Effects of the Huangkui capsule (黄葵胶囊) on chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and Meta-analysis
2023-02-15LIWeiXIAPingSUNWeiZHAOJingLIUQiongGENGLianyiZHOUYaoGAOKun
LI Wei,XIA Ping,SUN Wei,ZHAO Jing,LIU Qiong,GENG Lianyi,ZHOU Yao,GAO Kun
LI Wei,SUN Wei,ZHAO Jing,LIU Qiong,GENG Lianyi,GAO Kun,Division of Nephrology,Jiangsu Province Hospital of Chinese Medicine,Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine,Nanjing 210029,China
XIA Ping,the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University,Suzhou 215000,China
ZHOU Yao,Laboratory of Clinical and Experimental Pathology,Department of Pathophysiology,Xuzhou Medical University,Xuzhou 221009,China
Abstract OBJECTIVE: To collect data and investigate the effects of Huangkui capsule (黄葵胶囊,HKC) on chronic kidney disease (CKD).METHODS: PubMed,Embase,Cochrane Library,and three Chinese databases (China National Knowledge Infrastructure,Wanfang,and China Science and Technology Journal Database) were searched for articles published until October 2020.Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of HKCs used for treating CKD were reviewed.Data were organized and analyzed using RevMan 5.3 software.RESULTS: HKC significantly lowered the blood urea nitrogen (BUN) level [mean difference (MD)=-2.26;95%confidence interval (CI),-2.91 to -1.61],serum creatinine level (MD=-17.45;95% CI,-22.29 to -12.60),and 24-h urine protein content (MD=-0.73;95%CI,-1.00 to -0.46) and improved the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) (MD=10.69;95% CI,5.57 to 15.81)and serum albumin level (MD=2.20;95% CI,0.49 to 3.90).CONCLUSIONS: Our findings show that HKC could lower the BUN level,serum creatinine level,and 24-h urine protein content.HKC also improved GFR and serum albumin levels.However,high-quality RCTs in other countries with larger sample sizes are warranted to confirm these findings.
Keywords: renal insufficiency,chronic;Huangkui capsule;blood urea nitrogen;glomerular filtration rate;systematic review;Meta-analysis
1.INTRODUCTION
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a common and underrecognized condition.It can be defined as renal damage for at least 3 months,presenting as structural damage or functional abnormalities of the kidney with or without a decreased glomerular filtration rate (GFR).According to an epidemiological investigation,the global prevalence of CKD is approximate 8%-16%.1CKD poses a potential danger of cardiovascular events and cerebrovascular disease risk factors,2garnering wide attention in both China and the world.China has an estimated 10.8% of adults with CKD,3causing serious medical and economic burdens on the patients' families.Therefore,the effective treatment of CKD is a major topic for physicians.
Although many CKD prevention and control strategies have been studied in recent years,preventing the progression of CKD has been difficult with medical treatment.Hormonal and cytotoxic drugs are widely used to treat CKD in the early stages,despite adverse reactions.In the end stage,dialysis or kidney transplantation is performed to save the patient's life.Traditionally,the Chinese herb Huangshukuihua (FlosAbelmoschi Manihot) (AM) has been widely used to treat wet-heat syndrome,which is associated with inflammation.Currently,Chinese nephrologists have found that AM can lower urinary protein levels in patients with CKD.Huangkui capsule (黄葵胶囊,HKC),which is the commercial name of a pharmaceutical preparation of the extract of the AM flower,proved to be clinically efficient in treating nephritis,4CKD,5and diabetic kidney disease.6
In 2009,Laiet al.quantified the flavonoids of HKCby using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)and identified five flavonoids,hyperoside,myricetin,quercetin,and isoquercitrin.7and rutin is the main pharmacological and biologically active ingredient.However,our research found that the total flavonoids of HKC are better than monomers,suggesting the multitarget efficacy of HKC.Pharmacological studies have shown that the effects of AM may be related to the suppression of immune response and inflammatory damage,improvement of renal fibrosis,and anticoagulant effects.8Zhouet al9also reported that AM protects podocytes and reduces proteinuria.Our team’s previous research found that HKC can improve proteinuria in rats with adriamycin-induced nephropathy,10,11and has a significant protective effect on renal tubules.
However,there is still a lack of unequivocal evidence derived from a systematic review of the clinical efficacy of HKC.Therefore,this Meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the efficacy of HKC for CKD to provide a reference for nephrologists and to understand the drugs better.
2.MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1.Search strategy
A systematic literature search was performed using PubMed,Embase,Cochrane Library,and three Chinese databases (China National Knowledge Infrastructure,Wanfang,and Value in Paper) up to October 1,2020,using the following keywords: (Huangkui capsule OR Huang Kui OR Jiahuapian OR Abelmoschus Manihot)AND (CKD OR chronic kidney disease OR kidney diseases OR chronic kidney failure OR kidney inefficiency).
If necessary,information was missing,the first authors of these papers were contacted to obtain complete information.The literature was searched on October 1,2020,and papers published before that date were included.
2.2.Inclusion criteria
The inclusion criteria were as follows: (a) randomized controlled trial (RCT) of HKC to treat CKD published in China or abroad before October 1,2020;(b)RCTs that included patients diagnosed with CKD based on guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of CKD;(c)current intake of HKC alone or combined with other drugs for inclusion in the treatment group and placebo or conventional Western medicine,excluding any form of HKC,for inclusion in the control group;and (d)availability of at least one of the following measurements:blood urea nitrogen (BUN),serum creatinine (Scr),GFR,or 24-h urine protein.
2.3.Exclusion criteria
The exclusion criteria were as follows: (a) the diagnosis of CKD not conforming to the diagnostic standard;(b)renal damage caused by other reasons (some secondary kidney diseases,such as tumor-related kidney damage,kidney damage caused by autoimmune diseases,etc);(c)the use of proprietary Chinese medicine,including AM,in the control group;(d) the use of the unknown composition of Traditional Chinese Medicine in the treatment or control group;and (e) the lack of a control group or use of an incorrect statistical method.
2.4.Data extraction and processing
Data extraction was independently performed by two researchers.Disagreements were resolved by a third researcher.The basic information was extracted from each included article,including the name of the first author,year of publication,the number of subjects,sex,age,regions/countries,intervention method and dose,type of placebo,and duration of treatment.
2.5.Quality evaluation
This Meta-analysis was performed based on the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses statement for Meta-analysis of intervention studies.12
Two researchers independently evaluated the methodological quality in accordance with the standards of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions 5.1.0.12There were three possible answers for sequence generation,allocation concealment,blinding,incomplete data evaluation,selective result reporting,and evaluation of other sources of bias: “yes,”“no,” and “unclear.”
Disagreements between the two researchers were resolved through discussion or by a third researcher.Studies were evaluated using the software RevMan 5.3 software.
2.6.Statistical analysis
RevMan software (version 5.3) was used to estimate the effect of HKC.Consecutive variables for treatment efficacy are expressed as mean ± standard deviation and 95% confidence interval (CI).1
Heterogeneity was tested using χ2andI2tests.P< 0.10 in the homogeneous square test orI2> 50% was considered to indicate significant evidence of homogeneity among studies.In the presence of heterogeneity,we used a random-effects model to pool the data.Statistical significance was set atP≤ 0.05.To evaluate whether the overall effect was steady,a sensitivity analysis was performed by deleting one trial at a time,and the effect size was recalculated.Figure S1 illustrates this workflow.
3.RESULTS
3.1.Search results
A total of 669 articles (597 in Chinese and 72 in English)were retrieved using the search strategy.After excluding 326 duplicate articles,the titles,abstracts,and full texts of the remaining articles were read.Finally,13 qualified RCT articles were included in the study.Figure 1 shows the flowchart of the included and excluded studies.
Table 1 lists the characteristics of these 13 papers.All studies were performed in China,including a total of 863 patients,with 436 and 427 patients in the HKC and control groups,respectively.None of these studies reported adverse reactions to medical treatment.
3.2.Characteristics of studies included
All 13 articles were clinical RCTs in China.The intervention included HKC alone or combined with other medicines,except for the standard Western treatment.We included a total of 13 studies,two of which used Huangkui Capsules alone.Other clinical studies include Huangkui capsule+ARB or Huangkui capsule +Chinese patent medicine.To determine the effect of HKC on CKD,six studies were included with a followup duration of 56 d,while other studies showed a followup duration of 84 d.The details are presented in Table 1.
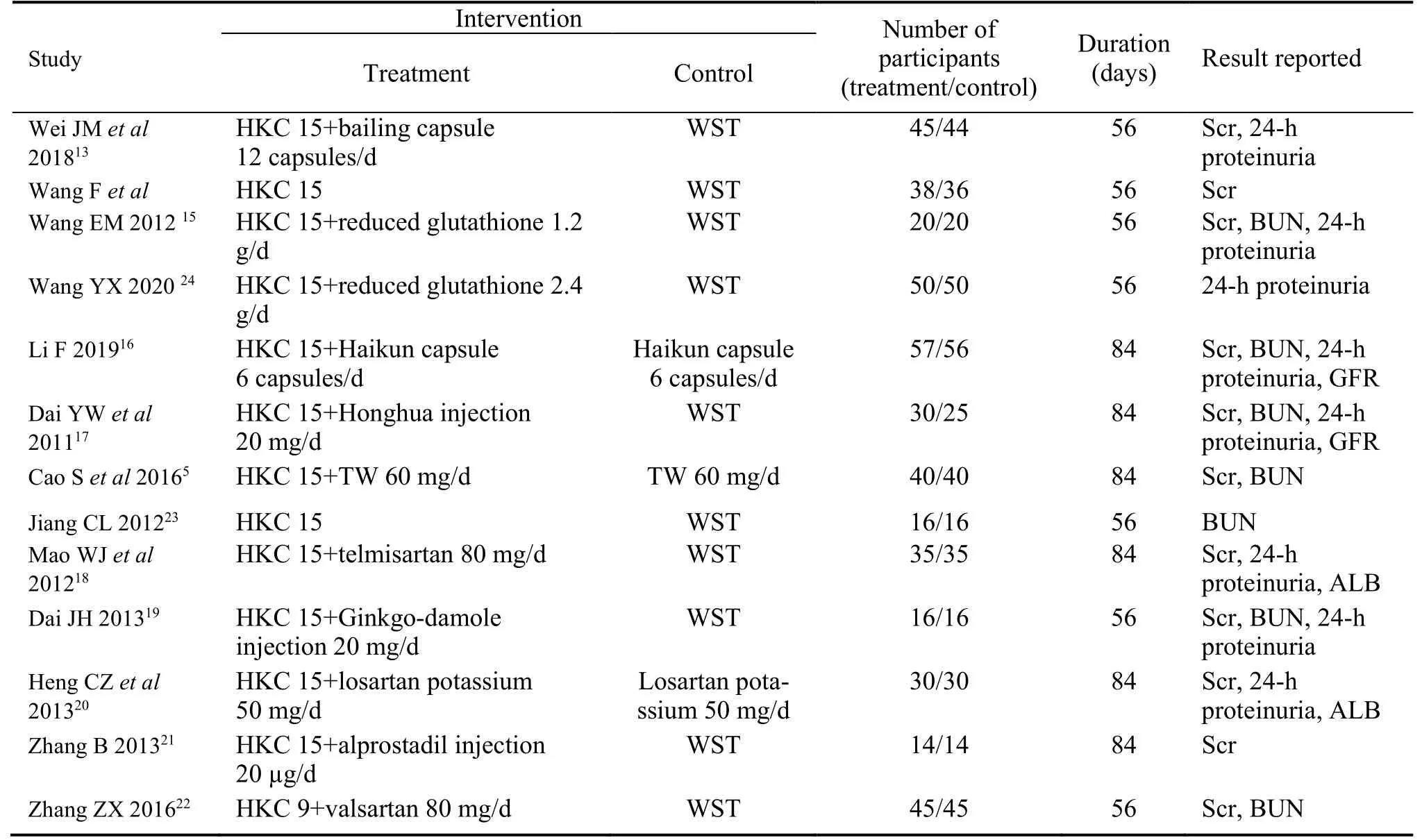
Table 1 Characteristics of included article
3.3.Risk-of-Bias assessment
For randomization,three studies described the methods and were deemed appropriate.Ten studies were described as randomized,but no methods have been described.None of the 13 studies mentioned the detailed methods of allocation concealment or used the doubleblinding method.All studies fully reported the results described in the method.No withdrawals or dropouts have been reported.Other risks of bias for the different diagnostic criteria were also assessed.All included studies showed a high-risk bias in at least one area(Figure 2A,2B).
3.4.SCR
A total of 11 RCTs evaluated the Scr of the experimental and control groups.5,13-22There were 370 patients in the experimental group and 353 patients in the control group.As shown in Figure 3A,these trials showed clinical heterogeneity (I2=68%,P=0.0005),so we used a random-effects model to analyze the data.Scr levels significantly reduced in the HKC group in 56 d (mean difference [MD]=-22.95;95%CI,-27.04 to -18.86;P < 0.000 01),in 84 d (MD=-13.10;95%CI,-18.37 to -7.84;P < 0.000 01),and overall (MD=-17.45;95%CI,-22.29 to -7.84;P < 0.000 01).
3.5.BUN
The mean change in BUN was calculated in seven studies,5,15-17,19,22,23and the pooled estimated mean changes in BUN were significantly reduced.The random-effects model was used to process the data because of the high heterogeneity (Figure 3B;I2=78%;P=0.0001).The BUN level was lower in the HKC group than in the control group (MD=-2.26;95%CI,-2.91 to -1.61;P=0.001).The subgroup analysis also showed that HKC had a marked effect on reducing BUN in both 56 and 84 d.
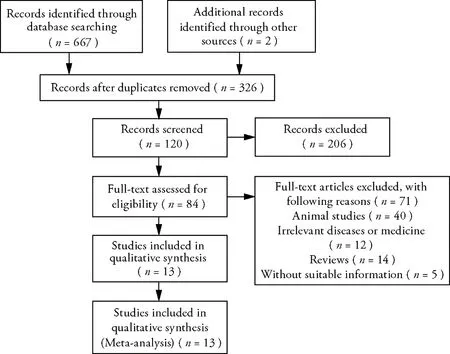
Figure 1 A flowchart of the characteristics of eligible articles
3.6.Quantification of 24-h urine protein
We pooled eight studies involving 474 participants who reported 24-h urine protein levels.13,15-20,24The 24-h urine protein decreased significantly (MD=-0.73;95%CI,-1.00 to -0.46;P< 0.000 01;Figure 3C).However,the statistical heterogeneity was high (I2=96%).There were also significant changes in subgroup studies (56 d:MD=-1.17,95%CI,-1.29 to -1.04,P< 0.000 01;84 d:MD=-0.38,95%CI,-0.43,-0.33,P< 0.000 01).
3.7.Serum albumin
Two RCTs involving 130 participants reported serum albumin levels as an outcome.18,20They demonstrated a significant difference in the estimated GFR between the groups (MD=2.20;95%CI,0.49 to 3.90;P< 0.000 01;Figure 3D).No evidence of statistical heterogeneity was found (I2=21%).
3.8.GFR
Two RCTs involving 135 participants reported the GFR as an outcome.5,17They demonstrated a significant difference in the estimated GFR between the groups (MD=10.69;95%CI,5.57 to 15.81;P< 0.000 01;Figure 3E).No evidence of statistical heterogeneity was found (I2=39%).
3.9.Publication bias
To detect possible publication bias,we analyzed the funnel plot of the 11 trials that compared HKC with standard Western medicine in terms of Scr and BUN.When Scr and BUN were pooled,a random-effects model was used.Figure 4 shows a funnel plot indicating the publication bias in the selected articles.
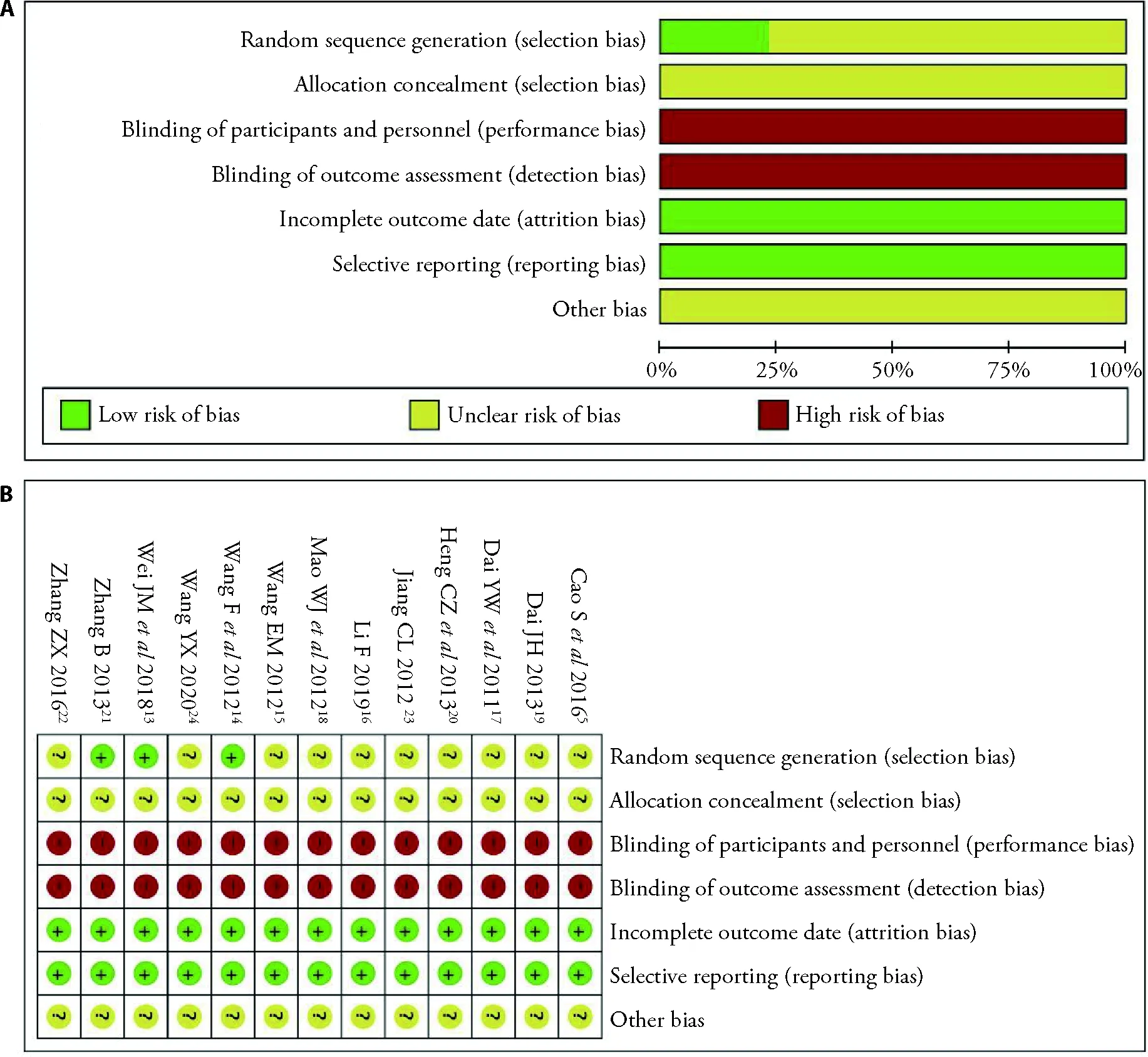
Figure 2 Risk of bias graph
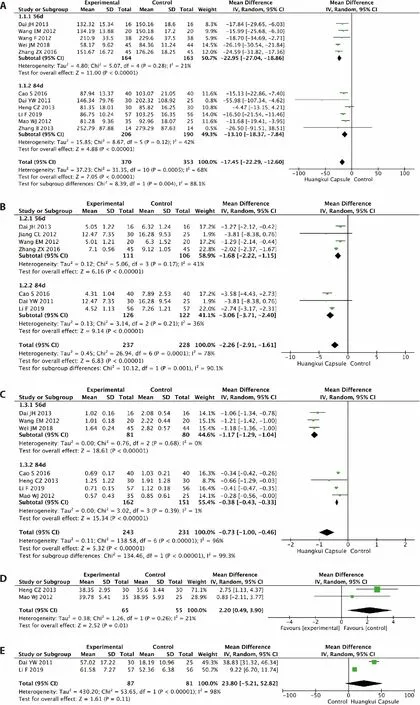
Figure 3 Results of the Meta-analysis of the efficacy of Huangkui capsule versus control group
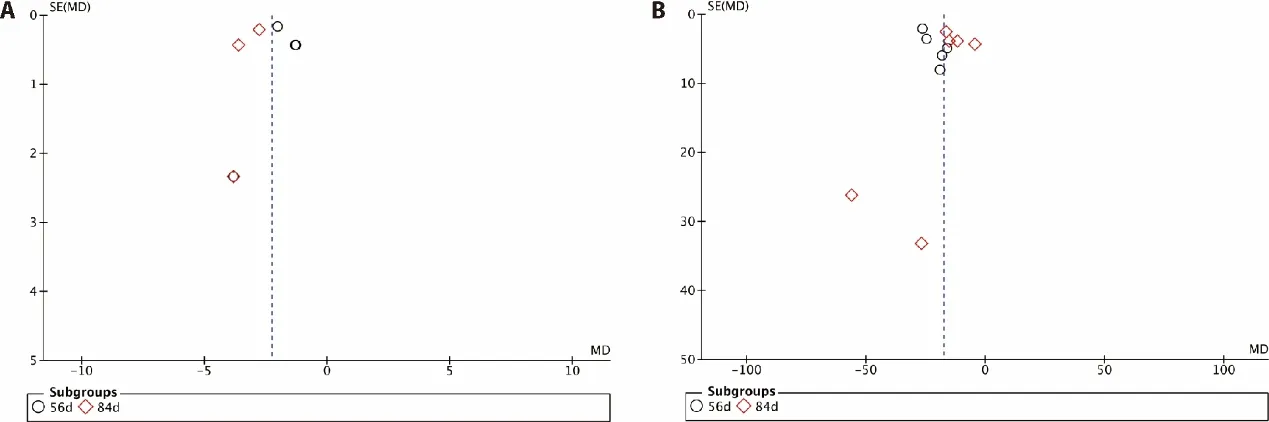
Figure 4 Funnel plot including studies
4.DISCUSSION
This review identified 13 RCTs involving 863 patients,with 436 and 427 patients in the HKC and control groups,respectively.Our research indicated that BUN,Scr,and 24-h urine protein levels were lower in the HKC group than in the control group.These data showed that HKC had a protective effect on renal function in patients with CKD.To reduce heterogeneity,we divided the cases into two subgroups.On days 56 and 84,HKC showed good effects.However,no studies have reported side effects;therefore,it is difficult to analyze adverse reactions.
Chinese medicine has a unique advantage in the prevention and treatment of CKD,which can effectively reduce BUN and Scr levels,protect the residual kidney,and promote kidney function.Huangshukuihua (Flos Abelmoschi Manihot)is the Chinese name of the AM flower.HKC,which is the commercial name of a pharmaceutical preparation of an extract of the AM flower,has been approved as a new class III drug in China by the State Food and Drug Administration to treat chronic glomerulonephritis.25,26In our previous study,HKC decreased proteinuria in rats with Adriamycin nephropathy.8,10,11Clinically,HKC can reduce proteinuria and delay renal failure.4It protects renal function by suppressing the immune response and inflammation,27improving renal fibrosis and protecting renal tubular epithelial cells.28,29According to the classic theory of Chinese Traditional Medicine,Huangshu-kuihua (Flos Abelmoschi Manihot) is mainly capable of clearing heat and dampness.Although there are many clinical studies on Huangkui capsules,there are very few studies comparing the therapeutic effects of Huangkui capsules on different TCM symptom patterns of CKD.We think this is the direction that should be studied in the future.CKD is a progressive disease.In the past decades,regardless of the underlying cause of kidney disease,the factors determining the rate of progression to end-stage kidney disease were urine protein level,initial degree of renal impairment,and blood pressure.HKC is wellknown among Chinese nephrologists because it can lower urine protein levels in patients.Its effectiveness in controlling proteinuria may be the reason why this treatment can improve kidney function.However,in recent years,HKCs have also effectively protected renal tubular cellsin vivoandin vitro.Further studies should be performed to elucidate the underlying mechanisms.Early interventions can prevent a progressive decline in kidney function and complications.Based on this meta-analysis,HKC may be a candidate treatment for early-stage CKD.This review has several limitations.First,although there were no restrictions on the language of publication in terms of the search strategy,all papers were written in Chinese and conducted in China.Therefore,due to publication restrictions,positional deviations should be considered.Most studies included in this retrospective analysis had methodological problems and potential risks of bias.Second,according to the Cochrane Collaboration's risk-of-bias tool criteria,most included RCTs were of poor quality,with missing information for allocation concealment,blinding,or intentional analysis.The total number of RCTs that only studied HKC was very small,so interventions in the treatment group were various across included studies,this does have a certain impact on the results.Third,why the effect of proteinuria treatment on day 56 is better than that on day 84? We have looked through many papers and have not found an answer.We believe that in future experimental design,we will go in-depth to search for potential causes.
Because of the possible limitations of this review,the effectiveness of the HKC requires further evidence for support.In conclusion,because the number of patients with CKD is growing every year,slowing down the development of CKD is still a crucial public health issue worldwide.Even in animal and clinical studies,HKC showed a marked effect on CKD progression,but there was no conclusive result for the treatment effect.HKC could lower the BUN level,serum creatinine level,and 24-h urine protein content.HKC also improved GFR and serum albumin levels.However,this conclusion should be carefully considered owing to the low quality of the included trials.
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine的其它文章
- Potential of natural medicines for treatment of osteoporosis: a narrative review
- Outlook on cultural inheritance and development
- Upholding fundamental principles and breaking new ground: ensuring positive efficacy and reaching new consensus
- General principle of high-quality academic development of traditional chinese medicine: “carrying on the essence,while pursuing innovations”
- Effects of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise combined with acupuncture on attention function of mentally-retarded adolescents: a randomised controlled trial
- Reveal the mechanisms of prescriptions for liver cancer' treatment based on two illustrious senior TCM physicians
