ABSTRACTS
2022-10-06
Microseismiceventrecognitionandfirstbreakpi-ckingmethodbasedonimagesemanticsegmentationnetwork.DENGFei1,JIANGPeifan1,JIANGXian-yi2,SHUAIPengfei1,andTANGYun1.OilGeophysicalProspecting,2022,57(5):1011-1019.
Precise picking of microseismic first breaks is one of the key aspects of microseismic monitoring. The traditional manual pickup method is time-consuming and inefficient, and it is likely to lead to problems such as failure to provide timely war-nings in practical applications. In recent years, the long short-term memory (LSTM) network model based on deep learning has been commonly used for microseismic first break picking, but the picking accuracy is low in a low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) environment, and the correlation between first arrivals of adjacent traces is neglected. To address the above problems, we propose a microseismic event recognition and automatic first break pickup method based on the image semantic segmentation network (D-LinkNet), which treats microseismic first breaks as a binary image classification problem. Experiments using actual microseismic data acquired in mines are conducted, and the experimental results reveal that the recognition accuracy of the method is significantly improved compared with that of the existing deep learning methods for multiple types of microseismic events including rock rupture and engineering blasting, and the average pickup error is significantly reduced; in particular, the average pickup error of low SNR data is much smaller than that of the LSTM method. Thus, the proposed method has good value for practical engineering applications.
Keywords: microseismic monitoring, first break, picking, image semantic segmentation network (D-LinkNet), long short-term memory network (LSTM)
1. College of Computer Science and Cyber Security, Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu, Sichuan 610059, China
2. Acquisition Technology Center, BGP Inc., CNPC, Zhuozhou, Hebei 072750, China
Optimalchargedesignmethodforsingle-boreholeshots.XUFeng1,HUANGLuming1,2,LIUFulie1,PANShulin1,HUANGYouhui3,andLIChongwen1.OilGeophysicalProspecting,2022,57(5):1020-1027.
In seismic exploration,the quality of seismic data acquisition is highly related to the explosive charge. Charge selection requires comprehensive demonstration by theoretical research and field tests. After single-borehole well cylindrical explosive is excited,wavelet energy distribution in various directions near the source is not uniform,resulting in the complexity of charge design. This study starts with collecting samples (soil samples) from the surface layer of the M area in western China and building five typical physical models by petrophysical parameter tests. Then,the wavelet fields in each model generated by excitation with the three commonly used explosives of trinitrotoluene (TNT),high-density ammonium nitrate,and ammonium ladder at different charges are simulated in the light of the explosion theory. An objective function based on excitation efficiency for charge design is proposed according to the spatial distribution ranges of effective energy and potential noise energy near the source. Furthermore,the optimal excitation charges for the three commonly used explosives in five typical lithologies of loess,limestone,igneous rock,mudstone, and sandstone are calculated theoretically. The validity and reliability of the proposed design method are confirmed by the outcome data of the charge tests conducted in the M area of Tarim.
Keywords: seismic exploration,explosive source,excitation charge,forward modeling
1. School of Geoscience and Technology,Southwest Petroleum University,Chengdu,Sichuan 610500,China
2. Guangxi No. 274 Geological Exploration Team,Beihai,Guangxi 536005
3. Department of Geophysical Prospecting Engineering,PetroChina Tarim Oilfield Company,CNPC,Korla,Xinjiang 841000,China
Four-componentrotationandfast-slowwaveseparationtechniquesfor3DvectorS-waveseismicdataofS-wavesources.GONGTing1,WANGZhaolei1,LUOWenshan1,WANGYongsheng2,YUEYuan-yuan3,andGUXiaodi1.OilGeophysicalProspecting,2022,57(5):1028-1034.
Shear wave (S-wave) exploration has great advantages in solving problems such as structural imaging in gas cloud areas and fine description of lithological oil-gas reservoirs. To address the problem of poor-quality of P-wave data in the Sanhu area of Qaidam Basin, BGP carries out a 3D multi-wave exploration experiment for the first time, which is jointly excited by P-wave and S-wave vibroseis and yields the 3D seismic data of nine components. In this study, we explore the four-component seismic data from the nine-component 3D seismic data, which are excited by the S-wave sources and received by the horizontal components of S-wave geophones. Different from P-waves, S-waves enjoy obvious vector characteristics. Previous research on S-wave processing technology was based on 2D S-wave processing or 3D converted wave seismic data processing, and the vector relationship of the complex wave field in 3D of S-waves was insufficiently considered; thus, it could not be applied to 3D S-wave seismic data. Through continuous research and exploration, supporting four-component processing techniques of vector S-waves with four-component rotation and fast-slow wave separation at the core are primarily formed, including vector rotation of four S-wave components, static correction, pre-stack gather processing, fracture azimuth determination, fast and slow wave separation, velocity analysis, and pre-stack migration imaging technology. These supporting techniques effectively solve the vector processing problem in S-wave exploration and obtain high-quality S-wave imaging results with a signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) comparable to that of P-waves. They boast great advantages in structural imaging in gas cloud areas and micro-fracture identification, which are essential for the prediction of lithologic reservoirs in the Sanhu area.
Keywords: S-wave source, vector processing, four components, S-wave splitting, fast and slow wave separation
1. Geophysical Research Institute, BGP Inc., CNPC, Zhuozhou, Hebei 072750, China
2. Exploration Department of Qinghai Oilfield Company, PetroChina, Dunhuang, Gansun 736202, China
3. BGP Research and Development Center, CNPC, Zhuozhou, Hebei 072750, China
Jointseismicdatareconstructionbasedontheaccele-ratedBregmanmethodandthresholditerationmethod.PANGYang1,ZHANGHua1,HAOYaju1,PENGQing1,LIANGShuang1,andHANZixuan1.OilGeophysicalProspecting,2022,57(5):1035-1045.
The reconstruction of missing seismic data traces plays an important role in seismic data processing. However,the majority of the existing reconstruction algorithms,held back by their low convergence speed and high computational cost,can barely meet the needs of mass data processing. This paper proposed a rapid reconstruction method combining the accelerated linearized Bregman method (ALBM) with a threshold iteration method,namely the iterative shrinkage-thresholding al-gorithm (ISTA). Besides,multi-scale and multi-directional curvelet transform was adopted as the sparse basis. ALBM converges rapidly in the early stage of iteration as it can obtain more effective signals from unthresholded curvelet coefficients. Nevertheless,its reconstruction accuracy is weakened by the increasing noise brought by the unthresholded curvelet coefficients in the later stage. In contrast,ISTA needs to threshold the curvelet coefficients all along. Although its convergence speed is slow in the early stage of iteration as most of the effective coefficients are filtered out,its reconstruction accuracy is high in the later stage owing to the restoration of weak effective signals. To maximize the advantages of the two algorithms,this paper presented two weighting parameter formulas (linear and exponential) in the range of 0~1. In this way,ALBM and ISTA were effectively combined linearly to ensure that ALBM played a major role in the early stage of iteration while ISTA dominated the later stage of iteration and thereby to enable this joint algorithm to iterate rapidly and accurately. In the combination process,a soft thresholding formula was adopted,and an exponential thresholding parameter formula was introduced. The theoretical simulation results demonstrate that compared with ALBM,ISTA,and traditional joint methods,the proposed accelerated joint method delivers fast calculation and an evident reconstruction effect.
Keywords: seismic data reconstruction,compressed sensing,accelerated linearized Bregman method (ALBM),iterative shrinkage-thresholding algorithm (ISTA),joint algorithm
1. State Key Laboratory of Nuclear Resources and Environment,East China University of Technology,Nanchang,Jiangxi 330013,China
StudyofsurfaceseismicinterferencewaveinloesstablelandbasedonVSPobservation.YANYou-ping1,ZHAOJuncai1,HUYadong1,GAOJun1,TANYong1,andWANGYunpeng1.OilGeophysicalProspecting,2022,57(5):1046-1056.
The interference waves in the seismic records of loess tableland areas with complex surface conditions are of various types. In particular,the kind of interference wave commonly known as “handlebar mustache” seriously affects effective reflected waves and is difficult to remove in subsequent processing. Studying the formation mechanism and the type of this interference wave can provide a basis for the design of a data acquisition scheme in the early stage and the formulation of a processing flow for subsequent denoising (of this interference wave). This paper starts with analyzing the frequency,energy,traveltime-distance curve, and velocity of the “handlebar mustache” interference wave in the seismic records,concluding that it is a refracted wave and its wavefield is likely to be one of a shear wave. Since this interference wave is an upgoing wave in the field seismic record and vertical seismic profile (VSP) observation can record its downgoing wave,it is determined to be a pure shear wave by analyzing the polarization,source,and frequency of the wavefield of the corresponding downgoing wave in the VSP record of the area. Further verification by actual Walkaway VSP records and off-line near-spread simulation records is conducted,and the “handlebar mustache” interfe-rence wave is determined to be a purely shear refracted wave.
Keywords:loess tableland,handlebar mustache,VSP,polarization analysis,pure shear wave,refracted wave
1. Huabei Branch Company of SINOPEC Petro-leum Engineering Geophysical Corporation,Zhengzhou,Henan 450000,China
Applicationandlimitationofimprovedstatisticalfilteringmethodinseismicdataprocessing.SONGXiaonan1,WANGHuazhong1,andYANGKai1.OilGeophysicalProspecting,2022,57(5):1057-1065.
Noise suppression technology of seismic data is in great demand for applications. In an abstract sense, seismic data can be considered as the composition of the seismic events determined by a certain time-distance relationship and the random noise determined by a certain statistical rule. The traditional statistical filtering based on weighted superposition often affects the event information in seismic data, which leads to unsatisfactory filtering effects. Therefore, the statistical filter should be improved according to the characteristics of seismic data. Filtering should be considered from a statistical perspective, and statistical filtering needs to track the seismic reflection events to adaptively design a flat window function that matches the geological characteristics of different regions. Therefore, we propose an anisotropic filter along the events to adaptively filters along the events in different regions, which conforms to the laws of seismic data. Then, synthetic data and real data verify the effectiveness of the proposed method in improving the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and retaining events. Finally, the quantitative and qualitative results of SNR, residual, and error curves are analyzed to state the application limitations of the statistical filter.
Keywords: filter design, statistical filter, event direction, quantitative error, signal-to-noise ratio
1. Wave Phenomenon and Intelligent Inversion I-maging Group (WPI), School of Ocean and Earth Science, Tongji University, Shanghai 200092, China
Multipleattenuationmethodbasedon3DparabolicRadontransformintheλ-fdomain.JINGHong-liang1,ZHANGShaohua2,FANGYunfeng1,MAGuangkai1,ZHANGQian3,andYANGXuelin1.OilGeophysicalProspecting,2022,57(5):1066-1075,1087.
In general, multiple attenuation by Radon transform means to process the model space involving forward transform and then returns to the time-space domain by inverse transform. How-ever, the convergence of the energy clusters in the Radon domain directly affects multiple removal, and the computational cost is high as the inverse operation of the matrix needs to be solved repeate-dly in the process of algorithm solving. For this reason, on the basis of 2D parabolic Radon transform, this study drew on the methods of Abbad et al. and took the lead in proposing a multiple attenu-ation method based on 3D parabolic Radon transform in theλ-fdomain. Thef-qx-qydomain of conventional 3D parabolic Radon transform was converted to a brand-newλx-λy-fdomain, and the idea of 2D Radon transform in theλ-fdomain was inherited. New variablesλxandλywere introduced to eliminate the dependence of conventional Radon operators on frequency. The computational efficiency was thereby significantly improved as the number of matrix operations was reduced. According to the spatial distribution characteristics of primary and multiple energy in theλ-fdomain, a 3D cone filter was designed to separate the primary from the multiple more effectively and reduce the error caused by the spatial truncation effect. The theoretical model and the actual data test yield the following conclusions: ① The proposed method lessens the influence of the spatial truncation effect, eliminates the dependence of transform ope-rators on frequency, effectively reduces the number of inverse operations of the matrix, and improves computational efficiency to more than eight times that of the method based on conventional 3D Radon transform. ② The proposed method still has the drawbacks of Radon-type methods, that is, when the velocity difference between the primary and the multiple is small, it fails to achieve a satisfactory multiple attenuation effect at a short offset.
Keywords: multiple attenuation, Radon transform, truncation effect,λ-fdomain, cone filter
1. Geophysical Technology Research Center, BGP Inc., CNPC, Zhuozhou, Hebei 072751, China
2. BGP Inc., CNPC, Zhuozhou, Hebei 072750, China
3. Processing Center, GRI, BGP Inc., CNPC, Zhuozhou, Hebei 072751, China
Integratedbroadbandandhigh-precisionquasi-3DprocessingtechnologyforgeologicaltargetsintheMesozoicofthenorthernSouthChinaSea.CHENShenghong1,2,3,ZHONGGuangjian1,WULu-shan1,2,3,WANGLiaoliang1,2,3,WUQilin4,andSHAOChanggao1,2,3.OilGeophysicalProspecting,2022,57(5):1076-1087.
As the structural and geological conditions of the Mesozoic of the northern South China Sea are more complex than those of the Cenozoic, conventional two-dimensional seismic data offers poor i-maging quality, which heavily restricts the implementation of oil and gas exploration targets. In response to the above problem, this study focused on tackling key issues for a quasi-three-dimensional (quasi-3D) seismic processing technology by investigating Target A in the Mesozoic of the Chaoshan Depression in the northern South China Sea and developed an integrated broadband and high-precision quasi-3D processing technology with the following technologies as its core: theτ-p-domain sparse inversion-based ghost wave attenuation by the bootstrap method, multiple elimination with the shallow water multiple attenuation (SWMA) + surface related multiple elimination (SRME) + Radon combination, 5D bin regularization by ma-tching pursuit and Fourier transform, and Gaussian beam prestack depth migration (CBM) based on velocity modeling combining full-waveform inversion (FWI) with fault-controlled tomographic inversion. The processing results reveal that the quality of the Mesozoic seismic data of Target A has been significantly improved, and the characteri-stics of the reflected wave groups and the development of faults in the formations are clear. This lays a solid foundation for the implementation of the Mesozoic traps in Target A and the evaluation of its oil and gas exploration potential. The proposed integrated broadband and high-precision quasi-3D processing technology is a set of practical technologies that well serve the oil and gas resource survey in the Mesozoic of the Chaoshan Depression in the northern South China Sea with complex sea conditions and complex structures. It also provides an important reference for oil and gas survey of similar marine targets around the world.
Keywords: northern South China Sea, quasi-three-dimensional, ghost wave, multiple, bin regularization, prestack depth migration
1.Sanya Institute of South China Sea Geology, Guangzhou Marine Geological Survey, Sanya, Hai-nan 572025, China
2.Key Laboratory of Submarine Mineral Resources, Ministry of Natural Resources, Guangzhou, Guangdong 510760, China
3.Academy of South China Sea Geological Science, China Geological Survey, Sanya, Hainan 572025, China
4.School of Petroleum Engineering, Guangdong University of Petrochemical Technology, Mao-ming, Guangdong 525000, China
Frequency-domainseismicnumericalmodelingbyapplyinghybridconjugategradientiteration.LIUWen’ge1,ZHOUMilu1,PENGHaotian2,LIUFulie1,andMOUQisong1.OilGeophysicalProspecting,2022,57(5):1088-1096.
At present, LU decomposition method or the Krylov subspace iteration method is usually used to solve the time-harmonic wave equation in frequency-domain seismic modeling. The direct decomposition method takes up a lot of memory and is time-consuming, and it can hardly simulate high-dimension, large-density seismic acquisition. The gene-ral Krylov subspace iteration method, however, converges slowly and may not converge while dea-ling with complex models. On the basis of the e-xisting conjugate gradient algorithms, an optimized Krylov subspace method-the hybrid conjugate gradient algorithm, is developed to solve time-harmonic wave equations. The numerical simulations of the layered medium model and the standard model indicate that compared with LU decomposition method, the proposed method can effectively reduce the memory requirement and calculation time on the premise of ensuring accuracy. Compared with the stable bi-conjugate gradient iteration method, it has better computational stability in dealing with complex models.
Keywords: frequency domain, seismic modeling, Krylov subspace, conjugate gradient, time-harmonic wave equation
1. School of Geoscience and Technology, Southwest Petroleum University, Chengdu, Sichuan 610500, China
2. Exploration and Development Research Institute, PetroChina Southwest Oil & Gasfield Company, Chengdu, Sichuan 610000, China
Frequency-dependentcharacteristicsofP-waveinfracturedporousmedia.ZHANGJinwei1,DINGRenwei1,LINNiantian1,andZHAOLihong1.OilGeophysicalProspecting,2022,57(5):1097-1104.
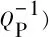
Keywords: fractured reservoirs, Chapman model, standard linear solid model, frequency dispersion, attenuation, characteristic frequency
1. College of Earth Science and Engineering, Shandong University of Science and Technology, Qingdao, Shandong 266590, China
Stratigraphicimagingwithseismicdatabasedonwaveequationmigration.CHENShengchang1,LIUYanan1,LIDaiguang1.OilGeophysicalProspecting,2022,57(5):1105-1113.
Stratigraphic imaging,an approximate inversion of the spatial variation of the physical properties of subsurface strata,is of great value for the exploration and development of lithological and unconventional reservoirs. In this paper,a stratigraphic imaging method involving the relative perturbation of wave impedance of the reflector is proposed according to the idea of wave equation migration. On the basis of a smooth subsurface me-dium model featuring accurate kinematic characte-ristics of seismic waves,a linear forward expression of seismic data based on the relative perturbation of wave impedance of the reflector is derived by applying the seismic wave propagation theory. Then,the relative perturbation of wave impedance is obtained through approximate inversion from seismic data according to the linear inversion theory. A method of stratigraphic imaging with seismic data that is based on wave equation migration and takes wave impedance variation as the main target is constructed. During stratigraphic imaging,angle decomposition of the wavefield generates angle-domain common imaging-point gathers for stratigraphic imaging. In contrast, stratigraphic imaging results under an angle-domain average can be obtained quickly when angle decomposition of the wavefield is not performed. When the seismic data are described by the acoustic wave equation,the proposed stratigraphic imaging method can be employed to obtain stratum imaging based on the relative perturbation of acoustic wave impedance. When the seismic data are described by the scalar wave equation,the proposed method can be applied to attain stratum imaging based on relative velocity perturbation. Compared with the reverse time migration method based on seismic data, the proposed stratigraphic imaging method has the same calculation process and a comparable amount of calculation. This method also achieves a satisfactory stratigraphic imaging effect when it is applied to a test with synthetic seismic data.
Keywords: seismic data,linear forward expression,relative perturbation of wave impedance,wave equation migration,stratigraphic imaging
1. School of Earth Sciences,Zhejiang University,Hangzhou,Zhejiang 310027,China
ModifiedOrthant-WiseLimited-memoryQuasi-Newtonalgorithmforfull-waveforminversion.QIHongyu1,FUHongsun1,andYANGLu1.OilGeophysicalProspecting,2022,57(5):1114-1119.
Full-waveform inversion (FWI) obtains high-resolution parameters of subsurface models by minimizing the errors between observed data and calculated data. Regularization techniques are o-ften used to overcome the ill-posedness of FWI. However,complex geological models are likely to have sharp boundaries and smooth characteristics at the same time,in which case a single regularization method usually fails to deliver satisfactory inversion results. Given the non-differentiability of the objective function involving hybrid regularization,this paper proposes a modified Orthant-Wise Limited-memory Quasi-Newton method for solving the corresponding regularization objective function. Numerical simulation experiments are conducted on the complex-constructed modified Marmousi model and BG Compass model,and the proposed method is compared with FWI without regularization and the proximal Limited-memory Quasi-Newton method. The results show that the proposed algorithm has obvious advantages in computational efficiency and quantitative analysis.
Keywords: full-waveform inversion (FWI),hybrid regularization,modified Orthant-Wise Limited-memory Quasi-Newton algorithm,proximal operator
1. School of Science,Dalian Maritime University,Dalian,Liaoning 116026,China
Multi-scalefullwaveforminversionbasedondoublediagonalfluxcorrectiontransport.YANGRuidong1,HUANGJianping1,YANGZhenjie1,MUXinru1,WANGZhaozhong2,andYANGShanshan3.OilGeophysicalProspecting,2022,57(5):1120-1128.
The continuous furthering of oil and gas exploration exposes seismic exploration to increasingly complex issues. Full waveform inversion (FWI) has become a highly promising velocity modeling method due to its high accuracy. Nevertheless,its inversion effect is largely affected by the accuracy of the initial model and the frequency range of the shot record. In actual seismic data processing,the accuracy of the initial velocity model is often not high,despite that an accurate initial velocity model is the key to preventing FWI from falling into local extreme values. Therefore,reducing the depen-dence of FWI on the initial model is vital. For this reason,a multi-scale FWI method based on double-diagonal flux correction is proposed in this paper. Specifically,the two-dimensional time-domain acoustic wave equation is corrected by the flux-corrected transport technology to obtain the corrected wavefields of different frequency components. On this basis,the calculation formulas for FWI gradient and step size are derived,and multi-scale inversion is carried out with the corrected wavefields from low frequency to high frequency. Simulation tests with a modified Marmousi model are conducted to verify the effectiveness of the proposed method. The results show that the proposed method effectively expands the medium- and low-frequency components of the wavefield and reduces the dependence of FWI on the initial model.
Keywords: full waveform inversion (FWI),acoustic wave equation,multi-scale,flux-corrected transport
1. School of Geosciences,China University of Petroleum (East China),Qingdao,Shandong 266580,China
2. Institute of Geology and Mineral Resources of Shandong Province,Jinan,Shandong 250100,China
3. RIPED Tarim Oilfield Company PetroChina,Korla,Xinjiang 841000,China
Phase-domainreservoirpredictiontechnology:acasestudyofchannelsandinChengdaoarea,ShengliOilfield.LUOHongmei1,YANGPeijie1,WANGYanguang2,MUXing1,andWANGChangjiang1.OilGeophysicalProspecting,2022,57(5):1129-1137.
Changes in lithology and physical properties alter the phase of the seismic signal. Therefore, effectively extracting and then analyzing phase information from seismic data are conducive to identifying special geological bodies and target reservoirs. For this reason, this paper proposes and implements a phase-domain reservoir prediction technology, the core of which is phase decomposition and reconstruction. Analyzing and determining the sensitive phase is the key to the success of phase-domain reservoir prediction, and it involves three steps. Step 1 is the phase decomposition and reconstruction of seismic traces, which produce phase-decomposed seismic data and phase gathers after phase reconstruction. Step 2 is sensitive phase analysis, whereby the phase most sensitive to reservoir changes can be obtained according to the seismic-geological characteristics of the study area. Step 3 is the analysis of phase-decomposed data bodies with the seismic attribute analysis technology, mainly involving profile analysis and slice analysis, to ultimately achieve reservoir prediction. The model analysis shows that synthetic seismic records fail to reflect the lateral differences in wave impedance in thin layers, whereas phase-decomposed data of synthetic seismic records amplify the subtle lateral impedance differences in thin layers so that they are easy to identify. The practical application reveals that the seismic attribu-tes of the data body in the sensitive phase depict the channel more clearly and offer higher resolution.
Keywords: phase domain, phase decomposition, phase reconstruction, phase-decomposed data, phase gather, reservoir prediction
1. Exploration and Development Research Institute, SINOPEC Shengli Oilfield Company, Dong-ying, Shandong 257015, China
2. SINOPEC Shengli Oilfield Company, Dong-ying, Shandong 257015, China
Characteristicsandreservoir-controleffectofUpper/MiddlePermianunconformitystructuresintheeastofFukangSag,JunggarBasin.TANGYong1,JIJie2,GUOWenjian1,CHENHong1,LIYan-ying3,andDONGFang3.OilGeophysicalProspecting,2022,57(5):1138-1147.
The high porosity and permeability zones in longitudinal structures of unconformity and the reservoir-cap combinations composed of different structural layers can form various types of litholo-gic stratigraphic traps. Therefore, through the combination of logging and seismic data and the integration of the upper and lower seismic reflection characteristics of unconformity, the Middle/Upper Permian unconformity in the east of Fukang Sag in Junggar Basin are divided into five types: parallel-parallel, parallel-cut, parallel-fold, overlap-cut, and overlap-fold. The logging data is used to construct the determinant parameter to identify unconformity structures and analyze their development laws and controlling factors. Then, the reservoir-control model of unconformity structures is built on the basis of the drilling results. The research reveals that the unconformity structures are mainly controlled by the erosion amount, lithology of mother rock, and the depth of the structures, and the thickness of the upper layer is negatively correlated with that of the intermediate layer in the unconformity structures. The unconformity area of overlap-cut is a favorable zone for developing oil and gas reservoirs. The water in the unconformity superstructure entering the sand body is a favora-ble target for oil and gas exploration of unconfor-mity, and it is easy to form stratigraphic overlying oil and gas reservoirs in the lake (sea) bay area. The research result can provide a reference to the exploration of unconformity reservoirs in other similar areas.
Keywords: Junggar Basin, Fukang Sag, Upper/Middle Permian, unconformity type, unconformity structures, reservoir-control effect
1. PetroChina Xinjiang Oilfield Company, Karamay, Xinjiang 831000, China
2. School of Ecology, Resource and Environment, Dezhou University, Dezhou, Shandong 253023, China
3. School of Geosciences, China University of Petroleum (East China), Qingdao, Shandong 266580, China
SeismicreflectioncharacteristicanalysisandreservoirinterpretationofPenglai9-1graniteburiedhillinBohaiSea.LIUPengbo1,LYUDingyou1,YUHaibo1,XIONGYu1,HUAnwen1,andDENGHui1.OilGeophysicalProspecting,2022,57(5):1148-1155.
Correctly understanding the geological significance of seismic reflection characteristics is the basis and key point of reservoir prediction in buried hills. Given the gentle top shape and internal inclined reflection structure of the Penglai 9-1 granite buried hill,this study starts with the characteristics of the weathered crust of this buried hill and presents a seismic reflection characteristic analysis and reservoir interpretation of the granite buried hill with 3D seismic,drilling,and other data through forward modeling. The research shows that the granite buried hill, subjected to strong weathering and leaching, exhibits vertical zoning. The reservoir is mainly developed in the sandy gravel weathering zone. The inclined reflection from inside the granite is the response of the fracture zone, and it is controlled by granite lithology and tectogenesis. The fracture zone is the basis for the development of the weathered crust reservoir. Only the inclined reflection development area allows the development of a favorable weathered crust reservoir. The magnitude of the amplitude of the reflected wave from the top of the buried hill is negatively correlated with the development degree of the weathered crust reservoir. The distribution of the favorable reservoir can be predicted by combining the magnitude of the amplitude from the top of the buried hill and the development degree of the inclined reflection from the inside. The area cha-racterized by a low amplitude from the top of the buried hill and dense inclined reflection from the inside is mainly located near the large fault on the east boundary of the granite body, and it is the most favorable area for reservoir development. The proposed method can provide a reference for the subsequent development of the granite buried-hill reservoir in Penglai 9-1 Oilfield and the exploration of similar buried hills.
Keywords: Bohai Sea,Penglai 9-1 granite buried hill,weathered crust,reservoir interpretation,inclined seismic reflection
1. Bohai Oilfield Research Institute, Tianjin Branch of China National Offshore Oil Company Ltd., Tianjin 300459, China
Strongcoal-seamreflectionsuppressionbyfastma-tchingpursuitbasedondictionarylearning.HANZhanyi1,SONGWei2,LIJiguang1,ZHAOCuixia1,ZHAOAiguo1,andMAXiaoyi1.OilGeophysicalProspecting,2022,57(5):1156-1163.
Weak effective signals are usually hidden in the upper, lower, and internal parts of strong coal-seam reflection signals. The research on methods to effectively separate weak effective signals from strong coal-seam reflection signals has attracted more and more attention, and matching pursuit is one of the effective algorithms to solve this problem. In the early days, the Gabor wavelet was used as the generating function of the matching wavelet, some other theoretical wavelets such as Morlet and Ricker wavelets are commonly used now, which are greatly different from the waveform characteristics of actual seismic data, which results in the generation of residual components in the matching process. To solve these problems, this paper introduces the dictionary learning algorithm to learn the atoms of the dictionary in the seismic data instead of predefining the atoms, which greatly improves the matching degree of signal decomposition. Aiming at the problem of unstable coal-seam reflection in the target area, we carry out dictionary learning according to a single event to build a unimodal dictionary with different amplitude, phases, dominant frequency, and polarity. Through the analysis of the attenuation of strong coal-seam reflection of post-stack and pre-stack data, it is verified that the new method is more reliable and effective than the conventional method in strong reflection suppression. The high-resolution time-frequency analysis of Wigner-Ville distribution based on the matching wavelet reveals the time-frequency attribute characteristics before and after the elimination of strong coal-seam reflection, which can provide technical support for accurate description of reservoirs near coal seams.
Keywords: strong coal seam reflection, matching pursuit, dictionary learning, Wigner-Ville distribution, matching wavelet
1. Geophysical Research Institute, SINOPEC Shengli Oilfield, Dongying, Shandong 257022, China
2. College of Geophysics, China University of Petroleum (Beijing), Beijing 102249, China
Influenceoflocalin-situstressoninterpretationofintervalvelocityandtectonic.LIUZhen1,LILi1,DAIJianwen1,andSHENShuirong1.OilGeophysicalProspecting,2022,57(5):1164-1173,1191.
In-situ stress is one of the main controlling factors affecting formation compaction. Changes in this stress inevitably lead to changes in compaction, which further affect interval velocity and tectonic interpretation based on seismic data. How-ever, no relevant literature has been found that quan-titatively analyzes the influence of lateral changes in in-situ stress on interval velocity and tectonic in-terpretation. For this reason, drawing on logging data and research results in civil engineering, solid minerals, drilling engineering, and other fields, this study simulated the stress field by the finite difference method and analyzed the influence me-chanism of local in-situ stress on interval velocity. The following understandings were gained from the analysis: ① Velocity variation on a local scale is mainly affected by the variation of the local stress field, and it has a great influence on the reserve evaluation of oil and gas fields at the initial stage of exploration. ② As for the drape anticline, the vertical in-situ stress decreases in the direction from the structural high to the wing, and the change quickens with the increase in burial depth. ③ Regarding the rollover anticline, the vertical in-situ stress increases in the direction to the fault, and the change speeds up as the fault draws near and burial depth increases. ④ Under the influence of in-situ stress, interval velocity and average velocity at the structural high are higher than those at the wing in these two types of structures, and the changes quicken with the increase in burial depth. Examples of drilled oil fields confirmed the above understandings. Therefore, the insitu stress field is one of the important geological factors affecting the variation of interval velocity, and it should be taken into account in seismic exploration.
Keywords: local in-situ stress, in-situ stress simulation, drape anticline, rollover anticline, interval velocity, average velocity
1. Shenzhen Branch of China National Offshore Oil Corporation, Shenzhen, Guangdong 518041, China
Predictionofthin(interbed)sandthicknessbasedonwellloggingforwardmodelingtemplateandGaussianprobabilityfield.DUXin1,2,FANTing’en1,2,FANHongjun1,2,DONGJianhua1,2,andZHOUJiannan1,2.OilGeophysicalProspecting,2022,57(5):1174-1181.
The classical wedge model experiment assumes that single sand bodies are developed under the background of mudstone, which contradicts the fact that the thin (interbed) layers are more extensively developed in real situations. Additiona-lly, the methods of employing functions to fit the relationship between seismic attributes and sand thickness for thin (interned) sand thickness have an accuracy limit. To this end, a new method for thin (interbed) sand thickness prediction is proposed based on well logging forward modeling template and Gaussian probability field. Firstly, seve-ral wedge models are built through reservoir logging curves of well logs in the W oilfield, and the relationship template of amplitude attribute vs thin (interbed) sand thickness suitable for the oilfield is obtained via convolution forward modeling. Semi-quantitative relationship between amplitude attri-butes and sand thickness is established. Secondly, based on data of thin (interbed) accumulated sand thickness and seismic amplitude attribute value of well points, Gaussian probability field of accumulated sand thickness vs amplitude attribute is constructed. Combined with the amplitude attribute vs thin (interbed) sand thickness relationship template, the most probable thin (interbed) sand thickness corresponding to seismic amplitude attributes is solved. Finally, attribute of thin (interbed) sand thickness and sand thickness confidence with maximum probability are obtained. The effectiveness and feasibility are verified through a 3D model containing several channels and actual oilfield data.
Keywords: thin interbed, accumulated sand thickness, forward modeling template, Gaussian probability field, sand thickness confidence
1. CNOOC Research Institute Ltd., Beijing 100020, China
2. State Key Laboratory of Offshore Oil Exploitation, Beijing 100020, China
Characteristicsoffaultactivityanditseffectonna-turalgasaccumulationinChanglingfaultdepression.WANGQi1,2,ZHANGWanfu3,SUNYonghe2,4,WANGYougong1,2,5,FUXiaofei1,2,andSUNLizhi3.OilGeophysicalProspecting,2022,57(5):1182-1191.
There are various types of gas reservoirs in the Changling fault depression of Songliao basin, and their distribution characteristics are closely related to fault activity. Therefore, against the tectonic evolution background of the basin, the expansion index(EI) of the extensional normal fault, throw-depth (T-Z) curve of the normal fault, inversion rate (RI) of the reverse fault, and the slip-distance curve are used to analyze the fault activity period and intensity for further classification of fault types and the analysis of the different control effects of different faults on gas accumulation. The results reveal that ①the Changling fault depression has developed four types of fault systems: the faults active in the rifting period, the faults active during the rifting-depression period, long-term (continuous activity from the rifting-depression period to the inversion period, the same below) active weak reverse faults, and long-term active strong reverse faults. ②Faults formed during the rifting period control the source rock of the Shahezi Formation and the volcanic reservoirs of the Yingcheng Formation. ③Faults active in the rifting-depression period not only control the distribution of source rock and volcanic reservoirs but also serve as oil and gas transport faults of the middle and lower gas reservoir combinations when they are in the source. ④Long-term active weak reverse faults control the distribution of source rock during the rifting period, act as transport faults during the depression period, and control shallow traps and adjust the gas reservoirs in the inversion period. ⑤Long-term active strong reverse faults can destroy the natural gas reservoirs formed in the depression period, and thus it is difficult to form large-scale natural gas accumulation around such faults. The above conclusions can be used as a reference to guide nature gas exploration in the southern Songliao Basin.
Keywords: Songliao basin, Changling fault depression, characteristic of fault activities, classification of faults, reservoir-control effect
1. School of Earth Sciences, Northeast Petroleum University, Daqing, Heilongjiang 163318, China
2. Heilongjiang Key Laboratory for Integrity Eva-luation of Oil and Gas Reservoir and Underground Storage, Daqing, Heilongjiang 163318, China
3. Geological Research Center, BGP Inc., CNPC, Zhuozhou, Hebei 072751, China
4. School of Petroleum and Natural Gas Enginee-ring, Chongqing University of Science and Techno-logy, Chongqing 401331, China
5. Sanya Offshore Oil & Gas Research Institute, Northeast Petroleum University, Sanya, Hainan 572025, China
Permeabilitypredictionofcarbonatereservoirsbyconventionalloggingwithadaptivemodel.XUPengyu1,ZHOUHuailai1,2,GUANJunjie1,CHENLi1,ZHOUJie1andSONGYusha1.OilGeophysicalProspecting,2022,57(5):1192-1203.
Permeability prediction of carbonate reservoirs by conventional logging data is mainly conducted through physical and fitting models. However, accurate physical parameters are difficult to obtain via traditional physical models, and it is also difficult to directly predict the permeability of carbona-te reservoirs with strong heterogeneity by fitting models. With optimized physical model and fitting model parameters, this paper employs the improved particle swarm optimization (IPSO) algorithm and optimizes the parameters of the physical model and machine learning model. Finally, an adaptive model for permeability prediction is proposed. Taking the second member reservoirs of Dengying Formation of Gaoshiti-Moxi block in north central Sichuan Basin as the research object, the paper validates the permeability prediction capability of the adaptive model by two experiments. The results are as follows. ① The prediction capability of the model can be improved by coupling physical model and machine learning model, which addresses the insufficient basic data of physical model during applications. ② The parameters of physical model and machine learning model can be more effectively optimized by the IPSO algorithm, and IPSO-XGBoost features better prediction performance with strong applicability. ③ IPSO is proved to be more suitable for determining the empirical coefficient in the discrete rock type (DRT) clustering algorithm. The adaptive model provides a new idea for the accurate prediction of carbonate reservoir permeability.
Keywords: carbonate IPSO-XGBoost, adaptive mo-del, DRT, permeability prediction
1. School of Geophysics, Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu, Sichuan 610059, China
2. State Key Laboratory of Oil and Gas Reservoir Geology and Exploitation, Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu, Sichuan 610059, China
Aconstrainedinterpolationcutmethodforgravityfieldseparation.MENGQingkui1,2,3,SHUQing1,2,GAOWei1,2,ZHOUJianxin1,2,ZHANGWenzhi1,2,andLIYong4,5.OilGeophysicalProspecting,2022,57(5):1204-1217.
Gravity data processing plays an important role in oil-gas exploration and basic geological research,and the separation of the gravity field is one of its key links. Systematically analyzing the basic principle of the interpolation cut method,this study demonstrates that the method cannot be directly applied to actual complex underground geological situations as its cut operator only considers the superposition situation where the local anomaly and the regional anomaly share the same bending direction. Then,starting with comprehensively consi-dering the types of the superposition relationship between a local anomaly and a regional anomaly,this study formulates a compensation scheme for the cut operator and proposes an interpolation cut method based on abnormal constraints,namely the constrained interpolation cut method. The trial calculation with the theoretical model verifies that the interpolation cut method does have the above problem. The multi-scale wavelet decomposition method is introduced for horizontal comparison. Among the three methods,i.e., the interpolation cut method, the constrained interpolation cut method, and the multi-scale wavelet decomposition method, the constrained interpolation cut method generates a local anomaly that has the strongest correlation with the theoretical one,and the correlation coefficient is 0.75. Compared with the interpolation cut method,the constrained interpolation cut method achieves a correction rate of 48% on the local anomaly, indicating an evident optimization effect. Drawing on the layer cut idea that the cut radius approximately equals the burial depth of the abnormal body proposed by predecessors,this study separates the Bouguer gravity anomalies in China’s land area and surrounding areas and obtains the gravity anomalies generated by the me-dium at the reference depth of 72 km to 76 km. A correction rate of over 50% is achieved in local a-reas, such as the Junggar basin and the Himalaya block,revealing a more realistic and reliable gravity anomaly value of this horizon. So,this new method can provide technical support for the study of the structural characteristics of the uppermost mantle. The Wan’an Basin and its surrounding areas in the South China Sea are further selected as the research object. The gravity anomaly in the Cenozoic sedimentary layer separated is largely consistent with the basement undulation shown in the seismic profile,indicating that the proposed method can be used for the inversion study of basement depth changes. The above results show that the constrained interpolation cut method improves the interpolation cut method and deserves practical application.
Keywords: gravity field separation,constrained interpolation cut method, theoretical model,example application
1. Key Laboratory of Airborne Geophysics and Remote Sensing Geology, Ministry of Natural Resources, Beijing 100083, China
2. China Aero Geophysical Survey and Remote Sensing Center for Natural Resources, Beijing 100083, China
3. School of Geophysics and Information Techno-logy, China University of Geosciences (Beijing), Beijing 100083, China
4. Institute of Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, Chinese Academy of Geological Science, Langfang, Hebei 065000, China
5. Key Laboratory of Geophysical Electromagnetic Probing Technologies of Ministry of Natural Resources, Langfang, Hebei 065000, China
Three-dimensionalmagnetotelluricforwardmodelingbyorderreductionbasedonblockrationalKrylovmethod.ZHOUJianmei1,LIUWentao1,LUKai-liang1,andLIXiu1.OilGeophysicalProspecting,2022,57(5):1218-1227,1262.
Three-dimensional (3D) magnetotelluric (MT) forward modeling requires solutions to electromagnetic field distribution of two polarization sources at several frequencies, thus leading to enormous computational costs. This paper accele-rates 3D MT forward modeling by order reduction based on block rational Krylov method. The novelty of this algorithm lies in the following aspects. First, the source-term explicit expression of MT is represented as planar current source, and the frequency-dependent electric field response is a produ-ct of a transfer function and a constant vector of the current source. As a result, the rapid solution of electric field response at all frequencies is reali-zed through the construction of a rational Krylov subspace, which avoids repeated solutions of large sparse linear equations with different frequencies. Second, the paper adopts the block Krylov technique to express polarizations of TE and TM as block source vectors and simplifies forward mode-ling response of the two polarizations into the construction of a block rational Krylov subspace. Additionally, an asymptotic convergence formula is introduced to obtain the optimal single repeated polarization of the Krylov method. Combined with direct solver, the forward modeling computational cost of 3D MT is reduced to a coefficient matrix decomposition and dozens of matrix back substitutions. This algorithm ensures the forward mode-ling accuracy and significantly improves the forward modeling speed. Numerical results of forward modeling in half space model and 3D DTM1 model show that compared with the conventional frequency-dependent forward modeling solutions, block rational Krylov can notably increase the modeling speed.
Keywords: magnetotelluric (MT), numerical simulation, transfer function, block rational Krylov method, forward modeling by order reduction
1. College of Geology Engineering and Geomatics, Chang’an University, Xi’an, Shaanxi 710054, China
AttitudeeffectonmarinemagneticsourceTEMdetectionsystem.ZHAOYue1,2,XUFeng1,2,CAOHuake3,4,andLIUJia1,2.OilGeophysicalProspecting,2022,57(5):1228-1240.
As marine oil and gas resources continuously develop, marine magnetic source transient electromagnetic (TEM) systems have drawn more and more attention in recent years. However, a stable attitude of transceiver loop devices is difficult to maintain in seawater during practical data collection due to the factors such as seabed environment, ocean currents, and uneven speed. The attitude changes of detection systems will alter the coupling between transceiver loop devices and underwater electrical anomalous bodies. This will lead to a certain deviation of observation data and reduce the reliability of interpretation results. First, based on the theory of electromagnetic field, this paper derives the three-component electromagnetic field expression in the frequency domain of arbitrary magnetic dipole source in the isotropic horizontal la-yered medium model under limited water depth. Then, the electromagnetic response characteristics of the marine magnetic loop source are analyzed by the superposition principle of electromagnetic fields. Second, by defining two coordinate sys-tems and their transceiver rotation matrix before and after attitude change, the paper builds a mathe-matical model of attitude changes in underwater towed magnetic source. Finally, taking the towed central loop TEM detection device in shallow water as an example, it analyzes the error distribution of observation data caused by the attitude change of the transceiver system. Additionally, the relationship between TEM response results and parameters of attitude change angle, attenuation time, sea depth, and seabed conductivity is also explained. The research results can help quantify the parameter design of the marine magnetic source TEM detection system and provide a theoretical basis for promoting and processing this method in the future.
Keywords: marine TEM method, magnetic source, attitude change, magnetic dipole model
1. Institute of Acoustics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100091, China
2. Beijing Engineering Technology Research Center of Ocean Acoustic Equipment, Beijing 100091, China
3. School of Geological Engineering and Geomatics, Chang’an University, Xi’an, Shaanxi 710054, China
4. Integrated Geophysical Simulation Lab of Chang’an University (Key Laboratory of Chinese Geophysical Society), Xi’an, Shaanxi 710054, China
ParallelalgorithmofseismicsignalfrequencycompensationbasedonCUDA.ZHANGQuan1, 2, 3,ZHANGJieming1,LEIQin1,PENGBo1,2,andLIUShuyan1,2.OilGeophysicalProspecting,2022,57(5):1241-1249.
The frequency compensation algorithm of seismic signals based on compressed sensing can effectively broaden the spectrum of seismic signals and improve the resolution of seismic data. Although the algorithm has a good frequency-broadening effect, it has low time efficiency in the face of high-dimensional and large-scale seismic data. Analysis shows that the bottleneck of the algorithm lies in massive algebraic operations for the reflection coefficient and convolution operations in signal reconstruction. Therefore, a parallel scheme based on CUDA is proposed for parallel optimization of the algorithm. Firstly, the organization form of seismic data is changed to make it more efficient and more suitable for parallel processing. Then, the serial code for computing the reflection coefficient is reconstructed, and a large number of lightweight threads of GPU are called by CUDA to parallelize the algebraic operations. Finally, the convolution calculation method of time-domain signals is changed by the convolution theorem, and the convolution operation of two time-domain signals is converted to the frequency domain by the cufft library function. The results reveal that the parallel algorithm achieves four times the overall speedup of the serial algorithm on the PC side on the pre-mise of ensuring computational accuracy.
Keywords: frequency compensation, CUDA, parallel computing, compressed sensing
1. School of Computer Science, Southwest Petroleum University, Chengdu, Sichuan 610500, China
2. State Key Laboratory of Oil and Gas Reservoir Geology and Exploitation (Southwest Petroleum University), Chengdu, Sichuan 610500, China
3. School of Information and Communication Engineering, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, Sichuan 611731, China
Thoughtaboutseismicresolutionandcountermea-suresofhigh-resolutionseismicexploration.YUNMeihou1,ZHAOQiufang1,andLiXiaobin1.OilGeophysicalProspecting,2022,57(5):1250-1262.
Seismic resolution has been leading the develo-pment of seismic exploration technology. On the basis of analyzing the relationship between seismic resolution and signal-to-noise ratio, this paper clarifies the quantitative method to characterize seismic data quality. After analyzing the seismic data interpretation limit, it defines seismic geologi-cal interpretability as the ability of seismic data to interpret geological details. The concepts and differences between high-resolution and high-precision seismic exploration are defined. Additionally, the factors affecting seismic resolution are analyzed and divided into internal factors of seismic wavelet and external factors of seismic exploration method and geological conditions. The technical approaches to improve the resolution and the future development direction are described from three aspects of seismic acquisition, processing, and interpretation.
Keywords: resolution, signal-to-noise ratio, fidelity, seismic data quality, high-resolution seismic exploration, high-precision seismic exploration
1. Institute of Resources & Environment, Henan Polytechnic University, Jiaozuo, Henan 454003, China
