An assessment Protocal of Ammonia Removal Efficacy for Air Purification Products
2023-11-29LiRongjieMaJiaoyingZhangTianyi
Li Rongjie,Ma Jiaoying,Zhang Tianyi
Whealth Lohmann Centralin (GZ) Co.,Ltd.,China
Abstract A device is designed to assess the ammonia removal effect of passive air purification products which derived the QB/T 2761-2006 Methods for determination of purificatory effect of indoor environment decontamination product.The device is composed of three parts: ammonia generator,ammonia removal device and ammonia collection device,which is made up of common laboratory equipment.The reagents used are common acid and alkali reagents in the laboratory.During the experiment,5.0mL of 25% concentrated ammonia water is added to the ammonia generator as the ammonia source,and filter paper is used as the sample carrier.Take 3.0g sample and add it to the filter paper,after the ammonia is absorbed by the filter paper with the sample,the residual ammonia is collected and measured by acid-base titration.The ammonia removal efficacy of the sample is calculated by the ammonia absorption amount of the blank sample and the sample to be tested.This method has the characteristics of simple equipment,small area,toxic or harmful substance free,and fabulous accuracy.Four different samples were tested,and the results matched the standard method.
Key words device designing;convenient;ammonia removal
With the development of society and the improvement of people’s living standards,the air quality of residential environments is receiving more and more attention,while promoting the development of air purification and fresh products[1].Odor mainly refers to substances that are volatile and can stimulate the olfactory organs and cause unpleasant reactions.According to their composition,there are mainly five categories: halogenated and alkane compounds,oxygenated compounds,sulfur compounds,and nitrogen-containing compounds[2].In daily life,halogens and alkanes mainly come from chemical related components (such as building decoration materials or solvent leakage),while oxygenated compounds and sulfur compounds mainly come from the rotten organic matter or secondary pollution of kitchen waste,[3]and nitrogen-containing compounds mainly come from animal feces,which are the main problems faced by pet or poultry keepers[4,5].The first two types of pollution are generally removed through professional means (such as seeking institutions specializing in formaldehyde removal) or maintaining good living habits to purify the air;Those who suffer from nitrogen containing pollutants need to do some cleaning frequently since animals are not completely controlled by humans.At present,there are some specialized deodorizing or air freshening products launched in the market for pet households,with the main purpose of making people unable to smell the ammonia odor in the environment.These products are mainly divided into physical deodorants,chemical deodorants,and biological deodorants based on their functional principles.
QB/T 2761-2006 Methods for determination of purificatory effect of indoor environment decontamination product is used for evaluating the removal performance of passive air purification materials for formaldehyde,benzene,and ammonia[6].This method uses an air test chamber,which has the disadvantages of occupying large space and inconvenient operation.For ammonia concentration testing,the recommended methods in this standard include Nessler’s reagent colorimetric method,sodium salicylate-sodium hypochlorite spectrophotometric method and ion selective electrode method[7,8].The first two methods use organic mercury,sodium nitroprusside and spectrophotometer,which have high threshold for laboratory hardware facilities and operators.What's more,testing steps such as sample collection,color reaction,and instrument analysis,making it difficult to achieve timely testing.The ion selective electrode method for sample determination is a good method with simple operation,time-saving and labor-saving.However,Not all laboratories have ammonia gas sensitive electrodes,limited the application of this method.
In this study,a device composed of common labwares are designed to determine the ammonia removal effect of passive air purification products simulating the standard of QB/T 2761-2006.The assessment of ammonia concentration is convenient.Ammonia gas is absorbed through the sample,and residual ammonia gas is collected with a syringe.Then,the residual gas is injected into a sulfuric acid solution,and the amount of residual ammonia is determined through sodium hydroxide titration and ion selective electronic electrodes.This study providing a new approach for evaluating the efficacy of passive air purification products.
1 Experimental procedure
1.1 Materials and apparatus
Sulfuric acid solution,approximately 0.1 mol/L;Sodium hydroxide standard solution,0.1 mol/L (prepared and calibrated according to the standard of GB/T601-2016);25% ammonia water;Syringes (5 mL× 3 pieces);Beaker (100 mL);Burette;Iodine flask (without glass stopper);Rubber stopper;Plastic conduit;and routine laboratory utensils such as filter paper,surface dishes,and dryers.
1.2 Device construction
As shown in Figure 1,iodine flask C is used for ammonia generation.During the test,5 mL of 25%concentrated ammonia water is filled inside,and the flask is tightly sealed with a rubber stopper.A catheter is used to balance the air pressure between the outside and the space above liquid.Above the iodine flask,syringe B (without piston) and syringe A are connected in sequence.A piece of filter paper with the sample to be tested is inserted inside syringe B (the filter paper is folded as a circular cake shape to ensure that gas can be filtered through the filter paper when passing through);The residual ammonia gas collected by syringe A is then slowly injected into a sulfuric acid solution;ammonium sulfate is generated while sulfuric acid is consumed.Therefore by titrating the excess sulfuric acid with standard sodium hydroxide solution,the ammonia content in the collected gas can be calculated,and so as the ratio of ammonia absorbed by the sample.

Figure.1 Experimental apparatus
1.3 Experimental Method
1.3.1 Simple pretreatment
A piece of filter paper is cut into approximately 20 cm × 20 cm,folded twice and placed on a watch glass.After dropping 3.0 g of the sample evenly,dry overnight in a desiccator.Meanwhile,replace the sample with pure water for control group.During the experiment,fold the dried filter paper into a strip about 2 cm wide,roll it into a circular cake like paper ball slightly larger than the inner diameter of syringe B,and stuff it into syringe B.
1.3.2 Ammonia absorption and residual ammonia collection
25.00 mL of sulfuric acid solution with a concentration of about 0.1 mol/L as the absorption solution of residual ammonia is added to a beaker by pipette.During ammonia absorption treatment,device is installed according to Figure 1.The volume of filtered ammonia is collected by extracting the piston handle of syringe A (each sample group collects same volume of gas,which can be determined by the scale on syringe A,and 53 mL of gas is collected in this experiment).The residual ammonia gas is slowly injected into the sulfuric acid solution to generate ammonium sulfate,and consumes sulfuric acid.The excess sulfuric acid is titrated with sodium hydroxide standard solution,and the volume of sodium hydroxide solution consumed in titration is recorded as Vx.In this experiment,the more of sodium hydroxide consumed,the more ammonia gas is absorbed by the sample in syringe B.
Ultrapure water is used as the control group,dripped to filter paper,dried,stuffed in syringe B,absorb ammonia gas and excess ammonia is absorbed with sulfuric acid solution as same as other samples .The volume of sodium hydroxide consumed is recorded as V1,which reflecting the ammonia content collected after absorption in control group.
Simultaneously perform reagent blank,repeat the same steps use the device shown in Figure 1,without adding ammonia water to the iodine flask C.Record the consumed sodium hydroxide solution as V0,reflecting the initial amount of the sulfuric acid solution.
1.3.3 Result calculation
The ammonia removal rate of sample is calculated as following formula:
In the formula,X stands for the ammonia removal rate of sample,%;V0stands for the reagent blank,mL;V1stands for the blank sample,mL;Vxstands for the V0stands for sodium hydroxide standard solution reacted with excess sulfuric acid,mL.
2 Results and discussion
2.1 The effect of injection speed on the absorption of residual ammonia by sulfuric acid solution during ammonia absorption
Residual ammonia gas is absorbed by the sulfuric acid solution after being absorbed by the sample is influenced by the concentration of sulfuric acid and injection speed.In this experiment,comprehensive consideration of safety and operability,the concentration of sulfuric acid solution is specified as 0.1 mol/L.And determination of ammonia injection absorption rate by control variates: First,25.00 mL of sulfuric acid solution with a concentration of about 0.1 mol/L is added to a 100 mL beaker by pipette,and cover with a watch glass.Collect ammonia gas according to the device shown in Figure 2,and then inject it into the sulfuric acid solution at different speeds.Here,syringe needle is about 2cm below the liquid level of sulfuric acid solution,collect 5 mL of ammonia each time,collect 5 times in each group,and titrate the sulfuric acid content.This experiment investigated 6 different absorption rates,including 5,10,15,20,25,and 30 seconds,and measured the remaining sulfuric acid concentration which reflects the absorption of ammonia by titration with sodium hydroxide.The results are shown in Figure 3.

Figure 2. Experimental apparatus for collecting ammonia
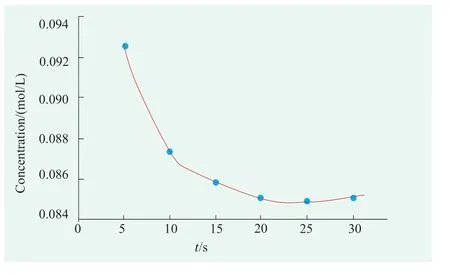
Figrue 3. Effects of ammonia absorbed by sulfuric acid solution
From Figure 3,it can be seen that when the collected ammonia gas is injected into a 0.1 mol/L sulfuric acid solution through a syringe,as the injection speed slows down,the absorption will become more complete.It is advisable to control the entire process for more than 20 seconds.In this experiment,the absorption of ammonia gas is completed within about 30 seconds,and the entire absorption process is maintained at a uniform and slow speed.
2.2 Impact of ammonia concentration
In this experiment,ammonia water in iodine flask C serves as the source of ammonia gas,and the total amount of ammonia has a direct impact on the results.It is necessary to ensure an excess of ammonia gas throughout the entire process.In this experiment,Ammonia solution with a concentration of 25% commonly used in laboratories was used to optimize the usage volume,and the ammonia gas was collected using the device shown in Figure 2.1,3,5,7,and 9 mL of ammonia was added to iodine flask C,and then collect the ammonia according to method before and absorb it with sulfuric acid solution.Every 3 times as a group and collected continuously.After collection,titrate the sulfuric acid content with sodium hydroxide solution (reflecting the ammonia collected of each group) to determine the attenuation of ammonia generated by adding different volumes of ammonia.When the ammonia content begins to decrease,record it as the Nth group,The results are shown in Table 1.
Based on the absorption of ammonia by the sample,in order to ensure an excessive and stable amount of ammonia collection,in this experiment,the minimum amount of ammonia added was ensured to be 5.0 mL.
2.3 Determination of filter Paper and Sample Dosage
According to experimental needs,a slow qualitative filter paper with stable chemical properties and uniform thickness is used as the base paper for loading samples in this device.In order for the sample to absorb ammonia gas more comprehensively,the base paper must be able to fill a certain cross-sectional area of syringe B well during the experiment,avoid large gaps for ammonia gas escaping without absorption.After practical comparison,in this experiment,the filter paper was cut to 20 cm × 20 cm size,after sample treatment and drying in a drying dish,fold it in half to a thick strip about 2 cm wide,roll it into a circular cake like paper ball slightly larger than the inner diameter of syringe B,and then insert it into the syringe,so that the sample on the filter paper can fully absorb the ammonia gas flowing through syringe B.
In terms of sample dosage,1.0,2.0,3.0,4.0,and 5.0 g of samples were added to the filter paper.And found that when the addition amount was less than 2.0 g,the sample cannot completely wet the filter paper,while more than 3.0 g,the filter paper cannot fully adsorb the sample,resulting in inaccurate experimental dosage.In this experiment,a combination of the filter paper,the sample usage was determined to be 3.0 g.
2.4 The influence of gas extraction speed on ammonia absorption by sample
Due to the impact of the extraction speed of syringe A on the absorption of ammonia gas by the sample,in previous experiments,it was found that if the extraction speed of syringe A is too fast,it will cause a certain negative pressure to be generated in syringe A.If the link between syringe A and syringe B is not fully sealed,it is easy to cause air to enter syringe A due to the negative pressure,affecting detection.The process needs to be controlled in about 18 seconds.In addition,if the speed is too fast,it is easy to cause insufficient reaction between the ammonia gas and sample in syringe B.Therefore,four common deodorants sold on the market are selected as examples,and 55 mL of gas is extracted from each experiment to investigate the impact of gas extraction speed on ammonia gas absorption.The results are shown in Figure 4.

Figure 4. The relationship between gas extraction and ammonia absorption of samples
In this experiment,all the selected samples were sufficient reacted with ammonia gas in 28 seconds,therefore,syringe A was uniformly extracted for 30 seconds.
2.5 Determination of residual ammonia collection volume
In order to determine the residual ammonia content more conveniently and quickly,acid-base titration method and ion selective electrode method were selected[8](other methods such as the Nessler's colorimetric method,which requires color derivation and special instrument operation is needed,are not conducive to rapid on-site determination,and toxic reagents are used),and were compared.In addition,the experimental results are greatly affected by the total volume of ammonia gas collected.Taking a deodorizing product produced by our company for example,and collect different volumes of ammonia gas to calculate its ammonia removal rate.Here,40,45,50,55,and 60mL of gas were collected,and the ammonia removal results of the sample are shown in Figure 5.
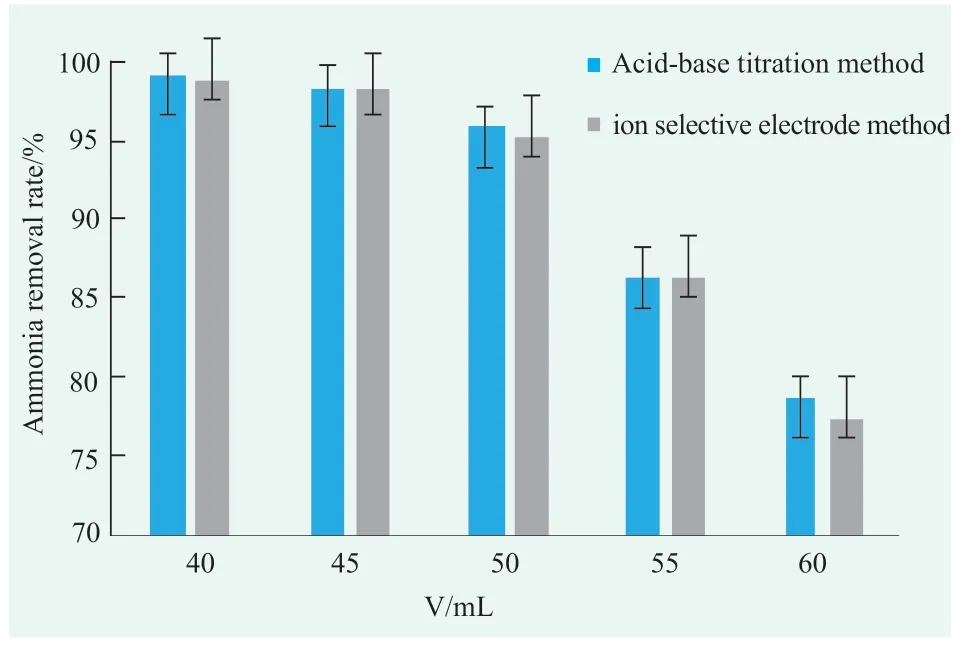
Figure 5. The relationship of volume acquisition and ammonia removal rate
From Figure 5,the detection of the two methods are close.Although the ion selective electrode method is easy operated,while the data distribution is relatively dispersed,insufficient precision.Titration method has lower instrumental requirements and good precision.
The ammonia removal rate of the sample is related to the gas collection volume.When the collection volume is less than 50mL.The ammonia removal rate of the sample decreases slightly with the increase of ammonia collection volume,the downward trend conforms to the linear formula of×100%.Here,a deodorant with ammonia removal rate is 90.6% (determined by method of QB/T 2761-2006 Method) is token as reference and calculated that the gas collection volume in this experiment is 53 mL.Finally,through the experiment,the ammonia removal rate of this sample is 90.3%detected by this experiment method.Therefore,the gas collection volume in this experiment is confirmed as 53 mL.
2.6 Practical application
Multiple deodorants with deodorization claims were selected from the market,and the ammonia removal efficacy of the method of QB/T 2761-2006 and this experiment method were compared as below.The results are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.Ammonia removal rate by different methods
3 Conclusion
Materials and apparatus used in this experimental method is easy to obtain.Process is simple,and the requirements for the laboratory and operators are not high.This method has been validated for its feasibility with ammonia removal rate,and there is no significant difference between the experimental results and the standard method.It provides a reference method for the development stage or post production testing of related products.
