An international comprehensive benchmarking analysis of synthetic biology in China from 2015 to 2020
2022-10-04MeiruJiangCongChenTaoChenChaoZhaoZhiwenWang
Meiru Jiang,Cong Chen,Tao Chen,Chao Zhao,Zhiwen Wang,*
1 Frontier Science Center for Synthetic Biology and Key Laboratory of Systems Bioengineering (Ministry of Education),SynBio Research Platform,Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemical Science and Engineering (Tianjin),School of Chemical Engineering and Technology,Tianjin University,Tianjin 300072,China
2 Center for Biosafety Research and Strategy,Tianjin University,Tianjin 300072,China
Keywords:Synthetic biology Scopus SciVal Output Citation impact Collaboration
ABSTRACT As a new interdisciplinary field,synthetic biology has led to valuable innovations in the fields of medicine,chemistry,agriculture,energy and environment.In this paper,we systematically review the development status of global synthetic biology in the past six years,and make an in-depth benchmarking analysis of the field in China.With the aid of Scopus and SciVal,we analyze the scholarly output of synthetic biology in the world and individual countries,including publication distribution,popular journals and eminent institutions.Furthermore,the research focus and concepts,citation impact and collaborations are also examined using numerical index methods such as the field-weighted citation impact(FWCI) and relative activity index (RAI),showing the differences between data more intuitively.This study aims to offer a comprehensive understanding of the research status of synthetic biology in China and the world,offering a benchmarked overview of the results as a reference to guide the development of this field in the future.
1.Introduction
Synthetic biology is an interdisciplinary field that combines biology,bioinformatics,computer science,chemistry,materials science and other disciplines to promote the systematic development of biotechnology using modularization,quantification and standardization [1].Building on advances in molecular,cell,and systems biology,many synthetic biologists have started attempts at targeted rework and optimization of natural biological systems or even the de-novo design of new biological components with specific functions,such as enzymes,genetic circuits and cells [2].With new technologies allowing more detailed and agile manipulation of microorganisms,synthetic biology offers great hope to enhance the yield,titer,and productivity of microbial processes and realize the requirements of commercialization [3].Aided by systems biology and metabolic engineering,a great deal of useful products,such as 1,3-propanediol [4] and 1,4-butanediol [5],have been produced by biological methods,which undoubtedly gave an impetus to the further development of synthetic biology [6].
Recently,research on synthetic biology has made a great number of significant achievements,including low-cost DNA synthesis,next-generation sequencing,multiplexed,efficient,and simple genome engineering technologies,and the availability of a large number of genome sequences [7],which plays an increasingly prominent role in supporting biological research.Hutchison and Venter used whole-genome design and complete chemical synthesis to minimize the genome ofMycoplasma mycoidesJCVI-syn1.0 as JCVI-syn3.0,the genetically simplest autonomously replicating cell found in nature[8].In 2019,the team of Milo in Israel constructed a new strain of autotrophicE.coli,which produced all its biomass using carbon from CO2and successfully realized autotrophy[9].In 2021,Eisenreich and Berg found thatHippea maritimahas a reverse TCA cycle that allows it to survive and grow in a CO2-rich environment,providing a new direction for the study of carbon utilization[10].The potential of synthetic biology tools in tackling societal challenges using biotechnology is not only embodied in fundamental scientific research,but also enables many practical applications,such as the production of biofuels [11-14],the biosynthesis of pharmaceuticals and diagnostics [15-20],the creation of multifunctional materials [21-25],as well as the mass production of chemicals and food ingredients [26-30].Moreover,in the face of the impact of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic on global health and security,synthetic biology technology has shown unprecedented application potential,providing unprecedented tools for virological research and vaccine development [31].Prof.Zhang and his team developed a novel CRISPR-based coronavirus RNA detection method called STOP (SHERLOCK testing in one pot) [32],which only requires three simple steps to complete the detection in one hour.In this context,synthetic biology is also receiving increasing attention from venture capitalists,sparking a new wave of investment.In spite of the global recession and rising unemployment,synthetic biology companies have received an astounding 78 billion dollars of private and public financing in 2020,which is 5 times higher than in 2016 [33,34].The growth trend in synthetic biology industry financing also reflects the enormous potential of synthetic biology.In the context of the sudden rise of synthetic biology around the world,related research in China has also achieved a large number of breakthroughs.For example,in genome synthesis and chromosomes engineering,a method for fast targeting and accurate repair of genomic defects was successfully established[35].Additionally,the first eukaryotic organism with a single linear chromosome was innovatively created by fusing the 16 chromosomes ofSaccharomyces cerevisiaeinto a single chromosome [36].There are also inspiring reports from other areas of synthetic biology,including genome-editing technology [37-44],genetic circuits [18,45-49],rational design based on genome-scale network models [50-52],as well as the construction of biological chassis cells [53-56] and cell factories[57-60].
Thus,significant achievements have been made in synthetic biology research in recent years.A clear understanding of the research status of synthetic biology from multiple perspectives,including the amount,types and influence of literature,will help guide the future development direction and open up new fields.However,to the best of our knowledge,there is still no in-depth benchmarking analysis of the current state of synthetic biology in China and the world.In this article,we retrieved the global publications related to synthetic biology in the Scopus database from 2015 to 2020,and evaluated the output,research focus and key concepts,citation impact and collaborations,after which we benchmarked the state of the field in China to the overall international situation.The analysis is based on a multidisciplinary corpus of publications selected through relevant keywords and aided by numerical index methods such as the field-weighted citation impact(FWCI) and relative activity index (RCI)to show the differences between data more intuitively.Based on this analysis,a more comprehensive understanding of synthetic biology research can be offered,so that possible solutions and development directions for the future can been proposed.
2.Methods and Data
2.1.Data collection and retrieval
We retrieved the data of publications related to synthetic biology from the Scopus database (http://www.scopus.com),which is the world’s largest database of abstracts and citations.It covers more than 20,000 journals published by more than 5,000 publishers in the fields of science,technology,medicine and social sciences,including more than 19,000 peer-reviewed journals,as well as book series,conference proceedings,patents and web pages[61].Compared with other single-indexed abstract repositories,Scopus is more comprehensive and covers a wider range of disciplines,allowing users to retrieve nearly 50 million articles from as far back as 1823.
Our research is based on the integrated use of Scopus and Sci-Val.We searched the Scopus database for research achievements,mainly including academic papers,monographs,patents and other academic outputs,related to synthetic biology,using the keyword‘‘Synthetic biology”.The searched text was set to ‘‘paper title,abstract,keywords”,and the time scope was limited to documents collected and preserved from 2015 to 2020(6 years).The retrieval date was January 18,2021.After searching using these criteria,the obtained data set was named ‘‘synthetic biology-world”.Then,additional criteria were used to filter subsets of relevant data for the top 10 most prolific countries or regions,as well as the top 10 institutions with the highest scholarly output in the world.In addition,another entry ‘‘China” was added to the previous keyword ‘‘synthetic biology”,to produce a data set comprising the top 20 most popular journals and institutions of China.
2.2.Data analysis tools
SciVal is a web-based analytical tool for scientific research management,discipline analysis and talent performance analysis launched by Elsevier [62].We used search keyword queries and constraint filters such as year of publication and country in SciVal to create a Research Area,which was subsequently used for additional analyses.SciVal can analyze and compare the publication set,based on basic data from Scopus,with more than 10 sciencemetric indicators to visualize research performance,benchmark relative to peers,as well as identify and analyze new,emerging research trends.
The relevant datasets described above were then all imported into SciVal to analyze the retrieved data.Then,each analysis result from SciVal was exported into an excel file.Excel 2007 software(Microsoft Corp.,USA)was used for statistical processing and Original 9.0.0 was used to draw trend figures.
2.3.Defined mathematical indicators
2.3.1.Field-weighted citation impact
In order to eliminate the influence of different research fields,specific time and other citation practices in the comparative evaluation of research results,we used the mathematical indicator FWCI to measure the citation impact [63].It compares the actual number of citations received by an article with the expected number of citations for articles of the same document type(article,review or conference proceeding paper),publication year and subject field.
The FWCI ofNarticles is defined as:
whereciis the number of citations received byipublication,andeiis the expected number of citations received by the average publication in the same year plus following 3 years.
When a similar publication belongs to more than 1 category,eiis calculated using the harmonic mean.For a publicationithat is part of 2 categories:

whereeAandeBare the fractional counts of publications and citations in category A and B,respectively,so thatiwill be counted as 0.5 publications in each ofeAandeB,and the citations it has received will also be shared between A and B [64].
The indicator is defined with reference to a global baseline of 1.00 and a FWCI of 1.00 indicates corresponds to the global average for similar publications.Therefore,the FWCI of ‘‘world”,based on the entire Scopus database,was defined as 1.00.An FWCI of more or less than 1.00 indicates that the entity’s publications have been cited more or less often than would be expected based on the global average for similar publications,respectively.
2.3.2.Compound annual growth rate
The compound annual growth rate(CAGR)was used to measure the year-on-year constant growth rate during a certain time,and was calculated using the formula:

whereV(tn)is the ending value,V(t0)is the beginning value,andtnt0is the number of years considered in the research [65].
The data on yearly publication output for the last six years related to synthetic biology were obtained using SciVal,and then exported into an excel file to calculate the corresponding CAGR value according to the above definition [66].
2.3.3.Relative activity index
In order to intuitively present the various fields that are prioritized by different countries,the degree of preference was quantified using the relative activity index (RAI) [67].The RAI is defined as a country’s share of publications in a subject field relative to the global total of publications in the same subject field.The RAI analyses in this paper are limited to synthetic biology and the numbers indicate the degree of preference to which a country attaches importance to various subject areas in synthetic biology.
To illustrate this calculation clearly,using subject area ‘‘Biochemistry,Genetics and Molecular Biology” in synthetic biology of China as an example.In the period of 2015-2020,China published 2,143 papers in synthetic biology overall,among which 1,237 papers were recorded in the subject area ‘‘Biochemistry,Genetics and Molecular Biology”.The world published 14,425 papers in synthetic biology overall,with 8,034 papers in the subject area ‘‘Biochemistry,Genetics and Molecular Biology” in the period 2015-2020.Therefore,the relative activity index for China in ‘‘Biochemistry,Genetics and Molecular Biology” is(1237/2143)/(8034/14425)=1.04.
3.Results and Discussion
3.1.Output of publications related to synthetic biology in China and the world from 2015 to 2020
From 2015 to 2020,a total of 14,425 articles on synthetic biology were published worldwide.The published data was exported from Scopus to compile a dataset and analyzed using SciVal.As shown in Fig.1,the total number of published articles has been on the rise to different degrees in the past 6 years.In 2016,the annual growth rate of published articles in the field reached 9.6%,and then remained stable at around 6% in 2018 and 2019.It is worth noting that the global output increased by only 0.7% in 2020,which may be attributed to the enormous influence of COVID-19 the year of the pandemic.The COVID-19 pandemic has not only become the greatest global health crisis of our time,but also caused a lot of inevitable damage in the development of many fields,such as economics,science,technology and culture [68].However,the output of China has been on an upward trend from 2015 to 2020,even continuing to grow in 2020 (Fig.1).In terms of output,we can conclude that Chinese researchers are paying increasing attention to synthetic biology and synthetic biology in China has been booming for the past 6 years.
Furthermore,in terms of quality,15.5% of publications in synthetic biology between 2015 and 2020 were among the world’s top 10%most cited publications,and the corresponding percentage for China was slightly higher,at 15.9%.CiteScore is another evaluation indicator that can be used to measure the quality of publications.It is based on the number of citations in different documents,including articles,reviews,conference papers,book chapters,and data papers by a journal over three years,divided by the number of the same document types indexed in Scopus and published in those same 3 years.According to this measure,about 49.1%of publications in synthetic biology were published the world’s top 10%of journals,indicating the high quality and innovative nature of the published articles in the field.
3.1.1.Distribution of synthetic biology outputs among the most prolific countries or regions
The trends in synthetic biology output of a single country,such as China,are not always consistent with the worldwide trends,as shown in Fig.1.Therefore,we investigated the distribution of synthetic biology output by country using SciVal,and ranked the top 10 most prolific countries or regions to further analyze the total annul publications and year-on-year constant growth rates in detail.In terms of total output,the two largest contributors were the United States and China,followed by the United Kingdom and Germany,which was shown in Fig.2(a).The total output of these four countries accounted for more than 70% of the world’s production.The next six countries or regions,including France,India,Japan,Spain,Italy and Canada,had similar publication output,which was much lower than the first four.In terms of the change trend of publication output from 2015 to 2020,only China has enjoyed high growth rates in Fig.2(a).Although the United States has the highest total output,the trend of increase is slow,and the output even slightly fell in 2020.Apart for China,only Japan,India and Spain showed a significant increase of output from 2019 to 2020,which is contrary to the world trend in Fig.2(b).The increase in the output of these countries is inseparable from relevant policy support by the government,which is directly reflected in the number of actors currently working in this space,the number of institutions funded,the input of funded projects and so on.Taking China as an example,the number of synthetic biology projects funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(NSFC) increased 2.7-fold between 2015 and 2019 [69].The situation in Japan is similar,where the Integrated Innovation Strategy 2019 was launched to implement the Fifth Basic Science and Technology Plan,which proposed to promote innovation through multi-faceted integration [70].As shown in Fig.2(b),the trend of India and Spain was almost the same in the last six years,and the output in 2020 increased more than 50%compared with 2017.Furthermore,the United Kingdom,France and Italy all showed basically stable trends,and their outputs did not change much during this period.

Fig.1.The total number of publications related to synthetic biology in the world and China from 2015 to 2020.

Fig.2.Number of articles and Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) for the top contributing countries or regions in synthetic biology.(a) Number of publications top 10 countries or regions from 2015 to 2020.(b) Number of publications top 10 countries or regions from 2015 to 2020,excepting the United States,China,the United Kingdom and Germany.(c) During 2015 to 2020,CAGR for the top 10 countries or regions.
In the past six years,the research of synthetic biology in China has made significant progress,and its scholarly output has been increasing each year.By 2020,the number of synthetic biology articles published in China has accounted for about 20% of the worldwide total,compared to only 11.2 % in 2015.Here,we used CAGR to measure the growth rate of the synthetic biology output of the top 10 countries or regions from 2015 to 2020.As shown in Fig.2(c),the CAGR of synthetic biology was close to 4.44 % year-over-year for the past six years,and it is obvious that China has the highest CAGR in publications among the top 10 most prolific countries or regions,at 17.56%.It is followed by India(9.82%),Canada(6.66%),Spain(6.50%),and Germany(5.73%),with CAGR values that are still much higher than the overall worldwide publication growth in synthetic biology.However,among the top 10 countries,6 countries still had a lower CAGR than the world average of 4.44%,especially Italy (-0.48%),France (0.70%) and Japan (1.27%).Therefore,China and India are the main players pushing the increase of synthetic biology output,while the United States and some European countries struggle to keep up with the global pace.
3.1.2.Top 10 institutions by number of publications in synthetic biology in China and the world
Table 1 shows the top 10 most productive institutions in the world in terms of scholarly output in synthetic biology between 2015 and 2020.The most productive institution was the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique(CNRS)of France,which pub-lished 408 scholarly output.The Chinese Academy of Sciences was second,with only a small number of publications fewer than CNRS.Remarkably,the output of the remaining 8 institutions was much lower than that of the top 2,by at least 70 or more.It should be noted here that both the CNRS and the Chinese Academy of Sciences encompass several sub-organizations,which at least partially explains their high output.The Chinese Academy of Sciences,for example,includes the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics,the Shanghai Institute for Biological Sciences,the Institute of Microbiology,Tianjin Institute of Industrial Biotechnology,and so on.Inorder to further analyze the cited quality of the output,the FWCI was introduced,as a more sophisticated way of normalizing the differences resulted from different fields,publication years and document types[71].An FWCI over 1.00 indicates that the publications have been cited more often than the global average for similar publications.In order to further analyze the quality of output,the 10 institutions were divided into two levels according to their FWCI (Table 1).The first level of quality (FWCI >2.00) includes 4 institutions,the Massachusetts Institute of Technology,Harvard University,University of California at Berkeley and Technical University of Denmark.The other top institutions are at the second level (FWCI <2.00),including the CNRS,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Imperial College London and Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zurich.Although the CNRS and the Chinese Academy of Sciences have the most scholarly output,they are not the highest ranked in terms of FWCI.The 10 institutions cover a wide area,with three in the United States,two in the United Kingdom and one each in France,China,Spain,Switzerland and Denmark.

Table 1 Top 10 institutions by number of publications in synthetic biology in the world from 2015 to 2020

Table 2 Top 10 institutions by number of publications among synthetic biology in China from 2015 to 2020
In addition,we also listed the top 10 Chinese institutions by number of publications in the field of synthetic biology in Table 2.The Chinese Academy of Sciences is also one of the top 10 institutions in China,with the highest scholarly output.Additionally,several of its sub-organizations have made important contributions to the 403 publications in synthetic biology,such as the Shanghai Institute for Biological Sciences,Tianjin Institute of Industrial Biotechnology,and the Qingdao Institute of Biomass Energy and Bioprocess Technology.The FWCI of the top 10 most productive Chinese institutions was between 0.90 and 1.60 (Table 2).Moreover,Tianjin University had the second highest scholarly output among the top 10 institutions by number of publications,followed by Tsinghua University and Shanghai Jiao Tong University.These three universities had similar outputs,and were second only to the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
3.1.3.Top 20 journals in terms of synthetic biology publications in China and the world
In order to estimate the quality of synthetic biology publications,we further analyzed the 20 most popular journals by scholarly output in China and the world,respectively,based on data directly downloaded from SciVal.Here,we investigated the top 20 most popular journals by publications,citations and the journal quartiles that are categorized into four levels (Q1-Q4).
As shown in Table 3,the largest proportion(45%)of the 20 most popular journals were in Q1,including 9 prestigious journals such asNature,Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,Nature Communications,Nucleic Acids Research and Metabolic Engineering.There were 5 journals at the level of Q2,includingACS Synthetic Biology,Journal of Biological Chemistry,Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology,andMicrobial Cell Factories.Apart from these,4 journals (such asScientific Reports) are in Q3 and 2 journals (such asMethods in Molecular Biology) are inQ4.Moreover,ACS Synthetic Biologyis the most popular journal of synthetic biology,with 703 publications from 2015 to 2020.This number is at least three times higher than any other of the 19 journals.In view of the citations,the journalProceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of Americahas the highest average number of citations per publication (32.32) among the top 20 journals,closely followed byNature(32.13).The data also showed that 70% of the 20 most popular journals had between 10 and 30 citations per publication.

Table 3 The 20 most popular journals by scholarly output in synthetic biology in the world between 2015 and 2020

Table 4 The 20 most popular journals by scholarly output among synthetic biology in China between 2015 and 2020
The 20 most popular journals for synthetic biology in China are shown in Table 4.The most popular journal among authors from China wasACS Synthetic Biology,which was also the most popular worldwide.The quartiles of the 20 journals did not show any obvious tendency,except that Q2 journals accounted for 35%.Furthermore,the second most popular was a Chinese journal,Chinese Journal of Biotechnology.In addition,there were other Chinese journals,CIESC Journal and China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica,among the top 20 Chinese journals in the list (Table 4).The third most popular journal wasMetabolic Engineering,and the following 2 journals wereMicrobial Cell Factories,followed byApplied MicrobiologyandBiotechnology.All these journals were more popular in China than in the rest of the world in terms of their ranking.In conclusion,except for partial preferences and the order,the 20 most popular journals in the field of synthetic biology in China and the world did not differ significantly.

Table 5 The FWCI for top 10 contributing countries or regions in synthetic biology from 2015 to 2020
3.2.Research focus of publications related to synthetic biology in China and the world from 2015 to 2020
Recently,synthetic biology has greatly developed in many subject areas,not just limited to biology,giving it the potential to make a profound contribution to many other fields,such as medicine [72] and material science [73].To better understand focus of recent studies in synthetic biology and possible future contributions of synthetic biology,it is conducive to analyze the subject areas according to strength and priorities,as well as the key concepts that frequently appear.Based on the distribution of the most popular subject areas related to synthetic biology in the world,we used the mathematical relative activity index to intuitively show the research priorities of the top 5 most productive countries or regions,and further benchmark the differences of synthetic biology keywords in China and the world using the revised keyword frequency index.The following results are based on the classification of published journals in the dataset,retrieved from SciVal.
3.2.1.Top 10 most popular subject areas of synthetic biology in the world
The top 10 subject areas according to the distribution data from SciVal and their number of publications are shown in Fig.3.More than a quarter of the publications in the field of synthetic biology was concentrated in ‘‘Biochemistry,Genetics and Molecular Biology (26.8%)”.Moreover,the publications related to synthetic biology also mainly focused on ‘‘Engineering (10.5%)”,‘‘Chemical Engineering (9.5%)”,‘‘Chemistry (8.5%)” and ‘‘Immunology and Microbiology(6.8%)”.In order to intuitively investigate the quality of citations in every field,FWCI was introduced and calculated using a value of 1.00 for the world as a whole.The normalized FWCI of the top 10 subject areas of synthetic biology in the period of 2015 to 2020 was 2%-47%higher than the world average of 1.00(Fig.3),which means that studies in the field of synthetic biology are more impactful in terms of the number of citations than the world average.What calls for special attention is that the normalized FWCI of ‘‘Computer Science” is only 1.02,indicating that the quality of this field is similar to the world average.In general,most of the top 10 subject areas of synthetic biology were far above the world average,illustrating the great strength of this field.
3.2.2.Research priorities of synthetic biology in the top 5 most productive countries or regions
The distribution of publications among the top ten subject areas in each country or region also reveals their own strengths and research priorities,which are connected to the local research base,social and economic power,as well as the national strategies and priorities [74].Using the data acquired from SciVal,we investigated the differences in research focus in synthetic biology of the top 5 most prolific countries,including the United States,China,the United Kingdom,Germany and France,in the top 10 most popular research fields mentioned above.In order to more intuitively analyze the differences between the 5 top countries,we introduced the mathematical relative activity index(RAI)to illustrate the focal areas of research.An RAI of 1.0 represents the world average for publications in the corresponding subject area,while number higher or lower than 1.0 implies that the country has a higher or lower share of publications in that are than the world average,respectively.Radar graphs were used in Fig.4 to present the RAI of the top 5 countries in the top 10 fields.The length of the reticulation in the radar chart represents the RAI.
As is shown in Fig.4(a),the United States showed the biggest focus on ‘‘Biochemistry,Genetics and Molecular Biology”,with a high RAI and the largest proportion of its publications in this,while the lowest focus was placed on ‘‘Pharmacology,Toxicology and Pharmaceutics”.Furthermore,the RAI of ‘‘Biochemistry,Genetics and Molecular Biology” in the United States was higher than in the 4 other top countries.In general,the differences in RAI between the 10 subject areas in the United States are not very large,ranging from 0.9 to 1.2,indicating that the United States has a balanced distribution among subject areas.
China showed a distinct focus in ‘‘Immunology and Microbiology”,with the highest RAI of 1.69 in Fig.4(b).This is likely related to China’s research strength in disease-related subject areas,which contributes to topics related to improving people’s health in this area [75,76].With the exception of ‘‘Engineering”,‘‘Medicine”,‘‘Agricultural and Biological Sciences” and ‘‘Computer Science”,most subject areas had RAI values above the world average,and the most prominent include the above mentioned ‘‘Immunology and Microbiology”,as well as ‘‘Chemical Engineering”,with RAI values 27% higher than the world average.
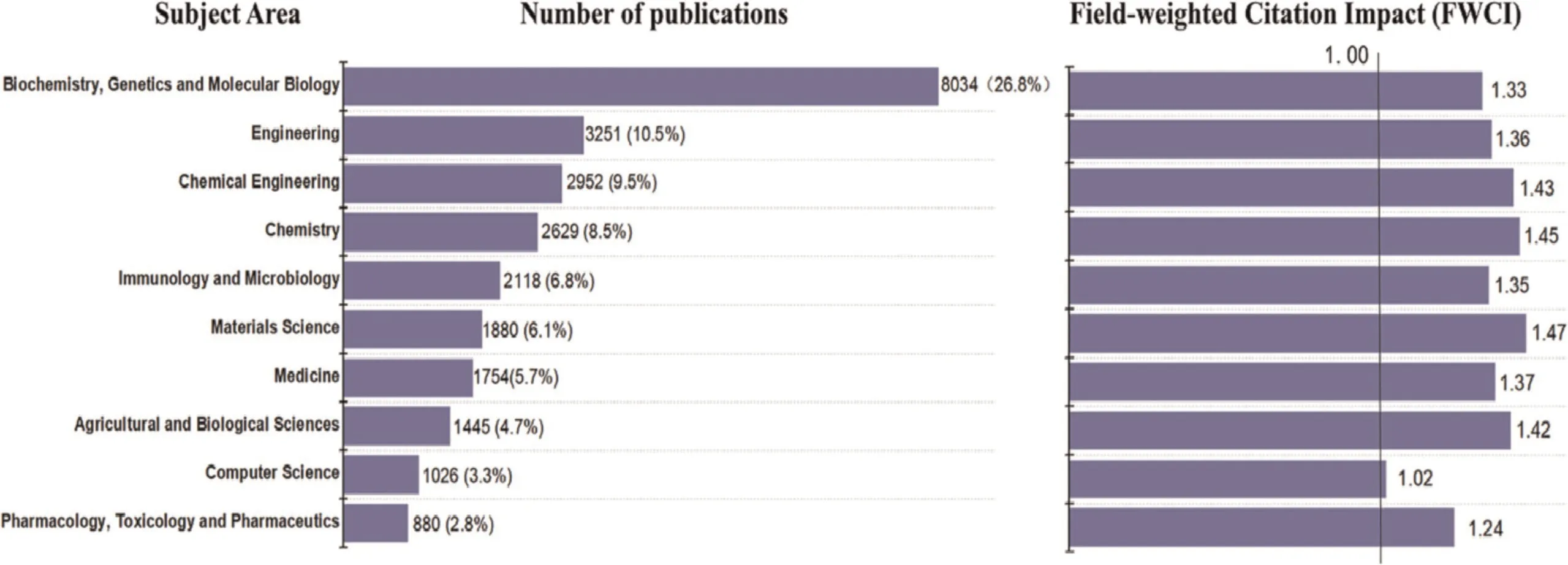
Fig.3.Breakdown and rebased field-weighted citation impact (FWCI) of synthetic biology by top 10 subject areas in the world,from 2015 to 2020.

Fig.4.Top 10 popular research focus according to synthetic biology output in the top 5 most prolific countries between 2015 and 2020.The vertical axis of the radar figure represents the value of RAI,and the horizontal axis corresponds to the top 10 contributing fields in the top 5 countries or regions.It should be noted that no publication in the subject area of ‘‘Pharmacology,Toxicology and Pharmaceutics” has been reported in the United Kingdom or France,so only 9 fields are covered in (c) and (e).

Fig.5.Top 50 key concepts of 14,426 publications related to synthetic biology in the world.The size of the label is proportional to the frequency with which it appears in the documents.And its color takes into account the growth trend that light blue and green represents the decline and growth in output respectively,and gray means growth rate is about zero.

Fig.6.Top 50 key concepts of 2,143 publications related to synthetic biology in China.The represent of the size of the label and its color is the same as above.
Similar to the United States,the United Kingdom had a balanced distribution of research activities across the 8 subject areas in Fig.4(c):its RAI was close to 1.0 in all areas except for‘‘Computer Science”,which had the highest RAI of 1.16,dominating synthetic biology research in the United Kingdom.It was followed closely by‘‘Engineering”,‘‘Agricultural and Biological Sciences Biochemistry”and‘‘Biochemistry,Genetics and Molecular Biology”,which all had RAI values above 1.00.
There was a clear distribution of research focus in Germany.There were four subject areas with RAI values higher above 1.0,including ‘‘Agricultural and Biological Sciences Biochemistry”(1.28),‘‘Chemistry”(1.26),‘‘Molecular Biology,Chemical Engineering”(1.12)and‘‘Genetics”(1.05)in Fig.4(d).The RAI of‘‘Medicine”and‘‘Immunology and Microbiology”in Germany was on par with the world average,at 0.96 and 0.98 respectively.However,the remaining 4 subject areas had obvious lower attentions than the world average.
The share of France’s publications in ‘‘Agricultural and Biological Sciences,Biochemistry”and‘‘Computer Science”was more outstanding than that of other areas,with RAI values of 1.49 and 1.33 in Fig.4(e),respectively.These two areas dominated the landscape of France’s research in synthetic biology and France had the biggest share of these areas compared among the 5 top countries.
In summary,the major research focus of most Europe countries was the field of ‘‘Agricultural and Biological Sciences,Biochemistry”,which is likely related to the countries’ characteristic geographic conditions and research bases [77,78],since the strengths of these countries lie in subject areas in the domain of natural sciences[79,80].In addition,the United State and the United Kingdom showed a relatively good balance among the ten or nine subject areas,while China pays particular attention to ‘‘Immunology and Microbiology” [81].
3.2.3.Key concepts of synthetic biology in China and the world from 2015 to 2020
The semantic fingerprint consists of all the key concepts derived from a piece of text,weighted to reflect their relative importance.The Elsevier Fingerprint Engine can be used to determine the semantic fingerprint based on data from SciVal.In this study,we obtained the top 50 most frequent concepts illustrated in the word clouds below,Fig.5 showing the worldwide view,and Fig.6 the most frequent concepts in publications from China.According to SciVal,the most frequently occurring key phrase ‘‘Synthetic Biology”was given a value of 1.00,and the remaining key phrases were given values between 0 and 1.00 based on their relative frequency.
As shown in Fig.5,there are four main key phrases in the word clouds,Synthetic Biology (the maximum value was 1),Metabolic Engineering (0.16),Scaffold (0.14) and Gene Regulatory Network(0.09),which are the top 4 most frequently used concepts.Except for Riboswitch and Bacteriophage,they all had positive or negative growth in scholarly output.There were 16 concepts showing a decrease,accounting for 32% of the top 50 concepts,which is exactly one half of the percentage of positive growth concepts.
Different from the rest of the world,some concepts other than synthetic biology were more frequent in China as shown in Fig.6.The second most frequently used key phrase in China was Metabolic Engineering,and its value of 0.35 was more than double the worldwide average.Thus,this concept is much more frequent in China’s scholarly publications.The same is true for other rankings,with China’s ninth-ranked key phrase having the same value as the fourth-ranked concept in the rest of the world as a whole.In addition,there were other 6 most frequent concepts had values greater than 0.10,including Biosynthesis (0.16),Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (0.14),Scaffold(0.12),Gene Regulatory Network (0.11),Gene Editing (0.10) and Biotechnology (0.10).By contrast,only 3 concepts had values over 0.10 for the world as a whole.Among the top 50 keywords in China,only nine concepts showed a decrease of academic output,and two saw a growth rate of zero.Overall,78%of the top 50 most frequent keywords exhibited an increase of scholarly output,which was 14% higher than the worldwide percentage.Moreover,compared with the world,the synthetic biology publications in China had more high-value key phrases,which occurred more often relative to the concept of‘‘Synthetic Biology”,while the concepts in the worldwide publications were relatively dispersed in various areas.
3.3.Citation impact of synthetic biology from 2015 to 2020
3.3.1.Citations and citation share among the top 10 most prolific countries or regions
The number of citations a paper received from subsequent published publications is widely accepted as an indicator of the quality or importance of reported research [82].Therefore,we analyzed the total citations and their share among the top 10 most prolific countries or regions mentioned in Fig.3(a).As shown in Fig.7,a similar situation was seen in the number of publications,whereby the United States had the largest total number of citations among the top 10 countries or regions.China ranked second,with slightly more total citations than the United Kingdom,which came in third,but the overall difference was not significant.Overall,the trend of total citations was similar to that of output,except for the nonlinear but similar relationship appearing in the last 5 countries or regions out of the top 10.
In order to more intuitively illustrate the number of citations of each country or region,the citation share was introduced to reflect the level of citations of each country in the world.It is defined as the country’s percentage of annual citations in synthetic biology publications as a percentage of the total number of corresponding citations in the world.The final calculation results are summarized in Fig.8.From 2017 to 2020,the United States showed a precipitous drop in its share of total citations,over 14%,which can be partly explained by the near-stagnation of the publication output.However,the constant volume of publications alone cannot have such a big impact on the citation share,and further reasons remain to be discovered.As shown in Fig.8(a),China has increased its share of citations in synthetic biology by 50% over the past six years.Although the citation share of China was lower in 2016 and 2018,the overall output still showed an increase in the two years as shown in Fig.1.This might due to that the growth rates of output in 2016(11.8%)and 2018(6.5%)were significantly lower than in the other three years(average 23.7%).And the citations are usually accrued by articles after they have been published,which both make sense for the low share in 2016 or 2018.In conclusion,most developed countries like the Unite States,the United Kingdom and France showed a decline in their share of citations in Fig.8(a) and 8(b) which is in line with the trend in output from 2015 to 2020.By contrast,Asian countries such as China and India were less affected by the decline and constantly pulling the overall level to a positive development.
3.3.2.Field-weighted citation impact among the top 10 most prolific countries or regions
In order to provide a more intuitive way to measure research impact,the FWCI was used to analyze the citation impact of the top 10 most prolific countries or regions.Table 5 lists the FWCI values of the top 10 contributing countries or regions in synthetic biology from 2015 to 2020.The average FWCI of synthetic biology in the whole world from 2015 to 2020 was 1.35.This indicates that synthetic biology is a popular research area with a high global impact,receiving 35% more citations than the global average(Table 5).Canada had the highest average FWCI among the top 10 (1.81),followed by Italy (1.69),the United States (1.68) and France(1.63).Notably,the FWCI of the United States has decreased 19%from 2017 to 2020,which also helps explain the steep decline in citation share mentioned above together with the stagnation in publication output over the three years.Canada and Italy showed a tremendous double increase between 2019 and 2020,which may be the main reason for pulling the average FWCI in the nearly six years.In particularly,the article by Chicco and Jurman,titled‘‘The advantages of the Matthews correlation coefficient (MCC)over F1 score and accuracy in binary classification evaluation,BMC Genomics 21(1)(2020)6[83]”published in 2020 was among the top 5 papers by highest citations,at 124.This perhaps contributed to the FWCI of Italy reaching 3.1 in the same year.Although a similar tremendous increase was seen in Canada in 2017 and 2020,we did not find a reasonable explanation in citation numbers to explain it,and the specific reasons still need to be further explored.Unfortunately,the average FWCI for synthetic biology of Asian countries,including China,India and Japan,has been lower than the world average over the last six years.

Table 6 Total citation count,average number of citations per publication and average FWCI for top 10 institutions with highest citations in synthetic biology from 2015 to 2020
In order to compare the top 10 countries or regions among themselves and with the global average,the FWCI was revised using the worldwide value to calculate a normalized FWCI,which is shown in Fig.9.After rebasing,Canada and Italy still had the highest average impact in this field,but countries such as Italy and Germany were rapidly improving based on the worldwide level from 2015 to 2020.The citation impact of the United States has decreased by 20% in the recent 3 years.Other Western countries among the top 10,with the exception of the United States,France and Spain,have made more or less progress in FWCI from 2019 to 2020.Among Asian countries,China,India and Japan are still below the worldwide average,which may partly be attributed to the research foundation and development level of related crossdisciplines and later start of related research.Although the FWCI of the world showed a decline in 2017 and 2019 (Table 5),India and Japan also performed below the worldwide average and scored consistently below China.
3.3.3.Synthetic biology citation impact of China between 2015 and 2020
In the recent three years,the citation share of China in synthetic biology has exhibited a continus increase,rising 40% from 2018 to 2020 in Fig.8(a).There is no doubt that China’s publications in synthetic biology are accounting for an increasing proportion of worldwide citations.However,the quality of publications,reflected in the FWCI still has rome for improvement,since the FWCI of China was below the worldwide average almost every year except for 2015 and 2019 (Table 5).Therefore,a more detailed analysis on the citation impact of China’s domestic publications is particularly important to dissect the reasons for this phenomenon and put forward improvement plans.Here we listed the top 10 most cited Chinese institutions in synthetic biology(Table 6),and analyzed their citation impact compared with the top 10 most prolific ones (Table 2).Most of them are also among the top 10 contributing institutions with the most published output,but Xiamen University and Fudan University only appear in the top 10 most cited institutions,indicating that are not high in quantitative output but outstanding in terms of citation impact.Among them,the average number of citations per publication of Xiamen University is 40.3 and the FWCI is 2.63,which were at least 1.34 and 0.65 times higher than the other institutions in citations per publication or FWCI respectively in Table 6.As the Scopus data shows,this could be attributed to the article ‘‘Gawande M.B.,Goswami A.,Asefa T.,Guo H.Z.,Biradar A.V.,Peng D.L.,Zboril R.,Varma R.S.,Core-shell nanoparticles:synthesis and applications in catalysis and electrocatalysis,Chem.Soc.Rev.44(21)(2015)7540-7590”[84] which has being cited 533 times,more than 7 fold of the second-most-cited publication from this institution.In addition,the Chinese Academy of Sciences also has the highest total number of citations.It is followed by Tsinghua University,Tianjin University and Shanghai Jiao Tong University,which each have far more citations than other institutions.As can be seen in Table 6,the FWCI of all the top 10 institutions with the highest number of citations was higher than China’s average (1.31),apart from Shanghai Jiao Tong University,indicating that China has a large number of highly cited quality institutions.However,the citation quality is slightly lower in the top 10 most prolific institutions (Table 2).Thus,in order to improve the citation impact of China,it is necessary to improve the citation quality of high-yield institutions,and encourage institutions with high citation quality to simultaneously increase the output of research results.

Table 7 The overall share of publications in synthetic biology by collaboration type of the top 10 most prolific institutions in China between 2015 and 2020
3.4.Collaboration among countries or regions in synthetic biology from 2015 to 2020
With the acceleration of globalization and increasingly close international exchanges,researchers in various fields have increasingly more opportunities to carry out frequent international collaborations [85].This type of collaboration trends to yield higher impact[86,87].In order to measure the impact and value of collaborations,a method which can be divided into international,national,institutional and single authorship is established by looking at co-authorship relationships in publications.The situation that authors are affiliated with multiple author research outputs from institutions in at least two different countries is defined as international collaboration.National collaboration indicates that the publication has multiple authors affiliated with multiple institutions,all of which are from the same country.Institutional collaboration is defined as multi-authored research where all authors are affiliated with the same institution.Single authorship is defined as single-authored research outputs.Using this definition,we analyze the collaborations among the top 10 contributing countries or regions and the top 10 most prolific institutions of China.
3.4.1.Global collaboration among the top 10 countries in synthetic biology from 2015 to 2020
In view of the worldwide collaborations in synthetic biology,national collaboration and institutional collaboration are major approaches to cooperation,which account for more than 60% in Fig.10.However,in the past six years,the trend of change between national collaboration and institutional collaboration went in opposite directions.The proportion of national collaboration has increased from 28.6%to 34.8%,and has surpassed institutional collaboration,while institutional collaboration declined 13.3% during the six years,indicating that national collaboration is increasingly more popular in the whole world in Fig.11.Furthermore,the proportion of international collaborations basically stayed within the range of 24% to 30%.Single-author publications are increasingly rare in the field of synthetic biology,and their proportion of 2020 was approximately half of that in 2015.

Fig.10.The overall share of publications by collaboration type of top 10 most prolific countries or regions in synthetic biology between 2015 and 2020.
Among European countries,such as the United Kingdom,Germany and Italy,international cooperation accounts for at least 50% of the total,while France had the highest proportion of international cooperation,reaching 60.7%in Fig.10,demonstrating that international collaboration is the dominating mode in academic output of synthetic biology in these countries.Although France had the highest proportion of international cooperation among the top 10 countries,its institutional cooperation accounted for the lowest share(3.4%)in Fig.10.Among Northern American countries,Canada had the absolute advantage in terms of international collaboration (51.3%) which is somewhat alike to European countries,while the United States had relatively equal distribution in the other three collaborations except for lower single author collaborations.Notably,the sudden increases in the proportion of international cooperation approximately coincided with sharp increases in FWCI (Table 5),which may reasonably explain the tremendous increase of FWCI mentioned in Section 3.3.2.Additionally,the data from Switzerland and Australia showcase the same rule that a high FWCI is accompanied by a high proportion of international cooperation in that year,which indicates the strengthen of international cooperation in increasing the quality of citations(Table S1 and Table S2,Supplementary Material).Among Asian countries,international and national cooperation were the major types of collaboration in China and Japan,accounting for 30% to 50%.China’s national collaboration and Japan’s international cooperation have been respectively rising 29.6% and 18.3% for the past 3 years in Fig.11.In addition,it is obvious that the share of single author cooperation in China is the lowest among the top 10 countries,at only 2.2%.Different from other Asian countries,India has a great share of institutional collaboration,which reached 42.9% in 2019.At the same time,this is the highest share of institutional cooperation among the top 10 countries.Moreover,India’s proportion of international collaboration has increased from 17.6% in 2016 to 40.0% in 2017,which is the biggest change over the six years.
3.4.2.Collaboration among the top 10 most prolific institutions of synthetic biology in China from 2015 to 2020
As described above,China had the biggest share of national collaboration,accounting for 41.7%of the total in the analyzed period of six years,while international cooperation only accounted for 35.4%,indicating the publications with domestic cooperation are more common than international collaboration as shown in Fig.10.Another obvious feature is that the proportion singleauthor cooperation is lowest in China.Hence,few publications in China are independently accomplished by only a single author.

Fig.11.Distribution of articles by collaboration type of the world and the top 10 most prolific countries or regions in synthetic biology from 2015 to 2020.
We further analyzed the share of cooperation among the top 10 most prolific institutions in China,as shown in Fig.12.All of the institutions were in line with the overall trend of China,where cooperation is dominated by national collaboration,apart from Shanghai Jiao Tong University and Zhejiang University.This means that most Chinese institutions publish articles in synthetic biology depending on native cooperation,such as Tianjin University and Jiangnan University.We additionally found that the years with a higher proportion of international cooperation tend to correspond to higher FWCI,such as the 75% international proportion of Zhejiang University in 2015 in Fig.12 and the year’s FWCI of 1.69(data from SciVal),which was 52% higher than this institution‘s average of the past six years.The same observation was made for Canada.Thus,the data indicate that international cooperation is more conducive to improving the influence of articles,so it may help us improve the citation impact in the future.Tsinghua University is one of the few institutions with single-author collaborations,and the overall share(7.1%)was the highest among the top 10(Table 7).Meanwhile,the proportion of national collaboration by Tsinghua University has increased over 9-folds from 2015 to 2020.The proportion of institutional collaboration by Shandong University was the highest among the top institutions in terms of all four types of collaboration,reaching over 10-fold than that of the Chinese Academy of Sciences(Table 7).Interestingly,East China University of Science and Technology and Wuhan University both exhibited abrupt peaks in national collaboration in 2016 and 2017,reaching at least twice their long-term average as shown in Fig.12.The same steep slope was found for international cooperation by some other institutions,such as Zhejiang University and Wuhan University.

Fig.12.Distribution of articles by collaboration type of the top 10 most prolific institutions of China in synthetic biology from 2015 to 2020.
4.Conclusions and Perspectives
Over the past few years,synthetic biology has advanced from completing proof-of-concept designs to a more precise platform focused on rational and high-throughput bioengineering [88]which showcases the remarkable opportunities in what has been called the century of biology [3].Here,we provide a comprehensive overview of the current research status and future orientation of synthetic biology in the world,as well as a deeper benchmarking of its status in China.Over the six years,about 49.1% of publications in synthetic biology were published in the top 10 journals of the world,and the publications related to synthetic biology in the world had an average FWCI of 1.35,receiving 35% more citations than the global average.Among the top countries,the United States had the largest total number of citations,but its citation share showed a decline in recent years similar to other developed countries,which is in line with the trend in output.In addition,international cooperation is the dominant mode of academic output of synthetic biology in developed countries apart from the United States,such as France,Germany and the United Kingdom.China has been steadily increasing its synthetic biology output over the past six years,with a 30 percent growth rate in 2020 even after the global downturn due to the COVID-19 pandemic.It can be credibly concluded that China is becoming a major power in pushing the growth of synthetic biology output,and the same is true for its citation share,indicating the effectiveness of Chinese government’s policy and financial support offered in recent years [69].However,the quality of citations reflected in the FWCI still has room for improvement.In fact,the FWCI of China was below the world average almost every year except for 2015 and 2019.Increasing the proportion of international collaborations and highly cited publications might be hopeful to effectively enhance the citation impact.Moreover,in view of both the total number and share of citations,there is still a gap between China and the United States over the past six years.In recent years,the United States has expanded its technological leadership and deepened the government’s scientific expertise in policymaking [89].In face of this situation,some significant efforts are needed to enhance the research strength and technical output of China if it wants to occupy a favorable position in research on synthetic biology.
Firstly,acting as the basis of innovation,the government of China should enhance the guidance in foundational research on synthetic biology and increase the emphasis on investment in this field.This can ensure the fundamental position of basic research while constructing a diversified research system.Secondly,more flexible mechanisms and frameworks need to be established as soon as possible to stimulate the translation of fundamental research results,which will further power technological innovation and economic growth.Thirdly,the breadth and dimension of synthetic biology research should be further increased.These efforts must include actively encouraging the know-how and capital of non-governmental organization (NGOs) to take part in the process of synthetic biology research,and improving the cultivation of interdisciplinary talent.
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic,bio-threats and bio-safety related concepts are receiving unprecedented attention and discussion[90],which is one of the future directions in synthetic biology.In the ‘‘post-epidemic” era,the subject area of ‘‘Immunology and Microbiology”will be the main focus of synthetic biology in China for a relatively long period of time.On the other hand,global warming and the surge of greenhouse gases have pose an increasing threat to the ecological environment.Synthetic biology has the potential to transform cheap and readily available one-carbon compounds into high-value-added products [91],which provides a powerful technical resource for the Chinese government’s commitment to achieve its ecological strategic goal of carbon offset by 2060.
Declaration of Competing Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Acknowledgements
The research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(21776209,21621004 and 21776208),Ministry of Education of the People’s Republic of China Humanities and Social Sciences Youth Foundation (21YJCZH232) and the Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin City (No.19JCYBJC21100).
Supplementary Material
Table S1——The proportion of international collaboration related to synthetic biology in Switzerland and Australia from 2015 to 2020.Table S2——The FWCI of Switzerland and Australia in synthetic biology from 2015 to 2020.Supplementary data to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2021.05.036.
杂志排行
Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering的其它文章
- Notes for Contributors
- Preparation and functional study of pH-sensitive amorphous calcium phosphate nanocarriers
- Crystallization thermodynamics of 2,4(5)-dinitroimidazole in eleven pure solvents
- Chiral LVFFARK enantioselectively inhibits amyloid-β protein fibrillogenesis
- Research on prediction model of formation temperature of ammonium bisulfate in air preheater of coal-fired power plant
- Insights into depolymerization pathways and mechanism of alkali lignin over a Ni1.2-ZrO2/WO3/γ-Al2O3 catalyst
