Exosomes-mediated tumor treatment:One body plays multiple roles
2022-09-06
Shenyang Pharmaceutical University,Shenyang 110016,China
Keywords:Extracellular vesicles Exosomes Multiple roles Tumor treatment
ABSTRACT Exosomes are vesicles secreted by a variety of living cells,containing proteins,RNA and other components,which are nanoscale capsules commonly existed in the body.Exosomes play important roles in a variety of physiological and pathological processes by participating in material and information exchange between cells,which can play multiple roles in tumor treatment.On the one hand,exosomes can be used as carriers and biomarkers,participate in the apoptosis signaling pathway and improve chemotherapy resistance,thus playing beneficial roles in tumor treatment.On the other hand,exosomes play unfavorable roles in tumor treatment.Tumor cell exosomes contain PD-L1,which is a nuclear weapon for tumor growth,metastasis,and immunosuppression.In addition,exosomes can not only promote the epithelial-mesenchymal transition process,tumor angiogenesis and chemoresistance,but also participate in the autocrine pathway.In this review,the multiple roles of exosomes and their prospects in the treatment of tumor were reviewed in detail.
1.Introduction
Up to now,despite various novel strategies have been developed in the treatment of tumor,the therapeutic effects are not always as satisfactory as expected[1].The main reason is that tumor cells can be transferred to normal tissues or cells,thereby making normal cells malignant.The degree of tumor progression is related to the specific microenvironment and the information transmission between tumor cells [2].Nanotechnology has many advantages in the treatment of tumor,for example,it has targeting effects and can produce less cytotoxicity,which can alleviate the toxic side effects of chemotherapy drugs[3-6].
Recently,exosomes as an emerging nanotechnology have become research hotspots in the treatment of tumor [7,8].In the early stage of the development of exosomes,exosomes were considered to be excess membrane proteins released by regulating membrane function during cell maturation [9].The average diameter of exosomes is about 40-100 nm [10].Exosomes are derived from multivesicular endosomes or MVBs,containing RNA,protein,microRNA,DNA fragments and other components,and are distributed in blood,urine,cerebrospinal fluid and other body fluids[11-13].
Nowadays,exosomes are considered to be secretory micro vesicles with functional activity [14,15].Exosomes have the advantages of extensive intercellular distribution,high contents,and stable properties.Exosomes can load with targeted drugs to achieve accurate delivery of tumor treatment to the tumor site.In addition,exosomes have good biocompatibility,biodegradability and low toxicity,and they are not easy to cause acute immune reactions,which make exosomes become attractive as nanocarriers for tumor treatment[16].
However,exosomes also have some shortcomings.For example,they can promote the communication between cells,including the interactions with stromal cells in tumor microenvironment,thereby promoting the metastasis of tumor cells to normal tissues and cells [17].Besides,as an antigen presentation system,exosomes can transmit certain inhibitory signals,make tumor cells immune tolerant,and play negative regulatory roles in the process of immune response [18].What’s more,exosomes contain angiogenin and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF),which can act on the surface receptors of endothelial cell membranes to promote tumor angiogenesis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) process [19,20].These disadvantages greatly hinder the application of exosomes in the treatment of tumor.
To overcome the aforementioned disadvantages,res earchers transformed these disadvantages of exosomes into advantages to conquer tumors in a creative way.The creative way is exosomes targeted nano-drug delivery strategy [21],such as introducing functional mRNA into exosomes[22]and selecting exosomes with strong tropism [23].In addition,the surface of exosomes can be modified,such as modifying proteins,polypeptides,small molecules,and other substances on the surface of exosomes,thereby giving exosomes new functions,and improving the targeting effect of exosomes[24].The applications of exosomes in tumor have entered a new era,which are very promising.In this review,the multiple roles of exosomes and their prospects in the treatment of tumor were reviewed in detail,which aims to help researchers have a deep understanding of exosomes and design new exosomes nano-delivery systems for tumor treatment.
2.Biological characteristics of exosomes
2.1.Composition
The main components of exosomes are lipids,nucleic acids,and proteins.The outermost layer of exosomes is a bilayer phospholipid membrane,which contains high levels of sphingomyelin,ceramide,cholesterol,short and long chain saturated fatty acids [25,26].The composition of exosomes from different sources is also different.For example,exosomes from intestinal epithelial cells contain many metabolic enzymes and specific A33 antigens,exosomes from B cells contain CD86 and MHC molecules,and exosomes from T cells have pro-apoptotic FAS L receptors on the surface of exosomes.Thery et al.[27] analyzed the components of dendritic cell-derived exosomes,and the results showed that the main components of exosomes were cytoplasmic proteins and extracellular proteins such as milk fat globule epithelial growth factors.The components of exosomes contained RNA,including miRNAs.miRNA could not only regulate genetic information,but also serve as a secretory factor that regulated cell communication[28,29].
2.2.Physiological functions
Exosomes are tiny spherical “information bundles”and they play a critical role in cell-to-cell communication.Exosomes have many functions,they can affect the immune system’s response to the microenvironment and allow tumor cells to escape from the immune system.In addition,exosomes can directly stimulate recipient cells and serve as carriers for protein and RNA transport [30,31].Li et al.found that glioma cell-derived exosomes could selectively package coding or non-coding RNAs to alter gene expression[32,33].
3.The beneficial roles of exosomes in tumor treatment
The effects of traditional tumor treatment methods are not very satisfactory and cannot solve the problems of tumor recurrence and metastasis.In recent years,as new therapeutic targets,exosomes are playing increasingly important roles in tumor treatment.Exosomes are related to tumor pathogenesis and tumor microenvironment.The number of exosomes secreted by tumor cells is much higher than that of normal cells.In view of this,inhibiting the release of tumor-related exosomes may be a relatively effective tumor treatment method[34].
Neurophospholipase 2 is the first molecule reported to be involved in exosomes secretion.The level of exosomes can be regulated through the neurophospholipase 2-dependent pathway,increasing the expression of neurophospholipase 2 will promote the formation of exosomes [35].The surface of exosomes is a lipid bilayer structure (less than 5 nm in thickness),which can protect it from degradation or damage by DNA enzymes [36,37].Exosomes have good biocompatibility,which means that exosomes are not potentially toxic and harmless to human tissues [38].The surface of exosomes can express a variety of integrins,which can bind to the adhesion molecules on the cell surface,thereby playing the targeting role [39].The small size of exosomes is the main advantage for the delivery of therapeutic drugs,allowing them to easily pass through the blood-brain barrier (BBB) [40].The above-mentioned advantages of exosomes play critical roles in the treatment of tumor and arouse great interests of researchers.
3.1.As drug delivery carriers
Exosomes are very competitive drug delivery nanocarriers because they can communicate between cells under physiological conditions,and have the advantages of low toxicity and good permeability [41].Exosomes have good stability,which can move long distances in the body and deliver therapeutic drugs to specific tissues or cells [21].In addition,exosomes have good hydrophilicity,which means that exosomes can not only deliver hydrophilic drugs,but also hydrophobic drugs by binding to lipids[42].
The encapsulation rate of exosomes in drug delivery systems is generally less than 30%,and the encapsulation rate of nanoparticles can reach more than 90%,which is much higher than that of exosomes.It has been reported that if exosomes are combined with nanoparticles,drug-loaded nanoparticles can improve the encapsulation efficiency of the drug delivery system,which provides a new direction for future researches on exosomes [43-46].Exosomes as carriers can increase drug accumulation at the tumor site,overcome the limitations of tumor treatment and induce cancer cell apoptosis.
If therapeutic drugs such as nucleic acid drugs are added to exosomes,they can be transferred to specific cells or tissues,thereby increasing the local concentration of therapeutic drugs and reducing side effects[47].Nanoparticles are a more popular type of drug release system for imaging or therapy,while exosomes are carriers for nanocapsules[48].Liposomes are synthetic vesicles with phospholipid membranes that can self-assemble in an aqueous environment to make them have different shapes and sizes,while nanoparticles generally use polymers to encapsulate or adsorb drug molecules [49].Nanoparticles can be modified to respond to the tumor microenvironment.He et al.designed composite materials that encapsulated triptolide in reduction-sensitive polymer nanoparticles,which could respond to glutathione,it could be targeted to treat liver cancer [50].The cell membrane had a strong protective effect,which could maintain the integrity of cells and enable cells to perform its normal function.If the cell membrane was used as carriers for targeted therapy,which could avoid the problem of drug leakage and greatly improve the therapeutic effects.For example,Ma et al.developed a cell membrane targeted self-delivery chimeric peptide,which had good biocompatibility and targeting and good tumor treatment effects[51].In recent years,responsive nanomedicine has been rapidly developed,among which light-responsive liposomes,its controllability and availability are quite attractive [52].Yu et al.developed a photoactivated liposome,which could load triptolide and Ce6,realize the synergistic treatment of photodynamic therapy (PDT) and chemotherapy,promote the apoptosis of tumor cells,and have good biocompatibility and tumor treatment effects [53].Exosomes have advantages compared to other nano drug delivery systems.Constitutively,exosomes resemble their own cellsin vivo,and they are non-immunogenic by nature[54].Since organic and nonorganic nanoparticles inevitably suffer from cytotoxicity,nontargeting,and immunogenicity in drug delivery,while exosomes can cross biological barriers and reduce cytotoxicity and immunogenicity[55,56].
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) had its unique pathological features,and its treatment had always been a difficult problem.Zhou et al.used bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells(BM-MSC)exosomes as carriers of PDAC treatment to increase the accumulation of drugs at the tumor site,improve the efficacy,and overcome pathological limitations[57].Kim et al.used exosomes as carriers to deliver plasmids to cancer cells,and produce synergistic cytotoxicity to ovarian cancer cells,thereby promoting ovarian cancer cell apoptosis(Fig.1)[58].
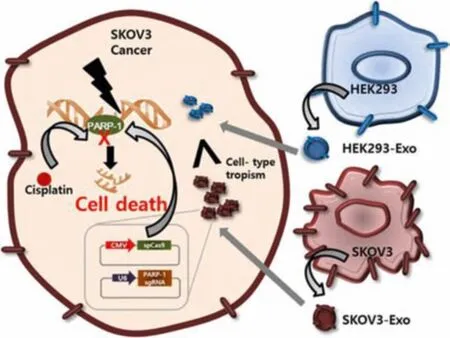
Fig.1-Effects of cancer-derived exosomes(SKOV3-Exo)on tumor therapy.As natural carriers,SKOV3-Exo could deliver the plasmid(CRISPR/Cas9)to cancer cells.Compared with the epithelial-derived exosomes(HEK293-Exo),the aggregation of tumor cells was accelerated,and tumor cell apoptosis was induced by inhibiting the activity of PARP-1.Reproduced with permission from[58].Copyright 2017 Elsevier.
Gemcitabine(GEM)is a drug for the treatment of pancreatic cancer.It had good effects,but it also had some shortcomings.Li et al.used exosomes to load the chemotherapeutic drug GEM to achieve targeted therapy of pancreatic cancer.In the study of the biological distribution of tumor-bearing mice,exosomes could increase the concentration of GEM at the tumor site,thereby significantly inhibiting tumor growth[59].Compared with conventional therapy,this exosomes therapy strategy could significantly inhibit tumor growth,and had low immunogenicity and toxicity.Exosomes could be used as carriers to deliver GEM for the treatment of pancreatic cancer,which might be suitable for delivering conventional chemotherapy drugs or combining with other therapies to achieve the purpose of synergistic anti-tumor.
Engineered exosomes had been designed as common nano delivery systems,which had triple functions.As shown in Fig.2,Zhan et al.constructed superparamagnetic nanoparticles clusters based on blood exosomes so as to target tumors.Then the chemotherapeutic drug doxorubicin(DOX),cholesterol modified single stranded miRNA-21 inhibitor (chol-miR21i),were assembled with exosomes to achieve the purpose of combined anticancer.In addition,the cationic lipid-sensitive endosomal peptide L17E peptide was introduced into the co-delivery system to promote the cytoplasmic release of goods,especially RNA.The nanosystem based on blood exosomes could integrate the three functions designed,so that DOX and chol-miR21i were coloaded into exosomes and delivered to tumor cells,thus improving the release of cytoplasm.After drug release,it could combine with RNA and inhibit oncogene expression by interfering with nuclear DNA activity,so as to inhibit tumor growth [60].Nanoengineering systems based on exosomes were likely to replace conventional therapeutic drugs for further development in the future.
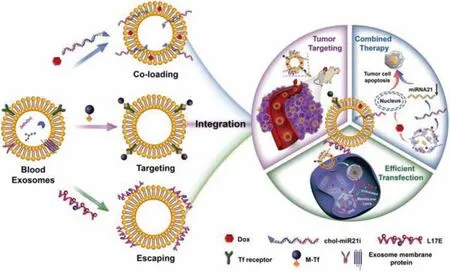
Fig.2-Schematic diagram of engineered blood exosomes for gene/chemotherapy combination therapy.The drug delivery nano-system combined drug and nucleic acid,which could significantly improve the anticancer effects of gene/chemotherapy combination.Reproduced with permission from[60].Copyright 2020 Ivyspring International Publisher.
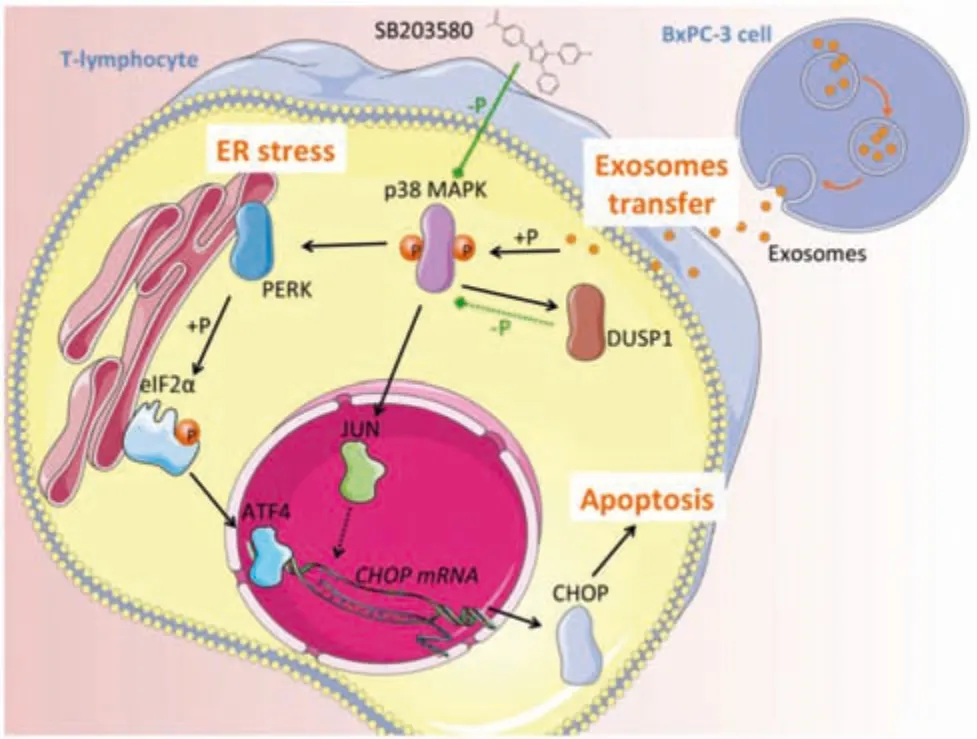
Fig.3-Exosomes participate in signaling pathways to inhibit tumor growth.Reproduced with permission from[73].Copyright 2020 Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology.
Exosomes have low immunogenicity,low toxicity,and the ability to cross BBB,which allows them to overcome the difficulties faced by viral vectors in repeated administration.As multifunctional drug carriers,exosomes can encapsulate small RNA,mRNA,protein and other substances,and they can stay in the target tissue for a long period of time.
3.2.As biomarkers
Exosomes are easily separated from blood samples,so exosomes have become the main source of biomarkers[61].Exosomes as biomarkers could inhibit the growth of tumor cells and be used for tumor prediction,prognosis,and treatment.In humans with primary pituitary adenoma (PA),the expression of lncRNA H19 was often decreased.Exosomes H19 could be used as biomarkers to inhibit the growth of tumor [62].Circulating exosomes miRNAs could be used as biomarkers for diagnosis of colorectal cancer(CRC),which had broad application prospects[63].
The serum exosomes miR-200 family,especially miR-200c-3p,could be used as a biomarker for the treatment of cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) [64].When serum exosomes miRNAs were abnormally expressed,exosomes miR-7977,for example,could be used as a biomarker to inhibit growth of tumor cells for the treatment of lung adenocarcinoma(LUAD)[65].The expression of miR-200c,miR-145 and miR-93 in serum of patients with ovarian cancer was significantly increased,especially the exosomes miR-145,which was a promising biomarker in ovarian cancer treatment [66].The presentation and treatment ways of metastatic CRC and non-metastatic CRC were different,so it was important to distinguish between them.Tang et al.[67] had demonstrated that serum exosomes miR-320d was a biomarker for differentiating metastatic CRC from non-metastatic CRC.
CDK6 and RHOU mRNA in serum exosomes could be served as biomarkers to predict the invasiveness of non-functional pituitary adenoma(NF-PAs).Exosomes as biomarkers played a critical role in clinical screening and postoperative treatment[68].Salivary exosomes miR-24-3p was an effective biomarker in the treatment of oral squamous cell carcinoma(OSCC)[69].As biomarkers,serum exosomes miRNA could be used to predict CRC,and had the advantages of high sensitivity and specificity[70].
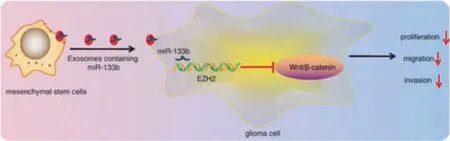
Fig.4-The effects of MSC-derived exosomes on glioma cells.Reproduced with permission from[74].Copyright 2019 Springer.
As tumor biomarkers,exosomes have unique advantages:(i) compared with other traditional biomarkers,exosomes have better specificity;(ii) exosomes contain many bioactive molecules,and the infection to other active molecules is less;(iii) exosomes have high activity and good stability,and they can be protected from the external environment;(iv)exosomes exist in body fluids,which is a very convenient detection method;these advantages endow exosomes with great potential as biomarkers [71].Differentially expressed RNA and protein in exosomes can affect the initiation and progression of gastrointestinal malignant tumors at different stages.Exosomes are promising sources of biomarkers and may be used for non-invasive detection of patients in the future.
3.3.Participate in the apoptosis signaling pathway
Apoptosis is currently the most studied and is a very classic programmed death process.Apoptosis has obvious morphological characteristics,including DNA fragmentation,cell membrane blistering,cell shrinkage,and the formation of apoptotic bodies,etc.[72].The mechanism of apoptosis is generally more complicated,and there are mainly two ways,namely,the exogenous way and the endogenous way.
Shen et al.found that exosomes from pancreatic cancer could be transferred to T lymphocytes and integrate with T lymphocytes,thereby activating the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38 MAPK) pathway of T lymphocytes,which was very important in the apoptotic signaling pathway.On the one hand,it could activate the endoplasmic reticulum stress,thereby activating the protein kinase R-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase-eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2Aactivating transcription factor 4-C/EBP homologous protein(PERK-eIF2a-ATF4-CHOP) signaling pathway to achieve the purpose of inducing tumor cell apoptosis.On the other hand,it could increase the level of dual specificity phosphatase 1(DUSP1)(Fig.3)[73].
Xu et al.found that exosomes containing miR-133b could inhibit the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Thus,the expression level of EZH2 was inhibited,and finally the metastasis and invasion of glioma cells were inhibited(Fig.4)[74].
Exosomes can be used for local or systemic comm unication between cells in a shuttle way [75].Ligands on the surface of exosomes can bind to receptors on the surface of target cells,thereby affecting the signal pathways of target cells [76].Deng et al.had reported that exosomes could improve neuronal death,inflammation,and affect apoptosis signaling pathways[77].
3.4.Improve chemical resistance
At present,the treatment way of cancer is mainly chemotherapy,among which chemotherapy play a critical role in inhibiting tumor growth.However,chemotherapeutic drugs have serious drug resistance,which will greatly reduce their therapeutic effects and cause pains to patients.Drug resistance has always been the focus of attentions of researchers [78].There may be two reasons for tumor drug resistance.On the one hand,it is due to genetic changes,and on the other hand,it may be due to the existence of the tumor microenvironment,which makes it difficult for chemotherapeutics to enter tumor cells [79].Exosomes can communicate information between cells and participate in the regulation of chemoresistance in the form of transporters,mRNA,and non-coding RNA(ncRNA)[80].
5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) is a drug to treat CRC,but the resistance of 5-FU is a serious problem that needs to be solved,which seriously affects the therapeutic effects [81].Liang et al.co-delivered functional inhibitory miRNA and anticancer drug 5-FU with exosomes to achieve the purpose of reversing the drug resistance of CRC,thereby enhancing the efficacy of tumor treatment,and providing a new drug-resistant tumor treatment method.Exosomes could deliver miR-21 inhibitors(miR-21i) and drugs to CRC HCT-116 cells (HCT-1165FR) and down-regulate the expression of miR-21,thereby inhibiting the proliferation of tumor cells,this strategy could effectively reverse the drug resistance of drug-resistant cells and achieve the purpose of effective treatment of tumors [82].This indicated that the combination of miRNA and chemotherapy drugs could achieve better synergistic anti-tumor effects,and this strategy was likely to be applied to clinical practice in the future.
Cao et al.found that exosomes could affect tumor microenvironment,and miR-27a exosomes produced by cells was a new method to treat prostate cancer(PCa)by inhibiting the expression of prostate cancer gene and improving the drug resistance in the process of treatment [83].Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is a type of lung cancer,accounting for about 80%-85%of the total number of lung cancer patients[84].Cisplatin(DDP)was a commonly used drug in lung cancer treatment,but the drug resistance and side effects of DDP were serious,so the effects were not satisfactory[85].Wu et al.co-cultured the parental and drug-resistant cells of the A549 and H1299 cell lines with BMSC-Exo.miR-193a mimics or si-LRRC1 transfected cells were used to detect the proliferation and apoptosis of NSCLC cells.The results suggested that BMSC-Exo up-regulated by miR-193a and down-regulated by LRRC1 could inhibit the invasion and proliferation of NSCLC cells.At the same time,if BMSC-Exo combined with upregulated miR-193a,it could reduce the tumor volume of NSCLC mice.This showed that exosomes miR-193a derived from BMSCs cells could reduce cisplatin resistance of NSCLC cells by targeting LRRC1[86].
In summary,exosomes can be used as drug delivery carriers,as biomarkers,participate in the process of apoptosis signaling pathways,improve chemoresistance,and play a vital role in tumor treatment through the above methods.The beneficial roles that exosomes played in tumor treatment were summarized in Table 1.
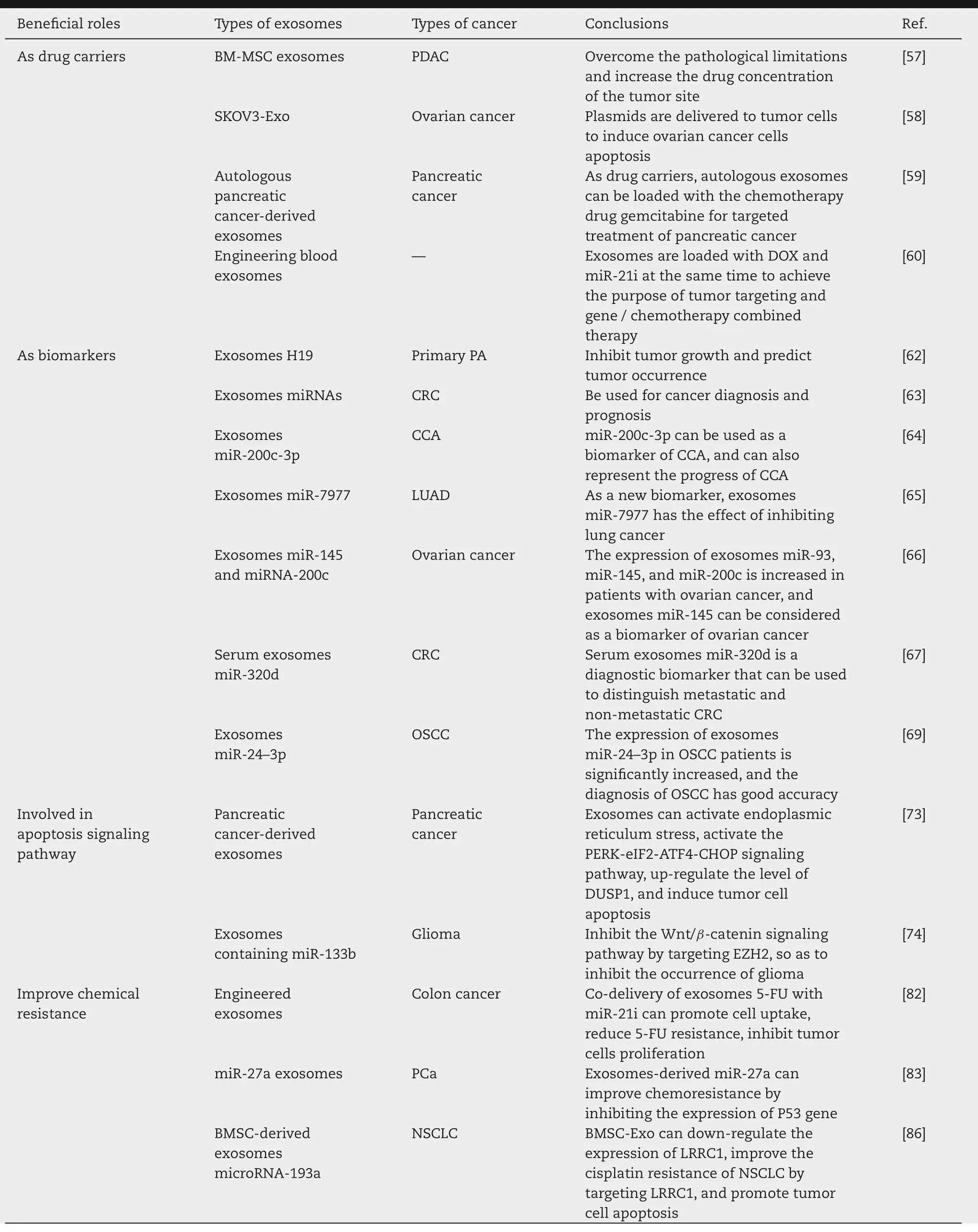
Table 1-The beneficial roles of exosomes in tumor treatment.
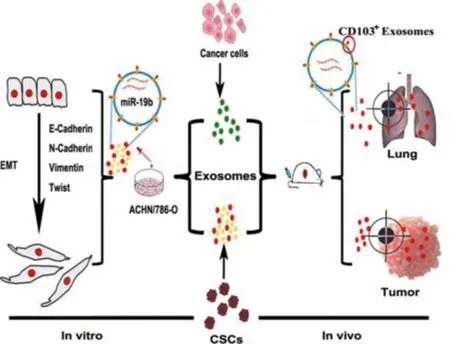
Fig.5-The effects of exosomes secreted by CSC on the process of EMT(Reproduced with permission from[93].Copyright 2019 BioMed Central.
4.The unfavorable roles of exosomes in tumor treatment
4.1.Promote the EMT process
EMT is the depolarization process of epithelial cells to mesenchymal cells,which can reshape the cytoskeleton and improve its migration ability.EMT is related to the metastasis and drug resistance of a variety of cancers,can promote tumor metastasis,and plays a key role in the process of drug resistance[87-89].EMT up-regulates chemotherapy resistance genes and is related to inhibit drug transporters from entering the nucleus [90].Tumor exosomes can participate in the process of EMT,tumor angiogenesis and tumor metastasis,which are closely related to tumor cell proliferation[91,92].
Studies have explored the effects of exosomes secreted by cancer stem cells(CSC)from patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma (CCRCC) on the process of EMT.Wang et al.found that exosomes could promote the proliferation of cancer cells and promote the process of EMT.As shown in Fig.5,on the one hand,exosomes could deliver miR-19b-3p to tumor cells and promote the process of EMT by inhibiting the expression of PTEN.On the other hand,exosomes had certain targeting properties and could accumulate in tumor cells and lungs.Exosomes could promote the process of EMT,the higher the proportion of CD103+exosomes in CCRCC patients,the stronger the regulation of CD103+exosomes on EMT.miR-19b-3p in exosomes could be used as a new target for CCRCC.In addition,the clearance of CD103+CSC exosomes might be helpful to the treatment of CCRCC,which was a new idea to inhibit its metastasis[93].
EMT was related to tumor growth and could predict tumor development[94].Exosomes from patients with gastric cancer could promote the metastasis of gastric cancer cells by promoting EMT signal transduction,thereby inhibiting the treatment of peritoneal metastasis and affecting the therapeutic effects[95].
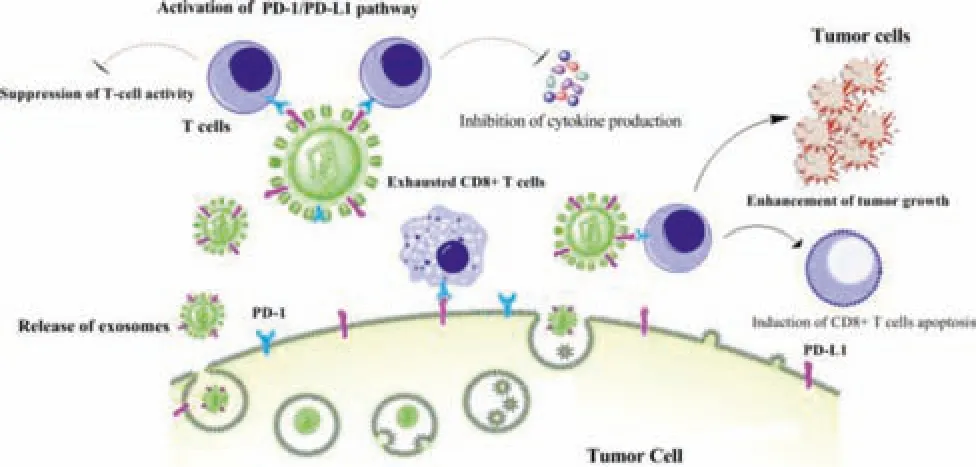
Fig.6-The roles of exosomes PD-L1 in cancer progression(Reproduced with permission from[99].Copyright 2021 BioMed Central).
4.2.Promote tumor growth,metastasis,and immunosuppression
Exosomes are the main components of extracellular vesicles,and tumor-derived exosomes contain immunosuppressive proteins,such as PD-L1.PD-L1 is the ligand of PD-1,and the interactions between them is a signal pathway inherent in the human body,which can avoid excessive activation of the immune response.When this signaling pathway is used by tumor cells,they can evade the surveillance of immune system,which is often called immune escape.
Some strategies have emerged,such as monoclonal antibodies that can block PD-1/PD-L1 interactions,but sometimes serious adverse reactions have occurred [96].Whiteside et al.found that tumor cells could produce abnormal tumor immune responses to improve tumor cell activity.This process could produce plenty of exosomes,and exosomes contained components that promote tumor cell growth,such as PD-L1,mRNA,and micro-RNA [97].Most importantly,there was an immunosuppressive protein PDL1 on the surface of exosomes secreted by tumor cells,and exosomes could transport PD-L1 to cells with low or no PD-L1 expression[98,99].
Exosomes PD-L1 is associated with the progression of various cancers,including melanoma,glioblastoma,and breast cancer [100].Exosomes can not only metastasize between cancer cells,but also between cancer cells and stromal cells.Cancer cells absorbed exosomes released by stromal cells,creating the microenvironment that promoted tumor growth,proliferation or invasion of cancer cells [101-103].PD-L1 could be secreted by tumor cells under exosomes,which could promote tumor growth in an immune-dependent manner.
Tumor-derived exosomes PD-L1 had inhibitory effects on tumor immunity.On the one hand,exosomes containing PD-L1 could inhibit the expression of IL-2 and IFN-γ,thus inhibiting the activity of CD8+Tcells.At the same time,exosomes with high PD-L1 expression could also induce CD8+Tcell apoptosis through PD-1/PD-L1 interaction.On the other hand,exosomes PD-L1 could induce the apoptosis of CD8+Tcells (Fig.6).In summary,exosomes PD-L1 could inhibit T cells immunity and promote tumor growth of different tumor types.At present,the specific mechanism of exosomes PDL1 was not very clear.However,it was clear that PD-L1 could interact with anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies,thus reducing the efficiency of tumor treatment.Exosomes secreted by normal cells were intuitive and important to human physiological activities.In the process of tumor treatment,the therapeutic drugs should be choosed to reduce side effects.In addition,the clearance of PD-L1+exosomes might also be an effective strategy for tumor treatment[99].
4.3.Promote tumor angiogenesis
The process of angiogenesis refers to the growth of new blood vessels based on existing blood vessels.In this process,many activities are involved,such as tumor cell metastasis,invasion,and differentiation [104].Angiogenesis occurs under many conditions.Tumor metastasis requires angiogenesis.New blood vessels can provide oxygen and nutrients for tumor cells[105].Angiogenesis plays a vital role in the process of tumor and is considered to be a target for tumor treatment[106-108].Exosomes miR-205 from ovarian cancer cells could be used as a target to promote angiogenesis and thus promoting tumor growth[109].
Tumor-derived exosomes were closely related to tumor occurrence and development,tumor metastasis,drug resistance,and angiogenesis.This was because that exosomes contained many substances,such as microRNA,mRNA,transcription factors,and proteins[110]Fang et al.found that the expression level of miR-103 was higher in HCC exosomes,and exosomes could deliver miR-103 to endothelial cells,which could increase the permeability of endothelial cells,promote angiogenesis,and create a microenvironment for tumor metastasis,thus promoting tumor metastasis.[111].miR-103 could be used as potential biomarkers and had important clinical significance.
Studies have shown that miR-221-3p can promote the EMT process of tumor cells to promote tumor development [112].In addition to promoting the process of EMT,angiogenesis is also crucial for tumor growth.Wu et al.have proved through experiments that exosomes from cervical squamous cell carcinoma (CSCC) can promote tumor cell metastasis to vascular endothelial cells through miR-221-3p,and promote angiogenesis by down-regulating the expression of THBS2,thereby promoting the occurrence and development of tumors.The miR-221-3p derived from CSCC may be a potential biomarker and new therapeutic target [113].Bao et al.found that exosomes could transfer miR-23a derived from nasopharyngeal carcinoma to human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs),and affect the growth and metastasis of HUVEC.miR-23a derived from exosomes could target TSGA10 and promote angiogenesisin vivoandin vitro[114].If miR-23a was used in combination with VEGF inhibitors,it might achieve good therapeutic effects and have a deep understanding of the patient’s disease characteristics.
4.4.Promote chemoresistance
In most cases,the researches on tumor drug resistance generally refer to the tumor cells themselves.For example,genetic changes can cause chemotherapeutic drugs to lose their activity,activate oncogenes,promote tumor development,and inhibit tumor cell apoptosis,etc.[115].Exosomes have also become a new hot spot in tumor biological drug resistance researches.
Malignant glioma is a malignant tumor,which is fatal[110].Temozolomide (TMZ) is a drug for the treatment of glioblastoma and has a certain curative effect.However,it has a certain degree of drug resistance,which is the key problem that needs to be solved in the treatment of glioblastoma [116].Zhang et al.found that the expression of lncRNA SBF2-AS1 was very high in TMZ resistant glioblastoma cells and tissues,its overexpression would lead to TMZ resistance,and inhibiting its expression would make resistant glioblastoma cells sensitive to TMZ.lncRNA SBF2-AS1 could be enriched in exosomes and promote temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma.Glioblastoma cells reprogramed the tumor microenvironment by secreting exosomes rich in lncSBF2-AS1,which promoted tumor chemotherapy resistance.Therefore,the exosomes lncSBF2-AS1 in serum could be used as a potential marker for resistant or refractory glioblastoma [117].To further highlight the therapeutic effect of TMZ,it is of great significance to specify an exclusive treatment strategy for glioblastoma patients who are resistant to TMZ.
Exosomes can regulate the tumor microenvironment,exchange information between cells,and play a vital role in the regulation of tumor drug resistance by transferring RNA and proteins.Tumor exosomes can mediate the drug resistance of tumors.Exosomes released by primary drugresistant tumors can regulate the biological function of tumor cells and enhance their chemical resistance.
4.5.Participate in the autocrine pathway
Some secreted proteins can maintain the stemness of stem cells through autocrine pathways,which is very important.Gu et al.found that most of the secreted proteins produced by hematopoietic stem cells(HSCs)matured in exosomes and were released by exosomes [118].Exosomes could promote tumor cells growth through the autocrine pathway.For example,the cytokine TGF-β1 in exosomes could combine with TGF-β1 receptor,which activated the anti-apoptotic pathway and promoted chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) cell proliferation and survival(Fig.7)[119].The autocrine pathway of exosomes was of great significance for tumor treatment and diagnosis.The genetic material carried by exosomes can be absorbed through autocrine pathways.Exosomes can also be absorbed by target tissues or organs through the circulatory system,so as to participate in a variety of physiological processes.
In summary,the PD-L1 contained in exosomes is a nuclear weapon for tumor growth and immunosuppression.Exosomes can promote the transformation of tumor cells into normal cells through signal-mediated pathways,promote tumor angiogenesis,and promote chemical resistance.It promotes the metastasis of tumor cells through autocrine pathways.Exosomes can adversely affect the treatment of tumors in the above-mentioned ways.The unfavorable roles played by exosomes in tumor treatment was summarized in Table 2.
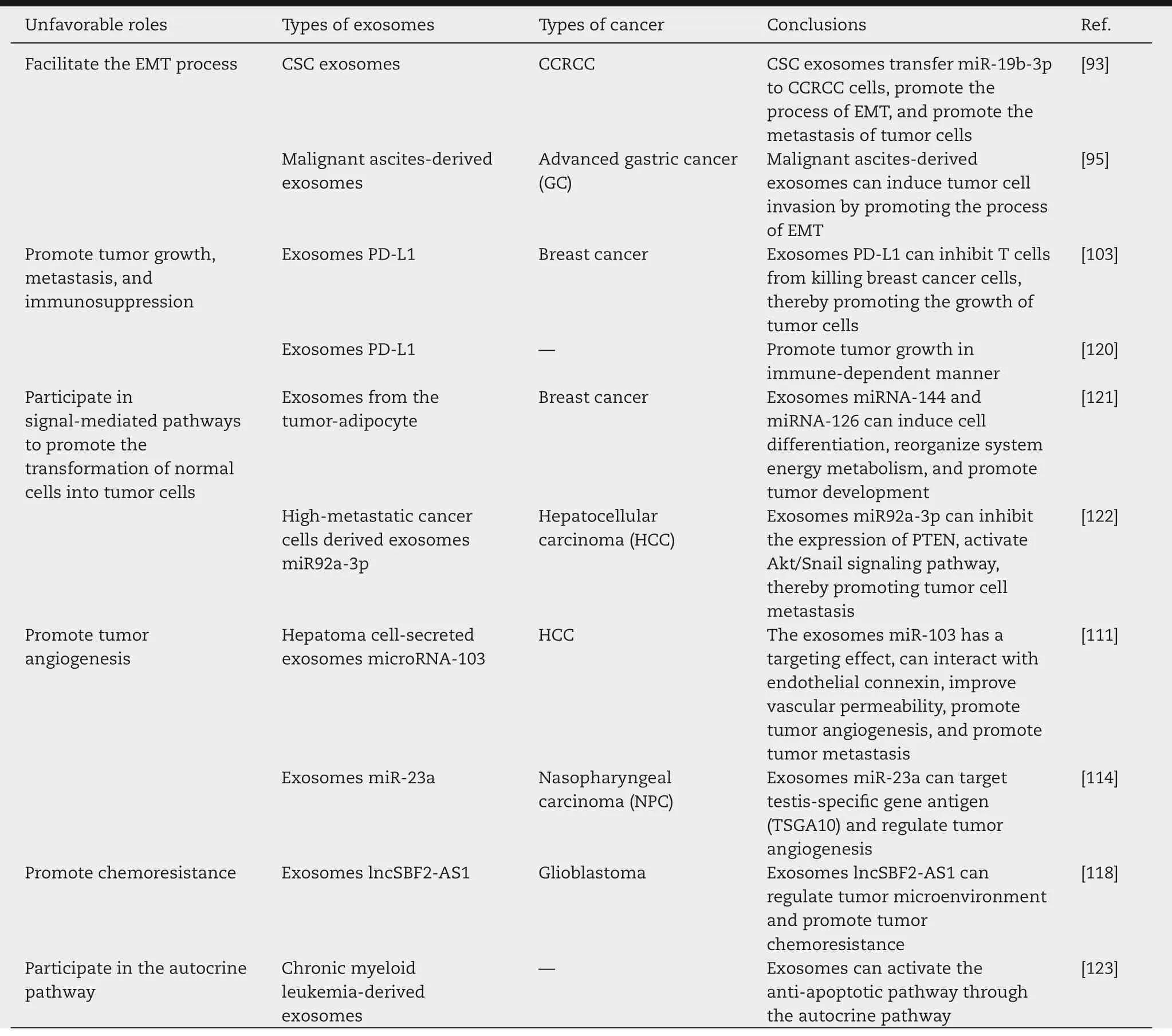
Table 2-The unfavorable roles of exosomes in tumor treatment.
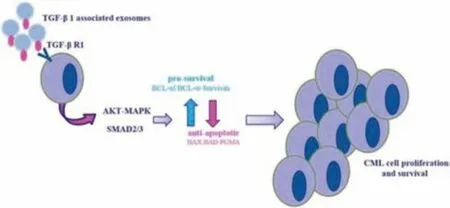
Fig.7-Working hypothesis of an autocrine loop mediated by exosomes.Construction of an autocrine signaling pathway by exosomes associated TGF-â1,thus promoting the proliferation of leukemia cells.(Reproduced with permission from[119].Copyright 2015 Springer.).
5.Using the multiple roles of exosomes to conquer tumors
Exosomes are a kind of cell-derived nano-scale microvesicles that can participate in the transportation of substances between cells.If therapeutic drugs are loaded into exosomes,the exosomes can deliver the therapeutic drugs to specific cells or tissues to achieve targeted drug delivery.Targeted drug delivery has certain advantages,which can increase local concentration of therapeutic drugs and reduce the toxic effects of drugs[47].
5.1.Exosomes nano drug delivery system
Targeted nano-drug delivery systems based on exosomes are currently an important research direction.Exosomes have a bilayer structure of phospholipids,which can protect drugs from chemical and enzymatic degradation[37].Exosomes can penetrate the BBB to improve the utilization of therapeutic drugs.Nano drug delivery system has enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect,which has unique advantages in cancer treatment applications [124].Combining the unique functions of exosomes with the versatility of nanoparticles can be a more effective platform for drug delivery[125].
Exosomes can stably encapsulate nucleic acids or proteins and improve the solubility of hydrophobic drugs.Wang et al.constructed exosomes nano-delivery system to achieve precise treatment of cancer (Fig.8).The magnetic Fe3O4nanoparticles could undergo self-polymerization with polydopamine (PDA) under alkaline conditions to obtain PDA-coated magnetic nanoparticles (Fe3O4@PDA).Then DOX could be loaded into exosomes by electroporation.Fe3O4@PDA magnetic nanoparticles could functionalize the surface of exosomes,and avidin and molecular beacon(MB) could be used to modify Fe3O4@PDA to make it have the ability of specific recognition,which could respond to external magnetic fields and target tumor sites.MB coated on its surface had a specific recognition ability,which could specifically recognize miRNA-21.In addition,PDA was a photothermal treatment agent that could convert nearinfrared light into heat energy for photothermal treatment of cancer.Under the irradiation of near-infrared light,the instability of exosomes could release the chemotherapeutic drug DOX for cancer treatment.This could kill target cancer cells and cause instability of exosomes,and promote the release of encapsulated DOX.The therapeutic diagnosis platform based on exosomes had the following advantages:(i)it could be realized by functionalization strategy;(ii) it could respond to the external magnetic field and had targeting ability;(iii) under photothermal conditions,exosomes membranes could be broken to release therapeutic drugs;(iv) synergistic therapy could significantly improve the therapeutic effects.This strategy provided a new idea for tumor treatment and diagnosis platform based on exosomes[126].
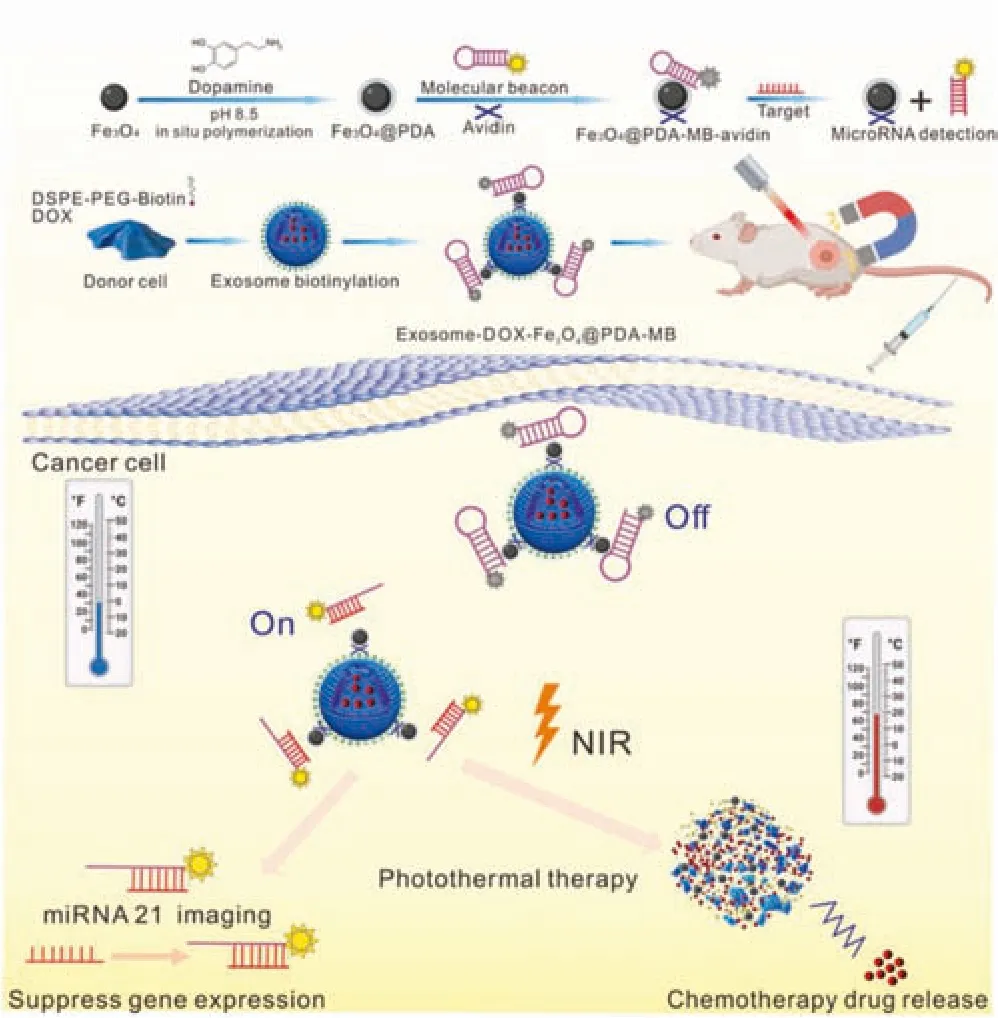
Fig.8-An exosomes nano-drug delivery system for targeted delivery and combined anti-cancer therapy under near-infrared irradiation.Reproduced with permission from[126].Copyright 2021 Biomaterials.
5.2.Exosomes targeted delivery strategy
In order to improve therapeutic effects of exosomes and reduce side effects of exosomes on normal cells,it is very important to improve targeted delivery ability of exosomes.The strategies for targeted delivery of exosomes include (i)modification of the proteins on the surface of exosomes to achieve targeted delivery [21];(ii)introduce functional mRNA into exosomes to achieve targeting[22];(iii)choose exosomes with strong tropism to achieve targeting[23];
Exosomes can encapsulate chemotherapeutic drugs such as DOX and the surface modifications of exosomes can deliver more drugs to the lesion sites.Tian et al.constructed iRGD peptide (CRGDKGPDC) modified exosomes which could improve the targeting capacity to tumor tissues.The researchers used mouse immature dendritic cells (imDC)to prepare exosomes,and combined withαv integrinspecific iRGD peptide (CRGDKGPDC) for targeting.The chemotherapeutic drug DOX was loaded onto the secretion functionalized by iRGD peptide by electroporation,and the drug loading efficiency could reach 20%.In theαv integrinpositive breast cancer cellsin vitro,iRGD exosomes showed high tumor-targeting ability and DOX delivery through confocal imaging and flow cytometry.After intravenous injection of the exosomes,it could specifically deliver DOX to tumor tissues,thereby inhibiting tumor growth.Targeted modification of the surface of exosomes could accurately deliver therapeutic drugs to the tumor site,reduce the side effects of drugs,and have great clinical application values.Other hydrophobic drugs could also target tumors in this way and high-yield,low-toxicity exosomes should be developed for tumor treatment[127].
Exosomes can transfer membrane proteins to recipient cells,or directly bind to the recipient cell membrane [128].Researchers used the membrane protein transmission function of exosomes to modify tumor cells,change the phenotype of tumor cells,and improve tumor immunogenicity.Kim et al.came up of a method to achieve tumor xenogenization (meaning that transforming self to non-self) by using fusogenic exosomes,which could introduce fusogenic viral antigens (VSV-G) onto the surfaces of cancer cells(Fig.9).First,developing a fusogenic exosomes platform by modifying the surfaces of exosomes with viral fusion proteins,namely mVSVG-exosomes.When tumor cells were modified by mVSVG-exosomes,it would be engulfed by phagocytes easier.Next,mVSVG-exosomes could activate dendritic cells through the TLR4 signaling pathway and produce effective anti-tumor immune effects.Tumor xenogenization caused by fusogenic exosomes provided a novel approach for cancer immunotherapy[129].
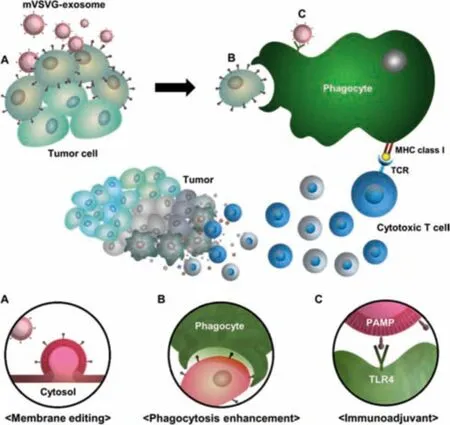
Fig.9-Strategies for the formation of tumor cell heterogeneity mediated by exosomes Reproduced with permission from[129].Copyright 2020 American Association for the Advancement of Science.
In recent years,exosomes have become effective carriers based on nucleic acid therapy for the treatment of tumors [130].The exosomes containing the target genes are obtained through the processes of purifying the exosomes and loading the mRNA.Yang et al.used the cell nanoporation method (CNP) to prepare a biochip that could be used to prepare exosomes containing therapeutic mRNA,microRNA,hairpinRNA and targeting peptides.The researchers transfected mouse embryonic fibroblasts or dendritic cells with plasmid DNA,stimulated the cells through local electrical stimulation,integrated the mRNA into the exosomes,and promoted the release of the entrapped mRNA and targeting peptides from the exosomes.As shown in Fig.10,the CNP system consisted of an array of nanochannels with a diameter of 500 nm.Plasmid DNA entered the cell through the nanochannel under transient electrical stimulation,and then released exosomes containing mRNA.These collected exosomes could pass through BBB or the blood-brain tumor barrier (BBTB) for tumor-targeted delivery.In a mouse model of glioma deficientin situphosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN),mRNA-loaded exosomes had tumor suppressor effects and could increase the survival rate of mice[22].
Due to the nano-effects and biocompatibility of exosomes,they can penetrate physiological barriers,and now have become extremely attractive carriers.Wang et al.had developed a DOX loaded bionic neutrophil exosomes (NEs-Exos) system for the treatment of glioma,which was inspired by the intrinsic characteristics of neutrophils,namely inflammatory chemotaxis and excellent BBB-crossing ability(Fig.11).The results in zebrafish and mouse models showed that NEs-Exos had a certain ability to penetrate the BBB.Furthermore,in the transwell BBB model and mouse brain inflammatory study,the results demonstrated that NEs-Exos could make a chemotactic response to inflammatory stimuli and target infiltrating cancer cells in inflamed brain tumors.After intravenous injection of NEs-Exos/DOX,it had a good effect of inhibiting tumor growth.This novel NEs-Exos/DOX delivery platform provided a new chemotherapy strategy for the treatment of glioma and other cancers.NEs-Exos/DOX had a good therapeutic effect on glioma,and the drug delivery system based on NEs-Exos was expected to be a platform for accurate tumor treatment[131].
6.Challenges of exosomes in cancer therapy
Cancer has always been a global concern.Traditional cancer treatment ways,such as chemotherapy and surgery,have obvious limitations[132].Exosomes play a vital role in tumor cells invasion and metastasis.Based on this,tumor exosomes may become a new candidate for cancer treatment,and may improve the prognosis and the effects of tumor therapy.
Exosomes can deliver therapeutic drugs,such as small interference RNA,microRNA,membrane-associated proteins,and chemotherapeutic drugs,so exosomes are important carriers for tumor therapy.In order to work effectively,immunomodulatory factors need an optimal microenvironment,and exosomes can play this role.Exosomes can activate all stages of tumor immune circulation,thereby inducing specific immunity of cancer cells[133].
Exosomes play a crucial role in the early diagnosis of cancer,but the means of isolation and detection are limited and lack of economic and effective means.Therefore,the development of methods for the isolation and detection of exosomes has great potentials [134].The researches on the applications of exosomes mainly include two technical obstacles: one is the simplification of the extraction process to improve the recovery rate of exosomes,and the other is the effective means to distinguish exosomes from other EVs[135].The traditional method of exosomes separation is multistep ultracentrifugation,which is tedious to operate,and the exosomes obtained are impure and are often contaminated by other types of EVs.As the key point of exosomes in tumor treatment lies in its targeting and delivery ability,therefore,it is necessary to avoid the existence of non-exosomes EVs,otherwise it will affect the therapeutic effects.Therefore,it is essential to build a rapid and accurate method for exosomes separation,and researchers should devote themselves to this research field.Secondly,the therapeutic effects of exosomes of different cellular origins may also be affected.Therefore,the cell sources of exosomes also need to be concerned.Obtaining exosomes from cancer cells should be avoided as they may contain carcinogenic driving forces that lead to cancer progression.
Exosomes have shown great potential in tumor therapy.Exosomes secreted by tumor cells (tumor-derived exosomes,TEX)may be a novel and non-invasive way to diagnose cancer.TEX can transfer tumor-specific signal molecules from tumor cells to tumor matrix,hematopoietic system and so on[136].
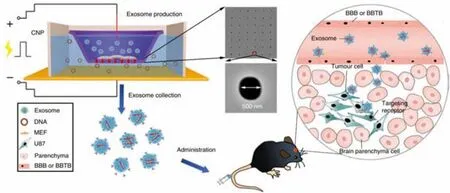
Fig.10-Exosomes load mRNA for targeted delivery of nucleic acids to treat tumors.Reproduced with permission from[22].Copyright 2020 Nature.
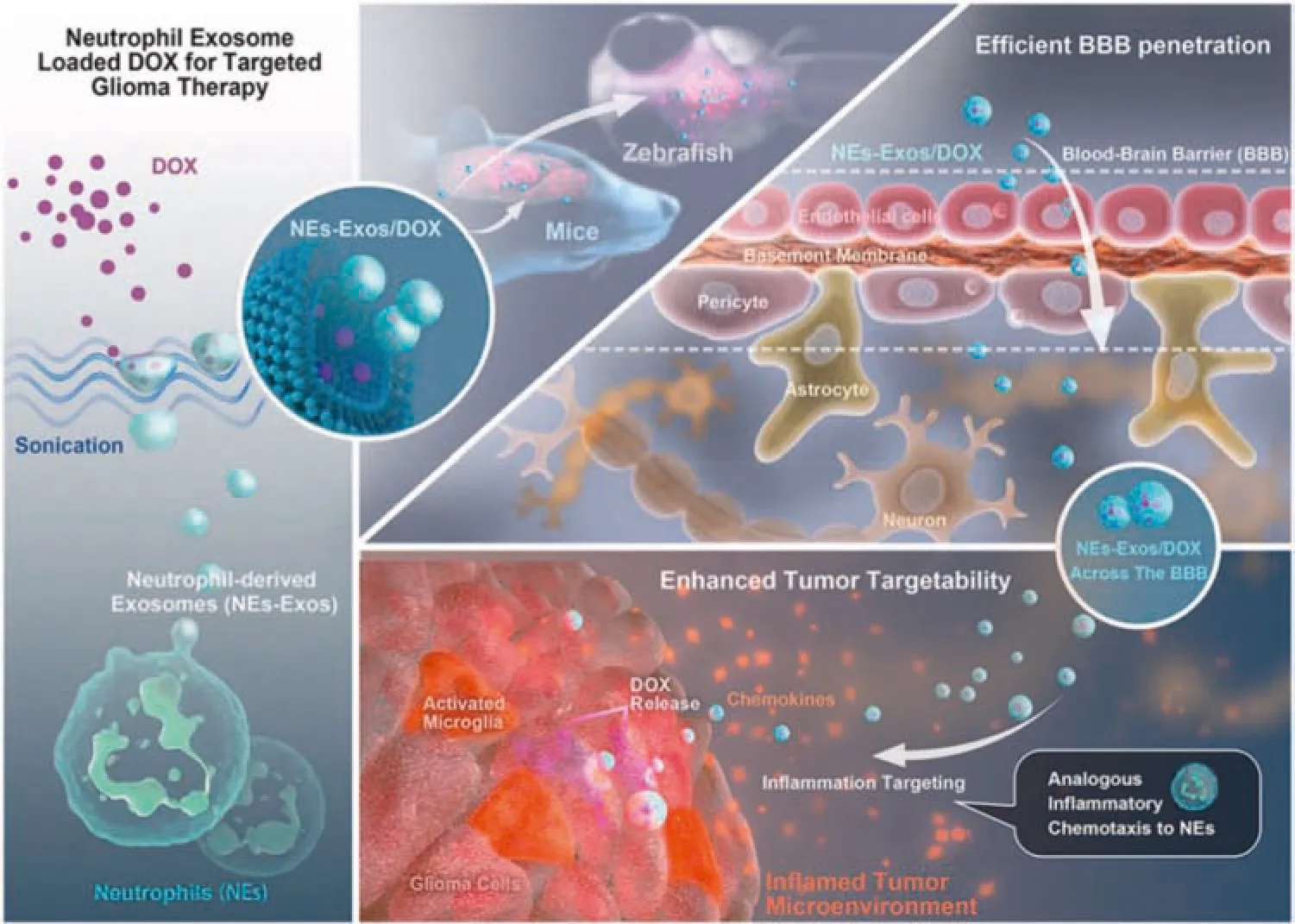
Fig.11-Schematic diagram of NEs-Exos drug delivery system loading DOX and improving the effect of anti-glioma treatment.Reproduced with permission from[131].Copyright 2021 Elsevier.
Before applying exosomes in cancer therapy,it is necessary to investigate exosomes deeply and accurately.Even if the same type of donor cells is used,the exosomes obtained from the cell culture will change and show different characteristics.Therefore,before the exosomes can become a reliable treatment platform,a scalable manufacturing process is needed to produce the exosomes in a rapid,repeatable,and economical manner.In order to make full use of the cancer therapeutic potential of exosomes,elucidating the exact mechanism of biogenesis,developing efficient and reliable separation methods,and understanding exosomes from different sources will be the direction of future research.How to maximize the therapeutic specificity and effectiveness of these vesicles throughout the body requires more research.
7.Conclusion
The discovery of exosomes will profoundly affect the understanding of human physiological and pathological processes.The researches on exosomes will appear a completely new dimension.Exosomes have multiple roles on tumor treatment,which are tightly associated with the immune status of the body and the degree of tumor progression.In addition,more and more studies are using exosomes as tumor vaccines for tumor therapy.In order to make them better used in clinical practice,more advanced technologies are needed to separate exosomes in order to obtain high-yield and high-purity exosomes.With the deepening of our understanding of exosomes,the application of exosomes will be more and more extensive,which is expected to bring new hope for the treatment of tumor patients.We should make good use of the multiple roles of exosomes to find a new breakthrough for tumor treatment,and turn the adverse effects of exosomes into favorable effects to realize accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment of tumor.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
杂志排行
Asian Journal of Pharmacentical Sciences的其它文章
- Application of chitosan-based nanoparticles in skin wound healing
- Hair follicle-targeting drug delivery strategies for the management of hair follicle-associated disorders
- Antibacterial biomaterials for skin wound dressing
- Changes in target ability of nanoparticles due to protein corona composition and disease state
- Elaborately engineering of a dual-drug co-assembled nanomedicine for boosting immunogenic cell death and enhancing triple negative breast cancer treatment
- Sequentially releasing self-healing hydrogel fabricated with TGFβ3-microspheres and bFGF to facilitate rat alveolar bone defect repair