Extraction of Astragalus Polysaccharides and Ganoderma lucidum Mycelia Polysaccharides and Their in Vitro Antioxidative Effects
2023-02-21HongpingLINYonglinHUANG
Hongping LIN, Yonglin HUANG
College of Life Science and Technology, Lingnan Normal University, Zhanjiang 524048, China
Abstract [Objectives]To explore the extraction and in vitro antioxidant effects of astragalus polysaccharides(APS)and Ganoderma lucidum mycelia polysaccharides(GLMPS).[Methods]By studying the polysaccharides of the herbal medicinal material Astragalus membranaceus and the fungal medicinal material Ganoderma lucidum mycelia, two polysaccharides were mixed according to different proportions and concentrations by using the principle of traditional Chinese medicine compound combination.The effect of polysaccharides on the scavenging ability of hydroxyl radical system was determined by salicylic acid method.[Results]When the compound ratios of GLMPS and APS were 1∶1, 1∶4, 1∶5, 4∶1, and 5∶1, the scavenging effect of compound polysaccharides was better than that of single-component polysaccharides, and with the increase of concentration, the scavenging effect increased.When the ratio of GLMPS and APS was 5∶1, the hydroxyl radical scavenging rate of the compound polysaccharide reached 59.77%, which was 18.72% higher than that of single GLMPS and 28.58% higher than that of single APS.The scavenging effect of compound polysaccharide is closely related to the compound ratio and concentration.[Conclusions]APS and GLMPS can obtain better hydroxyl radical scavenging ability than single-component polysaccharides through compounding in appropriate proportions.In addition, within a suitable concentration range, as the concentration increases, the scavenging ability also increases.
Key words Astragalus polysaccharides(APS), Ganoderma lucidum mycelia polysaccharides(GLMPS), Compound polysaccharide, Hydroxyl radical scavenging rate
1 Introduction
Astragalusmembranaceusis a famous traditional Chinese medicinal material in China.It is believed in traditional Chinese medicine that it has the effects of nourishing qi and securing the exterior, inducing diuresis to alleviate edema, and expelling pus.Its active components are widely used in lowering blood pressure, protecting the liver, anti-tumor, regulating blood sugar, enhancing the body’s immune function, and protecting the cardiovascular system[1-2].Ganodermalucidum, known as Ruicao(auspicious herb)in ancient times, has the functions of reinforcing the healthy qi and strengthening the body resistance.It is a traditional Chinese precious fungi medicinal material, and widely used in the medical field.In recent years, many scholars at home and abroad have proposed thatG.lucidumpolysaccharide has the effects of scavenging free radicals in the body, anti-oxidation, regulating immunity, anti-tumor, anti-aging, improving memory, inhibiting thrombosis, lowering blood sugar and protecting the liver[3-5].
Polysaccharides are the key to making medicinal materials play a therapeutic role, and are important active substances in medicinal materials.In this study, we used the principle of compound combination in traditional Chinese medicine prescriptions to explore the antioxidant effect of compound plant medicinal material APS and microbial medicinal material GLMPSinvitro, and provide a basis for further exploring the development and application of compound polysaccharides from a new perspective.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 MaterialsGanodermalucidummycelium(GLM)was provided by the microbiological laboratory of College of Life Science and Technology in Lingnan Normal University, and Astragalus decoction pieces were purchased from Wal-Mart Supermarket, Chikan District in Zhanjiang City.
2.2 Methods
2.2.1Preparation of GLMPS.(i)Activation of GLM.In a sterile ultra-clean workbench, a small hole with a diameter of about 1 cm was punched in the center of the PDA plate culture medium with a puncher, and a pure GLM block with a diameter of about 0.5 cm was placed in the center of the hole, cultured statically in a constant temperature incubator at 28 ℃ for 5 d.
(ii)GLM liquid fermentation culture.The GLM activated by the PDA plate medium and cultured for 5 d has covered the entire plate, and it is placed in the ultra-clean workbench together with the liquid medium that has been sterilized and cooled to room temperature.A mycelium block with a diameter of 0.5 cm was taken with a puncher at the edge of the GLM colony and inoculated into 100 mL of liquid medium.After inoculation, the liquid medium was placed in a constant temperature culture shaker protected from light, and the setting conditions were 28 ℃ and 160 r/min for 8 d of dark culture.After 8 d of liquid fermentation, it was found that the culture medium was clear and transparent, the mycelium balls were large and full, and the surface was thorny, indicating that the fermentation was good and there was no contamination from bacteria.
(ii)Extraction of GLMPS.The mycelial balls were obtained by filtering with gauze.After the mycelial balls were crushed by a soymilk machine, they were extracted with hot water, and the ratio of solid to liquid was adjusted to 1∶10.They were boiled and extracted in a water bath at 85 ℃ for 2 h, and repeated twice[6].The supernatant obtained from the two extractions was concentrated to a small volume using a rotary evaporator for the next step of alcohol precipitation.We modified the method of Tian Shuyuetal.[7], and used the alcohol precipitation method, slowly added absolute ethanol with a volume ratio of 1∶3 to the supernatant, and stirred while adding, fully dissolved the impurities in ethanol, placed in a refrigerator at 4 ℃ for precipitation for 10-12 h, and extracted the crude polysaccharide precipitate in GLM cells.After the GLM culture filtrate was concentrated to a small volume by a rotary evaporator, the GLM extracellular crude polysaccharide precipitate was extracted by the same operation as above.The obtained precipitates were combined, centrifuged at 4 500 r/min for 10 min, and the excess ethanol was poured off carefully, and dried at low temperature.Dissolved the precipitate with hot water and cooled down.Using the Sevag method, adjusted the volume ratio of n-butanol: chloroform: the polysaccharide solution to 1∶4∶16, fully shook for 30 min, centrifuged at 5 000 r/min for 10 min in a high-speed centrifuge, took the water phase and retained it, discarded the central protein layer and chloroform phase, repeated the above steps 5 times until no protein layer in the center[8].Using the alcohol precipitation method, added absolute ethanol with a volume ratio of 1∶3 to the obtained aqueous phase to precipitate protein-depleted GLMPS, dried at low temperature, sealed and stored at-3 ℃.
(iv)Process flow: Mycelium ball pulverizing → hot water extraction → supernatant and culture filtrate concentration →alcohol precipitation→ low temperature drying → hot water dissolving and cooling → Sevag method for protein removal→ retaining water phase → alcohol precipitation → low temperature drying → total GLMPS.
2.2.2Preparation of APS.(i)Removal of total saponins of astragalus[9].The decoction pieces ofAstragalusmembranaceuswere crushed and dried, and 5 times the amount of 95% ethanol was added and heated to reflux for 2 h, and repeated twice.The solid was collected and washed with 75% ethanol until the eluent was colorless, evaporated the ethanol to dryness, and dried at low temperature for later use.
(ii)Extraction of APS.Using the hot water extraction method, took the driedA.membranaceuspowder, adjusted the ratio of solid to liquid to 1∶10, boiled and extracted in a water bath at 80 ℃ for 2 h, and repeated the extraction twice[10].The supernatant from the two extractions was concentrated to a small volume using a rotary evaporator.The alcohol precipitation method was used to make the total alcohol content to 80%, and the precipitate was placed in a refrigerator at 4 ℃ for 10-12 h to obtain the crude polysaccharide precipitate ofA.membranaceus, which was centrifuged at 4 500 r/min for 10 min, then the excess ethanol was poured off carefully, and dried at low temperature, dissolved in hot water and cooled to room temperature, used the Sevag method, according to the ratio of polysaccharide solution∶Sevag reagent=5∶1, fully shook for 30 min, centrifuged at 5 000 r/min in a high-speed centrifuge for 10 min, took the water phase and retained it, discarded the central protein layer and chloroform phase, repeated the above steps 6 times until no protein layer in the center[11].Using the alcohol precipitation method, alcohol adjustment degree of the obtained water phase was 80%, and the obtained precipitate was protein-depleted APS, dried at low temperature, sealed and stored at-3 ℃.
(iii)Process flow:A.membranaceusdecoction pieces pulverizing and drying→heating and refluxing to remove total astragalus saponins→washing and drying→hot water extraction→alcohol precipitation→low temperature drying→hot water dissolving and cooling to room temperature→Sevag method to remove protein→retain water phase→alcohol precipitation→low temperature drying→APS.
2.2.3Determination of polysaccharide content.The polysaccharide content was determined by the phenol-concentrated sulfuric acid method[12].
2.2.4Preparation of standard curve: precisely weighed 100 mg of glucose with an electronic balance, shook up in a 100 mL volumetric flask, dissolved it to a constant volume, and obtained the glucose standard solution of 1.0 mg/mL, transferred to test tubes and added water to dilute to 0.02, 0.04, 0.06, 0.08 and 0.10 mg/mL, added 1 mL of 6% phenol reagent to each tube, shook evenly, slowly added 5 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid along the tube wall, shook up, let it stand to cool to room temperature, heated it in a water bath at 80 ℃ for 15 min, took it out, let it stand and cooled it for 15 min, and measured the absorbance at the wavelength of 490 nm, then took the distilled water as the blank control group to operate according to the above steps(Table 1).

Table 1 Reaction system for preparation of standard curve
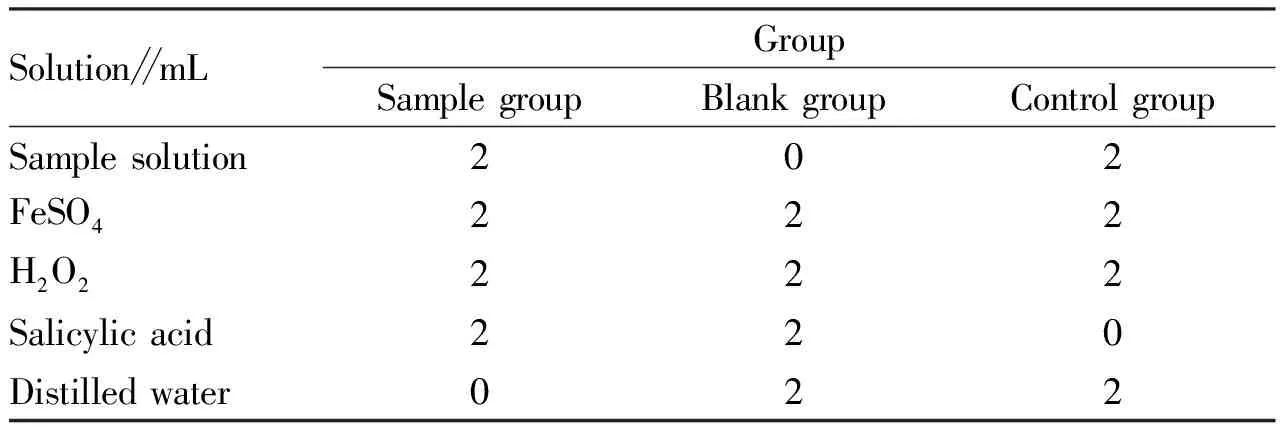
Table 2 Reaction system for determination of hydroxyl radical scavenging ability of sample polysaccharides
2.2.5Determination of sample content: precisely weighed 25 mg of the extracted polysaccharides to be tested, dissolved them in distilled water, and set the volume to a 100 mL volumetric flask.Separately pipetted 1 mL into test tubes, and measured the absorbance value of the solution according to the determination method in the standard curve with the sample liquid as the reference solution, and calculated the polysaccharide concentration of the solution to be tested according to the regression equation.
2.3 Compounding methodSeparately weighed 100 mg of GLMPS and APS, dissolved them in distilled water to a 100 mL volumetric flask, and shook up to obtain two 1.0 mg/mL sample solutions.Under the premise that the total concentration is 1.0 mg/mL, GLMPS and APS were compounded at the ratio of 1∶1, 1∶2, 1∶3, 1∶4, 1∶5, 2∶1, 3∶1, 4∶1, and 5∶1[1].The compounded sample was diluted to 0.1-0.9 mg/mL by adding distilled water in a gradient, and an appropriate amount of sample was taken according to the requirements of the Fenton reaction system for the determination of the hydroxyl radical scavenging ability.
2.4 Determination of the ability of polysaccharides to scavenge hydroxyl radicalsUsing Fenton reaction system: took several 10 mL test tubes and add 2 mL sample solution, 2 mL 6 mmol/L FeSO4and 2 mL 6 mmol/L H2O2in sequence, mixed well and let stand for 20 min to start the reaction.Then, added 2 mL of 6 mmol/L salicylic acid-ethanol solution to each test tube, mixed well, and let stand at 37 ℃ for 30 min.For the control group, the same volume of distilled water was used to replace the salicylic acid-ethanol solution, and for the blank group, the same volume of distilled water was used to replace the sample solution.Took the supernatant at 510 nm to measure the absorbance value of the sample group asAS, the absorbance value of the control group asAC, and the absorbance value of the blank group asA0.Then, calculated using the formula(1).
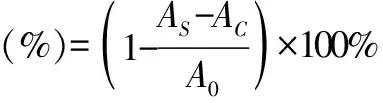
(1)
whereASis the average absorbance value of the sample group,ACis the average absorbance value of the control group, andA0is the average absorbance value of the blank group.
2.5 Statistical analysisAfter sorting out all the data, taking the type of polysaccharide as factor A and the concentration of poly-saccharide as factor B, a two-factor analysis of variance with a fixed model was established using SPSS.According to the obtained results of variance analysis, multiple comparisons were performed on the data of each group, and the clearance rate of each group of data was tested for significance, so as to further conduct comparative analysis on the ability of polysaccharides to scavenge free radicalsinvitro.
3 Results and analysis
3.1 Glucose standard curveThe glucose standard curve is shown in Fig.1.The regression equation of the standard curve for the determination of glucose by the phenol-concentrated sulfuric acid method is:y=9.118 6x+0.176 9,R2=0.995 8.
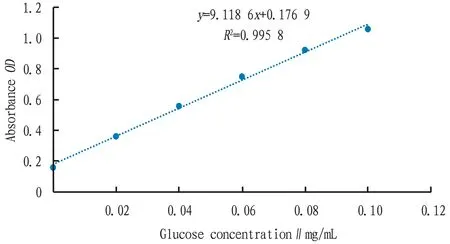
Fig.1 Glucose standard curve
3.2 Analysis of the yield and content determination results of polysaccharides from different sourcesFrom 2 500 mL of GLM culture fluid and its GLM, 3.026 g of total GLM polysaccharides were obtained and the calculated GLMPS yield was 1.210 4 mg/mL; 4.021 g of crude APS was extracted from 100 g ofA.membranaceusdried powder, and the calculated yield ofA.membranaceuscrude polysaccharide was 4.021%.The purity of GLMPS calculated by the glucose standard curve regression equation was 85.27%, and the purity of APS was calculated to be 51.64%.It can be seen that the purity of the two polysaccharides was relatively high, which could be analyzed and determined in the next step of hydroxyl radical scavenging ability.
3.3 Analysis of the ability of polysaccharides to scavenge hydroxyl radicalsThe hydroxyl radical scavenging ability was determined by Fenton’s method[13].The obtained data were counted, taking the concentration(mg/mL)as the abscissa and the hydroxyl radical scavenging rate(%)as the ordinate, the line graph was plotted(Fig.2).
As indicated in Fig.2-3, single GLMPS, single APS and various compound polysaccharides at different ratios all had obvious hydroxyl radical scavenging ability, which was positively correlated with the concentration.At low concentration(less than 0.5 mg/mL), single APS had higher hydroxyl radical scavenging rate than single GLMP; at high concentration(greater than 0.7 mg/mL), the hydroxyl radical scavenging rate was lower than that of the single GLMPS; when the concentration was 1.0 mg/mL, the hydro-xyl radical scavenging rate of both reached the maximum.The hydroxyl radical scavenging rate of single GLMPS at this concentration was 41.05%, which was 9.86% higher than that of single APS.
From Fig.2-3, it can be seen that the hydroxyl radical scavenging ability of most compound polysaccharides was significantly better than that of single polysaccharides.When the compound ratio of the two polysaccharides was 1∶1, 1∶4, 1∶5, 4∶1, and 5∶1, the compound polysaccharide shows a better effect of scavenging hydroxyl radicals, and the highest scavenging rate was 5%-18% higher than that of single-component polysaccharides.Specifically, when the concentration was 1.0 mg/mL and the compound ratio of polysaccharides was 5∶1, the hydroxyl radical scavenging effect was the best, and the highest scavenging rate reached 59.77%, which was 18.72% higher than the single GLMPS and 28.58% higher than the single APS, showing a good synergistic effect.When the compound ratio of the two polysaccharides was 1∶2, 1∶3, and 2∶1, the maximum hydroxyl radical scavenging rate was only 1.40%-3.62% higher than that of the single APS, which was lower than the maximum hydroxyl free radical of the single GLMPS.At low concentrations(less than 0.6 mg/mL), the hydroxyl radical scavenging rates of these three compound ratios of polysaccharides were lower than those of the two single polysaccharides, and no synergistic effect was shown.In addition, when the compound ratio of the two polysaccharides was 3∶1, the hydroxyl radical scavenging rate was lower than that of the single-component polysaccharide at a concentration of less than 0.7 mg/mL, and no obvious synergistic effect was shown.However, when the concentration was 1.0 mg/mL, the scavenging rate of the compound polysaccharide was higher than that of the single-component polysaccharide.
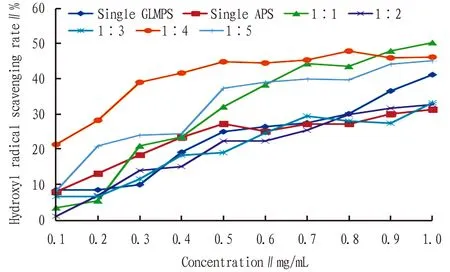
Note: The concentration ratios were the concentration ratios of GLMPS and APS.The same below.
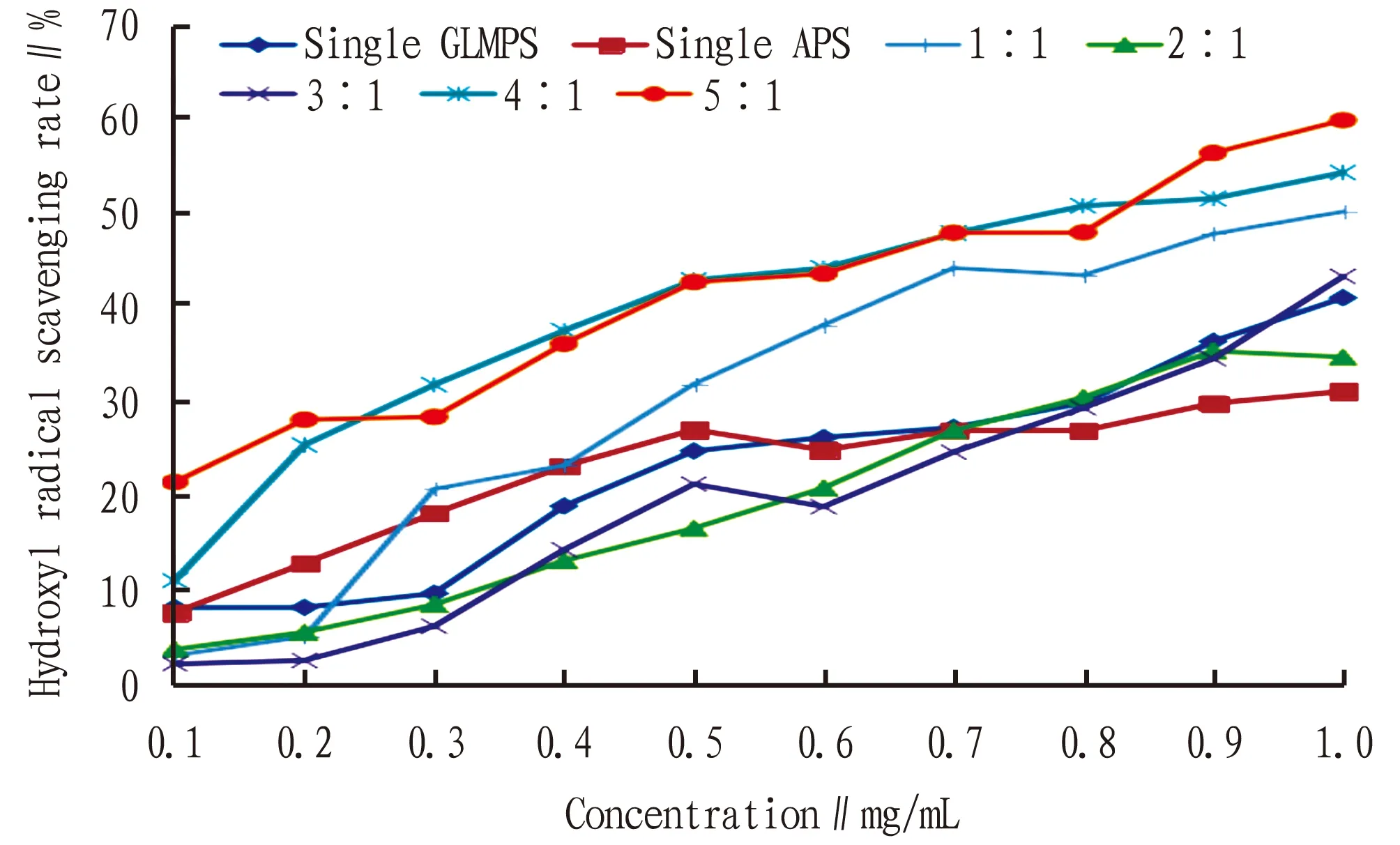
Fig.3 Effects of different ratios and concentrations of compound polysaccharide on scavenging hydroxyl radicals
The hydroxyl radical scavenging rates of different types of polysaccharides at different concentrations were summed and average value was calculated.Taking the polysaccharide type as the abscissa and the average hydroxyl radical scavenging rate(%)as the ordinate, a block diagram was plotted(Fig.4).As shown in Fig.4, when the compounding ratio of the two polysaccharides was 5∶1, the average scavenging rate was the highest, reaching 41.28%.Specifically, the compound ratios of 1∶4, 4∶1 and 5∶1 separately had an average scavenging rate of 40.38%, 39.78% and 41.28%, all were higher than 39%, indicating that the compound effect of polysaccharides under these three compound ratios was relatively better, and the scavenging effect of hydroxyl free radicals was better.By comparison, when the compounding ratios were 1∶2, 1∶3, 2∶1 and 3∶1, the average scavenging rate was lower than that of single-component polysaccharides, indicating that the compounding effect of polysaccharides under these four compound ratios was relatively poor.
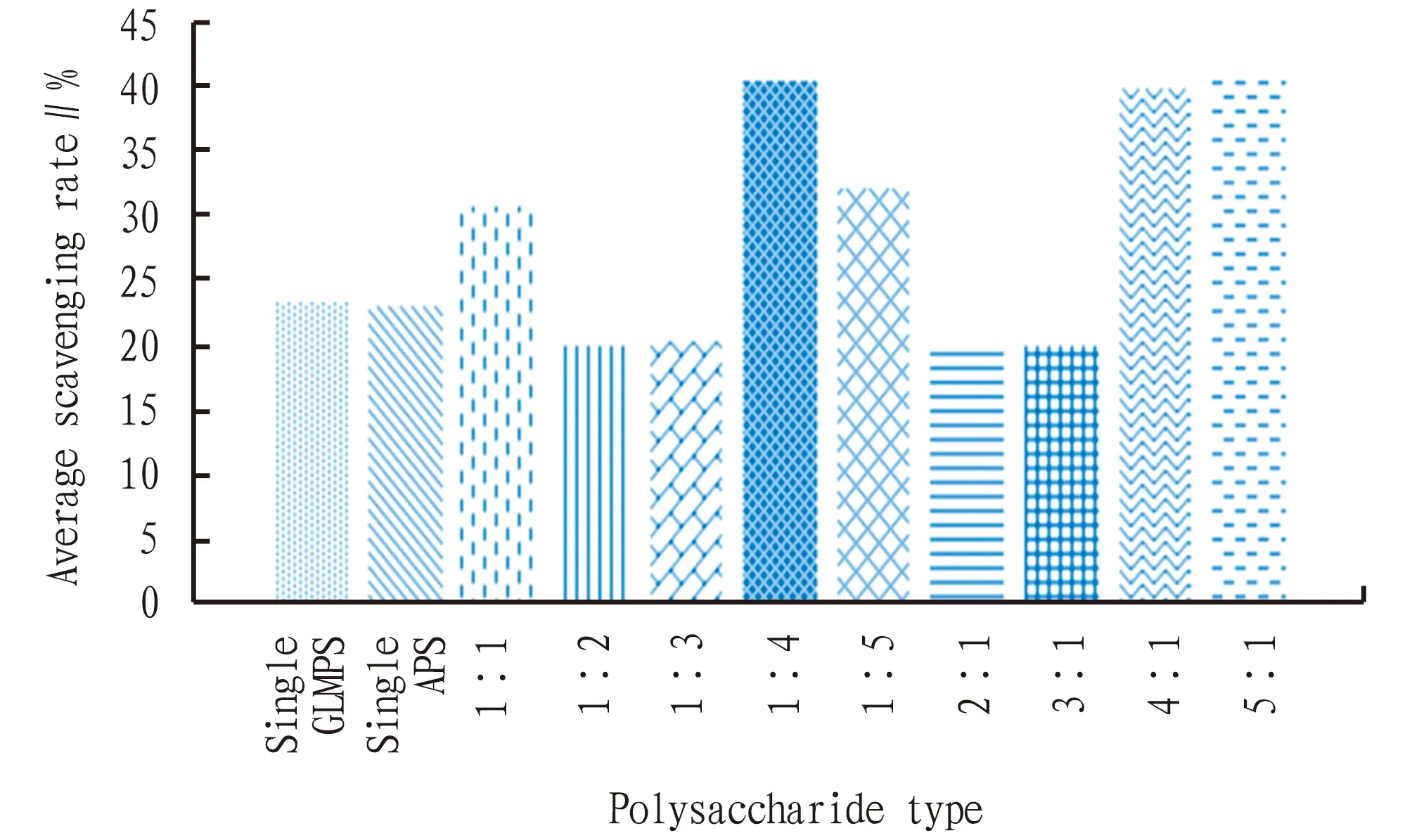
Fig.4 Average scavenging rate of different polysaccharide types
3.4 Statistical analysisThrough SPSS two-factor analysis of variance, multiple comparisons were made to the data of each group, and the scavenging rate of the data in each group was tested for significance.The results showed that among the 9 ratios of compound polysaccharide, the hydroxyl radical scavenging rate of the 5 ratio combinations was significantly higher than that of the single-component polysaccharide, and the difference was significant(P<0.05).We selected two groups of combinations(1∶1 and 4∶1)for analysis.The analysis results were shown in Table 3-5.
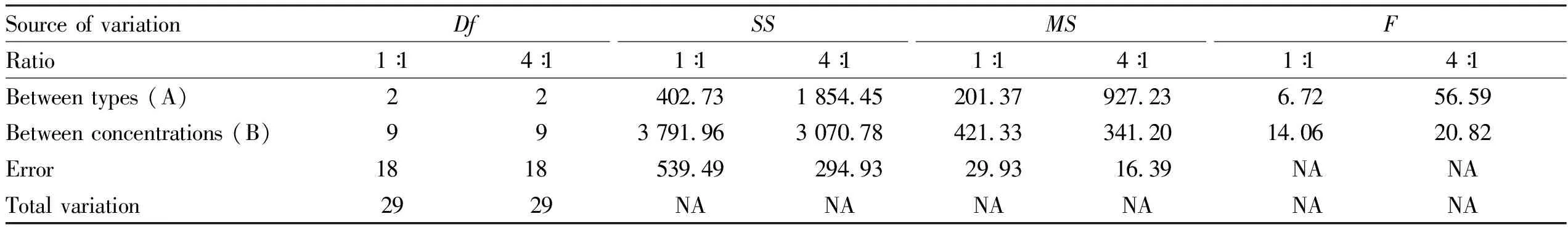
Table 3 Analysis of variance of effects of two factors on the combination of GLM and APS(1∶1 and 4∶1)on the scavenging rate of hydroxyl radicals

Table 4 Significance difference analysis of scavenging rate of different concentrations of GLM and APS(1∶1 and 4∶1)combinations
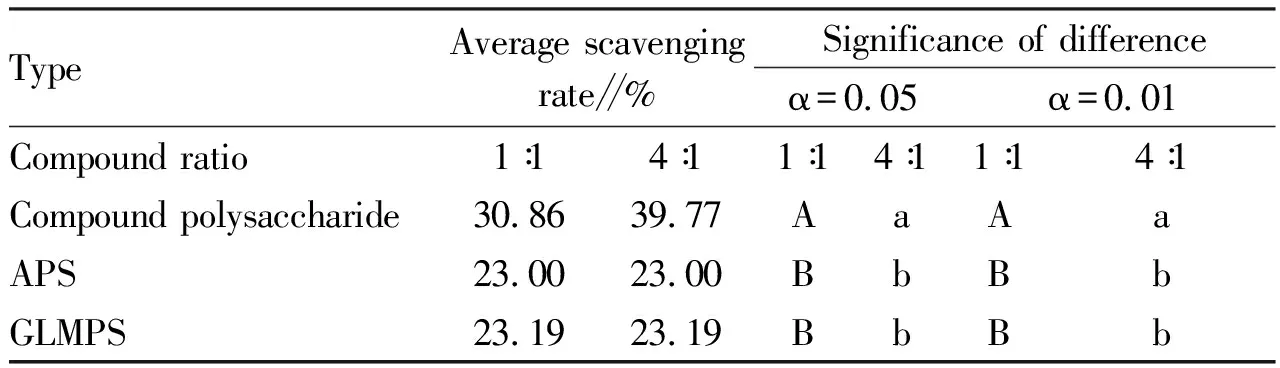
Table 5 Significance difference analysis of scavenging rate of different types of GLM and APS(1∶1 and 4∶1)combinations
4 Discussion
Through the research on the hydroxyl radical scavenging ability of compoundA.membranaceusand GLMPS, the results show that APS and GLMPS can obtain better hydroxyl radical scavenging ability than single-component polysaccharides through compounding in appropriate proportions, and within an appropriate concentration range, the scavenging ability will also increase with the increase of concentration.The research by Yu Chongetal.[14]showed that the scavenging rate of five compound fungal polysaccharides for hydroxyl radicals was 12.7%, 14.3%, and 17.6% higher than that of single-component polysaccharides at low, medium, and high concentrations.Wang Hongxunetal.[15]showed that compoundLyciumbarbarumGLMPS had a 4∶1 ratio and a concentration of 0.2 mg/mL in scavenging hydroxyl radicals, which was 13% higher than that of single-component polysaccharides.The research of Yin Yanlietal.[16]showed that the hydroxyl radical scavenging ability of compoundLentinusedodesmycelia polysaccharide GLMPS ratio of 1∶1 was more than 50% higher than that of single polysaccharide, which is consistent with findings of this study.In the case of single-component polysaccharides, although it shows good hydroxyl radical scavenging ability, it is slightly weaker than compound polysaccharide.It may be because polysaccharides undergo compounding, and at a certain ratio and concentration, the spatial conformation of polysaccharides changes, from a coiled conformation to a helical conformation.In this process, the hydrogen atoms on the polysaccharide hydrocarbon chains are quickly combined with hydroxyl radicals to generate water, which interrupts the peroxidation chain reaction of hydroxyl radicals, thus obtaining a good hydroxyl radical scavenging effect.Studies have shown that the structure of polysaccharides will affect the efficacy of polysaccharides to a certain extent.When the overall conformation of polysaccharides changes, the biological activity of polysaccharides will also change[17].G.lucidumandA.membranaceus, as well-known traditional Chinese medicinal materials in China, both have the effects of nourishing qi and securing the exterior.It is feasible to compound the two polysaccharides by using the principle of traditional Chinese medicine compound combination, so as to improve the biological activity of the polysaccharides.
AboutKIT
The Royal Tropical Institute(KIT)in Amsterdam is an independent centre of knowledge and expertise in the areas of international and intercultural cooperation, operating at the interface between theory and practice and between policy and implementation.The Institute contributes to sustainable development, poverty alleviation and cultural preservation and exchange.
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Research Status of Land Use and Carbon Emissions in China: A Visual Analysis Based on CiteSpace
- High-quality Development Evaluation System of Water Parks
- Recommendations for Using Crop Straws to Produce Organic Ferti-lizers in Liaoning Province
- Volatile Components and Antitumor Activity of Ganoderma lucidum Spore Oil and Its Molecular Distillation Components
- Evaluation of Uncertainty for Determination of Stevioside Content in Fermented Milk by HPLC
- Technique for Ecological Pond Breeding of Charybdis japonica
