Efficacy of tadalafil on improvement of men with erectile dysfunction caused by COVID-19:A randomized placebo-controlled trial
2024-02-25ImnShmohmmdiSeyedmohmmdKzemeyniMohmmdliSdighiTrHsnzdehAlirezDizvi
Imn Shmohmmdi,Seyedmohmmd Kzemeyni ,Mohmmdli Sdighi ,Tr Hsnzdeh ,Alirez Dizvi
a Department of Urology,Nemazee Hospital,Shiraz University of Medical Science,Shiraz,Iran
b Department of Urology,Shariati Hospital,Tehran University of Medical Science,Tehran,Iran
KEYWORDS Tadalafil;Erectile dysfunction;COVID-19;Sexual function
Abstract Objective: According to the high prevalence of COVID-19 and the subsequent risk of men’s sexual health,we decided to investigate the efficacy of tadalafil on improvement of men with erectile dysfunction caused by COVID-19.Methods: In this study,70 outpatients who were recovered from COVID-19 without acute respiratory distress syndrome with negative polymerase chain reaction test and a complaint of erectile dysfunction were divided into two groups:35 patients who received tadalafil 5 mg daily and 35 who received placebo.For each patient,basic assessment of sexual function was performed using the 5-item version of the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF-5) questionnaire.Then,treatment was started from 2 months after complete recovery of COVID-19 with negative polymerase chain reaction test for 3 months.At the end of the treatments,the patients were re-evaluated for sexual function using the complete version of IIEF questionnaire.Finally,the results before and after treatment in the intervention group were compared with those of the control group.Results: Treatment with both tadalafil and placebo improved the patients’ sexual function criteria compared to the baseline.However,this improvement was significantly higher in the intervention group with tadalafil than the control group with placebo (p<0.05).Conclusion: Daily administration of tadalafil 5 mg seems to be effective and safe for improvement of erectile dysfunction caused by COVID-19.
1.Introduction
The pandemic of COVID-19 with severe acute respiratory corona virus 2 (SARS-Cov2) has caused a wide range of diseases from asymptomatic patients to severe respiratory distress [1,2].The disease involves various organs of the body through cytokines as promoters of inflammatory and thrombotic processes in the microvascular system [3,4].Evidence shows that endothelial damage caused by the virus is a strong stimulant of systemic disorders [5].One of the disorders in COVID-19 patients is erectile dysfunction (ED),and its prevalence in the male population with COVID-19 is reported to be about 31.8% [6].ED is inability to attain or maintain penile stiffness for satisfactory sexual intercourse[7].Since ED is one of the main symptoms of endothelial dysfunction [8,9],hypotheses about the potential correlation between ED and COVID-19 have been proposed [10].It has also reported that COVID-19 is more common and severe in men,which can lead to ED.These two disorders have common risk factors including high blood pressure,obesity,diabetes,and a history of cardiovascular disease [11,12].In patients with post-COVID-19 ED,in addition to endothelial dysfunction,other mechanisms such as subclinical hypogonadism,psychological distress,pulmonary hemodynamic disturbance,and immunological disorders have been suggested as the causative factors[10].One of the approved and safe oral treatment for ED is the phosphodiesterase 5(PDE5) inhibitor such as sildenafil or tadalafil [13].Recent studies support oral PDE5 inhibitor potential adjuvant use in the protocols combating COVID-19 manifestation,especially along with the respiratory complication [14].According to the high prevalence of COVID-19 and the subsequent risk of men’s sexual health,we decided to investigate the efficacy of tadalafil on improvement of men with ED caused by COVID-19.
2.Patients and methods
The Institutional Ethics Committee of Tehran University of Medical Sciences approved our study protocol and all its procedures (IR.TUMS.MEDICINE.REC.1399.929 and IRCTID:IRCT20170807035551N2).This article is a randomized,double-blind,placebo controlled,clinical trial was conducted at Tehran Shariati Hospital,Iran from December 2020 to June 2021.All data that support the findings of our study are available on request from the corresponding author of this study.At first,257 patients(126 met inclusion criteria;131 did not) were assessed.Inclusion criteria were 30-50-year-old outpatients with ED following recovery from COVID-19 without acute respiratory distress syndrome with negative polymerase chain reaction test.After that,109 patients (39 met exclusion criteria;70 did not) who recovered from COVID-19 without acute respiratory distress syndrome with negative polymerase chain reaction test and with a complaint of ED were interested to participate in this investigation.Exclusion criteria were patients with anatomical penis disorder,history of penis trauma,history of neurological disorders(such as spinal cord injury,stroke,and migraine),cardiovascular disease,use of nitrate drugs,hypertension,diabetes,liver disease,hypogonadism,hyperlipidemia,hypotension,impaired laboratory tests,smoking,obesity,poor follow-up,positive history of nocturnal and morning erection,and a history of ED before COVID-19.Finally,70 patients were divided into two groups of intervention(recipient of tadalafil)and control(recipient of placebo) by using a computer-generated randomization table of equal numbers.Each group consisted of 35 patients(Fig.1).ED was defined as the inability to attain or maintain penile stiffness for satisfactory sexual intercourse at enrollment.Patients were enrolled after obtaining informed consents.A form containing demographic information including age,height,weight,education,socioeconomic status,and severity of ED was prepared for patients based on the 5-item version of the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF-5) questionnaire.Then,laboratory evaluations including serum creatinine,complete blood count,fasting blood sugar,liver enzymes,lipid profile,and total serum testosterone were recorded for patients.For each patient,basic assessment of sexual function including erectile function,orgasm function,sexual desire,intercourse satisfaction,and overall satisfaction was done using the complete version of IIEF questionnaire,and their scores were calculated.This study was double-blinded and none of the research personnel and patients was aware of the type of treatment.For blinding,completely similar capsules were considered for both groups with the same of appearance and packaging.The capsules prescribed for the intervention group contained tadalafil 5 mg,and the capsules prescribed for the control group contained 5 mg of sugar.Treatment was started from 2 months after complete recovery of COVID-19 with negative outcome of polymerase chain reaction test.Patients were treated with daily administration of one capsule for 3 months.Patients were advised to discontinue the drugs if they had side effects.At the end of treatments,the patients were re-evaluated for sexual function using the complete version of IIEF questionnaire,and their erectile function,orgasm function,sexual desire,intercourse satisfaction,and overall satisfaction were recorded.Finally,the results before and after treatment of patients in the intervention group were compared with patients in the control group.Data were analyzed using SPSS version 26(IBM Corp.,Armonk,NY,USA)with Chi-square test and Student’st-test.Ap-value of less than 0.05 was considered significant for all tests.
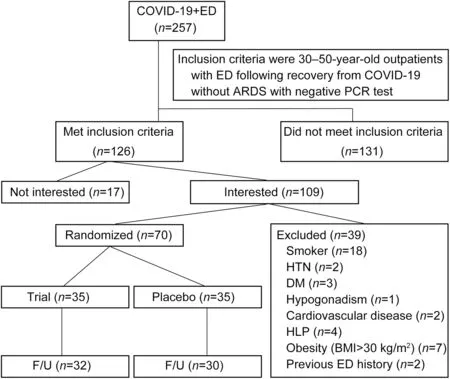
Figure 1 The study flow chart according to PRISMA statement.COVID-19,coronavirus disease 2019;ARDS,acute respiratory distress syndrome;BMI,body mass index;DM,diabetes mellitus;ED,erectile dysfunction;HTN,hypertension;HLP,hyperlipidemia;PCR,polymerase chain reaction;F/U,follow-up.
3.Results
During the study,eight patients were excluded from the study due to poor follow-up.Finally,the results before and after treatment were compared between 30 patients in the control group(placebo) and 32 patients in the intervention group (tadalafil 5 mg daily).Two patients reported transient dyspepsia,and only one patient reported transient headache as a complication during treatment.Nevertheless,all patients completed the course of treatment.The mean age of 62 patients with ED following COVID-19 was about 40 years,and none of the patients complained of ED before being infected with COVID-19.Distribution and comparison of basic and clinical demographic characteristics of patients in the two groups are shown in Table 1.

Table 1 Distribution and comparison of basic and clinical demographic characteristics of patients in the two groups.
As shown in Table 1,there was no significant difference between the two groups in terms of age,height,weight,level of education,socioeconomic status,or severity of ED(p>0.05).
Comparison of the patients’ laboratory data including serum creatinine,complete blood count,fasting blood sugar,liver enzymes,lipid profile,and total serum testosterone between the two groups are shown in Table 2.
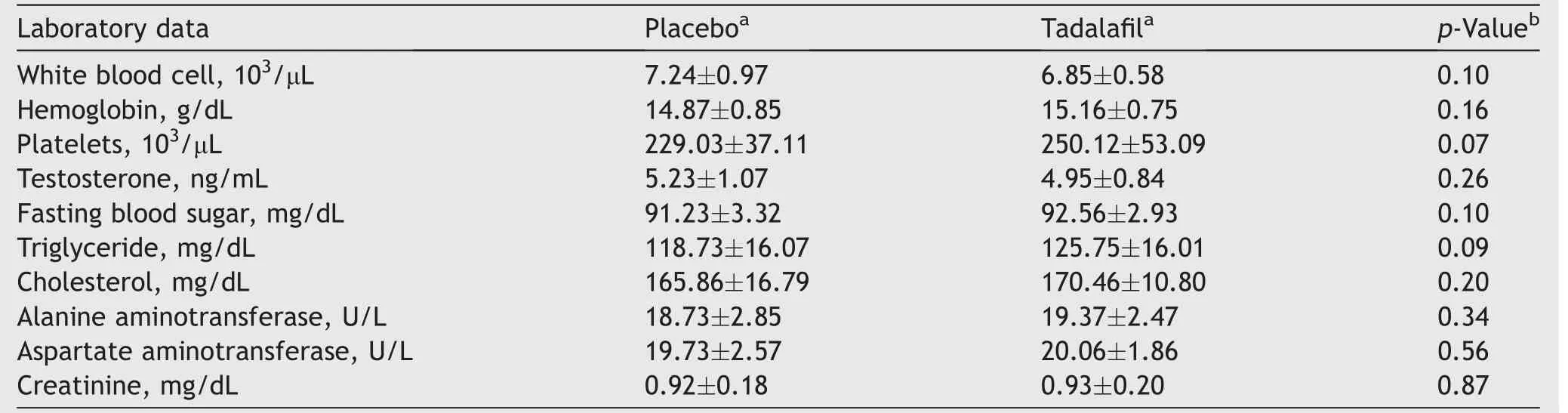
Table 2 Comparison of laboratory data of patients between the two groups.
The mean serum testosterone was 5.23 ng/mL in the placebo group and 4.95 ng/mL in the intervention group,which was not significantly different (p>0.05).Also,data analyses showed that there was no significant difference between the two groups in terms of other laboratory data(p>0.05).
The results of the patients’sexual function based on the complete version of IIEF questionnaire[7]in five subgroups including erectile function,orgasm function,sexual desire,intercourse satisfaction,and overall satisfaction before and after treatment between the two groups are shown in Table 3.According to Fig.2,treatment with tadalafil and placebo improved the patients’ sexual function criteria including erectile function,orgasmic function,sexual desire,intercourse satisfaction,and overall satisfaction compared to the baseline in both groups.However,this improvement was significantly higher in the intervention group with tadalafil than the control group with placebo(p<0.05).

Table 3 Comparison of the patients’sexual function scores before and after treatment between the two groups based on complete version of International Index of Erectile Function questionnaire.
4.Discussion
Recent studies investigated the effect of COVID-19 on male sexual health and reproduction,suggesting that COVID-19 impairs the quality of life and sexual function [15,16].A study confirmed that erectile function is an excellent indicator of systemic health and vascular function[17].Integrity of vascular endothelial function is essential for maintaining erectile function [18].Increased inflammatory cytokines such as TNFα,IL-6,and IL-1β in COVID-19 patients cause vascular endothelial dysfunction in multiple organs [19].In addition,endothelial dysfunction in the penile vessels causes ED [20,21].Moreover,increased inflammatory cytokines have been associated with clinical progression of sexual dysfunction,especially ED [22].Angiotensin converting enzyme 2 acts as the receptor for the SARS-CoV-2 virus and allows it to infect the cell.SARS-CoV-2 virus can cause testicular damage by binding to angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 expressed on mature Leydig cells [23,24].This damage impairs steroidogenesis and then leads to decreased serum testosterone level and subclinical hypogonadism.These conditions exacerbate ED [25,26].Testosterone suppresses inflammation and modulates endothelial function by increasing the levels of anti-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-10 and decreasing the levels of proinflammatory cytokines such as TNFα,IL-6,and IL-1β [27,28];thus,low serum testosterone level exacerbates ED.Furthermore,recent reports suggest that decreased blood oxygen saturation following pulmonary involvement in COVID-19 patients causes ED by reducing nitric oxide synthesis [29,30].
Sexual function is strongly associated with physical and mental health.In the recent COVID-19 pandemic,there were numerous reports of increased rates of post trauma stress disease,depression,and anxiety in the general population and especially in COVID-19 patients [31,32].These explain decreased sexual activity and libido in both gender during recent COVID-19 pandemic [33,34].In addition,hypogonadism following COVID-19 exacerbates mood disorders and decreases libido [35,36].Hamilton and Meston [37]showed that psychological stress inhibited the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis by increased serum cortisol levels,which could be a cause of sexual dysfunction.Carcedo et al.[38]reported that higher sexual satisfaction was associated with lower levels of depression and anxiety.

Figure 2 Comparison of the patients’ sexual domain scores before and after treatment between the two groups based on International Index of Erectile Function questionnaire.
One of the most effective treatments for ED is the PDE5 inhibitor class.Sildenafil since 1998 and Tadalafil since 2013 after FDA approval have been widely used to treat ED[39,40].PDE5 inhibitor blocks the catalytic action of the enzyme that degrades cyclic guanosine monophosphate,the downstream effector of the erection mediator nitric oxide;then,it facilitates the signal transduction mechanisms of the corpus cavernosal smooth muscle relaxation required for penile erection [41].Recent studies have suggested the possible role of this class of drugs in the management of COVID-19 [42].These drugs can play a role in the management of COVID-19 with their antiinflammatory,antioxidant,immune response regulation,and anti-apoptotic properties[43].In fact,these drugs are used to treat primary pulmonary hypertension by reducing vascular resistance [44].
Theoretically,daily administration of tadalafil could be useful for improving vascular endothelial function and reducing fibrosis.Therefore,administration of this drug may,on the one hand,improve pulmonary fibrosis and,on the other hand,improve the ED caused by COVID-19 [14].In addition,the results of our study confirm that daily administration of tadalafil 5 mg can improve ED caused by COVID-19.Patients in the intervention group who were treated with tadalafil had a significant improvement in sexual function parameters based on the complete version of IIEF questionnaire including erectile function,orgasm function,libido,sexual satisfaction,and overall satisfaction compared to those in the control group.However,patients in the control group showed less improvement of ED in the follow-up,which could be due to the role of psychological factors or reduction in the process of systemic inflammation over time.
The limitations of our study were the low sample size and impossibility of long-term follow-up.In addition,our study did not include another control group of those experiencing ED without a history of COVID-19 to further elucidate whether tadalafil has greater instead of worse efficacy between COVID-19 ED and regular ED.In addition,we could differentiate only organic ED from psychological ED,but we could not able to differentiate the other causes of ED.
5.Conclusion
Daily administration of tadalafil 5 mg seems to be effective and safe for improvement of ED caused by COVID-19.However,in the future,further studies are suggested with larger sample size and longer follow-up to confirm our results.
Author contributions
Study concept and design: Seyedmohammad Kazemeyni,Mohammadali Sadighi,Iman Shamohammadi.
Data acquisition: Iman Shamohammadi,Tara Hasanzadeh.Data analysis: Iman Shamohammadi,Alireza Dizavi.
Drafting of manuscript: Tara Hasanzadeh.
Critical revision of the manuscript: Iman Shamohammadi.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgements
We thank all individuals who contributed to this study.The authors would like to thank Shiraz University of Medical Sciences,Shiraz,Iran and also Center for Development of Clinical Research of Nemazee Hospital for language edition and Dr.Nasrin Shokrpour for editorial assistance.
杂志排行
Asian Journal of Urology的其它文章
- Transurethral resection of bladder tumor:A systematic review of simulator-based training courses and curricula
- Etiology and management of urethral calculi:A systematic review of contemporary series
- Oncologic outcomes with and without amniotic membranes in robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy: A propensity score matched analysis
- Single nucleotide polymorphism within chromosome 8q24 is associated with prostate cancer development in Saudi Arabia
- The risk of prostate cancer on incidental finding of an avid prostate uptake on 2-deoxy-2-[ 18F]fluoro-D-glucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography for non-prostate cancer-related pathology:A single centre retrospective study
- Prevention of thromboembolic events after radical prostatectomy in patients with hereditary thrombophilia due to a factor V Leiden mutation by multidisciplinary coagulation management
