A tale of duality: Community perceptions towards the ecotourism impacts on Simien Mountains National Park,Ethiopia
2024-01-11TewodrosABUHAYEndalkahewTESHOMEGashawMULU
Tewodros ABUHAY , Endalkahew TESHOME, Gashaw MULU
a Department of Political Science and Governance Studies, University of Gondar, Gondar, 196, Ethiopia
b Department of Development and Environmental Management Studies, University of Gondar, Gondar, 196, Ethiopia
c Department of Tourism and Hotel Management, University of Gondar, Gondar, 196, Ethiopia
Keywords:Ecotourism Perception of ecotourism impacts Ecotourism participation Protected area resident World heritage site Semien Mountains National Park (SMNP)Ethiopia
ABSTRACT: This study aims to analyze how park households perceive the economic, sociocultural, and environmental impacts of ecotourism in Simien Mountain National Park (SMNP), Ethiopia.We combined qualitative and quantitative techniques for data collection.A sequentially embedded mixed design that gives priority to quantitative data was used.We also employed a multistage sampling technique to select respondents from three districts or woredas,namely Debark, Janamora, and Beyeda woredas.Finally, 397 participants were involved in the study from a random selection of three villages from each district or woreda.Data were gathered using a survey questionnaire,interviews, and focus group discussions.Data were analyzed using both descriptive and inferential statistical methods, including means, standard deviations, analysis of variance (ANOVA), and logistic regression models.The findings from a logistic regression analysis revealed that ecotourism participation had a significant relationship with gender (B=1.850, P=0.023),level of education (B=0.238, P=0.032), geographical location (B=0.420,P=0.041), and occupation (B=0.920, P=0.019).This investigation suggested that males and individuals with a higher educational background are more likely to possess optimistic perspectives concerning the impacts of ecotourism.Furthermore, individuals residing in districts relatively near ecotourism destinations, those engaged in tourism-related work, and younger participants were recognized as having optimistic viewpoints regarding the impacts of ecotourism.In conclusion, the study highlighted the need for collaborative efforts among stakeholders to maximize ecotourism’s benefits and minimize negative effects in SMNP.To achieve this, it is recommended that the Ethiopian Wildlife Conservation Agency, the Ministry of Tourism, and local government should work together to develop sustainable tourism plans that enhance local livelihoods and park conditions.Efforts should focus on increasing the participation of females and individuals with lower education levels through training and resource provision.
1.Introduction
In recent decades, the conservation of biodiversity and the reduction of poverty have become international societal,economic, and political objectives in protected areas.Incorporating the basic necessities of local communities in protected areas is highly valued in order to maintain harmony between these two conflicting objectives of poverty eradication and ecosystem service promotion (Chaigneau et al., 2019).Numerous governments believe that ecotourism is one of the strategies for promoting conservation, generating income, and creating employment opportunities for communities living near protected areas (Brett, 2018; Holland et al., 2022).Ecotourism has grown in prominence as a method for promoting sustainable tourism and preserving natural habitats and biodiversity.Due to scenic beauty and abundant biodiversity, protected areas such as national parks, wildlife sanctuaries, and other conserved areas, are popular ecotourism destinations.However, the impacts of ecotourism in protected areas are complex and require careful consideration of economic, social, and environmental trade-offs (Teshome and Demissie,2018).
Studies have shown that ecotourism can be an effective conservation tool by generating economic benefits that can incentivize local communities to support conservation efforts.Ecotourism can also provide alternative livelihoods to local people, reducing pressure on natural resources and wildlife.However, other studies have shown that ecotourism can lead to the degradation of natural resources, the commodification of culture, and the displacement of local communities.For example, studies conducted in Bangladesh by Arowosafe et al.(2019) and Cabral and Dhar (2020)in India found that ecotourism has a positive impact on local economies and contributes to the conservation of protected areas.They further mentioned the negative impacts of ecotourism on the park resources, environment, and socio-culture of park communities.These findings contributed to the conclusion that local communities are supportive of ecotourism and recognize its potential benefits (Karayilan and Cetin, 2016).However, some studies have found that local communities are skeptical of ecotourism and have concerns about its impacts on their livelihoods and the environment (Gebremicael et al., 2018; Thompson et al., 2018).
One of the main reasons for the negative perceptions of local communities is their lack of participation.If they do not get involved with different ecotourism activities and benefit from the activities, local people in protected areas are more likely to have negative perceptions towards the development of ecotourism (Liu et al., 2012; Abdurahman et al., 2016).To successfully develop ecotourism in destination areas, it is crucial to understand the factors that affect local residents’ participation in ecotourism and their perceptions of its effects (Wang and Zhong, 2018).Since local communities’ opinions about ecotourism are influenced by how tourism is perceived to affect their communities, both favorably and negatively, the study of park communities’ attitudes towards tourism has been a significant research topic (Holladay and Ormsby, 2011; Xu et al., 2022).Several research results recommended that the ecotourism industry in the destinations needs to be successfully planned, carried out, and focused on the community in terms of management, decision-making, and benefit-sharing methods.This is because ecotourism would negatively impact the viability of the local environment and the living conditions of the residents (Wang and Zhong, 2018).
Ethiopia has established numerous protected areas throughout the country to safeguard its natural resources and biodiversity.Ethiopia has 22 protected areas, including national parks, wildlife reserves, and sanctuaries.However,it’s worth noting that the number and extent of protected areas can evolve over time as new areas are designated and existing areas are modified (Teshome et al., 2021).Ethiopia’s abundant fauna and diverse ecosystems have long attracted eco-tourists.It is generally acknowledged that ecotourism can benefit local communities by creating economic opportunities and promoting sustainable development (Gebremicael et al., 2018).However, it is also acknowledged that ecotourism can have deleterious effects on the environment and local inhabitants, which are not always mitigated.
Previous studies have highlighted the lack of research on the factors that influence how ecotourism affects local communities residing in and around protected areas in Ethiopia (Kimengsi, 2014; Chamboko-Mpotaringa and Tichaawa, 2021).Furthermore, these studies have also suggested that the negative attitudes of local communities towards ecotourism are often linked to their lack of participation in ecotourism activities.It is also important to note that previous research on the livelihood impacts of ecotourism in Ethiopian protected areas has largely focused on its role in enhancing livelihoods while ignoring its perceived impacts on local communities (Alemayehu et al., 2011;Huang et al., 2021).Consequently, there is a significant gap in the literature concerning the factors that influence local residents’ participation in ecotourism in Ethiopia and their perceptions of its impacts (Wondie et al., 2012; Angessa et al., 2022).
This study aims to address this gap by examining the perceptions of residents living in and adjacent to Semien Mountain National Park (SMNP) in Ethiopia towards ecotourism and identifying the factors that influence their participation in ecotourism.Specifically, this study addressed the following three questions:
(1) How do the park communities perceive the economic, socio-cultural, and environmental impacts of ecotourism?
(2) How do demographic factors influence the level of awareness of the economic, socio-cultural, and environmental impacts of ecotourism?
(3) How to evaluate the relationship between the demography of park respondents and participation in ecotourism activities?
2.Materials and methods
2.1.Study area
2.1.1.General information about Semien Mountains National Park(SMNP)
The research was undertaken in SMNP (13°06′44′′–13°23′08′′N, 37°51′26′′–38°29′27′′E), which is situated in the North Gondar Zone, Amhara National Regional State, Ethiopia.The park is a portion of the high mountain massif in northern Ethiopia.SMNP is one of nine national parks established to protect wildlife and habitats with exceptional scientific, educational, and recreational significance.The current total area of SMNP is approximately 23,178 hm2,bounded by the five districts or woredas namely Debark, Adarkay, Beyeda, Telemt, and Janamora.Regarding the management of the park, from 1996 to 2009, it was under the authority of the Amhara Regional National State,enabling the establishment of much closer links between the various local and regional stakeholders than existed previously.In 2009, the reconstituted Ethiopian Wildlife Conservation Authority (EWCA) took control, and most of the park staff were transferred to the new authority, providing necessary continuity in management and regional and national integration.The park is home to number of endangered and endemic species (Demssie, 2015).Within the roster of 21 majestic large mammal species, a concerning majority are evaluated on the endangered list.Among these,three species—Walia ibex (Capra walie), Ethiopian wolf (Canis simensis), and Gelada monkey (Theropithecus gelada)—are exclusive to Ethiopia, adding to their significance as flagship species for SMNP (Hurni and Ludi, 2000;Admasu, 2020).
2.1.2.Dependency relationship between SMNP and community residents
The local community and SMNP have a strong sense of interdependence and mutual benefit in various ways.The park is vital to the economic, social, and environmental well-being of the neighbour residents.The park’s ecotourism activities provide community members with employment opportunities as guides, explorers, porters, and in the hospitality industry.In addition, the park facilitates the sale of local products and services, contributing to the growth of local businesses and employment (Demssie, 2015; Teshome et al., 2021).
Additionally, the community has a socio-cultural dependence on the park, as it is intrinsically linked to their cultural identity and heritage.Traditional knowledge, practices, folklore, rituals, and traditional uses of natural resources associated with the park are preserved and promoted.Furthermore, the park’s presence is crucial for environmental preservation.It protects the rich biodiversity, unique ecosystem, and endangered species, ensuring the provision of ecosystem services for the direct benefit of the local population.These services consist of pure air and water,agriculturally fertile soil, and protection from natural hazards (Admasu, 2020).In exchange, the community contributes significantly to the park’s sustainable management.Their participation in ecotourism activities,conservation efforts, and adherence to sustainable practices contribute to the park’s long-term resource preservation.
2.1.3.Socio-economic system planning background of ecotourism development
The development of ecotourism in SMNP, is governed by a comprehensive planning framework that prioritizes biodiversity conservation, community involvement, livelihood enhancement, cultural preservation, sustainable resource management, and stakeholder collaboration.The framework seeks to preserve the park’s biodiversity while promoting sustainable tourism practices that benefit both the park and the surrounding communities.Participation and empowerment of the community are essential components of the planning process, ensuring their inclusion in decision-making.The framework also concentrates on improving livelihoods through employment and income generation opportunities.Priority is placed on cultural preservation, which respects and celebrates the distinctive cultural identity of the communities.This comprehensive approach guarantees the balanced and prosperous development of ecotourism in SMNP (Wondirad et al., 2021).
2.1.4.Significant concern of SMNP
SMNP holds significant historical and ecological importance as one of the first natural sites in Africa to be recognized and inscribed on the World Heritage List.However, it faces numerous challenges due to its location in the densely populated Ethiopian highlands where human settlements have long existed and rely heavily on the park’s resources.Over the years, the surrounding population has rapidly increased, leading to intensified human activities such as cultivation and grazing, which have negatively impacted the park’s biodiversity and ecological balance.Despite these challenges, the efforts of the park’s management and its partners have contributed to the stability of wildlife populations, particularly the highly endangered species like Walia ibex, Ethiopian wolf, and Gelada baboon.As a result of these conservation efforts, the park has been removed from the List of World Heritage in Danger, which is a positive step towards its preservation (Hurni and Ludi, 2000).
2.2.Research approaches
This study employed a mixed-methods approach to obtain both qualitative and quantitative data.The primary premise of the use of this investigation method is that combining qualitative and quantitative approaches yields a more comprehensive understanding of a research problem than either quantitative or qualitative approaches alone do(Creswell, 2014).The rationale for choosing a mixed approach for this study was also attributed to sharing the goal of understanding the world in which we live (Ward et al., 2016).The same source also states that both qualitative and quantitative researches share a unified logic, and the same rules of inference apply to both.Mixed-method studies are those that combine the qualitative and quantitative approaches to the research methodology of a single study or multiphased study.Of course, employing a mixed-methods approach has the advantage of triangulating findings by incorporating data from various sources.It helps to beat some barriers with the utilization of just one approach and to extend the validity of the expected result.This, in turn, aids in the collection of suitable and relevant data and also increases the validity of the conclusions drawn from the analyses of the whole set of knowledge.Closely tied to the arguments for integrating qualitative and quantitative approaches is the reason given for legitimately combining them.Hence, this study used both sources of data by combining them to triangulate the findings, increase the validity of the conclusions, and overcome the limitations of using a single approach.
The current study applied a sequential embedded mixed method, which uses one type of data to support research that is primarily based on another type of data.It is a mixed-method design that combines the collection and analysis of both quantitative and qualitative data within the framework of a traditional quantitative research approach or a qualitative research approach when emphasis or priority is placed on either quantitative or qualitative data (Creswell,2014).The study incorporated a qualitative data set into larger quantitative-based studies.In this case, the researchers have made an attempt to supplement or expand on the findings of one method with another.The supportive data sets(qualitative data) were gathered both before and after data collection and analysis of the primary data types of a specific study using the sequential embedded mixed method.The supportive data set was typically used to understand the research context and participants, as well as to develop survey instruments.They were then used to follow up on and explain quantitative results.Thus, quantitative and qualitative research strands were mixed or integrated during the data collection, analysis, and interpretation stages (Creswell, 2014).
2.3.Sampling design and procedure
SMNP was chosen in this study using the purposive sampling method, because it is one of the world heritage sites assumed to have contributed more favorably to the economic growth of the region in particular and the country as a whole.The park household communities were purposefully selected to understand their perceptions of ecotourism impacts.The participants were selected using a multistage probability selection technique.First, five municipalities bordering SMNP were selected purposefully because they are directly affected by protected area administration.Then,three districts from these municipalities were selected at random.Then, three representative villages were chosen at random from each district.Using the Yemane formula (Sarmah and Hazarika, 2012), a sample of 397 households was selected from the total target population of 41,438 households by systematic random sampling.In pursuit of a comprehensive understanding of the communities’ views on ecotourism impacts, a survey questionnaire was developed, comprising open-ended and rating scale questions.The data collection was undertaken between February and April 2022 and required the respondents to rate each item on a Likert scale of 1–5, indicating their levels of comprehension and support for ecotourism impacts on economy, socio-culture, and environment.To ensure the questionnaire’s clarity, dependability, and comprehensiveness, we conducted a pilot test, and performed a reliability analysis to validate the scale items’ dependability.Further, qualitative data were gathered through interviews and focus group discussions to supplement the quantitative data.The questionnaire, developed from a thorough analysis of existing literature on ecotourism development impact, was primarily designed to simplify quantitative data collection.With each scale item’s Cronbach’s alpha coefficient exceeding the minimum threshold of 0.700, the questionnaire’s dependability was assured.With respect to the data analysis of the study, for each variable, the frequency distribution and the fundamental descriptive statistics (mean and standard deviation) were computed.The Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) version 25 (International Business Machines Corporation (IBM),Armonk, New York, the USA) was used to evaluate and explain the results.The data were statistically analyzed using descriptive techniques like means and standard deviations, as well as inferential techniques likeT-test,F-test, analysis of variance (ANOVA), and logistic regression.Qualitative data were gathered using a variety of strategies to support the quantitative findings.
3.Results
3.1.Park communities’ perceptions of the positive impacts of ecotourism on economy, socioculture, and environment
This study aims to investigate the perceptions of park communities towards ecotourism development in SMNP in terms of economic, socio-cultural, and environmental impacts.We used a Likert scale with 17 items to measure the respondents’ perceptions of ecotourism’s impacts on employment opportunities, the improvement of living standards,local business development, community facilities, social relationships, and cultural identity and pride issues (Table 1).The scale required respondents to rate their agreement on statements ranging from 1 to 5, with a high score indicating a greater level of positive impact from ecotourism.
As shown in Table 1, respondents generally had a positive perception of the economic, socio-cultural, and environmental impacts of ecotourism.The mean score for the perceptions of economic impacts was 4.00, with a standard deviation of 0.78, the mean score for the perceptions of socio-cultural impacts was 4.09, with a standard deviation of 0.55, and the mean score for the perceptions environmental impacts of ecotourism was 4.03, with a standard deviation of 0.70.The small difference in the mean scores among groups indicated that people generally had similar perceptions of the effects implied by the statements.
As it is portrayed in Table 1, the park communities showed positive perceptions of economic impacts across most items.The mean scores for items indicated that the respondents agreed with these statements to a considerable extent.These findings advocated that the communities recognized the potential of ecotourism to generate economic benefits,improve their living standards, and create business opportunities within the local context.Furthermore, the items“ecotourism creates employment opportunities for local residents” and “ecotourism encourages investments and infrastructure improvement” received notably higher mean scores, indicating that the park communities perceived ecotourism as a significant source of employment and a catalyst for investment and infrastructure development.These perceptions highlighted the positive economic impacts of ecotourism in terms of job creation and overall local economic growth.However, the item “ecotourism promotes the development of local products by creating a new market” received a slightly lower mean score than the other five economic impact items except one, suggesting that park communities had a relatively less favorable view of the role of ecotourism in promoting local products and opening up new markets.Additional research may shed light on the underlying causes of this perception.
Regarding the respondents’ perceptions of socio-cultural impacts of ecotourism, they were also largely optimistic.“Ecotourism provides cultural exchange and education opportunities to the host community”, and “ecotourism facilitates the development of community facilities and services”, and “ecotourism creates new learning opportunities for residents” items received relatively higher mean scores than other statements.These findings suggested that park communities regarded ecotourism as a valuable tool for cultural exchange, educational enrichment, and the expansion of community facilities and services.Moreover, the items “ecotourism preserves cultural values and customs of the community” and “ecotourism increases pride in cultural identity” received slightly lower scores.These perceptions indicated that park communities acknowledged the significance of ecotourism for cultural preservation and identity.
The respondents had a favorable perception of ecotourism’s environmental impacts, and they believed that ecotourism had a significant positive impact on the park environment or the local environment.It is possible to understand that the communities in SMNP believed that ecotourism had benefited them.Additionally, in an interview with park officers, it was acknowledged that the communities largely agreed that the park’s development as an ecotourism destination sparked local efforts to protect the environment.The development of ecotourism could potentially address issues related to the conservation and development impacts on biodiversity, endangered species,people, and the environment.In contrast to the expected benefits, the outcomes of the interviews and focus group discussions indicated that ecotourism had also a detrimental effect on the wildlife and environment of the park.Human intervention within the park due to ecotourism activities significantly increased, leading to congestion of tourists in certain areas, which has a significant negative impact.The interviews and focus group discussions revealed several negative impacts of ecotourism on the park, including litter problems, unhygienic campsites, animal disturbance, and the utilization of wood for campfires and cooking.The establishment of infrastructure such as road construction and the importation of horses and mules from far-off places, also had a negative impact on the park’s resources.

Table 1Descriptive statistics for positive impacts of ecotourism perceived by the community residents in Semien Mountain National Park (SMNP).
3.1.1.Demographic differences in communities’ perceptions of economic impacts of ecotourism
The statistic results shown in Table 2 reveal notable differences in the economic perception of ecotourism among respondents based on their gender, age, education level, and location.Gender was found to significantly influence the economic impacts of ecotourism (F(397) =4.60,P=0.000), with male respondents reporting more positive perceptions than female respondents.Due to the physical demands of many ecotourism activities in the study area, males predominately participated in the economic activities, which contributed to the disparity in female participation rate.The interview and focus group discussion results further supported the following argument: “To participate in tourismrelated activities, individuals must possess physical strength and stamina since these activities often involve lengthy walks lasting up to 12 d.If community members are unable to provide tour services, they may choose to collaborate with each other, taking turns working and splitting the meager earnings.Generally, younger individuals, primarily males, tend to participate in these activities.”
The ANOVA analysis showed significant differences in how people perceived the economic impacts of ecotourism in different locations (F(394) =7.71,P=0.001).Post-hoc comparisons revealed that households in Debark Woreda rated the positive impact of ecotourism more highly than those in Beyeda Woreda and Janamora Woreda.The education level of respondents was also a significant factor, with respondents in the formal education sector or with college diploma-level education and above perceiving the economic impacts of ecotourism more positively than those with lower levels of education.This trend suggested that higher education levels may enable people to benefit more from ecotourism, as they are more likely to work as tour guides or interpreters.According to interviews, having higher levels of education also provided more opportunities to engage in lucrative ecotourism activities, which can improve individual livelihood survival skills.Additionally, younger respondents had a more favorable perception of the benefits of ecotourism than older respondents.
The study’s findings were reinforced by the insights gathered from focus group discussions and interviews, which highlighted the various ways that ecotourism can boost economic development by fostering the growth of hotels,lodges, resorts, restaurants, infrastructure, gift shops, travel and tour companies, and grocery stores.These facilities supported a range of ecotourism-related activities and provided employment opportunities for large numbers of people, while also serving as a platform for the production and distribution of regional goods such as food, livestock,and handcrafted tourist items.The discussants agreed that ecotourism has played a significant role in driving economic growth in the study area by expanding business opportunities and creating jobs.Ecotourism activities in the park have created employment opportunities for over 8000 people, or more than 2196 households (Teshome and Demissie,2018; Abuhay et al., 2019).However, the discussants also noted that the benefits of ecotourism were not evenly distributed, with some individuals reaping more benefits than others.The unequal distribution of benefits was also identified as a challenge by the respondents.For instance, some individuals may lack the resources or skills necessary to participate in ecotourism activities, limiting their ability to benefit from these opportunities.Moreover, some groups may face discrimination or exclusion from the tourism industry, further perpetuating inequalities.
3.1.2.Determinants on the perception levels of economic impacts of ecotourism
Table 3 provides communities’ perspectives on the economic impacts of ecotourism.This analysis examined the relationships between a number of crucial variables and the level of perception of ecotourism’s economic impacts.Variables include gender, age groups, various levels of education attained by individuals, geographic location, benefits derived from engaging in ecotourism activities, and degree of community attachment.By analyzing the logistic regression model coefficients, standard errors, Wald chi-square statistics, odds ratios,P-values, and confidence intervals for each variable, we obtained valuable information regarding the significance and magnitude of these associations, and identified patterns and tendencies that provided insight into the factors that influence communities’perceptions.
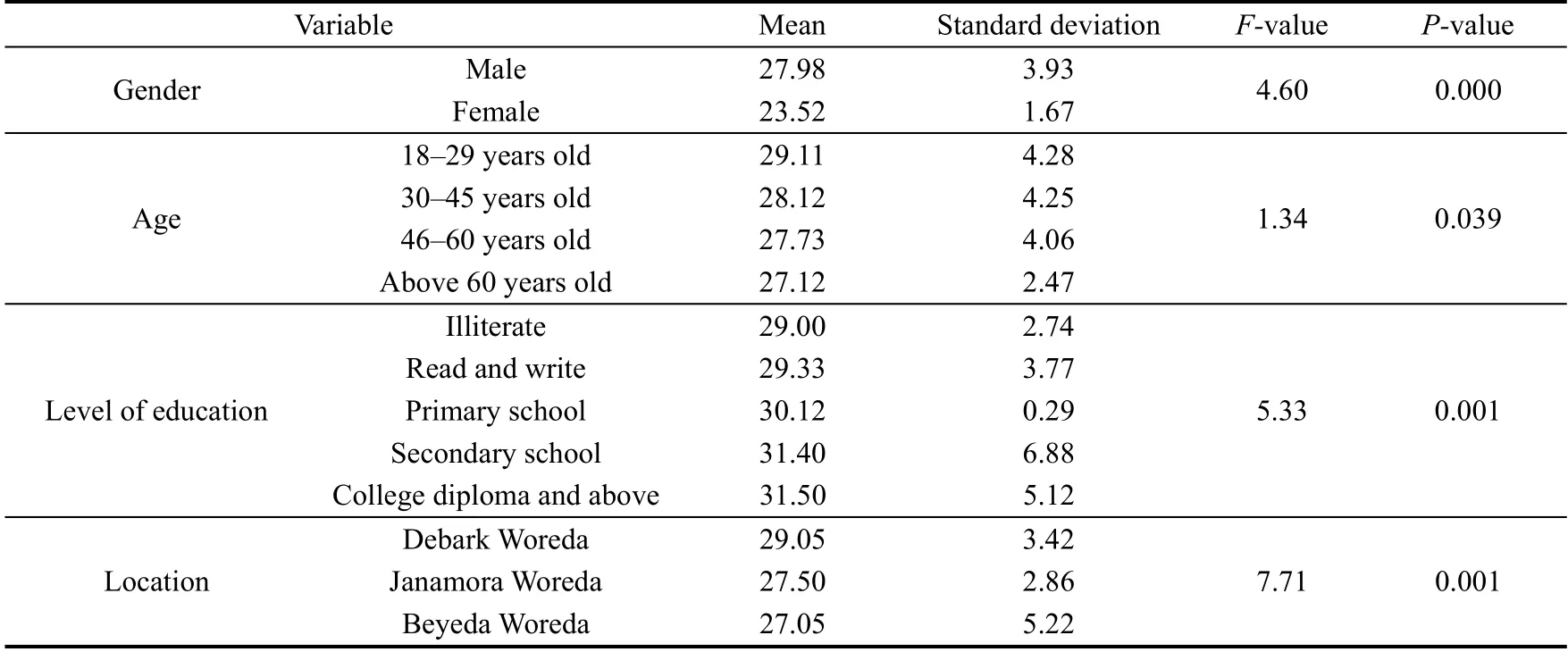
Table 2Summary of demographic differences in communities’ perceptions of economic impacts of ecotourism.
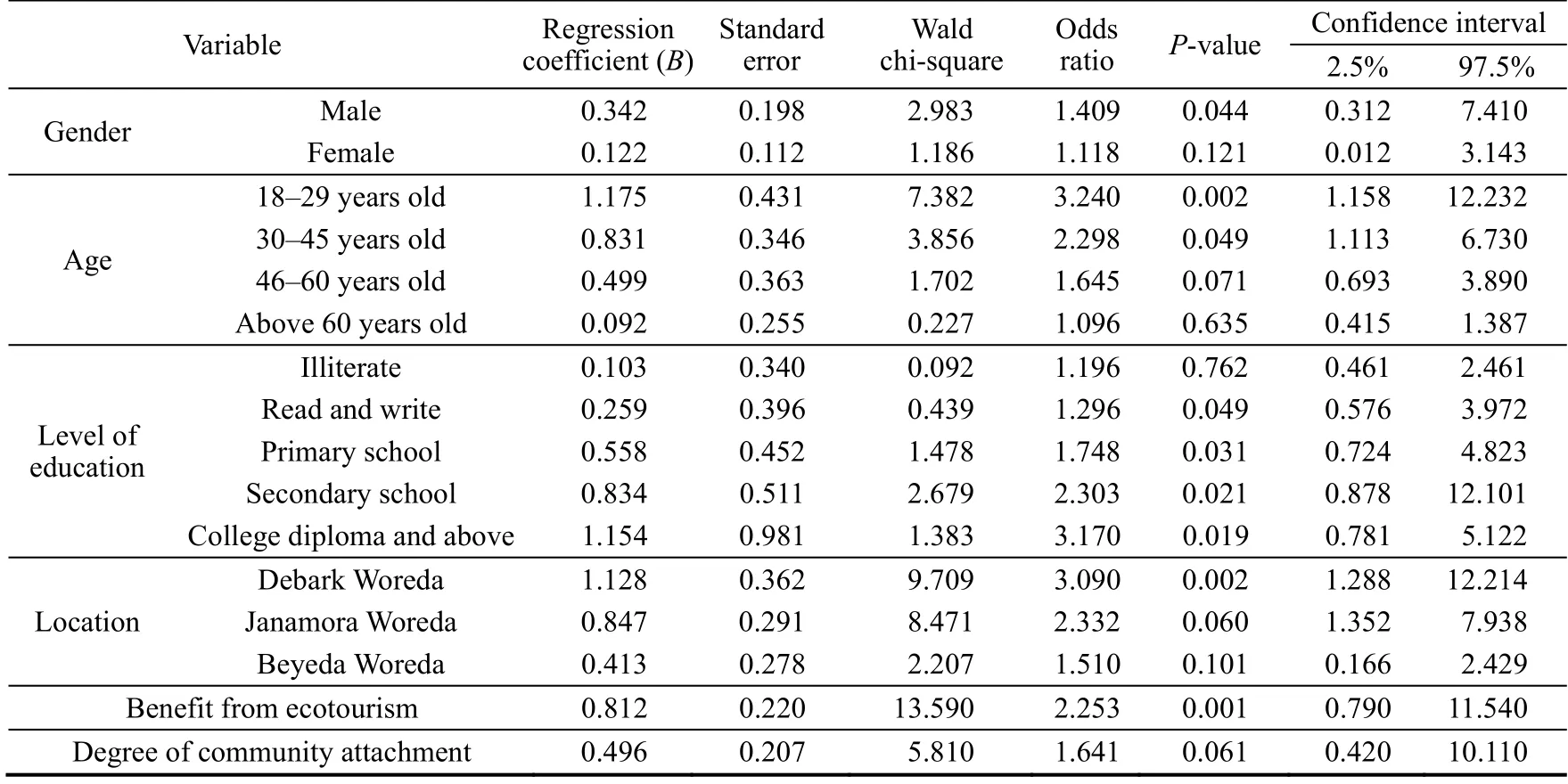
Table 3Determinants of communities’ perceptions of economic impacts of ecotourism.
The analysis of ordinary logistic regression, as illustrated in Table 3, highlighted the significant impacts of gender,age, education, location, benefit from ecotourism, and community attachment on shaping the communities’ perception of positive economic impacts of ecotourism.
Education emerged as an interesting variable, indicating a strong relationship with the perception of ecotourism’s positive economic impacts.The findings demonstrated that as education level increases, the perception of these positive impacts also increased.This is evident from the ordinary logistic regression model coefficients and odds ratios associated with different education levels.For example, individuals who have the capability to read and write displayed a regression coefficient of 0.259 and an odds ratio of 1.296, indicating a greater likelihood of perceiving the economic implications of ecotourism in a favorable manner compared to those who lack basic literacy skills.Moreover, individuals who have completed primary education or have achieved secondary education and beyond also exhibited higher coefficients and odds ratios, reinforcing the positive link between education and the perception of ecotourism’s economic benefits.
In relation to age groups, the analysis underscored that younger community members commonly perceived ecotourism as having significant positive economic impacts when comparing to older individuals.The regression coefficients and odds ratios associated with different age categories made this evident.An illustration would be the 18–29 years old age group showing a regression coefficient value of 1.175 and an odds ratio value of 3.240, signifying a stronger inclination towards perceiving the positive economic impacts of ecotourism.Furthermore, the age category between 30 and 45 years old showcased a coefficient value of 0.831 and an odds ratio value of 2.298, suggesting a comparatively high perception as well.Nevertheless, the regression coefficients were low for the older age groups of 46–60 years old and above 60 years old, indicating that the perception of positive economic impacts of ecotourism in these age groups presented a decreasing trend.
The analysis highlighted the influence of location on the communities’ perceptions.Residents of Debark Woreda exhibited a higher level of positive perception towards the economic impacts of ecotourism compared to residents of Beyeda Woreda.This is evident from the regression coefficient and odds ratio associated with the “location” variable.Residents of Debark Woreda have a regression coefficient of 1.128 and an odds ratio of 3.090, suggesting a stronger inclination towards perceiving positive economic impacts compared to residents of Beyeda Woreda.
In addition, the analysis showed how community attachment and direct benefits from ecotourism affect perception levels.Having a strong community attachment to the park tended to make community members perceive higher positive economic impacts.People who have directly gained from ecotourism also usually maintained higher perceptions of positive economic impacts of ecotourism.The community attachment and benefit from ecotourism variables were evident from the coefficients and odds ratios.Those people who maintained a strong link with the community demonstrated a regression coefficient of 0.496 and an odds ratio of 1.641, indicating their increased likelihood in perceiving positive economic impacts as opposed to those individuals with weaker links.Likewise,people who have directly enjoyed the advantages provided by ecotourism revealed a regression coefficient of 0.812 and an odds ratio of 2.253.This signified a reinforced understanding of beneficial results.
3.1.3.Demographic differences in communities’ perceptions of socio-cultural impacts of ecotourism
Based on the results presented in Table 4, the one-way ANOVA findings indicated that the socio-cultural impacts of ecotourism were significantly different based on respondents’ gender, age, and education level.Specifically, there was a significant difference in perceptions of the socio-cultural impacts of ecotourism among respondents with varying education levels.Post-hoc analyses revealed that individuals with higher education levels had more favorable perceptions of socio-cultural effects of ecotourism than those with lower education levels.Thereby, the level of positive perception of socio-cultural impacts of ecotourism decreased as education levels decreased.But the data showed that there were no significant differences in the perceptions of the socio-cultural impacts of ecotourism in the locations of respondents.
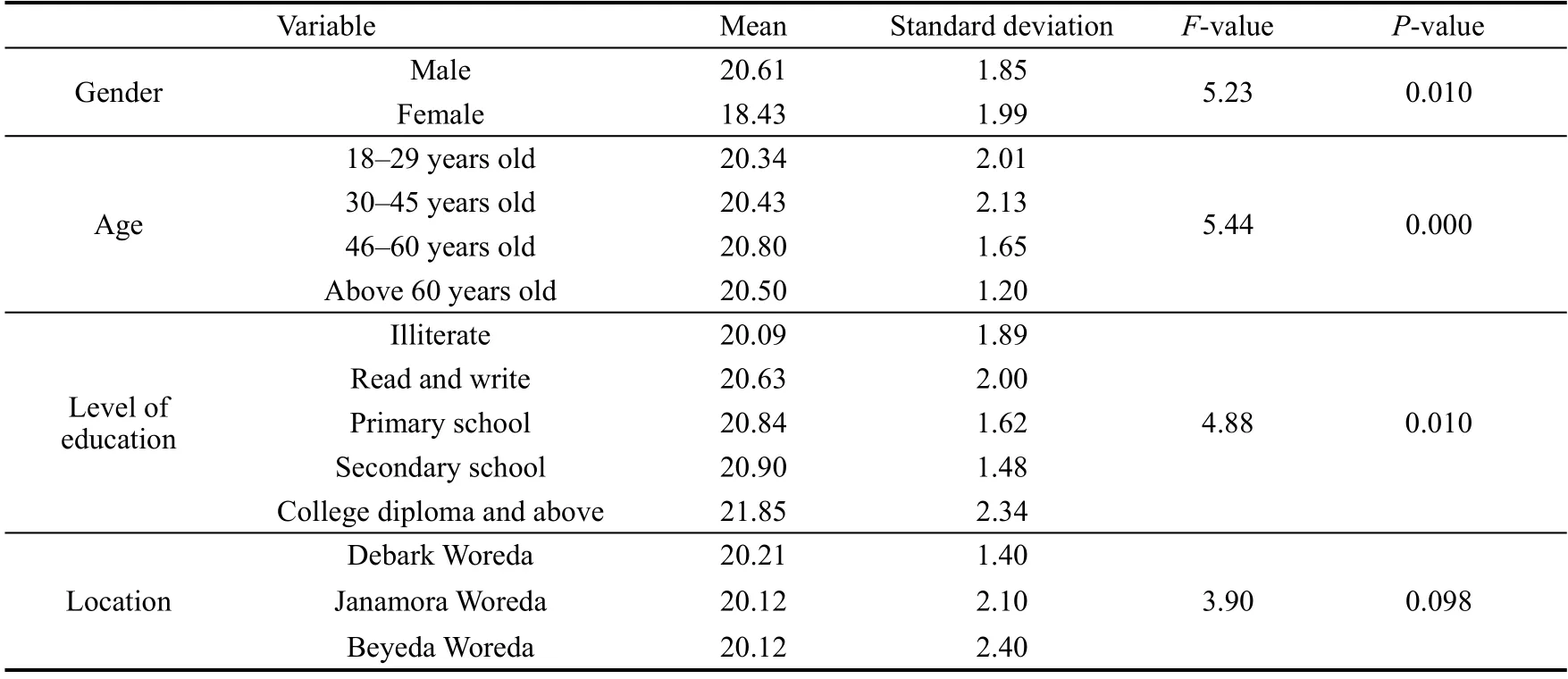
Table 4Summary of demographic differences in communities’ perceptions of socio-cultural impacts of ecotourism.
3.1.4.Demographic differences in communities’ perceptions of environmental impacts of ecotourism
Table 5 exhibits that when we looked at how ecotourism affected the environment based on people’s gender, age,and where they live, we didn’t find any big differences.The only thing that seemed to matter was the level of education.The test results (ANOVA for age, education level, and location, andT-test for gender) didn’t show any strong evidence that the differences we observed were real.So, the differences we saw in respondents’ assessments of the impacts of ecotourism on environment may simply be random and not due to any significant reasons related to gender, age, and location.
3.2.Park communities’ perceptions of the negative impacts of ecotourism on economy, socioculture, and environment
Table 6 presents the respondents’ perceptions of the negative impacts of ecotourism on economic, socio-cultural,and environmental dimensions.Regarding economic impacts, respondents expressed concerns about the negative impacts of ecotourism.They believed that ecotourism increased the prices of products and services, suggesting a potential economic burden on the local community.Furthermore, respondents perceived that ecotourism brought economic benefits only to a small number of residents, indicating a sense of inequality in the distribution of economic gains.Additionally, they felt that ecotourism primarily benefited businesses and people outside the locality, indicating a potential leakage of economic benefits.The average score for negative economic impacts was 4.10, suggesting a negative perception with a moderate level of agreement.

Table 5Summary of statistics scores on the environmental impacts of ecotourism.
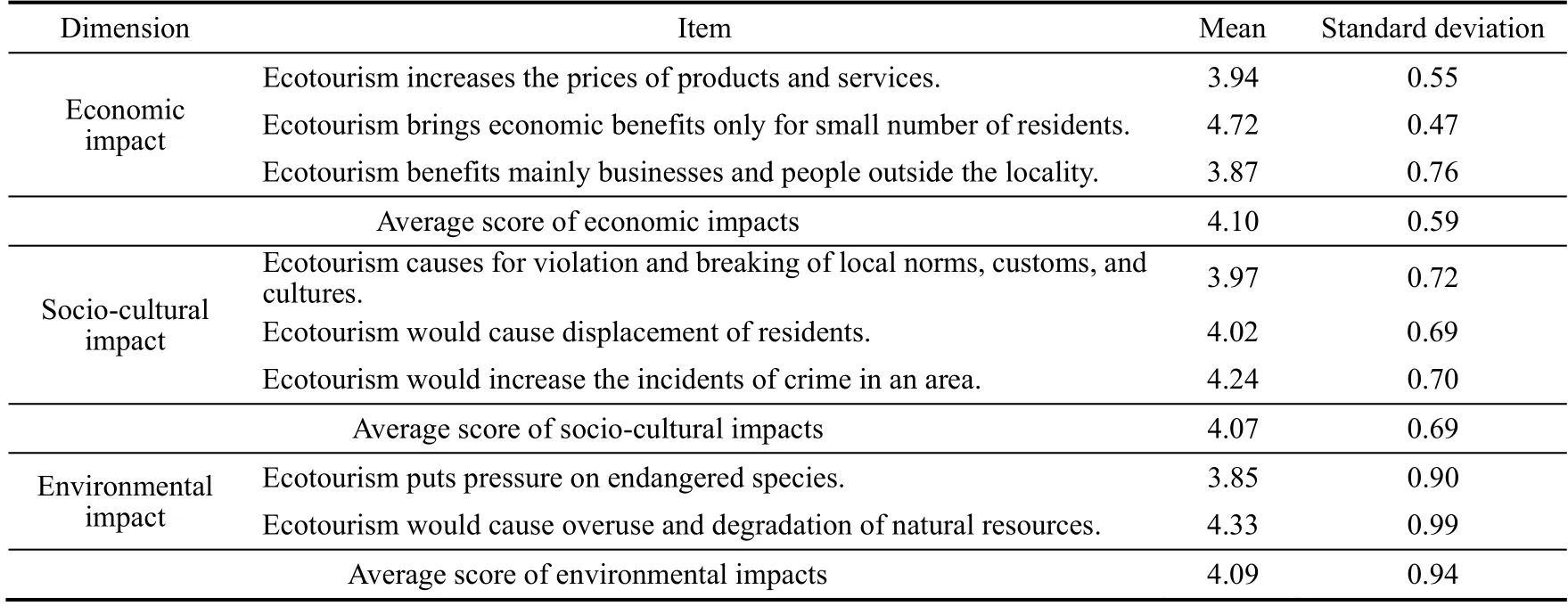
Table 6Descriptive statistics for negative impacts of ecotourism perceived by the community residents in SMNP.
In terms of socio-cultural impacts, respondents expressed concerns about the potential negative impacts of ecotourism.They believed that ecotourism could lead to the violation and breaking of local norms, customs, and cultures, indicating a threat to the preservation of cultural heritage.There were also concerns about the potential displacement of residents, suggesting that ecotourism development may result in the loss of homes and communities.Furthermore, respondents perceived that ecotourism would increase the incidents of crime in the area, indicating concerns about the potential negative social impacts.The average score for negative socio-cultural impacts was 4.07,indicating a negative perception with a moderate level of agreement.
Regarding negative environmental impacts, respondents recognized the potential detrimental effects of ecotourism.They believed that ecotourism puts pressure on endangered species, indicating concerns about the potential harm to vulnerable wildlife populations.Additionally, they felt that ecotourism could cause overuse and degradation of natural resources, suggesting worries about sustainability and long-term environmental impacts of ecotourism activities.The average score for negative environmental impacts was 4.09, indicating a negative perception with a moderate level of agreement.
In conclusion, the study findings revealed that respondents had negative perceptions of ecotourism impacts on economic, socio-cultural, and environmental dimensions.For the impacts on economy, they expressed concerns about the increased prices of goods and services, unequal distribution of economic benefits, and the potential negative effects on local businesses.Socio-culturally, concerns were raised about the violation of local norms and customs,displacement of residents, and increased crime incidents.Environmentally, respondents recognized the potential harm to endangered species and the degradation of natural resources.These perceptions highlighted the importance of implementing sustainable practices, involving local communities in decision-making processes, and carefully managing and mitigating the negative impacts of ecotourism.The findings emphasized the need for a balanced approach that addresses the concerns raised by the local communities while harnessing the potential benefits of ecotourism.
These results were consistent with the information gathered by focus group discussions and key informants, which showed that ecotourism raised living standards, expanded recreational and entertainment options, encouraged cultural change, and strengthened the host communities’ sense of cultural identity.In addition, focus group discussions and interview results suggested that ecotourism can lead to the displacement of local communities and traditional livelihoods, as well as the commodification of local cultures and traditions.Some respondents were concerned about the lack of regulation and enforcement of ecotourism activities, which can result in unsustainable practices and detrimental effects on the environment and local communities.
3.3.Park communities’ level of participation in ecotourism
As depicted in Table 7, a total of 252 households (equivalent to 63.5% of the entire sample) participated in ecotourism activities.The logistic regression model revealed that when all independent variables were considered together, they accounted for 42.1% of the variance of dependent variable.The logistic regression analysis further revealed that gender, education level, household location, and occupation were the four demographic variables that were significantly related to participation in ecotourism activities.Therefore, these variables were directly and significantly associated with the probability of households participating in ecotourism activities.The results of the logistic regression model also showed that age, marital status, landholding size, and family size had no significant effect on participation in ecotourism activities.
The findings revealed that males were more likely to participate in ecotourism than females, with a 1.850-unit increase in male participation resulting in a change in ecotourism participation.This can be attributed to the fact that ecotourism activities were generally considered to be more suitable for males than females due to the physical and courageous demands of activities such as hiking, camping, and trekking.The study revealed that participation in ecotourism activities increased by 0.238 for every one-unit increase in education level.Literacy or education was associated with 3.121 times higher odds of participation, suggesting that education plays a crucial role in fostering interest and awareness in ecotourism.Individuals with higher levels of education were more likely to work in ecotourism-related professions such as tour guiding and travel agency services.Additionally, individuals residing in specific locations, potentially those in close proximity to the core areas of ecotourism destinations or the main ecotourism activities in the park, were associated with 3.661 times higher odds of participating in ecotourism activities, indicating the influence of geographic location on ecotourism participation.Specifically, for every one-unit increase in the number of individuals in Debark district or Woreda, participation in ecotourism activities increased by 0.420.Lastly, the study revealed that participation in ecotourism activities increased by 0.920 for every one-unit increase in engaging in occupations related to ecotourism.
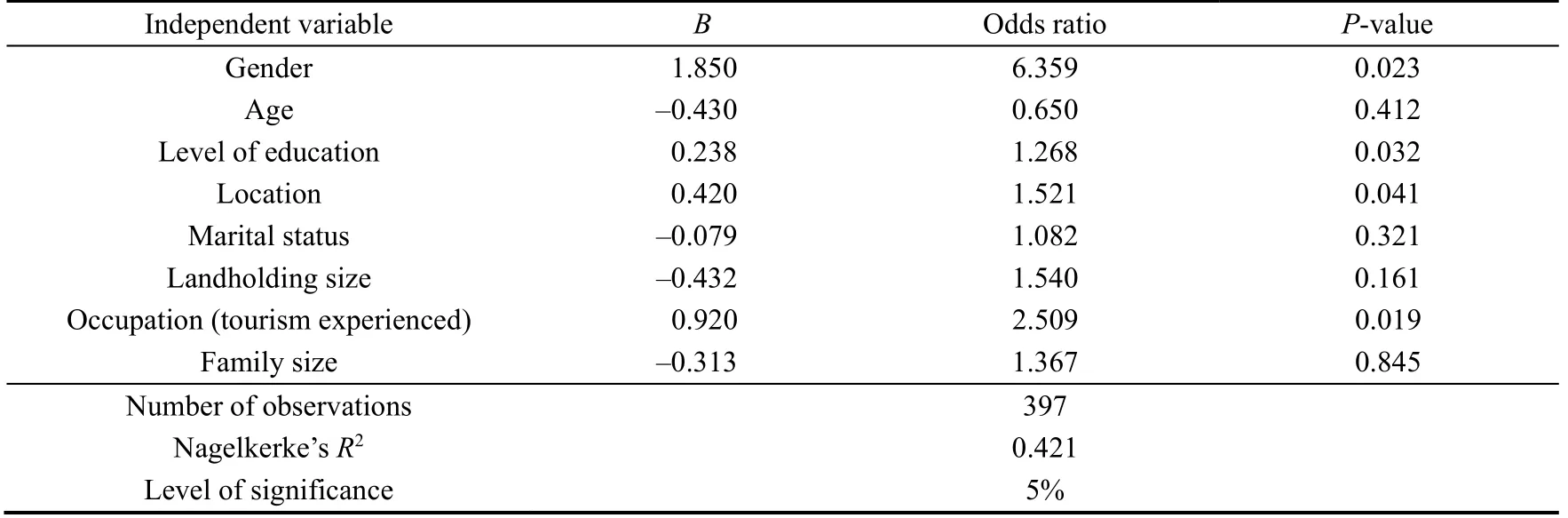
Table 7Determinants of participation in ecotourism activities for community residents in SMNP.
4.Discussion
The study’s findings demonstrated that the local communities in SMNP had both positive and negative perceptions of ecotourism impacts on socio-culture, economy, and environment.Additionally, local communities’ perceptions of the economic, socio-cultural, and environmental effects of ecotourism varied significantly according to their demographic characteristics, and the degree of participation in ecotourism activities was also related to their demographic characteristics.An interesting contradiction emerged in respondents’ perceptions of the distribution of economic benefits.While they acknowledged that their involvement was limited, they claimed that most of the revenue from ecotourism services went to communities outside the park.
Studies conducted in various national parks such as Komodo National Park in Indonesia by Kiss (2004), Kruger National Park in South Africa by Peach (2017), Bale Mountains National Park in Ethiopia by Gulte et al.(2022), and Maasai Mara National Reserve in Kenya by Holland et al.(2022), have revealed similar patterns in community perceptions of ecotourism.These studies demonstrated favorable community perceptions regarding the generation of revenue for the local community, while also highlighting ongoing criticism regarding the unequal distribution of benefits, particularly in rural areas.These findings further emphasized that ecotourism was not fully utilized as an alternative livelihood strategy, but rather served a limited supportive role.Additionally, these studies acknowledged the existence of negative impacts associated with ecotourism, particularly concerning from the environmental and socio-cultural dimensions.
On the contrary to what was discovered in this study and aforementioned studies, the experiences of different countries in Africa such as Ghana, Tanzania, and Egypt, and in other parts of countries such as Nepal and Costa Rica revealed that ecotourism served as an alternative means of making a living, allowing individuals to generate income in equitable sharing while preserving the local ecosystem and culture.In these countries, community owned ecotourism activities and served them sustainable means of generating income for the local communities (Koki, 2017;Agyeman et al., 2019).
The logistic regression analysis of the current study revealed that gender, education level, household location, and occupation in tourism industry were significantly related to participation in ecotourism activities.Similar to the current study, researches by Gashaw (2015) in Bale Mountains National Park, Saikia (2015) in India, and Dey et al.(2020) in Sundarbans found that younger individuals had more positive perceptions of ecotourism’s economic benefits than the older ones.The findings of these studies revealed that there was a negative relationship between age and perception and participation in ecotourism activities.Similar to this study, Zhang and Lei (2012) and Asfaw et al.(2021) revealed that the higher educated respondents showed higher levels of participation in ecotourism activities.They discovered a positive correlation between education level and perceptions of ecotourism impacts.Regarding gender, consistent with the current research results of a study by Aseres and Sira (2021), which showed that males had better perception towards ecotourism, and even they had better engagement in ecotourism activities.Similar to the current study, a research conducted by Zhang et al.(2020) in Qianjiangyuan National Forest Park in China found that people with positive perceptions were typically under 35 years old (young) and had a college degree or higher,and those with negative perceptions were typically over 60 years old and lacked a college degree.Ante et al.(2019)indicated that individuals living closer to the park perceived more positive impacts of ecotourism than the far ones.
Contrary to what was previously stated about age and education level, there are only a few studies that indicated an unexpected negative connection between these factors and community participation in ecotourism activities.For instance, if we considered the investigations conducted by Thompson et al.(2018) in the United Kingdom and Ruhanen (2019) in Costa Rica as examples, the findings demonstrated a negative association between educational qualifications and participation rates for ecotourism activities.The findings showed that individuals who had less formal education were more prone to engaging in ecotourism activities.Similarly, researchers also investigated how age influences participation in ecotourism activities among the local population.For example, the investigation by Thompson et al.(2018) in the United Kingdom surprisingly showed that there is a positive correlation between age and engagement in ecotourism activities.Gender differences were primarily observed in developing countries like Africa, as concluded from various studies.With the contrary to the current study, for instance, Zhang et al.(2020)thought there were no gender differences in the perception towards park and its benefit.
The discussion above highlighted that many studies indicate a favorable perception among park-adjacent communities regarding the socio-economic and environmental impacts of ecotourism.Nonetheless, there existed an acknowledged problem regarding unequal distribution of benefits, whereby the majority of revenues were directed towards communities situated outside the park.In spite of facing criticisms and challenges in developing ecotourism projects within some regions, success stories from Nepal, Tanzania, Ghana, and Costa Rica showed how communitybased ecotourism can bring about significant advantages.The illustrations revealed that ecotourism has the capacity to function as a sustainable and mutually advantageous field for both travelers and local communities.
5.Conclusions
The study’s findings demonstrated that the local communities near SMNP have a positive perception of the economic, socio-cultural, and environmental impacts of ecotourism.This implied that the host communities’perceptions of ecotourism benefits are correlated with how inclined they are to support the growth of ecotourism and attribute the improvement of their communities to tourism development.A closer look at the underlying statistics of the mean scores, however, revealed that the perceived impacts of ecotourism are only moderately positive, indicating that the advantages of tourism are not yet fully appreciated.Out of the three types of tourism impacts, the economic benefits of ecotourism to local communities have received the most attention in the study.Respondents had a more positive perception of ecotourism’s economic benefits than of its socio-cultural and environmental effects.
Additionally, the results of this study showed that locals’ perceptions of the economic, socio-cultural, and environmental impacts of ecotourism varied significantly according to their socio-demographic characteristics.Specifically, Men and respondents with higher levels of education (diploma holders than illiterates) felt the benefits of ecotourism more strongly than women and respondents with lower levels of education did.In addition, the respondents of residents in the Debark Woreda had a more favorable perception of the economic advantages of ecotourism than their rivals (Janamora Woreda and Beyeda Woreda).Overall, the results showed that the local communities’ perceptions of ecotourism’s economic impacts are more variable than those of its impacts on the environment and society in general.Additionally, the findings demonstrated that, of all the socio-demographic factors investigated, gender and educational attainment offered statistically significant variations on the three dimensions of ecotourism impacts taken into consideration by the current study.
6.Recommendations and implications
6.1.Policy recommendations
It is known that ecotourism has been used as one viable strategy to narrow and resolve the conflicting objectives of conservation and development in the park.With reference to this model, the study’s findings have important policy implications for the Ethiopian Wildlife Conservation Agency, the Ministry of Tourism, and other stakeholders.Hence,the researchers provide the following recommendations.To maximize benefits and reduce negative impacts,stakeholders should work closely together and step up their initiatives.Local government and the Ethiopian Wildlife Conservation Agency should develop sustainable plans for tourism to benefit nearby communities and improve living conditions in the park.They also should create a conducive atmosphere to increase the participation of females and individuals with lower levels of education in ecotourism activities and provide them with access to training and resources to enhance their skills and abilities.Additionally, the site must improve the variety of recreational activities to encourage tourists to stay longer and bring about the development of tourism industry.Finally, public education on the importance of ecotourism is essential to secure support for tourism development and establish sustained community development.
6.2.Implications for other similar protected areas
The study revealed that park-adjacent communities generally perceive ecotourism positively, but face challenges related to unequal benefit distribution.Successful examples from different regions underscored the significance of sustainable practices, community participation, and fair benefit sharing.Demographic factors such as education,gender, and proximity influence participation in ecotourism activities.Understanding the unique characteristics of local contexts is crucial for implementing effective interventions and maximizing the positive impacts of ecotourism.By considering these findings, other regions can learn the following lessons: prioritizing sustainable practices and community engagement, addressing issues of benefit distribution, considering the demographic factors influencing participation, and tailoring interventions to the specific needs and circumstances of each location.These insights can guide the development and management of ecotourism initiatives in other regions, ensuring long-term sustainability and mutual benefits for both communities and tourists.
The recommendations and findings of this study have broader implications for ecotourism development in regions beyond SMNP.The principles of collaboration, sustainable planning, inclusive participation, diversification of activities, and public education can serve as valuable guidelines for other destinations facing similar challenges.By adopting these strategies, regions worldwide can maximize the benefits of ecotourism, preserve natural resources,enhance community well-being, and promote sustainable development.These insights can inform and inspire policymakers, conservation organizations, and local communities in other countries to effectively harness the potential of ecotourism for balanced and inclusive growth.
Authorship contribution statement
Dr.Tewodros ABUHAY entered the data into SPSS and performed validity and filtering tests, and produced the manuscript’s first version.Dr.Endalkachew TESHOME provided feedback on the drafting of manuscript and suggested possible additions.Dr.Gashaw MULU contributed to contextual considerations and the comparison of the findings to previous research.
Ethics statement
Ethics approval was obtained from Institutional Review Board (IRB) of University of Gondar regarding the ethical aspects of this research.In addition, the participants provided their informed consent to participate in this study.
Declaration of conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the participants of this study, particularly the household heads and the park staff members in the study areas, for their sound input for this study.
杂志排行
区域可持续发展(英文)的其它文章
- Economic complexity and environmental sustainability in eastern European economies: Evidence from novel Fourier approach
- Supplemental feeding on rangelands: new dynamics of the livestock in the El Ouara rangelands in southern Tunisia
- Social interactions in periodic urban markets and their contributions to sustainable livelihoods: Evidence from Ghana
- How Himalayan communities are changing cultivation practices in the context of climate change
- Rural sustainable development: A case study of the Zaozhuang Innovation Demonstration Zone in China
- Toward a sustainable future:Examining the interconnectedness among Foreign Direct Investment (FDI),urbanization, trade openness, economic growth, and energy usage in Australia
