Cost-effectiveness Analysis of lnsulin Degludec and Liraglutide lnjection in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes
2023-09-26SunQuanZhangFangDongLi
Sun Quan,Zhang Fang,Dong Li
(1. School of Business Administration, Shenyang Pharmaceutical University, Shenyang 110016, China;2. ZTE Foundation, Shenzhen 518055, China)
Abstract Objective To analyze the cost-effectiveness of insulin degludec and liraglutide injection (IDegLira) compared with insulin glargine plus insulin aspart (IGar plus IAsp) in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM)based on the price of IDegLira before and after it was successfully admitted to the National Reimbursable Drug List (NRDL).Methods Cost and effectiveness parameters were obtained through systematic retrieval from PubMed,ScienceDirect,CNKI,and Wanfang database.A cost-effectiveness analysis (CEA) model was established to analyze the economics using IDegLira for T2DM patients with 1 to 5 years of medication.Results and Conclusion Before IDegLira was admitted to NRDL,its economic advantages over the IGlar plus Iasp regimen became more significant as patients’ medication time prolonged.After being admitted to NRDL,with 1 year of medication,the medical cost of IDegLira decreased by 2 853.91 yuan and the quality adjusted life years (QALY)increased by 0.120 55 than IGar plus IAsp.The sensitivity analysis was highly consistent with the results of the baseline result.After being admitted to NRDL,for patients with T2DM who have poor blood glucose control,IDegLira is absolutely an economic advantage scheme compared with IGar plus IAsp.
Keywords: insulin degludec and liraglutide injection;insulin glargine;insulin aspart;cost-effectiveness analysis
Diabetes,as a non-communicable disease recognized by the World Health Organization (WHO),is the fastest-growing “health emergency” in the world in the 21st century.Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM)accounts for more than 90% of all diabetes cases both in China and worldwide[1].
For T2DM patients who cannot control their diet and living habits,or who cannot achieve their blood glucose control goals by taking oral drugs,insulin injection is currently the most common medication scheme.For more than a century since the discovery of insulin by Banting and Mcleod,insulin has been prepared into varieties with different times and frequencies of injection,different proportions,and different specifications,providing a wealth of medication options for T2DM patients who need insulin to control their blood glucose.
The significant decrease in the secretion level of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) is also one of the important reasons for poor blood glucose control in patients with T2DM[2].A variety of GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RA) represented by liraglutide,semaglutide,and lixisenatide have been approved by the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA)for marketing in China,providing more medication choices for patients with T2DM in China.
A study showed that the simultaneous injection of insulin and GLP-1 RA could achieve a better hypoglycemic effect than injecting insulin or GLP-1 RA alone[2].Insulin degludec and liraglutide injection(IDegLira) is the world’s first combined preparation of basal insulin and GLP-1 RA.It was approved by the NMPA in October 2021 and was successfully admitted to the 2022 National Reimbursement Drug List (NRDL).The purpose of this study is to conduct a cost-effectiveness analysis comparing IDegLira with the combination regimen of insulin glargine injection +insulin aspart injection (IGar+IAsp) in Chinese patients with T2DM,based on the prices of IDegLira before and after admitting to NRDL.
1 Methods
1.1 Literature research method
Domestic and international literature about the safety,effectiveness,and economics related to IDegLira were retrieved through Chinese and English databases such as CNKI,Wanfang,PubMed,ScienceDirect,and Cochrane Library,providing reference for model parameter setting,research period,framework design and scenario analysis design.At the same time,the willingness to pay (WTP) threshold in this study would be set according to the payment preference of medical insurance payers for chronic disease drugs in China.
1.2 Model analysis method
1.2.1 Cost-effectiveness analysis
DUAL Ⅶ Phase Ⅲ clinical trial (NCT02420262)showed that for T2DM patients who received basal insulin combined with metformin could not control blood glucose,while taking IDegLira could achieve the same goal in HbA1cas basal-bolus insulin scheme,which also had the advantages of reducing the risk of hypoglycemia,controlling weight,reducing the frequency of injection,releasing from the injection requirement of meal-time dependence,and lowering daily insulin dose.Research related to the safety,efficacy,and cost-effectiveness of IDegLira overseas showed that the main differences between IDegLira and IGar plus IAsp were as follows: (1) Cost-related aspects: Insulin,self-monitoring blood glucose(SMBG),injection needle,cost of severe/non-severe hypoglycemia events;(2) Effective-related aspects:Severe/non-severe hypoglycemia,frequency of insulin injection,and the change of body mass index (BMI)[3].Therefore,a cost-effectiveness analysis (CEA) model is constructed based on the perspective of medical insurance payers to evaluate the incremental costeffectiveness ratio (ICER) of IDegLira compared with IGar plus IAsp.
1.2.2 One-way sensitivity analysis(OWSA)
OWSA is performed to observe the influence of different parameters on ICER when changing within a certain range.A 10% change in the cost of medication and related devices is used to get the variation in health utility value due to clinical events.The discount rate of cost and quality adjusted life years(QALY) are adjusted for a minimum value of 0.0% and a maximum value of 8.0%[4].A tornado chart is generated according to the variation of ICER brought by the up-and-down adjustment of each parameter.
1.2.3 Probability sensitivity analysis(PSA)
To investigate the uncertainty parameters,PSA is conducted based on a 1 000 times Monte Carlo simulation.According to the recommendations of “China Guidelines for Pharmacoeconomic Evaluations(2020 edition)”,all cost data should obey gamma distribution,the number of clinical events and changes,and discount rate should obey normal distribution.Besides,all health utility value parameters should obey beta distribution,and the data of distribution statistics of each parameter should conform to normal distribution[4].After the Monte Carlo simulation,the expected incremental cost,the expected incremental QALY,and the incremental cost-effectiveness scatter plot can be obtained.Then,the economic probability of the two regimens is analyzed by setting WTP to different values,and the cost-effectiveness acceptance curve (CEAC) can be drawn.
1.2.4 Price caps for IDegLira with economic advantage
Based on the WTP commonly used by medical insurance payers for chronic diseases in China,this study calculates the price cap of the IDegLira under different WTPs by univariate analysis to provide a pricing reference for medical insurance payers.
2 Model structure
2.1 Model simulation period and time horizon
The clinical trial period of the IDegLira varies from 26 weeks to 52 weeks and 104 weeks,and some of the trials will continue from 26 weeks to 52 weeks.Therefore,the cycle period in the model of this study is set at 1 year to analyze the cost-effectiveness of the IDegLira from 1 to 5 years.
2.2 Discount rate and WTP
According to “China Guidelines for Pharmacoeconomic Evaluations (2020 edition)”,the annual discount rate for both cost and QALY is set at 5.0%.The data from the National Bureau of Statistics show that China’s per capita GDP was 85 698.00 yuan in 2022.A cost-effectiveness threshold study based on Chinese population conducted by Cai,et al.[5]using the life value assessment method concluded that China’s WTP should be set at 1.45 times per capita GDP.Since T2DM is a chronic disease in China,which has a large number of patients who need longterm treatment,WTPs of chronic disease have a great impact on the current and future health insurance funds in China,the WTP of this study is set at 0.5 times per capita GDP.
2.3 Conversion of inflation rate
The cost parameters are mainly derived from the references and the drug bidding announcement platform.The data are time-sensitive and therefore need to be converted into 2022 level through the consumer and price index (CPI).The inflation rate is obtained by the CPI of healthcare residents published by the National Bureau of Statistics.
2.4 Cost parameter
2.4.1 Cost related to clinical events
The literature about the medical cost of nonsevere/severe hypoglycemia events based on T2DM patients in China is searched.After screening according to the sample size,research area,and article level,three research results are included in this study[6-8].By comparison,the medical expenses of non-severe hypoglycemia events in the research of Yue,et al.[8]and Lan,et al.[7]are high,which is not in line with the actual situation in China.Therefore,this study takes the expense data of Duan,et al.[6]as the default parameter,and carries out scenario analyses on the expense data of Yue and Lan.
2.4.2 Cost of diabetes-related medical resources
The cost parameters in both schemes are obtained from the public data of marketed drugs in China,with usage and dosage parameters of insulin from the DUAL VII clinical trial.As IDegLira is successfully admitted to the 2022 NRDL through the negotiation channel,the cost of IDegLira in the CEA model will be based on its price before and after its admission.The prices of IGar and IAsp are based on the average price of insulin volume-based procurement (VBP).All insulin injection needles are used by default with Novo needles’ domestic average bidding price.
The cost of SMBG mainly comes from needles and blood glucose test tablets,which are generally sold in combination in China,and the average price of SMBG is 5.00 yuan per group.Through system retrieval and conditional scanning,a total of 5 studies about SMBG frequency were included in the model[9-13].By comparison,the launch time of Han’s[10]research is closer,the sample size is more reasonable,and the research area is larger,which can better represent the national average.Therefore,the result of Han is preferred as the default parameter,and scenario analysis is carried out for the parameters in other studies.
It is common for T2DM patients in China to reuse injection needles.After searching and screening relevant literature,three studies met the standard[14-16].By comparison,the study time of Ji,et al.[15]is more recent,and the sample size and research methods are more representative.Therefore,the results of Ji,et al.are preferred as default parameter,and scenario analyses is carried out on the parameters of other studies (Table 1).See Table 2 for the price details of insulin,injection needle,and SMBG in each scheme.

Table 1 List of parameters related to hypoglycemia events and treatment preferences in the model

Table 2 List of cost parameters of the two schemes in the model*
2.5 Effect parameter
The effectiveness of the two schemes is quantified through the health benefits of severe/non-severe hypoglycemia,changes in BMI,and the difference in the frequency of insulin injections between both schemes by QALY.
2.5.1 Basic health utility values of patients with T2DM in China
Pan,et al.[17]conducted a study about the healthrelated quality of life (HRQoL) of 289 patients with T2DM in China,and the health utility value of T2DM patients in China was 0.876,and the result was used as the basic health utility value of T2DM patients in the model.
2.5.2 Changes of health utility values caused by hypoglycemia events
Through literature search and screening,two studies were included in the study[18,19].Although the research sample of Evans et al.covers multiple countries,the data reliability is not as good as that of Foos,et al.[19]because the data comes from the Internet.Therefore,the results from Foos,et al.[19](-0.003 35,-0.013 70) are taken as the default parameters of the model,and parameters from Evans,et al.[18](-0.006,-0.069) are subjected to scenario analysis.
2.5.3 Changes in health utility values due to changes in BMI
Through searching and screening,a total of three research results are included[20-22].There are T1DM patients and T2DM patients in the sample selected by Hakim,et al.[21].Compared with the research conducted by Ridderstråle,et al.[22],although Bagust,et al.[20]research was published longer time ago,the research sample is more consistent with the BMI requirement of the recruited patients in DUAL series clinical trials (all participants are T2DM patients with BMI > 25 kg/m2).Hence,the result of Bagust and Beale (-0.006 1) is used as the default parameter in the model.The results of Ridderstråle,et al.[22](-0.021 0) and Hakim,et al.[21](-0.028 5) are used for scenario analysis.
2.5.4 Changes in health utility values due to different injection frequencies
Ridderstråle,et al.[22]studied the utility values of T2DM patients based on different insulin injection schemes in the UK,Denmark,and Sweden,and found that the dis-utility for the patient who injected insulin four times a day was -0.090 3,twice a day was -0.049 9,and once a day was -0.006 7.As no studies on utility loss due to injection frequency in Chinese are available,the results of Ridderstråle,et al.[22]are used in the model,see Table 3 for details.

Table 3 List of parameters associated with health utility in the model
3 Economic evaluation results
3.1 Cost-effectiveness analysis based on the price of IDegLira pre-admission to NRDL
3.1.1 Baseline analysis
Within 1 year of medication,the total cost of IDegLira scheme is 26 783.64 yuan,the health benefit is 0.86377 QALY.But the total cost of IGar plus IAsp is 15 910.70 yuan,and the health benefit is 0.743 23 QALY.IDegLira scheme generates a cost increment of 10 872.93 yuan and a health benefit increment of 0.120 55 QALYs,with ICER of 90 196.44 yuan/QALY(approximately 1.05 times per capita GDP).ICER decreases gradually with the increase of medication time,the ICER within 5 years of medication is 31 075.22 yuan/QALY (approximately 0.36 times per capita GDP).
When taking 0.5 times per capita GDP as WTP,IDegLira scheme has an economic advantage over IGar plus IAsp scheme if medication is not less than 4 years.With the increase in medication time,its economic advantage becomes more significant (Table 4).

Table 4 Cost-effectiveness results based on the price of the IDegLira pre-admission to NRDL
3.1.2 OWSA
The main parameters in the model are analyzed by OWSA based on the medication time for 1 to 5 years respectively.The results show that the cost and daily dose of the IDegLira are the most important parameters affecting ICER.The ranking of the impact of each parameter on the results within 1 to 5 years of medication is shown in Table 5.

Table 5 OWSA results based on the price of the IDegLira pre/post-admission to NRDL
3.1.3 PSA
(1) Monte Carlo simulation: After Monte Carlo simulation for 1 000 times,IDegLira generates a cost increment of 11 104.09 yuan and a health benefit increment of 0.120 55 QALY within oneyear medication,ICER is 911 827.95 yuan/QALY(approximately 1.07 times per capita GDP).ICER decreases gradually with the increase of medication time,the ICER within 5 years of medication is 31 690.96 yuan/QALY (approximately 0.37 times per capita GDP),see Fig.1 for details.Monte Carlo simulation results are consistent with baseline results over 1 to 5 years of medication,which reflects the high stability of the model.

Fig.1 Monte Carlo simulation results based on the price of the IDegLira pre-admission to NRDL
(2) Economic advantage of IDegLira under different WTP: Within 1 year of medication,when the WTP is higher than 88 582.70 yuan/QALY (about 1.03 times per capita GDP),IDegLira is the treatment with economic advantage.Within 2 years of medication,when the WTP is higher than 59 000.00 yuan/QALY(about 0.69 times per capita GDP),IDegLira is the treatment with economic advantage.Within 3 years of medication,when the WTP is higher than 45 551.10 yuan/QALY (about 0.53 times per capita GDP),IDegLira is the treatment with economic advantage.Within 4 years of medication,when the WTP is higher than 36 477.80 yuan/QALY (about 0.43 times per capita GDP),IDegLira is the treatment with economic advantage.Within 5 years of medication,when the WTP is higher than 30 024.45 yuan/QALY (about 0.35 times per capita GDP),IDegLira is the treatment with economic advantage (Fig.2).

Fig.2 CEAC based on market access price of IDegLira
3.1.4 Scenario analysis
The uncertainty of this study mainly comes from the risk of hypoglycemia events caused by two schemes,health utility values and duration of medication.Therefore,this study takes 0.5 times per capita GDP as WTP and carries out scenario analysis with the cost of severe/non-severe hypoglycemia events,the frequency of needle use,and the utility loss related to clinical events taken as parameters.The results of scenario analysis based on the price of IDegLira pre-admission to NRDL are shown in Table 6.

Different times of daily insulin injection have the most obvious influence on the ICER.When IGar plus IAsp scheme only inject twice a day instead of four times,the ICERs within 1 to 5 years of medication increase by 50.4% compared with the baseline results,which are higher than WTP,but the ICER is close to WTP in the scenario of a 5 years of medication,which means that IDegLira will show economic advantage when patients use it for more than 5 years.Except for the daily injection times of IGar plus IAsp,the scenario analysis results of other parameters are not worse than the baseline results.
Based on the medication characteristics of patients with T2DM in China,this study includes the factors of needle reuse in the model,but this is not recommended because it may bring risks such as injection site infection and blood infection.Therefore,there is another scenario in this study and the needle reuse is not considered.In this scenario,the ICER of drug use for 1 to 5 years is 69 060.50,46 417.71,35 100.88,28 314.47,23 793.29 yuan/QALY,respectively.ICERs are higher than 0.5 times per capita GDP only in the first two years of medication.
3.2 Cost-effectiveness analysis based on the price of IDegLira post-admission to NRDL
3.2.1 Baseline analysis
The baseline results shows that,within 1 year of medication,the cost of IDegLira scheme is 13 058.90 yuan(including treatment costs of 11 046.21 yuan,hypoglycemia events costs of 2 012.68 yuan),with IGar plus IAsp scheme 15 910.70 yuan (including treatment costs of 6 294.90 yuan,hypoglycemia events costs 9 615.80 yuan).The health benefit is consistent with the result based on the price of IDegLira preadmission to NRDL,the total utility value generated after 1 year of IDegLira is approximatly 0.86 QALYs,the total utility value for the IGlar+IAsp regimen is approximatly 0.74 QALYs,and the utility benefit from IDegLira is approximatly 0.12 QALYs(including a utility benefit of 0.028 93 QALYs from hypoglycemic events,a BMI difference of utility benefit of approximatly 0.01 QALYs and a utility benefit of approximatly 0.08 QALYs from a reduction in the number of injections).The incremental cost is 2 851.80 yuan,and the incremental health benefit is approximatly 0.12 QALYs,which indicates that compared with the IGar plus IAsp,IDegLira can save cost and obtain health benefits within one year of medication.
According to the results based on the price of IDegLira pre-admission to NRDL,within 2 to 5 years of medication,the economic advantages of IDegLira will also become more obvious based on the price of IDegLira post-admission to NRDL (Table 7).
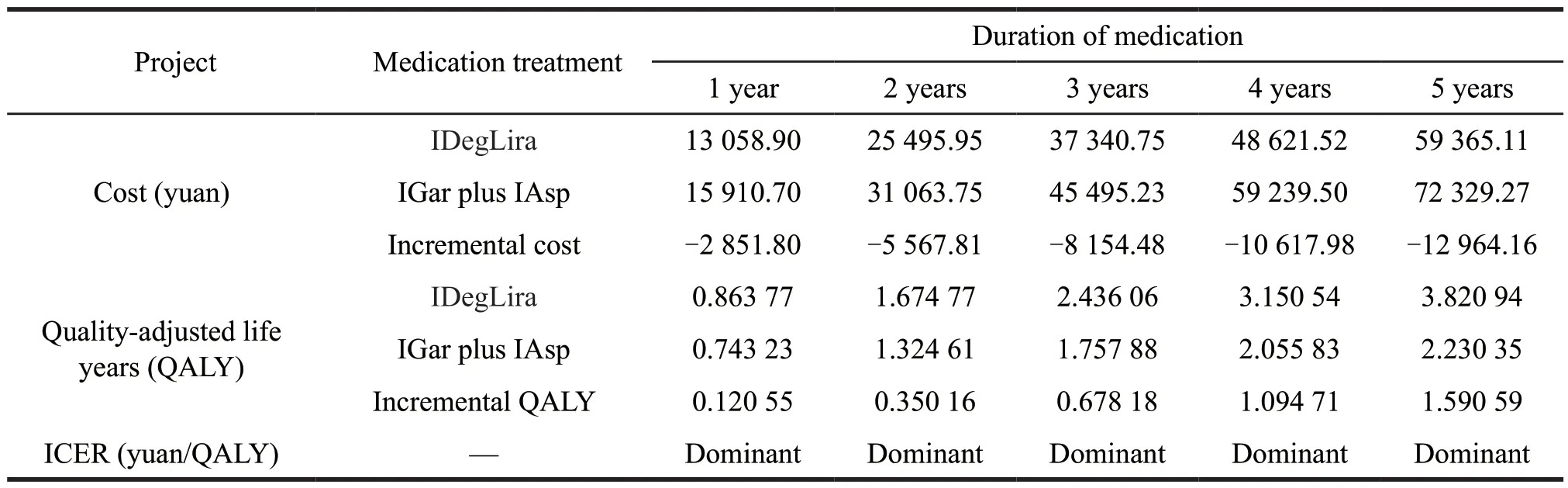
Table 7 ICER based on the price of IDegLira post-admission to NRDL
3.2.2 OWSA
The main parameters in the model are analyzed by OWSA based on the medication time of 1 to 5 years respectively.The results show that the cost and daily dose of the IDegLira are the most important parameters affecting the model results,which are consistent with that based on the price of IDegLira pre-admission to NRDL.Within the medication of 1 to 5 years,the impact of each parameter of the scenario based on the price of IDegLira post-admission to NRDL on the outcome is the same as that of preadmission to NRDL.
3.2.3 PSA
(1) Monte Carlo simulation: As is shown in Fig.3,after Monte Carlo simulation 1 000 times,IDegLira generates -2 583.70 yuan in incremental cost and 0.120 31 QALYs in incremental health benefit within 1 year of medication,and ICER is -21 474.25 yuan/QALY.Only 0.3% of the simulated ICERs are greater than WTP,which shows that IDegLira has an absolute economic advantage.According to the baseline results,the economic advantage of IDegLira within a longer medication time will be better than that of 1 year.

Fig.3 Incremental cost-effectiveness scatter plot based on the price of IDegLira post-admission to NRDL within 1 year of medication
(2) Economic advantage of IDegLira under different WTP: Within 1 year of medication,regardless of the value of the WTP,IDegLira scheme is always the economically dominant one,and its economic advantage rises with the increase of WTP.And according to the baseline results,the economic advantage of IDegLira within a longer medication time will be better than that of 1 year,see Fig.4 for details.

Fig.4 CEAC based on the price of IDegLira post-admission to NRDL within 1 year of medication
3.2.4 Scenario analysis
Scenario analysis results showed that the ICER < 0 for any scenario within 1 to 5 years of medication,indicating that IDegLira is the economic advantage treatment in any scenario.The result based on the price of IDegLira pre-admission to NRDL follows the same pattern as that of post-admission of NRDL,in which the ICER keeps decreasing with the increase of medication duration.Based on the price of IDegLira post-admission to NRDL,and without considering the reuse of injection needles,the ICERs within 1 to 5 years of medication are also less than 0.
3.3 Economic price caps for IDegLira
The ICER from the price of IDegLira preadmission to NRDL to that of post-admission to NRDL is calculated using Microsoft Excel®VBA,the relationship between ICER and the price of IDegLira under different medication durations is presented in Fig.5.The results of Goal Seek show that,within 1 year of medication,the price cap of IDegLira with economic advantage is 381.98 yuan/package (ICER=WTP),and 433.64 yuan/package within 2 years of medication,484.44 yuan/package within 3 years of medication,534.38 yuan/package within 4 years of medication,and 583.47 yuan/package within 5 years of medication.
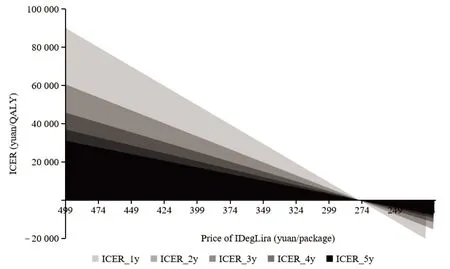
Fig.5 Economic price caps for IDegLira
To sum up,when using the price of IDegLira pre-admission to NRDL,it will be economical when patients take it for no less than 4 years.After admission to NRDL,no matter how long the treatment takes,the economy of IDegLira is better than that of IGar plus IAsp.
4 Discussion and Suggestions
4.1 Analysis of the model results
A CEA model was conducted between IDegLira and IGar plus IAsp based on the price of IDegLira preadmission and post-admission to NRDL respectively to obtain the economy results of patients injecting IDegLira for 1 to 5 years.For T2DM patients,when using 0.5 times per capita GDP as WTP,IDegLira shows a cost-effective advantage for patients to inject IDegLira for no less than 4 years before admitting to NRDL.However,IDegLira shows an obvious economic advantage within 1 year of medication after admitting to NRDL,which not only saves costs but also brings health benefits.The results of OWSA show that the cost of IDegLira is the most influential parameter to ICER,the results of PSA testify to the stability of the model,and the results of scenario analysis show that the parameters from different sources have little effect on the model results.
Through the calculation of the price cap,IDegLira shows absolute economic advantages after admitting to NRDL.From this,we can draw the following inferences: (1) For health service departments,the demand for the price reduction of chronic disease drugs (no matter common or innovative varieties) which applies to NRDL admission by negotiation channel is high;(2) The price reduction of IDegLira is slightly lower than the average price decrease of drugs that admitting to NRDL by negotiation channel (60.1%),which means that the medical insurance department has the determination to encourage innovative drugs for chronic disease to be covered by medical insurance so that patients can obtain more benefits through medical insurance reimbursement.
4.2 Shortcomings of the research
Due to the limitations of the availability of parameters and model size,the research has the following shortcomings.
Firstly,the research results of DUAL series of clinical trials show that severe/non-severe hypoglycemia events are the most clinical adverse events during clinical trials.At the same time,many factors can cause adverse events,it is difficult to determine whether it is caused by insulin injection,so this study only considers hypoglycemia as a clinical adverse event.However,in the DUAL Ⅶ clinical trial,compared with the patients treated with IGar plus IAsp,the patients treated with IDegLira have an increased risk of nausea (11.11%vs.1.58%),diarrhea(6.35%vs.3.95%) and influenza (7.14%vs.4.14%).These adverse events may affect the medication compliance of patients with T2DM,and the medical cost and clinical efficacy may be changed due to them.
Secondly,the control regimen adopted in this study is not the only medication regimen except IDegLira for T2DM patients with poor blood glucose control in China.There are many control regimens for DUAL series clinical trials,but only IGar plus IAsp is used as a basal-bolus scheme.Thus,this study only chooses IGar plus IAsp as the control regimen.However,other basal-bolus regimens as well as additional treatment regimens supplemented with GLP-1 RA are also recommended by related guidelines,so the control regimen in this study may deviate from T2DM patients’ actual medication choices.
In addition,to date,subjects in the DUAL series clinical trials are mainly from Europe and the United States.One clinical trial,based on Japanese subjects,chose IDegLira as the control scheme,which is inconsistent with that of this study.In addition,due to the different frameworks,the results of clinical trials based on Japanese subjects are not included in this study.Considering that there are many ethnic groups in the United States,it is more reasonable.Therefore,the clinical trial data of IDegLiravs.Basal-Bolus therapy in China are not available,this study adopts the results of DUAL clinical trial in the United States as the model parameter values,but the parameter values obtained from the American population will be somewhat biased against the real situation in China.
Finally,the average number of SMBG in the two schemes in this study is the same.However,due to the different risks of hypoglycemia caused by different medication regimens,the SMBG conditions of T2DM patients with two dosing regimens may not be consistent with the model assumptions.Since SMBG is not the main factor affecting ICER,it has little impact on the conclusions of this study.
4.3 Suggestions
4.3.1 Solving the problem of marketing innovative drugs
The clinical trial results of IDegLira show excellent safety and effectiveness.Besides,this study finds that IDegLira has a strong economic advantage after admitting to NRDL,which is a cost-effective drug choice for T2DM patients with poor blood glucose control.China has a large group of patients with chronic diseases.As to innovative medication for chronic diseases,the relevant departments should,based on patients’ affordability,cut the access restrictions to relevant enterprises to ensure the guaranteed supply of medical institutions at all levels through appropriate mandatory measures.Then,patients can choose safer and more cost-effective drugs.
4.3.2 Implementing post-listing re-evaluation
Since China has hundreds of millions of patients with T2DM,ensuring the safety and effectiveness of drug use is critical.As an innovative insulin approved by NMPA for less than two years and marketed for only one year,whether the safety and effectiveness of IDegLira in the real world are consistent with the results of clinical trials still needs further verification.IDegLira was admitted to NRDL,so its market size is expected to expand significantly.Therefore,relevant departments should conduct long-term monitoring of the true value of IDegLira through collecting realworld data and conducting post-listing re-evaluation.
4.3.3 Adjusting NRDL admitting mechanism
The huge price reduction range of IDegLira before and after admitting to NRDL is the result obtained by health service departments through market share permission,which is an important measure to benefit patients.
At the same time,for highly innovative varieties,especially those with large patient volumes,the “onesize-fits-all” NRDL admitting mechanism is hard for some innovative enterprises.In addition,China’s NRDL admitting price is almost the lowest one in the world.For enterprises with a globalization strategy,China’s market pricing is bound to have an impact on that overseas,resulting in related enterprises having to explore paths beyond NRDL admitting channel.For patients with unmet clinical needs,innovative drugs that bypass the NRDL admitting channel will undoubtedly greatly increase their economic burden.Therefore,patients who cannot afford such high drug prices have to choose alternative treatment,and the therapeutic effect will be greatly reduced.
Therefore,relevant departments should formulate a reasonable WTP for innovative varieties from multiple dimensions such as clinical demand for drugs,social value,affordability of health insurance funds,accessibility of drugs,innovation incentives,to improve the willingness of innovative pharmaceutical enterprises to negotiate with NMPA,which can bring more medication choices for patients in need.At the same time,for innovative varieties with short marketing time,we can refer to the flexible price control mechanism implemented in Britain and France to adjust the payment price regularly based on realworld evidence.Otherwise,we can sign a risk-sharing agreement with enterprises to ensure the safety and effectiveness of drugs in the NRDL.
The flexible adjustment mechanism of the NRDL admitting strategy is an effective means to ensure the safety of drugs in the catalogue,and to avoid unfair market competition,which deserves the attention and practice of relevant departments.
5 Conclusion
Based on the price of IDegLira pre-admission and post-admission to NRDL,this study carried out a CEA study with IGar plus IAsp as the control scheme in the treatment of T2DM patients.Before the NRDL admission,although the medical cost is high,IDegLira shows economic advantage with more than 4 years of medication,which has lower risks of severe/nonsevere hypoglycemia events,better control of BMI,and fewer daily injection times.After admission to NRDL,IDegLira can save cost,while having better clinical efficacy,which is an absolute economic advantage scheme.
To sum up,after being admitted to NRDL,IDegLira is absolutely an economic medication choice for Chinese T2DM patients whose blood glucose cannot be controlled by injecting basic insulin.
杂志排行
亚洲社会药学杂志的其它文章
- Effect of the Policies to Prevent Drug Shortage and Stabilize Drug Prices in Medical lnstitutions
- Research on the Countermeasures for the Development of Biopharmaceutical Industrial Parks in China
- Research Progress in FDA’s Focus Areas of Regulatory Science for Drugs and Suggestions for China
- Hypersensitivity Reaction Caused by Intravenous Gadolinium-based MRI Contrast Agents
- A Systematic Review of Patient-Reported Outcome Measurement for Psoriasis in Chinese Population
- Exploration and Research on the Integrated Development of “Internet Plus Medical Treatment”
