Bibliometric analysis of quality of life in peritoneal dialysis patients
2023-03-07ZiRanSunHongMeiHanXiaoChenSunKaiYueZhu
Zi-Ran Sun,Hong-Mei Han,Xiao-Chen Sun,Kai-Yue Zhu
1Graduate School of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Tianjin 301617,China.2Department of Nursing,First Teaching Hospital of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Tianjin 300192,China.
Abstract Objective:Nowadays,the medical model is constantly changing,and the problem of how to improve the quality of life of peritoneal dialysis patients arises at a historic moment.This paper observes the publication and cooperation of research countries and institutions related to the quality of life of peritoneal dialysis patients,understands the research hotspots,explores the research trends,and provides a reference for further research by scholars. Methods: The search database was the Web of Science core collection,the search terms “peritoneal dialysis” and “quality of life”,the document type “Article or Review”,the language “English” and the period from 1985 to 2022. Results: A total of 1,597 literature were retrieved,and the number of documents showed an annual increase.The United States has the highest volume and centrality of publications and the most cooperation with other countries.The institution with the largest number of articles is the University of Toronto in Canada.The top three most highly cited documents were analyzed to derive the knowledge base of the research area.According to the analysis of keywords,there are high-frequency keywords such as “quality of life” and “peritoneal dialysis” and 11 keyword clusters.Understand the changing trends and frontiers in the research field through timeline maps and mutated words. Conclusion: The comparison of quality of life between peritoneal dialysis and haemodialysis and the study of factors influencing the quality of life is a hot research topic.With the gradual deepening of the research,it is suggested that future research should focus on the intervention research of influencing factors and clarify the intervention measures to improve patients’ quality of life.
Keywords: peritoneal dialysis; quality of life; Web of Science; bibliometric analysis introduction
Background
End-stage kidney disease (ESKD) refers to the end stage of various chronic kidney diseases [1].Patients must undergo renal replacement therapy (RRT) to maintain life.The prevalence of ESKD and the number of patients undergoing RRT are increasing rapidly around the world.It is estimated that in 2030,the number of patients undergoing RRT in the world will more than double that in 2010,reaching 5.439 million,with the fastest growth in Asia[2].Peritoneal dialysis (PD) is one of the crucial RRT measures for ESKD patients [3].It can take advantage of the semi-permeable membrane characteristics of the peritoneum to remove excess water and metabolites in the body.The application of PD technology shows an increasing trend.It is estimated that the global annual growth rate of PD is 8%,which is higher than that of hemodialysis (about 6–7%) [4].Especially in China,the annual growth rate of PD is 20% [5].With the continuous improvement of PD equipment and technology,the gradual development of national economy and the improvement of people’s material living standards,the basic complications of dialysis,such as intraabdominal infections,have been significantly reduced.However,the higher requirements for improving PD patients’ survival rate and quality of life are also put forward[6].Quality of life is essential in the treatment and decision-making of ESKD.It is also considered an important index to evaluate the effect of dialysis treatment.At present,there are many researches on the quality of life of PD patients;however,there is no literature that provides a systematic and objective analysis of research findings in this area.Therefore,this study uses CiteSpace software to make a systematic,comprehensive and objective analysis of the research field through the method of bibliometrics in order to show the evolution path of the research field,discover research hotspots,explore frontier issues and possible development directions.
Methods
Design
This bibliometric study aims to investigate and map the research results in the fields related to the quality of life of PD patients.
Literature source and retrieval strategy
Web of Science (WOS) is an essential database for accessing global academic information,featuring more than 13,000 authoritative,high-impact academic journals from around the world,covering natural sciences,engineering technology,biomedicine,social sciences,arts and humanities and other fields.WOS contains references cited in papers.Through a unique citation index,users can use an article,a patent number,conference literature,a journal or a book as key words to retrieve their citations,easily trace the origin and history of research literature,or track its latest progress [7].The search was carried out in the WOS core collection database with the key words of“peritoneal dialysis” and “quality of life”.The literature type was“Article or Review” and the language was “English”.The retrieval time was from 1985 to March 10,2022.Export the qualified literature data,select other file formats,full records and references as the export content,choose the plain text format to save,and name it as“download_*.txt”.A total of 1,595 articles were selected.
Literature analysis and research tool
The tool selected in this study is CiteSpace software.The software is a visualization tool based on JAVA platform developed by Dr.Chen Chaomei.It is used by researchers in various disciplines for literature research because of its good Chinese compatibility,visual scientific knowledge graph and other functions [8].In the CiteSpace software,the time span is set from January 1998 to March 2022; the time slice span is 5 years; the node types are “Country”,“Institution”,“Reference” and “Keyword” respectively; the cutting mode is Pathfinder method,and other options default to get network analysis views of different countries/regions,institutions,co-cited documents and keywords.
Results
Annual volume of articles and citation frequency
A total of 1,595 articles on the quality of life of PD patients were retrieved.The annual number of articles and cited frequency fluctuated slightly but showed an upward trend as a whole.The total cited frequency was 48,696,of which more than 5,678 in 2021.The detailed results are shown in Figure 1.The average number of citations per article is 30.53,and the H-index is 102.

Figure 1 Annual volume of articles and citation frequency
Distribution of the author’s country
A co-occurrence analysis of literature on the quality of life of PD patients in different countries is presented in Figure 2.A total of 119 nodes,195 lines with a density of 0.0278 are generated,where larger node fonts indicate more publications from that country.More connecting lines indicate closer cooperation between countries.Countries with node centrality > 0.1 were marked using circles,and the thicker the circle,the higher the centrality.Centrality is an important index to determine the development and evolution process of a discipline and to predict the development trend of the discipline.The higher the centrality is,the more critical it is in the development process of the discipline field [9].The top three countries in the number of articles were 319 in the United States (accounting for 20.00%),131 in China (8.21%) and 109 in Canada (6.83%).The top three countries with high centrality are the United States(centrality is 0.54),Australia (0.17) and Britain (0.15).There are also the most connections between the United States and other countries,indicating extensive cooperation between the United States and other countries.The centrality of 0.01 in China and the low number of connecting lines indicate that there is less cooperation between China and other countries.In the future,international cooperation can be strengthened to explore the quality of life of PD patients in order to promote their development.
Distribution of the author’s institution
This paper makes a co-occurrence analysis of the literature on the quality of life of PD patients in different institutions,further judges whether there is a cooperative relationship among the institutions,and identifies the institutions with a large number of papers through the size of the nodes in the map [10].A total of 302 nodes and 428 connections are generated,with a density of 0.0094.It can be found that there is a certain cooperative relationship between various institutions.The detailed results are shown in Figure 3.The University of Toronto in Canada has the largest number of articles,with a total of 50 articles,with a centrality of 0.18.
Co-citation analysis of the literature
From the perspective of bibliometrics,citing articles form a research frontier,and cited articles constitute a knowledge base.The knowledge base will be stable for a long time and more sensitive to the changes of the research frontier,so the co-cited articles are analyzed[11].A total of 701 nodes and 874 connections were generated,with a density of 0.0036,as shown in Figure 4.The top 10 co-cited articles are selected and ranked according to the number of articles,as detailed in Table 1.

Table 1 Top 10 articles co-cited

Figure 2 Network analysis of co-countries

Figure 3 Network analysis of co-institutions
Keyword analysis of literature
Keywords reflect the internal characteristics of documents,which explain or express the core content of documents and reflect the implied information of documents [12].Moreover,in the process of document retrieval,keywords are easy to obtain,so analyzing keywords is a vital bibliometrics method for further study and research [13].Keyword clustering refers to the induction of the same or similar subject words.The results can objectively reflect the composition of the current research topics in this field to explore the current research situation in the field and predict research hotspots[14,15].CiteSpace software is used for keyword analysis (Figure 5)and keyword clustering analysis (Figure 6) of literature.Log-likelihood ratio is used to generate 459 nodes and 1,326 connections,with a density of 0.0126 and a modularity Q of 0.5363,which lies in the optimal range of 0.4–0.8,indicating that the community structure is remarkable,with a mean silhouette of 0.7559> 0.7,which means that the clustering is reasonable and convincing,and 11 clusters are obtained [8].

Figure 4 Co-citation analysis of literature

Figure 5 Keyword analysis of literature
Research hotspot and frontier analysis
Research hotspots and frontier are generated under the same analysis principle; the keyword knowledge graph is based on word frequency analysis,so the frontier analysis is detected based on hot research fields.Research hotspot analysis is shown by timeline visualization.The timeline visualization depicts clusters along a horizontal timeline,which can draw the changing trend of research hotspots in a field over time [16].The main 11 clusters are presented in Figure 7.Each one can indicate the evolution of research in the field of quality of life of PD patients from 1998 to 2022.A Burst term is a keyword that appears suddenly or increases sharply in frequency of use within a short period of time[17].Overall,it can predict the research frontiers in this research area.These keywords may be new research trends and directions in the quality of life for PD patients,as listed in Table 2.

Table 2 Top 20 keywords with the strongest citation bursts
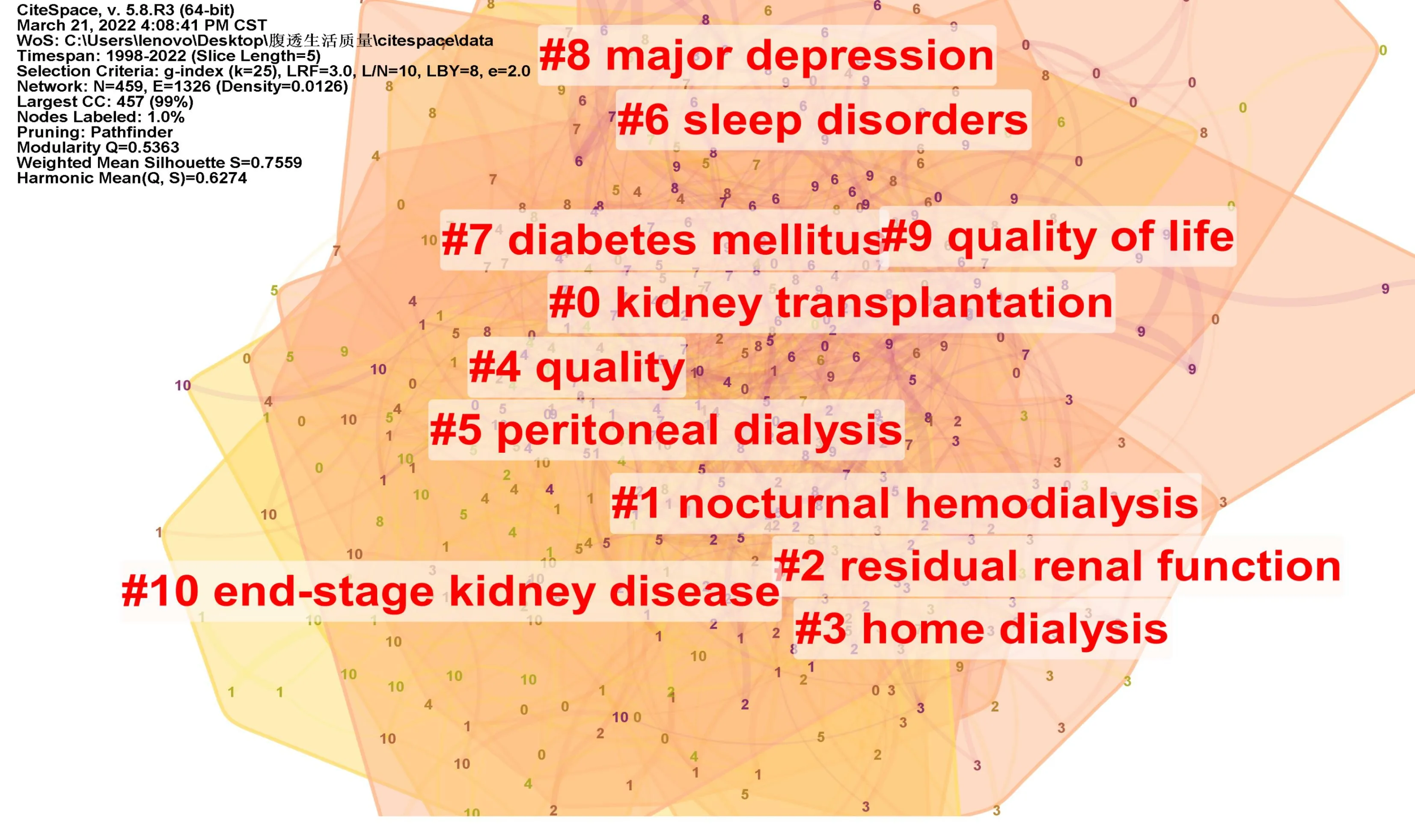
Figure 6 Keyword cluster analysis of literature

Figure 7 Timeline view of the 11 largest clusters
Discussion
Basic features
The quality of life of PD patients continues to be valued and concerned.From 1998 to 2021,the number of documents published in this field has risen steadily.Combining the number of publications and centrality,it can be found that the regions and institutions of publication are mainly distributed in countries such as the United States,Canada,Australia and the United Kingdom,which reflect a better consistency and have a strong centrality.This reflects the close academic exchange and fruitful academic achievements in the field of quality of life in PD in these countries,forming a network of domestic and international cooperation.China has a high number of publications,but its centrality is low,which reflects that the cooperation between China and other countries is relatively insufficient,so it is necessary to strengthen the cooperative network between China and other countries.
Knowledge base
Through the network analysis of the co-cited literature to understand the knowledge basis in the field of quality of life of PD patients.The first three co-cited literature analysis shows that the main research direction is to compare the quality of life and survival rate between PD and hemodialysis and to study the effects of demography,renal function and dialysis characteristics on the quality of life of patients.Although renal transplantation is the first choice for patients with ESKD,most patients need dialysis while waiting for transplantation or as the only treatment.The question of which dialysis method provides the best survival rate and quality of life remains unsolved.
Research hotspots
Combining keyword clustering tags and high-frequency keywords for analysis,it was concluded that current research hotspots focus on the selection of RRT modalities for patients with chronic kidney disease or ESKD,the development and intervention of dialysis complications such as diabetes,depression and sleep disorders,and the evaluation of dialysis quality such as residual renal function,mortality and quality of life.There is a crossover between PD research hotspots and previous research on the subject.As can be seen,the highly cited literature provides a rich theoretical underpinning for future research,leading to a gradual diversification and refinement of research directions.
Research Frontiers
Combining timeline plots and mutation words for analysis can explore cutting-edge developments in the field of quality-of-life research in PD patients.Between 1998 and 2007,quality of life and survival in patients on continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis,renal transplantation or haemodialysis was a hot research topic.When we refer to the quality of life in patients with chronic diseases,we refer to health-related quality of life (HRQOL),which refers to the perceived physical and mental health of an individual or group over time.At the individual level,HRQOL includes perceptions of physical and mental health (e.g.,energy levels,mood) and their associated factors,including health risks and conditions,functional status,social support and socioeconomic status.ESKD has a great impact on the HRQOL of patients.Renal replacement therapies such as haemodialysis and PD only partially correct the patient’s symptoms and cause additional changes in the patient’s lifestyle,which can affect quality of life.The definition of dialysis adequacy should therefore include the patient’s perceived HRQOL.The quality of life of dialysis patients is closely related to morbidity and survival; the better the quality of life,the lower the morbidity and the higher the survival rate [18].There are many factors that influence the HRQOL of dialysis patients,including protective factors such as haemoglobin level,economic level,education level and physical activity,and risk factors such as co-morbidity,malnutrition,depression and being female.
Over time,the research on the quality of life is more in-depth and more meaningful.From 2008 to 2022,with the continuous improvement of dialysis technology and the extension of patients’survival time,the quality of life and sleep quality of PD patients have increasingly attracted the attention of clinical medical staff.The researchers further explored the effects of dialysis complications,such as sleep disorders and depression on patients’ quality of life.Good sleep plays a vital role in maintaining normal physiological function and also improves patients’ quality of life.A number of studies have confirmed that the incidence of sleep disorders in PD patients is high,and a variety of influencing factors and sleep disorders interact with each other to affect the quality of life of patients [19–21].For example,malnutrition is significantly related to depression,sleep disorders and the decrease of quality of life.Active and effective prevention and treatment of malnutrition can improve the sleep quality of PD patients and significantly reduce the prevalence and mortality [22].Active correction of anaemia in PD patients,correct use of erythropoietin and effective improvement of the nutritional status of patients are important in improving their sleep and quality of life[23].Depression and anxiety can lead to sleep disorders,and sleep disorders can also lead to depression [24,25].However,at present,there are few literature reports on how to intervene in anxiety and depression of PD patients and whether active intervention can improve the quality of life of patients.It is suggested that future research could be directed towards interventions that target intervenable factors such as sleep disorders,depression,malnutrition and anaemia to define further interventions to stop the development of the disease in order to improve the quality of life of patients.
Conclusion
In this study,CiteSpace software was used to analyze the research on the quality of life of PD patients from the establishment of WOS core collection database to 2022.This paper shows the publishing and cooperation of different countries and institutions,co-cited literature,keyword analysis and keyword cluster analysis,as well as timeline charts and mutation words,were presented to identify hotspots,trends,and frontiers in the research field and provide researchers with new perspectives for further research.This study only searched the WOS core collection database,which may not be comprehensive due to the incomplete search,and only used CiteSpace software for the analysis,which does not preclude using other analysis software to reach different conclusions.Most of the studies are in quantitative approaches.Therefore,performing qualitative studies to assess the quality of life of PD patients is recommended.
