Isolated esophageal tuberculosis:A case report
2022-09-22IbrahimaDialloOmarTourElhadjiSouleymaneSarrAbdoulSowBinetaNdiayePapaSilmanDiawaraCherifMouhamedDialAbabacarMbengueFatouFall
INTRODUCTION
Tuberculosis is endemic in Senegal,where it constitutes a major public health problem.In 2020,12808 new cases of tuberculosis were reported in Senegal,the majority of which were pulmonary (National Controlling Tuberculosis Program,data not published).Extrapulmonary forms of tuberculosis are frequent,whether or not they are associated with pulmonary involvement.In the digestive tract,the terminal ileum and the cecum are most often affected.Esophageal localization is rare,especially in its isolated form.We report herein a case of isolated esophageal tuberculosis in an immunocompetent patient who responded well to antibacillary treatment.
At first the King and all the kingdom were terrified. All except the Princess, that is. She trusted her littlest knight and upon hearing the whole story set about immediately to make a healing salve for the dragon s eyes.
CASE PRESENTATION
Chief complaints
A 58-year-old patient was seen in our department for dysphagia that had developed over 3 mo.
History of present illness
The patient had dysphagia that had been evolving for 3 mo with non-quantified weight loss,nonselective anorexia,and nocturnal fever.
History of past illness
The patient had undergone appendectomy at 23-years-old.
Personal and family history
Consent was obtained from the patient.
The parrot, finding she was not much alarmed, told her who he was, all that her mother had promised him and the help he had already received from a Fairy who had assured him that she would give him means to transport the Princess to her mother s arms
Physical examination
The authors have read the CARE Checklist (2016),and the manuscript was prepared and revised according to the CARE Checklist (2016).
Laboratory examinations
Then I saw an old woman and child coming along the road. When they reached the flowers the child quickly plucked, one. I felt great horror and then heard the old woman say, What beautiful flowers. Don t pick them. The next day, I couldn t see the flowers anymore. The grass and leaves on the ground were almost dried. I was in a world of great sorrow.
Imaging examinations
The thoracoabdominal computed tomography (CT) scan did not show any mediastinal lymph nodes in contact with the esophagus or other foci of tuberculosis.
ENDOSCOPIC EXAMINATION
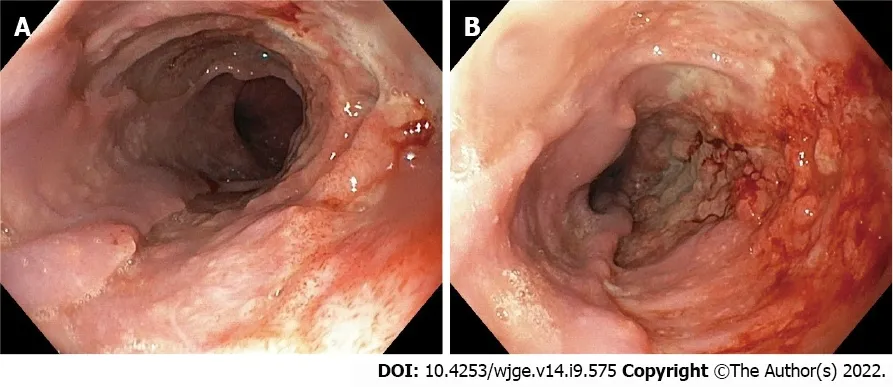
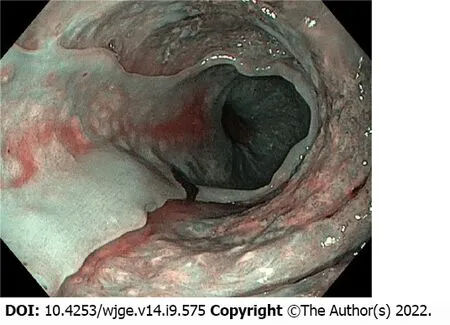
Upper gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy showed a jagged appearance of the thoracic esophageal mucosa for about 12 cm,stopping 3 cm above the cardia,with large irregular ulcers and raised contours.Nodules were present both at the level of the ulcers and in the normal-appearing mucosa (Figure 1A).Chromoendoscopy with narrow-band imaging did not detect areas that might suggest dysplasia or carcinoma (Figure 1B).
ANATOMICAL PATHOLOGY
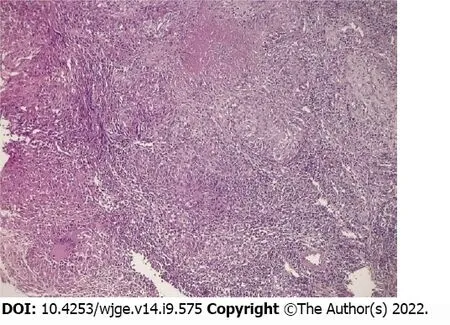
Esophageal biopsies revealed a deep loss of wall tissue,reaching the muscularis mucosa.The normal tissue was replaced by granulation tissue containing a tuberculoid granuloma with several follicles consisting of epithelioid and multinucleated Langerhans histiocytes,surrounding a caseous necrosis (Figure 2).Neither culture of tissue samples nor PCR test for
were performed.Sputum and gastric acid liquid after aspiration were negative for acid-fast bacilli (AFB).
FINAL DIAGNOSIS
Isolated esophageal tuberculosis.
The most common symptom during esophageal tuberculosis is dysphagia (90% of cases),which was the main sign in our patient.Odynophagia,pyrosis,and chest pain may also be present[4].The occurrence of coughing at mealtime should raise suspicion of an esotracheal or esophageal-mediastinal fistula,which is present in 13%-50% of cases[5].The presence of hematemesis can also provide further evidence of a fistula[6].
TREATMENT
An antituberculosis treatment was initiated [rifampicin,isoniazid,ethambutol,and pyrazinamide (RHEZ) and administered for 2 mo,and with rifampicin and isoniazid (RH) for 4 mo].The patient showed good tolerance.
OUTCOME AND FOLLOW-UP
Described for the first time in 1837 by Denonvilliers during an autopsy,infectious esophagitis due to tuberculosis is rare,even in countries with high tuberculosis endemicity.The esophageal localization represents 0.2%-1% of tuberculosis cases of the GI tract[1,2].This low incidence can be explained by several mechanisms that allow the esophagus to fight infection,in particular,peristaltic movements leading to emptying of the contents into the stomach,and the presence of mucus and saliva lining the mucosa and its squamous epithelium[1].These mechanisms provide a barrier against primary contamination caused by the ingestion of food or saliva containing germs such as
.However,secondary contamination by contact with neighboring organs,especially in cases of tuberculosis in paraesophageal lymph nodes,is possible[3].Blood-borne contamination is rare.
DISCUSSION
The patient’s outcome was favorable,with a clear improvement of dysphagia after 15 d of treatment,which disappeared after 5 wk.Upper digestive endoscopy after 4 mo of treatment showed a normal esophageal mucosa.Six months after stopping the treatment,the patient was well,had regained weight,and did not complain of dysphagia.
Elizabeth and I are 18 now, and about to graduate. I think about our elementary-school friendship, but some memories have blurred. What happened that day in fifth grade when Beth suddenly stopped speaking to me? Does she know that I ve been thinking about her for seven years? If only we could go back, discover what ended our relationship.
She said she had enough money to stay in a hotel until she found an apartment and a job. She had always wanted to live in a big, exciting city like New York. That s where I can start my own business, she said, and maybe find a man I can depend on!
The endoscopic appearance of esophageal tuberculosis is variable and nonspecific.In our patient,the lesion was located in the lower two-thirds of the esophagus and consisted of a large ulcer with raised contours,associated with micronodules.The esophagus can be affected throughout its length,although the lesion is most often located in the middle third[3,7,8],because of the extensive lymphoid tissue in this region.Endoscopy may show an ulcer of variable size,superficial with regular contours or irregular and infiltrative simulating neoplasia,or show a more or less ulcerated budding aspect of the mucosa[3,9].An extrinsic compression aspect with a mucosa of normal appearance can also be found[8].Endoscopic ultrasound can be helpful for diagnosis,allow analysis of the thick esophageal wall,and guide biopsies[7].It also allows for exploration of the mediastinum and performance of fine-needle biopsy of potentially involved lymph nodes[7].Thoracic CT scan often shows a thickening of the eso-phageal wall and allows for searching of adjacent lymph nodes,pulmonary location,or esotracheal or esophagomediastinal fistulas.
Biological investigations (blood count,liver function tests,glycemia,renal function,and C-reactive protein) were normal.The viral serologies for hepatitis B,hepatitis C,and human immunodeficiency virus were negative.
Histology can help in the diagnosis of esophageal tuberculosis.Mucosal biopsies during upper GI endoscopy can show the presence of a tuberculous granuloma or AFB in about 50% of cases[10,11],but sometimes neither of these lesions is found[12].In our patient,an epithelioid gigantocellular granuloma with caseous necrosis was present on histology (Figure 3),confirming the diagnosis of esophageal tuberculosis.To improve diagnostic success,deep biopsy samples should be taken from ulcerated areas,as granulomas are most often found in the submucosa[1,8,11].If endoscopic biopsies are not contributive,deep esophageal biopsy or fine-needle aspiration of a satellite lymph node,guided by endoscopic ultrasound,make it possible to find an epithelioid granuloma on histology (reportedly in 94.7% to 100% of cases,with caseous necrosis and/or AFB present in 55% to 75% of those cases)[7,11].Histological samples are also used for PCR or culturing methods to identify
.If an epithelioid granuloma without caseous necrosis is present,a differential diagnosis with sarcoidosis,Crohn’s disease,or a carcinoma must be considered.
It took a long time to find myself, and I had to live alone to do it. But I am not lonely. I am free for the first time in my life. I am Tandaleah, the Fire Goddess of the Volcano, spelled with two Ds and I m living happily ever after.
The treatment of esophageal tuberculosis is essentially medical,according to the standard protocol (rifampicin,isoniazid,ethambutol,and pyrazinamide daily for 2 mo,followed by rifampicin and isoniazid daily for 4 mo) for at least 6 mo.However,the optimal duration is not clinically established.In the case of fistula,clips are the reference treatment for lesion closure[11,13].The outcome during treatment for esophageal tuberculosis is favorable and without sequelae in almost all cases[3,7,8,11].In our patient,no sequelae were noted during the follow-up.Upper digestive endoscopy,4 mo after the beginning of treatment,was normal.The patient had no complaints at 6 mo after the end of treatment.
CONCLUSION
Esophageal tuberculosis is a rare cause of infectious esophagitis,even in a country where tuberculosis is endemic.Nevertheless,esophageal tuberculosis should be considered when dysphagia is associated with atypical ulcerated lesions of the esophageal mucosa.The presence of gigantocellular epithelioid granulomas on esophageal biopsies confirms the diagnosis.The patient’s outcome is generally favorable after antibacillary treatment,as illustrated by our observation.
Diallo I performed the upper digestive endoscopy,followed up with the patient,and wrote the manuscript;Touré O,Sow A,and Ndiaye B contributed to collecting the patient’s clinical data,and participated in the follow-up;Sarr ES and Dial CM conducted the anatomopathological examinations;Diawara PS conducted the biological tests;Mbengue A performed the radiological examinations;Fall F supervised the manuscript;all authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
The patient’s other personal and family histories were unremarkable.
All authors report no relevant conflict of interest for this article.
The patient was in good general condition (World Health Organization performance status of 0),with a body mass index of 21.55 kg/m².Clinical examination was normal.
The old people were very unhappy at the thought that they must part with him, but they said nothing, and began to collect all that he would want for his travels, and were careful to add a pair of new boots
This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers.It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial (CC BYNC 4.0) license,which permits others to distribute,remix,adapt,build upon this work non-commercially,and license their derivative works on different terms,provided the original work is properly cited and the use is noncommercial.See: https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by-nc/4.0/
Senegal
Ibrahima Diallo 0000-0001-5635-0665.
That night, both of them couldn t sleep, toss9 and turn(), toss and turn. After hours, the old man couldn t take it anymore, he knows that he still loves her, and he can t carry on life without her, he wants her back, he wants to tell her, he is sorry, he wanted to tell her, I love you.
Wu YXJ
A
Wu YXJ
1 Diallo I,Omar Soko T,Rajack Ndiaye A,Klotz F.Tuberculose abdominale.
2019;37: 1-13 [DOI: 10.1016/S1155-1968(19)92375-3]
2 Debi U,Ravisankar V,Prasad KK,Sinha SK,Sharma AK.Abdominal tuberculosis of the gastrointestinal tract: revisited.
2014;20: 14831-14840 [PMID: 25356043 DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i40.14831]
3 Zhu R,Bai Y,Zhou Y,Fang X,Zhao K,Tuo B,Wu H.EUS in the diagnosis of pathologically undiagnosed esophageal tuberculosis.
2020;20: 291 [PMID: 32859167 DOI: 10.1186/s12876-020-01432-7]
4 Vahid B,Huda N,Esmaili A.An unusual case of dysphagia and chest pain in a non-HIV patient: esophageal tuberculosis.
2007;120: e1-e2 [PMID: 17398209 DOI: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2005.12.026]
5 Nagi B,Lal A,Kochhar R,Bhasin DK,Gulati M,Suri S,Singh K.Imaging of esophageal tuberculosis: a review of 23 cases.
2003;44: 329-333 [PMID: 12752007 DOI: 10.1034/j.1600-0455.2003.00069.x]
6 Jain SS,Somani PO,Mahey RC,Shah DK,Contractor QQ,Rathi PM.Esophageal tuberculosis presenting with hematemesis.
2013;5: 581-583 [PMID: 24255751 DOI: 10.4253/wjge.v5.i11.581]
7 Tang Y,Shi W,Sun X,Xi W.Endoscopic ultrasound in diagnosis of esophageal tuberculosis: 10-year experience at a tertiary care center.
2017;30: 1-6 [PMID: 28575247 DOI: 10.1093/dote/dox031]
8 Xiong J,Guo W,Guo Y,Gong L,Liu S.Clinical and endoscopic features of esophageal tuberculosis: a 20-year retrospective study.
2020;55: 1200-1204 [PMID: 32881605 DOI: 10.1080/00365521.2020.1813799]
9 Seo JH,Kim GH,Jhi JH,Park YJ,Jang YS,Lee BE,Song GA.Endosonographic features of esophageal tuberculosis presenting as a subepithelial lesion.
2017;18: 185-188 [PMID: 28139030 DOI: 10.1111/1751-2980.12454]
10 Park JH,Kim SU,Sohn JW,Chung IK,Jung MK,Jeon SW,Kim SK.Endoscopic findings and clinical features of esophageal tuberculosis.
2010;45: 1269-1272 [PMID: 20568972 DOI: 10.3109/00365521.2010.501524]
11 Dahale AS,Kumar A,Srivastava S,Varakanahalli S,Sachdeva S,Puri AS.Esophageal tuberculosis: Uncommon of common.
2018;2: 34-38 [PMID: 30483561 DOI: 10.1002/jgh3.12043]
12 Rana SS,Bhasin DK,Rao C,Srinivasan R,Singh K.Tuberculosis presenting as Dysphagia: clinical,endoscopic,radiological and endosonographic features.
2013;2: 92-95 [PMID: 24949371 DOI: 10.4103/2303-9027.117693]
13 Rana SS,Mandavdhare H,Sharma V,Sharma R,Dhalaria L,Bhatia A,Gupta R,Dutta U.Successful closure of chronic,nonhealing tubercular esophagobronchial fistula with an over-the-scope clip.J Dig Endosc 2017;8 (1) : 33-5.[DOI: 10.4103/0976-5042.202820]
杂志排行
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy的其它文章
- Simulation-based mastery learning in gastrointestinal endoscopy training
- Endoscopic ultrasound elastography for malignant pancreatic masses and associated lymph nodes:Critical evaluation of strain ratio cutoff value
- Screening for hilar biliary invasion in ampullary cancer patients
- Endoscopic therapy using a self-expandable metallic stent with an anti-migration system for postorthotopic liver transplantation anastomotic biliary stricture
- Clinical profile,diagnostic yield,and procedural outcomes of single balloon enteroscopy: A tertiary care hospital experience
- Role of endoscopic ultrasound in evaluation of patients with missed common bile duct stones
