Electroacupuncture stimulation attenuates corpus striatum white matter injury in rats with cerebral ischemia by inhibition of Nogo-A/NgR pathway
2023-06-19MATongjun马同军DONGWenqing董文青MIAOHuachun缪化春WUFeng吴锋DepartmentofAnatomyWannanMedicalCollegeWuhu241002China
MA Tongjun (马同军), DONG Wenqing (董文青), MIAO Huachun (缪化春), WU Feng (吴锋)Department of Anatomy, Wannan Medical College, Wuhu 241002, China
Abstract
Keywords: Acupuncture Therapy; Electroacupuncture; Brain Ischemia; Corpus Striatum; White Matter; Nogo Proteins; Nogo Receptors; Rats
Ischemic stroke is a serious neurological disorder with a high incidence.Cerebral ischemia leads not only to gray matter injury but also to white matter injury due to low blood flow, which is an important factor in long-term neurological deficits after a stroke[1-3].The corpus striatum is prone to ischemia.Cerebral ischemia leads to white matter injury in the corpus striatum and reduces the expression level of myelin basic protein(MBP) in the ischemic corpus striatum[4-5].MBP is a protein abundant in the myelin sheath in the central nervous system (CNS) and is often used as a specific myelin marker; the reduced MBP level is an early marker of white matter abnormalities[5].The expression levels of myelin-associated growth inhibitor (neurite growth inhibitor A, Nogo-A) and Nogo-A receptor (NgR)were increased in brain tissue after cerebral ischemia.Nogo-A limits the regeneration and repair of adult CNS fibers by binding to NgR[6-7].The World Health Organization has listed acupuncture as an effective treatment for stroke[8].Electroacupuncture (EA), a therapy using modern electrical stimulation combined with traditional acupuncture, has been widely used in the treatment of ischemic stroke[9].Our group showed that EA rescued the upregulated Nogo-A and NgR in the corpus callosum of rats with focal cerebral ischemia(FCI).This helped to reduce nerve injuries[10].However,whether the Nogo-A/NgR pathway is associated with white matter injury in the corpus striatum after cerebral ischemia? What are the effects of EA on the Nogo-A/NgR pathway? All of these are still unclear.In this study,we investigated the effects of EA on corpus striatum white matter injury and the Nogo-A/NgR pathway by establishing an FCI rat model to provide further an experimental basis for the clinical application of EA.
1 Materials and Methods
1.1 Main equipment and reagents
Middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO)embolization thread (model: 2432A2, Beijing Cinontech Co., Ltd., China); SDZ-Ⅲ Hwato brand EA instrument(Suzhou Medical Supplies Factory Co., Ltd., China);Hwato brand acupuncture needles of 0.30 mm in diameter and 25 mm in length (Suzhou Medical Supplies Factory Co., Ltd., China); Luxol fast blue (LFB)staining solution (Lot No.DK0009, Regan Biotech Co.,Ltd., China); MBP antibody (Lot No.M3821, Sigma, USA);Nogo-A antibody (Lot No.ab62024, Abcam, USA); NgR antibody (Lot No.DF13593, Affinity Corporation, USA);GAPDH antibody (Lot No.AF7021, Affinity Corporation,USA); SABC kit (Lot No.SA1022, Wuhan Boster Bioengineering Co., Ltd., China).
1.2 Establishment and intervention of rat model with FCI
Forty-four specific-pathogen-free grade male Sprague-Dawley rats with a body mass of 180-220 g were selected [License No.SCXK (Hu) 2018-0004].The rats were first divided into a normal group (n=10), a sham-operation group (sham group,n=10), and a modeling group (n=24) using the random number table method.The 20 rats successfully modeled in the modeling group were randomly divided into a model group (n=10) and an EA group (n=10).
The FCI model was established by the MCAO method with reference to the modeling method of LONGA E Z,et al[11].Rats were anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of sodium pentobarbital at 30 mg/(kg·bw) and fixed on the operating table.An anterior median cervical incision was made, and the right common carotid artery (CCA), external carotid artery (ECA), and internal carotid artery (ICA) were separated by using a glass split needle, the vagus nerve was stripped, and the proximal end of the ICA was ligated.A wire bolt was inserted into the ICA by approximately (18.5±0.5) mm from the bifurcation of the ECA and ICA, following a wire bolt scale until the origin of the middle cerebral artery was blocked.The ICA was ligated and the incision was sutured to complete the modeling.The rats were left to wake up naturally, and the activity status was scored to evaluate the neurological function according to the scoring criteria[11](1 point: inability to fully extend the left front paw; 2 points: turning in a circle to the left side while walking; 3 points: leaning to the left side while walking).
The normal group served as a blank control.The sham group received vessels and vagus nerve isolation only without embolization.The model group was not further treated, and the EA group started EA stimulation at points 24 h after modeling.Referring to the literature[12], Baihui (GV20) and the left Zusanli (ST36)were selected for the treatment with a sparse-dense wave at a frequency of 2 Hz/10 Hz and a current of 1 mA, 30 min each time for 14 d.
1.3 Sampling and indicator determination
1.3.1 Grouping and sampling on demand
At the end of the treatment, rats were anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of sodium pentobarbital at 30 mg/(kg·bw).Five rats in each group were selected,perfused with normal saline, and fixed with 4%paraformaldehyde overnight.Brain tissues containing the corpus striatum around the ischemic foci were collected for LFB and immunohistochemistry (IHC)staining after paraffin embedding.Corpus striatum tissues around the ischemic foci were collected from the other 5 rats after anesthesia on ice plates for protein analysis (Western blotting, WB).
1.3.2 LFB staining
Paraffin sections of brain tissue (5 μm in thickness)were sequentially placed in xylene, gradient ethanol for dewaxing, and LFB staining solution.The sections were placed in an oven at 60 ℃ for 3 h; rinsed with 95%ethanol and distilled water in sequence; fractionated with Luxol fraction solution, followed by color separation with 70% ethanol, dehydration by gradient alcohol (90%, 95%, 100%) and xylene transparency, and then sealed with neutral gum.The right corpus striatum was observed under a 400× light microscope and photographed.The average optical density (AOD) value(AOD = Integrated optical density ÷ Area) of rat myelin staining in each group was analyzed using Image-Pro Plus 6.0 software.
1.3.3 IHC staining
Paraffin sections (5 μm in thickness) of brain tissue were prepared, blocked with goat serum, added with antibody dilutions containing MBP (1:100), Nogo-A(1:100), or NgR (1:100), incubated overnight at 4 ℃ in the refrigerator, added with secondary antibody dilutions, incubated at 37 ℃ for 40 min, rinsed, added with DAB chromogenic solution, and sealed with neutral gum after color development.The images were observed and acquired under a 400× microscope, and the AOD of the three proteins’immunoreactivity in rat right corpus striatum of each group was measured by using Image-Pro Plus 6.0 software.
1.3.4 WB for related proteins
According to the assay method in the literature[10],the right corpus striatum tissue of rats in each group frozen in the refrigerator at -80 ℃ were homogenized and the total protein was extracted by adding protein lysate.Equal amounts of total proteins (80 μg) were separated for 1.5 h by SDS-PAGE gels.The proteins were transferred to PVDF membranes for 1.5 h with a constant current of 300 mA.The membranes were blocked with 5% skimmed milk for 1 h at room temperature; the MBP, Nogo-A, NgR, and GAPDH antibodies (all 1:1 000) were added to the membranes,respectively, and then incubated overnight in a refrigerator at 4 ℃.The membranes were washed with TBST for 10 min × 3 times and transferred to a solution containing horseradish peroxidase-labeled sheep antirabbit immunoglobulin G (1:1 000).The membranes were washed after 1 h of shaking, developed with ECL chemiluminescent solution, and images were acquired using an Amersham Imager 600 system.The grayscale values of the target and internal reference bands were analyzed using ImageJ software, and the relative protein expression was the ratio of the target band to the internal reference band.
1.4 Statistical analysis
Data were analyzed using the SPSS version 26.0 statistical software.The mean ± standard deviationwas used for the measurement data conforming to normal distribution, and one-way analysis of variance was used for the comparisons among multiple groups,and the least significant difference test was used for the comparisons between two groups.Measurement data that did not conform to a normal distribution were expressed as median (lower quartile, upper quartile)[M (QL, QU)], and rank-sum test (Mann-WhitneyU-test)was used for paired comparisons among multiple groups or between two groups.P<0.05 indicated that the difference was statistically significant.
2 Results
2.1 Comparison of the neurological deficit score
Rats in the normal group and the sham group did not show neurological deficits.Rats in the model group showed a significantly higher neurological deficit score on day 14 of cerebral ischemia than that in the normal group and the sham group (P<0.01).The neurological deficit score in the EA group was significantly lower than that in the model group on day 14 of cerebral ischemia (P<0.01), indicating that EA could improve the neurological deficit in rats with cerebral ischemia(Table 1).

Table 1 Comparison of the neurological deficit score among groups on day 14 [M (QL, QU)] Unit: point
2.2 Histological changes of myelin sheath in rat corpus striatum
The LFB staining results showed that the fiber bundles were densely arranged in the normal group and the sham group and were sparsely arranged in the model group.The AOD value of the model group was significantly lower than that in the normal group and the sham group (P<0.05).Compared with the model group, the EA group showed a significantly denser fiber bundle arrangement and significantly higher AOD value(P<0.05).See Figure 1 and Figure 2.
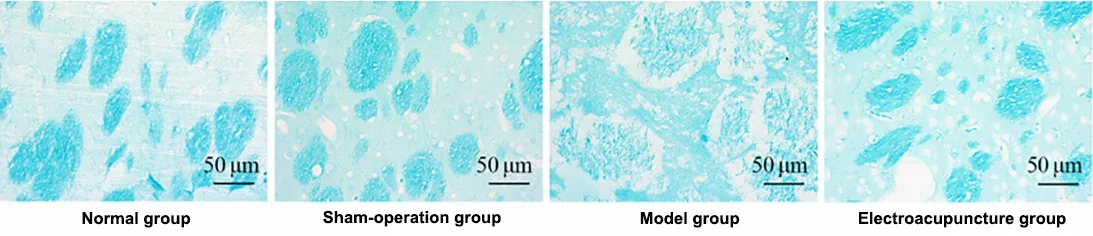
Figure 1 Morphology of the white matter in rat corpus striatum in each group (Luxol fast blue staining, ×400)

Figure 2 Comparison of the corpus striatum myelin staining results among groups
2.3 Changes in the myelin-associated protein expression
IHC staining showed that the MBP immunoreactive product in the normal group and the sham group was stained dark, while the Nogo-A and NgR positive products were stained light.Compared with the normal group and the sham group, the staining of MBP immunoreactive product was lighter and the AOD value was lower in the model group; meanwhile, the Nogo-A and NgR staining was darker, and the AOD values were higher (P<0.05).EA treatment significantly increased the AOD value of MBP in the white matter of the corpus striatum on the ischemic side with darker staining compared with the model group (P<0.05), while the AOD values of Nogo-A and NgR were significantly lower than those in the model group with lighter staining(P<0.05).See Figure 3 and Figure 4.
2.4 Changes in the MBP, Nogo-A, and NgR protein expression
WB assay revealed that the relative MBP protein expression in the model group was lower than that in the normal group and the sham group (P<0.05).The relative MBP protein expression level was significantly higher in the EA group compared with the model group(P<0.05).The relative protein expression levels of Nogo-A and NgR were opposite to the expression trend of MBP: the relative protein expression levels of Nogo-A and NgR in the model group were significantly higher than those in the normal group and the sham group(P<0.05) and were significantly lower in the EA group compared with the model group (P<0.05).See Figure 5 and Figure 6.

Figure 3 Expression of MBP, Nogo-A, and NgR in the corpus striatum of rats (immunohistochemistry staining, ×400)
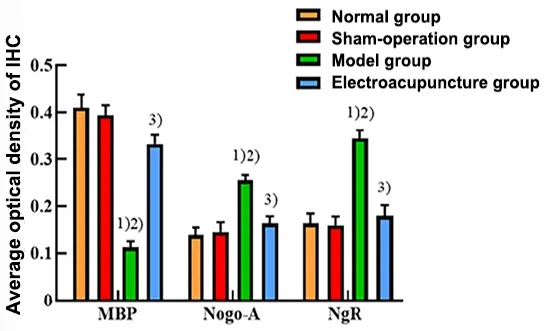
Figure 4 Comparison of the average optical density values of immune response of MBP, Nogo-A, and NgR in the rat corpus striatum

Figure 5 Bands of MBP, Nogo-A, NgR, and an internal reference in the rat corpus striatum (Western blotting)
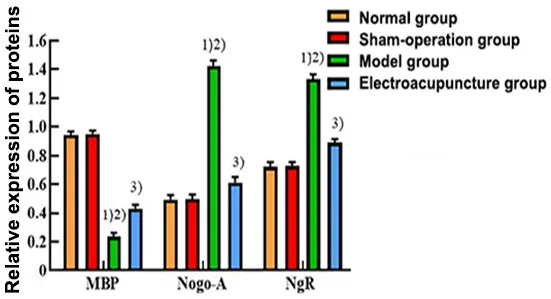
Figure 6 Comparison of the relative expression of MBP,Nogo-A, and NgR proteins in the rat corpus striatum
3 Discussion
The corpus striatum is the largest nucleus of the basal ganglia.Many afferent and efferent fibers are present in the corpus striatum, one of the areas susceptible to cerebral ischemia[4,13].Diffusion tensor imaging revealed that the white matter fiber was significantly lost in the corpus striatum of MCAO rats on day 14 of ischemia.The nerve fibers were relatively intact in rats taking the antithrombotic capsules[14].LFB staining in this experiment showed that the corpus striatum white matter fiber bundles on the ischemic side were severely injured after 14-day FCI.After EA treatment, the white matter fiber bundles in the ischemic corpus striatum were relatively intact,indicating that EA significantly attenuated ischemiainduced injuries in the corpus striatum white matter and had a neuroprotective effect.
As a specific marker of myelin, MBP expression usually decreases significantly during demyelination, an early marker of white matter abnormalities[15].Exercise promotes MBP expression in the ischemic corpus striatum and reduces demyelination[16-17].To further analyze and verify the protective effect of EA on ischemic white matter injuries, MBP expression in the corpus striatum was detected by IHC and WB.The results showed that the corpus striatum MBP expression in the ischemic side of the EA group rats was significantly higher than that in the model group,indicating that EA treatment of cerebral ischemia could rescue the decreased MBP expression and produced a neuroprotective effect on ischemic cerebral white matter injuries.
EA, a combination of traditional acupuncture and modern electrotherapy, has been widely used in the clinical treatment of stroke and other diseases.Many animal experiments have revealed the neuroprotective effects of EA on ischemic stroke, including inhibition of apoptosis after ischemic injuries and promotion of neurogenesis, angiogenesis, and neuroplasticity[18-19],with complex mechanisms.Baihui (GV20) and Zusanli(ST36) are commonly used points in clinical and experimental studies on stroke treatment.Traditional Chinese medicine theory believes that Baihui (GV20)gathers Yang Qi.Stimulation to Baihui (GV20) provides energy to the body.Stimulation to Zusanli (ST36)invigorates Qi and blood to regulate the overall function of the body[8,20].Previous studies have shown that EA rescues the overexpressed Nogo-A and NgR in the corpus callosum of rats with FCI and contributes to the improvement of neurological injuries[10].After cerebral ischemia, the protein expression levels of Nogo-A and NgR were increased in the brain, where Nogo-A limited the regeneration and repair of adult CNS fibers by binding to NgR[21-22].Nogo-A and NgR-mediated inhibitory signaling pathway plays an important negative regulatory role in CNS injuries[23].Nogo signaling blockade with NgR1 antagonist has been reported to reduce the conversion of oligodendrocyte precursor cells to astrocytes and to increase oligodendrocyte formation in mice after a stroke;electron microscopy observation showed that the ratio of myelin sheath thickness to axon diameter after a stroke was reduced or fully restored to the control state,suggesting that NgR1 inhibition played a reparative role in white matter stroke[24].After anti-Nogo-A immunotherapy, contact ability in rat forelimbs can be significantly restored, which is also effective in the long term for neuroplasticity after a stroke[25].EA downregulates the Nogo-A/NgR/RhoA/Rock signaling pathway in the peripheral cortex of cerebral-ischemia,providing a less inhibitory environment for axonal regeneration after cerebral ischemia[26].In this study,Baihui (GV20) and Zusanli (ST36) were selected for 14-day treatments to investigate the regulatory effect of EA on the Nogo-A/NgR signaling pathway.IHC and WB results consistently showed that the Nogo-A and NgR expression levels in the corpus striatum on the ischemic side of the model group rats were significantly higher than those in the normal group and the sham group,while the Nogo-A and NgR expression levels in the EA group were significantly lower than those in the model group.The results showed that EA inhibited cerebral ischemia-induced activation of the Nogo-A/NgR signaling pathway in the corpus striatum, but the specific regulatory mechanism of the Nogo-A/NgR signaling pathway needs to be investigated further.
In summary, EA inhibits cerebral ischemia-induced activation of the Nogo-A/NgR signaling pathway and alleviates the decreased MBP expression in the corpus striatum and myelin injury, exerting a neuroprotective effect on cerebral white matter.This study provides a new theoretical and experimental basis for the treatment of cerebral ischemia with EA.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no potential conflict of interest in this article.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Academic Leader Reserve Project of Wannan Medical College [皖南医学院学术带头人后备人选人才项目, No.校政(2019) 81 号].
Statement of Human and Animal Rights
The treatment of animals conformed to the ethical criteria in this experiment.
Received: 5 March 2022/Accepted: 19 September 2022
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science的其它文章
- Study on the antipyretic mechanism of large pushing Tianheshui for young rabbits with endotoxin-induced fever
- Effects of different moxibustion time on knee cartilage morphology and the expression of TNF-α and IL-10 in rats with knee osteoarthritis
- Effects of horse-riding squat exercise plus Governor Vessel-regulating Tuina therapy on static balance function in patients with stroke
- Observation on the efficacy of traditional Qigong exercise combined with Tuina manipulations in treating lower cervical disc herniation
- Clinical study of treating somatoform pain disorder with the combination of electroacupuncture and duloxetine
- Clinical observation of Tuina combined with Bu Zhong Yi Qi Tang in the treatment of rectocele
