Reflections on Cultivating Critical Thinking in Foreign Language Courses in the Context of Integrating Ideological and Political Theories in All Courses
2023-11-05XuHaiyan
Xu Haiyan
Taizhou Vocational &Technical College
Wang Yaguang*
Shenyang University of Technology
Abstract: The education reform of integrating ideological and political theories in all courses is crucial in fostering virtue through education.In the new era,foreign language courses are increasingly prominent in moral education.Learning a language is not just about mastering its language form but also about critically examining the cultural connotations and thinking patterns embedded within it.Therefore,cultivating students’ critical thinking skills should be a key focus in foreign language education.First,this paper examines the importance of fostering students’ critical thinking in foreign language courses.Second,considering the characteristics of Chinese college foreign language courses,we propose that if we want to cultivate critical thinking among students through foreign language courses,we need to effect pattern transformations across four aspects:teaching philosophy,teaching content,teaching methodology,and teaching evaluation.These transformations also present requirements for foreign language teachers.They should focus on enhancing their comprehensive literacy,including ideological and political literacy,teaching design skills,and the ability to integrate teaching materials with logical thinking.And China’s Standards of English Language Ability (the CSE) serves as an important reference indicator for implementing these transformations.
Keywords: ideological and political theories teaching in foreign language courses,critical thinking,the CSE
For college students,foreign language courses serve as important bridges for them to learn about cultural exchanges between China and the rest of the world.Therefore,it is particularly important to give full play to the educational function of the ideological and political courses in foreign language teaching in the new era.The essence of integrating ideological and political theories in all courses is to foster virtue through education.Critical thinking advocates for analyzing and solving problems through skills and awareness pertaining to logic and rational thinking;it is crucial in shaping students’ outlooks on the world,life,and values and is an essential aspect of fostering individual virtue.The educational function of foreign language courses can be fully realized by prioritizing critical thinking as the fundamental starting point in their ideological and political education.
Extensive research has been conducted in the academic community on fostering critical thinking skills through foreign language courses.However,in the context of integrating ideological and political theories in all courses,there is a pressing need for further research on fostering students’ critical thinking abilities through these courses.Considering this,we chose to explore the concept of integrating ideological and political theories in foreign language courses and examine its crucial role in fostering students’ critical thinking abilities.Additionally,we delved into four key transformations in cultivating critical thinking under new circumstances and emphasized that foreign language teachers should adapt rapidly in order to optimize the effectiveness of ideological and political education within courses.
The Necessity of Fostering Critical Thinking in the Context of All-Staff,Whole-Process,and All-Round Education
Many researchers have reached a consensus that ideological and political theory education in foreign language courses should not be considered an independent subject.The integration of ideological and political education into foreign language courses goes beyond merely allocating time to teach ideological and political content in the class (Xu,2019).In terms of curriculum goals,integrating ideological and political theory education in foreign language courses aims to align the courses with ideological and political education,thus promoting the synergistic effect of value guidance and knowledge transfer and fostering the comprehensive development of socialist successors who possess a strong sense of Chinese identity,familial bonds,and national pride.Compared with other courses,integrating ideological and political elements into foreign language teaching is urgent.To this end,the teaching objectives of foreign language courses should not only meet the requirements for language learning but also aim to develop students’ critical thinking.The attitude of mechanical borrowing should be avoided in foreign language teaching,and it is essential to prioritize critical thinking in foreign language learning.
So,what is critical thinking? Scholars such as Peter Facione defined critical thinking as the process of purposeful and self-regulatory judgment,which encompasses several dimensions,such as interpretation,analysis,and evaluation (Facione,1990,p.2).In short,critical thinking highlights the importance of an individual’s thought process and their ability to analyze and reason based on credible evidence using established criteria.In this new context,the development of critical thinking is intricately linked to the overarching objective of education.On the one hand,we should proactively adapt to the new requirements of the strategy of “introducing Chinese culture abroad”and establish a high-quality training system for foreign language talents.On the other hand,we need to incorporate ideological and political education into foreign language courses to fulfill the fundamental task of fostering virtue through foreign language education.Additionally,we should equip students with critical thinking skills and attitudes that enable them to adopt a dialectical perspective toward the world.This will effectively cultivate a scientific ideology,values,and behavioral norms among students,thereby nurturing their potential as indispensable contributors to social development.
Four Transformations in Fostering Critical Thinking in the Context of Integrating Ideological and Political Theories in All Courses
In the context of integrating ideological and political theories in foreign language courses,the traditional teaching mode falls short of meeting the requirements for ideological and political education and cultivating students’ critical thinking abilities.Therefore,it is necessary to reexamine the current teaching model and take the initiative to transform it based on the actual situation.In this paper,we will present our analysis of the theoretical basis and key contents of the critical thinking cultivation transformation from four aspects: teaching philosophy,teaching content,teaching methodology,and teaching evaluation.
Transformations in Teaching Philosophy: From Disseminating Cultural Knowledge to Foster Critical Thinking Ability
Foreign language teaching serves as a crucial conduit for talent cultivation,and a keen understanding of what kind of talent we should cultivate is an important prerequisite in doing so.In this regard,it is valuable to draw upon both our traditional educational philosophies and contemporary Western approaches.In Chinese history,there is a famous argument that states,“A gentleman is unlike an implement” in the Political Section (Weizheng) of theAnalects of Confucius.In ancient times,the term “gentlemen” referred to individuals who possessed noble conduct and moral character,aligning with the value orientation of cultivating “talent” in today’s universities.The argument emphasizes that one of the most important characteristics of a gentleman is that he is not merely an “implement” to be used.A “gentleman” should possess the ability to think independently,form opinions based on critical analysis,and solve problems autonomously;otherwise,he cannot be deemed a genuine “gentleman.” In the new era,the government advocates cultivating talents who care about their family and country and possess an international perspective.These individuals should also not be confined to being “implements.” They should be equipped with critical thinking rather than unthinkingly following others.
It is imperative to acknowledge that there are huge changes taking place in each industry in this age.With the emergence of new technologies and challenges,some industries are flourishing while others are gradually being marginalized.In addition,the technology and market demands of various industries are constantly evolving.Taking the translation industry as an example,the continuous integration of artificial intelligence,big data,and other technologies in this field has given rise to a plethora of professional translation machines,leading to a profound transformation in the essence of this industry (Cai,2019,pp.48–54+92).Under these circumstances,in the future,students may be engaged in jobs that do not exist today,use technologies that have not yet been invented,and solve problems that have not yet been exposed.The traditional teaching philosophy that emphasizes the transmission of cultural knowledge has evidently failed to meet the social demands for talent.The most crucial skill for students today is the capacity to think independently so that they can fully adapt to career changes.
In this context,the value of foreign language courses lies not only in improving the knowledge structure but also in fostering students’ comprehensive abilities.Critical thinking advocates for students to take the initiative in exploration and develop the ability to identify and solve problems,which is a crucial aspect of enhancing their innovative capacity.On May 28,2021,Xi Jinping,general secretary of the Communist Party of China (CPC) Central Committee,when addressing a meeting conflating the general assemblies of the members of the Chinese Academy of Sciences,the Chinese Academy of Engineering (CAE),and the national congress of the China Association for Science and Technology (CAST),stressed that we should value the cultivation of critical thinking among students and officially incorporate it into our country’s teaching philosophy.From this point of view,we should reform our teaching philosophy regarding future foreign language courses in colleges and universities by gradually shifting from disseminating cultural knowledge to fostering critical thinking abilities among students.We should also encourage students to discover and solve problems on their own,thus realizing the core objective of foreign language courses for fostering students’ moral character and overall development.
Transformation in Teaching Content: From Language Content Teaching to Guidance on Thinking Patterns
Teaching content serves as a crucial conduit for fostering students’ critical thinking abilities.Teaching content that is in-depth,comparable,and thought-provoking plays an essential role in fostering students’ critical thinking abilities.Unfortunately,for a long period of time,the focus of foreign language textbook compilation has been on imparting language knowledge.Under this framework,the selection of textbook materials primarily emphasizes the use of original texts,focusing on humanistic topics built upon the basic requirements for language learning.Currently,despite the conscious efforts made by many textbook editors to avoid merely selecting original materials and to incorporate language materials with characteristic Chinese elements into textbooks,they still face challenges in timely responding to the limitations in foreign language teaching due to publishing constraints and other factors.In the context of integrating ideological and political theories in foreign language courses,the selection of teaching content should follow the CSE’s development concept and focus on creating an English teaching environment that promotes students’ critical thinking abilities while meeting their demands.
Teaching materials and language resources are not only the embodiment of language but also the container of ideas.When selecting textual materials,teachers should not only consider the fundamental requirements of scientificity,normalization,and standardization but also prioritize the ideological nature of the text itself.It is crucial to choose texts that contain speculative elements which can facilitate students’ critical thinking.A workman must first sharpen his tools if he is to do his work well.The CSE provides a comprehensive framework to assess the language proficiency of learners at different levels in terms of both comprehension and expression abilities.With its broad applicability,it serves as an invaluable standard reference for selecting appropriate text materials.The differences in ability among learners at different language levels in the CSE are primarily reflected through the understanding and expression of specific behavioral elements within a given context.Corresponding standards for comprehension and expression are provided to guide learners for further improvement (Liu,2019,p.20).The accuracy with which these behavioral elements are described at each level reflects learners’ language comprehension ability and cognitive behavior.The language ability descriptors at levels 1 to 9 incorporate the behavioral elements based on Benjamin S.Bloom’sTaxonomy of Educational Objectives in the Cognitive Domain,which encompasses the cognitive processes involved in language comprehension and necessitates a range of critical thinking abilities such as interpretation,analysis,evaluation,inference,and explanation.Teachers can use the descriptive framework provided by the scale to evaluate texts and determine if they contain critical elements based on students’ language levels and corresponding ability descriptors.Then,they can move on to the first step in text screening.Next,the teaching content should be designed to effectively increase the emphasis on scientific knowledge.With the rapid advancement of science and technology,a well-designed science education program plays a crucial role in enhancing our comprehension of future social development.This idea could be considered as a reference for incorporating ideological and political education into foreign language courses,providing students with a platform to explore multi-dimensional knowledge resources.It is also a more rational approach to fostering critical thinking.
Transformation in Teaching Methodology: From Traditional Approaches to Inquiry-Based Teaching
According to Li Zhiyi,there are five levels of classroom teaching in universities: silence,answering questions,dialogue,critical thinking,and debate (Li,2018,pp.24–29).In foreign language teaching,guiding students to reflect on what they have learned and to pose insightful questions is one of the criteria to measure whether students possess rational critical thinking abilities,as well as an exemplary manifestation of the implementation of ideological and political theory education in foreign language courses.To achieve this,the inquiry-based teaching model is undoubtedly a perfect approach.The inquiry-based teaching model originated from the inquiry theory of American educators such as Richard Suchman and John Dewey,which emphasizes a thorough exploration of problems during the teaching process.This teaching method involves collaborative exploratory activities between teachers and students (See Figure 1).
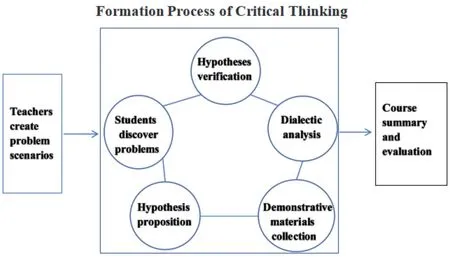
Figure 1 Relationship Between Inquiry-Based Teaching and the Cultivation of Critical Thinking.
In specific practices,teachers need to meticulously deliberate the formulation of problem scenarios to ensure that the complexity of the problems is moderate and coherent.In terms of answer settings,it is ideal to provide some open-ended answers that may spark controversy.In the implementation of the course,teachers should actively guide students on how to make an inquiry and provide them with a favorable learning environment or resources that can effectively foster their critical thinking skills.Students should be provided with sufficient time and space for exploration,as well as the opportunity to independently experience and analyze problems.After gathering enough information,students can organize and summarize the information process or existing demonstrative data to develop their own perspectives or arguments.In addition,students are expected to substantiate their personal arguments with ample evidence and demonstrate inclusivity in their presentations.After the representative students have shared their perspectives,teachers can facilitate a comprehensive discussion within and between the groups regarding the content of the presentation.Teachers should actively encourage students to ask questions and inspire them by raising some heuristic questions if necessary.The essence of this process is to stimulate the enthusiasm of students and give them timely encouragement.After the discussion has ended,teachers should guide students in reaching a conclusion and summarizing the overall process of verifying their own hypotheses,thus completing the full circle of critical thinking training.
It should be noted that the use of heuristic questions in the classroom is an important component that impacts the quality of classroom teaching.It is also a key element in determining whether classroom teaching can effectively cultivate an environment conducive to questioning and debating,which aligns with the principles of the “five-emphases” teaching method that encompasses emphases on interest,perception,accumulation,migration,and habits.While conventional critical questions like “Are you satisfied with his answers? Do you think that is the truth?” can incorporate critical thinking attitudes and skills,they may not align with the cognitive abilities of learners at different levels.The language ability scale based on usage focuses on describing the typical language behaviors of learners and users with different levels of proficiency,providing a comprehensive understanding of their abilities (Liu &Han,2017,p.78).In classroom teaching,we can use the CSE descriptors as a helpful guide for asking critical questions to ensure that the questions raised focus on language use and critical thinking.Taking the reading comprehension subscale as an example,it categorizes learners’ comprehension ability into three levels based on different descriptors: recognizing and extracting written information,summarizing and analyzing written information,and criticizing and evaluating written information (Liu,2019,p.107).Creating questions according to the three-level descriptors of the scale can effectively prevent passive teaching and facilitate the organized implementation of teaching activities with an emphasis on question-and-answer sessions,dialogue,questioning,and debate.The descriptors of the scale are based on Bloom’s revised model,and the heuristic questions,formulated in accordance with these descriptors,are employed to investigate students’ memory and understanding of what they have learned through question-answering and dialogue-based teaching methods.
Additionally,it also focuses on exploring students’ higher-order cognitive abilities by employing questioning techniques and debate-oriented teaching approaches.The heuristic questions formed according to the scale descriptors create a learning environment that facilitates cognitive deepening,guiding learners from low-order thinking to high-order thinking.It is also the natural outcome of exploring new learning modes in the modern era.
Transformation in Teaching Evaluation: From a Single-Dimension Evaluation System to a Diversified One
Evaluation is a crucial aspect of teaching that aids in determining whether the learning objectives have been achieved.TheCollege English Curriculum Requirements(2020 edition)highlights the significance of integrating evaluation throughout the curriculum system and encourages active participation from students,teachers,and relevant education administrators in the process.Moreover,it is essential to comprehensively utilize various means and methods to foster the healthy development of the curriculum.Due to the particularity of ideological and political theory education in foreign language courses,the evaluation criteria and forms of critical thinking in this context not only emphasize the development of students’ language proficiency and critical thinking skills but also necessitate a multi-dimensional perspective to assess the effectiveness of the curriculum on students’ core values and other aspects of ideological and political education.
The evaluation approaches need to be diversified in order to scientifically examine students’various abilities and effectively guide their overall development.Currently,the evaluation methods utilized for evaluating learners’ academic performance are no longer confined to a uni-dimensional model of summative evaluation,and diverse forms of assessment have garnered significant attention.
First,we should pay attention to the combination of summative evaluation and formative evaluation.In this context,it is necessary to adopt a combined evaluation model that includes both summative evaluation and formative evaluation.The summative evaluation typically employs large-scale standardized tests,which can effectively assess learners’ language proficiency,critical thinking abilities,and ideological and political awareness based on the CSE descriptors.In contrast,formative evaluation performs better in capturing students’ learning trajectories and plays a pivotal role in fostering their language acquisition and critical thinking development.Regular formative evaluation can be conducted through various means,including course presentations,class discussions,and oral reports.Nevertheless,establishing a sustainable and consistent learning trajectory through this approach is challenging.On the other hand,tracking students' learning process through the use of recording portfolios is undoubtedly an effective method for enhancing their critical thinking skills and language development.Additionally,this approach offers an ideal platform for observing the long-term impact of foreign language teaching.
Second,we should promote the integration of self-evaluation and peer evaluation.The incorporation of ideological and political theory education into foreign language courses necessitates the adoption of a combined evaluation method that includes both self-evaluation and peer evaluation in order to effectively assess learners’ language learning processes.The purpose of both self-evaluation and peer evaluation is to assist language learners in gaining a more accurate understanding of their own language proficiency levels.The use of both approaches can enhance learners’ understanding of their progress in language learning.The CSE offers self-evaluation tools for various language skills,including listening comprehension,reading comprehension,oral expression,written expression,interpretation,and translation.These tools provide learners and peers with detailed indicators and reference standards to assess their learning levels more effectively.
Next,the evaluation also requires a specific standard for reference.The CSE scale (2018)adopts the descriptor “can do” to assess learners’ language proficiency levels (Liu,2019).It places a particular emphasis on developing learners’ critical thinking (Liu &Han,2018) and includes descriptors related to ideological and political awareness (Liu,2020,pp.38–42).In the context of integrating ideological and political theories in foreign language courses,cultivating critical thinking should be based on observing students’ performance in both language learning and ideological and political awareness.Therefore,the CSE descriptors can be used as a reference standard for guiding academic assessments of foreign language courses and evaluating learners’critical thinking abilities.Of course,while the CSE descriptors do include ideological and political theories,different teachers may interpret these theories differently in various modules and units of the foreign language courses.Therefore,when using the scale in teaching practice,users can optimize and improve the descriptors based on their own teaching content while following the three capability indicators of accuracy,fluency,and complexity in foreign language learning.
Requirements Facing Foreign Language Teachers in Fostering Students’Critical Thinking Abilities
The core objective of integrating ideological and political theories in all courses is to foster virtue.The key lies in fostering students’ critical thinking abilities,with teachers serving as the guiding force in all teaching activities.In this context,with the emergence of transformations in teaching philosophy,teaching content,teaching methodology,and teaching evaluation during the development of critical thinking in foreign language courses,teachers engaged in foreign language teaching are faced with new requirements.
Requirements for Teachers’ Ideological and Virtuous Awareness
At the current stage,teachers engaged in foreign language teaching should set a good example to further enhance the educational function of the ideological and political theories in foreign language courses.They should proactively enhance their study of Marxist theory and continuously elevate their personal ideological and virtuous literacy while concurrently enhancing their expertise.At the ideological level,it is imperative for them to stay up to date on the latest social trends,meticulously examine the essence of various ideological and political information,and accurately master the profound implications of national educational policies.In the teaching process,teachers should actively integrate the rich cultural heritage and mainstream values of the Chinese nation.They should also proactively explore the ideological and political education elements within the curriculum while demonstrating and leading a critical appreciation of both Chinese and Western cultures.This will ultimately create a harmonious balance between value guidance and knowledge transmission.
Requirements for Teachers’ Teaching Design Skills
To foster students’ critical thinking,foreign language teachers should enhance their ideological and political awareness and literacy while also implementing practical modifications in teaching methodologies.This includes actively aligning with the CSE scale,adopting an inquiry-based teaching model,and establishing a comprehensive teaching design system to cultivate students’critical thinking abilities.First,it is necessary to determine the teaching objectives by referring to the capability descriptors in the CSE.TheCollege English Curriculum Requirements(2021 edition) categorizes the teaching requirements into three levels: basic requirements,intermediate requirements,and advanced requirements based on the CSE.Teachers can design unit objectives according to students’ actual learning situation using the “can do” descriptors at corresponding levels in order to demonstrate the required language knowledge and skills,intercultural communication ability,and critical thinking ability.Second,an inquiry-based teaching model should be implemented for problem design.Teachers can use the eight one-way skill descriptors of the CSE,such as listening comprehension,reading comprehension,oral expression,written expression,organization ability,and pragmatic ability,to identify key areas for teaching and create appropriate problem scenarios based on students’ actual language proficiency levels.The CSE descriptors that incorporate hierarchical cognitive thinking patterns can effectively enhance teachers’ capacity in designing foreign language courses.
Requirements for Teachers’ Ability to Integrate Teaching Materials
To effectively teach a foreign language,teachers must possess the ability to thoroughly comprehend the textbooks and the ability to interpret the profound connotations beyond them and be good at integrating various teaching materials and carrying out secondary development of the textbooks.According to Wang Duqin et al.,the process of secondary development of teaching materials involves modifying,deleting,or adding content to the given materials in order to meet specific teaching needs (Wang et al.,2016,p.2).Considering that most foreign language teachers in colleges and universities typically hold degrees in English,which belongs to the humanities and social sciences field,many of them lack systematic training in interdisciplinary fields.Consequently,their ability to teach content that goes beyond their own knowledge structure is inevitably limited.In the new era,it is crucial for teachers to provide students with essential scientific content and background knowledge of Chinese culture,as this will greatly enhance their critical thinking abilities and help them cultivate scientific values.As educators,they should adapt to the educational requirements in the modern era and expand their knowledge base in interdisciplinary fields.Additionally,efforts should be made to integrate and organize various resources and explore ideological and political elements embodied in the teaching materials based on the dual subject relationships between teachers and students.To be specific,it is necessary to explore the thinking patterns and logical basis underlying the texts by explicating both the language usage and text structure.This not only poses a challenge to traditional language teaching methods but also presents a new demand for teachers in the modern era.
Requirements for Teachers’ Logical Thinking Literacy
When it comes to fostering students’ critical thinking abilities,logic is an essential component that cannot be overlooked.Logic represents the law of thinking and is a crucial element in constructing arguments and making sound reasoning.Chinese scholars of logic widely recognize that critical thinking and logic are mutually supportive and interdependent.For instance,in 2005,Wu Zhihong published a book entitledCritical Thinking—Using Logical Argument as a Tool,which serves as a valuable resource for teaching critical thinking in our country.Xiong Minghui also pointed out that formal logic and informal logic are the underlying foundations of critical thinking (Xiong,2016).In the context of integrating ideological and political theories in foreign language courses,it is important for teachers to continuously improve their logical abilities so that they can provide more accurate assessments of students’ language output in various forms,such as speech,debate,and writing.Additionally,teachers should also offer timely and effective feedback and guidance to better assist students in developing critical thinking abilities characterized by rigorous logic and careful reasoning.
Conclusion
The cultivation of students’ critical thinking abilities is more pressing in the context of integrating ideological and political theory in foreign language courses.To better achieve the educational goals of foreign language courses,it is necessary to implement four transformations in college foreign language teaching.In terms of teaching philosophy,it is necessary to promote a shift from simply disseminating cultural knowledge to cultivating critical thinking abilities.In terms of teaching content,priority should be given to guiding students’ thinking patterns rather than focusing solely on superficial language instruction.In terms of teaching methodology,traditional approaches should give way to the inquiry-based model.In terms of teaching evaluation,a multi-dimensional evaluation system should be created to replace the current uni-dimensional approach.In this process,teachers not only need to fully grasp the implications of integrating ideological and political theory in foreign language courses but also constantly improve their comprehensive quality and knowledge structure to meet students’ needs.It is worth noting that the current research on fostering students’ critical thinking abilities within the context of the extensive foreign language curriculum is still insufficient.However,it is generally acknowledged that prioritizing critical thinking and nurturing students’ moral character are the basic requirements of integrating ideological and political theory in foreign language courses.Through this paper,we presented some reflections on how to cultivate students’ critical thinking abilities.Only by taking the initiative in making timely and effective transformations in the new era and making concrete efforts to improve the overall quality of foreign language courses can foreign language teachers achieve the goal of the courses and contribute to further curriculum reform in this subject.
杂志排行
Contemporary Social Sciences的其它文章
- Research on the Formation Mechanism for the Co-agglomeration of Producer Services and Manufacturing in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area
- Evaluation of Green Development Efficiency in Chongqing Municipality Based on Super-SBM and Malmquist Models
- A Literature Review on “Non-Marriage”: A Global Comparative Perspective
- Value Orientation and Dimension Expansion of City Image Communication: A Case Study of Chengdu
- The Institutional Framework of Common Prosperity in the Process of Chinese Modernization
- An Exploration of Key Features of Major-Country Diplomacy with Chinese Characteristics
