Clinical observation and experimental study on Kangfuxin fluid in treating indwelling needle-related phlebitis
2022-12-06LiFangZouYingDongNiShanXuJingYuQuanLingNaDaiJunFangLiu
Li-Fang Zou, Ying Dong, Ni-Shan Xu, Jing-Yu Quan, Ling-Na Dai, Jun-Fang Liu*
1School of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, 510515, China.
2The Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan, 030001, China.
Abstract
Objective To investigate the therapeutic effect of Kangfuxin Fluid on indwelling needle-related phlebitis by observation of clinical samples and pharmacological study.
Methods Eighty-five patients with indwelling needle-related phlebitis in the neurosurgery department of a Grade A hospital in Shanxi Province from June 2019 to November 2021 were randomly divided into the study group (43 cases) and the vehicle group (42 cases). Patients in the study group were treated with KFX, and patients in the control group were treated with hydrocolloid dressing. The time for symptoms (such as redness and pain) to disappear was recorded. The effect of tissue repair was evaluated by the fin crosscutting model and the anti-inflammatory effect was evaluated by the inflammatory models. Q-PCR assay was used to detect the mRNA expression levels of IL-6 and TNF-α in LPS-stimulated zebrafish. The effect on promoting angiogenesis was evaluated by the intersegmental blood vascular defect model of zebrafish.
Results The curative effect of the study group was better than the control group. The pain resolution time and the swelling resolution time in the study group were (1.67 ± 0.90) d and (2.25 ± 0.92) d,respectively, shorter than those in the control group (P < 0.05). KFX can improve the ISV index,increase the regeneration length of the fin, inhibit the migration of neutrophils in three inflammatory models and reduce the mRNA expression levels of IL-6 and TNF-α in LPS-stimulated zebrafish.
Conclusion KFX exerts great clinical efficacy in the treatment of indwelling needle-induced phlebitis which may be associated with inflammation inhibition, angiogenesis promotion, and tissue repair.
Keywords Kangfuxin, Phlebitis, Inflammation, Wound Healing, Zebrafish
Highlights
Phlebitis is the most common complication of intravenous infusion.Applying 50% magnesium sulfate or hydrocolloid dressing is the main treatment for phlebitis, but the curative effect is not satisfactory.Kangfuxin Fluid (KFX) is the ethanol extract of the dried body ofPeriplaneta AmericanaL., which can relieve the pain, redness and swelling caused by phlebitis in clinical observation. Moreover, we found that KFX could significantly inhibit the mRNA expression of IL-6 and TNF-α, reduce the infiltration of inflammatory cells and reverse the vascular injury induced by VEGF receptor inhibitor and promote tissue repair in the zebrafish disease models.
Background
Phlebitis is a common complication with an incidence rate of 30%-80% in intravenous infusion [1], which will not only make patients bear a greater pain but also increase the difficulty of nursing staff venous puncture and increase the incidence of nurse-patient dispute [2]. The treatments for phlebitis are mainly applying 50% magnesium sulfate or hydrocolloid dressing [3, 4], but the curative effect is still unsatisfactory and may even lead to co-infection and delay wound healing.
Kangfuxin Fluid (KFX) is the ethanol extract ofPeriplaneta Americana L.,which is effective in promoting blood circulation and promoting tissue repair and is mainly used to treat trauma, gastrointestinal ulcers and oral ulcers [5]. At present,there are few clinical reports on the treatment of phlebitis with KFX, which mainly focus on the application of KFX in combination with other drugs [6, 7], and only a few works of literatures found that using KFX alone have a therapeutic effect on phlebitis caused by chemotherapy in the elderly [8]. However, there is no research on using KFX alone on treating phlebitis caused by other pathological factors and its pharmacological mechanism on phlebitis.
Zebrafish have a high degree of developmental and genetic composition similarity to humans, and the advantages of embryonic translucency, rapid reproduction, short experimental cycle and low maintenance cost make it a novel model for drug activity evaluation [9]. Therefore, we observed the clinical efficacy of wet compress with KFX alone in the treatment of indwelling needle phlebitis and used the zebrafish disease model to investigate its pharmacological mechanism. According to our research, we are committed to providing scientific references for the clinical care of phlebitis patients and providing a theoretical basis for KFX in the treatment of phlebitis.
Information and methodology
Source of cases
Clinical data of 85 patients with indwelling needle-related phlebitis in neurosurgery at a tertiary hospital in Shanxi Province were investigated from June 2019 to November 2021. The study protocol was informed to the families and agreed by the medical ethics committee of the hospital. And the ethics number was(2021)YX No.(260).
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Inclusion criteria: ①patients with phlebitis after infusion of non-chemotherapy drugs; ②patinets with good compliance and clear consciousness who could cooperate with treatment. Exclusion criteria: ①patients with impaired consciousness, mental disorders and no normal behavior; ②patients with limb perception impairment; ③patients with acute local skin inflammation, rash, skin breakdown or scarring; ⑤patients with diabetes mellitus with nerve endings disorder.
Grouping and treatment
In the control group, the patients were treated with hydrocolloid transparent dressing and the efficacy was observed every 24 h, while in the research group,sterile gauze soaked with KFX was applied to the affected area and wrapped with plastic film to maintain the moisture level of the drug. The gauze was changed once a day, the length and width of the redness, swelling and induration were measured, and the pain score was assessed every day.
Observation index and evaluation criterion
The latest American Society for Intravenous Infusion Nursing criteria for determining the degree of phlebitis was used. Grade 0 indicates no symptoms;grade 1 indicates erythema at the puncture site with or without pain; grade 2 indicates erythema and/or edema at the puncture site with pain; grade 3 indicates erythema at the puncture site with pain, streak formation, and visible venous cords;grade 4 indicates pain at the puncture site with erythema, streak formation, and visible venous cords > 2.54 cm in length.
The pain was judged by the numerical method, according to the numerical pain scoring method from 0 to 10, 1–3 was classified as mild pain, 4–6 as moderate pain, 7–9 as severe pain, and 10 as very severe pain.
The efficacy evaluation criterion was as follows: healed as the symptoms of skin redness or swelling completely subsided after 6 h, the skin color returned to normal,pain disappeared, and the elasticity of the vein wall was restored; Effective as the symptoms of skin redness or swelling subsided and pain disappeared 1–2 d after treatment; Hard nodes disappeared, effective as the symptoms of skin redness or swelling subsided, pain disappeared, and hard nodes shrunk less than 1×1 cm after 3–4 d after treatment; Ineffective as phlebitis remained after 5 d of treatment. The effect is that the symptoms of skin redness or swelling subsided and the pain disappeared after 5 d of treatment, and the nodules were reduced to less than 1 cm;The ineffective is that phlebitis still did not improve after 5 d of treatment and even the ulcerated surface at the puncture site of the indwelling needle increased.
The above indexes were observed and evaluated by two deputy chief nursing officers who had been engaged in nursing work in neurosurgery for 15 years or more and had rich clinical experience.
Materials
Drugs and reagents
KFX was purchased from Good Doctor Pharmaceutical Group Co, (Sichuan,China) and was diluted 100, 150, 200 and 250 times with PBS respectively.Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), epidermal growth factor (EGF), Tricaine,Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and methylene blue were purchased from Sigma,(USA). Sorafenib was purchased from Shanghai Aladdin Bio-Chem Technology Co., Ltd, (Shanghai, China). Copper sulfate (CuSO4) was purchased from Damao Chemical Reagent Factory, (Tianjin, China). Dexamethasone sodium phosphate injection (DEX) was purchased from Runhong Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd (Henan,China). AG RNAex Pro RNA extraction reagent was purchased from Accurate Biotechnology Co., Ltd, (Hunan, China). PrimeScript™ RT Master Mix (Perfect Real Time) and TB Green® Premix Ex Taq™ II (Tli RNaseH Plus) were purchased from Takara, (Japan).
Instruments
Zebrafish experimental breeding system (Shanghai Hai Sheng Biological Experimental Equipment Co, Ltd.); ZXSD-A1090 biochemical incubator(Shanghai Zhicheng Company); MVX10 body fluorescence microscope, SZX7 Stereo Microscope (Olympus Corporation, Japan); PM1000 ultra-micro cell injection pump, YP10001 electronic balance (Shanghai Youke Instruments Co,Ltd.); real-time quantitative PCR instrument (Roche, Switzerland, LightCycler96);ultra-micro spectrophotometer (DeNovix DS-11+); gradient PCR instrument (ABI Veriti 96).
Animals
Wild-type AB line and transgenic zebrafish lines, namelyTg(corolla: GFP;Lyz:DsRed),Tg(Fli1: GFP) zebrafish used in the experiments were provided by the Human Disease Zebrafish Model and Drug Screening Laboratory, School of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Southern Medical University.
Collection and culture of zebrafish embryos
Before the experiment, zebrafish were placed in the spawning tank in the ratio of male:female = 1:1 or 1:2 and separated by a partition. The partition was removed early the next morning and embryos were collected after a 30-minute chase. The embryos were cleaned with egg water and placed in a petri dish and then incubated in a constant temperature incubator.
Determination of embryo survival
The 72 hpf zebrafish embryos were randomly placed in 12-well plates with 20 embryos per well. The stock solution of KFX was diluted 100, 150, 200 and 250 times with egg water respectively. Then the larvae were treated with 2 mL of drugcontaining or normal culture solution by group. The survival of embryos was recorded every 24 h for 96 h.
Determination of embryo hatching rate
The 4 hpf zebrafish embryos were treated with or without the diluted solution of KFX (250, 275 and 300 times). When the zebrafish developed to 48 hpf, the embryo incubation was recorded every 4 h, and the observation continued until 72 hpf.
Copper sulfate induced inflammation model
The 72 hpf zebrafish embryosTg(corolla: GFP;Lyz: DsRed) were exposed to 20 μM CuSO4with or without DEX (15 μg/mL) / KFX (stock solution diluted 250,275 and 300 times). 2 h later, the migration of neutrophils was observed under the microscope.
Tail transection-induced inflammation model
The 72 hpf zebrafish embryosTg(corolla: GFP;Lyz: DsRed) anesthetized with 0.02% tricaine, and then part of the caudal fin was quickly cut off at the same position. The injured larve were treated with or without DEX/KFX. Photographs were taken to record the number of neutrophils that accumulated at the injured area after 4 h.
LPS-induced inflammation model
The 72 hpf zebrafish embryosTg(corolla: GFP;Lyz: DsRed) anesthetized with 0.02% tricaine were microinjected with 2 nL of PBS/LPS (2 mg/mL), and then treated with or without DEX/KFX. After 12 h for treatment, fluorescent neutrophils were visualized under the microscope in real time.
Histopathological observation
After microinjected LPS and treated with the drug for 12 h, zebrafish in each group were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde at room temperature for 24 h, and then wrapped in mirror wiping paper for routine dehydration. Dehydrated zebrafish were embedded in paraffin at 65 ℃, sectioned with a paraffin microtome, and finally stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). The stained sections were sealed with drops of neutral gum. After the slides were dried, the infiltration of inflammatory cells in the zebrafish yolk sac was observed under a microscope and photographed.
Survival analysis
The 3 dpf microinjected zebrafish embryosTg(corolla: GFP;Lyz: DsRed) were treated as described above. The survival of embryos in each group was observed and recorded every 24 h for 96 h.
Quantitative real-time PCR (QRT-PCR)
Total RNA was extracted from 30 zebrafish embryos. After reverse transcription of RNA into cDNA, the cDNA was used as a template for quantitative real-time PCR using Light Cycler ® 96 System Real Time PCR. β-actin was used as an internal reference gene, and all the primers were synthesized by Sangon Biotech(Shanghai) Co., Ltd.. The primer sequences used in this work are shown in Table 1.

Table 1 qRT-PCR primer sequences
Vascular defect model
The 12 hpf zebrafish embryosTg(Fli1: GFP) were co-treated with sorafenib (0.5 μM) and KEX. After 12 h, the membrane was broken and continued to be treated for 24 h. The formation of internode blood vessels was observed under a fluorescence microscope and the intersegmental blood vessel index was calculated.
Intersegmental vascularity index (ISV index) = intact intersegmental vessels ×1 + incomplete intersegmental vessels × 0.5.
Evaluation of promoting regeneration of caudal fin of KFX
The 72 hpf zebrafish embryos (AB) were anesthetized with 0.02% Tricaine, and part of the caudal fins were quickly cut off at the same position according to uniform standards and photographed at 0 hpw. Then the embryos were randomly placed in a 48-well plate with one embrymo per well and 10 embryos in each group and treated with or without EGF (20 ng/mL)/KFX. The zebrafish caudal fin regeneration was observed and the length of caudal fin regeneration was measured by CellSence after 72 h.
Statistical analysis
SPSS 22.0 was used for statistical analysis of clinical data. The measurement data were expressed as mean ± standard error of mean (SEM).t-test was used for comparison of mean between two groups, and count data were expressed as frequency (constituent ratio).χ2test was used for comparison between two groups,and rank sum test was used for data of rank variables, with the test levelα=0.05.Graph Pad Prism 5.0 software was used to analyze the data of animal experiments. The means of multiple samples were analyzed by one-way ANOVA and TurkeyPosthoctest. All experimental data were expressed as SEM. WhenP< 0.05, the difference was statistically significant.
Results
There were no statistically significant differences in gender, age, underlying diseases, phlebitis grade and other clinical data between the two groups (P> 0.05),as shown in Tables 2 and 3.
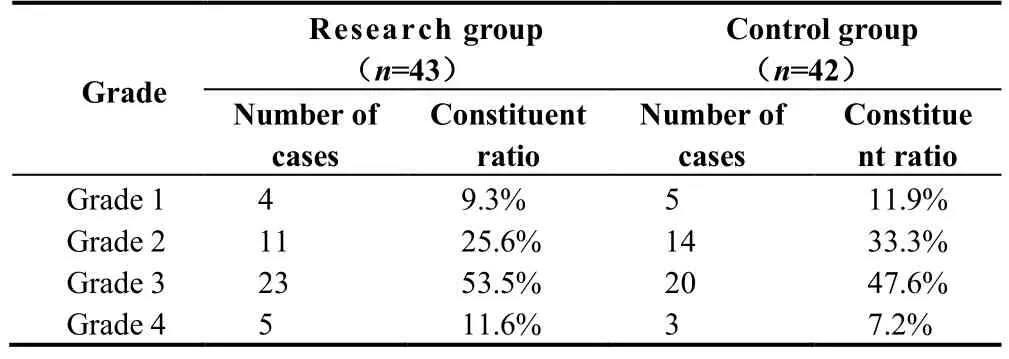
Table 2 Classification of phlebitis in two groups
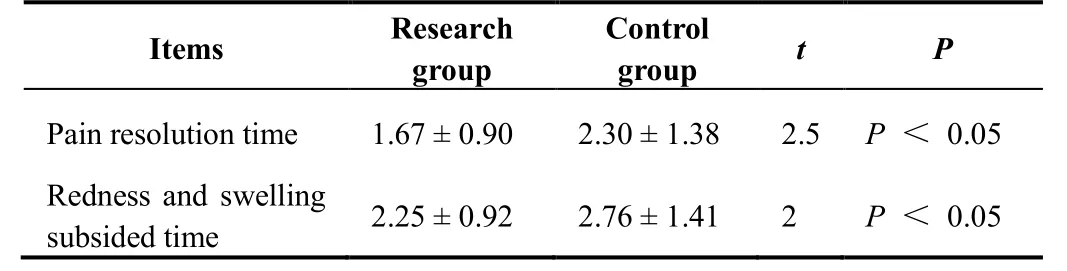
Table 3 Clinical symptom relief time of phlebitis patients in two groups (d)
Comparison of symptom relief time between two groups
The results showed that the local pain relief time of patients given KFX wet compress was (1.67 ± 0.90) d, and the relief time of redness and swelling was (2.25± 0.92) d, which were shorter than (2.30 ± 1.38) d and (2.76 ± 1.41) d in the hydrocolloid dressing group, and the differences were statistically significant(Tables 4 and 5).

Table 4 Clinical data of phlebitis patients in two groups

Table 5 Relief time of clinical symptoms of phlebitis grading in two groups (d)
Toxic effect of KFX on zebrafish
To confirm the concentration of the subsequent experiments, we tested the toxicity of KFX in zebrafish. The results showed that high concentrations of KFX were lethal to 3 dpf zebrafish embryos, and its toxicity increased with the increase of dose and time. With the prolongation of administration time, zebrafish gradually developed turbidity of yolk sac, the curvature of spine and slowing of heart rate after treatment with 100, 150 and 200 times dilutions of KFX. No toxic reaction was found after 250, 275, or 300 times dilutions of KFX were applied to 4 hpf zebrafish embryos for 72 h, and the embryo hatching rate of each group was approximately the same (Figure 1B). Therefore, KFX with dilutions of 250, 275 and 300 times were selected as the high, medium, and low concentrations in the subsequent study.

Figure 1 The toxicity of KFX. (A) The survival curves of 3 dpf zebrafish embryos treated with KFX at different dilution ratios; (B) The incubation rate of 4 hpf zebrafish embryos treated with KFX at different dilution ratios. ***P<0.001.
According to the above research results, KFX wet compress had better intervention effect than hydrocolloid dressing on indwelling needle phlebitis.
KFX could inhibit inflammation induced by different factor in zebrafish
To determine the anti-inflammatory effect of KFX, three classical zebrafish inflammation models were used for this study. When an external stimulus or infection occurs, the neutrophils and macrophages will migrate to the infection site to clean up microorganisms and apoptotic cells [10], so inflammation can be evaluated by observing fluorescent neutrophils in transgenic zebrafish. As shown in Figure 2, among the three inflammation models, the number of neutrophils migrating to the inflammation site was significantly higher in the model group than in the control group (P< 0.001), indicating that the copper sulfate, severed caudal fin and microinjection of LPS into the yolk sac induced inflammation models were successfully established.

Figure 2 KFX could inhibit the migration of neutrophils in three inflammatory models of zebrafish. (A) Representative fluorescent images of zebrafish in three inflammatory models (×2); (B) Quantitative analysis of the number of neutrophils migrating to inflammatory sites. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 versus LPS group,###P<0.001 versus control group.
In the copper sulfate-induced inflammation model, the number of neutrophils migrating to the site of inflammation was reduced in KFX group, all of which were significantly different compared to the model group. In the tail transection-induced inflammation model, the number of neutrophils migrating to the site of inflammation was reduced in the zebrafish in the KFX (250, 275) group, with significant differences compared to the model group (P< 0.001,P< 0.05). In the LPS-induced inflammation model, the number of neutrophils migrating to the site of inflammation was reduced in the zebrafish in the KFX (250, 275, 300) group,which were significantly different compared to the model group (P< 0.001). These results suggested that KFX has a certain therapeutic effect on inflammation caused by chemical factors, mechanical damage and bacterial infection.
KFX reduced the inflammatory response in zebrafish LPS-induced model
When local inflammation occurs in the organism, it often causes infiltration of immune cells [11]. To determine whether KFX could improve the infiltration of inflammatory cells at the yolk sac site of zebrafish after LPS stimulation, H&E staining of histopathological sections was performed on endotoxin-stimulated zebrafish from each group in this study. As shown in Figure 3A, compared with the control group, a large number of inflammatory cells were recruited at the cut surface of the yolk sac, and the infiltration of inflammatory cells at the yolk sac site was reduced after the administration of different dilutions of KFX and DEX treatment. Necrosis of the yolk sac, slowing of the heart rate and eventually, death can occur after microinjection of LPS in zebrafish yolk sac [12]. Therefore, in this study, zebrafish microinjected with LPS was administered continuously for 96 h and their survival was observed. As shown in the results of Figure 3B, after the microinjection of LPS into the yolk sac, the mortality of the model group reached 100% in 72 h. After 96 h treatment with different dilutions of KFX, the survival time of zebrafish in KFX (250, 275) groups was significantly prolonged.Interleukin 6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) are important proinflammatory factors involved in the acute inflammatory response. In order to further verify that KFX could reduce the inflammatory response caused by LPS,the mRNA expression levels of IL-6 and TNF-α were detected by Q-PCR. The results in Figure 3C suggested that the mRNA expression levels of IL-6 and TNF-α were significantly reduced by 250-fold dilution of KFX (P< 0.001). These results indicated that KFX could reduce the inflammatory response in the zebrafish endotoxin model by reducing the expression of IL-6 and TNF-α at the transcriptional level.
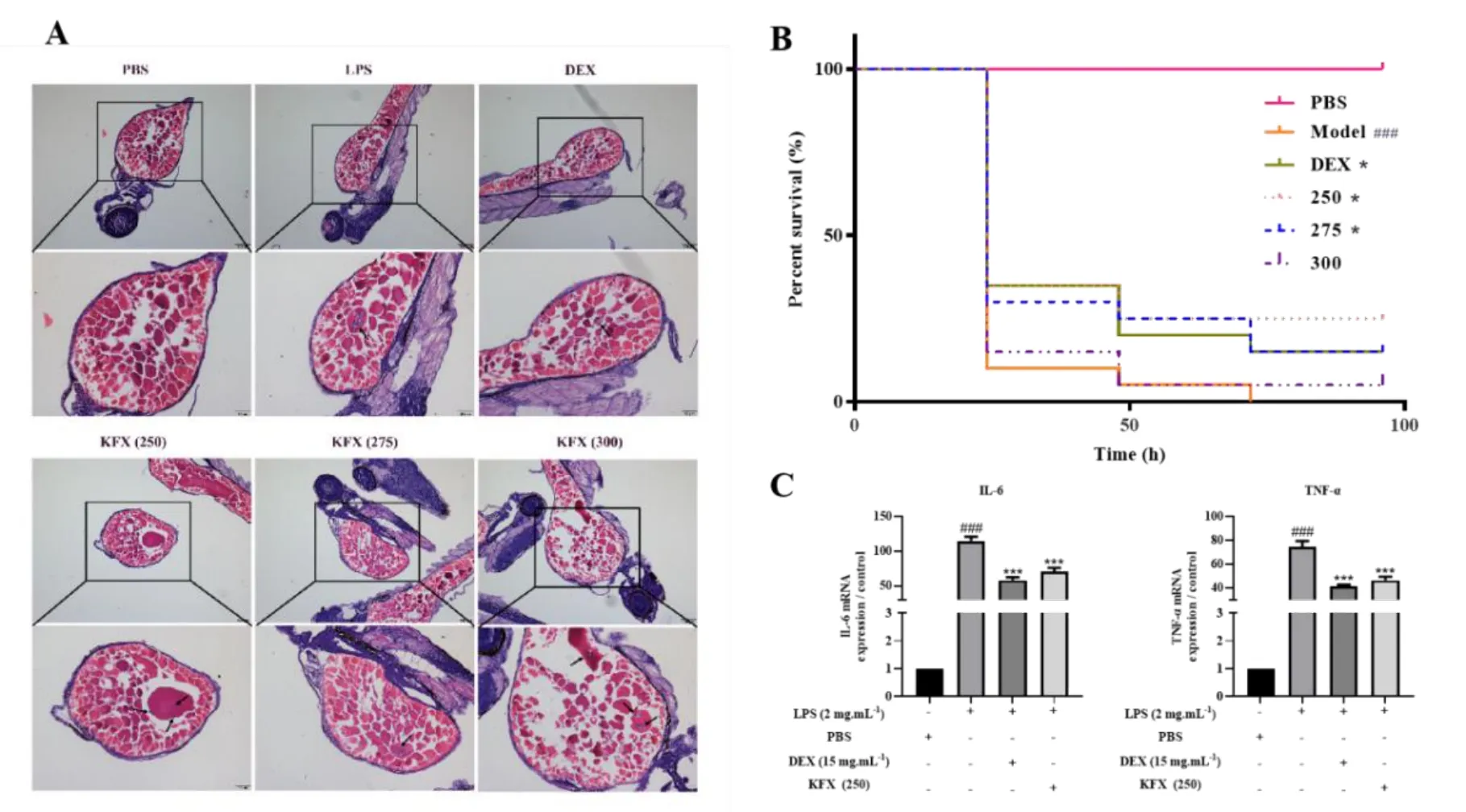
Figure 3 KFX could reduce inflammation in endotoxin model of zebrafish. (A) KFX could reduce the infiltration of inflammatory cells in yolk sac. (H&E staining,×100, ×200); (B) KFX could prolong the survival time of LPS-stimulated zebrafish; (C) KFX could decrease the mRNA expression levels of IL-6 and TNF-α induced by LPS. *P<0.05, ***P<0.001 versus LPS group, ###P<0.001 versus PBS control group. Comparisons between curves were made with the Log-rank test.
KFX promoted intersegmental angiogenesis in zebrafish
Sorafenib, an inhibitor of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor(VEGFR), can cause vascular injury in zebrafish. In view of this, we used it to investigate the protective effect of KFX on injured blood vessels. After 36 h of coadministration with KFX and sorafenib to 12 hpf zebrafish, the intersegmental vessels of zebrafish in the model group were defective (Figure 4), and the intersegmental vessel index ISV index was significantly decreased (P< 0.001). In contrast, the different doses of KFX administration groups could promote angiogenesis (P< 0.001). Therefore, our results showed that KFX could effectively reverse vascular injury induced by VEGFR inhibitors.
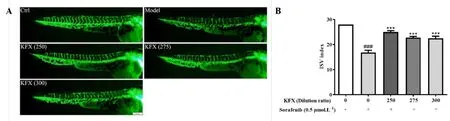
Figure 4 KFX could promote the formation of internode vessels in zebrafish. (A) Representative fluorescent image of KFX promoting angiogenesis (×3.2); (B)Quantitative analysis of ISV index in zebrafish. ***P<0.001 versus sorafenib group, ###P<0.001 versus control.
KFX could promote the regeneration of zebrafish caudal fins
Zebrafish caudal fin has the advantages of simple structure, fast regeneration speed and simple operation, which has attracted more and more attention as a regeneration model [13]. As shown in Figure 5, compared with the model group,the length of caudal fin regeneration in KFX (250, 275) groups was larger.Moreover, at the above concentrations, there was no significant difference in the effect of KFX (250) in promoting caudal fin regeneration compared with the positive drug group. Thus, these results indicated that KFX could effectively repair tissue damage caused by physical factors.

Figure 5 KFX could promote the regeneration of the tail fin of zebrafish. (A) Representative image of zebrafish promoting regeneration of tail fin (×6.3); (B)Quantitative analysis of tail fin regeneration length. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 versus model group.
Discussion
Indwelling needle phlebitis is a common complication during the infusion of neurosurgical patients [14]. The main reason for this complication is that the infusion drug with high osmotic pressure stimulates the venous wall, and the catheter movement causes friction damage to the inner wall of the vessel during the indwelling process of the needle, which leads to the increase of vascular permeability, redness, swelling, pain in the infusion area, and the stiffening and contraction of the venous vessels [15]. Currently, hydrocoll oid transparent dressings are often used for the treatment of phlebitis. However, there are still some defects in the nursing effect of this method. For example, the amount of hydrocolloid dressing exudate is large so it is easy to dirty the mattress of patients.And its absorption capacity is weak, which is not conducive to the absorption of wound exudation and easy to causes further infection [16], especially the puncture site of indwelling needle is not easy to heal, so it is extremely important to find effective and safe nursing drugs for the treatment of phlebitis.
KFX is often used in the treatment of ulcerative diseases in clinics [17], so our study observed the clinical effect of the treatment of KFX in indwelling needle phlebitis. In this study, we found that KFX wet compress had a significant curative effect, especially for grade 3 and above phlebitis. The drug could shorten the treatment duration of phlebitis, relieve the pain, redness and swelling of patients,and reduce the physical pain brought by phlebitis, so it is worthy of clinical application and promotion. However, KFX wet compress is easy to pollute bed sheets. How to optimize the use of KFX liquid in the clinic has become a problem that we need to further study and think about.
Previous studies have shown that irritation of the venous vessel wall by indwelling needles and drugs is the main causative factor for phlebitis. During intravenous infusion, indwelling causes mechanical damage to the intima of blood vessels. The stimulation of drugs aggravates the inflammatory reaction of the venous wall and releases inflammatory factors, thereby activating the inflammatory cascade [18]. At the same time, the production of inflammatory factors also aggravates the inflammatory response of the vessels, which further causes vascular damage [19]. Our study showed that KFX has different degrees of anti-inflammatory effects on oxidative stress, mechanical damage and bacterial endotoxin-induced inflammation, which can effectively reduce the mortality of zebrafish caused by LPS and reduce the infiltration of inflammatory cells. A high concentration of KFX (250-fold dilution) significantly inhibited neutrophil migration and inflammatory cell infiltration and prolonged the survival time of zebrafish. Medium concentration (275 times dilution) of KFX was the second most effective, but low concentration (300 times dilution) of Kangfuxin solution had no significant effect on tail-transcetion inflammation model, suggesting that KFX had a better effect on inflammation induced by CuSO4and LPS than physical injury.IL-6 and TNF-α are important pro-inflammatory factors that mediate the acute inflammatory response [20], and KFX can significantly inhibit their expression levels of them. Vascular tissue damage caused by intravenous infusion is mainly manifested by vascular endothelial cell dysfunction and the shedding of endothelial cells [21]. VEGF is an endothelial-specific growth factor that induces angiogenesis. When vascular tissue is injured, VEGF mediates the proliferation,differentiation and chemotaxis of endothelial cells to promote vascular repair [22].In contrast, KFX can reverse the neovascularization deficit induced by VEGF receptor inhibitors and promote angiogenesis. Among three concentration, the ISV of zebrafish in the KFX (250-fold dilution) group were almost intact, while the ISV of zebrafish in the KFX (275, 300-fold dilution) group were still partially missing. In general, with the increase of concentration, the protective effect on the vessels was enhanced. Modern studies have shown that the mechanism of wound healing in the zebrafish caudal fin is essentially the same as that in humans or mammals [23, 24]. Therefore, the zebrafish caudal fin regeneration model is commonly used to study the role of drugs in promoting tissue repair [25]. Our results showed that KFX (250, 275-fold dilution) groups both had a superior effect on repairing injured tail. However, the 300-fold dilution of KFX had no significant effect on tissue repair. The results of this study also showed that KFX was able to promote the repair and regeneration of injured tissues, suggesting that KFX may avoid the defect of difficult healing of the ruptured surface after indwelling needle puncture.
Conclusion
In conclusion, KFX wet compress can be used to treat indwelling needle phlebitis,which can effectively relieve patients’ pain, redness and swelling, and this effect may be related to anti-inflammation, promoting vascular renewal and accelerating tissue repair.
杂志排行
TMR Modern Herbal Medicine的其它文章
- Phytochemical screening and traditional medicinal potential of Albizia lebbeck (L.) Benth: An update
- New flavanone-monoterpene hybrids as α-glucosidase inhibitors from the root bark of Morus alba
- Thinking and practice on clinical safety evaluation of combination of traditional Chinese medicine and western medicine
- Role of traditional herbal medicine in the treatment of malaria
- Development status and trend of traditional Chinese medicine database
