Protective Effect and Mechanism of n-butanol Extract from Diploclisia glaucescens (B1.) Diels on Rats with Adjuvant Arthritis
2023-10-31ChuhuiZHOUZhouyanHUANGFengxianZHAOYongCHENXianxianLIUXiaolianLIANGWenliLI
Chuhui ZHOU, Zhouyan HUANG, Fengxian ZHAO, Yong CHEN, Xianxian LIU, Xiaolian LIANG, Wenli LI
Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530200, China
Abstract [Objectives] To study the protective effect and mechanism of n-butanol extract of Diploclisia glaucescens (B1.) Diels on rats with adjuvant arthritis. [Methods] A rat adjuvant arthritis (AA) model with similarities to a clinical RA (rheumatoid arthritis) patient was used, and the model was made by injection of Complete Freund’s adjuvant (CFA). Body mass and joint swelling degree were used as indicators, and the organ index was calculated and the synovial tissue of rats was examined under microscope to evaluate the protective effect of n-butanol extract on arthritis. The effects of n-butanol extract on TNF-α, IL-1β and PGE2 contents in rat serum were detected by ELISA kit. [Results] Arthritic rats experienced significant weight loss; the n-butanol extract reduced the joint swelling in rats. It exerted an effect on rat organs and reduced the contents of TNF-α, IL-1β and PGE2 in rat serum, and also reduced synovial inflammation in rats. [Conclusions] The n-butanol extract of D. glaucescens can protect rats with adjuvant arthritis by reducing the content of inflammatory factors.
Key words Diploclisia glaucescens (B1.) Diels, n-butanol extract, Rats with adjuvant arthritis
1 Introduction
Diploclisiaglaucescens(B1.) Diels belongs to Diploclisia in family Menispermaceae. It mainly grows in the south and southwest of China. It is cold in nature and bitter in taste. It belongs to the liver, spleen, kidney meridian; It is commonly used in the treatment of rheumatic bone pain, urinary tract infection, snakebite and other diseases[1-2]. At present, the report ofD.glaucescensonly stays in the study of chemical composition[3-4], and the activity of pharmacology is rarely reported. Studies have shown that plants in this family contain alkaloids and have good anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects[5-7]. Previously, our team used three anti-inflammatory models to evaluate the anti-inflammatory effects of different extracts ofD.glaucescens. Through experimental screening,D.glaucescensn-butanol extract was selected as a site with good anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect, and it was speculated thatD.glaucescensn-butanol extract contained potential anti-inflammatory active components. Therefore, we used the rat AA (adjuvant arthritis) model with similarity to clinical RA (rheumatoid arthritis) patients to investigate the efficacy ofD.glaucescensextracts in the treatment of arthritis, and further elucidate the efficacy and clinical application ofD.glaucescensin the treatment of arthritis.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Materials
2.1.1Drugs and reagents.D.glaucescenswas collected in Laibin City of Guangxi and identified by associate professor Guo Min from Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine as dried canes ofDiploclisiaglaucescens(B1.) Diels. Tripterygium Glycosides Tablets (Grand Pharmaceutical Huangshi Feiyun Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., batch No.:20200401); Complete Freund’s adjuvant (CFA, Sigma, Batch No.:SLBK1731V); formalin fixative (Guangzhou WEXIS Biotechnology Co., Ltd., batch No.:19050503); ETDA decalcification solution (Beijing Solarbio Technology Co., Ltd., batch No.:20201119); TNF-α kit (Beijing Chenglin Biotechnology Co., Ltd., No.:202011); IL-1β kit (Beijing Chenglin Biotechnology Co., Ltd., batch No. 202011), PGE2kit (Beijing Chenglin Biotechnology Co., Ltd., batch No.:202011).
2.1.2Experimental animals. Kunming SD rats of clean grade, weighing 180-220 g, were purchased from Hunan SJA Laboratory Animal Co., Ltd., with the animal production license number of SCXK (Xiang) 2019-0004. Animal feeding environment: clean animal room, room temperature of (25±1) ℃, humidity of about 65%, artificial photoperiod of 12 h of light and 12 h of darkness. The rats were fed with standard rodent feed, drinking water was ultrapure water, and the rats were fed freely, adaptive feeding for 7 d before the experiment.
2.1.3Experimental instruments. Thermo scientific microplate reader (Shanghai Kehua Laboratory System Co., Ltd.); 0-150 mm digital vernier caliper (Shanghai Nine Quantity Hardware Tools Co., Ltd.); BX53F microscope (Olympus Corporation); Constant temperature water bath (HWS26, Shanghai Baidian Instrument Equipment Co., Ltd.); electronic analytical balance (EL204, Mettler-Toledo Instruments (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.); pipette (Eppendorf Research plus, Eppendorf, Germany).
2.2 Methods
2.2.1Preparation of test product. Took the dried old stem ofD.glaucescens, crushed it, took a proper amount of coarse powder, put it into a round bottom flask, added 95% ethanol to soak it for 12 h according to the liquid-to-solid ratio of 1:10, heated and refluxed it for 3 times, 2 h each time, filtered it with 8 layers of gauze, and combined the filtrates. The filtrate was concentrated to a thick paste with a rotary evaporator, and the thick paste was dried with a freezer to obtain alcohol extracts. The alcohol extract was heated with pure water to dissolve the concentrated drug into a suspension, first with petroleum ether (60-90 ℃) to extract colorless, then with ethyl acetate to be colorless, and finally saturated with water n-butanol solvent to extract to colorless. The extract was concentrated into a thick paste by rotary evaporator, and the thick paste was dried in a freezer to obtain n-butanol extract (the paste yield was 3.57%). Using different extracts and dosages to refer to acute toxicity and pre-experimental results, the extracts of different extracts were dissolved with 0.5% sodium carboxymethylcellulose, and the positive drug triptolide polyglycoside tablets[8](9 mg/kg) n-butanol extract was separately formulated with high (0.11 crude drug g/kg), medium (0.22 crude drug g/kg), and low (0.44 crude drug g/kg) mass concentration liquid.
2.2.2Animal modeling, grouping and administration. Referring to the classical modeling method[9-10], 70 male SD rats were selected as above. After 7 d of adaptive feeding, 1 mg/mL Complete Freund’s adjuvant (CFA) 0.2 mL was injected into the right hind foot of each rat to induce inflammation. Seven days after modeling, the rats were divided into 5 groups according to the degree of joint swelling, namely the model group, the positive group and the high, medium and low dose groups of Tripterygium glycosides tablets n-butanol extract, with 10 animals in each group, and another 10 male rats without modeling treatment were taken as the blank control group, and the blank control group was injected with normal saline. On the day of grouping, the rats in each group were given the corresponding drugs by intragastric administration, while the rats in the control group and the model group were given 0.5% sodium carboxymethylcellulose by intragastric administration at a volume of 10 mL/kg once a day for 30 consecutive d.
2.2.3Indicator detection. Measurement of body mass: The body mass of rats in each group was measured on day 0, 7, 14, 28 and 42 after modeling, and the changes of whole body and body mass of rats were observed. Joint swelling measurement: The ankle diameter of each group of rats was detected with vernier calipers on the 0thd before modeling and the 1st, 7th, 14th, 21stand 30thd before administration, and the joint swelling degree was calculated.
Joint swelling=Joint diameter after administration-Joint diameter before modeling.
2.2.4Collection and handling of samples. On the 31stday after administration, the rats were anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of 10% chloral hydrate, and blood was collected from the abdominal aorta. Before blood collection, the rats were fasted for 12 h without water. The blood was naturally coagulated at room temperature for 30 min. The blood was centrifuged at 2 500 rpm for 20 min, and then the upper serum was taken. The levels of TNF-α, IL-1β and PGE2in serum were detected. After the animals were sacrificed, the liver, kidney, spleen and thymus of the rats were stripped, washed with normal saline and weighed, and the organ index was calculated (Organ index = Organ wet mass/Body mass). The ankle joints of rats were cleaned with normal saline and fixed in 10% formalin fixative for 7 d, and then moved into 10% EDTA decalcification solution for decalcification treatment for 30 d, and the decalicification solution was changed at an interval of 4 d. When the bone was easily penetrated by acupuncture without resistance, the decalicification was stopped, and he staining was carried out for microscopic examination. The histopathological changes of synovium were observed under microscope.
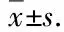
3 Results and analysis
3.1 Observation of general symptoms in ratsBefore modeling, the rats were in good condition, with normal activities, drinking and eating, shiny fur and light yellow urine. After modeling, except for the normal group, the activity of rats in the other groups decreased significantly, the amount of drinking and eating decreased significantly, the color of fur lacked luster, and there was diarrhea, which was the most serious in the model group, and there was no significant difference in urine color between the rats in each group and the normal group.
3.2 Effect on body mass of ratsBefore modeling, there was no significant difference in the body weight of each group. After modeling, the body mass of rats in the positive group and the model group was significantly lower than that in the normal group. From the 28thday, the body mass of rats in the model group decreased with the severity of inflammation. The body mass of rats in the model group was significantly lower than that in the normal group due to inflammation, and there was no significant difference in body weight among other groups (Table 1).
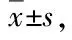
Table 1 Effect on body mass of rats with arthritis ( n=10, g)
3.3 Effect on the degree of joint swelling in ratsThe swelling of the right hindfoot reached the peak on the 2ndto 3rdday after the injection of Complete Freund’s adjuvant (CFA), which was the early inflammatory reaction (primary reaction period), and the symptoms gradually relieved after two days, which was the acute inflammatory remission period (7-10 d). On 11th-18thday, the joints swelled again, the rats with symptoms of inflammation were restricted, food intake decreased, tiredness, and symptoms of inflammation gradually decreased or subsided after the 26thday. Compared with the control group, the degree of joint swelling in the model group was significantly increased (P<0.01), and the degree of joint swelling was maintained at a high level one week after modeling (the first day of administration). Compared with the model group, the joint swelling of rats in the high and medium concentrations of n-butanol extract ofD.glaucescenson the 7thday of administration tended to decrease (P<0.05,P<0.01), which was significant in statistical analysis. The n-butanol extract ofD.glaucescenshas a therapeutic effect on adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats (Table 2).
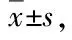
Table 2 Effect on joint swelling of rats with arthritis ( n=10, mm)
3.4 Effects on rat organsCompared with the blank control group, the liver index of the high, medium and low concentration ofD.glaucescensn-butanol extract groups and the model group increased, and the kidney index and thymus index of the medium and low concentration ofD.glaucescensn-butanol extract groups increased (P<0.05,P<0.01). When the n-butanol extract groups were compared with the model group, there was a difference in liver index in theD.Glaucescensn-butanol extract high concentration group (P<0.05), and there was a difference in spleen index and thymus index in theD.Glaucescensn-butanol extract low concentration group (P<0.05), and the data were shown in Table 3.
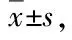
Table 3 Effects of arthritis on rat organs ( n=10)
3.5 Effect on the content of TNF-α, IL-1β and PGE2in serum of ratsCompared with the blank control group, the serum levels of IL-1β, TNF-α and PGE2in the model group were significantly increased (P<0.01), while the serum level of IL-10 was significantly decreased (P<0.01); compared with the model control group, the levels of IL-1β, TNF-α and PGE2in the serum of rats in the high dose group of n-butanol fraction ofD.Glaucescenswere significantly decreased (P<0.01). The serum levels of IL-1β, PGE2and TNF-α were significantly decreased (P<0.01) in the medium dose group of n-butanol fraction ofD.Glaucescens; the levels of IL-1β and PGE2in the serum of rats in the low dose group of n-butanol fraction ofD.glaucescenswere significantly decreased (P<0.01), and the data were shown in Table 4.
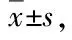
Table 4 Effect of arthritis on the contents of TNF-α, IL-1β and PGE2 in serum of rats ( n=10, ng/L)
3.6 Effects on comparative pathological changes of ankle joint in ratsIn the normal control group, the synovial tissue structure of the rat ankle joint was clear, the synovial cells were arranged neatly, and there was no inflammatory cell infiltration, synovial cell proliferation, capillary congestion and edema. Synovial inflammation was obvious in the model group, with obvious synovial tissue edema, synovial cell disorder with cell proliferation, capillary proliferation, and a large number of inflammatory cell infiltration. Compared with the model group, the inflammatory reaction of synovium in each dose group ofD.Glaucescensn-butanol and Tripterygium glycosides tablets was alleviated to different degrees, and the pathological changes in the middle and high dose groups were similar to those in the Tripterygium glycosides tablets group, with synovium cells arranged neatly and a small amount of inflammatory cells infiltrated (Fig.1).
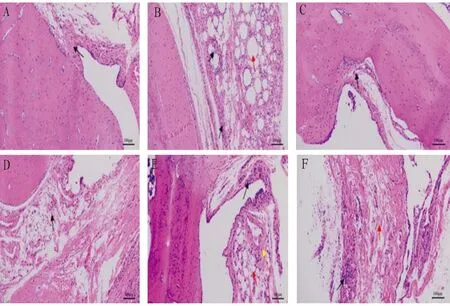
Note: A. Normal control group, B. Model group, C. Tripterygium glycosides tablet group, D. High dose group, E. Medium dose group, F. Low dose group.
4 Conclusions
Arthritis is an autoimmune disease. It has a high incidence in China at present. The cause and mechanism of arthritis have not been clarified. The pathogenesis may be related to autoimmune system disorders, family heredity, living environment and other factors[11]. It is characterized by the damage of joint structure, deformity and possible loss of its physiological function. In addition, it can lead to synovial hyperplasia and fibrosis, nebula, cartilage destruction and other pathological processes[12]. Previous experiments prove thatD.glaucescenshas anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects, and the anti-inflammatory and analgesic components are mainly distributed in the n-butanol extract. The anti-inflammatory mechanism ofD.glaucescensmay be related to the inhibition of the production of inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-1β and PGE2in the body, thus reducing inflammation. In this study, the pharmacological mechanism ofD.glaucescensin the treatment of arthritis was studied for the first time. The n-butanol extract ofD.glaucescenswas evaluated in the treatment of arthritis, and the anti-inflammatory mechanism of medicinal materials was clarified from the content of inflammatory factors and the pathological changes of ankle joint. This makes up for the blank ofD.glaucescensin the actual clinical application but no modern pharmacological research, provides experimental basis for clinical medication, provides a theoretical basis for the in-depth study of the material basis of anti-inflammatory efficacy ofD.glaucescensmedicinal materials, and provides a broader idea and reference for the development of safe, stable and effective anti-inflammatory products.
杂志排行
Medicinal Plant的其它文章
- Quality Control of Zhuang Medicine Xiaoyan Zhiyang Lotion
- Research Progress and Ideas on the Anti-liver Fibrosis Effect of Ethnic Medicine Plumbagin Based on microRNAs/TLR4/NF-κB and NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation
- Gastroprotective Effect of Alpinia zerumbet (Pers.) Burttet Smith on Ethanol-induced Gastric Ulcers in vivo and vitro
- Exploring the Mechanism of Blumea balsamifera (L.) DC in Preventing and Treating Alzheimer’s Disease Based on HPLC-ESI-HRMS and Network Pharmacology
- Observation on Therapeutic Effect of Erxian Decoction on Relieving Low Back Pain after PVP of PMOP-derived Vertebral Fracture
- Effects of Early-stage Phased Rehabilitation Training on Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
