多鳞(Sillago sihama)高密度遗传连锁图谱构建及生长性状QTL定位分析*
2023-01-17田昌绪朱奕安林星桦叶明慧张玉蕾朱春华李广丽
田昌绪 朱奕安 钟 键 林星桦 叶明慧 黄 洋 张玉蕾 朱春华 李广丽
田昌绪1, 2朱奕安1钟 键3林星桦1叶明慧1黄 洋1, 2张玉蕾1朱春华1, 2李广丽1, 2①
(1. 广东海洋大学水产学院 广东省名特优鱼类生殖调控与繁育工程技术研究中心 广东省水产动物病害防控与健康养殖重点实验室 广东湛江 524088; 2. 南方海洋科学与工程广东省实验室(湛江) 广东湛江 524088; 3. 湛江海关技术中心 广东湛江 524022)



1 材料与方法
1.1 作图家系及DNA提取
1.2 GBS文库构建及高通量测序
1.3 SNP标记筛选与过滤
使用FASTP(0.18.0) (Chen, 2018)对测序后的raw data进行SNP过滤。筛选标准为: (1) 去除含有未知核苷酸(N)≥10%的reads; (2) 去除phred质量评分≤20及碱基≥50%的reads; (3) 删除含接头的reads。过滤后的clean reads用于组装分析。使用Burrows-Wheeler Aligner (BWA) (Li, 2009) (0.7.12; 比对参数为-k 32 -M)采用mem算法将过滤后的reads比对到参考基因组(SRA PRJNA642704); 比对后结果使用软件picard (http://sourceforge.net/ projects/picard/.) (1.129)进行标记。使用变异检测软件GATK (Van Der Auwera, 2013) (3.4~46) (设置参数: -Window 4, -G_filter “QD<2.0 || FS>60.0 || MQ<40.0”)进行群体SNP检测, SNP标记过滤标准为: 去除分型比例低于30%的位点, 去除杂合比例大于75%的位点, 按理论比对标记位点的基因型比例进行卡方检验,值小于0.001的位点视为严重偏分离位点并去除, 保留分离类型为母本杂合型lmxll、父本杂合型nnxnp和双亲杂合型hkxhk的标记。使用ANNOVAR软件(Wang, 2010)进行功能注释SNP。
1.4 遗传图谱构建

1.5 生长相关性状QTL定位及候选基因预测

2 结果
2.1 生长相关性状的表型参数

图1 多鳞F1代全同胞家系体重(a)、体长(b)、体厚(c)、体高(d)、背鳍前长(e)及眼径(f)性状表型数据频率分布(n=161)
2.2 多鳞作图家系GBS测序数据及SNP筛选
群体变异检测共获得205 471个SNP位点, 这些位点中转换标记有120 302个, 占58.54%, 颠换标记有85 169个, 占41.46%。根据亲本的基因型确定标记的分离类型(亲本测序深度不低于4), 保留分离类型为母本杂合型lmxll、父本杂合型nnxnp和双亲杂合型hkxhk的标记, 共筛选获得143 886个多态性SNP位点(表1); 随后, 对标记进一步过滤, 去除分型比例低于30%、或杂合率大于75%的位点、或严重偏分离的位点, 共保留107 406个高质量的SNP标记用于后续作图分析。

表1 多鳞作图群体中杂合子SNP位点的分离模式
2.3 多鳞遗传连锁图谱构建

如表2所示, 24个连锁群长度介于65.059 cM (LG23)与114.276 cM (LG08)之间, 平均长度89.783 cM,各连锁群标记平均遗传距离介于0.383 cM (LG04)至0.554 cM (LG22)之间。其中, LG01连锁群分布有最多的SNP标记(232个), 其连锁群长度为112.766 cM, 标记平均距离为0.486 cM; 而LG23上分布有最少的SNP标记(131个), 其长度为65.059 cM, 平均遗传距离为0.497 cM。
2.4 生长相关性状QTL的定位
2.5 候选基因的预测

表2 多鳞整合遗传图谱基本信息统计
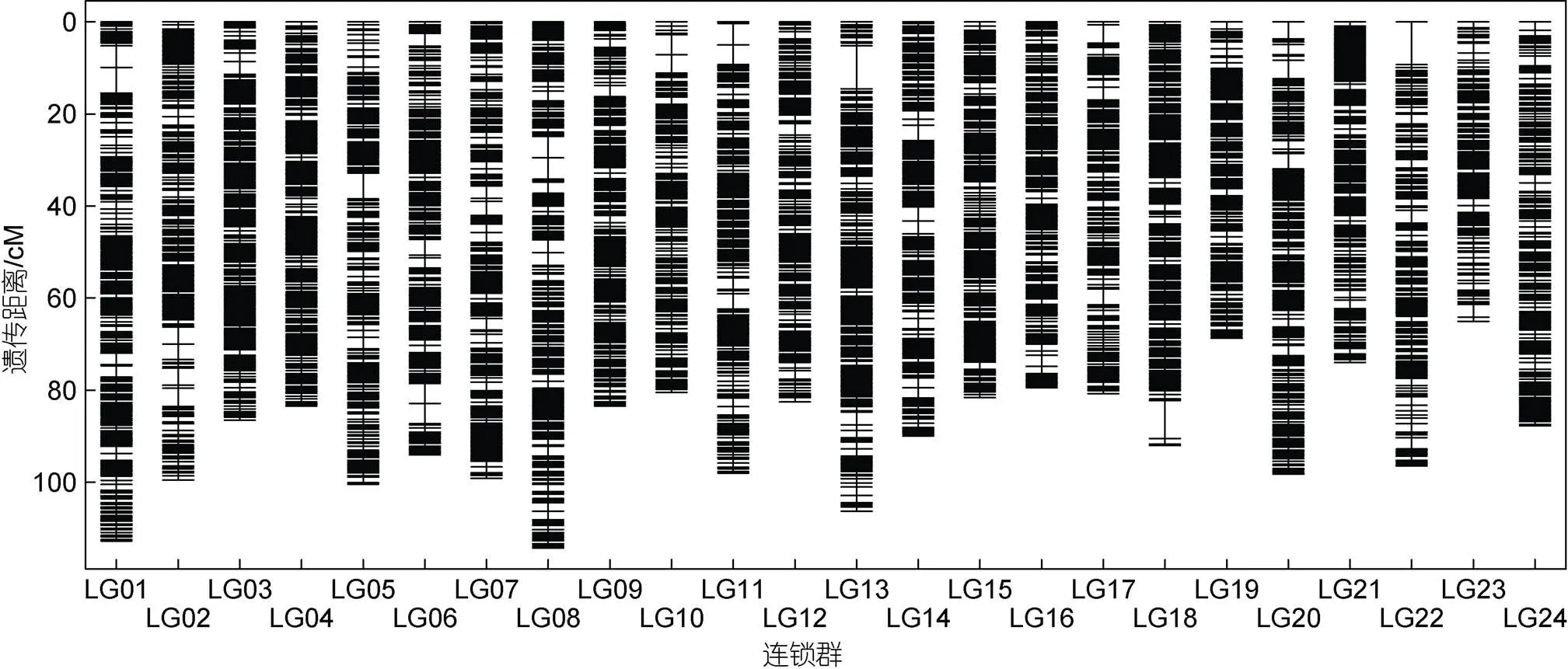
图2 多鳞高密度遗传连锁图谱
注: 遗传图谱展示了24条连锁群(LG01~LG24)的SNP标记分布及其遗传距离(cM)。遗传距离由左侧的比例尺表示, 单位为厘摩(cM)。连锁群上的单条线表示SNP标记

图3 多鳞体重(a)、体高(b)、体厚(c)、眼径(d)、体长(e)、背鳍前长(f)性状的QTL定位以及关联分析
注: LOD曲线,轴和轴分别对应所在染色体位置和LOD值。红色水平虚线表示LOD显著性阈值3.0

表3 复合区间定位法定位多鳞生长性状相关QTL结果

表4 多鳞20个QTL区间内已知生长相关基因信息
3 讨论




4 结论
叶华, 王志勇, 2011. 水产动物遗传连锁图谱构建和QTL研究现状[J]. 海洋科学, 35(1): 105-110.
李进波, 盛婧, 李想, 等, 2014. 五种DNA提取方法对鱼加工制品DNA提取效果的比较[J]. 生物技术通报(4): 43-49.

陈军平, 胡玉洁, 王磊, 等, 2020. 鱼类遗传连锁图谱构建及QTL定位的研究进展[J]. 水产科学, 39(4): 620-630.
桂建芳, 包振民, 张晓娟, 2016. 水产遗传育种与水产种业发展战略研究[J]. 中国工程科学, 18(3): 8-14.

BROMAN K W, WU H, SEN Ś,, 2003. R/qtl: QTL mapping in experimental crosses [J]. Bioinformatics, 19(7): 889-890.
CHEN S F, ZHOU Y Q, CHEN Y R,, 2018. fastp: an ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor [J]. Bioinformatics, 34(17): i884-i890.
DONG C J, JIANG P, ZHANG J F,, 2019. High-density linkage map and mapping for sex and growth-related traits of largemouth bass () [J]. Frontiers in Genetics, 10: 960.
ELSHIRE R J, GLAUBITZ J C, SUN Q,, 2011. A robust, simple genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS) approach for high diversity species [J]. PLoS One, 6(5): e19379.
FENG X, YU X M, FU B D,, 2018. A high-resolution genetic linkage map and QTL fine mapping for growth-related traits and sex in the Yangtze River common carp () [J]. BMC Genomics, 19(1): 230.
GUO W J, HE S, LIANG X F,, 2021. A high-density genetic linkage map for Chinese perch () using 2.3K genotyping-by-sequencing SNPs [J]. Animal Genetics, 52(3): 311-320.
HUANG Q C, ZHANG S, DU T,, 2020. Modulation of growth, immunity and antioxidant-related gene expressions in the liver and intestine of juvenileby dietary vitamin C [J]. Aquaculture Nutrition, 26(2): 338-350.
KAIZUKA T, HARA T, OSHIRO N,, 2010Tti1 and Tel2 are critical factors in mammalian target of rapamycin complex assembly [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 285(26): 20109-20116.
KESSUWAN K, KUBOTA S, LIU Q,, 2016. Detection of growth-related quantitative trait loci and high-resolution genetic linkage maps using simple sequence repeat markers in the kelp grouper () [J]. Marine Biotechnology, 18(1): 57-84.
LI H, DURBIN L R, 2009. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows–Wheeler transform [J]. Bioinformatics, 25(14): 1754-1760.
LI Z Q, XUE Q, XU J X,, 2020. The role of RBM10 mutations in the development, treatment, and prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma [J]. Cell Cycle, 19(21): 2918-2926.
LIN X H, HUANG Y, JIANG D N,, 2021Chromosomal-level genome assembly of silver sillago () [J]. Genome Biology and Evolution, 13(2): evaa272.
LIU H Y, FU B D, PANG M X,, 2016. QTL fine mapping and identification of candidate genes for growth-related traits in bighead carp () [J]. Aquaculture, 465: 134-143.
LIU D, GUO Y S, WANG Z D,, 2012. Phylogenetics inferred from mitogenome and control region of Silver Sillago,[J]. Mitochondrial DNA, 23(4): 255-263.
PAN Y Y, LIN X H, CHEN F Y,, 2021. Genome-wide identification and expression profiling of glutathione S-transferase family under hypoxia stress in silver sillago () [J]. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part D: Genomics and Proteomics, 40: 100920.
PENG W Z, XU J, ZHANG Y,, 2016. An ultra-high density linkage map and QTL mapping for sex and growth-related traits of common carp () [J]. Scientific Reports, 6(1): 26693.
SHEN H F, ZHANG W J, HUANG Y,, 2021. The dual function of KDM5C in both gene transcriptional activation and repression promotes breast cancer cell growth and tumorigenesis [J]. Advanced Science, 8(9): 2004635.
TSIGENOPOULOS C S, LOURO B, CHATZIPLIS D,, 2014. Second generation genetic linkage map for the gilthead sea breamL [J]. Marine Genomics, 18: 77-82.
TIAN C X, LIN X H, SAETAN W,, 2020. Transcriptome analysis of liver provides insight into metabolic and translation changes under hypoxia and reoxygenation stress in silver sillago () [J]. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part D: Genomics and Proteomics, 36: 100715.
VAN DER AUWERA G A, CARNEIRO M O, HARTL C,, 2013. From FastQ data to high-confidence variant calls: the genome analysis toolkit best practices pipeline [J]. Current Protocols in Bioinformatics, 43(1110): 11.10.1-11.10.33.
VAN OOIJEN J W, 2011. Multipoint maximum likelihood mapping in a full-sib family of an outbreeding species [J]. Genetics Research, 93(5): 343-349.
WANG X H, FU B D, YU X M,, 2018. Fine mapping of growth-related quantitative trait loci in Yellow River carp () [J]. Aquaculture, 484: 277-285.
WANG K, LI M Y, HAKONARSON H, 2010. ANNOVAR: functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 38(16): e164.
WENG Z Y, YANG Y, WANG X,, 2021. Parentage analysis in giant grouper () using microsatellite and SNP markers from genotyping-by-sequencing data [J]. Genes, 12(7): 1042.
XU D D, ZHANG W C, CHEN R Y,, 2021Chromosome-scale assembly and high-density genetic map of the yellow drum,[J]. Scientific Data, 8(1): 268.
YANG W, WANG Y R, JIANG D N,, 2020. ddRADseq- assisted construction of a high-density SNP genetic map and QTL fine mapping for growth-related traits in the spotted scat () [J]. BMC Genomics, 21(1): 278.
YOU X X, SHAN X X, SHI Q, 2020. Research advances in the genomics and applications for molecular breeding of aquaculture animals [J]. Aquaculture, 526: 735357.
ZHANG G S, LI J, ZHANG J J,, 2020. A high-density SNP-based genetic map and several economic traits-related loci in[J]. BMC Genomics, 21(1): 700.
ZHANG S Y, ZHANG X H, CHEN X H,, 2019Construction of a high-density linkage map and QTL fine mapping for growth- and sex-related traits in channel catfish () [J]. Frontiers in Genetics, 10: 251.
ZHANG G Q, ZHANG X H, YE H Z,, 2018Construction of high-density genetic linkage maps and QTL mapping in the golden pompano [J]. Aquaculture, 482: 90-95.
ZHOU Y L, WANG Z W, GUO X F,, 2021. Construction of a high-density genetic linkage map and fine mapping of QTLs for growth and sex-related traits in red-tail catfish () [J]. Aquaculture, 531: 735892.
ZHU C, TONG J, YU X,, 2014. A second-generation genetic linkage map for bighead carp () based on microsatellite markers [J]. Animal Genetics, 45(5): 699-708.
CONSTRUCTION OF A HIGH-DENSITY GENETIC LINKAGE MAP AND QTL DETECTION OF GROWTH TRAITS OF SILVER SILLAGO ()
TIAN Chang-Xu1, 2, ZHU Yi-An1, ZHONG Jian3, LIN Xing-Hua1, YE Ming-Hui1, HUANG Yang1, 2, ZHANG Yu-Lei1, 2, ZHU Chun-Hua1, 2, LI Guang-Li1, 2
(1. Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Aquatic Animal Disease Control and Healthy Culture, Guangdong Research Center on Reproductive Control and Breeding Technology of Indigenous Valuable Fish Species, Fisheries College, Guangdong Ocean University, Zhanjiang 524088, China; 2. Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Zhanjiang), Zhanjiang 524088, China;3. Zhanjiang Customs District Technology Center, Zhanjiang 524022, China)
Construction of high-density genetic map and quantitative trait loci (QTL) mapping are powerful tools for identifying genetic markers and candidate genes that may be responsible for such polygenic trait as growth. The first SNP-based high-density genetic linkage map was constructed by sequencing 163 silver sillago () individuals (2 parents and 161 F1offspring) according to a genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS) method. The consensus map spanned 2 154.803 cM, on average marker interval of 0.455 cM. In total, 4 735 SNPs were assigned to 24 linkage groups (LGs). Then, the QTL of 6 growth related traits was mapped via composite interval mapping (CIM), including body weight, body length, body thickness, body height, pre-dorsal length, and eye diameter. Twenty significant QTLs were identified on 8 LGs and explained 0.14%~8.42% of the phenotypic variance. The logarithm of odds (LOD) value ranged from 3.02 to 4.23. Specially, 8 QTLs were distributed on one linkage group (LG08), and the regions showed overlapping on LG08. Through the functional annotation of the genes in the candidate QTL interval, 19 potential growth-related genes were screened, including,,,,,,,,,,,, and. These genetic markers and candidate genes are useful genomic resources for marker-assisted selection (MAS) in silver sillago and the QTLs are useful tools for growth mechanism analysis of this fish.Key words; genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS); quantitative trait loci (QTL); growth-related traits; candidate genes
Q953; S917.4; S965
10.11693/hyhz20220500118
*广东省基础与应用基础研究基金, 2021A1515010733号, 2019A1515110619号; 广东海洋大学创新强校工程项目, 2019KTSCX060号; 2021年广东省科技创新专项资金, SDZX2021041号; 广东省南美白对虾现代种业产业园项目, K22221号; 广东海洋大学科研启动经费资助项目, R19026号; 广东大学生科技创新培育专项资金资助项目, pdjh2022b0239号; 2022年国家级大学生创新创业训练计划项目, 202210566003号; 海关总署2021年科技项目, 2021HK205号。田昌绪, 博士, E-mail: tiancx@gdou.edu.cn
李广丽, 教授, E-mail: ligl@gdou.edu.cn
2022-05-04,
2022-07-04
