Silage Fermentation Technology and Its Effects on Growth Performance of Local Pigs
2023-06-28YunjianZHANGZhenyanYANGLixiaMENGXibaoFENG
Yunjian ZHANG, Zhenyan YANG, Lixia MENG, Xibao FENG
1. Laiwu District Administrative Law Enforcement Coordination and Supervision Bureau, Jinan 271100, China; 2. Jinan Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Jinan 250316, China
Abstract This paper first introduced the silage fermentation technology, including the selection of strains and activation expansion technology, the screening of high-quality fermentation raw materials, and the comparative experiment of fermentation process. It discussed feeding methods for sows and growing-finishing pigs at different breeding stages. In addition, it analyzed the effects of fermented silage on the growth performance of local pigs at various stages. Finally, it is concluded that silage fermentation can improve the water retention performance of pork, improve the quality of pork from local pigs, increase economic benefits, and achieve the purpose of saving costs and increasing efficiency.
Key words Silage fermentation, Strain selection, Growth performance, Local pigs, Pork quality
1 Introduction
China is rich in local pig breed resources. According to statistics, there are currently 83 local pig breeds in China, including 42 national-level and 39 provincial-level ones. Every local pig breed is a gift of nature. Today’s unique germplasm gene bank has been formed under the selection and breeding of hardworking and intelligent working people for generations. With the improvement of living standards, consumers start to pursue high-quality pork with complete color, flavor and taste, looking for the "old flavor" when they were young. The mellow meat quality of local pig breeds has long been deeply rooted in the hearts of the people, and the local characteristic breeds that have been domesticated for many years have made their debut on the stage of history. Meat quality is mellow, unique flavor, high fecundity, strong stress resistance and omnivorous rough feeding ability are the advantages of local pig breeds different from hybrid pigs. Generally, the digestion ability of local pig breeds is better than other breeds, with larger belly or even mopping the floor, so they can digest bulky green roughage with higher crude fiber content, such as peanut seedlings, sweet potato tendrils, tubers, fruits and vegetables and other agricultural and sideline products.
In the opinion of Zhang Weili, there are common characteristics in the traditional formula of local pig feed in China[1]: (i) Most of the feeds are coarse powder, such as bran, grass powder,etc.with rich in proportion, so they play the role of anti-oxidation in meat. (ii) Most of the feeds are tuber feed, dregs, bean dregs,etc., which can improve the intestinal microecology and prevent meat odor. (iii) Most of the feeds are fermented thinner materials, such as fermented grass, carrots, pumpkins and other thinner materials. Fermented thinner can produce aromatic esters, and can improve the flavor of meat. These indicate that the traditional folk fermented feed for feeding pigs plays an important role in the process of forming the unique meat quality of local pig breeds.
Silage fermentation technology is to collect and beat rich and diverse silage and use high-quality micro-ecological preparations for fermentation. In the fermented silage, indigestible crude protein, non-starch polysaccharides and other macromolecular substances are decomposed, and partly decomposed into small molecular nutrients such as glucose, amino acids and vitamins, thereby improving the digestion and absorption rate and nutritional value of the feed. The mixed feed of fermented silage and concentrate improves feed palatability and the growth performance of local pigs. Silage fermentation technology increases the proportion of agricultural and sideline feed materials in the local pig feed formula, and is also an important link in the fat deposition of local pigs and the formation of "fat and lean" high-quality pork.
2 Silage fermentation technology
The fermented silage can be stored for a long time. After successful fermentation, the silage smells slightly sour and mellow, has a soft texture, is rich in vitamins, lysine, organic acids (such as lactic acid), bacterial protein,etc., and the palatability of the feed is significantly improved. Long-term feeding of fermented silage can improve the intestinal flora of pigs, improve the quality of meat, make the feces of pigs lubricated and not dry, and prevent the long-term retention of feces in the intestinal tract from producing toxins that are absorbed and affect the quality of pork.
2.1Selectionofstrainsandactivationexpansiontechnology
2.1.1Selection of strains. The strains with better fermentation effect and effective live bacteria content can be selected through comparative experiments.
2.1.2Activation and expansion technology of strains. First, it is necessary to evenly mix 90 kg of water +10 kg of fermentation broth +1 kg of coenzyme, place in an airtight plastic container, control the temperature at 30-35 ℃ for fermentation. During the fermentation process, a large amount of gas generated in the fermentation vessel should be regularly emptied. When the pH of the expansion solution drops to 3.5-4.5, the expansion and activation is successful. The expansion and activation technology of strains can effectively save the cost of strains used for fermentation.
2.2Screeningofhigh-qualityfermentationrawmaterials
First, it is necessary to ensure that the fermentation raw materials are fresh and free from mold and deterioration. Second, it is necessary to choose raw materials such as coarse feed and seasonal silage, mainly to save costs.
2.3ComparativeexperimentoffermentationprocessThrough the comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of the fermentation tank, fermentation tank, fermentation bag and porcelain vat fermentation process, the fermentation tank fermentation process that is more suitable for the fermentation of coarse feed and silage is selected.
2.3.1Construction of the fermentation tank. (i) Site selection: the fermentation tank should be selected in a place with high terrain, sunny, good drainage, close to the pig house, easy to take and feed, no manure field, and no pollution source. (ii) Building structure: brick-concrete structure is generally used. (iii) Specification: The specifications of each fermentation tank are preferably 6 m long, 2 m wide and 1.5 m high, so as to facilitate the production, preservation and use of fermented feed. Each pig farm (household) chooses to build a suitable number according to its own actual situation. (iv) Waterproof treatment of the fermentation tank: it is preferred to do waterproof treatment more than 2 times to prevent the leakage of the fermentation liquid, which is a key step that affects the success of the fermentation.
2.3.2Preparation of fermented feed. (i) Selection of fermentation raw materials. According to the local agricultural and sideline product resources, the materials are generally based on coarse feed, seasonal silage, vegetable leftovers, and tuber plants, with the purpose of saving costs and ensuring freshness. (ii) Leak-proof treatment for the fermentation tank. The fermentation tank is treated with multiple layers of cement for waterproofing, and a clean and sterilized plastic cloth is laid on the bottom to prevent leakage. It is necessary to spread 20-30 cm thick hay powder or garlic powder on the bottom of the fermentation tank to hold the water and prevent the juice from seeping out. (iii) Beat the feed into slurry and put into the tank. Put the silage or vegetable leftovers into the pool, and it is advisable to be half full to prevent the juice from overflowing after fermentation. (iv) Anaerobic treatment. Compact the silage in the tank with a grate, and inject clean water about 5 cm higher than the grate to create an anaerobic environment for fermentation. (v) Inject the fermentation broth. At the same time of beating and water injection, add 0.5 kg of dry yeast and 1 kg of fermentation broth per 2 m2. (vi) Sealing and isolation. After injecting the fermentation froth, cover the surface of the fermentation tank with 20-30 cm hay powder or garlic skin powder for compaction, and seal the fermentation tank to prevent oxidation and mildew.
2.3.3Precautions. (i) Raw materials. It is required that the purchased fermentation raw materials are of good quality and free from rot and mildew. The fermented feed is generally yellowish in color, soft in texture, with mellow, sour and fruity aromas. When the pH after fermentation is in the range of 3.5-4.5, indicating that the fermentation is fully utilizable. (ii) Storage of raw materials. The purchased fermentation raw materials should be beaten in time to avoid a large amount of accumulation, and it is preferred to beat while collecting, prevent the destruction of vitamins and trace elements and loss of nutritional value due to a large amount of accumulation of heat, and effectively prevent rot and mildew. (iii) Anaerobic fermentation. The beaten silage should be sealed for anaerobic fermentation to prevent the entry of air and harmful bacteria from causing fermentation failure. (iv) Fermentation effect. The fermentation time is 2 d in summer, 4 d in spring and autumn, and more than 7 d in winter. Too low temperature in winter is an important factor affecting whether the fermentation is complete. It is recommended to use floor heating or use grass grids to build compartments around the fermentation tank, and fill the surface with grass powder to keep warm. In addition, it is necessary to observe at any time, and add strains in time according to the fermentation situation to ensure complete fermentation. The fermented feed should have moderate humidity and a delicate smell. (v) Storage. A tarpaulin or color steel tile roof is set above the fermentation tank to prevent the fermentation effect from being affected by the entry of rain and snow, causing fermentation failure. (vi) Use. Prevent fermentation silage from oxidation and mildew. Cut a small opening from the corner of the fermentation tank when using it, and cover it in time when it is used up. During use, observe the fermentation situation in time, and it is strictly forbidden to feed moldy silage to sow.
3 Feeding methods of sow and growing-finishing pigs in different breeding stages
3.1FeedingstandardsofsowgreenfermentedfeedatdifferentbreedingstagesEmpty sow should be fed with the fermented concentrate, added with 20%-30% fermented silage. Early gestation sow (from mating to-84 d after mating): fermented concentrate feed with 30% fermented silage; late gestation sow (84 d-farrowing): fermented concentrate feed with 20% fermented silage; lactating sow: fermented concentrate with 10% fermented silage, soak thoroughly and feed raw. The amount of feed concentrate is calculated according to 3%-5% of the pig’s body weight. The fermented coarse feed and silage are added according to the ratio of the amount of concentrate, the ratio of feed to water is 2:1, and the thick paste is suitable. Soak the feed for 1 h in summer and 8-10 h in other seasons. Feed one time in the morning and evening, and drink water freely. The nutritional standards of local pigs are shown in Table 1.
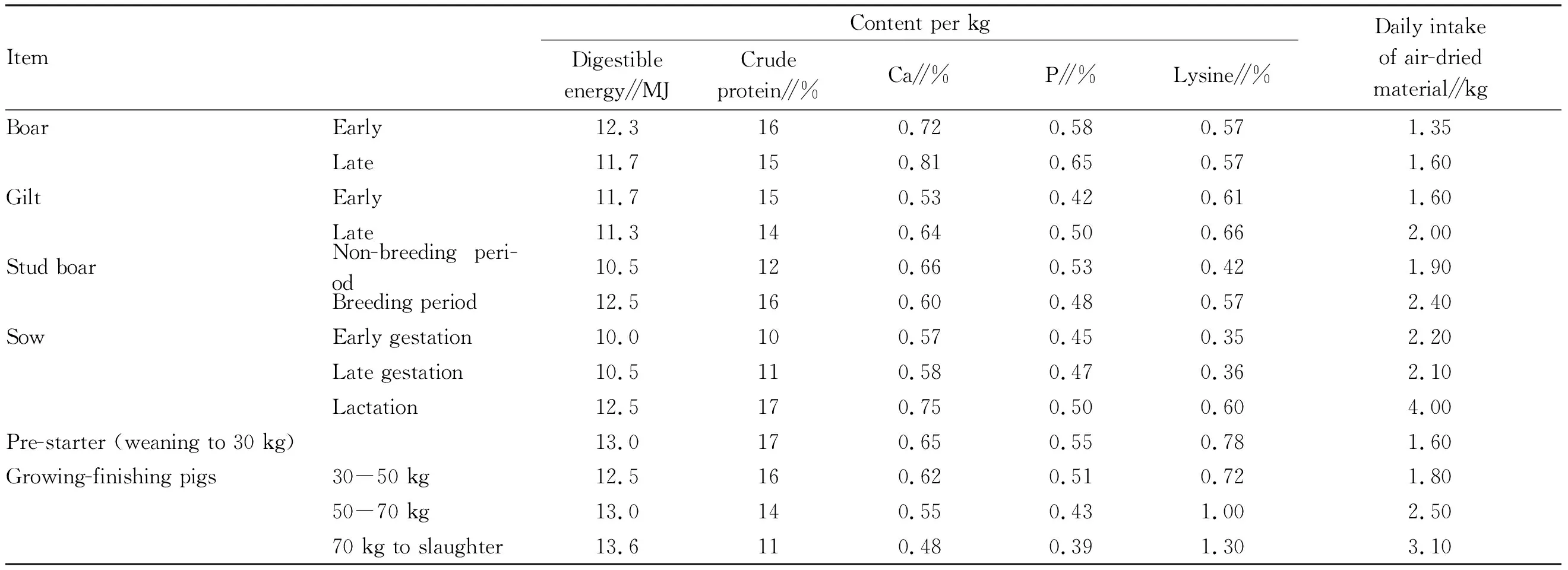
Table 1 Nutritional standards of local pigs
3.2Feedingstandardsofsilagefermentedfeedforgrowing-finishingpigsindifferentstagesFor 30-50 kg of pigs, use the pre-fattening feed, added with 10-20% of fermented silage; 50-70 kg of pigs are fed with mid-term fattening feed, added with 10%-20% of fermented silage; 70 kg-slaughter pigs are fed with post-finishing feed, added with 8%-10% of fermented silage. The fermented coarse feed and silage are added according to the ratio of the amount of concentrate, the ratio of feed to water is 2:1, and the thick paste is suitable. Soak the feed for 1 h in summer and 8-10 h in other seasons. Feed three times a day, drinking water is free. The diet composition and nutritional levels of local pigs are shown in Table 2.
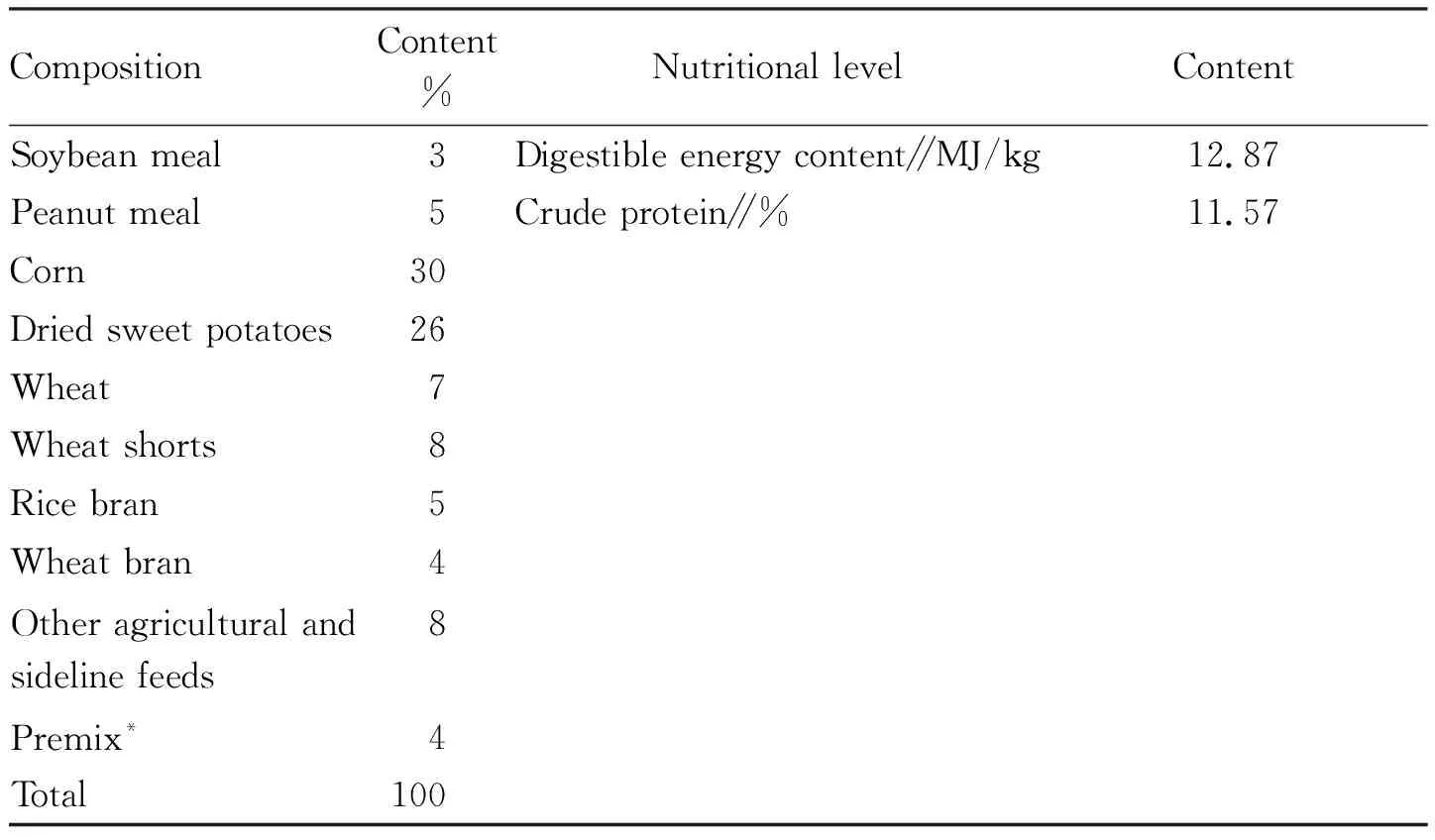
Table 2 Diet composition and nutritional level
4 Effects of fermented silage on the growth performance of local pigs at different stages
4.1EffectsonsowproductionperformanceAdding an appropriate proportion of fermented silage can increase the farrowing rate of sow breeding by 5.11 percentage points, and reduce the repeat rate by 2.33 percentage points. The estrus rate can increase by 5.14 percentage points within 10 d after weaning, the estrus interval after weaning can be shortened by 1.32 d, and the number of days of gestation is shortened by 1.03 d.
4.2EffectsonsowfarrowingperformanceAdding an appropriate proportion of fermented silage can increase the average litter size by 0.63, and the average live litter size can increase by 1.98. On the 22ndd of lactation, the average live litter size is increased by 1.10, the average birth litter weight increased by 1.62 kg, the average birth individual weight increased by 0.14 kg, and the weaned litter average weight increased by 16.01 kg.
4.3EffectsonsowproductioncostsThrough calculating, feeding sows with proper proportion of fermented silage, each sow can increase the economic benefit by 1 500.64 yuan annually.
4.4Effectsontheproductionperformanceofgrowing-finishingpigsThrough experimental research, it was found that after slaughtering growing-finishing pigs using fermented silage, the pH, meat color, and marbling were significantly improved; the water loss rate was reduced by 35.6 percentage points. The slaughter rate and lean meat rate increased by 1.14 and 1.67 percentage points, respectively, the back fat thickness decreased by 0.33 cm, the feed-to-weight ratio decreased by 0.15, and the economic benefit increased by 315.2 yuan per growing-finishing pig.
5 Conclusions
Integrating key links such as fermented feed, nutrient control, fermentation tank production process, and feeding standards, Silage fermentation wet feeding technology provides standardized technical regulations for feeding local breed pigs and breaks through the traditional extensive feeding mode. Through feeding fermented silage, the estrus rate, mating farrowing rate, litter average litter size, number of live piglets, and number of live piglets after weaning of sows have been significantly improved. Besides, it increases newborn litter weight, average individual weight, and weaned litter weight, decreases repeat rate, and shortens estrus interval and gestational days. In addition, the silage fermentation feeding technology improves the water retention performance of pork and the quality of local pig pork, increases economic benefits, and achieves the purpose of saving costs and increasing efficiency.
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Analysis on Value Rationality of Traditional Farm Tools in the Taomin Area
- Techniques and Precautions of Sod Culture in Citrus Orchards in Sichuan Province
- Research Progress in Biological Control of Soft Rot of Amorphophallus konjac
- Treatment of Heavy Metal Pollution in Sediment and Its Resource Utilization in Building Ceramics
- Impacts and Demonstration Effects of Applying Long-acting Slow-release Fertilizer on Economic Yield of Peanut
- Effects of Different Dwarfing Rootstocks on Growth, Yield and Fruit Quality of ‘Tianhong 2’ Apple Trees
