Multifunctional properties of a polar spin chain compound[N(C3H7)4][Cu(C8H4NO4)]·H2O exhibiting both one-dimensional magnetism and nonlinear optical activity
2024-04-05AngLiYnhongWngHotinTinAlimujingYlikunYvesJournuxMinLuoHonghengLu
Ang Li ,Ynhong Wng ,Hotin Tin ,Alimujing Ylikun ,Yves Journux ,Min Luo ,Hongheng Lu,*
a Key Laboratory of Material Chemistry for Energy Conversion and Storage,School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering,Hubei Key Laboratory of Bioinorganic Chemistry & Materia Medica,Huazhong University of Science and Technology,Wuhan 430074,China
b Key Laboratory of optoelectronic Materials Chemistry and Physics,Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Fuzhou 35002,China
c Institut Parisien de Chimie Moléculaire,IPCM,Sorbonne Université,CNRS,Paris F-75252,France
Keywords: Multifunctional properties Magnetic property Nonlinear optical property Evaporation One-dimensional chain
ABSTRACT Functional materials with multiple properties are urgent to be explored to reach high requirements for applications nowadays.In this work,a new multifunctional one-dimensional (1D) chain compound[N(C3H7)4][Cu(ohpma)]·H2O 1 (ohpma=deprotonated N-(2-hydoxyphenyl)oxamic acid) exhibiting both 1D antiferromagnetic and nonlinear optical properties,which are both originated from the same polar[Cu(C8H4NO4)] magnetic units,has been successfully synthesized by evaporation at room temperature.Bis-polydentate nature of the (ohpma)3- ligand with constrained tridentate and bidentate coordination sites conducts Cu2+ ions coordinating in different geometries and forms 1D chains along the c axis,which are further separated by the [N(C3H7)4]+ cations.And the 1D magnetic chains further exhibit noncentrosymmetric polar arrangement.Nonlinear optical study shows polar compound 1 exhibits a discernible second-harmonic generation (SHG) efficiency and the calculation of the partial density of states indicates that the SHG efficiency of 1 is mainly originated from the polar [Cu(C8H4NO4)] magnetic units.Moreover,magnetic susceptibility shows a broad maximum around 70 K with strong intrachain interaction of J/kB=-113.0 K but no long-range order is observed down to 2 K,suggesting that 1 shows a good 1D magnetism.Both good 1D magnetism and SHG activity suggest that 1 could be as a potential multifunctional material,particularly.
Currently,the high demand for industrial applications requires multiple properties in one material for achieving device microminiaturization.One-dimensional (1D) Heisenberg spin chain antiferromagnets are of great interest due to their novel quantum phenomena such as quantum disordered state,spin charge separation,and so on [1-10].Meanwhile,nonlinear optical (NLO) materials are of great importance due to their laser applications [11,12].However,it is relatively difficult to achieve both magnetic and nonlinear properties in one material because magnetic property require unpaired electrons in outer shell of transition metal ion while noncentrosymmetric structure for nonlinear optical property need transition metal having d0configuration with Jahn-Teller(JT) distortion.Presently,it is well studied that magnetic property and NLO property can be both importantly influenced by symmetric configuration and polyhedral distortion of central metal-anion coordination sphere [13-15].Inorganic oxyanions (SO42-[16,17],IO3-[18,19],PO3-[20,21],SeO32-[22-24],BO33-[25,26],etc.[27-29]) are usually utilized to bridge neighboring magnetic ions for desirable magnetic lattices,and create asymmetric building units for non-centrosymmetric structure with second-harmonic generation (SHG) activity.As well,mixed anions together with specific configuration could affect the distortion of magnetic metal octahedra MO6for adjusting magnetic property as well as resulting in other new properties including NLO property [30-35].Furthermore,organic ligands can also be applied to synthesize various structural inorganic-organic hybrid magnetic materials with diverse metal-anion coordination environments.Particularly,oxamate ligands can provide a rich chemistry and are proved to be efficient tools for building target compound with a special bisbidentate coordination mode [36,37].Also,it is very chemically flexible with wide range ofN-substituted substrates,of which bisbidentate oxamate bridging group can mediate a strong ferro-or antiferromagnetic coupling between adjacent paramagnetic ions in a distorted N-replaced metal coordinated environment [38-40].To explore the reactivity of multi-polydentate oxamate-based ligands in novel magnetic compounds,we have been investigating the ethylN-(2-hydroxyphenyl)oxamate ligand (H2Et-ohpma,Fig.1a).And the addition of organic base will cause the hydrolysis of ester group of the H2Et-ohpma,which makes it better to coordinate with metals forming low-dimensional structures.As a result,homo-[41] or hetero-[42] metallic antiferromagnetic 1D compounds were successfully synthesized.It is very clear that orthosubstituted phenolato group can effectively restrict central paramagnetic metal ions around oxamate group in 1D direction,and then the phenolato-oxamato co-bidentate-tridentate ligand can specifically give access to 1D chain configuration with distorted Nreplaced MNO4square-pyramidal coordination environment.Moreover,their anisotropy and crystal fields for different magnetic exchange interactions can be consciously tuned by use of different N-substituted substrates.Meanwhile,the asymmetric ohpma ligand provide possibility to create non-centrosymmetric structures.
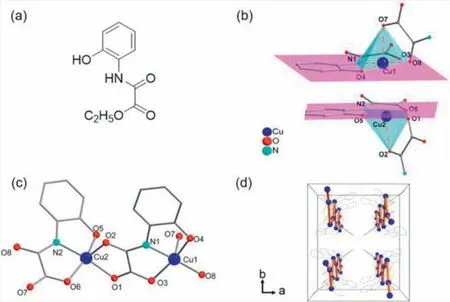
Fig.1.(a) Representation of the H2Et-ohpma ligand.(b) Schematic view of the configurations of the two Cu ions.(c) Perspective view of the asymmetric unit of 1.N(C3H7)4+,H2O molecules and H atom have been omitted for clarity.(d) Representation of the chain in the packing of 1,through the intrachain Cu···Cu bonds(orange).N(C3H7)4+ cations,H2O molecules and H atoms have been omitted for clarity.
Thus,functionalized H2Et-ohpma ligands can be used as effective building units to experimentally realize novel 1D spin chain in a non-centrosymmetric structure.In this work,by using H2Etohpma ligand,we present a successful realization of a novel polar 1DS=1/2 chain compound [N(C3H7)4][Cu(C8H4NO4)]·H2O1exhibiting both 1D antiferromagnetic and NLO properties.Most importantly,different from other reported multifunctional materials,both 1D magnetism and nonlinear optical activity are from the specific Cu square pyramids in1,despite it is common to state that magnetism and second order nonlinear optical activity is contradictory.Its structure has been characterized by single-crystal and powder X-ray diffraction,and their magnetic and NLO properties are also investigated.
Compound1crystallizes in the orthorhombic system with the polarIba2 space group.Phase purity was confirmed by powder Xray diffraction (PXRD) as shown in Fig.S2 (Supporting information).The asymmetric unit of1consists of two crystallographically non-equivalent Cu atoms and ohpma ligands (Figs.1b and c),although two metal ions have similar coordination spheres.Each Cu ion is coordinated to two ligands.One ligand bindsviaits nitrogen and oxygen atoms of the oxamate part (N1,O3 for Cu1;N2,O6 for Cu2) and another oxygen atom from phenol (O4 for Cu1;O5 for Cu2),a secondviatwo oxamate oxygen atoms (O7,O8 for Cu1;O1,O2 for Cu2).The geometries of the two penta-coordinated CuⅡions were further calculated by the free program SHAPE 2.1[43].Interestingly,the calculated results show that the Cu1 and Cu2 exhibit different geometries.The geometry of Cu1 could be viewed as vacant octahedron while square pyramid for Cu2 (Table S2 in Supporting information),which are defined by four O atoms and one N atom from the H2Et-ohpma ligand.The Cu-centered square pyramid sphere is bridged with each other through oxamate group to form the 1D linear chain along thecaxis with intrachain Cu···Cu separation of 5.240(1) ˚A.Hydroxyl oxygen atoms (O9 and O10) from uncoordinated H2O,can form strong intramolecular OH···O interactions with phenol and oxamate oxygen atom (O5 and O7).The O···H distances are 1.91 ˚A and 2.09 ˚A.The O-H···O angles are 165° and 150°,respectively.Additionally,intramolecular hydrogen bonds are also observed between two H2O molecule with the O···O distance in the range of 2.842 ˚A,and angle of O10-H···O9 is 150° (Fig.S3 in Supporting information).Cu-N/Oeq(eq: equatorial plane) bond lengths average to 2.021 ˚A (1.901(5)-2.024(4)˚A),with Cu-O longer apical distances of 2.237(4) and 2.286(4) ˚A.O/N-Cu-O/N angles vary from 83° to 99° for an averaged deviation to orthogonality of 6°.The constraint of the ligand’s tridentate coordination mode makes a shorter Cu-N (amide) and Cu-O(carboxylate) bond length than some reported mono-oxamate Cu complexes [44-46],with an O3-Cu1-O4 angle of 165.78° and O5-Cu2-O6 angle of 163.34°.
Compound1consists of an anionic oxamato-bridged Cu chain with tetrapropylammonium counter-cations and uncoordinated H2O molecule (Fig.2a).Adjacent chains are rather well separated from each other by the peripheral phenyl groups of the ligands and the bulky tetrapropylammonium cation,which afford an effective spacing between the metal ions of neighboring chains.The shortest interchain Cu···Cu distance is 12.0972(10) ˚A along thebaxis and 11.1474(9) ˚A along theaaxis.They are quite larger than that of reported oxamate-metal 1D chains,indicating that bulky cation can play a great role in well separating neighboring chains.Noticeably,adjacent chains alongaandbaxes are enantiomers while ligands are assembled clockwisely (left-handed) and anticlockwisely (right-handed),respectively (Fig.1d and Fig.S4 in Supporting information).It is quite different from the homochiral lefthanded helical {(HNEt3)[Cu(ohpma)]} chain which contains chiralP32space group using the same ligand and metal that we published recently [41] and we have already observed that consecutive absolute SPY-5-14(A) configuration can induce enantiomer excess 1D helical chain.Very obviously,different configuration of1is attributed to the utilization of N(C3H7)4+instead of HNEt3+.Cu1 and Cu2 confer SPY-5-14(C) and SPY-5-23(A) absolute configuration (Fig.S5 in Supporting information) [47],and the ohpma lig-ands between adjacent chains arrange antiparallelly in forms of intrinsic enantiomers.Therefore,symmetric and non-polar countercation can greatly equilibrate enantiomeric formation in the case of spontaneous resolution.Contrast to the enantiomers from racemic ligands,it is less common to synthesize enantiomers when the reactants are achiral.To the best of our knowledge,this is the first time that a heterochiral phenomenon has been discovered in subchain unit of oxamate-based inorganic-organic hybrid compounds.Since compound1crystallizes in a polar space group,acentric units of1are needed to be further analyzed.From above discussion,non-polar counter-ion N(C3H7)4+,lattice water and specific arrangement of phenyl part from ohpma organic ligand with asymmetric environment in a unit cell reveals an almost cancelation of polarization.And the tetrahedral [CuNO4] secondary building unit(SBU) are growing into a polar chain along thecaxis with same direction.The net dipole moment of the [CuNO4]nchain in compound1is canceled out along theaandbaxes while not along thecaxis,thus resulting in a net dipole moment orientated along thecaxis (Fig.2b).Selected bond length and the oxidation state of Cu ion with +2 valance is confirmed by bond valence sum (BVS) calculations using values reported by Brese and O’Keefe [48] as shown in Table 1.

Table 1Selected bond lengths,and BVS calculations for 1.
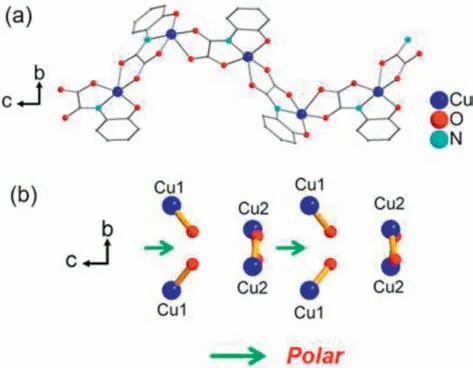
Fig.2.(a) Structure presentation of 1 along the a axis.N(C3H7)4+,H2O molecules and H atoms have been omitted for clarity.(b) The polar direction along opposite direction of the c axis.
Since the compound1crystallized in a non-centrosymmetric space group,the NLO performance was studied.As shown in Fig.S8 (Supporting information),it exhibited a SHG effect,about 0.2 times that of industry-used KH2PO4(KDP),which is larger than the reported compounds such as Ln2(SeO3)2(SO4)(H2O)2[Ln=Sm (0.05 × KDP);Dy (0.04 × KDP);Yb (0.12 × KDP)][49],(3-chlorobenzylammonium)2CuCl4(0.25 ×α-SiO2) and (4-chlorobenzylammonium)2CuCl4(0.25 ×α-SiO2) [50].To clarify the origin of the SHG effect,the partial density of states (PDOS)was first calculated because the NLO properties of compounds are closely related to their electronic transitions near the forbidden band.As shown in Fig.S9 (Supporting information),the electronic states near the forbidden band of1are mainly occupied by Cu-3d C-2p and O-2p orbitals.It is clear that these orbitals are provided by theπ-conjugated C-O units of the oxamate groups of the ohpma ligands from the [Cu(C8H4NO4)] units,which has also been reported in other literature [51,52].And it also corresponds to the calculated electron density map (Fig.S10 in Supporting information).In other words,the SHG efficiency of1is mainly provided by [Cu(C8H4NO4)] units.
Meanwhile,the magnetic properties of1were studied in the temperature range of 2-300 K under an applied DC field of 1000 Oe (Fig.S11a in Supporting information).As shown in Fig.3,subtracted magnetic susceptibility shows a broad maximum at 70 K,which is originated from short-range order between neighbouring Cu2+ions along the chain.A minimum at 34 K and then a sharp increase appears at low temperature.This feature is atrributed to a small amount of a Cu(II) uncoupled impurity (4.33%),which referred as Curie tail (Fig.S11b in Supporting information).The Weiss temperature ofθ=-8.72 K and the negative result indicates that the dominant magnetic interaction in1is antiferromagnetic (Fig.S12 in Supporting information).

Fig.3.The intrinsic magnetic susceptility at 0.1 T from 2 K to 300 K for 1.The corresponding fit to a Fisher fitting beteween 40-300 K (red).
To analyze the real magnetic property of1,the Fisher’s empirical law [53] for aS=1/2 1D regular chain was used to fit the intrinsic magnetic susceptibility after subtracting Curie tail(Fig.3a).
withx=|J|/T;Nbeing Avogadro’s number,βbeing the electronic Bohr magneton,kis the Boltzmann constant,Jis the magnetic coupling constant,gis the gyromagnetic Lande factor with the value of 2 andχ0is the temperature-independent Van Vleck term.The best fit parameters obtained from Eq.1 areJ/kB=-113.0 K andχ0=-2.07 × 10-4emu/mol.The large negative value ofJindicates that the intrachain interaction is a strong antiferromagnetic coupling.
In comparison to other oxamate-bridged Cu2+homometallic compounds,the result shows a relatively weaker antiferromagnetic interaction in1[54].The splitting ofdorbitals in a distorted square pyramidal field of Cu2+is shown in Fig.4.Because of the distorted square pyramid coordination sphere of copper (Since Cu1 and Cu2 are under same coordination sphere,only Cu1 is discussed in detail as below),the Cu1-O7 bond length is the largest.This means that the delocalized spin density onto the O7 oxygen atom is very weak.In fact,the high spin densities are localized on the O3,O4,O8 and N1 plane which thedx2-y2orbital that contains the single electron of the Cu2+ion distribute,perpendicular to the elongated JT axis withdz2orbital.
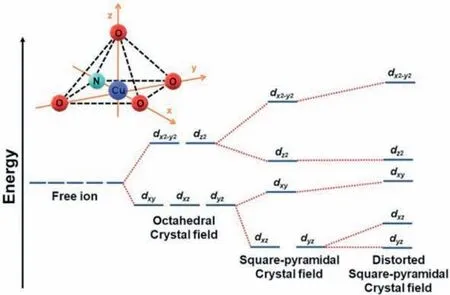
Fig.4.Scheme of compound 1 CuNO4 distorted square pyramidal field and the splitting of d orbitals in a square planar field,with the effect of distortion.
In comparison to the examples in the literature where the magneticdx2-y2orbitals of neighboring copper ions share the same plane with the oxamato bridge,the interaction with the oxamate bridge is much weaker because it only occurs on the amide function (N1,O3) side.This considerably reduces the overlap between the magnetic orbitals of the neighboring magnetic centers.The interaction is proportional to the overlap between magnetic orbitals,so a lower overlap results in a lower interaction as observed in1.For comparison,another helical copper chains with the 2-dimethylaminoethyl(oxamato) ligand present the same phenomenon with intrachain interactions of -121.1 and -106.7 K[55] close to the value of this work.
In conclusion,a new multifunctional material [N(C3H7)4]-[Cu(C8H4NO4)]·H2O1constructed by an ortho-substituted phenyloxamate ligand has been synthesized.Nonlinear optical study shows that polar compound1exhibits a discernible secondharmonic generation (SHG) efficiency.As well,the magnetic susceptibility results indicate that1exhibits good 1D magnetism with strong intrachain interaction but no conventional long-range antiferromagnetic order observed.This work proves that the use of specific ligand could provide a promising way to explore new multifunctional materials.
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declared that they have no conflicts of interest to this work.We declare that we do not have any commercial or associative interest that represents a conflict of interest in connection with the work submitted.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Dr.Laurent Lisnard at Sorbonne Université for his helpful discussion on magnetism.This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(NSFC,No.22101091),the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No.2019kfyXKJC016),the Innovation and Talent Recruitment Base of New Energy Chemistry and Device (No.B210003) and Knowledge Innovation Program of Wuhan-Basic Research.
Supplementary materials
Supplementary material associated with this article can be found,in the online version,at doi:10.1016/j.cclet.2023.108780.
杂志排行
Chinese Chemical Letters的其它文章
- The 3rd Xihua Chemistry and Biomedicine Forum
- Professor Hualiang Jiang: A tribute to an esteemed visionary chemist and pharmacist
- Recent advances in visible light-mediated chemical transformations of enaminones
- Development of porphyrin-based fluorescent sensors and sensor arrays for saccharide recognition
- Recent advances of versatile reagents as controllable building blocks in organic synthesis
- Synthetic host-guest pairs as novel bioorthogonal tools for pre-targeting☆
