Establishment of a TLC Identification Method for Ensete wilsonii
2024-01-24YongjingSUAoXIEWenwenLIANGFanglinZENGHaichengWENWeiWEI
Yongjing SU, Ao XIE, Wenwen LIANG, Fanglin ZENG, Haicheng WEN, Wei WEI
Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530001, China
Abstract [Objectives] The paper was to establish a TLC identification method for Ensete wilsonii. [Methods] Using β-sitosterol as the reference, the effects of preparation methods of test solutions, developing solvents, developing distances and color developing agents on TLC analysis were investigated, and the best TLC conditions for E. wilsonii were determined. [Results] The test solution prepared with 90% methanol solvent was dotted on TLC silica gel G plate, and developed with dichloromethane-toluene-methanol=10:5:1.5 as the developing solvent. Then the plate was sprayed with 10% sulfuric acid ethanol solution, and dried with hot blast for color development. Finally, the plate was examined under an ultraviolet lamp at 365 nm. The TLC results of E. wilsonii obtained showed good separation and color development effect, and the spots were clear and characteristic. [Conclusions] This method is safe, specific, and easy to operate, and can be used as a TLC identification method for E. wilsonii.
Key words Ensete wilsonii; TLC identification; Developing solvent; Color developing agent
1 Introduction
Ensetewilsoniiis the whole plant ofE.wilsonii(Tutcher) Cheesman, distributed in the south and southwest provinces of China and eastern Asian countries,etc.It is often harvested in spring and summer[1]. It is sweet and bland in taste and cool in nature; the root has the effects of clearing away heat and toxic materials, inducing diuresis to reduce edema, and cooling blood and relieving pain; the flower bus have the effects of lowering blood pressure and convergence; and the fruits have the effects of relaxing bowels[2]. Modern studies have shown thatE.wilsoniihas pharmacological effects such as treating hypertension and lowering blood sugar[3-6], and the plants of this species contain volatile oil[7], phenols[8], alkaloids[9], β-sitosterol[10]and other chemical components. Therefore, the above compounds can be used as index components in the subsequent evaluation of the quality standard ofE.wilsonii. So far, there is no perfect and feasible quality control system for the quality control ofE.wilsonii. Therefore, this paper identifiedE.wilsoniiby thin layer chromatography (TLC), in order to provide a reference for the establishment of the quality standard ofE.wilsonii.
2 Materials
2.1 Instruments and reagentsEL204 electronic balance (Mettler Toledo Instruments Co., Ltd.); HWS-24 electric thermostatic water bath (Shanghai Qixin Scientific Instrument Co., Ltd.); DHG-9203A electric thermostatic drying oven (Taizhou Sujing Experimental Instrument Technology Co., Ltd.); UPK-II Utope series ultra-pure water machine (Chengdu Ultra-pure Technology Co., Ltd.); KQ5200DE ultrasonic cleaner (Kunshan Ultrasonic Instrument Co., Ltd.); DFY-500 swinging pulverizer (Wenling Linda Machinery Co., Ltd.); ZF-7 dark box three-purpose ultraviolet analyzer (Shanghai Jiapeng Technology Co., Ltd.); silicone G plate (Qingdao Ocean Chemical Co., Ltd.). Methanol and other reagents were analytically pure, and the water was ultra-pure water.
2.2 Medicinal materialsTen batches ofE.wilsonii(identified as the whole plant ofE.wilsonii(Tutcher) Cheesman by professor Wei Songji at Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine) were collected from the field, and the sample information is shown in Table 1. β-sitosterol reference (batch No.: MUST-13101515, purity≥98.0%) was produced by Beijing Century Aoke Biotechnology Co., Ltd. The appearance ofE.wilsoniiis shown in Fig.1.
3 Methods and results
3.1 Investigation of TLC conditionsThin layer chromatography was carried out according to the TLC method in General Rule 0502 of theChinesePharmacopoeia(Volume IV, 2010 edition)[11].
3.1.1Investigation of different extraction conditions. By comparing three different extraction solvents of methanol, ethanol and water, different extraction concentrations of 30%, 50%, 70% and 90% methanol, two different extraction methods of reflux and ultrasound, and three different extraction time of 20, 40 and 60 min, the extraction conditions were finally determined as follows: the crude powder of this product was screened by No.2 sieve and shaken well; 2 g of crude powder was loaded into a 50 mL grinding conical flask, added with 10 mL of 90% methanol and extracted by ultrasound for 40 min; after filtered, the supernatant was used as the test solution. Preparation of reference solution: appropriate amount of β-sitosterol reference was weighed and added with methanol to prepare a reference solution with the concentration of 1 mg/mL.

Fig.1 Appearance of Ensete wilsonii
3.1.2Investigation of development systems with different polarities. YBJ-1 medicinal materials were prepared into test solution by the method described in Section3.1.1, dotted on the silica gel G plate, and developed with three development systems with different polarities: dichloromethane-acetone-methanol (8.5:1.5:1), dichloromethane-toluene-methanol (10:5:1.5) and cyclohexane-ethyl acetate-methanol (8:2:1). The plate was taken out and dried with hot blast, and then developed color with 10% sulfuric acid ethanol solution. The examination results under an ultraviolet lamp at 365 nm showed that the main spots had clear color when dichloromethane-toluene-methanol (10:5:1.5) was used as the developing solvent, showing good development effect.
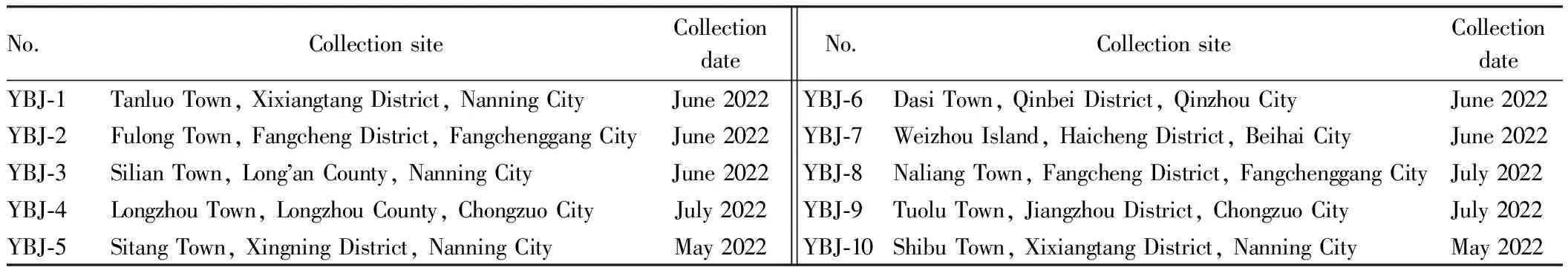
Table 1 Sample information of Ensete wilsonii
3.1.3Investigation of different color developing agents. YBJ-1 medicinal materials were prepared into test solution by the method described in Section3.1.1, dotted on the silica gel G plate, and developed with dichloromethane-toluene-methanol (10:5:1.5) as the developing solvent. The plate was taken out and dried with hot blast, and then developed color with 10% sulfuric acid ethanol solution, 10% aluminum trichloride ethanol solution, and 5% aluminum trichloride ethanol solution. The examination results under an ultraviolet lamp at 365 nm showed that the main spots had clear color when 10% sulfuric acid ethanol solution was used as the color developing agent.
3.1.4Investigation of different developing distances. Approximately 5 μL of each test solution was absorbed and developed at the distances of 13, 14 and 15 cm, with dichloromethane-toluene-methanol (10:5:1.5) as the developing solvent. After dried with hot blast, the plate was sprayed with 10% sulfuric acid ethanol solution for color development. The examination results under an ultraviolet lamp at 365 nm showed that various spots had clear size and color at the developing distance of 15 cm. Therefore, the developing distance of 15 cm was selected.
4 TLC identification
In summary, TLC identification method forE.wilsoniiwas determined as follows: the test solution and reference solution were prepared according to the method described in Section3.1.1; 5 μL of each batch of test solution and 3 μL of reference solution were dotted on the same silica gel G plate, and developed with dichloromethane-toluene-methanol (10:5:1.5) as the developing solvent; the plate was then taken out and dried with hot blast, and then developed color by spraying 10% sulfuric acid ethanol solution. The examination results under an ultraviolet lamp at 365 nm showed that the test solution showed the spots of the same color at the corresponding position of reference solution (Fig.2).
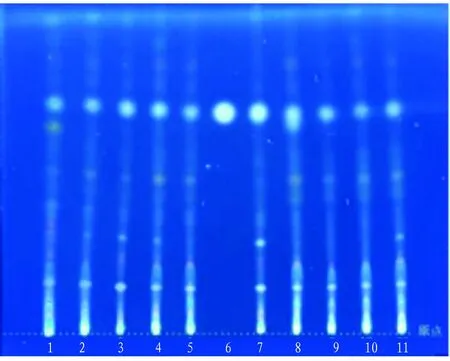
Note: 1. YBJ-1; 2. YBJ-2; 3. YBJ-3; 4. YBJ-4; 5. YBJ-5; 6.β-sitosterol reference; 7. YBJ-6; 8. YBJ-7; 9. YBJ-8; 10. YBJ-9; 11. YBJ-10. Chromatographic conditions: Silica gel G thin layer plate; Manufacturer: Qingdao Ocean Chemical Co., Ltd.; batch No.: 20220608; Specification: 20 cm×20 cm; Dot-shaped sampling, sample size: 5 μL; Temperature: (24.7±2) ℃; Relative humidity: 46RH% (±4%); Developing solvent: dichloromethane-toluene-methanol (10:5:1.5).
5 Discussion
This paper investigated in detail the conditions of TLC identification, systematically screened the preparation method of test solution, developing solvents of different polarities, developing distances and color developing agents in the chromatographic system, and finally determined the best TLC conditions. The test solution was prepared with 90% methanol as the extraction solvent, and dotted on silica gel G plate at the sample size of 5 μL, and developed with dichloromethane-toluene-methanol=10:5:1.5 as the developing solvent. After sprayed with 10% ethanol sulfate solution for color development, the solutions were examined under an ultraviolet lamp at 365 nm. The results showed that the method had the characteristics of simple operation, strong specificity, good stability and clear spots. In conclusion, the TLC identification method established in this paper is simple and easy to operate, economical and practical, with obvious qualitative characteristics and intuitive results, and can provide a certain reference for the quality evaluation standard ofE.wilsonii.
杂志排行
植物病虫害研究(英文版)的其它文章
- Resistance of Microbial Community of Artemisia annua L. to Pathogenic Fungi
- Research on Blended Teaching Mode: A Case Study of Floristry
- Effects of Low Temperature Stress on Germination and Physiological Characteristics of Different Sweet Maize Varieties
- Investigation and Analysis of Main Diseases of Landscape Plants in the Main Urban Area of Lu’an City
- Determination of Ten Kinds of Alpha-2 Agonists Residues in Animal Derived Food by UHPLC-Triple Quadrupole/Composite Linear Ion Trap Mass Spectrometry
