Umbilical displacement:a mini review
2023-01-21MahboobehSalmanianFatanehHashemDabaghian
Mahboobeh Salmanian,Fataneh Hashem-Dabaghian
1School of Traditional Medicine, Iran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran 1114733311, Iran.2Department of Traditional Medicine, Institute for Studies in Medical History,Persian and Complementary Medicine,School of Persian Medicine,Iran University of Medical Sciences,Tehran 1145847111,Iran.
Abstract Background: Umbilical displacement is a known disorder in folk medicine of different cultures.The various causes, clinical signs and symptoms are attributed to this disorder and different diagnostic and therapeutic methods are mentioned.Methods:To follow the aim of the study, Persian medicine literature, Google Scholar, Google,PubMed, Scopus and Web of Science were searched with no limit of the publication date and the article type (original papers and literature reviews).The searched terms were Navel, Umbilicus and other synonyms in Persian, Turkish, Russian, German, Chinese and Indian language, Dislocation,Sliding, Displacement, Deviation, Falling, Ptosis, Folk medicine and combination of these words.We also corresponded with several experts in traditional medicine via LinkedIn.All available descriptive evidence related to umbilical displacement was retrieved, and the contents were presented as categories including the disorder name, attributed signs and symptoms, and the diagnostic and therapeutic methods.Results: This disorder is called“Taharok-e-Sorre” in Persian medicine, “Nawikkatin” in Erbil (Iraq), “Dharan or Nabhi Sarakna”in Hindi,“Göbek düşmesi”in Turkish,Bēn tún in Chinese and“Cirro”in the people of Mayan community and Spanish, and “смещен пупoк”in the folk medicine of the Kurgan Bashqir.Hard work, pregnancy, childbirth, fear, lifting heavy objects, rapid and sudden movements, trauma or fall and slipping of the foot are said to be causes of umbilical displacement.Umbilical displacement is associated with several symptoms such as diarrhea,constipation, abdominal pain, anorexia, anxiety, and depression.Conclusion: In this mini-review,umbilical displacement was expressed from the viewpoint of different cultures.New cases of umbilical displacement has been reported in new articles,and the pathology of umbilical displacement has been explained from the perspective of Persian medicine.
Keywords:umbilical displacement; Persian medicine; navel; peritoneal adhesion
Background
There are numerous diagnostic and therapeutic conceptual frameworks in traditional and folk medicine, which differ from conventional or academic medicine[1].Considering the popularity of traditional medicine in different countries,these differences should be evaluated, explained, and introduced to the conventional medicine practitioners.One of these concepts is “umbilical displacement” (UD)which means that the umbilicus is not in a proper position and is slippery, drooping, or knotted.It is a well-known subject in the folk medicine of different countries; however, it has been less discussed in the textbooks of traditional medicine and is not known in academic medicine.This disorder is called “Taharok-e-Sorre” in Persian medicine (PM), and is known in some other cultures with different terms [2].A quick Google search with term “navel displacement” or its synonyms in different languages such as “Nabhi Talna”, “Göbek düşmesi”, “Dharan” or “Nabhi Sarakna” shows, that this disorder is not uncommon in traditional medicine of other countries.
The abdominal wall is formed of the skin, the superficial fascia and fat, the superficial sheath of the abdominal muscle, the rectus abdominis, the deep layer of the sheath, the subperitoneal connective tissue, and the peritoneum, respectively [3].Due to the special position of the umbilicus, it is connected to the muscles of the abdominal wall, diaphragm and pelvis through the linea alba.It connects directly to the bladder through the median and lateral umbilicus ligaments and is connected to the liver via the round ligament of the liver (ligamentum teres hepatis).The peritoneum is located behind the umbilicus, and connects it to the gastrointestinal tract and genitourinary system [4, 5].
This regularity and integrity are so much important in the PM, and any distortions of the umbilicus may cause some signs and symptoms,especially in the abdominal region.There is no much information about the signs and symptoms of UD in PM books, but this disorder is very commonly seen in daily clinical work.Although there is no clinical evidence for the efficacy of the intervention in UD, but PM practitioners have reported many cases, which umbilicus manipulation could eliminate many signs and symptoms of patients such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, anxiety, and even infertility.
Since this disorder is unknown in conventional medicine, this study was conducted to introduce “UD” through review the available evidence about this disorder, its accompanying signs and symptoms and the recommended methods of UD management in different countries(Table 1) [6–19].
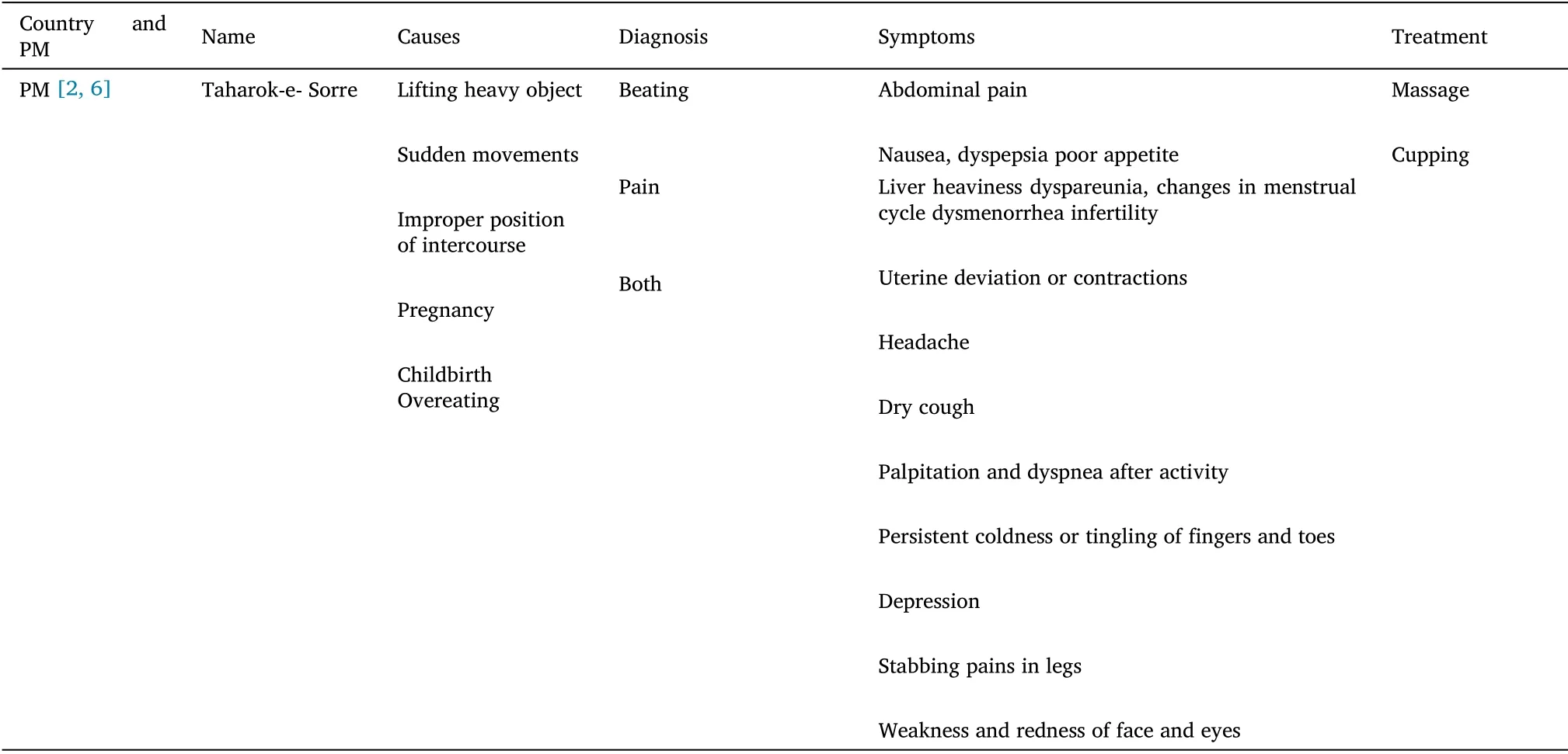
Table 1 UD in different countries
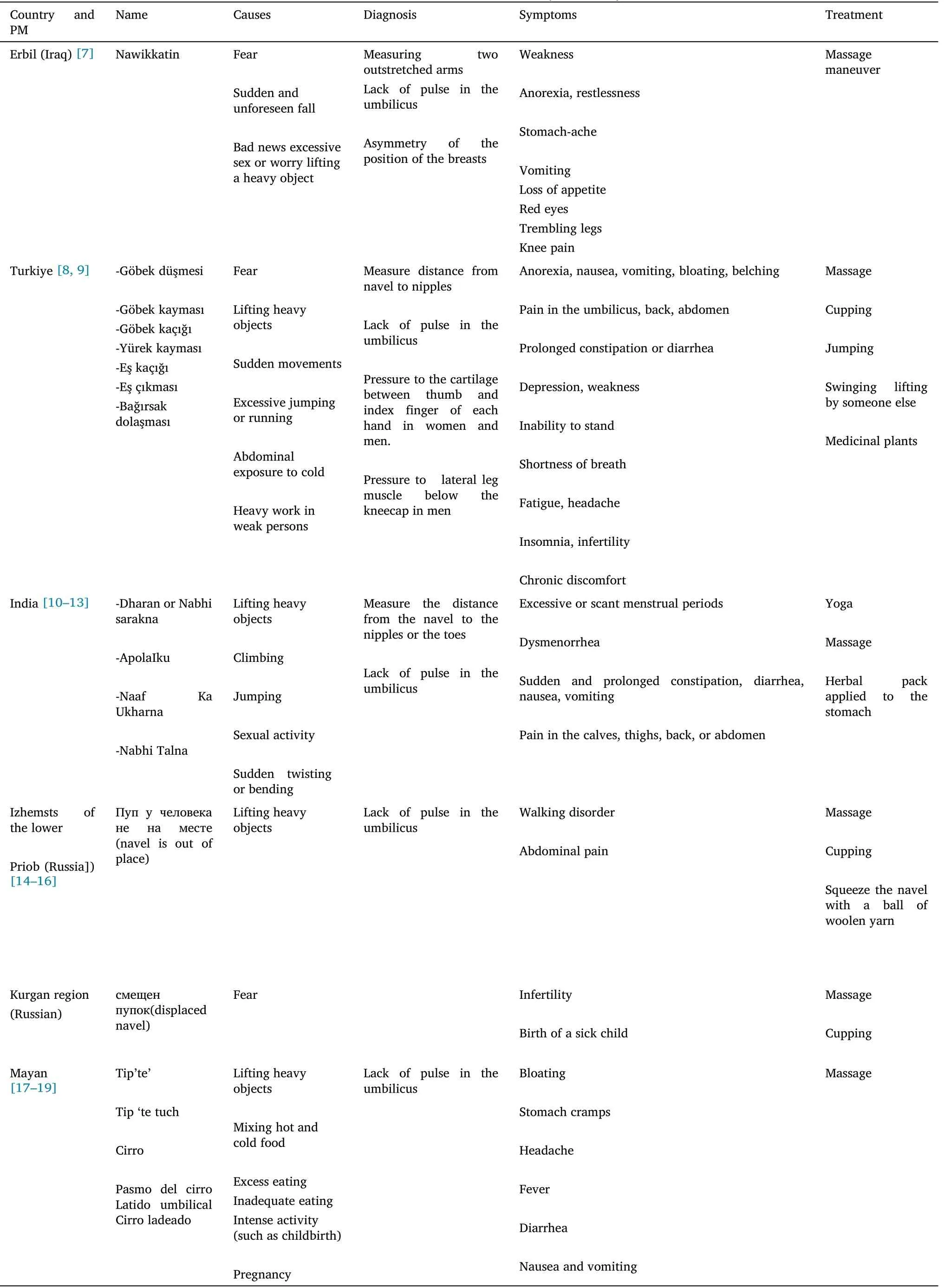
Table 1 UD in different countries (continued)
Methods and materials
In this review,PM literature,Google Scholar,Google,PubMed,Scopus and Web of Science were searched with the following terms of navel,umbilicus, and other synonyms of the “Navel” in Persian, Turkish,Russian, Spanish, German, Chinese and Indian language.The other searched terms were dislocation, sliding, falling, movement,displacement, deviation, ptosis, folk medicine and traditional medicine.We also searched LinkedIn information about this disorder in any countries, sent an e-mail to authors of traditional medicine and asked questions about this disorder.All available evidence related to UD, including its definition, diagnosis and treatment were retrieved and the contents were presented as categories including the name of the disorder, its attributed signs and symptoms, and its diagnostic and therapeutic method.
Results
Based on “Exir-e-Azam”, which is one of the main textbooks of PM,“Taharok-e-Sorre” is the synonym of UD, and is explained under the category of peritoneal diseases.There are different theories about the pathology of UD.Some PM scholars believe, that the abdominal muscles, which are around the navel move from their place, then the umbilicus moves from its position and deviates to one side.Some scholars also believe that the intestine moves from its place and causes the umbilicus to deviate [2, 6].
In Erbil (Iraq), UD is known as “Nawikkatin” and it is believed that not only UD could occur after physical/mechanical, but also due to mental stress factors.The UD after an unforeseen fall means that the fall is etiologically related to the fall of the soul [7].
In Turkiye, UD or navel falling is known as“Göbek düşmesi” (navel displacement); different causes and also numerous signs and symptoms are attributed to UD.They believe, that the navel is the center of gravity of the person’s body, and might be dislocated due to many reasons.It is important to know in which direction the umbilicus has moved.If the umbilicus moves down,it causes diarrhea.If it moves upwards, it causes nausea, anorexia, back pain, persistent thirst, and pain in the abdomen.The treatment of UD, which is called“Göbek çekme” is done in different ways.In abdominal massage, the person with UD lies in a supine position.The massager’s thumb is placed in the navel and constantly rotates clockwise.It is believed that once a person’s navel falls out,it is more likely to fall out in the future.In addition,it is believed that untreated UD is thought to cause serious health problems such as persistent diarrhea or constipation, inability to stand upright and even infertility in women.Treatment of chronic UD is difficult or even impossible.As delays in treatment increase the severity of the disease,the healer can help to treat the patient.Healers use two methods,arm-to-arm and kick.In the arm-to-arm method,the patient and the healer stand back-to-back, clasping each other’s arms.The healer bends to the ground.As a result, the patient lies on his back, with his legs dangling in the air,and the healer shakes him.This process is repeated several times.In the tapping method, the patient and the healer lie down so that the soles of their feet touch each other.The healer strikes the patient’s foot several times with his foot [8, 9].UD is known as “Dharan or Nabhi Sarakna” in India.“Nabhi” or“Dharan” translates as the navel or umbilicus, and Sarakna means movement or displacement.
UD is known as “Dharan or Nabhi Sarakna” in India.The term Nabhi is derived from the words“Nah-Bandhe”.It means to bind or tie to the central point just like the spokes of a wheel held at the nave.It is located in the abdominal or “gut” area of the solar plexus and is identified with the assertion of will and initiative.Nabhi is an abode of Pranas (vital energy).Indian healers believe, that the positioning of the umbilicus in its accurate site is important for the movement of Prana in the body, and they have several ways to treat UD; one of which is the asana positioning in yoga.This position could expand or stretch the rectus abdominal muscles,and is believed to be effective in UD after 3–4 days.Thereafter, to prevent the recurrence, patients are encouraged to practice the “asana” positioning to strengthen the stomach and back muscles [10, 11].
In northeastern India, UD is known as “ApolaIku” and could occur in any age groups.It causes severe pain and discomfort in the person,because the umbilicus is twisted inside.The therapist improves the navel by massaging with oil.Also,sometimes the treatment is done by simultaneously tapping of the patient’s feet heel [12].
Based on Russian folk medicine, UD is believed to cause gait disorder and with the treatment of UD, the spine is corrected [13].Diseases such as osteochondrosis, muscles diseases, joints, skin diseases,hearing loss,and even colds were considered to be associated with disruption of the internal organs.Visceral chiropractic consisted of rhythmic squeezing of the abdomen with the hands[14].In the folk medicine of the Bashqir people of the Kurgan region, such a diagnosis is widely used for female infertility [15].
In Tajik, the terms “ухoд пупка в стoрoну” or (leaving the navel to the side) and “ухoд пупка” or (displaced navel) seem to be used to describe UD, which is considered one of the reasons for women infertility [16].
The Volga Germans also know the disorder of navel falling.They believe that a person who is physically exhausted may experience UD.Symptoms include nausea and vomiting.For treatment, the patient should lay on his back on the floor, a small flat coin or an object is placed over her navel,and a small candle is attached to the coin.They light the candle and place a glass on the candle, allowing it to rest on its stomach for a while.When the candle goes out, it burns the air in the glass, creating a suction on the stomach muscles, which put the umbilicus back in place [20, 21].
In the Mayan language “tip’te” and in the Spanish language“Cirro”is a small “organ” located below the navel.The Cirro beats like the heart and determines the speed of all parts of the body.Its vitality can be sensed by sinking fingers into the navel to see if it “jumps”; Cirro may be coming out of its original position.The form of massage calledSobadais one of the most important therapeutic practices in Yucatán(Mexico), today.It deals with the “repositioning” of several internal organs of the human body, that are considered momentarily “out of place”.Treatment of dislocated Cirro consists mostly of circular massages around the navel clockwise[17, 19, 22].
The center of gravity is the point at which all of the body mass and weight are equally balanced or equally distributed in all directions.Very generally, the center of gravity for humans is located in the vicinity of the umbilicus.Phidias number determines the ratio between the man’s height and the height of the man’s umbilicus.It is generally known that the Phidias number is the most harmonic ratio in the nature of things.It is well known that the general center of gravity of an upright standing man is below the umbilicus by 0.05,and it is 0.1 in women; since their umbilicus is lower than the one of the men by 0.05 [19].
Common clinical findings in the middle-crossed syndrome in a right-handed,right-footed individual are as follows;these findings are typically reversed for a left dominant individual.(1) In gait, the umbilicus deviates leftward on right foot ground contact but stays central on left ground contact.(2) In active straight leg raise testing,the umbilicus deviates rightward on the right leg lift but stays central on the left leg lift.(3) “In supine lateral ball roll, the umbilicus deviates leftward (and/or the right hip drops), when moving across the ball to the left but stays central when moving to the right”[23].
A clinical study was performed on 44 nulliparous women, whose pregnancies had reached at least 37 weeks’ gestation.The results showed the umbilicus and supra- or infraumbilical linea nigra deviation to the right side in 31 women (70.5%); it also remained in the midline in 13 cases.Displacement of the umbilicus and adjacent structures commonly occurs in term pregnancy; the pressure of the uterus on the ligamentum teres and falciform ligament determines that displacement is invariably toward the right side[24].
In addition to deviation,the umbilicus sometimes rotates and moves in place.The analysis of supra- and infraumbilical linea nigra in puerperal women showed the predominance of what the authors named “anti-clockwise spiralization of the linea nigra sign”.“It is believed that this situation may be due to the 270 anti-clockwise rotation of the mesentery, which occurs during the return of the physiological omphalocele to the abdominal cavity around the 10th week of embryonic life [25].
In the normal infant,the umbilicus marks the central point between the crown of the head and the soles of the feet; whereas in the achondroplasic child the central point of the body is above the umbilicus, sometimes as high as the xiphoid process, and this relationship continues throughout life [26].
The ratio of the distance from the mid umbilicus to the lower end of the xiphoid process and the upper edge of the symphysis is referred to as the umbilical index.In cirrhotic patients without ascites or obesity,the distance between the xiphoid and umbilicus is more than the distance between the umbilicus and symphysis pubis (Tanyol’s sign)[27, 28].
An upward deflection of the umbilicus on flexion of the neck(Beevor’s sign), is the result of paralysis of the inferior portion of the rectus abdominis muscle.The condition may be caused by the spinal cord injury at or below the level of Thorasic vertebra 10.It has also been observed in patients with facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy [29].
Oppenheim described UD as unilateral paralysis of the abdominal wall.It may develop in association with herpes, malaria, typhoid,alcoholism, gout and diabetes.The symptoms are unilateral or bilateral pain in the region of the abdomen,tenderness to the pressure of the corresponding nerve stems and paresthesia.This is followed by a unilateral or bilateral absence of the abdominal reflex, anesthesia and degenerative paralysis of the abdominal muscle.In unilateral paralysis, the umbilicus deviates to the healthy side.The affected side is more prominent and shows a globular swelling, especially after coughing, screaming, straining or in an attempt to move the trunk against resistance, and the umbilicus is drowning more towards the sound side[30].
In 1921, Schlesinger described temporary UD in certain cases of gastric ulcers and acute cholecystitis, which is called “die Nabelverziehung”.An acute abdominal lesion, causing unilateral rigidity of the rectus abdominis could cause lateral UD during straining,which lasts several seconds.This transitory UD is toward the diseased side, because of the more marked muscular contraction.The displacement varies much in different cases (up to 4 cm).This UD is valuable in cases where other symptoms, such as tenderness in pressure have been disappeared in a persisting gastric ulcer [31].
Dr.Tui and Dr.Meyer encountered a physical condition, that was a prolonged displacement of the “linea alba” and the umbilicus to the affected side with skin surface disturbances in the form of folds; it creases on the side, which the linea alba and the navel are drawn.They reported four cases of active duodenal ulcers,four cases of acute appendicitis, and one case of penetrating ulcers near the gastric cardia, with UD.The side toward, which the displacement occurs in these acute abdomen conditions is the side of greater rigidity as determined by palpation [32].
So far,only one case series clinical study has been performed on UD.In this study, 20 patients were diagnosed with UD.Gastrointestinal problems were the most observed sign and symptoms reported by patients and the majority of patients reported some psychological problems.There are different methods to treat UD, including (a)taking a nerve that passes under the armpit and applying intense pressure to the extent, that the patient goes unconscious due to the severity of the pain; (b) patient sitting on all fours, while the other person firmly holds both knees with the hands; (c) the patient bend at the back, so that the abdominal muscles are stretched, the patient hangs, and the abdominal muscles stretch; (d) placing a half-walnut filled with raw turpentine or placing an onion-sized object such as a bag of wheat or salt on the navel [33].
Conclusion
This review tried to introduce a belief in folk medicine and showed,that UD is known in the folk medicine of different countries.As we have seen, not only UD has been reported in many cases in folk medicine, but also in modern medicine.The pathology of UD has not been explained in the articles.
According to the scholars of PM, The pathology of the UD in PM is the retention of peritoneal fluid(liquid and gaseous) between theSarband theSephagh[34].If the peritoneal fluid does not move, adhesion of the peritoneal bilayer occurs.According to the PM literature, there are eight muscles under the skin on the abdomen that are stretched up, down, and diagonally.Abdominal membrane is below these muscles; it is called theSephagh, and below theSephaghis theSarb[35].TheSephaghis the first membrane, that covers all the abdominal organs;It is connected to the spine from both sides,from the top to the diaphragm; from the bottom to the bladder and pelvis.Sarbis a thin layer of fat that extends to the stomach and all the intestines; this fat curtain is useful for digestion in the stomach (the stomach receives enough heat from the front bySarb[36].By these definitions,it seems that theSarbis omentum, and theSephaghis visceral peritoneum.
The peritoneum is a single layer of squamous mesothelial cells resting on a loose connective tissue containing blood vessels,lymphatics, and nerves.Anatomically, the peritoneum is divided into a parietal and visceral peritoneum.The parietal peritoneum lines the diaphragm, abdominal walls, and pelvic cavity.The parietal peritoneum is continuous with the visceral peritoneum, which encloses the intraperitoneal organs and forms the omentum and mesenteries of the abdominal cavities [3].The parietal and visceral layers of the peritoneum are separated by a small volume of fluid,typically 50–100 mL in total in adults, that facilitate frictionless movement of the abdominal organs,for example,loops of the bowel to freely slide over one another during peristalsis.If this normal property is lost by obliteration, adherence to bowel surfaces occurs [37].Persistent adhesions can prevent the normal sliding of the viscera during peristalsis and movements of the body, such as respiration.Small-bowel obstruction or intestinal mal rotation, infertility, chronic abdominal and pelvic pain are the most common consequences of peritoneal adhesions [38].
Adhesions form following a number of injuries to the peritoneum,including mechanical trauma, drying, blood clotting, and foreign object implantation, after surgery or after intra-abdominal inflammatory processes, such as appendicitis, acute cholecystitis,acute diverticulitis, and pelvic inflammatory disease [39, 40].Injury to the peritoneum leads to the release of fibrin, which causes adjacent serosal surfaces to stick together and form fibrinous adhesions.Removal of this fibrin before fibroblast invasion prevents the formation of permanent fibrous adhesions.Normal peritoneum has fibrinolytic activity [41].It is likely that visceral manipulation by repeatedly disrupting fibrin bridges does not allow the fibroblast invasion needed to create adhesions [42].
It seems that our scholars, without access to well-equipped laboratories and advanced tools, found some points, researching them can bring us new perspectives and methods to prevent the occurrence of serious diseases in the peritoneum.
Various treatment methods for UD, such as cupping, massage, yoga,various maneuvers and examining the mechanism of effect of the used methods can help to solve many problems and complaints of patients with nonspecific clinical diagnosis.
This study was a brief introduction to UD, its probable causes, and sign and symptoms.Undoubtedly, we are at the start point, and further studies are needed to show the true nature of UD and its pathology.For example, imaging of the abdominal wall might help to understand the changes in the abdominal wall anatomy occurring in patients with UD.In addition, descriptive studies with control groups could show the differences between UD patients and normal individuals in terms of signs and symptoms or the risk factors.Finally,further interventional studies should be performed to evaluate the efficacy of different methods of PM in UD treatment.
杂志排行
Traditional Medicine Research的其它文章
- Transcriptome sequencing analysis of ursolic acid-mediated proliferation suppression on cutaneous T-cell lymphoma cells
- HPTLC-MS:an advance approach in herbal drugs using fingerprint spectra and mass spectroscopy
- Targeting biosignatures of hyperglycemia and oxidative stress in diabetes comorbid depressive rats: effectiveness of hydroethanolic extract of the whole plant of Ludwigia octovalvis
- Rhizoma paridis saponins protected against liver injury in diethylnitrosamine-induced mice
- Phytochemicals, polyphenols content, in vitro antioxidant and antibacterial activities of Albizia coriaria Welw ex.Oliver flowers
