Progress on traditional Chinese medicine in improving hepatic fibrosis through inhibiting oxidative stress
2023-12-03ZhenLiJunFengZhuHaoOuyang
Zhen Li,Jun-Feng Zhu,Hao Ouyang
Abstract Hepatic fibrosis is a common pathological process that occurs in the development of various chronic liver diseases into cirrhosis and liver cancer,characterized by excessive deposition of the extracellular matrix.In the past,hepatic fibrosis was thought to be a static and irreversible pathological process.In recent years,with the rapid development of molecular biology and the continuous in-depth study of the liver at the microscopic level,more and more evidence has shown that hepatic fibrosis is a dynamic and reversible process.Therefore,it is particularly important to find an effective,simple,and inexpensive method for its prevention and treatment.Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) occupies an important position in the treatment of hepatic fibrosis due to its advantages of low adverse reactions,low cost,and multi-target effectiveness.A large number of research results have shown that TCM monomers,single herbal extracts,and TCM formulas play important roles in the prevention and treatment of hepatic fibrosis.Oxidative stress (OS) is one of the key factors in the occurrence and development of hepatic fibrosis.Therefore,this article reviews the progress in the understanding of the mechanisms of TCM monomers,single herbal extracts,and TCM formulas in preventing and treating hepatic fibrosis by inhibiting OS in recent years,in order to provide a reference and basis for drug therapy of hepatic fibrosis.
Key Words: Hepatic fibrosis;Oxidative stress;Traditional Chinese medicine monomer;Single herbal extract;Traditional Chinese medicine formula
INTRODUCTION
The prevalence of hepatic fibrosis ranges from 2% to 19%,and it remains a major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide[1,2].It leads to notorious complications such as ascites,portal hypertension,hepatic encephalopathy,and liver failure,and increases the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma,posing a heavy burden on individuals,society,and healthcare systems[3,4].Currently,Western medical treatments for hepatic fibrosis include antiviral drugs,corticosteroids,hepatoprotective drugs,and liver support,but they have low efficacy rates,significant resistance,and side effects[5].Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM),as a unique medical approach in China,has better safety and effectiveness and is widely used to treat hepatic fibrosis[6].Continuous oxidative stress (OS) in the liver can induce biological changes in hepatocytes,leading to fibrotic changes in the liver[7].Based on this,experts and scholars have conducted relevant experimental studies to demonstrate that TCM monomers,single herbal extracts,and TCM formulas can significantly improve the condition of hepatic fibrosis by regulating OS.Therefore,this article reviews the progress in the the understanding of the mechanisms of TCM in preventing and treating hepatic fibrosis by using OS as a starting point to provide references for the clinical treatment of hepatic fibrosis with TCM.
MECHANISMS OF HEPATIC FIBROSIS
Hepatic fibrosis is a chronic wound healing response to cellular damage and inflammation caused by increased synthesis and deposition of extracellular matrix (ECM) components and decreased or unbalanced ECM degradation (Figure 1)[8,9].Various etiologies such as alcohol abuse,viral hepatitis infection,genetic abnormalities,non-alcoholic fatty liver disease,autoimmune disorders,and other non-infectious diseases can cause continuous wound healing response and liver injury,leading to hepatic fibrosis[10].The main mechanism of hepatic fibrosis is believed to be the activation of myofibroblast precursor cells,which leads to an increase in ECM deposition surrounding the sinusoidal cell layer in the Disse space[11,12].ECM increase is the main feature of hepatic fibrosis,and the ECM is composed of five types of substances,collagen,non-collagenous proteins,elastic fibers,proteoglycans,and glycosaminoglycans.It is mainly divided into basement membrane and interstitial matrix according to its distribution site[13].In human patients and rodent models of liver disease,fibrotic livers contain multiple types of collagen (types I,III,and V),non-fibrillar collagens (IV and VI),and glycosaminoglycans and proteoglycans (such as fibronectin,tenascin,laminin,basement membrane proteoglycans,decorin,biglycan,and fibrillin)[11].
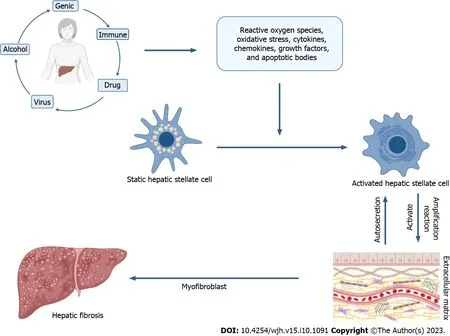
Figure 1 The mechanism of hepatic fibrosis. Due to various factors such as alcohol abuse,viral hepatitis infection,genetic abnormalities,alcoholic fatty liver disease,autoimmune diseases,and medications,the body may produce an excessive amount of reactive oxygen species,leading to oxidative stress.At the same time,these factors may also induce cells to release cytokines,chemokines,growth factors,and apoptotic bodies,as well as activate hepatic stellate cells (HSC) and transform them into myofibroblasts.Consequently,large amounts of extracellular matrix (ECM) substances,such as collagen,non-fibrillar collagens,glycosaminoglycans,and proteoglycans,are autosecreted.The presence of these ECM substances can further stimulate the autosecretion of HSCs,ultimately resulting in fibrosis and impaired liver function.
In addition,hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) (Ito cells and lipocytes),portal-resident fibroblasts (portal or central veins),epithelial cells undergoing epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition,bone marrow-derived fibroblasts,vascular smooth muscle cells,and sinusoidal peri-hematopoietic stem cells are the main cell types that produce the ECM during hepatic fibrosis[14].In human patients,HSCs constitute 5%-8% of the total liver cells involved in growth,differentiation,and regeneration.They are not only the main source of myofibroblasts but also the main cell type leading to hepatic fibrosis[15].Portal fibroblasts are thought to play an important role in fibrosis in cholestatic liver disease[16,17].The static HSC to myofibroblast differentiation is a multi-step process involving reactive oxygen species (ROS),cytokines,chemokines,growth factors,and apoptotic bodies from hepatocytes[18].Chronic liver injury involves HSCs undergoing phenotypic activation towards myofibroblasts,which is characterized by increased expression of cell markers such as alpha-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) and collagen.In addition,transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-β1) inhibits liver regeneration during HSC to myofibroblast differentiation,ultimately leading to hepatic fibrosis[19].
OS-MEDIATED HEPATIC FIBROSIS
OS refers to the imbalance between the normal oxidant scavenging enzyme system [such as superoxide dismutase (SOD),catalase,and glutathione (GSH)] and the production of ROS in the cells,which is considered a key driving factor in hepatic fibrosis[20].Oxidants,also known as ROS,include superoxide anion radicals,hydrogen peroxide,hydroxyl radicals,and singlet oxygen[21].In addition,they also contain some nitrogen oxides,lipid peroxide radicals,and hypochlorous acid.The process of oxidant formation begins with oxygen being reduced to water,resulting in the production of free radicals such as superoxide anion radicals,hydrogen peroxide,and hydroxyl radicals[22].
Under physiological conditions,ROS are the result of normal cellular metabolism and are maintained in dynamic equilibrium with antioxidants[23].Under pathological conditions,excess ROS can stimulate pathological oxidativereductive signal transduction,leading to OS.Various organic compounds such as DNA,lipids,carbohydrates,and proteins are structurally damaged,resulting in cell damage and various diseases[24].Leeet al[25] first demonstrated a possible molecular link between enhanced lipid peroxidation and induced collagen gene expression in cultured fibroblasts,suggesting that OS plays a direct pathogenic role in hepatic fibrogenesis.Sustained OS in the liver directly or indirectly affects hepatocytes and alters the structure of cell membranes and organelles,causing damage,necrosis,and apoptosis[26].These processes lead to cell damage and the release of various cytokines and growth factors,inducing quiescent HSC activation into myofibroblasts expressing α-SMA as a characteristic marker[27].Activated HSCs lose lipid droplets (vitamin A),rapidly proliferate,and upregulate many genes,especially collagen,fibronectin,laminin,and hyaluronic acid,beginning to increase the synthesis of connective tissue proteins,especially collagen,leading to fibrosis formation and further development into liver cirrhosis and even liver cancer[19,28].In addition,excess ROS also enhance the secretion of the fibrogenic factor TGF-β1,which is highly involved in HSC activation,exacerbating ECM deposition in the liver and progressing to hepatic fibrosis[29].The mechanism of OS-mediated hepatic fibrosis is shown in Figure 2.
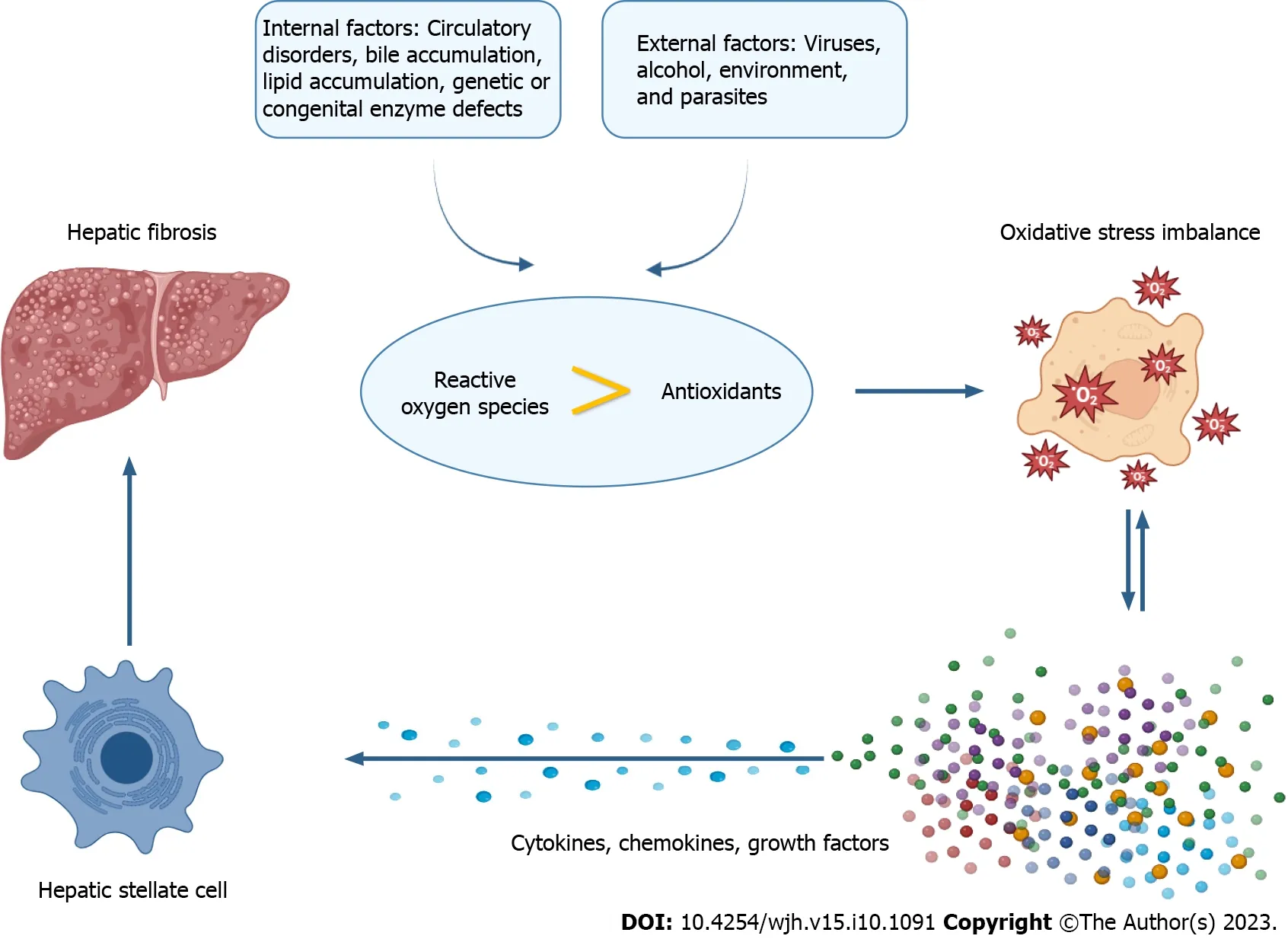
Figure 2 The mechanism of oxidative stress-mediated hepatic fibrosis. Circulatory disorders,bile accumulation,lipid accumulation,genetic or congenital enzyme defects,as well as factors such as viruses,alcohol,environment,and parasites,can all contribute to an imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen species and the body’s ability to remove them,resulting in oxidative stress.This imbalance can further stimulate the secretion of cytokines,chemokines,and growth factors,which in turn activate hepatic stellate cells and contribute to the development of hepatic fibrosis.
UNDERSTANDING HEPATIC FIBROSIS FROM TCM PERSPECTIVE
Ancient literature did not have a clear concept of “hepatic fibrosis” as a disease name.Based on its main clinical manifestations of hypochondriac pain,palpable masses in the hypochondrium,and jaundice,modern physicians categorize it under disease categories such as distension and swelling,hypochondriac pain,accumulation,and jaundice[6].The Ling Shu section of the Huangdi Neijing states: “If the evil is in the liver,then there is pain in both flank regions,the patient feels cold,and stagnant blood circulates within,causing restricted joint movements,and occasional foot swelling.Acupuncture at Jia Jian was used to activate the meridian around the liver area and warm up the stomach,extract blood through veins to eliminate stagnant blood,and take out the green vein by the ear to alleviate cramps[30].” The Huangdi Neijing says: “Wind,cold,and dampness combined cause obstruction of channels and collaterals,known as arthralgia.Furthermore,if this occurs in spring,it is called tendon arthralgia.Tendon arthralgia continues stubbornly and is further affected by evil forces,which reside in the liver interior.All organs have junctions,so if an illness remains lingering,it will settle in the junction of that organ.Since the liver’s junction is with the tendons,the arthralgia continues,and when affected by evil forces,it settles in the liver[31].” Therefore,the TCM understanding of the pathogenesis of hepatic fibrosis can be summarized as weakened vital qi,allowing external pathogenic factors such as excessive exposure to the “Six Pathogens” or inappropriate emotional responses from the “Seven Emotions” to invade,resulting in Qi stagnation and blood stasis[32].This progression is often slow and persistent,ultimately leading to hepatic fibrosis.Based on classic single herbal extracts and TCM formulas,many effective preventive and therapeutic TCM formulas have been developed and applied clinically.Currently,TCM monomers,single herbal extracts,and TCM formulas can regulate HSCs and ECM expression levels by affecting OS,achieving a state of balance between yin and yang in the body,and thereby preventing and treating hepatic fibrosis[33].Therefore,this article analyzes and discusses the research progress in preventing and treating hepatic fibrosis through the inhibition of OS by using TCM monomers,single herbal extracts,and TCM formulas,based on recent domestic and international studies on hepatic fibrosis,in order to provide a theoretical basis for future research.
MECHANISMS OF TCM IN ANTI-FIBROSIS
As TCM has shown good therapeutic effects in various chronic diseases,its role and mechanism in preventing and treating hepatic fibrosis have attracted widespread attention from scientists.Scholars from various countries have begun using modern pharmacological research methods to explore the mechanisms of TCM in anti-fibrosis.It has been confirmed that TCM monomers (such as flavonoids,glycosides,alkaloids,and polysaccharides),single herbal extracts(such asSalvia miltiorrhiza,Ginkgo bilobaleaf,clove basil,Ceratonia siliquapod extract,grape seed,pomegranate extract,Taraxacum officinaleroot extract,andMyrtus communis),and TCM formulas [such as Yin-Chen-Hao-Tang (YCHT),Xiaochaihu Tang (XCHT),Fu Zheng Hua Yu Fang,Chunggan extract,and Huangjia Ruangan Granule] can be used to inhibit OS and prevent and treat hepatic fibrosis (Figure 3).
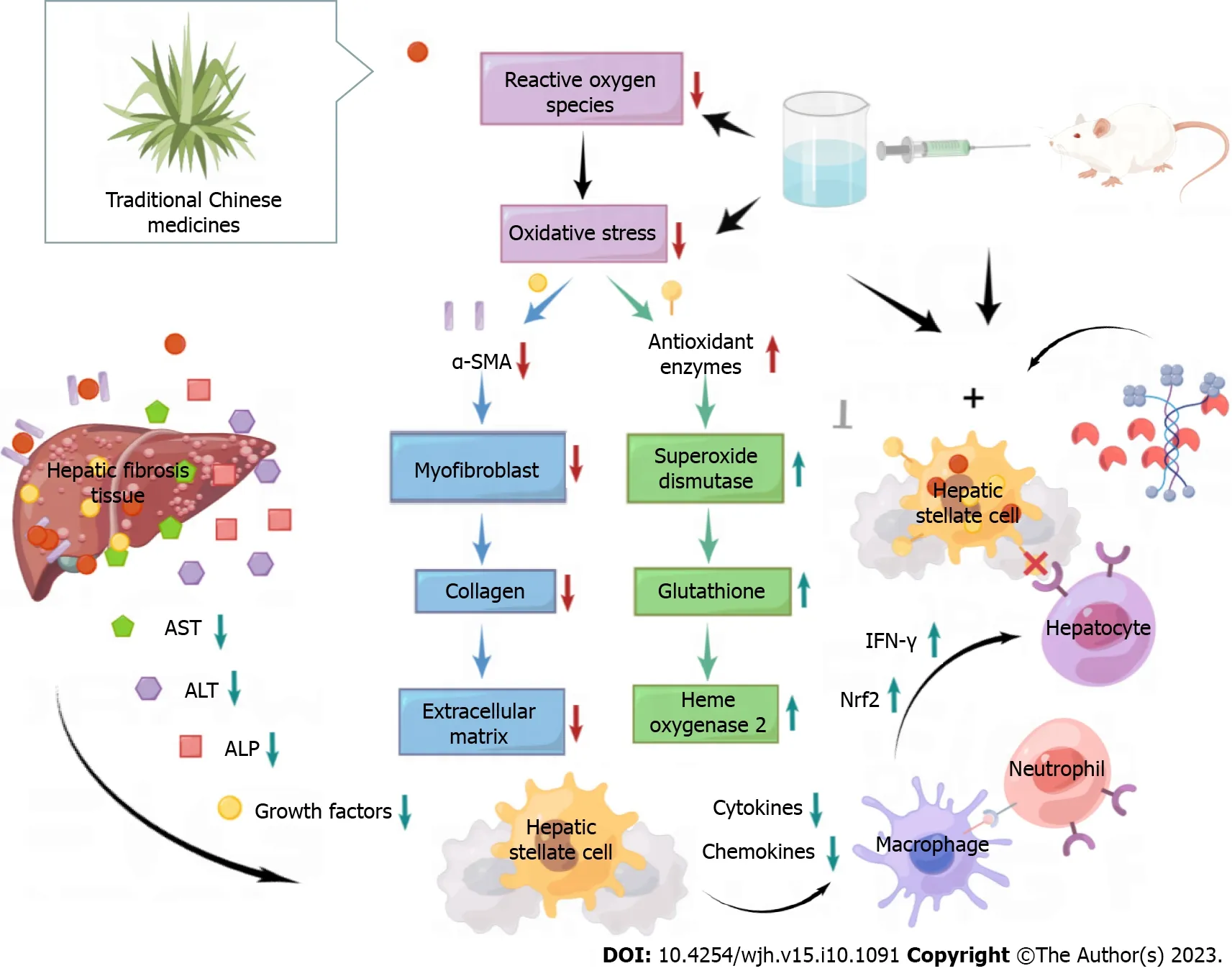
Figure 3 Treatment of hepatic fibrosis by oxidative stress mediated by traditional Chinese medicine. Traditional Chinese medicine employs various mechanisms to reduce the production of reactive oxygen species in the body,thereby suppressing oxidative stress reactions.They can enhance the secretion of antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase,glutathione,and heme oxygenase 2,as well as increase the activity of interferon-γ and nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor.Moreover,traditional Chinese medicine can inhibit the secretion of growth factors,cytokines,chemokines,macrophages,and neutrophils.They can also hinder the activation of quiescent hepatic stellate cells into myofibroblasts and facilitate the degradation of extracellular matrix components like collagen.These actions contribute to the protection of liver function and hepatocytes,ultimately mitigating and reversing hepatic fibrosis.ALP: Alkaline phosphatase;ALT: Alanine transaminase;AST: Aspartate aminotransferase;α-SMA: Alpha-smooth-muscle actin;IFN-γ: Interferon-γ;Nrf2: Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor.
TCM MONOMERS
In recent years,numerous experimental studies have demonstrated that TCM monomers,such as flavonoids,glycosides,alkaloids,and polysaccharides,can reduce the activation rate of HSCs by inhibiting OS and reducing excessive ECM deposition.This in turn can suppress hepatic fibrosis and connective tissue proliferation or improve liver function and delay the progression of hepatic fibrosis.
FLAVONOIDS
Flavonoids are a class of compounds that belong to the family of polyphenols.They are widely found in plant-based foods such as vegetables,fruits,and grains[34].Flavonoids are known for their beneficial effects on human health,such as antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties[35].The most common flavonoids include quercetin,kaempferol,and myricetin,which are found in many fruits and vegetables[34].Flavonoids have been linked to a reduced risk of chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease,cancer,and diabetes[36].Briefly,the consumption of flavonoid-rich foods is an important part of a healthy diet.Extensive pharmacological research has shown that flavonoids possess the ability to inhibit the pathological production of ROS,suppress OS,boost the antioxidant capacity of the body,and offer protection against hepatic fibrosis[37].
Quercetin is an important plant chemical substance belonging to the polyphenolic flavonoid group[38].The chemical formula of quercetin is C15H10O7,and its structure shares a common flavonoid nucleus composed of two benzene rings linked by a heterocyclic pyran ring[39].Quercetin is commonly found in various fruits and vegetables,including apples,berries,cherries,red leaf lettuce,onions,and asparagus,with small amounts present in pepper,broccoli,peas,and tomatoes[40].It is well known that onions contain the highest levels of quercetin[41].Quercetin is one of the most extensively researched flavonoids and has been found to exhibit exceptional antioxidant activity.Its effects on GSH and ROS activity,as well as its regulation of various signaling pathways including heme oxygenase 1/nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor (Nrf2),mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK),Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)/phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K),and 5’adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase have been demonstrated in numerous studies[42].Studies have also shown that quercetin can enhance the activities of antioxidant enzymes like SOD and increase GSH levels.Furthermore,it can inhibit OS,down-regulate inflammatory cytokine expression,and reduce tissue histopathological changes induced by thioacetamide,thus mitigating hepatic fibrosis[43].In addition,Khodarahmiet al[44] proposed that quercetin can improve hepatic fibrosis by inhibiting ROS-related OS-mediated inflammatory cascades.Concisely,these findings suggest that quercetin has potential therapeutic benefits for hepatic fibrosis through its ability to enhance antioxidant enzyme activities,reduce OS and inflammation,and inhibit ROS-mediated cascades.However,more research is needed to fully understand the mechanism of action and optimal dosage of quercetin for treating hepatic fibrosis.
Isorhamnetin,with the chemical formula C16H12O7,is a 3’-O-methylated gut metabolite of quercetin[45].Isorhamnetin belongs to the flavonoid family,more specifically the flavonol group[46].It can be found in several plants,such as sorbus,ginkgo leaves,or cactus,which have traditionally been used as medicinal plants in various cultures[47].In vitro,isorhamnetin can scavenge diphenylpicrylhydrazyl and 2,2’-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonate) radicals,inhibit liver mitochondrial lipid peroxidation,and exhibit antioxidant activity[48].Furthermore,isorhamnetin can block TGF-β1-induced ROS production and GSH depletion,reduce phosphorylated Smad3,TGF-β1,α-SMA,and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression,and collagen expression in primary mouse HSCs and LX-2 cells,alleviate OS,and inhibit HSC activation,thereby preventing hepatic fibrosis[49].These findings suggest that isorhamnetin may have potential therapeutic applications for hepatic fibrosis.
Naringin is a natural organic compound with the molecular formula C15H12O5[50].Naringin and its glycosides are present in various herbs and fruits,including grapefruit,Buddha’s hand citron,lime,tart cherry,tomato,cocoa,Greek hay,water mint,and legumes[51].Due to its hydroxyl substituents,naringin exhibits high reactivity towards ROS and reactive nitrogen species and has strong inhibitory effects on lipid peroxidation in mouse liver,brain,and heart tissues[52].In 2017,Hernández-Aquinoet al[53] reported that administration of naringin could potentially prevent an increase in liver enzymes such as alanine transaminase (ALT),alkaline phosphatase (ALP),gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase,and GSH peroxidase (GSH-Px).Additionally,naringin was shown to enhance the body’s antioxidant capacity and effectively prevent liver inflammation,hepatocyte necrosis,and hepatic fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)[53].Building on this work,Hernández-Aquinoet al[54] conducted further research in 2019 and found that naringin has the potential to inhibit OS and exert its anti-fibrotic effect by blocking the nuclear transcription factor-κB (NF-κB),TGF-β-Smad3,and c-Jun N-terminal kinase-Smad3 pathways.These findings suggest that naringin could be a promising candidate for treating human fibrosis.
Additionally,Mallotus apelta(Lour.) Muell.Arg.leaf andBidens bipinnataL.contain total flavonoids along with other beneficial compounds such as puerarin,hesperidin,alpinetin,fisetin,glabridin,morin,and astilbin.These compounds have been shown to inhibit OS and promote a stable internal environment within the body,thereby improving hepatic fibrosis (Table 1).
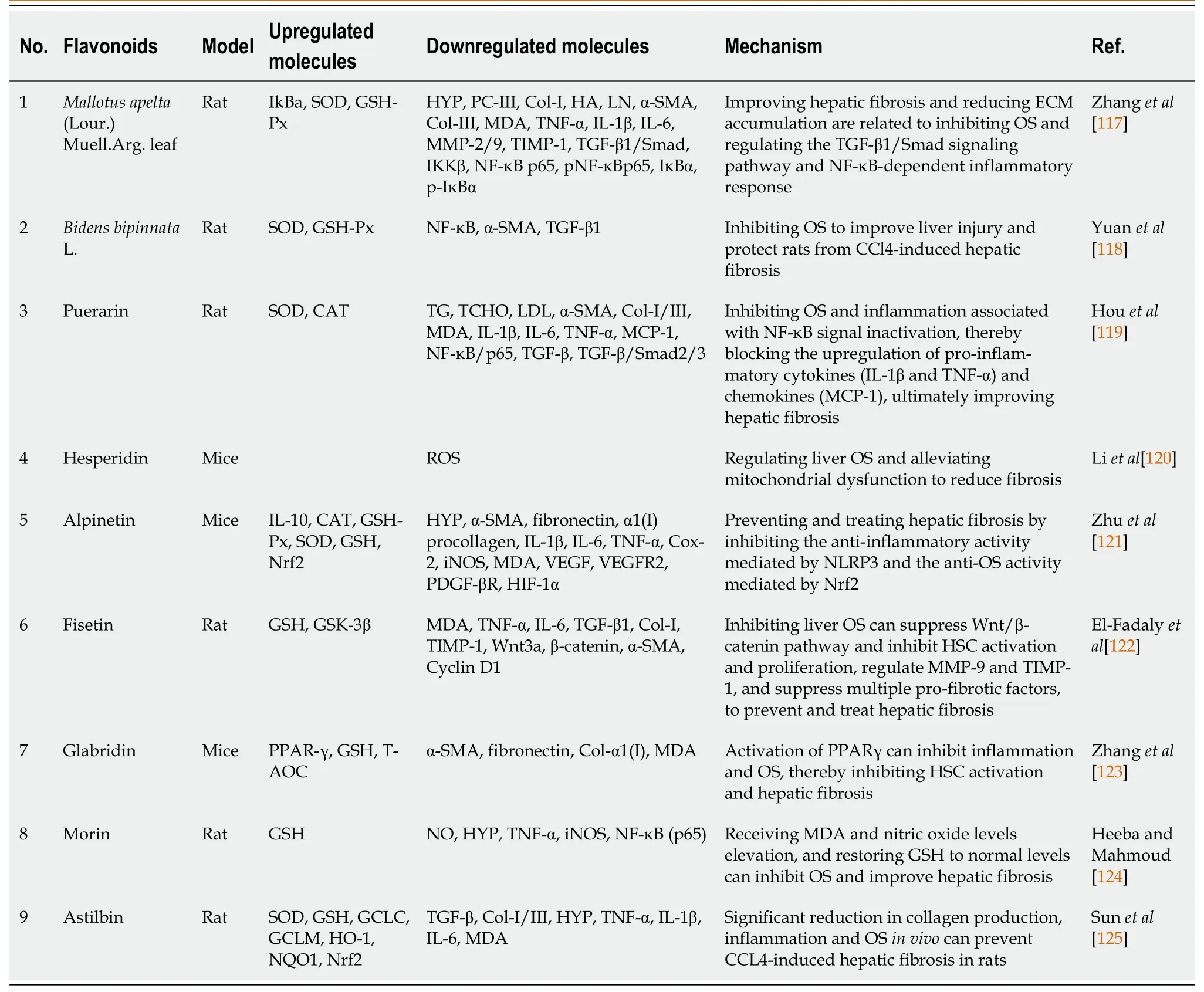
Table 1 Flavonoids improve hepatic fibrosis by inhibiting oxidative stress
GLYCOSIDES
Glycosides are a diverse group of biologically active compounds that are widely distributed in the plant kingdom[55].They consist of a sugar molecule linked to a non-sugar compound,such as a flavonoid or terpenoid.Glycosides have been extensively studied for their pharmacological properties,which include anti-inflammatory,antibacterial,antifungal,and antioxidant effects[56].In particular,glycosides have been found to possess potent antioxidant properties that can prevent or reduce OS in various tissues and organs,including the liver[57].
Saikosaponin-D is a type of glycoside monomer component extracted from the dried roots ofBupleurum chinenseDC.andBupleurum scorzonerifoliumWilld,both plants belonging to the Umbelliferae family[58].Its molecular formula is C42H68O13[58].Saikosaponin-D possesses various pharmacological effects such as antioxidant,sedative,antiviral,anti-inflammatory,immune-regulatory,hepatoprotective,and anticancer activities[59].Saikosaponin-D can delay the development of hepatic fibrosis by alleviating liver cell damage caused by OS[57].Researchers such as Queet al[60] have proposed that saikosaponin-D may downregulate the ROS/MAPK signaling pathway.This not only significantly inhibits the proliferation and activation of HSC-T6 cells induced by OS but also reduces the deposition of the ECM,such as tissue inhibitors of TGF-β1,hydroxyproline,collagen-1,and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-1,which indicates its potential as a therapeutic agent for hepatic fibrosis[60].However,despite its promising pharmacological properties,the clinical use of saikosaponin-D is limited due to its low bioavailability and poor water solubility.Further research is needed to develop effective delivery systems and optimize its pharmacokinetic properties to allow for its use in clinical settings.
Resveratrol glucoside is a polyphenol and monocrystalline natural compound belonging to the stilbene class[61].Vitaceae,Liliaceae,and Leguminosae families are the important sources of resveratrol glucoside extraction[62].It is mainly isolated from the rhizome and roots ofPolygonum cuspidatum,and also found in daily foods such as grapes and red wine[62].Various studies have shown that resveratrol glucoside has a variety of pharmacological activities,such as anti-inflammatory,anti-apoptotic,anti-tumor,lipid-lowering,and cardiovascular protective effects,particularly strong antioxidant pharmacological activity[63].Resveratrol glucoside has been shown to have antioxidant biological activity and therapeutic action on many liver diseases,including hepatic fibrosis.For example,resveratrol glucoside has been found to inhibit the production of 4-hydroxydecenoic acid in the liver and the expression of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase 4,thereby reducing OS and inflammation and improving chronic liver injury and fibrosis[64,65].Moreover,research has demonstrated that resveratrol glucoside can also downregulate the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase 4 enzyme,thus decreasing TLR4/NF-κB p65 signaling pathway-related inflammatoryreactions and macrophage expression,which suggests that it could be an effective therapeutic agent for preventing and treating hepatic fibrosis[66].To sum up,resveratrol glucoside shows promise as a natural compound for preventing and treating chronic liver injury and fibrosis.Further research is needed to fully understand its mechanisms of action and optimal dosage for therapeutic use.
Geniposide is an organic compound with the molecular formula C17H24O10[67].It is derived from the dried mature fruit ofGardenia jasminoides Ellis,a plant belonging to the Rubiaceae family[68].Geniposide is mainly found inGardenia jasminoides,but has also been detected in other commonly used Chinese herbal medicines such asEucommia ulmoides,Rehmannia glutinosa,andScutellaria baicalensis[68].Geniposide not only upregulates endogenous antioxidant enzymes to slow down cell damage,but also increases the activity of antioxidant enzymes and pathways such as liver lipid peroxidation,GSH S-transferases,GSH,GSH-Px,and copper-and zinc-containing SOD,which can prevent OS damage,protect hepatocytes,and improve hepatic fibrosis[69].The study by Yanget al[70] investigated the protective effects of geniposide on hepatic fibrosis in a rat model induced by CCl4administration.The researchers found that geniposide treatment significantly reduced hepatic fibrosis and improved liver function,as evidenced by decreased levels of serum ALT,aspartate aminotransferase (AST),and ALP.Further analysis revealed that geniposide exerted its anti-fibrotic effects through multiple mechanisms[70].First,geniposide increased the activities of two important antioxidant enzymes,SOD and GSH-Px,which scavenge free radicals and protect cells from oxidative damage.This was accompanied by a reduction in the levels of malondialdehyde (MDA),a biomarker of lipid peroxidation,in the liver tissue[70].In brief,the study suggested that geniposide has potential as a therapeutic agent for hepatic fibrosis by targeting OS.However,further studies are needed to confirm these findings in human subjects and to explore the optimal dosage and duration of geniposide treatment.
In addition,glycoside compounds such as baicalin,vitexin,and forsythoside A (Table 2) can also improve hepatic fibrosis by inhibiting the body’s OS,regulating intestinal flora bile acid metabolism,increasing antioxidant and phase IIdetoxification enzyme activity.To recap,the evidence suggests that glycosides can prevent or reduce hepatic fibrosis by inhibiting ROS production,reducing OS,and modulating HSC activation.These findings highlight the potential of glycosides as therapeutic agents for hepatic fibrosis and other OS-related diseases.However,further studies are needed to elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying the protective effects of glycosides and identify optimal doses and treatment regimens.
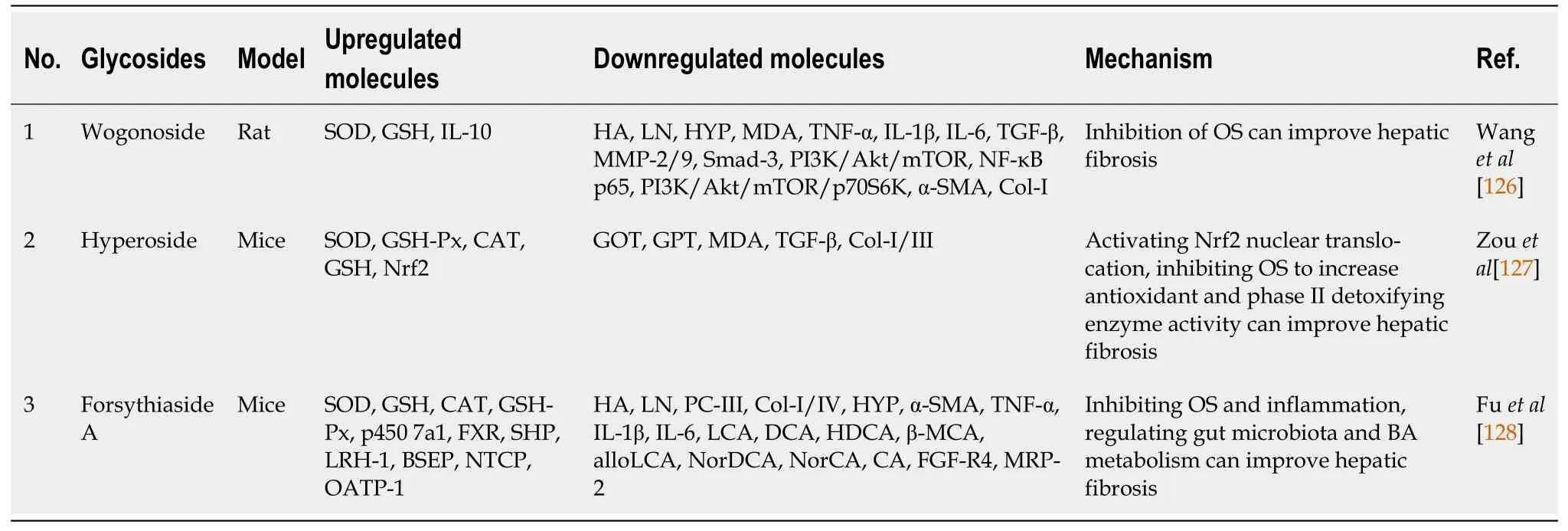
Table 2 Glycosides improve hepatic fibrosis by inhibiting oxidative stress
ALKALOIDS
Alkaloids are a class of naturally occurring organic compounds that are characterized by their bitter taste and basic properties[71].They are found in many plants and have a wide range of biological activities,including analgesic,antiinflammatory,and anti-cancer properties.Alkaloids have complex interactions with ROS and hepatic fibrosis[72].
Some alkaloids have protective effects against hepatic fibrosis by reducing ROS production and promoting antioxidant activity.Further research is needed to better understand the mechanisms underlying these effects and to identify new alkaloids with potential therapeutic applications in hepatic fibrosis.
Berberine is a naturally occurring compound found in various plants such as goldenseal,barberry,and oregon grape[73].It has been widely used in traditional medicine for its anti-inflammatory,anti-microbial,and anti-diabetic properties[74].In recent years,there has been growing interest in the potential of berberine as a treatment for hepatic fibrosis.Studies have shown that berberine has potent antioxidant properties that help reduce OS and ROS levels in the liver[75].It achieves this by activating various cellular defense mechanisms that protect liver cells from oxidative damage[75].Furthermore,studies suggest that berberine can prevent the activation of HSCs,which are responsible for producing the scar tissue that leads to hepatic fibrosis[76].Domitrovićet al[77] demonstrated that the administration of high-dose berberine (9 mg/kg) is effective in reducing OS,decreasing the expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and TGF-β1,increasing MMP-2 levels,and promoting the removal of fibrous deposits to ameliorate hepatic fibrosis.In essence,these findings suggest that berberine has great potential as a therapeutic agent in the treatment of hepatic fibrosis.By reducing OS and preventing the activation of HSCs,berberine may help slow or even reverse the progression of hepatic fibrosis.However,further research is necessary to fully understand the mechanisms through which berberine exerts its beneficial effects on hepatic fibrosis.
Betaine,also known as trimethylglycine,is a naturally occurring compound found in many foods,including spinach,beets,and whole grains[78].It is used as a dietary supplement to improve athletic performance,promote liver health,and reduce the risk of liver disease[79].Research suggests that betaine may help to alleviate hepatic fibrosis by reducing OS.In a study conducted by Bingület al[80],betaine supplementation was found to significantly reduce ROS levels,decrease lipid peroxidation,and increase antioxidant enzyme activity in rats with hepatic fibrosis induced by CCl4exposure.Additionally,betaine treatment reduced collagen deposition and improved liver function in these rats,indicating that it may have therapeutic potential for hepatic fibrosis[81].Another study conducted by Kimet al[82] investigated the effects of betaine on OS and fibrosis in liver cells.The researchers found that betaine treatment reduced ROS levels and lipid peroxidation,increased GSH levels (an important antioxidant in the body),and inhibited the expression of fibrotic markers in HSCs,the primary cells responsible for hepatic fibrosis.These results suggest that betaine may exert its antifibrotic effects by modulating OS and reducing fibrogenic signaling pathways in liver cells[82].In conclusion,the relationship between betaine and hepatic fibrosis is complex,but emerging evidence suggests that betaine may help to alleviate hepatic fibrosis by reducing OS,inhibiting fibrogenic signaling pathways,and promoting liver function.Further research is needed to fully elucidate the mechanisms underlying betaine’s therapeutic effects on hepatic fibrosis and determine optimal dosages and treatment durations for clinical use.
Lycorine is a natural alkaloid that is found in various plant species such as the Amaryllidaceae family[83].It has been known to possess multiple pharmacological properties,including anti-cancer,anti-inflammatory,and antiviral activities[84].Recently,lycorine has also been studied for its effect on hepatic fibrosis,a chronic condition that occurs due to the accumulation of ECM proteins in the liver tissue.Lycorine has been shown to inhibit ROS production and reduce OS,thereby reducing HSC activation and regulating the fibrotic process[83].Furthermore,lycorine may also have a protective effect against liver injury caused by OS.In a study conducted on animal models of acute liver injury induced by CCl4,lycorine was found to prevent liver damage by reducing OS and inflammation in liver tissue[85].To conclude,the relationship between lycorine,ROS,OS,and hepatic fibrosis is complex and multifaceted.More research is needed to explore the potential therapeutic effects of lycorine in hepatic fibrosis and other related liver diseases.However,the current evidence suggests that lycorine may hold promise as a natural therapeutic agent for hepatic fibrosis.
To put it briefly,alkaloids have shown potential as therapeutic agents for the treatment of hepatic fibrosis.However,more research is needed to determine their efficacy and safety,especially at higher doses.It is important to work with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of action for managing hepatic fibrosis and to monitor liver function regularly.
POLYSACCHARIDES
Polysaccharides are complex carbohydrates that play an important role in the body’s physiological processes[86].They are found in a variety of sources,including plants,fungi,and animals,and are known for their ability to confer a range of health benefits[86].One area where polysaccharides have shown particular promise is in the treatment of hepatic fibrosis.Recent research has suggested that polysaccharides may offer a promising alternative for managing hepatic fibrosis.In particular,studies have shown that certain polysaccharides have antioxidant properties,which can help reduce OS in the liver.OS is known to play a key role in the development and progression of hepatic fibrosis.
Cordycepsis a type of fungus that has been used for centuries in traditional medicine to treat a variety of ailments[87].In recent years,researchers have been investigating the therapeutic potential of Cordyceps polysaccharides,one of the main bioactive compounds found in the fungus[88].Cordyceps polysaccharides have been shown to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties,making them a promising candidate for treating hepatic fibrosis,a condition characterized by scarring and damage to the liver[89].Cordyceps polysaccharides protect hepatocytes from hydrogen peroxideinduced mitochondrial dysfunction by reducing ROS production and regulating mitochondrial apoptotic signalingviacytochrome C,apoptosis regulator Bax,and mitochondrial-related apoptotic proteins in HepG2 cells[90].In addition,studies have shown that Cordyceps polysaccharides can reduce the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and cell apoptosis by regulating TLR4/myeloid differentiation factor 88/NF-κB,Bcl-2/Bax,and caspase family signaling pathways,thereby reducing OS,serum enzymes,α-SMA,Col-III,TGF-β1,p-Smad3,and collagen volume fraction,inhibiting OS,enhancing the body’s antioxidant defense system,and improving hepatic fibrosis[91].Recapitulating,Cordyceps polysaccharides have demonstrated hepatoprotective effects against liver injury caused by OS.They can regulate various signaling pathways to promote liver cell survival,reduce fibrosis,and improve liver function.These findings suggest that polysaccharides may be a promising therapeutic agent for liver diseases.
The relationship between polysaccharides,OS,and hepatic fibrosis is complex,and additional research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms underlying this relationship.However,these findings suggest that polysaccharides may offer a promising new avenue for the treatment of hepatic fibrosis.
SINGLE HERBAL EXTRACTS
Single herbal extracts such asSalvia miltiorrhiza,Ginkgo bilobaleaf,clove basil,Ceratonia siliquapod extract,grape seed,pomegranate extract,Taraxacum officinaleroot,andMyrtus communishave demonstrated significant potential in combating hepatic fibrosis.These extracts target OS pathways,regulate HSC activation and apoptosis,and inhibit collagen deposition in liver tissue,as outlined in Table 3.
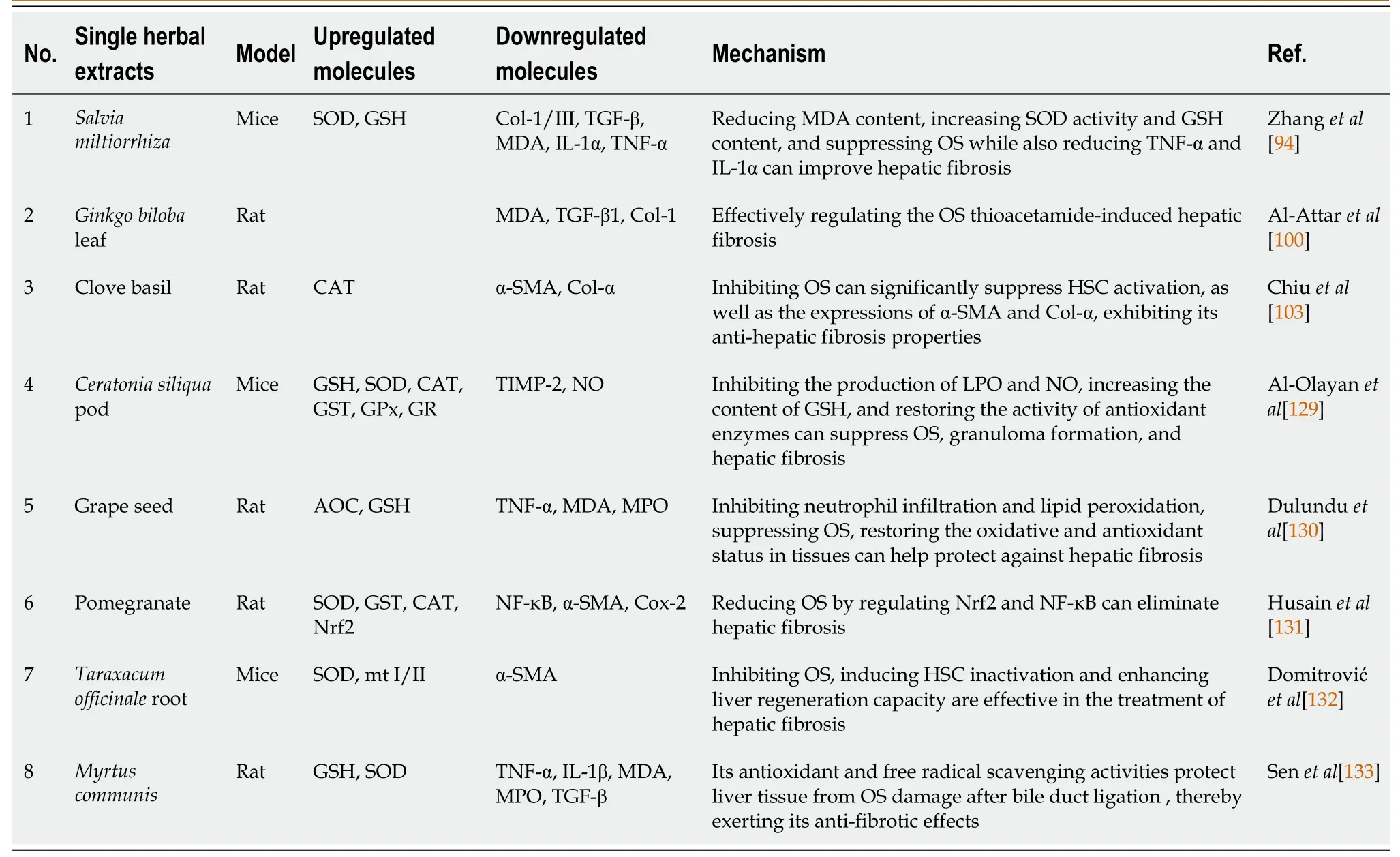
Table 3 Single herbal extracts improve hepatic fibrosis by inhibiting oxidative stress
Salvia miltiorrhiza,also known as Danshen,is a TCM that has been used for centuries to treat various ailments,including liver disease[92].Recent studies have shown that one of the mechanisms by whichSalvia miltiorrhizaexerts its hepatoprotective effects is through the modulation of OS pathways in the liver[93].Research has demonstrated thatSalvia miltiorrhizacan alleviate hepatic fibrosis by reducing the generation of ROS and the consequent activation of HSCs[94].In a recent study,Zhanget al[94] investigated the effect ofSalvia miltiorrhizaon ROS-induced hepatic fibrosis in rats.The researchers found that treatment withSalvia miltiorrhizasignificantly reduced the levels of ROS and lipid peroxidation products in the liver tissue,and also inhibited the activation of HSCs[94].Furthermore,they observed thatSalvia miltiorrhizatreatment increased the expression of antioxidant enzymes,such as SOD and catalase,which help protect against OS in the liver[95].Another study by Wanget al[96] explored the potential molecular mechanisms underlying the anti-fibrotic effects ofSalvia miltiorrhiza.The researchers found thatSalvia miltiorrhizacould inhibit the expression of fibrogenic genes in HSCs,such asCol-Iandα-SMA,by downregulating the activity of the TGF-β signaling pathway,which is known to be a key regulator of fibrogenesis in the liver[96].Moreover,they observed thatSalvia miltiorrhizatreatment reduced the production of ROS and enhanced the activity of antioxidant enzymes in HSCs,which may contribute to its anti-fibrotic effects[97].Summarily,these studies provide evidence thatSalvia miltiorrhizacan protect against hepatic fibrosis by modulating OS pathways in the liver.Further research is needed to fully understand the molecular mechanisms underlying this effect and to explore the potential ofSalvia miltiorrhizaas a therapeutic agent forhepatic fibrosis.
Ginkgo bilobaleaf is a popular herb that has been used for centuries for various health benefits[98].Ginkgo contains flavonoids and terpenoids,which are known to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties[45].These compounds make ginkgo a potential treatment option for hepatic fibrosis[99].Ginkgo bilobaleaf has the potential therapeutic effect of effectively regulating OS induced by thioacetamide and exerting an effect on thioacetamide-induced hepatic fibrosis[100].Studies have demonstrated thatGinkgo bilobaleaf can inhibit HSC activation and reduce collagen deposition in liver tissue by regulating OS pathways[100].In addition,Ginkgo bilobaleaf has been found to upregulate the expression of Nrf2,a transcription factor that plays a key role in the cellular response to OS[101].This suggests thatGinkgo bilobaleaf may be a promising therapeutic agent for hepatic fibrosis.
Clove basil,also known asOcimum gratissimum,is a species of basil that is native to parts of Africa and Asia[102].It has been used in traditional medicine to treat a variety of conditions,including liver diseases.Recent studies have demonstrated the potential of clove basil extract in preventing the development of hepatic fibrosis through its antioxidant properties.Clove basil contains high levels of phenolic compounds,such as rosmarinic acid,which have potent antioxidant activity.Studies have shown that the clove basil extract possesses anti-hepatic fibrosis properties by inhibiting serum-induced HSC activation and reducing the expression of α-SMA and Col-a[103].This effect is attributed to the antioxidant components in the extract,which suppress OS and prevent hepatic fibrosis[103].Additionally,studies have shown that clove basil extract can maintain levels of ALT and AST,as well as MDA,catalase,and α-SMA levels induced by CCl4,indicating its ability to protect the liver from oxidative damage and promote healing of hepatic fibrosis[104].Synthetically,clove basil extract has the potential to be used as a therapeutic agent in the treatment of hepatic fibrosis due to its antioxidant and anti-HSC activation properties.However,further studies are needed to explore its mechanism of action and its potential use in clinical settings.
These findings suggest that single herbal extracts may be a potential treatment option for hepatic fibrosis.However,more research is needed to fully understand their effectiveness and potential side effects.It is important to consult with a healthcare professional before taking any herbal supplements,including clove basil.
TCM FORMULAS
The TCM formula stands out for its multi-component,multi-target,and low adverse reaction properties.It employs syndrome differentiation treatment and holistic therapy to regulate the body functions and status,improves prognosis,and eliminates pathogenic factors without harming healthy ones.As a result,TCM formulas show remarkable potential in preventing and treating hepatic fibrosis.This article presents a summary of TCM formulas (Table 4) which have beenreported to prevent and improve hepatic fibrosis by inhibiting OS.
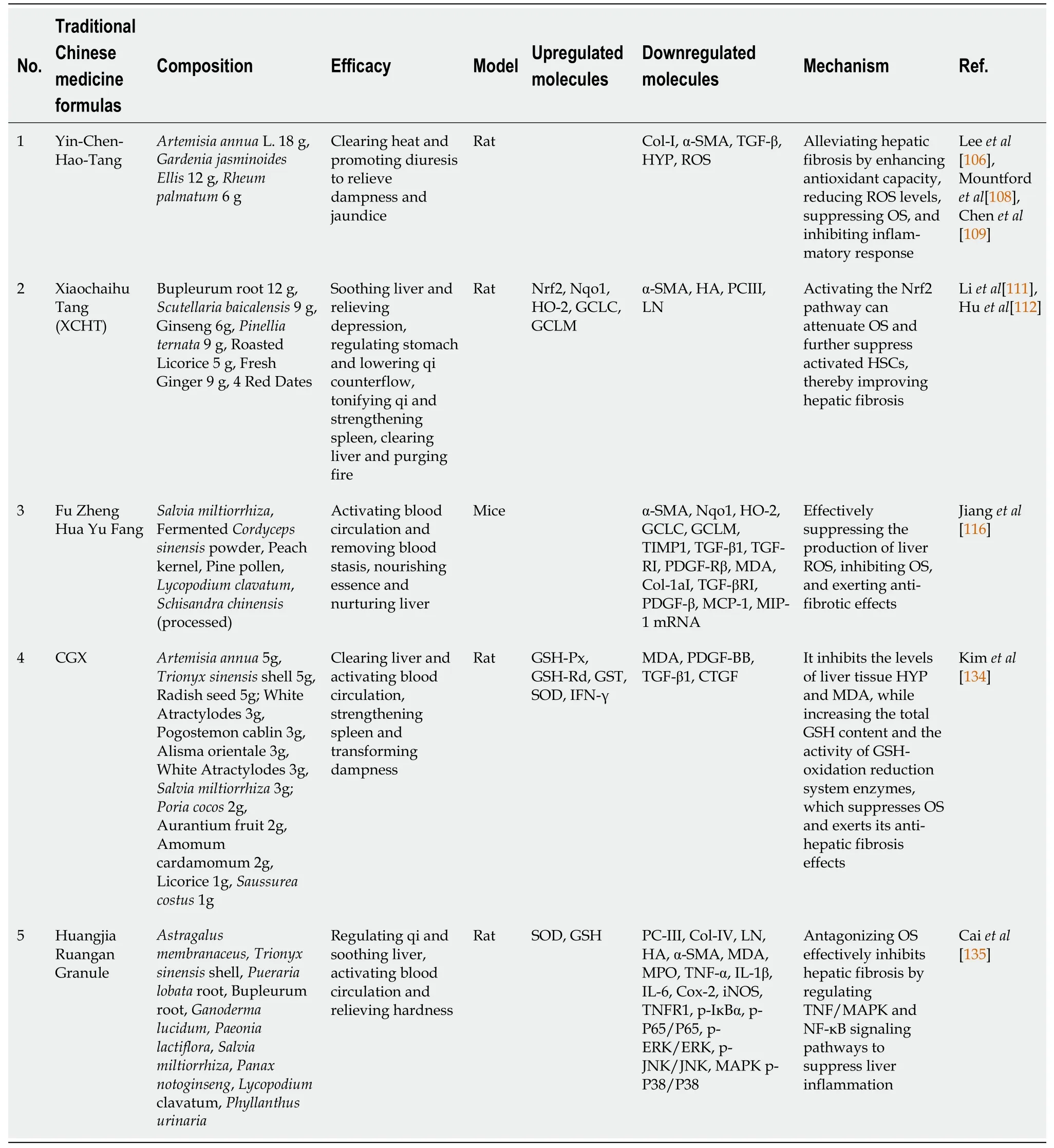
Table 4 Traditional Chinese medicine formulas improve hepatic fibrosis by inhibiting oxidative stress
YCHT is a TCM formula that has been used for centuries to treat liver diseases[105].It is composed of three herbs,Artemisia annua L.(Qing Hao),Gardenia jasminoides Ellis(Zhi Zi),andRheum palmatum L.(Da Huang),and is commonly used in clinics in China and other Asian countries[105].Studies have suggested that YCHT can decrease ROS production and alleviate hepatic fibrosis.One of the mechanisms by which YCHT works is by regulating the balance between the pro-and anti-inflammatory cytokines in the liver[106].Inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α,interleukin (IL)-6,and IL-1 β are known to promote ROS production and hepatic fibrosis[107].YCHT inhibits the expression of these cytokines and promotes the secretion of anti-inflammatory cytokines such as TGF-β and IL-10,which can reduce ROS production and hepatic fibrosis[108].Another mechanism by which YCHT inhibits ROS production is by increasing the expression of antioxidant enzymes,such as SOD[109].SOD converts superoxide radicals,one of the primary ROS,into hydrogen peroxide,which is less toxic.This conversion reduces OS in the liver and improves liver function[109].In short,the beneficial effects of YCHT on hepatic fibrosis may be attributed to its antioxidant properties.Further studies are needed to fully elucidate the underlying mechanisms and to establish its clinical efficacy and safety for the treatment of hepatic fibrosis.
XCHT is a TCM formula that has been used for centuries to alleviate various ailments,including hepatic fibrosis[110].Recent studies have shown that XCHT may effectively reduce hepatic fibrosis by inhibiting ROS and OS pathways.Recent research has suggested that XCHT can suppress the production of ROS and reduce OS,leading to improvement in antioxidant capacity[111].XCHT contains various active compounds such as baicalin,baicalein,and saikosaponin[111].These compounds have all been shown to possess potent antioxidant properties,which may help to explain XCHT’s ability to reduce oxidative liver damage and improve hepatic fibrosis[111].Furthermore,XCHT has shown promising results in treating hepatic fibrosis by increasing levels of Nqo1,HO-2,GCLC,and GCLM -key components of the Nrf2 pathway in the liver[111].This mechanism of action is likely responsible for its effectiveness in improving hepatic fibrosis.XCHT has been found to upregulate OS through the Nrf2 pathway,while also inhibiting the proliferation and activation of HSCT6 cells,which contributes to its ability to improve hepatic fibrosis[112].To put it briefly,XCHT has shown promise in reducing hepatic fibrosis by inhibiting ROS and OS pathways,enhancing antioxidant capacity,and modulating the immune system and ECM remodeling processes.Further research is needed to fully understand the molecular mechanisms underlying XCHT’s therapeutic effects in hepatic fibrosis and to optimize its clinical application in treating hepatic fibrosis.
Fuzheng Huayu Fang is a formula used in TCM for treating liver diseases and related complications[113].This formula aims to strengthen the body’s immune system,promote blood circulation,and reduce inflammation,hence helping to alleviate the symptoms associated with liver disorders[114].Fuzheng Huayu Fang contains several herbs with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties that help to regulate ROS levels and protect liver cells from damage[115].For instance,the herb Danshen (Salvia miltiorrhiza) has been shown to reduce ROS levels and inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in liver cells,thereby improving liver function and reducing hepatic fibrosis[96].Moreover,some studies have found that Fuzheng Huayu Fang can also help to lower OS and inflammation by regulating the expression of genes involved in these processes[116].To cut a long story short,Fuzheng Huayu Fang is a useful formula for treating hepatic fibrosis due to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.By reducing ROS levels and promoting liver regeneration,this formula can help to alleviate the symptoms associated with liver disorders and improve the overall health of the liver.
In essence,TCM formulas have shown great potential in preventing and treating hepatic fibrosis.These formulas can regulate the body’s functions and status and improve prognosis without causing adverse reactions.The mechanisms underlying their anti-fibrotic effects involve the suppression of ROS production,inhibition of HSC activation,and regulation of cytokine expression.Further studies are needed to validate their efficacy and safety in clinical practice.
DISCUSSION
Hepatic fibrosis is a compensatory response to liver injury and is also a risk factor for liver cirrhosis,liver cancer,and liver failure.Although the pathogenesis of hepatic fibrosis is complex and not fully understood,OS has been shown to play an important role in the development of hepatic fibrosis diseases.Therefore,the inhibition of OS can prevent hepatic fibrosis and related liver diseases.TCM is a treasure of Chinese traditional medicine,with unique advantages and profound connotations.TCM monomers,single herb extracts,and TCM formulas are increasingly being studied by researchers for their low adverse reactions,cost-effectiveness,and broad targeting of multiple pathways in the prevention and treatment of hepatic fibrosis.Based on the development of modern scientific technologies such as pharmacology and genomics,TCM monomers,single herb extracts,and TCM formulas have been extensively studied for their molecular mechanisms of anti-hepatic fibrosis by targeting OS and intracellular signal transduction processes,achieving good results and having broad application prospects.
However,there are also some issues that need to be addressed at present: Clinical trials are still lacking,and current studies on the role of TCM monomers,single herb extracts,and TCM formulas in inhibiting OS to treat hepatic fibrosis are mainly focused on animal experiments,with limited large-scale clinical trials,which limits the further research and transformation of these TCM monomers,single herb extracts,and TCM formulas.Therefore,how to apply the results of basic experiments to clinical practice and verify the anti-fibrosis effects of TCM monomers,single herb extracts,and TCM formulas in large-scale clinical trials has become another challenge in the treatment of hepatic fibrosis.
In addition,the structure-activity relationship study is not sufficient.Since most polysaccharides,single herb extracts,and TCM formulas are mixtures,their pharmacological mechanisms are difficult to fully elucidate,and they may be limited to the accumulation of effective components of single herb extracts or may be the result of the formation of a systemic pharmacological mechanism of mixtures.This limits the practical application of these TCM in clinical practice.Therefore,TCM theory should be combined with modern medical theory.Based on the summary of previous research,individual differences in pathogenesis and disease progression should be analyzed to further explore how TCM inhibits OS to address hepatic fibrosis.
As well as,some people may be allergic to certain TCMs.If symptoms such as rash,itching,difficulty breathing,or throat swelling occur,medication should be immediately discontinued and medical help should be sought.Additionally,individuals with pre-existing health conditions or those taking other medications should consult healthcare professionals before starting any TCM treatment.This is crucial to ensure the absence of potential drug interactions or worsening of current health issues.Besides,it is important to purchase Chinese medicine products from reputable suppliers to ensure their quality and safety.Counterfeit or adulterated products can pose serious health risks and should be avoided.In summary,while TCM can provide therapeutic benefits,understanding and addressing potential adverse reactions and preventive measures associated with its use are crucial.By following proper guidelines,consulting healthcare professionals,and using legitimate products,risks can be minimized and benefits can be maximized.This will help find better inducing effects,with fewer adverse reactions and lower prices for TCM,providing a more reliable theoretical basis for achieving true and effective reversal of hepatic fibrosis.
CONCLUSION
Hepatic fibrosis is a condition characterized by inflammation and excessive growth of fibrous tissue in the liver,resulting from long-term exposure to harmful factors.OS is considered a key mechanism in the development and progression of hepatic fibrosis.TCM monomers,single herb extracts,and TCM formulas play important roles in treating hepatic fibrosis by inhibiting OS.This review summarizes the role and effectiveness of TCM monomers,single herb extracts,and TCM formulas in inhibiting OS for the treatment of hepatic fibrosis,based on relevant research.The findings demonstrate that TCM monomers,single herb extracts,and TCM formulas possess significant antioxidant properties,effectively reducing OS levels in the liver and alleviating the occurrence and progression of hepatic fibrosis.
FOOTNOTES
Author contributions:Zhu JF and Li Z designed the study;Li Z searched,analyzed,and,and summarized the literature results;Li Z and Ouyang H collected the data and wrote the manuscript;Zhu JF and Li Z checked and revised the article;all authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Supported bythe Construction Project of Traditional Chinese Medicine Specialty in Yueyang Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine;Preclinical Study of a New Chinese Herbal Medicine for the Treatment of Ascites of Liver Cirrhosis (Spleen and Kidney Yang Deficiency Type) with the Clinical Formula of Qigui Xiaogu Cataplasm,No.23S21 900100;National Natural Science Foundation of China,No.82 074386;Clinical Research Plan of SHDC,No.SHDC2020CR3095B;and Construction of Special Disease Alliance of Traditional Chinese Medicine in East China Area and Municipal Level,Shanghai Special Disease Alliance of Traditional Chinese Medicine for Liver Cirrhosis Ascites (Water Sickness).
Conflict-of-interest statement:The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Open-Access:This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers.It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license,which permits others to distribute,remix,adapt,build upon this work non-commercially,and license their derivative works on different terms,provided the original work is properly cited and the use is non-commercial.See: https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by-nc/4.0/
Country/Territory of origin:China
ORCID number:Zhen Li 0000-0002-2940-6464;Jun-Feng Zhu 0000-0003-0245-4092;Hao Ouyang 0000-0001-6930-2363.
S-Editor:Lin C
L-Editor:Wang TQ
P-Editor:Yuan YY
杂志排行
World Journal of Hepatology的其它文章
- Inflammatory pseudotumors in the liver associated with influenza: A case report
- Exercise training as an intervention for frailty in cirrhotic patients on the liver transplant waiting list: A systematic review
- Prevalence and risk factors of lymphatic dysfunction in cirrhosis patients with refractory ascites: An often unconsidered mechanism
- Liver disease epidemiology and burden in patients with alterations in plasma protein metabolism: German retrospective insurance claims analysis
- Challenges and dilemmas in pediatric hepatic Wilson’s disease
- Dietary salt in liver cirrhosis: With a pinch of salt!
