Ghrelin regulates insulin resistance by targeting insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor via miR-455-5p in hepatic cells
2024-03-26GUOZhanhongJUYuejunSHENTingZHANGLinqiSHENGZhongqiWURunzeKONGYinghong
GUO Zhan-hong, JU Yue-jun, SHEN Ting, ZHANG Lin-qi, SHENG Zhong-qi, WU Run-ze,KONG Ying-hong
Department of Endocrinology, Changshu No.2 People’s Hospital, Changshu 215500, China
Keywords:
ABSTRACT Objective: To explore the mechanism by which ghrelin regulates insulin sensitivity through modulation of miR-455-5p in hepatic cells.Methods: HepG2 cells were treated with or without DAG (1 μM).Glucose consumption, intracellular glycogen content, phosphorylation of PI3K and Akt stimulated by insulin, expression of miR-455-5p, as well as IGF-1R protein level were analyzed.In addition, bioinformatic analysis, dual luciferase reporter assay, miR-455-5p mimic or inhibitor treatment was conducted to investigate the molecular mechanisms.Results: High glucose treatment upregulated miR-455-5p expression but reduced glucose consumption and glycogen content.DAG reversed the effect of high glucose on glucose metabolism, increased protein level of IGF-1R and phosphorylation of PI3K/Akt stimulated by insulin, as well as downregulated miR-455-5p expression.Bioinformatic analysis indicated IGF-1R was the target of miR-455-5p.Dual luciferase reporter assay, as well as transfection with miR-455-5p mimic/inhibitor confirmed that DAG activated IGF-1R/PI3K/Akt signaling via inhibiting miR-455-5p.Conclusion: DAG improves insulin resistance via miR-455-5pmediated activation of IGF-1R/PI3K/Akt system, suggesting that suppression of miR-455-5p or activation of DAG may be potential targets for T2DM therapy.
1.Introduction
Diabetes is associated with genetic predisposition or unhealthy lifestyle.According to the International Diabetes Federation (IDF),more than 400 million populations around the world living with diabetes, of which 90% are T2DM[1].Insulin resistance (IR) is major patho-physiological mechanism of T2DM.The liver is a vital organ that involved in glucose metabolism.IR in liver causes the abnormality of hepatic glucose disposal, thereby speeding up the progress of T2DM[2].PI3K/Akt system regulates cell proliferation,differentiation, as well as metabolism[3].It involves in regulating serum glucose by insulin, activating glucose transporter proteins,promoting glycogen synthesis and modulating the process of glycolysis[4].Dysregulation of PI3K pathway is closely related to human diseases including T2DM, obesity and cancer[3].Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) is a tyrosine kinase receptor[5],which activates its downstream PI3K/Akt pathway and improves insulin sensitivity[6].
MiRNAs are non-coding endogenous RNAs, which inhibit or cleave target mRNA by binding to the 3′ untranslated region (3’-UTR) of targets and thereby regulate gene expression.Recent studies found some miRNAs are negative regulators of human IGF-1R mRNA, including miR-130a-3p[7] and miR-520b[8].Previous study found that upregulation of miR-455-5p may decrease glycolysis or glucose uptake by suppressing the IGF-1R signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells[9].A study found miR-455-5p was upregulated in Chinese individuals suffered from T2DM[10].The upregulation of miR-455-5p may suppress many metabolismrelated biological processes, including adipogenesis and insulin signaling pathways[11].These studies demonstrated a correlation between miR-455-5p and T2DM.However, molecular mechanisms by which miR-455-5p influence insulin sensitivity remain to be fully elucidated.Des-acyl ghrelin (DAG) is a peptide secreted by gastrointestinal tract,which regulates many metabolic processes[12].Clinical studies have shown that higher levels of ghrelin can improve insulin sensitivity in obese individuals after weight loss induced by dieting[13].Recent studies have confirmed that long-term exogenous application of DAG stabilizes blood glucose and insulin levels[14] and improves insulin sensitivity, which may be related to its regulation of oxidative stress and inflammatory responses in insulin resistant states[15].Still,DAG’s exact mechanism of action against insulin resistance remains unknown.
HepG2 human hepatoma cells has been widely used for the study of hepatocyte glucose homeostasis, such as hepatic glucose production and regulation of the insulin signaling pathway.Here, we established an insulin resistant HepG2 cell model to assess whether DAG improves insulin resistance via the miR-455-5p/IGF-1R/PI3K pathway.
2.Materials and methods
2.1 Cell culture and DAG treatment
The HepG2 cell line was purchased from Shanghai Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology (China).Cells were cultured in DMEM (Gibco, USA) with 10% fetal bovine serum (Bovogen Biologicals, Australia) including 1% antibiotics (Biosharp Life Sciences) under the condition of 37℃ and 5% CO2.HepG2 cells were exposed to 5.5 mmol/L (Normal Control group) or 30 mmol/L glucose (Insulin Resistance group and Pharmacological Intervention group), high concentrations of insulin (100 mmol/L) was added to construct an insulin resistance model of HepG2 cells.DAG (1 μM, Cozmo-Lab, USA) was added in Insulin Resistance group and Pharmacological Intervention group for 48 h to assess the effect of DAG on glucose metabolism, next treated with 100 mmol/L of insulin for 0.5 h before harvesting.
2.2 Cell transfection
miR-455-5p mimic/inhibitor were synthesized by Public Protein/Plasmid Library (PPL, China) and transfected into HepG2 cells using LipofectamineTM 3 000 Transfection Reagent (Invitrogen,USA).24 h post transfection, miR-455-5p expression was measured using miRNA fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) assay to verify successful transfection.Expression of IGF-1R, PI3K/Akt pathway were detected by western blot analysis.
2.3 miRNA fluorescence in situ hybridization
FITC-labeled specific probe against miR-455-5p was designed and synthesized by Sangon Biotech.The miR-455-5p FISH assay was conducted using a FISH Kit (RiboBio Corporation).Cells were imaged using confocal microscope (Nikon Corporation, Japan).
2.4 Cell viability assay
The viability of HepG2 cells incubated with DAG (from 0 to 4 μmol/L) was detected using MTT Assay Kit (Solarbio Life Sciences,China).Cells were incubated with DAG (0, 0.5, 1.0, 2.0 and 4.0 μmol/L) for 24 h.Then, MTT solution (5 mg/mL 20μL/well) was added and incubated for 4 h.The supernatant was removed, then MTT crystals were dissolved in 150 μL of Dimethyl Sulfoxide for 0.5 h.The absorbance was recorded by multimode microplate reader(PerkinElmer, Victor Nivo 3S, USA) at 490 nm.
2.5 Glucose consumption assay
24 h post transfection, glucose uptake was determined in the medium by a Glucose Content Assay Kit (Solarbio Life Sciences,China).The absorbance was recorded using multimode microplate reader (PerkinElmer, Victor Nivo 3S, USA) at 505 nm.
2.6 Measurement of glycogen content
Glycogen content was measured by Glycogen Assay Kit (Solarbio Life Sciences, China).The absorbance was recorded by microplate reader (PerkinElmer, Victor Nivo 3S, USA).The glycogen content was calculated and expressed as μg/106cells.
2.7 Dual luciferase reporter assay
We used TargetScanHuman release 7.2 to predict miR-455-5p targeting to the IGF-1R gene.Dual luciferase reporter assay was performed to confirm the direct binding of miR-455-5p to the 3’-UTR of IGF-1R mRNA.The wild-type (WT) and mutant (MUT) IGF-1R 3′UTR were cloned into psiCHECK-2 vector (Promega, USA)respectively.The vector contains firefly luciferase reporter gene and renilla luciferase gene.Then the miR-455-5p/control mimic(5 pM), the reporter gene plasmids IGF-1R-WT (0.16 μg/well) or IGF-1R-MUT (0.16 μg/well) were transfected into HepG2 cells by LipofectamineTM 3 000 Transfection Reagent.24 h later, the relative luciferase activity was detected.
2.8 Western blot analysis
48 h after transfection, cells were lysed in RIPA Buffer (Solarbio Life Sciences, China).The protein concentration was determined using Protein Assay Kit (Thermo Fisher, USA).The protein were separated on SDS-PAGE (Biosharp Life Sciences, China),transferred to PVDF membranes (Amresco, USA).The membranes were incubated with primary antibodies at 4 ℃ overnight and secondary antibodies at 25 ℃ for 1 h.Chemiluminescence imaging was performed using a Gel Doc System (Syngene, G:BOX, USA).Antibodies against phosphorylated-PI3K (#13857), PI3K (#4249),phosphorylated-Akt (#9271), Akt (#9272) were purchased from CST(1:1 000 dilution, USA).Antibodies against IGF-1R (#AP59586)were purchased from Abcepta (1:1 000 dilution, China).Antibodies against GAPDH (ab9485) were purchased from Abcam (1:2 500 dilution, UK).
2.9 Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism 9.The data are expressed as mean(±s).One-way analysis of variance and Student’s t-test were used to calculate p-values.P < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
3.Results
3.1 Effects of DAG on cell viability
MTT assay was performed to determine cytotoxic effect of DAG.HepG2 cells were treated with DAG (from 0 to 4 μmol/L) for 24 h.The results showed the cell viability was unchanged (Fig.1A, Tab.1).Indicating that the concentration of DAG (1 μM) used in this study do not damage the cells.
3.2 DAG improved insulin resistance in HepG2 cells under high glucose condition
Several studies have shown that DAG promotes glucose consumption and upregulates insulin-dependent signaling pathways in many types of cells[14, 15].We established a model of insulin resistance using HepG2 cells, then intervened with DAG (1 μmol/L).Compared to those in normal control group, high glucose treatment obviously reduced glucose consumption in HepG2 cells from 1 hour and reached a maximum at 12 h after stimulation with insulin (Fig.1B, Tab.2).Treatment with 30 mmol/L glucose for 48 h caused significant reduction of glucose consumption (Fig.1C, Tab.3) and intracellular glycogen content (Fig.1D, Tab.3).Meanwhile,expression of IGF-1R, phosphorylated-PI3K, and phosphorylated-Akt were decreased (Fig.1E), which was consistent with the results of previous research[16].DAG (1 μmol/L) notably increased glucose consumption (Fig.1C, Tab.3) and glycogen content (Fig.1D, Tab.3), and increased expression of IGF-1R, phosphorylated-PI3K, and phosphorylated-Akt under high glucose condition (Fig.1E).These results suggest DAG may upregulate the IGF-1R/P13K/Akt pathway,thereby improving insulin sensitivity.
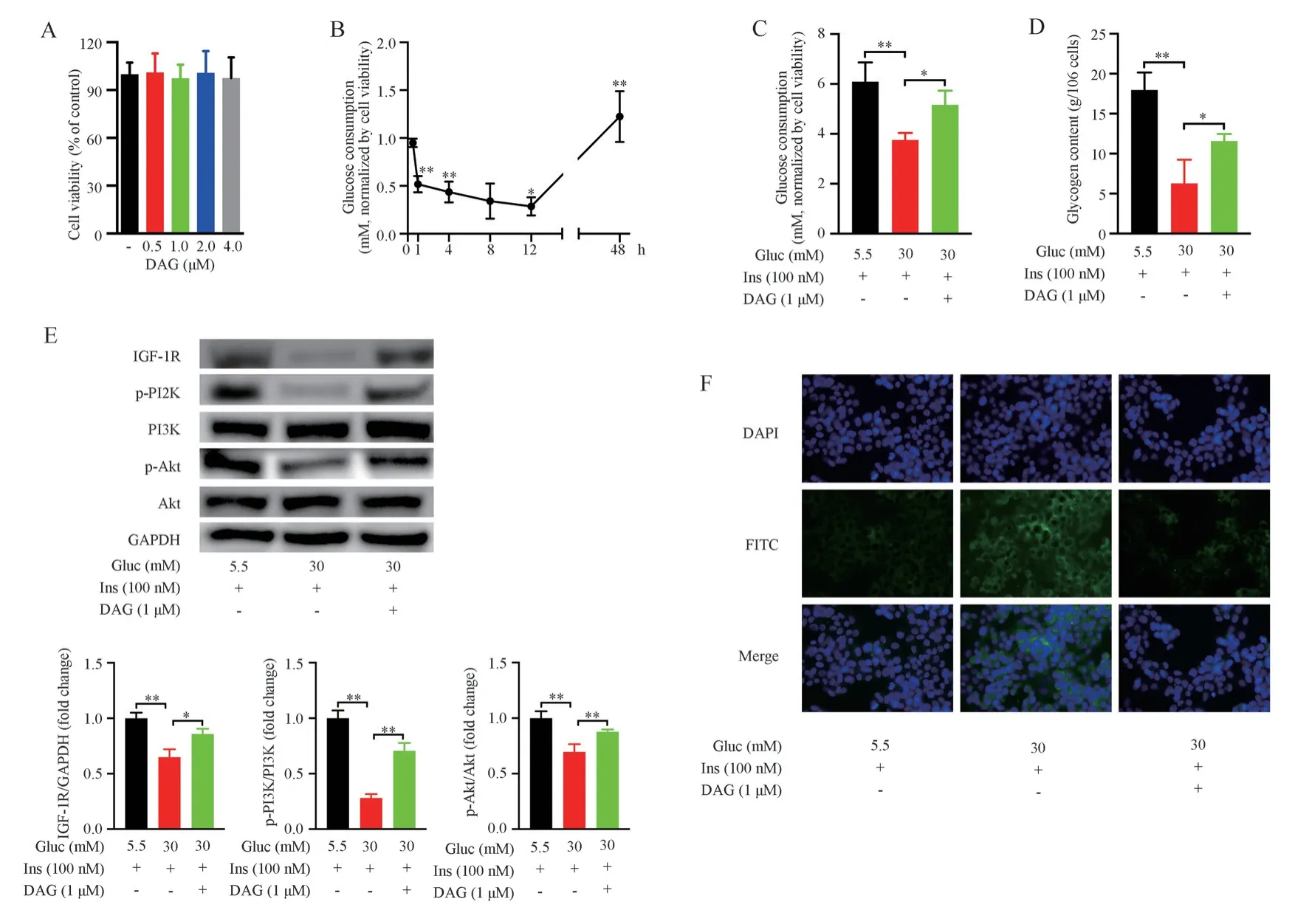
Fig 1 Insulin resistant HepG2 cells induced by high glucose

Tab 1 The viability of HepG2 cells
3.3 IGF-1R was a direct target of miR-455-5p
Bioinformatics analysis predicted specific miR-455-5p binding site on the 3’-UTR of IGF-1R (Fig.2A).We performed dual luciferase reporter assay to verify whether miR-455-5p targets IGF-1R.Compared with normal control (NC) mimic group, luciferase activity decreased obviously after cotransfected with IGF-1R-WT/miR-455-5p (Fig.2B).However, the luciferase activity remained unchanged after transfection with miR-455-5p and IGF-1R-MUT (Fig.2B).The effect of miR-455-5p upon the expression of IGF-1R was confirmed by Western blot.IGF-1R protein level reduced obviously after upregulation of miR-455-5p (Fig.2C).Our findings revealed IGF-1R is a direct target of miR-455-5p.
3.4 DAG alleviated insulin resistance through miR-455-5p-mediated IGF-1R/PI3K/Akt system under high glucose condition
To assess the involvement of miR-455-5p in the regulation of IGF-1R pathway by DAG in high (30 mM) glucose induced HepG2 cells, we explored the changes in miR-455-5p and protein levels of total IGF-1R, phosphorylated-PI3K, as well as phosphorylated-Akt.miR-455-5p was increased under high glucose condition (Fig.1F).Treatment with DAG for 48 hours partially reversed high glucoseinduced miR-455-5p upregulation in HepG2 cells (Fig.1F), elevated IGF-1R, phosphorylated-PI3K, and phosphorylated-Akt protein levels (Fig.1E).Then, we overexpressed or knocked down miR-455-5p using either its mimic or inhibitor respectively, and examined miR-455-5p expression by FISH (Fig.3A, Fig.4A).These findings revealed miR-455-5p overexpression abolished the effect of DAG on the upregulation of IGF-1R, phosphorylated-PI3K, as well as phosphorylated-Akt (Fig.3D).Meanwhile, glucose consumption and intracellular glycogen were decreased compared with those treated only with DAG (Fig.3B, Fig.3C, Tab.3).The miR-455-5p inhibitor increased IGF-1R, phosphorylated-PI3K, and phosphorylated-Akt(Fig.4D), which promoted glucose uptake and glycogen synthesis(Fig.4B, Fig.4C, Tab.3).The results revealed that DAG might down-regulate miR-455-5p expression and then activate the IGF-1R/PI3K/Akt pathway to partially ameliorate high glucose-caused insulin resistance in HepG2 cells.
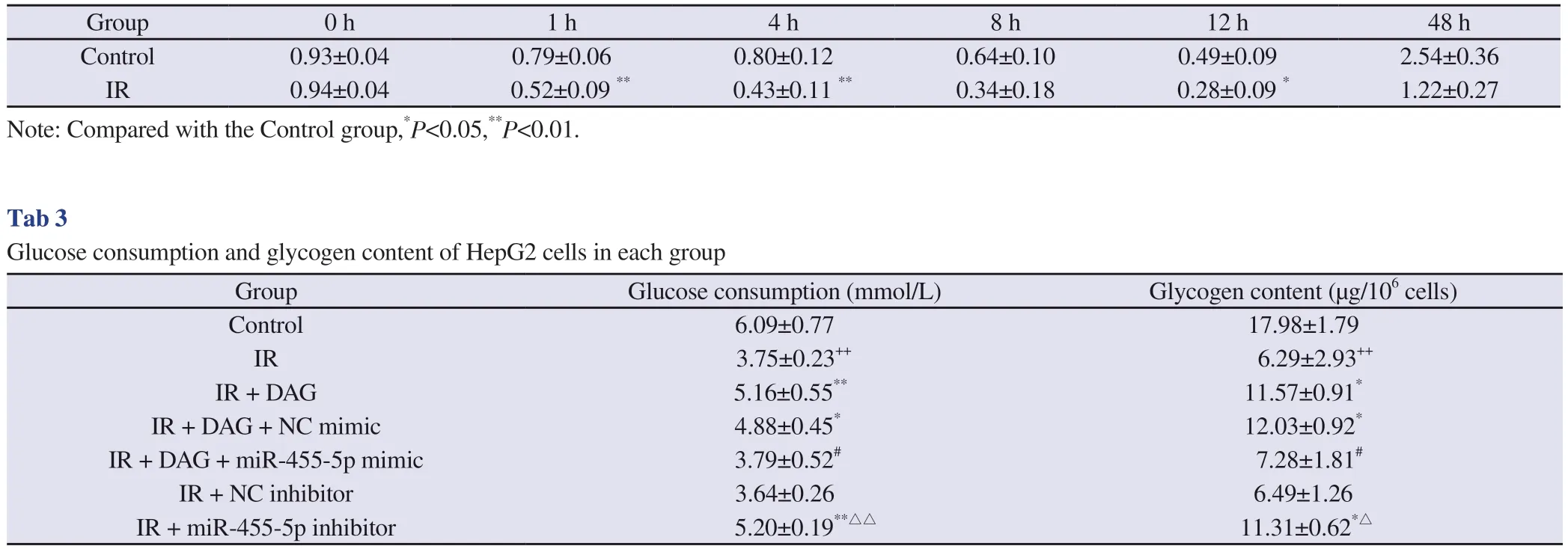
Tab 2 Time-course profiles of glucose consumption after stimulation with insulin under high glucose condition (IR group) com-pared to those in the control group

Fig 3 miR-455-5p overexpression partially prevents the ameliorative effect of DAG on insulin sensitivity
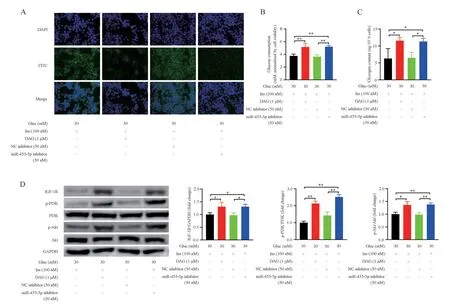
Fig 4 miR-455-5p inhibitor partially abolishes the inhibitory effect of high glucose on the IGF-1R pathway
4.Discussion
Over recent years, with changes in lifestyle, the incidence of T2DM increases rapidly throughout the world, which remains the important cause of disease burden all around the world[17].Insulin resistance is the important physiopathologic mechanisms in T2DM.The liver plays a significant role in the maintenance of glycemic homeostasis,it is also the most crucial target organ for insulin action[18].Hepatic insulin resistance has been considered as a major factor for impaired glucose uptake and utilization, and then causes the development of compensatory hyperinsulinemia, depleted glycogen stores and elevated gluconeogenesis[19].Thus, improving hepatic glucose metabolism is of great significance for alleviating insulin resistance in patients with T2DM.Discovered in 1999, ghrelin was initially recognized to promote growth hormone secretion[20].Acyl ghrelin(AG) plays global physiological role in the adjustment of metabolism through the GHS-R1a receptor, which regulates feeding behaviors,energy balance and gastrointestinal peristalsis[21].Des-acyl ghrelin(DAG) shows antagonistic effects against AG in regulating energy balance, gastric and small intestine motility[22].Furthermore, DAG also has beneficial effect on glycemic homeostasis, which can decrease serum glucose level and improve insulin resistance[23].Findings of this study are as follows: 1.DAG improves insulin resistance under high glucose condition.2.DAG activates PI3K/Akt signaling pathway to promote glucose uptake as well as glycogen synthesis.3.DAG may activate IGF-1R/PI3K/Akt pathway via downregulating miR-455-5p expression, which may be the potential mechanism of DAG treatment in attenuating insulin resistance in HepG2 cells.
IGF-1R is a transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the tyrosine kinase receptor family, which regulates cell growth and energy metabolism via activating PI3K/Akt pathway[24, 25].Akt modulates the process of glycogen synthesis and gluconeogenesis through phosphorylation of PEPCK, G6Pase and GSK-3β [19, 26].Consistent with previous findings[16], the IGF-1R protein in insulin resistant HepG2 cells was significantly decreased.While relative expression of total PI3K and Akt did not change obviously, phosphorylation of PI3K/Akt decreased obviously under high glucose condition,indicating decreased PI3K/Akt pathway activity.Dysregulated PI3K/Akt signaling leads to an imbalance in glucose metabolism which inhibits glucose uptake and glycogen synthesis.Studies have confirmed that des-acyl ghrelin (DAG) treatment enhances glucose uptake and insulin sensitivity[23, 27].Our findings demonstrated that DAG treatment upregulated the levels of IGF-1R as well as enhanced phosphorylation of PI3K/Akt proteins, which promoted glucose uptake and glycogen synthesis.
As a class of regulatory molecules, miRNAs participate in the regulation of insulin sensitivity.For example, high fat diet leads to IR and dysfunctional glucose metabolism, which are associated with misregulation of miRNAs, including miR-27a[28], miR-29b-3p[29] and miR-144[30].It has been shown that miR-455-5p can inhibit glucose uptake in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell via suppressing IGF-1R/Akt/GLUT signaling pathway[9], which is consistent with our findings.Here, we concentrated on the function of miR-455-5p upon regulating insulin sensitivity by repressing IGF-1R in insulin resistant HepG2 cells.We confirmed the binding of miR-455-5p to the 3’UTR of IGF-1R mRNA.We identified that miR-455-5p expression was increased obviously, while IGF-1R protein significantly reduced under insulin resistant condition.The inhibition of IGF-1R protein expression caused a decrease in the phosphorylation of PI3K/Akt signaling, which in turn resulted in reduced glucose uptake and glycogen synthesis.IGF-1R protein was upregulated after transfection with miR-455-5p inhibitor,downregulated following transfection with miR-455-5p mimic,indicating miR-455-5p may modulate the IGF-1R protein expression.miR-455-5p inhibitor protected against high glucose-induced decreased IGF-1R protein, downregulated the phosphorylation of PI3K/Akt signaling, led to decrease in glucose uptake and glycogen synthesis.Our findings indicated that miR-455-5p downregulation contributes to activation of IGF-1R and its downstream PI3K/Akt signaling, thus improved insulin resistance.
DAG significantly reduced miR-455-5p in HepG2 cells induced by high glucose, indicating that DAG-mediated downregulation of miR-455-5p might contribute to its effect on insulin resistance.miR-455-5p upregulation prevented ameliorative effect of DAG on insulin resistance in insulin resistant HepG2 cells.miR-455-5p inhibitor partly abolished the inhibitory effect of high glucose on IGF-1R/PI3K/Akt pathway.These data indicated that DAG might down-regulate miR-455-5p expression to ameliorate high glucoseinduced dysregulation of IGF-1R/PI3K/Akt system, which might be a potential therapeutic target for reversing insulin resistance as well as stabilizing glycemic control in patients with T2DM.
Taken together, this study demonstrates that high glucose treatment upregulates miR-455-5p in HepG2 cells, which in turn reduces the protein levels of IGF-1R, phosphorylated-PI3K, as well as phosphorylated-Akt expression, then impairs insulin signaling and ultimately leading to insulin resistance in T2DM.DAG’s effect on insulin resistance in HepG2 cells was shown via the miR-455-5p/IGF-1R signaling pathway.This study suggests that the inhibition of miR-455-5p or upregulation of DAG may be potential targets for T2DM therapy.
杂志排行
Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Mechanism of stilbene glycosides on apoptosis of SH-SY5Y cells via regulating PI3K/AKT signaling pathway
- Protective effect of camellia oil on H2O2-induced oxidative stress injury in H9C2 cardiomyocytes of rats
- Mechanism of Yanghe Pingchaun granules on airway remodeling in asthmatic rats based on IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 signaling axis
- Pharmacodynamic study and mechanism of action of Linggui Zhugan Decoction in the intervention of Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- Bioinformatics and network pharmacology identify the therapeutic role and potential targets of diosgenin in Alzheimer disease and COVID-19
- Meta analysis of the efficacy of western medicine combined with Qiliqiangxin capsule versus western medicine alone in the treatment of chronic heart failure
