计算模拟研究卡宾在聚烯烃功能化中的反应机理
2023-07-10王菲梁欣如杨孟尧艾兴茹徐海梅张亚宁张成根于淑媛
王菲 梁欣如 杨孟尧 艾兴茹 徐海梅 张亚宁 张成根 于淑媛
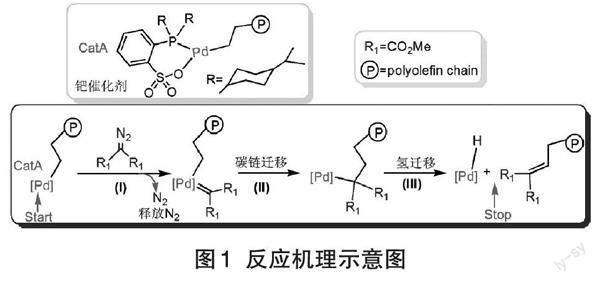


【摘 要】 采用密度泛函理论对卡宾在钯催化聚烯烃链端功能化反应中的机理进行了计算模拟。研究结果表明:卡宾首先插入带有聚烯烃链的催化剂CatA中并释放出N2,随后聚烯烃链会迁移插入卡宾与中心金属原子的Pd-C键中,发生碳迁移反应;再经过氢转移,聚烯烃链的H原子迁移到催化剂中心金属Pd原子上,形成链端含有不饱和双键的聚烯烃产物。整个反应能垒为19.0 kcal/mol,该过程为强烈的放热反应(-52.3 kcal/mol),因此反应容易进行,这也与实验结果相符。研究卡賓在钯催化聚烯烃链端功能化反应中的机理将有助于新型聚烯烃的功能化设计。
【关键词】 卡宾;聚烯烃;钯催化剂;仿真模拟;链端功能化
Computational Simulation Study on the Mechanism for Carbene in Functionalization of Polyolefin
Wang Fei, Liang Xinru, Yang Mengyao, Ai Xingru, Xu Haimei, Zhang Yaning,
Zhang Chenggen, Yu Shuyuan*
(Langfang Normal University, Langfang 065000, China )
【Abstract】 The mechanism of carbene in Pd-catalyzed chain end functionalization of polyolefin was simulated by density functional theory. The results show that carbene is first inserted into the catalyst CatA with polyolefin chain and N2 is released. Then the polyolefin chain migrates into the Pd-C bond between carbene and the central metal atom, resulting in carbon migration reaction. After hydrogen transfer, Hydrogen (H) atom of polyolefin chain is transferred to Pd atom of catalyst, forming polyolefin product with unsaturated double bond at the end of the chain. The energy barrier of the whole reaction is 19.0 kcal/mol, and the process is a strong exothermic reaction (-52.3 kcal/mol), so the reaction is easy to carry out, which is also consistent with the experimental results.The study on the reaction mechanism of carbene in palladium-catalyzed functionalization of polyolefin will be helpful for the design of new polyolefin functionalization.
【Key words】 carbene; polyolefin; palladium catalyst; simulation; chain end functionalization
〔中图分类号〕 O641.3 〔文献标识码〕 A 〔文章编号〕 1674 - 3229(2023)02- 0041 - 05
0 引言
当前,聚烯烃材料应用广泛,对聚烯烃的功能化改进一直是重要的研究方向。烯烃与其他单体或者化合物结合可以改变分子链结构,进而功能化聚烯烃。过渡金属催化的烯烃与极性单体的配位聚合是功能化聚烯烃合成的最直接方法。深入研究催化反应机理能够为烯烃功能化改性的研究提供更多的理论指导,推动功能化聚烯烃合成的发展,从而提高聚合物的表面性能、黏附力、印染性、耐溶剂性以及与其他高分子材料的相溶性和共混性等重要性能。[1-2]
卡宾作为一种高活性中间体,在有机催化反应方面有着不可替代的研究价值和应用价值,同时在有机合成、大分子催化、医药和材料合成、聚合反应[3-4]方面应用广泛。链端功能化聚烯烃可以引入卡宾类化合物,通过优化条件使烯烃单体和卡宾结合,改变聚烯烃分子链结构。王晓明等[5]采用膦磺酸钯催化剂,将卡宾作为一类新型共聚单体迁移插入过渡金属-碳键,获得了链端功能性聚烯烃。然而,到目前为止还没有使用理论计算的方法对反应机理进行研究。因此,本研究采用密度泛函理论 (DFT)计算方法研究烯烃催化反应中卡宾的反应机理,这将有助于新型聚烯烃的开发。
膦磺酸钯催化链端功能化聚烯烃反应的机理如图1所示[5]。卡宾首先插入聚烯烃链端并释放出N2,随后聚烯烃链会迁移插入卡宾与中心金属原子的Pd-C键中,发生碳迁移反应;再经过氢转移,聚烯烃链的H 原子迁到催化剂中心金属Pd原子上,形成链端含有不饱和双键的聚烯烃产物,过程中钯催化剂可以重复利用。
1 计算部分
使用Gaussian 16软件[6]进行了密度泛函理论计算模拟。在B3LYP-D3(BJ)[7-10]/BSI水平上进行构型优化,使用频率分析方法确定所有结构处于最小值(无虚拟频率)或过渡状态(TS,具有特定虚拟频率)。BSI代表联合基组I,其中Pd使用SDD基组[11],非金属原子使用6-31G(d,p)基组。在M06-2X[12,13]/BSII水平上,使用SMD[14]溶剂效应模型(甲苯作为溶剂)和单点能量计算进一步精确了能量结果。BSII代表联合基组II,其中Pd使用SDD基组,非金属原子使用6-311+G(d,p)基组。本文讨论反应曲线能量变化时使用M06-2X/BSII水平下的自由能。在B3LYP/BSI水平上计算了NBO电荷和Wiberg键指数[15]。M06-2X//B3LYP组合方法被用来处理各种过渡金属催化反应,并且证明了其可靠性[16-18]。
2 结果与讨论
图2列出了反应途径中的能量曲线;图3 列出了反应中的优化构型;图4给出了反应中过渡态的前线轨道图形(最高占据轨道HOMO和最低空轨道LUMO)。如图2和图3所示,反应从已经形成了烯烃链的钯催化剂(CatA)开始。在CatA的构型中,Pd-C1 和Pd-O1 的键长分别是2.027 ?和2.145 ?。CatA先与卡宾(Carb1)配位形成中间体IM1,放热1.9 kcal/mol。由于配位效应,IM1构型中Pd-C1键(2.043 ?)和C2-N1键(1.322 ?)比反应物(CatA + Carb1)中的相应键(2.027 ?和1.319 ?)长;而N1-N2键(1.129 ?)比反应物(CatA + Carb1)中的相应键(1.132?)短。
然后,随着Pd-C2键的缩短形成释放N2的过渡态TS1,吸热20.9 kcal/mol。从过渡态TS1的最低空轨道LUMO (图4)可以看出N2释放的反应特征。与中间体IM1构型相比,过渡态TS1中的Pd-C2键(2.058 ?)缩短了1.546 ?;而C2-N1键(1.890 ?)拉长了0.568 ?;N1-N2键长从1.129 ?減少到1.104 ?,非常接近于N2中N1-N2键长(1.106 ?)。
过渡态TS1之后,反应在释放出N2的同时生成中间体IM2,放热17.0 kcal/mol。在中间体IM2构型中,Pd-C2键进一步缩短到1.919 ?,说明催化剂中心金属Pd与卡宾的相互作用进一步增强了。接下来,随着烯烃碳链C1原子向C2原子方向发生链转移,反应到达三元环过渡态TS2,吸热10.6 kcal/mol。从过渡态TS2的前线轨道(HOMO和LUMO,图4)可以看出碳链迁移的反应特征。与中间体IM2构型相比,过渡态TS2中的Pd-C1键(2.257 ?)拉长了0.168 ?;而Pd-C2键(1.896 ?)缩短了0.023 ?。随着碳链迁移的完成,C1和C2成键,生成中间体IM3,放热58.1 kcal/mol。与过渡态TS2构型相比,中间体IM3中的C1-C2键(1.483 ?)显著缩短了0.852 ?;同时,Pd-C2键(2.130 ?)拉长了0.234 ?。
中间体IM3之后,反应达到四元环氢迁移过渡态TS3,稍微吸热2.9 kcal/mol。从过渡态TS3的最低空轨道LUMO (图4)可以看出氢迁移的反应特征。与中间体IM3构型相比,过渡态TS3中的C1-C2键(1.431 ?)缩短了0.052 ?;而Pd-C2键(2.158 ?)拉长了0.028 ?。接下来随着H1原子从C1转移到Pd原子上,反应在生成催化剂组分CatN的同时到达产物PR,放热9.7 kcal/mol,过程中钯催化剂可以重复利用。CatN构型中Pd-H1键(1.546 ?)比TS3中相应键长(1.595 ?)缩短了0.049 ?;在产物PR的构型中,C1-C2键进一步缩短到1.346 ?,形成双键。
在整个卡宾插入及两次链转移的反应过程中,释放N2的过渡态TS1的能量最高,是整个反应的决速步骤,反应能垒为19.0 kcal/mol,这个能垒不高;并且整个反应为强放热反应,ΔG = -52.3 kcal/mol,因此反应容易进行,这也与实验结果相符。[5]
在整个卡宾参与的钯催化聚烯烃链端功能化反应中,C1-H1键逐渐延长直到断裂,而C1-C2从结合到逐渐形成双键。表1给出了反应中的一些重要化学键的Wiberg键指数(WBI)和重要原子的自然电荷(QNBO)。随着反应的进行,从反应物(CatA + Carb1)到产物(CatN + PR), C1-H1键的WBI (0.894 ~ 0.000)逐渐降低,表明C1-H1键断裂;同时,N1-N2键的WBI从2.457逐渐增大到3.026,表明N1-N2键形成三键,以自由气体的形式释放;C1-C2键的WBI从0.093逐渐增大到1.779,Pd-H1键的WBI从0.186逐渐增大到0.665,表明C1-C2双键和Pd-H1单键的形成。
3 结论
本文采用密度泛函计算方法对卡宾参与钯催化聚烯烃链端功能化反应的机理进行了模拟研究。反应机理为:卡宾首先插入带有聚烯烃链的催化剂CatA并释放出N2;随后聚烯烃链会迁移插入卡宾与中心金属原子的Pd-C键中,发生碳迁移反应;再经过氢转移,聚烯烃链的H 原子迁到催化剂中心金属Pd原子上,形成链端含有不饱和双键的聚烯烃产物,钯催化剂(CatN)再生。整个反应能垒不高(19.0 kcal/mol),并且是一个强烈的放热反应(-52.3 kcal/mol),因此反应很容易进行,与实验结果相符。对卡宾存在下钯催化聚乙烯链端功能化反应机理的深入研究将有助于类似功能化合物的开发。
[參考文献]
[1] 简忠保. 功能化聚烯烃合成:从催化剂到极性单体设计[J]. 高分子学报, 2018(11):1359-1371.
[2] 陈敏, 陈昶乐. 官能团化聚烯烃:新催化剂、新聚合调控手段、新材料[J]. 高分子学报, 2018(11):1372-1384.
[3] Xin N, Jing X, Zhang C G, et al. N-Heterocyclic Carbene Silver Complex Modified Polyacrylonitrile Fiber/MIL-101(Cr) Composite as Efficient Chiral Catalyst for Three-Component Coupling Reaction[J]. Nanomaterials, 2022, 12 (23), 4175.
[4] Cao J, Xu G, Li P,et al.Polyacrylonitrile Fiber Supported N -Heterocyclic Carbene Ag(I) As Efficient Catalysts for Three-Component Coupling and Intramolecular 1,3-Dipolar Cycloaddition Reactions under Flow Conditions[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2017, 5(4):3438-3447.
[5] Wang X, Nozaki K. Selective Chain-End Functionalization of Polar Polyethylenes: Orthogonal Reactivity of Carbene and Polar Vinyl Monomers in Their Copolymerization with Ethylene[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2018, 140(46):15635-15640.
[6] Frisch M J, Trucks G W, Schlegel H B, et al. Gaussian 16, Revision C.01[Z]. Gaussian Inc., Wallingford CT, USA, 2016.
[7] Becke A D. Density-functional thermochemistry. III. The role of exact exchange[J]. Journal of Chemical Physics, 1993, 98(7):5648-5652.
[8] Grimme S, Antony J, Ehrlich S, et al. A consistent and accurate ab initio parametrization of density functional dispersion correction (DFT-D) for the 94 elements H-Pu[J]. Journal of Chemical Physics, 2010, 132(15):154104.
[9] Grimme S, Ehrlich S, Goerigk L. Effect of the damping function in dispersion corrected density functional theory[J]. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 2011, 32(7):1456-1465.
[10] Smith D G, Burns L A, Patkowski K, et al. Revised damping parameters for the D3 dispersion correction to density functional theory[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2016, 7(12), 2197-2203.
[11] Miehlich B, Savin A, Stoll H, et al.Results obtained with the correlation energy density functionals of becke and Lee, Yang and Parr[J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 1989, 157(3):200-206.
[12] Zhao Y, Truhlar D G. Density Functionals with Broad Applicability in Chemistry[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2008, 41(2):157-167.
[13] Zhao Y, Truhlar D G. Benchmark Energetic Data in a Model System for Grubbs II Metathesis Catalysis and Their Use for the Development, Assessment, and Validation of Electronic Structure Methods[J]. Journal of Chemical Theory & Computation, 2009, 5(2):324-333.
[14] Marenich A V, Cramer C J, Truhlar D G. Universal Solvation Model Based on Solute Electron Density and on a Continuum Model of the Solvent Defined by the Bulk Dielectric Constant and Atomic Surface Tensions[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2009, 113(18):6378-6396.
[15] Reed A E, Curtiss L A, Weinhold F. Intermolecular interactions from a natural bond orbital, donor-acceptor viewpoint[J]. Chemical Reviews, 1988, 88(6):899-926.
[16] Ren X, Lu Y, Lu G, et al. Density Functional Theory Mechanistic Study of Ni-Catalyzed Reductive Alkyne-Alkyne Cyclodimerization: Oxidative Cyclization versus Outer-Sphere Proton Transfer[J]. Organic Letters, 2020, 22(6):2454-2459.
[17] Yang Y F, Chen G, Hong X, et al. The Origins of Dramatic Differences in Five-Membered vs Six-Membered Chelation of Pd(II) on Efficiency of C(sp3)-H Bond Activation[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2017, 139(25): 8514-8521
[18] Yu S Y, Peng X, Wang F, et al. Density Functional Theory Study of the Regioselectivity in Copolymerization of bis-Styrenic Molecules with Propylene Using Zirconocene Catalyst[J]. Catalysts, 2022, 12(9): 1039.
[收稿日期] 2023-03-06
[基金項目] 河北省高等教育教学改革研究与实践项目(2021GJJG359); 河北省一流本科立项建设课程《高分子化学》;廊坊师范学院大学生创新创业项目(X202210100016)
[作者简介] 王菲(2001- ),女,廊坊师范学院化学与材料科学学院学生。
[通讯作者] 于淑媛(1977- ),女,博士,廊坊师范学院化学与材料科学学院教授,研究方向:计算化学。
