Scientists Reveal Mechanism Behind Preferential Recognition of H2A.Z Nucleosome during DNA Replication Initiation
2023-11-15ZHOUZheng
In higher eukaryotes, DNA replication ensures precise transmission of genetic information from parental DNA to progeny, and the correct selection of replication origins is a critical step in this process.A very recent study has shown that nucleosomes containing histone variant H2A.Z recruit SUV420H1, a histone H4 lysine 20 specific methyltransferase.Moreover,SUV420H1 promotes the H4K20 dimethylation, which can recruit the origin recognition complex to fulfill the selection and licensing of the replication origins.
On August 2, 2023, the research group of Prof.ZHOU Zheng from the Institute of Biophysics (IBP)of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with Prof.LI Guohong and Prof.ZHU Ping, also from IBP, and Prof.LONG Haizhen from the Shenzhen Bay Laboratory, reported the high-resolution cryo-electron microscopy structure of the human SUV420H1 bound to H2A.Z nucleosome, revealing the molecular mechanism of SUV420H1’s preferential recognition of H2A.Z nucleosome and catalysis of H4K20me2.This study, for the first time, unravels the mechanism of preferential recognition of H2A.Z in the context of the nucleosome and broadens our understanding of histone variants.
Their results were published inMolecular Cellentitled “Structural Insight into H4K20 Methylation on H2A.Z-Nucleosome by SUV420H1.”
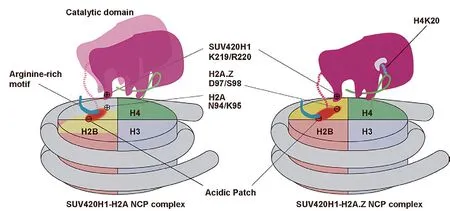
Schematic view of SUV420H1 structures bound to H2A.Z nucleosome (Image by Prof.ZHOU Zheng’s group)

Cover: Huang et al.reveal the intricate mechanism by which the methyltransferase SUV420H1 preferentially recognizes H2A.Z-containing nucleosomes to catalyze H4K20me2 modification.The artwork showcases SUV420H1, portrayed as a whimsical elf, skillfully illuminating the histone marker, represented by a magical wand, amidst the chromatin landscape.(Image by Prof.ZHOU Zheng’s group)
The researchers replaced H4 to lysine 20 residue with a S-ethyl-L-cysteine (Ecx), a modification which stabilizes the SUV420H1-H2A.Z nucleosome interaction and led to determination of the complex structure at a 3.2 Å resolution.The structure revealed SUV420H1’s interactions with the H4 N-terminal tail, the DNA,and the acidic patch of nucleosome.Particularly, the H4 N-terminal tail adopts a lasso-like structure that precisely positions H4K20 into the catalytic center of SUV420H1.
Notably, the researchers identified an SUV420H1 KR-loop in close proximity to the H2A.Z-specific residues D97/S98 (corresponding to H2A residues N94/K95).The KR-loop plays a role in conferring SUV420H1’s preference for the H2A.Z nucleosomein vitro.Its mutations decrease the cellular level of H4K20me2,the DNA replication initiation, and the growth rate of cell.These findings are in full agreement with earlier studies, which indicated that H2A.Z D97/S98 governed SUV420H1’s preference for the H2A.Z nucleosome.
H2A.Z is a key histone variant involved in numerous biological processes.Prof.ZHOU Zheng’s research group is dedicated to investigating the mechanisms underlying H2A.Z recognition and function.This study revealed how SUV420H1 preferentially recognizes the H2A.Z nucleosome to deposit the H4K20me2 marks and provided novel insights into the regulation of DNA replication initiation.
杂志排行
Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Sciences的其它文章
- Could Gut Bacteria Hold a Cure for Sepsis?
- Looking into the Tissue Adjacent to Tumors
- Daya Bay Collaboration Awarded 2023 High Energy and Particle Physics Prize by European Physical Society
- Largest Optical Time-domain Survey Telescope in Northern Hemisphere Goes into Operation
- CAS Paleogeneticist Awarded UNESCO Prize
- “Magnetically Arrested Disk”Revealed by Multiwavelength Observation
