Study on the mechanism and active components of Radix et Rhizoma Rhei in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease based on molecular docking
2022-10-10MengZhangDaBaoChenJingYaLiChunChunZhaoYanWangBiaoCaiPengZhou
Meng Zhang, Da-Bao Chen, Jing-Ya Li, Chun-Chun Zhao, Yan Wang,2, Biao Cai,2,3, Peng Zhou,2,3✉
1. College of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Anhui University of Chinese Medicine, Hefei 230012, China
2. Institute of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Anhui Academy of Chinese Medicine Sciences, Hefei 230012, China
3. Anhui Province Key Laboratory of Chinese Medicinal Formula, Hefei 230012, China
Keywords:Alzheimer's disease Radix et Rhizoma Rhei N L R P 3/C a s p a s e-1/G S D M D signaling pathway Molecular docking technology
ABSTRAC T Objective: To explore the mechanism and active components of Radix et Rhizoma Rhei in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease (AD) based on molecular docking. Methods: 22 major components of Radix et Rhizoma Rhei were screened from TCMSP and related literatures,which docked with the key targets of NLRP3/Caspase-1/GSDMD signaling pathway.NLRP3, Caspase-1, GSDMD inhibitors MCC950, ML132 and LDC7559 were used as positive control to analyze the docking results. Results: The docking results showed that the main components of Radix et Rhizoma Rhei had different degrees of binding with NLRP3,Caspase-1 and GSDMD targets, and the potential active components were mutanochrome and physciondiglucoside. Conclusion: Molecular docking predicts that the main components of Radix et Rhizoma Rhei may act on NLRP3/Caspase-1/GSDMD signaling pathway, and the active components may be mutanochrome and physciondiglucoside, which provides theoretical basis for revealing the anti-inflammatory mechanism and active components of Radix et Rhizoma Rhei in the treatment of AD.✉Corresponding author: ZHOU Peng.
1. Introduction
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a central degenerative disease with progressive dementia as the main clinical manifestation. Its main clinical manifestations are cognitive impairment, memory impairment and personality disorders [1]. The main pathological features are senile plaques (SP) formed by amyloid β-protein(Aβ) deposition in nerve tissue, neuro fibrillary tangles (NFTs)formed by abnormal phosphorylation and aggregation of tau protein in cells, and extensive loss of hippocampal neurons [2].Studies have proved that NLRP3 inflammasome is the most characteristic of neurodegenerative diseases, especially in AD [3]. Activation of NLRP3 inflammasome leads to Caspase-1-mediated production of IL-1β and IL-18 in microglia, which can be used as a key molecular target for AD treatment by regulating neuroinflammation[4].NLRP3 signaling pathway is an important signaling pathway in AD inflammatory response, and its downstream Caspase-1 and GSDMD signaling pathways may also be related to the occurrence of AD[5].
Radix et Rhizoma Rhei is the rhizome of Polygonum, Radix et Rhizoma Rhei in Tang Dynasty or medicinalRadix et Rhizoma Rhei . It is also called Huangliang, Huoshen, skin, general, etc,which has the functions of attacking stagnation, clearing damp and heat, relieving fire, activating blood, removing blood stasis and detoxification. Its main components include chrysophanol,emodin, rhein, aloe emodin, Physcion, and panaxirin, etc. the important active components are anthraquinone compounds and their derivatives [8].Traditional Chinese medicine believes that ad belongs to the category of "dementia", the main disease is located in the brain, and its etiology belongs to the deficiency of the origin and excess of the brain. The deficiency of the origin is mostly kidney essence deficiency and brain marrow insufficiency. The excess of the origin is mostly related to phlegm turbidity and blood stasis. The treatment principle can consider tonifying the kidney and filling the essence, and promoting blood circulation, removing blood stasis and eliminating phlegm [9]. Therefore,Radix et Rhizoma Rhei has the effect of promoting blood circulation and removing blood stasis,which can improve the cognitive function of AD patients.
Modern pharmacology studies show that Radix et Rhizoma Rhei has antibacterial, anti-tumor, anti-virus, brain and heart protection activities, and can also improve brain memory function [10,11]. Its effective components can play an important role in the treatment of AD by producing anti-inflammatory, anti apoptosis and antioxidation stress, which provides theoretical basis for the followup clinical treatment of AD. However, the mechanism ofRadix et Rhizoma Rhei in the treatment of AD is still unclear. Therefore,we need to explore the target of Radix et Rhizoma Rhei,and use molecular docking method to explore whether the main active components ofRadix et Rhizoma Rhei can act on ad through NLRP3 / Caspase-1 / GSDMD pathway, and find its potential active components, so as to provide theoretical basis for later clinical research and development of new drugs.
Molecular docking technology is mainly aimed at one or more target proteins related to targeted diseases. The relevant software is used to conduct virtual screening on the traditional Chinese medicine compound library. According to the results of Vina score after docking, the candidate compounds that specifically bind to the disease target proteins are searched, and the active compounds are screened. This method improves the efficiency of chemical activity evaluation and provides a new direction for the further research of traditional Chinese medicine resources [13].
In this study, the main active compounds in Radix et Rhizoma Rhei were moleculardocking with key targets in the NLRP3/Caspase-1/GSDMD inflammatory signaling pathway with the aid of molecular docking technology, so as to explore the relevant mechanism of action of Radix et Rhizoma Rhei in the treatment of AD, and provide direction and ideas for the future research on the prevention and treatment of AD by traditional Chinese medicine.
2. Materials and methods
2.1 Screening of active components fromRadix et Rhizoma Rhei
Through Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology Database and Analysis Platform(TCMSP) (http://lsp.nwu.edu.cn/tcmsp.php) [14], "Radix et Rhizoma Rhei " as keywords, to retrieve all the chemical composition of Radix et Rhizoma Rhei,Oral bioavailability (OB) and drug likeness (DL) of the chemical components were screened according to the ADME characteristics,and OB≥30% and DL≥18% were set as the screening conditions for active molecules, and 16 active components of Radix et Rhizoma Rhei were screened out. Combined with relevant literature studies,six active compounds including chrysophanol (MOL001729)[15,16],emodin (MOL000472)[17,18], Physcion (MOL000476), chrysophanol glucoside (MOL002244), emodin anthrone (MOL003353) and Rheosmin (MOL002287) were added [19,20], and a total of 22 active components were obtained. The structure of compounds in mol format was downloaded. (Table 1)
2.2 Target screening
"NLRP3", "Caspase-1" and "GSDMD" as the key words, the AD-related protein targets were retrieved from the 3D protein structure database PDB(http://www1.rcsb.org/)[21], and the optimal targets were determined as 6npy[22], 1rwx[23]、5wqt[24] based on the relevant literature, and the 3D structure in PDB format was downloaded.
2.3 Component-target molecular docking
According to the condition of Radix et Rhizoma Rhei active ingredients as ligands, via the PDB database of protein targets for receptors, through the CB-DOCK website (http://clab.labshare.cn/cb-dock/php/blinddock.php) for molecular docking [25].The Vina score of each compound and three targets was obtained respectively.The Vina score was the score of the complex obtained by molecular docking of receptor and ligand with corresponding pocket parameters by Vina program. The lower the score, the more stable the ligand binds to the receptor.
In addition, considering the consistent binding sites as far as possible, the docking results of NLRP3, Caspase-1, GSDMD inhibitors MCC950, ML132 and LDC7559 with the corresponding targets were selected as positive reference.
3. Molecular docking results
Molecular docking results showed that the major chemical components of Radix et Rhizoma Rhei had good binding with NLRP3, Caspase-1 and GSDMD targets. Among them, the first three compounds of Radix et Rhizoma Rhei with high binding affinity to NLRP3 protein target were Mutatochrome, beta-sitosterol and Physciondiglucoside ( Table 2, Figure 1). The top three binding affinity with Caspase-1 protein target were Mutatochrome, Emodin-1-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside, and Physciondiglucoside ( Table 3,Figure2, ). The top three binding affinity with GSDMD protein targets were Mutatochrome, Physciondiglucoside, and Emodin-1-Obeta-D-glucopyranoside ( Table4, Figure 3).
In summary, the docking results of the main chemical components of Radix et Rhizoma Rhei with AD-related NLRP3, Caspase-1, and GSDMD targets include Mutatochrome and Physciondiglucoside,indicating that it may be a potential active component Among them,Mutatochrome has the best binding effect, and the Vina scores of NLRP3, Caspase-1, and GSDMD targets are the lowest, respectively-11.9, -9.0, and -7.6. The binding effect was better than that of specific inhibitors.

Table 1 The main chemical components of Radix et Rhizoma Rhei
Table 2 The docking results of the main chemical components of Radix et Rhizoma Rhei with the NLRP3

Figure 1 Schematic diagram of active ingredients of Radix et Rhizoma Rhei docking with NLRP3.

Figure 2 Schematic diagram of active ingredients of Radix et Rhizoma Rhei docking with Caspase-1.

Table 3 The docking results of the main chemical components of Radix et Rhizoma Rhei with the Caspase-1

Table 4 The docking results of the main chemical components of Radix et Rhizoma Rhei with the GSDMD
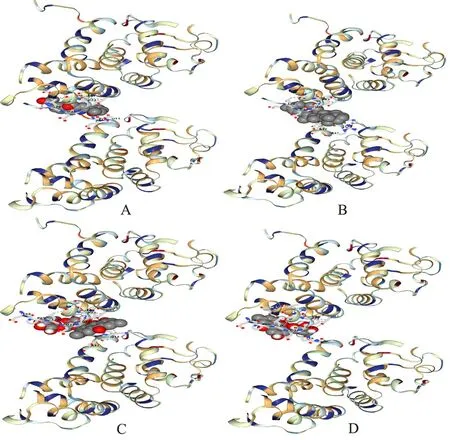
Figure 3 Schematic diagram of active ingredients of Radix et Rhizoma Rhei docking with GSDMD
4. Discussion
NLRP3 is a family protein of nucleotide oligomerized domain like receptor, and it is an intracellular sensor, which can detect various microbial motifs, endogenous risk signals and environmental stimulants, which leads to the formation and activation of NLRP3 inflammatory body [26]. Among all kinds of inflammatory bodies,NLRP3 inflammatory corpuscles are the most characteristic of neurodegenerative diseases, especially in AD.
Studies have found that silenced Caspase-1 and inhibited the expression of GSDMD in APP/PS1 transgenic mice, reduced the expression of Caspase-1 in cortex and hippocampus of mice,reduced cell pyroptosis, and improved the cognitive function of mice, suggesting that NLRP3/Caspase-1 pathway mediated cell pyroptosis is related to the pathogenesis of AD. At the same time,Aβ-induced increased expression of NLRP3/Caspase-1 pathway in cortical neurons was found to induce cell pyroptosis in vitro. The deposition of Aβ and the aggregation of misfolded proteins will activate NLRP3-ASC-Pro-Caspase-1 inflammasome, which will then activate Caspase-1, promote the secretion of inflammatory cytokines IL-1β and IL-18, trigger cell pyrotosis, and then lead to cell death, resulting in loss of neurons, and eventually trigger AD[27-30].Thus, NLRP3 inflammasome may be a key therapeutic molecular target for AD by regulating neuroinflammation.At present, traditional Chinese medicine has the characteristics of stable action, small side effects, high tolerance, multi-component,multi-target and multi-channel effect, especially in chronic inflammation. However, due to the limitations of various conditions,the research on anti-inflammatory drugs and their mechanisms is facing difficulties. Molecular docking technology has been successfully used in the virtual screening of active components of traditional Chinese medicine and the determination of action targets.By docking the active components of traditional Chinese medicine with the targets related to signal pathway, we screened out the active components closely combined with specific targets, thus constructing the relationship between drug disease target [31]. However, there are still some limitations in the research ideas and methods of molecular docking technology in the field of traditional Chinese medicine, and the compounds with the lowest docking score may not be the best ligands, which need to be combined with other methods, or further in vitro and in vivo experiments.
In this study, tcmsp was used to analyze the 22 main active components in Radix et Rhizoma Rhei, which had a good combination with the key targets of NLRP3/Caspase-1/GSDMD signaling pathway, reflecting the characteristics of "multi-component multi-target" of traditional Chinese medicine.The results showed that among the 10 compounds with strong binding affinity to NLRP3 protein target, the best compound was Mutatochrome, followed by anthraquinones, which mainly contained 7 anthraquinones, including Physciondigluc-oside,Emodin-1-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside,Chrysophanol glucoside, Rhein and Chrysophanol, Emodin and Emodin anthrone. Mutatochrome has the strongest binding affinity with Caspase-1 protein target, while Other top-ranked anthraquinone compounds are Emodin-1-O-beta-D- glucopyranoside,Physciondiglucoside, Emodin, Emodin anthrone and sennoside E_qt,sennoside D_qt and Rhein. The strongest binding affinity to GSDMD protein target is Mutatochrome.Other compounds are mainly anthraquinone compounds, mainly including Physciondiglucoside and Emodin-1-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside, Chrysophanol, Sennoside E_qt and Emodin. These results suggest that Radix et Rhizoma Rheimay play an anti-inflammatory role by acting on NLRP3/Caspase-1/GSDMD signaling pathway, and provide a theoretical basis for revealing the anti-inflammatory mechanism of Radix et Rhizoma Rheiin the prevention and treatment of AD. In addition, the compounds with the strongest binding to the three targets of NLRP3/Caspase-1/GSDMD signaling pathway in Radix et Rhizoma Rhei are Mutatochrome, followed by anthraquinones, which indicates that Mutatochrome and anthraquinones are expected to participate in the treatment of AD as monomers or lead compounds after structural modification, which provides a basis for further experimental verification in vivo and in vitro To provide scientific hypothesis and theoretical basis for further study on the anti-inflammatory mechanism of Radix et Rhizoma Rhei in the prevention and treatment of AD.
Author contributions
Zhang Meng Project implementation and article writing
Chen Dabao Project implementation, and picture editing
Li Jingya Project implementation, and picture editing
Zhao Chunchun Project implementation, and picture editing
Wang Yan paper revising
Cai Biao paper revising and the supply of subject source
Zhou Peng Project designing, paper revising and the supply of subject source
杂志排行
Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Research progress of autophagy in acute lung injury induced by multiple factors
- Research progress and comparison of the establishment of animal models of radiotherapy or chemotherapy-induced oral mucositis
- Based on the national patent database to explore the rule of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of hyperlipidemia
- Nonsurgical intervention for neuroclaudication due to lumbar spinal stenosis: Interpretation of the 2021 American Association for the Study of Pain Guidelines
- A mechanism to improve early diabetic nephropathy by modulating autophagy-related mechanisms with Yuye Decotion
- Meta analysis of the effect of aerobic exercise on inflammatory factors and glucose and lipid metabolism in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
