Niaoduqing granules inhibits TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human renal tubular epithelial HK-2 cells
2022-09-06ChuYingHuoHuaYiYangWeiMinNingLinZhongYuChunLinFanJingYuQuanLiErDengZhiLingYuJunShanLiuHuiHuiCao
Chu-Ying Huo,Hua-Yi Yang,Wei-Min Ning,Lin-Zhong Yu,Chun-Lin Fan,Jing-Yu Quan,Li-Er Deng,Zhi-Ling Yu,Jun-Shan Liu*,Hui-Hui Cao*
1Traditional Chinese Pharmacological,Third Level Research Laboratory of State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine,School of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Southern Medical University,Guangzhou 510515,China.2Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Chinese Medicine Pharmaceutics,School of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Southern Medical University,Guangzhou 510515,China.3Dongguan Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Dongguan 523000,China.4Guangdong Province Key Laboratory of Pharmacodynamic Constituents of TCM and New Drugs Research,College of Pharmacy,Jinan University,Guangzhou 510632,China.5Center for Cancer and Inflammation Research,School of Chinese Medicine,Hong Kong Baptist University,Kowloon Tong,Hong Kong,999077,China.
Abstract Objective Chronic renal failure (CRF) is a worldwide public health burden.Niaoduqing granules (NDQ) is widely used for CRF treatment in China.However,the underlying mechanism of NDQ is not fully studied.This study is aimed to investigate whether NDQ ameliorate CRF by inhibiting transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1)-induced EMT in human renal tubular epithelial HK-2 cells.Methods 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenylterazolium bromide assay and colony formation assay were used to investigate the cytotoxicity of NDQ in HK-2 cells.Morphological changes of HK-2 cells after TGF-β1 or/and NDQ treatment were observed under a microscope.Wound-healing,migration and invasion assays were performed to determine the cell movement,migratory and invasive abilities,respectively.Western blot analysis was carried out to examine the protein levels of TGF-β receptor I (TβRI) and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT)-associated factors.Fluorescence confocal microscopy was applied to observe the organization of filamentous actin.Results NDQ suppressed TβRI expression dose-dependently.NDQ inhibited TGF-β1-stimulated EMT in HK-2 cells,supported by the evidences that NDQ prevented morphology change,attenuated cell migration and invasion,downregulated EMT factors and reorganized filamentous actin distribution in TGF-β1-stimulated HK-2 cells.Conclusions NDQ attenuates chronic renal failure which may be associated with inhibition of TβRI expression and EMT process.
Keywords Chronic renal failure;Niaoduqing granules;TGF-β1;Epithelialmesenchymal transition;TGF-β type I receptor
Background
Chronic renal failure (CRF),a common result of chronic kidney disease (CKD),has become a health problem in the world [1].Renal fibrosis is the main pathological feature of CRF,and inhibition of renal fibrosis is regarded as an effective therapeutic approach for CRF [2].
Emerging evidence implicates that epithelialmesenchymal transition (EMT) of renal tubular promotes renal fibrosis.EMT is a process that epithelial cells lost their epithelial characteristics and transform into mesenchymal cells with mesenchymal characteristics.Transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) is known as a trigger of EMT and plays a pivotal role in renal fibrosis [3,4].Activation of TGF-β1 mediates EMT and eventually leads to fibrosis in human renal,while inhibition of TGFβ1 activation alters the EMT process and reduces fibrosis,indicating that blockade of TGF-β1 signaling is a therapeutic strategy for CRF [5].
Niaoduqing granules (NDQ),a Chinese medicine preparation,which includedRadix et Rhizoma Rhei,Radix Astragali,Cortex Mori,Radix Sophorae Flavescenstis,Rhizoma Atractylodies macrocephalae,Poria,Radix Paeoniae Alba,Radix Polygoni Multiflori,Radix Salviae MiltiorrhizaeandHerba Plantaginis(Table S1),is frequently used for CRF treatment.Clinical studies showed that NDQ reduced serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen,improved renal function,and also alleviates CKD progression in patients with moderate-to-severe renal insufficiency efficiently [6,7].In animal models,NDQ was found to reduce tubulointerstitial fibrosis and relieve CKD in rat,which were related with the modulation of TGF-β and erythropoietin signaling pathways [6,8,9].However,it’s still unclear that if NDQ attenuates CRF by inhibiting TGF-β1-induced EMT.
In this study,we first demonstrated that NDQ downregulated the expression level of TGF-β receptor I(TβRI) in human renal tubular epithelial HK-2 cells,inhibited TGF-β1-induced EMT and dysregulated the distribution of filamentous actin (F-actin),which may account for the treatment of CRF by NDQ.
Material and Methods
Drug and reagents
NDQ (National drug standard No: WS3-229(Z-033)-2000(Z)) was obtained from Guangzhou Kangchen Pharmaceutical Co.,Ltd.(Guangzhou,China) and granules were dissolved in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS)at a concentration of 1.25 g/mL.
TGF-β1 peptides was purchased from Biosynthesis Biotechnology (Beijing,China).3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenylterazolium bromide (MTT) was obtained from Thermo Fisher Scientific (Waltham,MA,USA).4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole,dihydrochloride (DAPI) was obtained from Beyotime Biotechnology (Shanghai,China).Antibodies against vimentin,N-cadherin,snail and slug were purchased from Cell Signaling Technology (Danvers,MA,USA).Antibodies against TβRI was purchased from abcam (Cambridge,UK).Rhodamine phalloidin was purchased from cytoskeleton (Denver,CO,USA).Other reagents were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (St.Louis,MO,USA).
Cell line and cell culture
Human kidney tubular epithelial cell line HK-2 was obtained from Otwo Biotech (Shenzhen) Inc.(Shenzhen,China).HK-2 cells were cultured in RPMI-1640 with 10%fetal bovine serum (Sijiqing,Hangzhou,China) and 1%penicillin-streptomycin (Gibco,Waltham,MA,USA) in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2at 37oC.
Cell viability assay
The viability of NDQ in HK-2 cells was determined by MTT assay as previously described [10].Cells (104/well)were seeded in 96-well plates for 24h and then exposed to different concentrations of NDQ for 24h,48h and 72h,respectively.After treatment,the supernatant was discarded and 30 μL of MTT solution (5 mg/mL) was added and incubated for another 4h at 37oC;and then,the supernatant was discarded and the purple formazan crystals were dissolved in 100 μL of dimethyl sulfoxide and the absorbance was measured at 570 nm by a microplate reader (Multiskan FC,Thermo Scientific,USA).
Colony formation assay
HK-2 cells (300/well) were seeded in 6-well plates for 24 h and then treated with NDQ at different concentrations.After incubated for 24h,cells were washed with PBS and cultured in fresh medium for 10 days.Then,cells were fixed in 75% alcohol at 4oC and stained with Giemsa dye[11].
Cell morphological observation
HK-2 cells (105/well) were seeded in 6-well plates and incubated for 24h.Cells were then serum-starved for 24 h followed by NDQ treatment for 24h with or without TGFβ1.After that,cells were washed with PBS and morphological changes were observed under a microscope(IX 53,Olympus,Tokyo,Japan).
Cell migration and invasion experiment
For wound healing experiment,HK-2 cells (3×105/well)were seeded in 6-well plates for 24h and serum-starved for another 24h.Cells were then scratched in a straight line with 200-μL pipette tips and treated with different concentrations of NDQ in the presence or absence of TGFβ1.Images of HK-2 cells were acquired with a microscope(IX 53,Olympus,Tokyo,Japan) at 0h,12h and 24h,respectively.
In the Transwell migration assay,HK-2 cells (105/well)were seeded in Transwell chamber with RPMI-1640 medium for 24h and 400 μL of RPMI-1640 medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum was added into the bottom chamber.Cells were then incubated with NDQ for 24h under TGF-β1-stimulated or unstimulated conditions and chambers were fixed using 75% alcohol before stained with Giemsa dye.After that,cells remaining on the upper surface of the membrane were removed by wiping and the images of migrated cells were obtained under a microscope(IX 53,Olympus,Tokyo,Japan).The invasion assay shared the same method with the Transwell migration assay,the only difference was,matrigel was applied in the Transwell chamber before cells were seeded.
Western blot analysis
HK-2 cells (3×105dish) were seeded in 60 mm dishes for 24h and serum-starved for another 24h.After treated with different concentrations of NDQ for 48h with or without TGF-β1 stimulation,cells were harvested and washed with cold PBS and then lysed for 15 min at 4oC with Radio Immunoprecipitation Assay (RIPA) buffer (0.1 mM phenylmethanesulfonyl foride,0.1 mM sodium orthvanadate,0.1 mM dthiothreitol and phosphatase inhibitor).After centrifugation at 13,500 rpm for 15 min,supernatants were collected as total protein.The protein concentrations were determined by a BCA protein assay kit.The method of Western blotting was performed as previously described [12].Protein levels were quantified by ImageJ 1.4.3 (National Institutes of Health,USA).
F-actin fluorescence confocal microscopy
HK-2 cells (3×105dish) were seeded in confocal dishes for 24h.After incubated in serum-free medium for 24h,cells were exposed to NDQ for another 24h in the presence or absence of TGF-β1.Cells were then fixed with 4%paraformaldehyde and permeabilized with 0.5% TritonX-100 in PBS.After blocked with 5% bull serum albumin for 15 min at room temperature,cells were incubated with 100 μL of rhodamine phalloidin (70 nM) for 1h at room temperature.Subsequently,cells were washed and counterstained with 100 μL of DAPI.The fluorescence was observed by confocal microscopy (LSM800,Carl Zeiss,Oberkochen,Germany).
Statistical analysis
All data were expressed as the means ± standard error of mean (SEM) and analyzed by Graphpad Prism 5.0 software (Graphpad software Inc.,USA).Tukey’s test was used for multiple comparison.The values were considered statistically significant whenP<0.05.
Results
Cytotoxicity of NDQ in HK-2 cells
To determine the cytotoxicity of NDQ in HK-2 cells,MTT assay and colony formation assay were used.The results showed that NDQ inhibited the proliferation of HK-2 cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner (Figure 1A).However,NDQ exerted no significant cytotoxicity in HK-2 cells at the dosage below 5 mg/mL (Figure 1B) and data from colony formation assay further confirmed this result(Figure 1C).We therefore use NDQ with the dosage of 5 mg/mL for further study.
NDQ downregulates the expression level of TβRI in HK-2 cells
TGF-β1 signaling is considered to have a pivotal role in renal fibrosis and EMT process [5].It is reported that the activation of TGF-β1 signaling is initiated by the binding of TGF-β1 ligand to TGF-β receptor II (TβRII) and TβRI[13].Therefore,we wonder whether NDQ affect the expression of TβRI.HK-2 cells were exposed to indicated concentrations of NDQ for 48h,followed by Western blot analysis.As shown in Figure 2,NDQ downregulated the expression level of TβRI in a dose-dependent manner.Our finding suggested that NDQ may blocked TGF-β1 signaling through repression of TβRI.
NDQ attenuates the morphological changes in TGF-β1-stimulated HK-2 cells
TβRI is critical in TGF-β1 signaling,which mediates downstream and leads to EMT [14].Based on the evidence that NDQ downregulated the expression level of TβRI,we suspected NDQ exerts inhibitory effects on TGF-β1 signals and subsequently suppresses EMT in renal epithelial cells.TGF-β1,a well-known inducer of EMT,was added and incubated with HK-2 cells for 24h after serum-starved for 24h to establish a model of EMT in HK-2 cells.The morphology of HK-2 cells was changed and became slender and fibroblast-like after simulated with TGF-β1 (Figure 3,red arrow),while NDQ prevented cells from these morphological changes.

Figure 1 Cytotoxicity of NDQ on HK-2 cells.(A) NDQ inhibited the proliferation of HK-2 cells in a time- and dose-dependent manner.(B) NDQ showed no significant effect on the viability of HK-2 cells at the dosage below 5 mg/mL.(C) NDQ had no obvious long-term cytotoxicity on HK-2 cells at the dosage below 5 mg/mL.

Figure 2 NDQ downregulates TβRI expression in HK-2 cells.HK-2 cells were treated with indicated concentration of NDQ and the expression level of TβRI was determined by Western blot analysis.The representative figures (left) and the relative expression levels analyzed by ImageJ 1.4.3 software (right) were shown.***P <0.001,versus Control group.One-way ANOVA,post hoc comparisons,Turkey’s test.Columns,means;error bars,SEM.
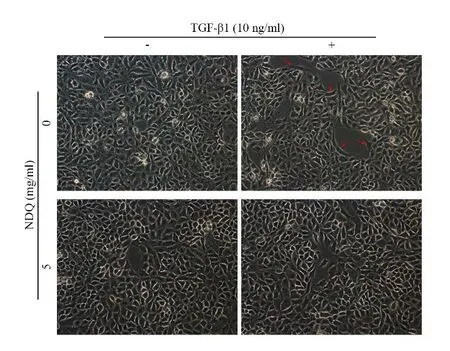
Figure 3 Morphology changes in HK-2 cells.Cells were serum-starved for 24h and then exposed to vehicle or NDQ for 24h with or without TGF-β1 stimulation.Fibroblastlike morphology changes were observed in TGF-β1-stimulated HK-2 cells (red arrow) and these changes were attenuated after NDQ treatment.

Figure 4 NDQ inhibits TGF-β1-induced upregulation of EMT-associated factors in HK-2 cells.HK-2 cells were serum-starved for 24h and then treated with indicated concentration of NDQ for 48h in the presence or absence of TGF-β1.Expression levels of N-cadherin,vimentin,snail and slug were examined by Western blotting using specific antibodies.The representative figures (upper) and the relative expression levels analyzed by ImageJ 1.4.3 software (bottom) were shown.*P <0.05,**P <0.01 and***P <0.001,versus Control group.##P <0.01 and ###P <0.001,versus TGF-β1 group.One-way ANOVA,post hoc comparisons,Turkey’s test.Columns,means;error bars,SEM.
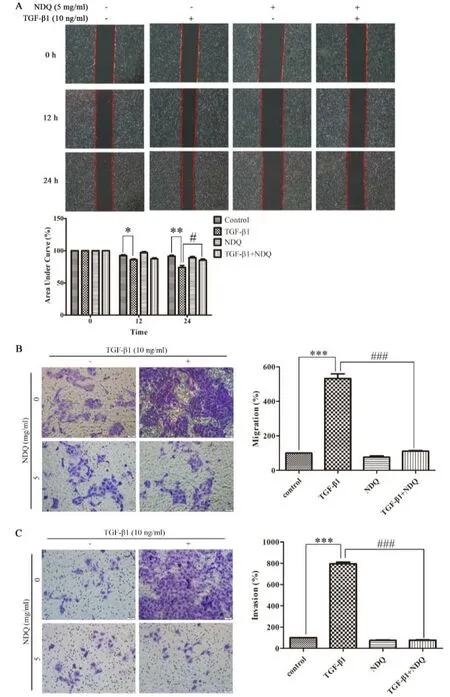
Figure 5 NDQ attenuates cell migration and invasion in TGF-β1-stimulated HK-2 cells.Cell migration was measured by wound-healing (A) and Transwell migration assay (B),and invasive ability of HK-2 cells was measured by Transwell invasion assay (C).Relative migrated areas were quantified by ImageJ 1.4.3 software.Quantification of migrated and invasive cells were analyzed by Graphpad Prism 5.0 software.***P <0.001,versus Control group.###P <0.001,versus TGF-β1 group.One-way ANOVA,post hoc comparisons,Turkey’s test.Columns,means;error bars,SEM.
NDQ inhibits TGF-β1-induced EMT in HK-2 cells
To verify the effect of NDQ on TGF-β1-induced EMT,we determined the expression levels of EMT-associated protein,including N-cadherin,vimentin,slug and snail.Our data showed that TGF-β1 upregulated the expression levels of N-cadherin,vimentin,slug and snail,while NDQ prevented the induction of EMT by TGF-β1,with downregulation of the N-cadherin,vimentin,slug and snail expression levels (Figure 4).
NDQ inhibits cell movement,migration and invasion in TGF-β1-stimulated HK-2 cells
When cells undergo EMT,cell adherence is attenuated and cell mobility is enhanced [15].To investigate the effects of NDQ on cell movement in HK-2 cells,wound-healing assay was performed.We found that TGF-β1 promoted cell movement,nevertheless,NDQ inhibited the TGF-β1-induced cell movement in HK-2 cells (Figure 5A).Further evidences were provided by Transwell migration assay and invasion assay.As shown in Figure 5B,TGF-β1 remarkably enhanced the migratory ability of HK-2 cells.However,NDQ treatment reduced cell migration.As such,the invasion assay result also demonstrated that NDQ reversed cell invasion induced by TGF-β1 in HK-2 cells(Figure 5C).
NDQ reorganized the arrangement of F-actin in TGFβ1-stimulated HK-2 cells
F-actin,an important component of cytoskeleton,involves in cell migration and invasion [16].We subsequently detected the arrangement of F-actin followed by NDQ treatment.Rhodamine phalloidin was applied to visualize the distribution of the F-actin in HK-2 cells.As shown in Figure 6,TGF-β1 increased the expression and longitudinally distribution of F-actin.Compared to TGFβ1-stimulated cells,NDQ treatment decreased the intensity and reorganized the distribution of F-actin in HK-2 cells.These data further validated that NDQ attenuated TGF-β1-induced EMT in HK-2 cells.

Figure 6 NDQ reorganized the distribution of F-actin.HK-2 cells were serum-starved for 24h and then exposed to vehicle or NDQ (5 mg/mL) in the presence or absence of TGF-β1 for another 24h,the distribution of F-actin was visualized by confocal after rhodamine phalloidin staining.Left,F-actin;middle,DAPI;right,merge.
Discussion
As a burden on global health,CRF is mainly featured by tubulo-interstitial fibrosis,regardless of the initial etiology of the renal disease.Hence,renal fibrosis is a universal feature of CRF and contributes dramatically to end-stage renal failure [17].There are two main therapeutic strategies for CRF to improve renal function: dialysis and renal transplantation.Nevertheless,these therapies lead to the increased risk of cardiovascular problem [18].Clinical observation showed that NDQ dramatically alleviate renal dysfunction and tubulointerstitial fibrosis for CKD patients at stage III to stage IV [19].Previous studies about CRF treatment tended to choose NDQ as a positive medicine,indicating its certain efficacies [20-23].In this study,we demonstrate that NDQ contributes to CRF by downregulation of TβRI expression level,inhibiting the EMT processing and rearranging the F-actin organization.
Renal fibrosis is a characteristic by which CKD develops into CRF.Previous studies have reported that EMT is a phenotypic conversion that has emerged as a critical role in renal fibrosis and contributes to the progression of CRF [24].TGF-β1 has a predominant role in the progress of CRF.Accumulating evidences have pointed out that TGF-β1 activates its downstream to contribute to EMT and renal fibrosis.TGF-β receptors,including TβRI and TβRII,participates in TGF-β signals.At the cell membrane,TGF-β1,serving as a ligand,first binds to TβRII and subsequently recruits TβRI and induces its activation.After receptor binding,TGF-β1 exerts its cellular functions and promotes the EMT process [25].Hence,the activation of TβRI is pivotal in TGF-β1 signaling.It was reported that TβRI downregulation led to EMT suppression in TGF-β-stimulated nasal epithelial cells [14].Previous research also suggested that suppressed TGF-β1/TβRI/Smads signaling activationin vivo and in vitro,suppressing the EMT and collagen deposition to alleviate renal fibrosis that the inhibition of renal fibrosis was regarded as an effective therapeutic approach for CRF [26].In this study,we first demonstrated that NDQ inhibits the expression level of TβRI in human renal tubular epithelial HK-2 cells,while previous study revealed that NDQ downregulated the expression level of TβRI in CRF rats [9].We will further investigate if NDQ inhibit the membrane TβRI levels and the effects of NDQ on TβRI transcription,translation or post-translation.
The occurrence of EMT leads to the loss of epithelial markers of renal tubular cells,the development of invasive and metastatic in cells and the increased of mesenchymal features in morphology,such as spindle-cell-like morphology.Moreover,during the EMT process,the expression of the epithelial markers,including E-cadherin,is downregulated,whereas the mesenchymal markers,such as N-cadherin,snail,slug,and vimentin are increased.N-Cadherin is the main contributors to reduced cell - cell adhesion in epithelial tissues and eventually lead to cell dedifferentiation,tissue disorder and increased cell invasion capacity,ultimately,to metastasis.Vimentin is an intermediate filament protein and acts as a cytoskeletal element,which is also known as a mesenchymal marker.Besides,EMT-inducing transcription factors include snail and slug.Especially,snail is associated with the initial cellmigratory phenotype and is regarded as an early marker of EMT [27,28].In our research,TGF-β1 alternated the morphology of HK-2 cells,while NDQ prevented cells from these changes.It was also found that NDQ attenuated cell migratory and invasive abilities as well as inhibited TGF-β1-induced upregulation of EMT markers including N-cadherin,snail,slug and vimentin in HK-2 cells,indicating that NDQ inhibited TGF-β1-induced EMT in HK-2 cells.These results were in agreement with a previous study by Lu et al.[29].However,Lu et al.used rat serum containing NDQ for the mechanistic study and our research is the first-time use NDQ directly in human renal tubular epithelial cells and demonstrates its inhibitory effects on EMT.
For years,EMT is considered as a binary process with cells individually detach from tissue.However,recent studies demonstrate epithelial cells and mesenchymal cells are co-exist as a cluster in many cases,which is called hybrid E/M phenotype and this phenotype presents more migratory and invasive properties [30].This concept indicates an alternative EMT process in NDQ intervention.In this regard,more experiments will be needed to explore the extent of NDQ-induced EMT suppression.Recent research also suggested that transcription factors like GRHL2 or OVOL2 may be the crucial EMT drivers,whether NDQ inhibit the expression levels of the other regulators is unknown and deserves further exploration [31,32].
F-actin is an important protein of muscle thin filaments,which constitute the eukaryotic cytoskeleton.Remodeling of F-actin facilitates cell migration and invasion [16,33].At the final process of EMT,the cells reorganize their cortical actin cytoskeleton to enable dynamic cell elongation and directional motility [34].Thus,F-actin reorganization directly controls cell migration/invasion.Since EMT is characterized by increased cell migration/invasion and actin stress fiber formation,F-actin plays an important role in renal fibrosis.Our results showed that NDQ significantly reduced F-actin intensity and remodeled its organization in HK-2 cells.These evidences strongly suggest that NDQ suppresses CRF through cell migration and invasion via reorganizing the arrangement of F-actin.It should be pointed out that once TβRI is activated,the canonical Smad signaling and non-canonical Smad pathways are generally activated to regulate gene transcription for performing physiological functions.Although the inhibition of the protein expression of TβRI by NDQ was demonstrated,the specific pathways that it regulates need further exploration [35-37];and animal model is also encouraged for the further study of NDQmediated effects.
Conclusion
In conclusion,we first demonstrated that the renoprotective effect of NDQ is partially attributed to the downregulation of TβRI,which account for the inhibition of TGF-β1-induced EMT in HK-2 cells (Figure 7).This study provides a pharmacological basis for the clinic use of NDQ in the treatment of CRF.

Figure 7.The underlying mechanism of NDQ on preventing epithelial cells from TGF-β1-induced EMT.→ refers to a promoting effect;⊥ refers to a blockage effect.
Data availability or Code availability
Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to huizizheng@hotmail.com (Hui-hui Cao).
Abbreviations
CRF,chronic renal failure;CKD,chronic kidney disease;EMT,epithelial-mesenchymal transition;TGF-β1,transforming growth factor-β1;NDQ,niaoduqing granules;TβRI,TGF-β receptor I;F-actin;filamentous actin;PBS,phosphate-buffered saline;MTT,3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenylterazolium bromide;DAPI,4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole,dihydrochloride;TβRII,TGFβ receptor II.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Guangdong Province Universities and Colleges Pearl River Scholar Funded Scheme (GDHVPS2018),the National Hong Kong Scholars program (XJ2016059),the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (2020A1515011239),the Guangzhou Science and Technology Project(202102021241),the Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine of Guangdong Province (20211253) and the Guangzhou Consun Pharmaceuticals Co.,Ltd..These funding bodies played no role in the design of the study;collection,analysis and interpretation of data;and in writing the manuscript.
Author contributions
Chu-Ying Huo and Hua-Yi Yang carried out the experiments,data analysis and manuscript writing.Wei-Min Ning performed the statistical analysis and prepared figures.Lin-Zhong Yu and Chun-Lin Fan participated in experimental work and results writing.Jing-Yu Quan and Li-Er Deng carried out the experiments and discussion writing.Zhi-Ling Yu,Jun-Shan Liu and Hui-Hui Cao designed and supervised the study.All authors have read and agreed to publish this manuscript.
杂志排行
TMR Modern Herbal Medicine的其它文章
- A review of the ethnobotanical value,phytochemistry,and pharmacology of Physalis pubescens L.
- Effects of Euphorbiasteroid on gene expression in lung cancer cells based on gene chip
- Standardization and Quality control parameters of Kayam Churna
- The genus Strobilanthes: phytochemistry and pharmacology
- Traditional Chinese medicine as monotherapy or combined with oseltamivir in the treatment of H1N1 influenza: a systematic review and meta-analysis
