Meta-analysis effects of levosimendan on mortality and hemodynamics in patients with sepsis
2023-11-23ZHAOMingruiZHENGRuiYANGYuanzheng
ZHAO Ming-rui, ZHENG Rui, YANG Yuan-zheng
Emergency and Trauma College, Hainan Medical University, Haikou 571199, China
Keywords:
ABSTRACT Objective: To investigate the effect of levosimendan on 28-day mortality in patients with sepsis.Methods: The English databases including Embase, PubMed, Web of Science,Cochrane Library and Chinese databasesincluding China National Knowledge Infrastructure(NKI), Wan fang Data, VIP, CBM were searched with levosimendan, sepsis and septic shock is as search terms.The published clinical randomized controlled trials of levosimendan injection were searched and the primary outcome measures of 28-day and 30-day mortality were included.Secondary outcome measures were left ventricular ejection fraction, left ventricular work index, cardiac index, and lactic acid.The literature retrieved is from the establishment of the database to October 2022.Stata 14.0 software was used for all data consolidation,publication bias monitoring and sensitivity analysis.Results: A total of 15 studies with 1 337 patients were included in this meta-analysis.The results showed that at the 28-day mortality of patients with sepsis in the levosimendan group was not statistically superior to the 28-day mortality in the control group [RR=0.91, 95% CI(0.78~1.06), Z=1.24, P=0.22].However,levosimendan can increase left ventricular ejection fraction, decrease left ventricular function index, increase cardiac index and decrease lactic acid in patients with sepsis.Conclusion:There is insufficient evidence to support a reduction in 28-day mortality in sepsis patients with levosimendan.However, levosimendan showed positive results on hemodynamic parameters,and more clinical trials are needed to verify the application of levosimendan in hemodynamic parameters of sepsis.
1.Introduction
Sepsis is a disease in which infection leads to a systemic immune response that produces both pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory mechanisms, and coagulation interacts with the immune system and endothelium, resulting in impaired hemodynamics and ultimately multiple organ dysfunction[1].When inflammatory factors, including cytokines, nitric oxide, complement system and lipopolysaccharide (LSP), act on myocardial cells,cardiac function is inhibited[2].Septic cardiomyopathy SCM was first described in 1958, and it still lacks a clear and consistent definition.The most common definition is reversible myocardial dysfunction due to sepsis, characterized by LVFE< 50% as diagnostic criteria, left ventricular dilation, and early return to normal clinical status[3].In addition, it has been found that the activation of toll-like receptors (TLRS), nuclear factor KB,mitochondrial dysfunction, endothelial dysfunction, autonomic nervous regulation and other aspects are associated with sepsis cardiomyopathy (SCM), but the specific pathogenesis remains unclear[4].According to existing studies, septic cardiomyopathy can be defined as an acute syndrome of cardiac dysfunction associated with sepsis and unrelated to myocardial ischemia, but there is still a lack of clear diagnostic criteria and strict evidence-based medicine definition of septic cardiomyopathy[5].
Levosimendan is calcium ion sensitizer, a new type of positive inotropic drugs.Compared with positive inotropic drugs,levosimendan does not increase the concentration of Ca2+in cardiomyocytes, but plays a strong role through the sensitivity of myocardial contractile proteins to Ca2+, so it is called calcium sensitizer[6].Therefore, levosimendan did not increase the influx of Ca2+in cardiomyocytes during excitatory systolic coupling, nor did it affect the diastolic function of myocardium due to the obstruction of outflow of Ca2+in cardiomyocytes due to the increase of intracellular Ca2+[7].Currently, it is widely used in acute heart failure patients with poor therapeutic effect of traditional positive inotropic drugs, and can also be used in the treatment of cardiogenic shock, pulmonary hypertension, perioperative cardiac surgery and other diseases.In the 2021 International Guidelines for the Management of Sepsis and Septic Shock, dobutamine is recommended to be added to norepinephrine and levosimendan is not recommended for patients with septic shock and cardiac insufficiency when volume and arterial pressure are sufficient.This recommendation is presented as weak and of low quality evidence [8].However, compared with dobutamine in the treatment of sepsis and septic shock, the improvement of mortality and cardiac function indicators is still controversial.A comparative study of levosimendan versus dobutamine or a blank control group was conducted to evaluate the clinical effect of levosimendan on 28-day mortality and hemodynamics.To provide reference for clinical treatment from the perspective of evidencebased medicine.
2.Data and methods
2.1 Selection of documents
Inclusion criteria: (1) Subjects were >18 years old and diagnosed as meeting international or Chinese guidelines for the treatment of sepsis or septic shock;(2) no contraindications to levosimendan application; (2) Levosimendan was applied in the intervention group;The control group was other positive inotropic drugs or other blank controls.There is no dose schedule or time limit for infusion; (3)Study type: randomized controlled trial; (4) Report 28-day mortality or 30-day mortality data.
Exclusion criteria: (1) duplication;(2) animal experiments or in vitro studies;(3) Patients with sepsis or septic shock were not clearly diagnosed;(4) Excluding the use of positive inotropic drugs or combined with adult drugs except levosimendan; (5) Conference articles and master and erudite papers.
2.2 Literature retrieval strategy
References were obtained from two researchers who independently searched the following databases: CNKI, Wanfang Data, VIP, China Biomedical Literature Database, Embase, PubMed, Web of Science,and Cochrane library.The search time was updated from the database to October 1, 2022.There are no language restrictions.In addition, references included in the study and related meta-analysis were tracked to supplement the relevant literature.The retrieved literature was imported into Noteexpress literature management software, and duplicates and non-randomized controlled studies were eliminated according to the title and abstract of the literature.Unable to judge the literature, further reading the full text of literature to screen out the literature meeting the inclusion criteria.Consult with the third researcher in case of inclusion disagreements.
Search the above database by the combination of subject words and free words.Chinese search terms include:休克,脓毒性、脓毒症、脓毒血症、脓毒性休克、感染性休克、左西孟旦、随机对照试验、随机对照实验、随机对照研究。English search terms include:Sepsis, Bloodstream Infection,Bloodstream Infections,Infection, Bloodstream, Pyemia, Simendan,Levosimendan, Randaomized controlled trialetc.
2.3 Literature quality evaluation
The included literature was assessed independently by two investigators using the Cochrane risk bias assessment tool.The evaluation included whether random allocation was used, whether the allocation scheme was hidden, whether blind, whether there was selective reporting of research results, and whether there were other sources of migration.
2.4 data extraction
The required data were extracted from the included literature: (1)basic literature information: first author and publication date;(2)Basic information of the subjects (age, gender, diagnosis and the number of experimental group and control group);(3) Intervention measures (drug name, dosage and duration of infusion used in experimental group and control group);(4) Outcome indicators:primary outcome indicators (28-day mortality or 30-day mortality),secondary outcome indicators (left ventricular ejection fraction, left ventricular work index, cardiac index, lactic acid).
2.5 statistical method
Stata MP 14 software was used for statistical analysis and forest map drawing.Relative risk (RR) and 95% confidence interval were used to represent the biclassification data.Continuity variables were represented by weighted mean difference (WMD) and 95%confidence interval (CI) Q test was used to test the heterogeneity of each study.IfI2of Q test is less than 50%, andP>0.1 of Q test,it is considered that all studies are homogeneous, and fixed-effect model is used for analysis.IfI2of Q test is greater than 50% andP<0.1, heterogeneity is considered in all studies, and random effects model is adopted for analysis[9].The Stata MP 14 software was used to determine whether publication bias existed in Egger’s linear regression quantitative detection and evaluation.IfP<0.05 suggested publication bias, shear and supplement method and single study examination were used for sensitivity analysis.IfP>0.05 indicates no significant publication bias, the results are reliable.
3.Result
3.1 Literature search results
A total of 345 articles were obtained according to the search strategy.There were 172 duplicate literatures, 69 reviews and systematic reviews, 12 animal experiments, 7 conference papers and graduation papers, 73 literatures with inconsistent research content and experimental design were excluded, 3 literatures with inclusion criteria were obtained through other channels, and 15 literatures were finally included in the meta-analysis.A total of 1337 patients were enrolled, of which 672 were enrolled in the experimental group(levosimendan group) and 665 were enrolled in the control group(other positive inotropic agents or placebo) (Figure 1).The literature was evaluated according to the Cochrane risk Bias assessment tool(Figure 2).
Both Roald Dahl s poem of the tale and Stephen Sondheim s musical, Into the Woods, have Red Riding Hood overcome the wolf and later appear wearing a fur coat made of the wolf s fur, instead of the identifying red cloak.

Fig 1 Flow chart in literature inclusion
3.2 Results of meta-analysis
3.2.1 28-day mortality analysis
Fifteen articles reported 28-day mortality rates between levosimendan and the control group, and two articles reported 30-day mortality rates.The results showed that the 28-day mortality of sepsis patients in the levosimendan group was not statistically superior to that in the control group (Fixed effect RR=0.91, 95%confidence interval [CI] [0.78-1.06],Z=1.24,P=0.22>0.05) (Figure 3, 4).
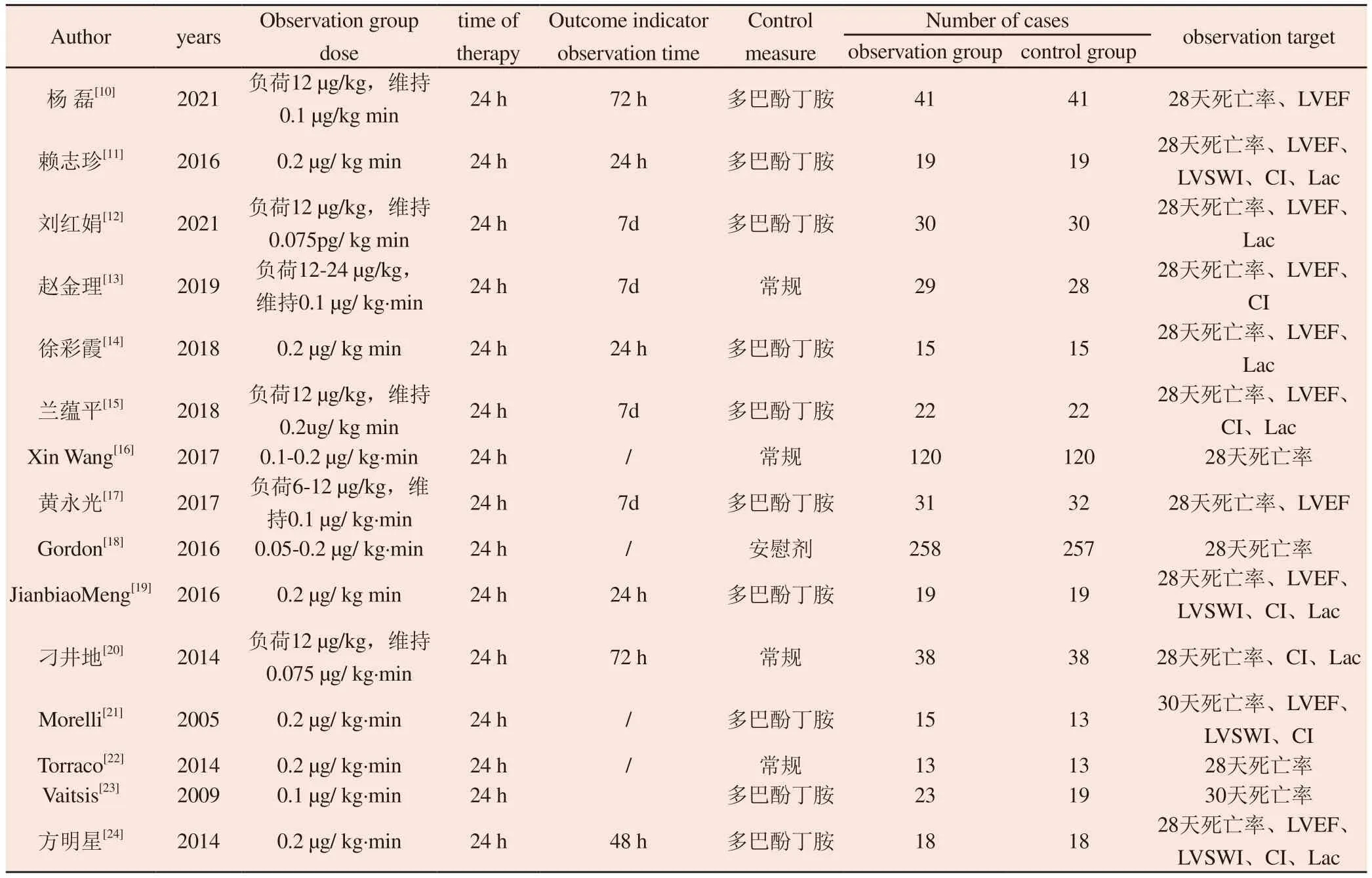
Tab 1 Characteristics of included literature
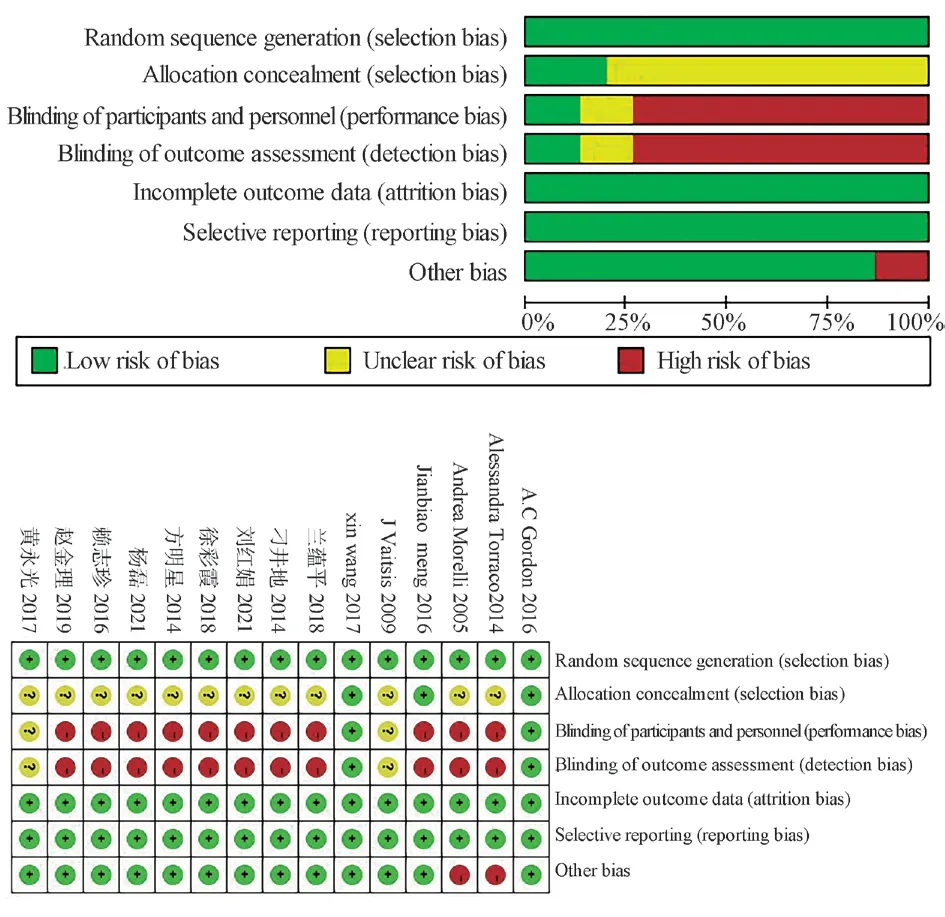
Fig 2 Quality assessment of the included literature
3.2.2 Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) analysis
Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of levosimendan and control group was reported in 10 literatures.The results showed that the left ventricular ejection fraction of patients with sepsis in levosimendan group was statistically different from that in control group, and the intervention effect was significant.(Fixed effect WMD=5.328, 95% confidence interval [CI] [4.19-6.47],Z=9.17,P=0.000<0.05) (Figure 5).
3.2.3 Left ventricular work index (LVSWI) analysis
The left ventricular work index (LVSWI) of levosimendan and control group was reported in 4 literatures.The results showed that LVSWI in the treatment of sepsis patients in levosimendan group was statistically different from that in the control group, and the intervention effect was significant.(Random effects WMD=4.458,95% confidence interval [CI] [2.98-5.93],Z=5.92,P=0.000<0.05)(Figure 6).
3.2.4 Cardiac index (CI) analysis
Cardiac index (CI) of levosimendan and control group was reported in 7 literatures.The results showed that the CI of the levosimendan group in the treatment of sepsis patients was statistically significant compared with the control group.(Random effectsWMD=0.507, 95%confidence interval [CI] [0.33-0.68],Z=5.71,P=0.000<0.05) (Figure 7).
3.2.5 Lactic acid (Lac) analysis
Lactic acid results (Lac) of levosimendan and control group were reported in seven articles.According to the results of meta-analysis,Lac in the treatment of sepsis patients in levosimendan group was statistically different from that in the control group (fixed effectsWMD= 0.969, 95% confidence interval [CI] (1.23 ~ 0.71),Z= 7.27,P= 0.000 < 0.05) (figure 8).
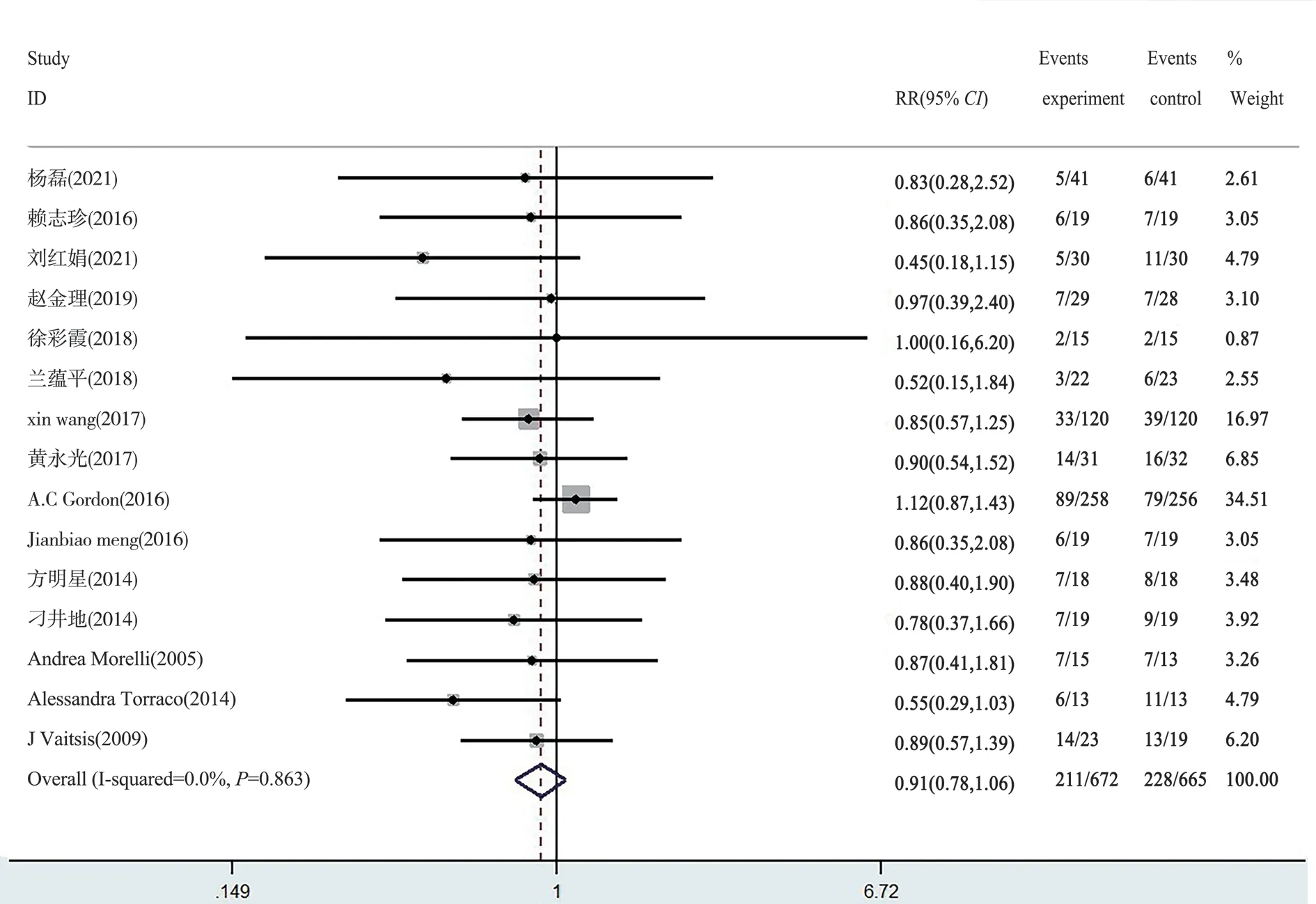
Fig 3 Forest map of 28-day mortality

Fig 4 Funnel plot of 28-day mortality

Fig 5 Forest map of left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF)
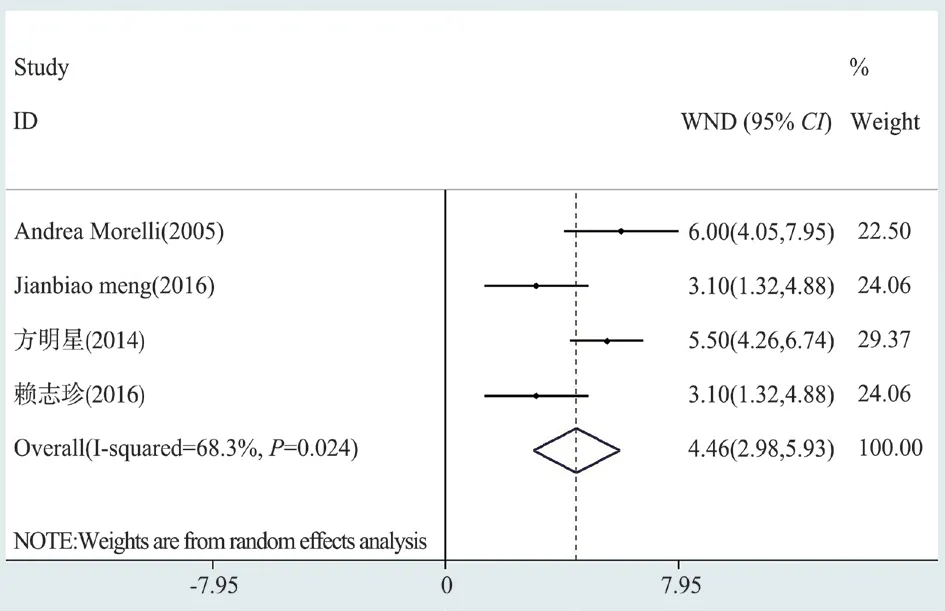
Fig 6 Forest map of left ventricular work index (LVSWI)
3.3 Publication bias evaluation
The publication bias of 15 articles included in the evaluation of the influence of levosimmondal on the 28-day mortality of sepsis patients was roughly symmetrical in the distribution of funnel plot scatter points, and the Egger’s test was used to quantitatively evaluate publication bias, andP=0.015<0.05 was obtained, indicating the existence of publication bias.The shear supplement method was further used to further test the publication bias.No virtual shear supplement literature or data was added to the corrected results by the shear supplement method.At the same time, a single study wasused to assess the impact of each included article on the 28-day mortality outcome, and the results showed that the combined association and inter-study heterogeneity after excluding any article had little effect on the total combined effect size, and the results were reliable and acceptable (Figure 9, 10).
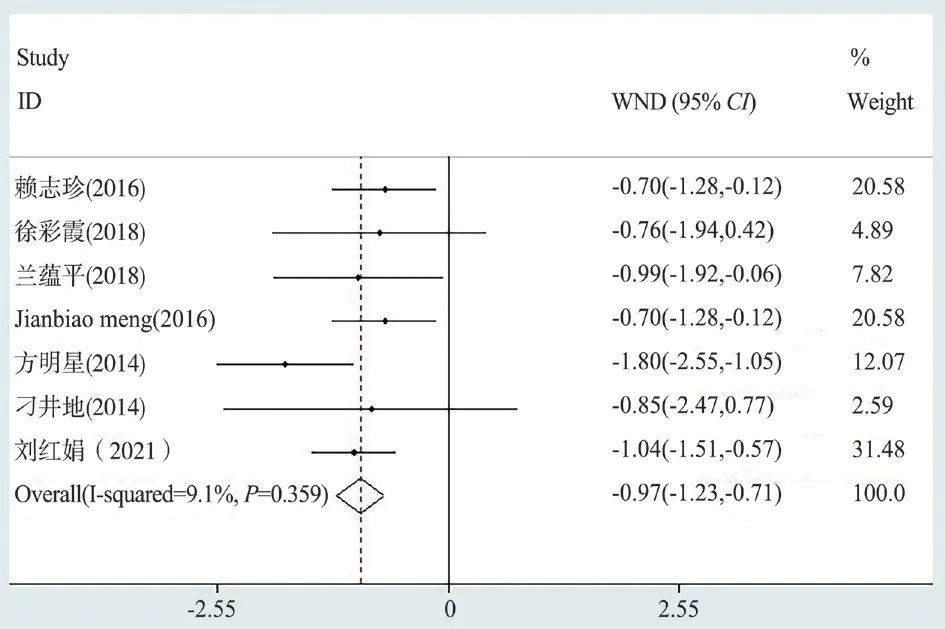
Fig 8 Forest map of lactic acid (Lac)
To evaluate the bias of the results of 10 articles included in the secondary outcome index LVEF, the funnel plot scatter distribution was roughly symmetrical, and the Egger’s test was used to evaluate publication bias quantitatively, andP=0.814 > 0.05 was obtained,indicating a stable result (Figure 11).
To evaluate the bias of the results of 7 articles included in the secondary outcome index CI, the funnel plot scatter distribution was roughly symmetrical, and the Egger’s test was used to evaluate publication bias quantitatively, andP=0.205 > 0.05 was obtained,indicating a stable result (Figure 12).
To evaluate the bias of 7 articles included in Lac, the funnel plot scatter distribution was roughly symmetrical, and the Egger’s test was used to evaluate publication bias quantitatively, andP=0870 >0.05 was obtained, indicating a stable result.

Fig 9 Correction chart of 28-day mortality by shear supplement method
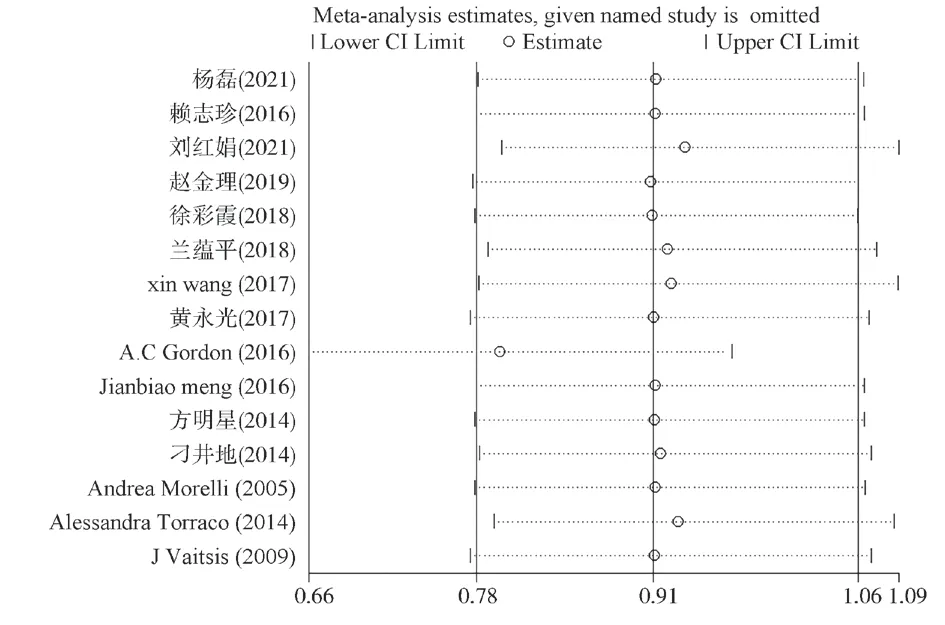
Fig 10 Impact assessment of a single study on 28-day mortality
Fig 11 Egger’s test of LVEF
Fig 12 Egger’s test of CI
Fig 13 Egger’s test of Lac
4.Discussion
4.1 Effect of levosimendan injection on mortality
In this study, 15 literatures with 28-day mortality or 30-day mortality as primary outcome indicators were included (all randomized controlled studies).A meta-analysis was used to conduct a comprehensive quantitative analysis of Levosimendan injection on mortality.There was no significant difference in mortality outcomes at 28 days between the treatment group (levosimendan) and the control group (conventional therapy or other positive inotropic drugs).Levosimendan showed no significant difference in the 28-day mortality of sepsis patients compared with the control group.The conclusion was consistent with the meta-analysis published by Fang Feng[25] et al in 2019 and Guo Qingqing[26] et al in 2021.Levosimendan could not reduce the mortality of sepsis patients,which was consistent with the conclusion of this study.However,In a meta-analysis by Zangrillo[27] et al., levosimendan was associated with significantly reduced mortality in patients with septic shock compared to standard positive inotropic drug therapy.Yang Chunbo[28]et al.found in a meta-analysis study on the clinical efficacy of patients with septic cardiomyopathy that levosimendan could reduce the mortality of patients with septic cardiomyopathy compared with dobutamine.The reasons for the different results may be that the included literature and research objects are different,and the statistical methods used are slightly different.Therefore,more prospective multi-center clinical studies are needed for further research to increase the evidence-based medical basis.
In terms of the influence of levosimendan on hemodynamic indexes, the results showed that the left ventricular ejection fraction(LVEF), left ventricular work index (LVSWI), heart index (CI)and lactic acid (Lac) of sepsis patients had significant statistical differences compared with the control group.In other words,levosimendan can increase left ventricular ejection fraction, decrease left ventricular function index, increase cardiac index, and decrease lactic acid in sepsis patients compared with other positive inotropic drugs or conventional therapy.In 2010, Bergh et al.[29] conducted a randomized double-blind clinical study on patients with acute onset chronic heart failure, comparing levosimendan with dobutamine,and the results showed that the hemodynamic improvement in the levosimendan infusion group was due to dobutamine.In a prospective single-center study on the hemodynamics of levosimendan on end-stage stable heart failure, Emil et al.[30] found that levosimendan was associated with improved hemodynamics in study subjects.The above literature showed positive significance for the hemodynamic outcome of levosimendan in patients with heart failure.In addition, a retrospective study published by Hu Aihao[31] et al.in 2021 on the effects of levosimendan combined with recombinant human brain natriuretic peptide for injection on left heart function and hemodynamics in septic shock patients showed that levosimendan combined with recombinant human brain natriuretic peptide for injection could improve left heart function and hemodynamics in septic shock patients.Levosimendan has been poorly studied in the treatment of sepsis and septic shock, and still shows a positive advantage over other positive inotropic drugs in the published literature, which is consistent with the results of this study.However, more clinical data are needed for further and specific research results.
Limitations of this meta-analysis: the sample size of most of the included articles was small, and the proportion of patients studied in one article accounted for one-third of the total number of Meta articles.This may lead to deviations between the final results and the actual clinical situation and experimental results.For the main outcome indicators, some studies used 28-day mortality, some used 30-day mortality, and different outcome indicators data may also have biases on the results of the study.In addition, the drugs used in the control group were different, including dobutamine, conventional treatment group and epinephrine.The types of drugs used, dosages and drip rates of drugs were different, which would also cause deviations in the results.Among the secondary outcome indicators,there were differences in the time of data collection and recording.The experimental data came from different time after enrollment,such as 24 h, 48 h and 72 h.Meanwhile, the number of studies and experiments that could be included in the secondary outcome indicators was small, which may lead to the deviation in the results.Therefore, more prospective multi-center clinical trials are needed to further improve the efficacy of levosimendan in patients with sepsis and septic shock.
In summary, compared with dobutamine or conventional treatment,levosimendan could not reduce the mortality of sepsis patients,but could increase LVEF and CI, and decrease LVSWI and Lac.However, the sample size of this meta-analysis is insufficient and there is a lack of high-quality literature support.The conclusions obtained need more clinical data support, and should also be used with caution in clinical application.The application of levosimendan in septic cardiomyopathy still needs further exploration in the future.
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Research progress in mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis
- Research progress and prospects of arenavirus
- Application of OCTA in diabetic retinal microangiopathy
- Meta-analysis of influencing factors associating with treatment outcome of multidrug resistant tuberculosis
- Association of novel and legacy PFAS with reproductive hormones in women of child-bearing age
- Regulation of Quan Du Zhong capsule on VEGF/bFGF and expression of Bcl-2/Bax and Caspase-3 protein in the repairing process of canine femoral head necrosis
