seismicity indicators[J].Computer-Aided Civil and Infrastructure Engineering,24(4):280-292.
Perol T,Gharbi M,Denolle M.2018.Convolutional neural network for earthquake detection and location[J].Science Advances,4(2):e1700578.
Qin B,Huang F,Huang S,et al.2022.Machine learning investigation of clinopyroxene compositions to evaluate and predict mantle metasomatism worldwide[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,127(5):e2021JB023614.
Radford A,Wu J,Child R,et al.2019.Language models are unsupervised multitask learners[J/OL].(2019)[2023-02-15].https://cdn.openai.com/better-language- models/language_models_are_unsupervised_multitask_learners.pdf
Rong K,Yoon C E,Bergen K J,et al.2018.Locality-sensitive hashing for earthquake detection:A case study of scaling data-driven science[J/OL].(2018-07-24)[2023-02-15].https://arxiv.org/abs/1803.09835v1.
Rosenblatt F.1958.The perceptron:A probabilistic model for information storage and organization in the brain[J].Psychological review,65(6):386-408.
Ross Z E,Meier M-A,Hauksson E.2018.P wave arrival picking and first-motion polarity determination with deep learning[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,123(6):5120-5129.
Ross Z E,Yue Y S,Meier M A,et al.2019.Phaselink:A deep learning approach to seismic phase association[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,124(1):856-869.
Rouet-Leduc B,Hulbert C,Lubbers N,et al.2017.Machine learning predicts laboratory earthquakes[J].Geophysical Research Letters,44(18):9276-9282.
Saad O M,Huang G,Chen Y,et al.2021.Scalodeep:A highly generalized deep learning framework for real-time earthquake detection[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,126(4):e2020JB021473.
Seydoux L,Balestriero R,Poli P,et al.2020.Clustering earthquake signals and background noises in continuous seismic data with unsupervised deep learning[J].Nature communications,11(1):3972.
Shcherbakov R,Zhuang J,Zller G,et al.2019.Forecasting the magnitude of the largest expected earthquake[J].Nature Communications,10(1):1-11.
Shreedharan S,Bolton D C,Rivière J,et al.2021.Machine learning predicts the timing and shear stress evolution of lab earthquakes using active seismic monitoring of fault zone processes[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,126(7):e2020JB021588.
Silver D,Huang A,Maddison C J,et al.2016.Mastering the game of Go with deep neural networks and tree search[J].Nature,529(7587):484-489.
Silver D,Schrittwieser J,Simonyan K,et al.2017.Mastering the game of go without human knowledge[J].Nature,550(7676):354-359.
Song Z,Zhang Z,Zhang G,et al.2022.Identifying the types of loading mode for rock fracture via convolutional neural networks[J].Journal of geophysical research:solid Earth,127(2):e2021JB022532.
Steinberg A,Vasyura-Bathke H,Gaebler P,et al.2021.Estimation of seismic moment tensors using variational inference machine learning[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,126(10):e2021JB022685.
Waldhauser F,Ellsworth W L.2000.A double-difference earthquake location algorithm:Method and application to the northern Hayward fault,California[J].Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America,90(6):1353-1368.
Wang F,Song X,Li J.2022.Deep learning-based h-κ method(HKNET)for estimating crustal thickness and vp/vs ratio from receiver functions[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,127(6):e2022JB023944.
Wang J,Xiao Z,Liu C,et al.2019.Deep learning for picking seismic arrival times[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,124(7):6612-6624.
Wiszniowski J,Plesiewicz B M,Trojanowski J.2014.Application of real time recurrent neural network for detection of small natural earthquakes in Poland[J].Acta Geophysica,62:469-485.
Withers M,Aster R,Young C,et al.1998.A comparison of select trigger algorithms for automated global seismic phase and event detection[J].Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America,88(1):95-106.
Wu Y,Lin Y,Zhou Z,et al.2017.Cascaded region-based densely connected network for event detection:A seismic application[J/OL].(2017-11-29)[2023-02-15].https://arxiv.org/abs/1709.07943.
Wu Y,Lin Y,Zhou Z,et al.2018.Seismic-net:A deep densely connected neural network to detect seismic events[J/OL].(2018-01-17)[2023-02-15].https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1802.02241.
Wyss M.1997.Second round of evaluations of proposed earthquake precursors[J].Pure and Applied Geophysics,149:3-16.
Xiao Z,Wang J,Liu C,et al.2021.Siamese earthquake transformer:A pair-input deep-learning model for earthquake detection and phase picking on a seismic array[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,126(5):e2020JB021444.
Yeck W L,Patton J M,Johnson C E,et al.2019.GLASS3:A standalone multiscale seismic detection associator[J].Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America,109(4):1469-1478.
Yoon C E,OReilly O,Bergen K J,et al.2015.Earthquake detection through computationally efficient similarity search[J].Science advances,1(11):e1501057.
Yu S,Ma J.2021.Deep learning for geophysics:Current and future trends[J].Reviews of Geophysics,59(3):e2021RG000742.
Zhang M,Ellsworth W L,Beroza G C.2019.Rapid earthquake association and location[J].Seismological Research Letters,90(6):2276-2284.
Zhang X,Reichard-Flynn W,Zhang M,et al.2022.Spatiotemporal graph convolutional networks for earthquake source characterization[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,127(11):e2022JB024401.
Zhang X,Zhang J,Yuan C,et al.2020.Locating induced earthquakes with a network of seismic stations in Oklahoma via a deep learning method[J].Scientific Reports,10(1):1941.
Zhao M,Chen S,Fang L,et al.2019.Earthquake phase arrival auto-picking based on U-shaped convolutional neural network[J].Chinese Journal of Geophysics,62(8):3034-3042.
Zheng J,Lu J,Peng S,et al.2018.An automatic microseismicor acoustic emission arrival identification scheme with deep recurrent neural networks[J].Geophysical Journal International,212(2):1389-1397.
Zhou Y,Yue H,Fang L,et al.2022.An earthquake detection and location architecture for continuous seismograms:Phase picking,association,location,and matched filter(PALM)[J].Seismological Research Letters,93(1):413-425.
Zhou Y,Yue H,Kong Q,et al.2019.Hybrid event detection and phase-picking algorithm using convolutional and recurrent neural networks[J].Seismological Research Letters,90(3):1079-1087.
Zhu S,Li S,Peng Z,et al.2021.Imitation learning of neural spatio-temporal point processes[J].IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering,34(11):5391-5402.
Zhu W,Beroza G C.2019.PhaseNet:A deep-neural-network-based seismic arrival-time picking method[J].Geophysical Journal International,216(1):261-273.
Zhu W,McBrearty I W,Mousavi S M,et al.2022a.Earthquake phase association using a Bayesian Gaussian mixture model[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,127(5):e2021JB023249.
Zhu W,Tai K S,Mousavi S M,et al.2022b.An end-to-end earthquake detection method for joint phase picking and association using deep learning[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,127(3):e2021JB023283.
Zou S,Chen X,Brzozowski M J,et al.2022.Application of machine learning to characterizing magma fertility in porphyry Cu deposits[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,127(8):e2022JB024584.
Advancements of Deep Learning in Seismic Monitoring and Prediction
JIA Luozhao1,MENG Lingyuan2,YAN Rui1
(1.Henan Earthquake Agency,Zhengzhou 450018,Henan,China)(2.China Earthquake Networks Center,Beijing 100045,China)
Abstract
This article provides an overview of deep learning methods and their application in earthquake monitoring and prediction.It introduces mainstream methods such as feedforward neural networks,convolutional neural networks,recurrent neural networks,transformer networks,autoencoders,generative adversarial networks,and deep reinforcement learning networks.The article summarizes their application in phase picking,phase correlation,event detection,earthquake location,signal and event classification,and earthquake prediction.It also discusses the progress,advantages,challenges,and future directions of deep learning in earthquake monitoring and prediction.This summary serves as a valuable reference for applying deep learning in earthquake monitoring and prediction.
Keywords:deep learning;seismic monitoring and prediction;earthquake detection;earthquake location;seismic forecasting
*收稿日期:2023-05-09.
基金項目:国家重点研发计划(2021YFC3000705);中国地震局震情跟踪定向工作任务(2023010111).
第一作者简介:贾漯昭(1982-),高级工程师,主要从事数字地震学和数值分析研究.E-mail:123@eqha.gov.cn.
通信作者简介:孟令媛(1983-),研究员,博士,主要从事地震活动性和地震危险性研究.E-mail:meng.lingyuan@hotmail.com.
贾漯昭,孟令媛,闫睿.2024.深度学习在地震监测预报中的应用进展[J].地震研究,47(3):336-349,doi:10.20015/j.cnki.ISSN1000-0666.2024.0037.
Jia L Z,Meng L Y,Yan R.2024.Advancements of deep learning in seismic monitoring and prediction[J].Journal of Seismological Research,47(3):336-349,doi:10.20015/j.cnki.ISSN1000-0666.2024.0037.
