Spatial Distribution Pattern and Influencing Factors of Physical Bookstores of Large Cities: A Case Study of Three National Central Cities in Western China
2023-12-16LIURuikuanLIJiuquanCHANGFangMAJiayao
LIU Ruikuan ,LI Jiuquan ,CHANG Fang ,MA Jiayao
(1.College of Urban and Environmental Sciences,Northwest University,Xi’an 710127,China;2.School of Tourism & Research Institute of Human Geography,Xi’an International Studies University,Xi’an 710128,China)
Abstract: As cultural facilities,physical bookstore is an important part of urban infrastructure.Influenced by the development of social economy and the internet,physical bookstores also have become a combination of cultural space and tourism experience.In this case,it is necessary to explore the spatial characteristics and influencing factors of physical bookstores.This study uses Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise (DBSCAN),spatial analysis and geographical detectors to calculate the spatial distribution pattern and factors influencing physical bookstores in national central cities/municipality (hereafter using cities) in western China.Based on spatial data,population density,road density and other data,this study constructed a data set of the influencing factors of physical bookstores,consisting of 11 factors along 6 dimensions for 3 national central cities in western China.The results are as follows: first,the spatial distribution pattern of physical bookstores in Xi’an,Chengdu,and Chongqing is unbalanced.The spatial distribution of physical bookstores in Xi’an and Chongqing is from southwest to northeast and are relatively clustered,while those in Chengdu are relatively discrete.Second,the spatial distribution pattern of physical bookstores has been formed under the influence of different factors.The intensity and significance of influencing factors differ in the case cities.However,in general,the social factor,business factor,the density of research facilities,tourism factor and road density are the main driving factors in the three cities.There is a synergistic relationship between public libraries and physical bookstores.Third,the explanatory power becomes stronger after the interaction between various factors.In Xi’an and Chengdu,the density of communities and the density of research facilities have stronger explanatory power for the dependent variable after interacting with other factors.However,in Chongqing,the traffic factors have stronger explanatory power for the dependent variable after interacting with other factors.The results could provide a practical reference for the sustainable development of physical bookstores and encourage a love of reading among the public.
Keywords: spatial characteristics;physical bookstores;influencing factor;Density-Based Spatial
1 Introduction
As city’s cultural landmarks,physical bookstores play an important role in the development of leisure and cultural spaces.After the reform of the bookstore management system in the 1980s,the operating techniques and strategies of China’s physical bookstore have changed.A peak in the number of bookstores was reached at the beginning of the 21st century (Liu,2018).However,the operation process of physical bookstores is not completely smooth.With the impact of online operations and consumers’ escalating demands,the offline physical bookstores are facing a serious survival problem(Chen et al.,2021).Under the influence of a series of policies and the background of cultural and tourism integration,the development of physical bookstores has rebounded and gradually moved toward the integration and development of diversified formats,realizing crossborder operations.
Interest in physical bookstores has steadily grown among scholars,with many subjects involved,such as publishing,library and information science,sociology,and geography.Existing studies have focused on the process and shortcomings in the operation of traditional physical bookstores (Miller,1999;Chen and Cheng,2013).They found that consumers prefer the products,environment and atmosphere of physical bookstores rather than prices and services (Turley and Milliman,2000).The impact of online bookstores,the high operating costs of physical bookstores,and the lack of management talent are the main reasons for the losses of physical bookstores (Gan et al,2020).To address these issues,some scholars have proposed corresponding countermeasures (Nguyen et al.,2019),and they analyzed consumers’ online reviews of physical bookstores to improved operations (Wang et al.,2020).Other studies have paid attention to the business model (Liao,2022;Luo,2023),the transition and comparison of online and offline sales of physical bookstores (Yeh et al.,2009).They believed that physical bookstores are heavily influenced by online sales.Therefore,it is necessary to respond to the diverse needs of readers in the digital age (Hung and Tang,2021) and change their business model.
As for the future of physical bookstores,the scholars have different views.Based on the perspective of the media ecosystem,a study believes that the future positioning of physical bookstores may be ‘book-buying stores’,‘cultural exchange platforms’ and ‘cultural channel operators’,transforming from book marketers to channel operators (Yang,2012).However,from the perspective of urban cultural space,physical bookstores should innovate their business concepts,enhance the advantages of the internet,and develop diversified business models (Hou,2021).Some physical bookstores have achieved success by combining cultural and creative products with online sales.In addition,others have achieved transformation by changing the inventory structure and highlighting the regional culture in their design.With the comprehensive development of bookstores,consumers engage in behaviors such as reading,learning,buying books and drinking coffee.They have found that physical bookstores have multiple attributes of cultural,consumption and leisure (Kunc and O’brien,2017;Artusi et al.,2020).Others have studied the spatial structure of physical bookstores and the behavioral characteristics of different consumer groups and analyzed their interaction with the space (Sun and Wang,2016).Meanwhile,more attention has been paid to the behaviors of special consumer groups (Karp,1973;Doucé et al.,2013).
In recent years,sociologists have focused on analyzing the characteristics of consumer behavior and the internal functional divisions in physical bookstores,and they have tried to deconstruct the value of physical bookstores as cultural spaces (MacDonald and Black,2000;Huang,2020).Furthermore,existing studies focus on the spatial distribution pattern and use geographical detectors,Statistical Product and Service Solutions(SPSS),Geographically Weighted Regression (GWR)and other methods to analyze the influencing factors.For example,in Wuhan,the spatial distribution pattern of physical bookstores is affected by urban development.Traditional-type physical bookstores are relatively concentrated in urban centers,while new-type physical bookstores favor new urban districts (Gan et al.,2020).The physical bookstores in Xi’an are mainly concentrated in the central and the southern districts(Liu and Li,2021).However,the book retail industry in Nanjing is characterized by clustering-periphery dispersion (Jiao and Li,2016).Previous studies have shown that there are many factors affecting the spatial distribution of physical bookstores,including location,the economy,traffic,the social factor,the cultural factor,population density,and the number of university students(Gan et al.,2020;Li et al.,2020;Liu and Li,2021).At present,more physical bookstores are being built,and they are unevenly distributed in urban areas.It is important and necessary to study their spatial distribution pattern and the main influencing factors.
However,existing studies have three limitations.First,most studies analyzed the status of physical bookstores.It is necessary to study the physical bookstores’spatial clustering characteristics and the comparative analysis of differences among cities and researches in this field are not enough.Second,most of the existing cases are large cities in the eastern China.Relatively little attention has been paid to inland cities,especially cities in twestern China.It is necessary to analyze the pattern and driving factors of physical bookstores in western China.Third,the operation mode of physical bookstores changes with people’s needs.It is extremely important to explore the relationship between physical bookstores and tourist attractions in the context of cultural and tourism integration,which needs to be studied continuously.
This study focused on the differences in the spatial distribution pattern of physical bookstores among three national central cities/municipality (hereafter using cities) in western China,Xi’an,Chengdu and Chongqing,and quantitatively analyzed the influencing factors based on Point of Interest (POI) data.This study aims to: 1) visualize the development direction and clustering hot spots of physical bookstores through Standard Deviation Ellipse (SDE) and Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise (DBSCAN);2) clarify the importance of factors influencing the spatial distribution pattern of physical bookstores by geographical detectors.The results could not only provide reference for the location and business model of physical bookstores in cities,but also provide cases for the construction of cultural service systems in different types of big cities.
2 Materials and Methods
2.1 Study area
National central cities are important supports for China’s urbanization strategy.Their profound economic basis,prosperity culture and the spending power of residents provide conditions for the diversification of physical bookstores.Achieving western development is of great significance to coordinating regional development.Since the implementation of the strategic,the economic development and the improvement of people’s living standards in the western region.Meanwhile,human’s demand in spirit is increasing.In the era of creating a nation of avid readers in China,physical bookstores have been attracting attention,and their layout has a great impact on the quality of life.Chengdu,Xi’an and Chongqing are cities/municipality with a large number of physical bookstores and they are also the cities favored by influencer bookstores and brand chain bookstores.The three cities have splendid history,brilliant culture,abundant tourism resources,convenient traffic conditions and diversify business formats,which provide supporting conditions for the development of physical bookstores.The development of physical bookstores in these cities has a promising future.
Although all three are cities in western China,they have different regional influences.Xi’an is the capital city of Shaanxi Province and located in the Guanzhong Plain,radiating to the northwest region.Chengdu is the capital city of Sichuan Province and located in the Chengdu Plain.Chongqing,a beautiful mountain city,is the only municipality in the central and western China.The three cities have formed a sound pattern of cultural industries,including physical bookstores.However,the natural conditions and socio-economic backgrounds of the three cities have significant differences,which can have different impacts on the spatial layout of physical bookstores in the cities.Taking the three cities as cases,it is of great practical and theoretical significance to compare and analyze the spatial distribution and influencing factors of physical bookstores from a macro perspective (Fig.1).
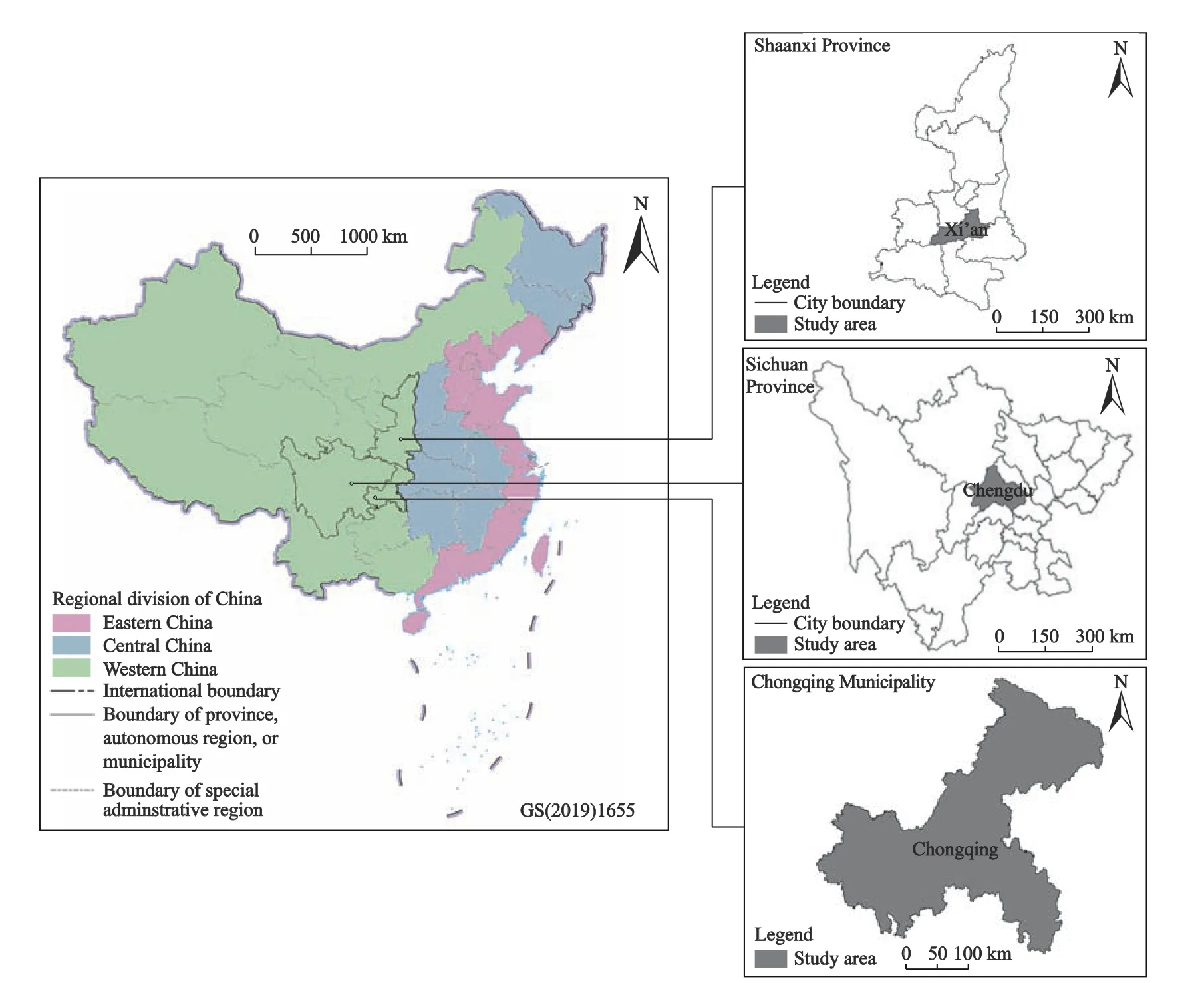
Fig.1 Location of study area in China.Regional distribution data of Eastern,Central and Western China are based on the Resource and Environmental Science and Data Center of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (http://www.resdc.cn)
2.2 Data sources and index system
The data include POI data,road density data,population density data.This study obtained POI data from Amap (https://www.amap.com/) in 2021,including physical bookstores,leisure and shopping facilities,bus stops,subway stations,communities,public libraries,research facilities,universities,tourist attractions,and city centers.Road density data were obtained from the Open Street Map (OSM) (https://www.openstreetmap.org) in 2021.The population density data were obtained from WorldPop (https://hub.worldpop.org) in 2020.
This study constructed a comprehensive index system for influencing factors from six dimensions (Table 1),e.g.,business,traffic,social,cultural,tourism,and location.This indicator system is more comprehensive than the systems of existing studies (Li et al.,2020;Liu and Li,2021).To provide a better interpretation,we took the density of leisure and shopping facilities for each study unit as an explanatory variable for the business factor.The density of bus stops per study unit,the road density,and the distance to subway station were taken as explanatory variables for the traffic factor.The density of communities for per study unit and population density were taken as explanatory variables for the social factor.In terms of the cultural factor,we took the distance to public library,the density of research facilities,and the distance to university as explanatory variables.For tourism factor,the distance to tourist attraction was used as an explanatory variable.For the location factor,the distance to city center is used as explanatory variable.

Table 1 Index system of influencing factors of spatial distribution pattern of physical bookstores
2.3 Research methods
2.3.1 DBSCAN
DBSCAN is a density-based clustering algorithm that can find the random shape of spatial clusters and identify outlier data quickly (Ester et al.,1996).It mainly includes two parameters: Eps (the radius of neighborhood of a point) and MinPts (the minimum number of points within the radius of neighborhood that becomes the core points).This method has good practicability and applicability in spatial data clustering (Zhou et al.,2019),and it is widely used in many fields,such as human geography and urban planning (Rodriguez and Laio,2014).In this study,we used the algorithm to identify physical bookstore clusters.The DBSCAN algorithm was written in Spyder to import the coordinates of the physical bookstore and determine the parameters to obtain the clustering results.Finally,the clustering results were visualized by GIS.
2.3.2 Nearest neighbor index
The nearest neighbor index (NNI) can reflect the degree of clusters and the distribution of points in the study area.It is expressed as the ratio of the ‘average observation distance’ to the ‘expected average distance’.The expected average distance is the average distance between neighbors in a hypothetical random distribution (Zhan et al.,2018).This study used the average nearest neighbor index to analyze the difference in physical bookstores.The formula is as follows:
whereRis the nearest neighbor index.The smaller the index is,the greater the degree of clustering of the elements in the urban spatial.R=1 implies a random distribution.R<1 implies a clustering distribution;R>1 implies a discrete distribution.is the average distance of the actual nearest neighbors,is the ideal nearest distance (Zhao and Liu,2021).Dis the density of physical bookstores,andnis the number of physical bookstores.Ais the study area.
2.3.3 Standard Deviation Ellipse
SDE is a spatial statistical method that describe the data distribution and demonstrate the directional,dispersive and central trend of geographic elements accurately(Zhao and Zhao,2014).It uses the azimuth to represent the main directional trend of the data distribution,the major axis to indicate the direction of the trend,and the minor axis to indicate the direction of minimum diffusion,respectively.The larger difference between the major axis and minor axis is,the more obvious the directionality of the data;conversely,the less obvious the directionality.Based on the parameters of the SDE,this study performed a comparative analysis of the spatial distribution patterns and directional trend of physical bookstores among the three cities.
Geographical detectors are used to reveal the spatial differentiation of geographic elements and influencing factors and to identify the interactions among multiple factors (Wang et al.,2010).There are four modules about it: risk detector,factor detector,ecology detector,and interaction detector.It can overcome the limitations of traditional statistical methods and explore the influence mechanism of the spatial heterogeneity of elements without many assumptions.The module was used in the natural sciences and to study the influence of the geoeconomy (Song et al.,2017) and cultural facilities (Zhao et al.,2018),as well as in research in digital financial inclusion (Zhang et al.,2023) and other fields.This study used the factor detector and interaction detector modules to clarify the main factors that cause the spatial pattern of physical bookstores and the types of interactions between factors.The calculation formula is as follows (Eqs.(2)):
whereq-value is used to express the degree of interpretation of an independent variable for a dependent variable;h=1,2…,Lrepresents the classification of the influencing factorX;NhandNare the numbers of samples in layerhand the whole area,respectively;andSSWandSSTare the sums of the intralayer variance and the total variance of the whole area,respectively. δh2and δ2are the variance of stratumhand the whole area,respectively.q∈[0,1].Theq-value is used to measure the explanatory power of the independent variables.A largerqvalue in the interval indicates a stronger explanatory power of influencing factors.Whenq=1,Xcompletely explains the spatial pattern of physical bookstores.In contrast,whenq=0,Xindicates a completely random spatial occurrence of the spatial pattern of physical bookstores.
3 Results and Analyses
3.1 Spatial pattern of physical bookstores
3.1.1 Spatial cluster characteristics
Based on the actual clustering situation,we determined the relevant parameters (Table 2),and the clustering results are as follows (Fig.2).We rank the cluster with less than 20 points as level-5,those with 21-50 as level-4,those with 51-100 as level-3,those with 101-300 as level-2,and those with more than 300 as level-1.There is 1 level-1 cluster and 12 level-5 clusters in Xi’an;1 level-1 cluster,2 level-4 and 10 level-5 clusters in Chengdu;1 level-2 cluster,4 level-4 and 6 level-5 clusters in Chongqing.In Xi’an,physical bookstores are mostly gathered near the city center,with less distribution in the surrounding districts.There are differences incluster level,and the distribution is unbalanced.In Chengdu,the largest cluster is near the city center,and lower-level clusters are relatively evenly distributed in the surrounding areas of the city.The level-2 clusters in Chongqing are in the western part of the city,and the cluster scale is lower than that in Xi’an and Chengdu.Lower-level clusters are mostly distributed in the northwest part of the city,and few are distributed in the eastern part of the city (Fig.2).

Table 2 Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise (DBSCAN) parameter for three studied cities in 2021
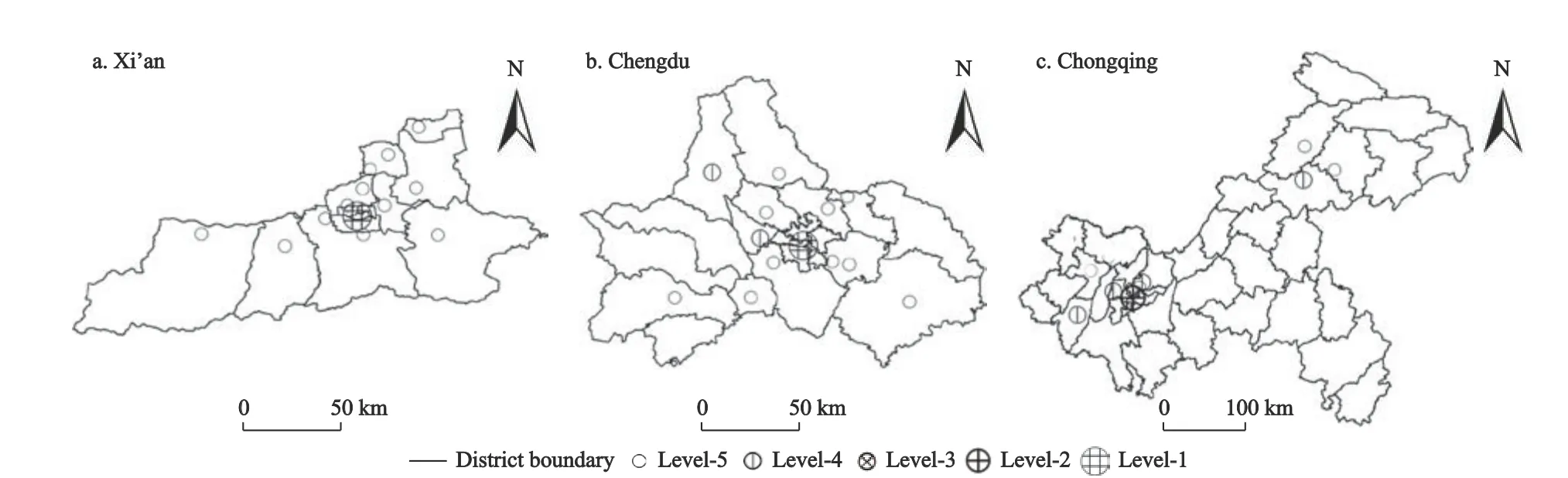
Fig.2 Cluster classification of physical bookstores for three studied cities in 2021
On the whole,according to the analysis results of the nearest neighbor illustration in Table 3,the index of Xi’an is 0.374,that of Chengdu is 0.412,and Chongqing is 0.325.The nearest neighbor index of Chongqing is the smallest,indicating that the degree of clustering of physical bookstores in Chongqing is the greatest,followed by Xi’an and Chengdu.
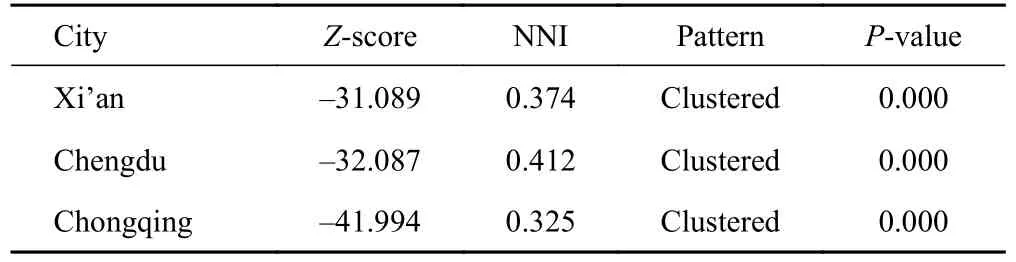
Table 3 Nearest neighbor illustration (NNI) for three studied cities in 2021
3.1.2 Directional distribution characteristics
The results indicate that the difference between the major and minor axes of the ellipse in Xi’an is significant.The overall distribution shows a distribution trend from southwest to northeast.The difference between the major and minor axes of the ellipse in Chengdu is relatively small.In general,the distribution trend of physical bookstores in the east-west direction is dominant.Compared with Xi’an and Chengdu,there is a significant difference between the major and minor axes of the ellipse in Chongqing,and the overall distribution trend of Chongqing is from southwest to northeast (Fig.3).
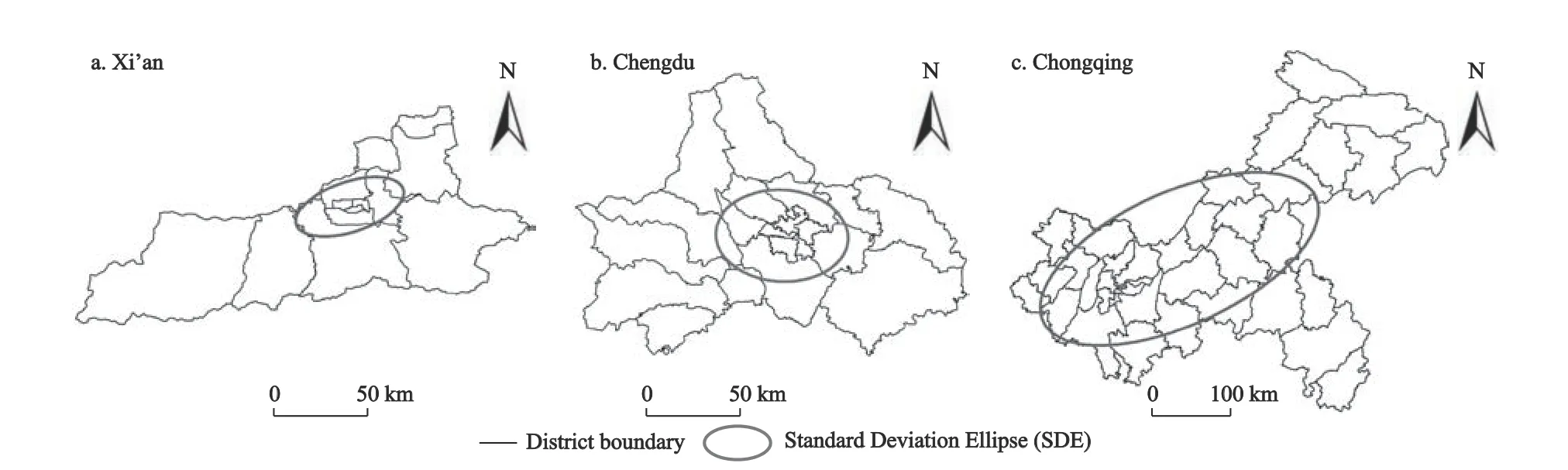
Fig.3 Direction distribution of physical bookstores for three studied cities in 2021
3.2 Analysis of influencing factors for the spatial pattern of physical bookstores
3.2.1 Factor detector
By this time the Three Bears thought their porridge would be cool enough, so they came home to breakfast. Now Goldilocks had left the spoon of the Great, Huge Bear, standing5 in his porridge.
The statistical characteristics of variables are shown in Table 4.This study used the natural breaks method to classify each index,and factor detector was used to analyze the explanatory power of influencing factors.Theqvalue represents the explanatory power of the independent variable.The larger theq-value is,the stronger the explanatory power for the density of physical bookstores.Ranked based onq-value from largest to smallest,as shown in Table 5.

Table 4 Descriptive statistical analysis of dependent and independent variables affecting the spatial distribution pattern of physical bookstores for three studied cities in 2021
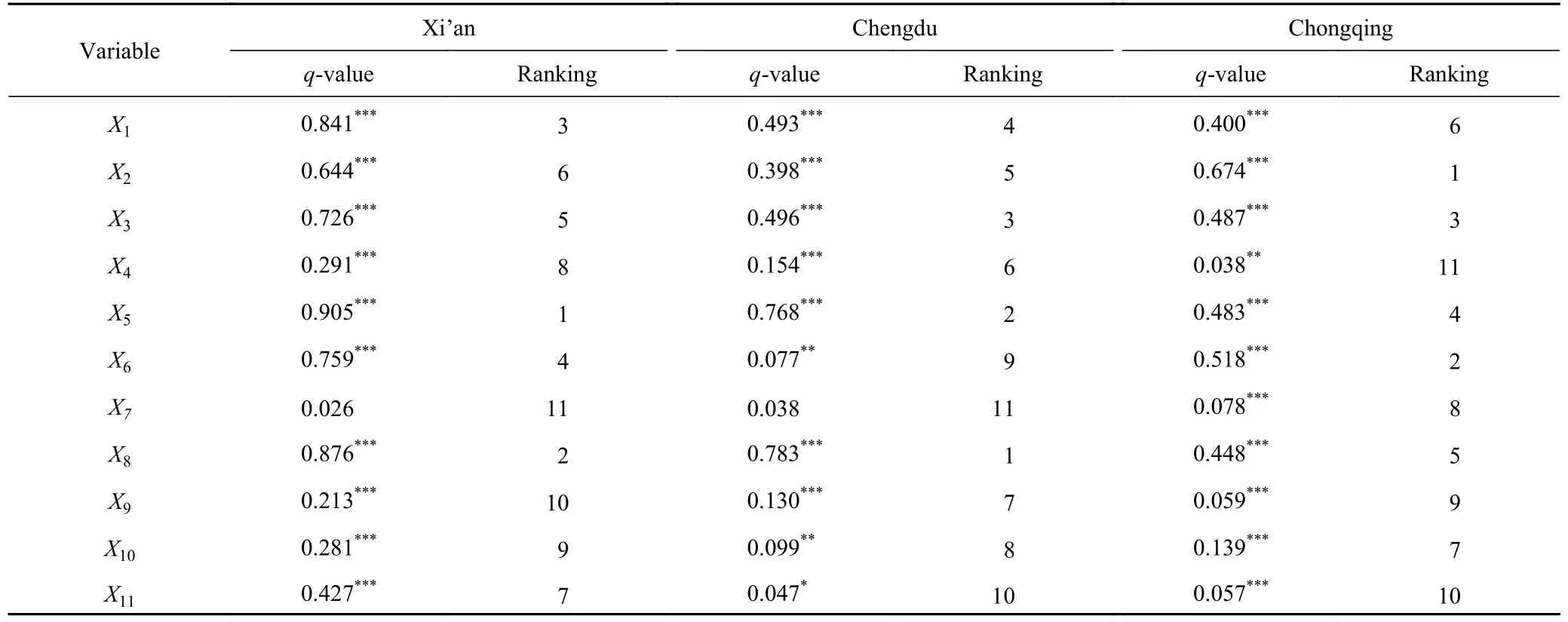
Table 5 The results of factor detector for three studied cities in 2021
As shown in Table 4,Xi’an has the highest density of physical bookstores in the valid area.In contrast,Chongqing has the lowest density of physical bookstores.Chengdu has many physical bookstores,but they are scattered in various areas;thus,the density is relatively small.The results are consistent with Fig.3 and Table 3.As shown in Table 5,each factor had a difference influence on the spatial distribution pattern of physical bookstore among the three cities.
For Xi’an,except for the distance to public library,which was not significant,other factors had a greater impact on the spatial distribution of physical bookstores.Among them,theq-value of the density of communities ranked first.Ranking the remaining influencing factors in descending order as the density of research facilities,the density of leisure and shopping facilities,population density,road density,the density of bus stops,the distance to the city center,the distance to subway station,the distance to tourist attraction,and the distance to university.As physical bookstores mainly serve consumers,they are crowd dependent;thus,the density of communities and population density have a strong influence on the dependent variable.Regarding the cultural factors,Xi’an has more research institutions and universities,which have a relatively high demand for physical bookstores,which in turn influences the location of their spaces.Moreover,the business factor played an important role in the spatial distribution pattern of physical bookstores.As a business type,physical bookstores are clustered with other facilities in terms of spatial distribution.Therefore,the density of research facilities,the density of leisure and shopping facilities affect the location of physical bookstores.
For Chengdu,the distance to public library was not significant,and other factors had a significant effect on the spatial distribution of physical bookstores.Ranking the remaining influencing factors in descending order as the density of research facilities,the density of communities,road density,the density of leisure and shopping facilities,the density of bus stops,the distance to subway station,the distance to university,the distance to tourist attraction,population density,the distance to city center.The spatial distribution pattern of physical bookstores is more influenced by the density of research facilities and communities,which also fully shows that physical bookstores in Chengdu have crowd dependence and the agglomeration effect of similar business forms.Traffic accessibility is also one of the important factors.Convenient traffic conditions and a good business environment provide excellent conditions for the location of physical bookstores in Chengdu.
For Chongqing,all factors have significant impact on the spatial distribution pattern of physical bookstores.Ranking the influencing factors in descending order as the density of bus stops,population density,road density,the density of communities,the density of research facilities,the density of leisure and shopping facilities,the distance to tourist attraction,the distance to public library,the distance to university,the distance to the city center and the distance to subway station.Due to the particularity of Chongqing’s terrain,traffic accessibility has a greater impact on the spatial pattern of physical bookstores.Compared with the subway,the density of bus stops and road density are the priority factors in the spatial pattern of physical bookstores.Convenient traffic will have a greater impact on the location of physical bookstores.
3.2.2 Interaction detector
All factors were assessed for interactions,and the results are shown in Fig.4.Further observing the results,we found that pairs of influencing factors had an enhanced relationship,including bifactor enhancement and nonlinear enhancement.Most of the interactions demonstrated bifactor enhancement,while some demonstrated nonlinear enhancement.The interaction detection results show that the spatial pattern of physical bookstores was affected by various factors,with regional differences.
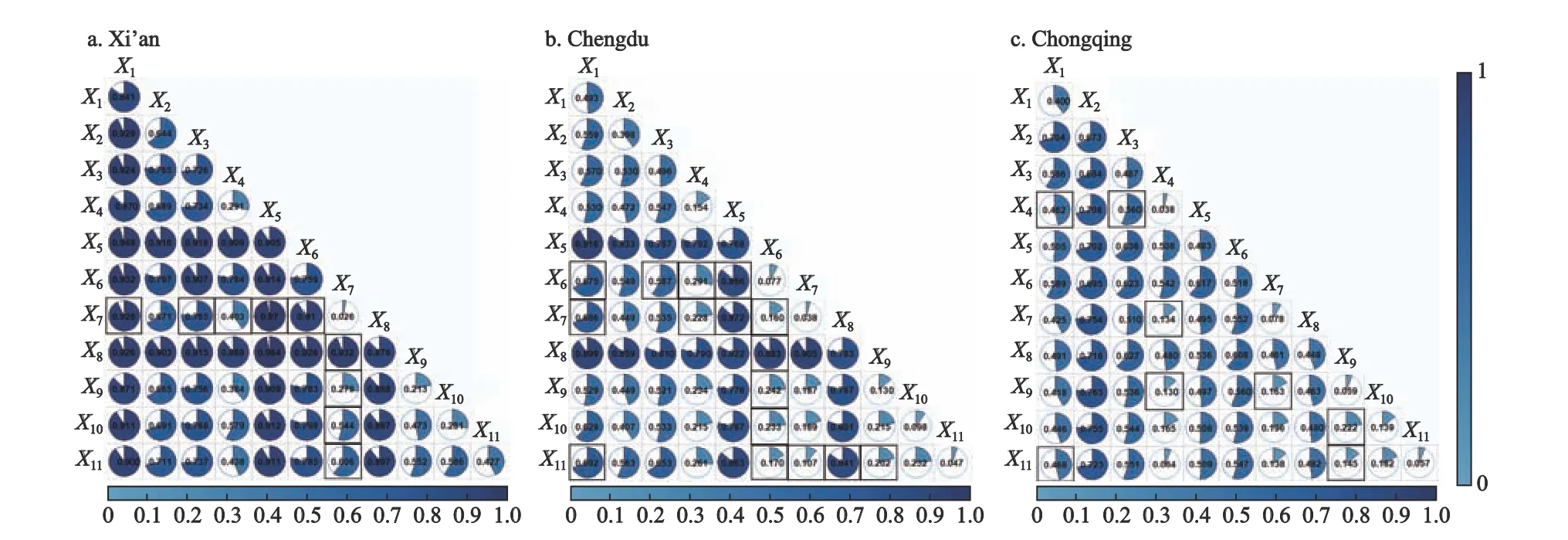
Fig.4 The results of interaction detector influencing the spatial pattern of physical bookstores for three studied cities in 2021.Meanings of X1-X11 see Table 1.Bold frames represent nonlinear enhancement.Unbolded frames represent bifactor enhancement
For Xi’an,regarding the interaction of factors,the density of communities and the distance to public library have the strongest explanatory power with aqvalue of 0.970.The distance to university and the distance to public library have the weakest explanatory power,with aq-value of 0.279 only.Although public libraries were not significant,the interaction of this factor with the density of communities produces a bifactor enhancement effect.The interactive explanatory power of the distance to university is weak;thus,it has less influence on the spatial distribution of physical bookstores in Xi’an.For Chengdu,regarding the interaction of factors,the density of communities and the density of leisure and shopping facilities have the strongest explanatory power with aq-value of 0.916.However,the interaction between the distance to public library and city center has the weakest explanatory power with aq-value of 0.107 only.The interaction is weakly explained by the distance to public library and the distance to city center on the spatial distribution of physical bookstores in Chengdu.For Chongqing,the interaction between the density of bus stops and the distance to university is nonlinear enhancement,and it has the strongest explanatory power with aq-value of 0.765.Meanwhile,the interaction between the distance to city center and distance to subway station has the weakest explanatory power with aq-value of 0.064 only.The explanatory power of the interaction is not significant because the effects of both individually are relatively small.
Fig.4 shows that the interaction between the tourism factor and other factors is relatively weak in the three cities.In the interaction detector results for Xi’an,the density of leisure and shopping facilities has stronger explanatory power when interacted with other factors.In Chengdu,the density of research facilities has stronger explanatory power when interacted with other factors.For Chongqing,the explanatory power is stronger after the interaction of the traffic factors and population density with other factors.For the three cities,the explanatory power of the tourism and location factors is stronger when interacted with other factors.This result also indicates that the spatial distribution of physical bookstores in cities is influenced by a combination of factors and that the magnitude of the influence of different factors varies from city to city.
4 Discussion
The main contributions of this study are as follows:first,the subject of the study is meaningful.As part of a city’s cultural facilities,physical bookstores serve people together with other facilities.Previous studies have examined the business models (Liao,2022;Luo,2023),and analyzed the influencing factors of physical bookstores in the cities of Xi’an (Liu and Li,2021),Nanjing (Zuo et al.,2019),and Wuhan (Zhu et al.,2020).The study of urban infrastructure is meaningful and continuous,especially in new era,where cultural facilities are becoming increasingly important.It is of great significance to discuss the similarities and differences of urban physical bookstores.This study enriches urban geography with a comparative analysis of the spatial distribution pattern of physical bookstores in three national central cities in western China.Second,regarding the research methods,this study introduces a big data algorithm from machine learning to identify spatial hot spots and to classify clusters of physical bookstores.This novel approach provides a way to quantify clusters with random shapes,and it can find key clusters in spatial timely.It provides a reference for other studies.Finally,compared with previous studies,we reconsider influencing factors of spatial distribution characteristics of physical bookstores.We pay attention to the differences among three cities and found that physical bookstores in cities are affected by different factors.Additionally,the results verified a strong correlation between commercial factors and the spatial distribution of physical bookstores.It shows that the tourism factor has some influence on the spatial distribution of physical bookstores.
The empirical results of this study are also meaningful.Through spatial analysis,we found that the spatial distribution pattern and the degree of clustering of physical bookstores differed in each city.The DBSCAN results show that physical bookstores form more clusters in all three cities.However,Chengdu has the most highlevel clusters,which are scattered throughout the city,while Chongqing has many low-level clusters.Physical bookstores in Xi’an and Chengdu form larger clusters near the city center,while Chongqing does not.The NNI results show that the spatial pattern of physical bookstores is clustered in all three cities,but the SDE results show that the spatial layout of physical bookstores in each city is differently.Xi’an and Chongqing show a trend from southwest to northeast and Chengdu shows a trend in the east-west.The geographical detectors results show that the physical bookstores do not exist in isolation,but are closely linked to other facilities.All three cities are influenced by commercial,traffic,social and cultural factors,but there are some differences.Physical bookstores in Xi’an are heavily influenced by the city center,where they form larger clusters.Due to the overall high number,Chengdu’s physical bookstores also form larger clusters in the city center,and all have relatively high-level clusters in the city.In contrast,Chongqing has a lower density of physical bookstores than Chengdu and Xi’an.
Through this study,we found that the results for three studied cities were similar.The distance to university and public library had less influence on the spatial distribution of physical bookstores.The reason is that universities have their own libraries that can meet the daily reading needs of instructors and students.Public libraries and physical bookstores provide public cultural services jointly.There is no conflict between the nonprofit nature of libraries and the profit-driven nature of physical bookstores.It is not the main factor affecting the location of physical bookstores.Due to the city’s development history,Xi’an presents a typical circular structure,with various commercial developments in the city center being more mature.Xi’an is more influenced by the distance to the city center than Chengdu and Chongqing.In addition,we also found that the spatial distribution of physical bookstores is inseparable from business and tourism factors,in addition to the traffic,cultural and demographic factors.The spatial distribution of physical bookstores is consistent with that of leisure and shopping facilities which can enrich the spare activities of people (Shang,2021).The findings also indicate that tourist attractions are one of the influencing factors for the spatial distribution of physical bookstores.In China,many physical bookstores have become leisure and cultural attractions that attract residents and tourists.
In future,we will pay more attention to the development of urban physical bookstores and examine their evolutionary mechanisms under the spatial and cultural turn.In addition,we plan to focus on consumer perception and behaviors,analyze the spatial production process of physical bookstores,regard physical bookstores as the cultural representation of the third space,create a good urban cultural consumption space,and achieve a more sustainable development of urban cultural industry.
5 Conclusions and Policy Implications
5.1 Conclusions
Physical bookstores provide spaces for people to buy books,read,and relax,which is one of the ways to meet people’s spiritual and cultural needs.The development of physical bookstores is closely related to urban cultural service facilities.However,there are great differences in the spatial distribution characteristics of physical bookstores in big cities.In view of this problem,this study takes three national central cities in western China as the cases,which have rapid social and economic development and urgent need of cultural space.And this study constructs an index system to systematically analyze the key factors influencing the layout of physical bookstores in the study areas.The main conclusions are as follows:
From the spatial distribution pattern of physical bookstores in the three cities,they all form a high-level cluster near the city center.There are differences in the spatial distribution direction of physical bookstores in different cities.Chongqing has the highest agglomeration level of physical bookstores,followed by Xi’an,and the spatial distribution of physical bookstores in Chengdu is relatively dispersed.
Factor detection suggests that many variables significantly contribute to explaining the spatial distribution pattern of physical bookstores.However,there are differences in the degree of influence of each factor.There are commonalities in the factors influencing the spatial distribution of physical bookstores in the three cities.For example,they are influenced by traffic,social,business,tourism,and location factors.For Xi’an and Chengdu,the population density and the density of research facilities have a substantial influence.For Chongqing,the traffic factor has the greatest impact.For Xi’an and Chengdu,the distance to public library is not statistically significant.It has a small impact on the spatial distribution pattern of physical bookstores in Chongqing.
The spatial distribution pattern of physical bookstores is affected by multiple factors,such as business,traffic,social,cultural,tourism and location factors.In the interaction detector results for Xi’an and Chengdu,the explanatory power of the density of communities and science facilities is stronger when interacted with other factors.This is not the case in Chongqing,where traffic and population density are more strongly explained by interaction with other factors.Among the three cities,the tourism factor and the location factor interacted with other factors to explain the dependent variable more strongly.
5.2 Policy implications
In this study,physical bookstores relatively gathered in the city center.This situation will affect people’s access to cultural facilities.Therefore,the location of bookstores in cities should consider multiple factors.Physical bookstores of different levels,sizes and themes will be set up according to people’s reading habits and amounts.For example,bookstores that choose to be located near primary and secondary schools should mainly serve students and sell learning materials.Bookstores located near tourist attractions should be compound.In the city,only a balanced distribution of various types of physical bookstores can better provide cultural services for people.The government should continuously emphasize the importance of cultural facilities and build distinctive and classic bookstore to create a fair urban commercial and cultural space.The government should create a system of physical bookstores covering urban and rural to promote the healthy development of physical bookstores vigorously.In addition,we need to combine big data with media publicity to optimize operation of physical bookstores.In order to create virtual and real interaction of public reading space.The coexistence of online bookstores and physical bookstores should be realized to compensate for the lack of offline bookstores.
From the research results,we can find that physical bookstores in the three cities are influenced by factors such as cultural,business and tourism factor.Consumers can buy books or enjoy other products in such facilities for leisure and entertainment purposes.Under the background of the integration of culture and tourism,the role of physical bookstores is becoming increasingly obvious.In the future of urban development,physical bookstores must innovate their business model so as to provide open and equal cultural space.As the symbol of civilization,physical bookstores not only play a role in urban cultural space but also is a vital element of urban competitiveness in China.Thus,policy support should be strengthened to promote the transformation and development of physical bookstores.In the future,we should strive to create new-type physical bookstore that integrates books,coffee,and leisure and combine physical bookstores with tourist attractions to provide people with space for cultural tourism to meet people’s spiritual needs and improve the quality of life.
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design.Data collection and analysis were performed by LIU Ruikuan,CHANG Fang and MA Jiayao.Materials were prepared by LIU Ruikuan and LI Jiuquan,and funded by LI Jiuquan.The first draft of the manuscript was written by LIU Ruikuan,and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript.All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
杂志排行
Chinese Geographical Science的其它文章
- Bibliometrics-based Research Hotspots and Development Trends in Ecohydrology of Dammed Rivers
- Effects of Groundwater with Various Salinities on Evaporation and Redistribution of Water and Salt in Saline-sodic Soils in Songnen Plain,Northeast China
- Increasing Anthropogenic Mercury Pollution over the Last 200 Years Revealed by Lagoonal Sediments from Hainan Island,South China
- Detection of Multi-dimensional Driving Forces of Public Environmental Concern in China: Based on Spatial Heterogeneity Perspectives
- Projected Regional 1.50°C and 2.00°C Warming Threshold-crossing Time Worldwide Using the CMIP6 Models
- Leave or Stay? Antecedents of High-level Talent Migration in the Pearl River Delta Megalopolis of China: From a Perspective of Regional Differentials in Housing Prices
