基于台区变压器二次侧电压变化的配电网故障区段定位
2022-09-02张耘浩张文海肖先勇
张耘浩,张 姝,张文海,肖先勇
基于台区变压器二次侧电压变化的配电网故障区段定位
张耘浩,张 姝,张文海,肖先勇
(四川大学电气工程学院,四川 成都 610065)
随着配电网精品台区的建设,越来越多的监测装置向台区低压侧延伸,为配电网的故障定位提供了新的思路。提出了一种基于台区变压器二次侧电压变化的配电网故障区段定位方法。分析了配电网发生故障后的台区变压器侧的电压变化规律,利用故障路径与非故障路径下监测点三相电压幅值变化差异辨识故障区段。通过采用改进的最近邻聚类法,在电压监测集合中辨识出距离故障不同位置的监测点集,能够对监测信息进行快速的分区。该方法不需要10 kV线路的监测数据,仅需要配电台区10 kV/0.4 kV变压器低压侧电压幅值变化信息,监测采集装置安装维护方便。通过大量仿真表明,该方法能够适应不同中性点的接地方式、故障类型和过渡电阻,具有较强的适用性。
配电网;电压监测装置;故障区段定位;变电站二次侧;改进的近邻聚类法
0 引言
配电网由于直接连接用户,其供电可靠性至关重要。但是由于配电线路常年受风雨、树碰、沟道等恶劣环境的影响,导致配电网故障频发。据统计数据表明,电网85%以上故障是由配电网引起[1-4]。因此,准确、可靠的配电网故障定位技术对缩短故障查找时间、加快故障恢复、提高供电可靠性具有重要意义。目前故障定位技术主要包括故障区段定位和故障测距[5]。由于配电网拓扑结构复杂、线路参数不准等问题导致精确的故障位置判定非常困难[6-7]。因此,故障区段定位对缩小故障查找范围更有实际作用。
目前的故障区段定位方法众多[8-14],主要可以分为基于故障过流信息的区段检测和基于零序电流特征提取的故障区段识别[12-13]。基于故障过流信息的定位方法主要是矩阵法。文献[15]根据生成的网络描述矩阵和故障信息矩阵,对这两个矩阵运算得到故障判断矩阵。文献[16]把节支关联矩阵和故障信息矩阵相乘求得故障区段。矩阵法原理简单,计算速度较快,但是该方法的容错性较差,所以很多研究在矩阵法的基础上加入了智能算法以增强它的容错性。文献[17]基于故障电流信号并联叠加特性和逼近关系理论,利用代数关系描述模型关系。文献[18]通过建立适当的优化分析模型,提出了一种基于基因易位的改进二进制粒子群算法的配电网故障定位方法。由于故障指示器不能灵敏的反映小电流接地系统的单相接地故障过流信息,因此大多数研究考虑零序电流特征进行故障区段定位。
基于零序电流特征提取的故障区段识别方法主要根据零序电流的极性[19-21]和相似程度[22-25]来实现。文献[19]计算故障方向参数,根据故障点前后方向参数极性相反的特征确定故障点所在的线路区段。文献[20]引入一阶差分方程,并求出相邻检测点之间的差分乘积,利用其正负值判定故障区段。文献[21]用相空间重构方法提取暂态相电流故障方向测度,建立优化模型,实现故障区段定位。文献[22]通过不断放大故障特征,获取零序电流幅值稳态量,与设定阈值比较。文献[23]以馈线段两端零序电流暂态分量的幅值特性的匹配程度为判据,通过与设定的阈值相比较,确定了故障区段。文献[24]通过时频矩阵中元素的计算得到能量相似度,确定故障区间。文献[25]通过相邻检测点之间暂态零模电流的相关系数来确定故障区段,但是该方法数据传输量较大,并且需要在每个分支测点都安装设备,如果部分测点不能得到数据,会影响定位结果。
无论是基于故障指示器还是基于暂态零序电流的故障区段方法都需要配电线路上的监测信息,即便是配网自动化健全的线路,也难以保证每个区段均安装有终端装置,而对于尚未实施配网自动化的区域,在线路上增加监测装置较为困难。随着各地精品台区的打造,越来越多的智能监测装置在低压变压器侧安装,可获得大量台区低压侧的电气量信息。文献[26]提出了一种利用变压器低压侧的负序电压变化的故障定位方法,但是该方法并不适用于对称性故障。文献[27]提出了一种接入辅助电阻的故障定位方法,该方法在故障时短时接入小电阻比较线路低压侧电压跌落情况,由于其需要额外的操作装置,限制了方法使用的范围。
本文提出了一种基于配电网台区变压器二次侧三相电压量测的故障区段定位方法。该方法利用故障前后三相电压幅值变化规律,通过改进的最近邻聚类法在电压监测集合中辨识出距离故障不同位置的的监测点集,再结合线路拓扑和故障路径判定故障点所在区段。该方法不需要10 kV线路的监测数据,仅需要配电台区10 kV/0.4 kV变压器低压侧电压幅值变化信息,监测采集装置安装维护方便。同时,通过改进的最近邻聚类法能够对监测信息进行快速的分区,对配网自动化水平不高地区的故障检测具有参考价值。
1 台区变压器二次侧电压变化特征
1.1 变压器一/二次侧电压变换关系
配电网10 kV/0.4 kV的变压器通常采用Dyn11的接线方式,如图1所示。
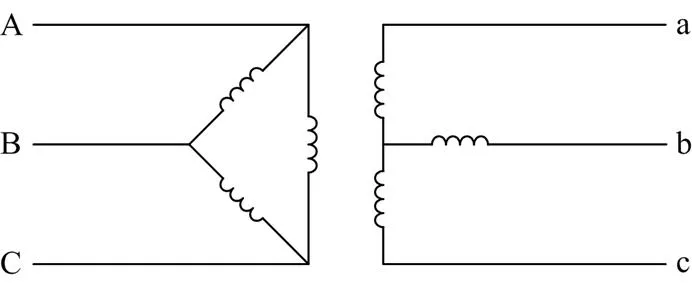
图1 变压器简单示意图
当配电网线路侧发生不对称故障时,利用对称分量法对变压器高低压侧的电压进行分析,可获得高压侧相电压正序、负序和零序的差值表达式,以AB相为例,如式(1)所示。
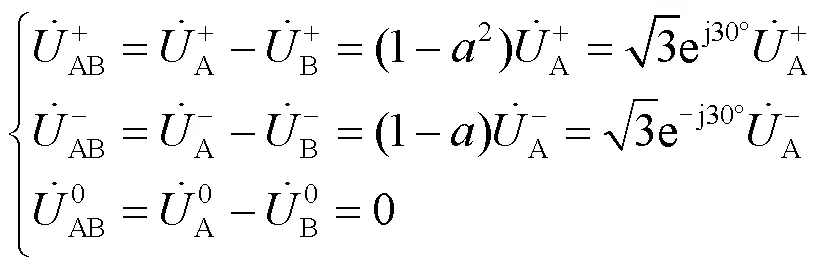
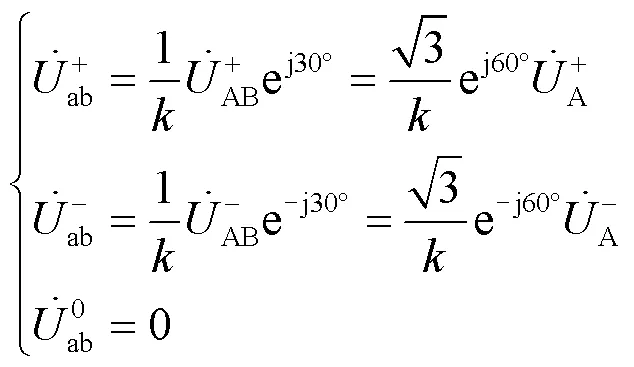
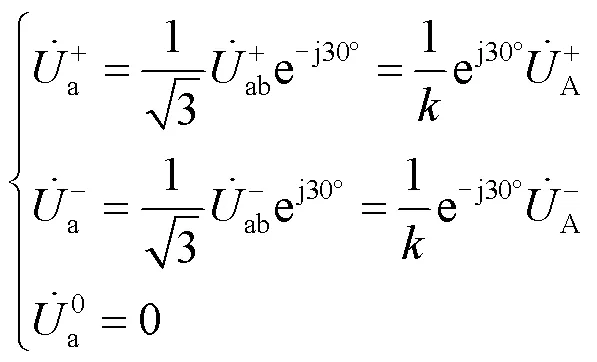
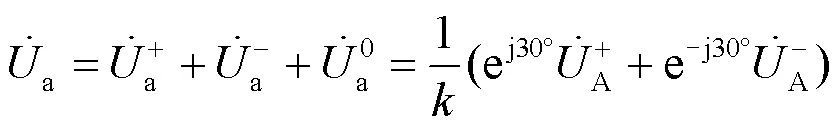
由对称分量变换矩阵可得:
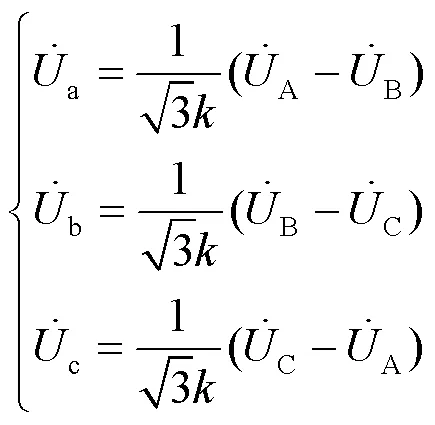
当线路发生对称故障或者正常运行时,变压器低压侧电压表达式如式(6)所示。
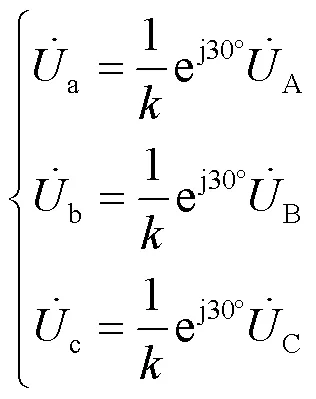
1.2 故障前后电压变化特征
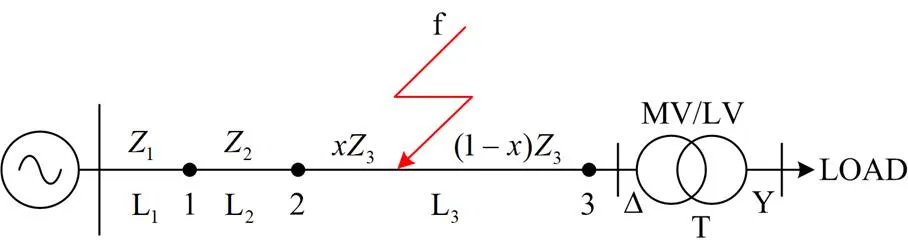
图2 故障线路图
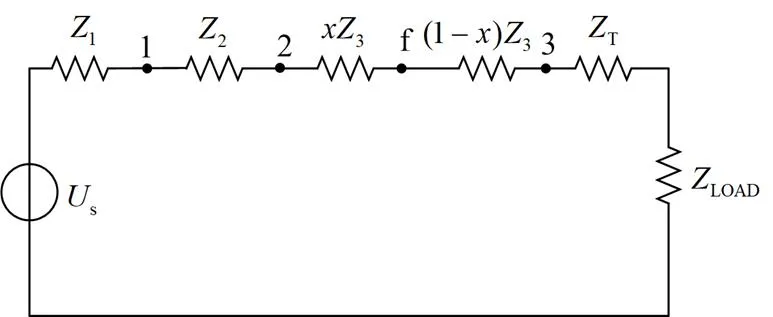
图3 单线等效图
由基尔霍夫电压定律(KVL)可得
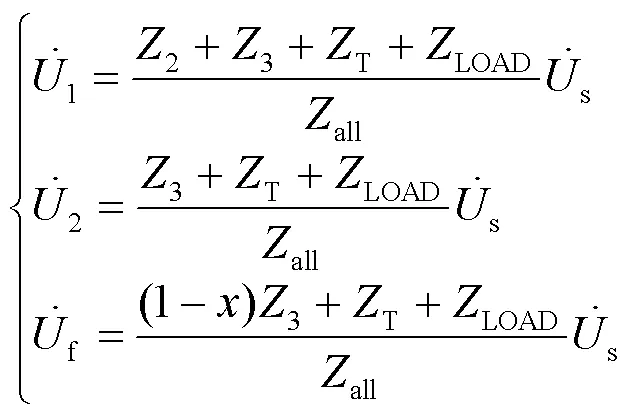
将式(7)代入式(6)中可以得到对应节点变压器低压侧的相电压,以A相为例,低压侧电压如式(8)所示。
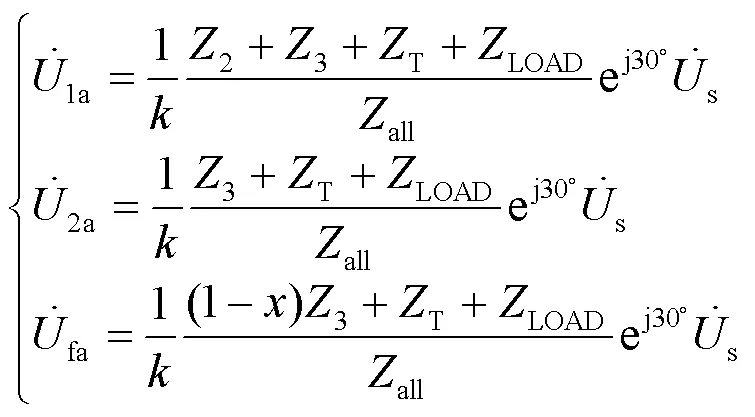
发生单相接地故障后的序网络如图4所示。线路的零序阻抗分别为,为线路并联电导之和,为线路对地电容之和,为故障电流,为故障电阻。当故障发生时,由于故障下游故障电流较小,推导时近似开路等效。
故障点的正负零序电压如式(9)所示。
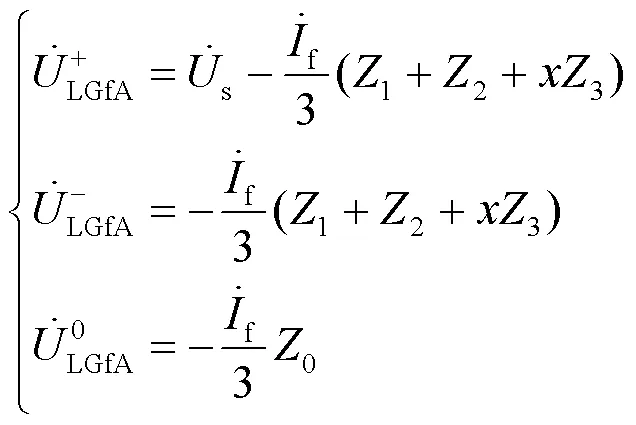
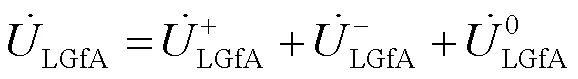
由对称分量法,可得故障点f处的高压侧B相电压如式(11)所示。
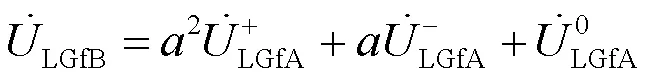
则把式(10)和式(11)代入式(5),可得故障点f处的变压器低压侧a相电压,如式(12)所示。

由式(12)和式(8),可获得变压器T低压侧监测点的电压变化,如式(13)所示。
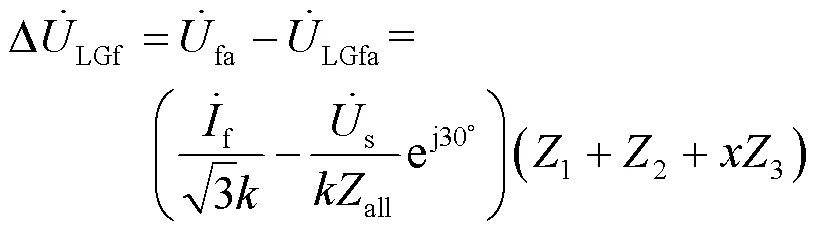
同理节点2和节点1处低压侧的电压变化分别如式(14)和式(15)所示。
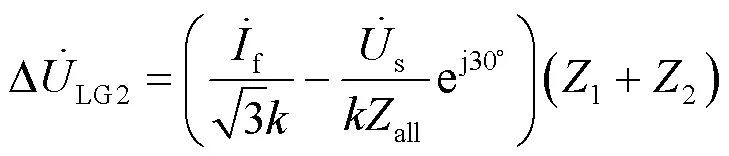
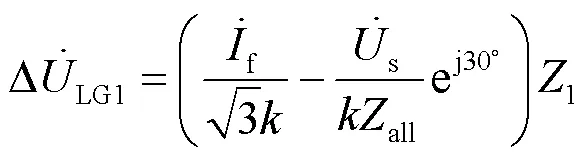
由式(13)—式(15),可知:
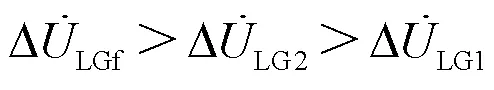
不同故障类型故障后的电压变化特征推导见附录。
2 故障区段定位方法
如图5所示的配电网拓扑结构,其中在配电网变压器T1—T4的低压侧安装有4个电压监测装置。
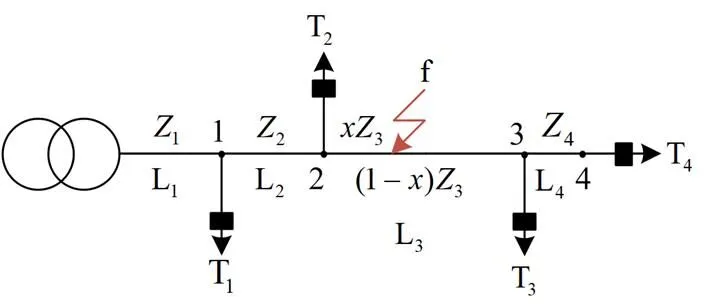
图5 有4个台区的配电网拓扑图
2.1 改进的最近邻聚类法
最近邻聚类法能够将多个样本自动地分为不同的监测点集合,由于其简单易行在聚类算法中广泛应用。
以此类推,直到将个数据都进行分类。
以此类推,直到将个数据都进行分类。
2.2 故障区段定位流程
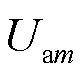
(2) 用改进的最近邻聚类法对个电压数据进行聚类,获得最大的集合,则该集合为故障处下游的所有监测点集合,其余的集合为故障处上游的监测点集合。
(3) 根据拓扑结构,分别找出故障处上游和下游监测点集合的公共节点。若监测点T都在该节点电流流向的下游则该点即为公共节点。
(4) 取故障处上游和下游监测点集合中的最大值,分别对应两个监测点,则距离这两个监测点最近的公共节点,即可判定出故障区段。流程如图6所示。
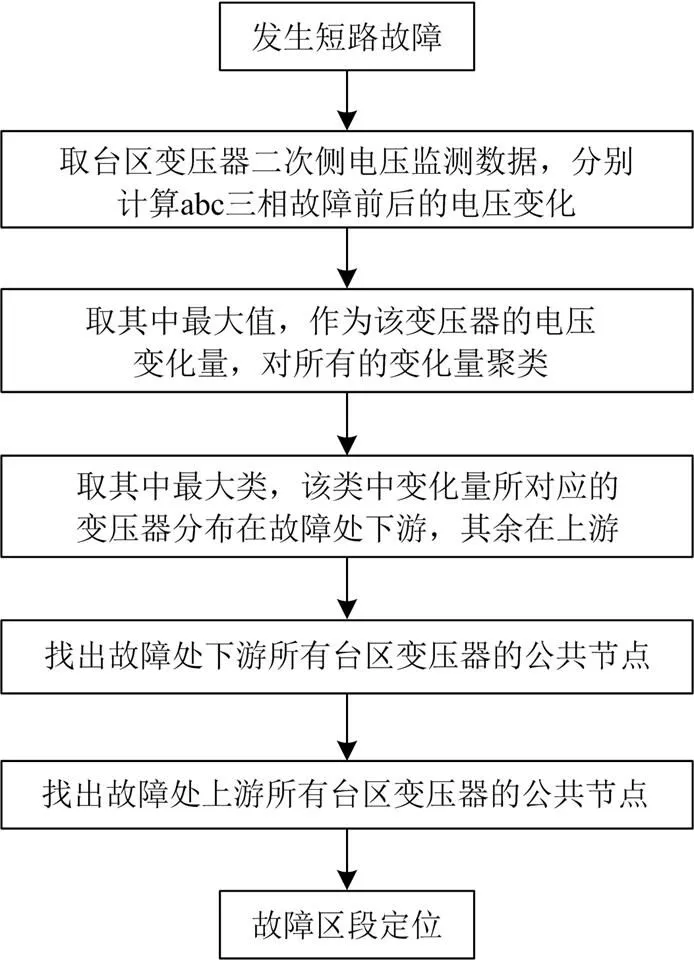
图6 故障区段定位流程图
3 仿真验证
本节利用PSCAD/EMTDC对中压配电网进行建模,如图7所示,该线路由总长为67.5 km的架空线路组成,其中含有5个10 kV/0.4 kV的变压器,假设中性点接地方式为小电阻接地,每个变压器低压侧均安装有电压监测装置。

图7 测试电网拓扑图
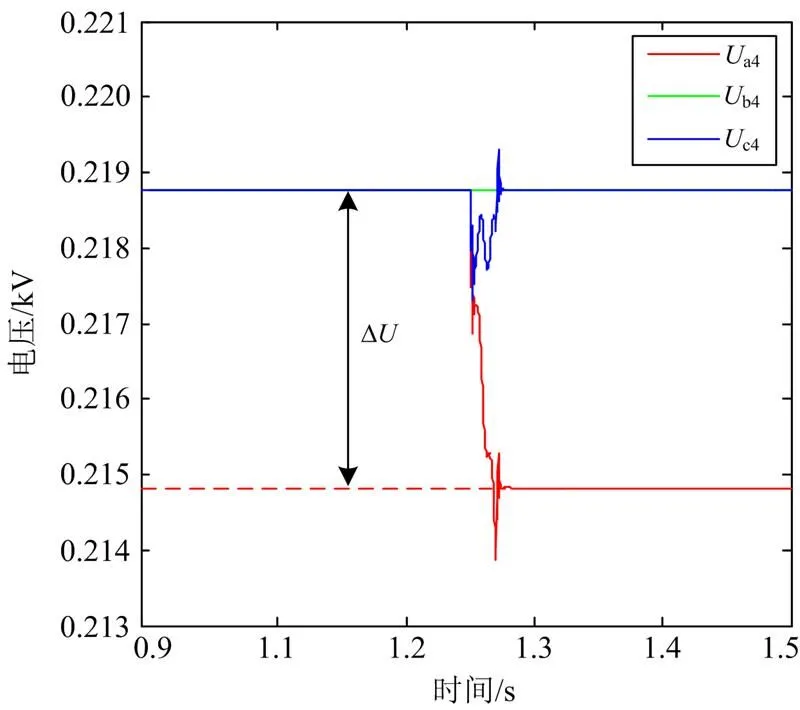
图8 电压变化图
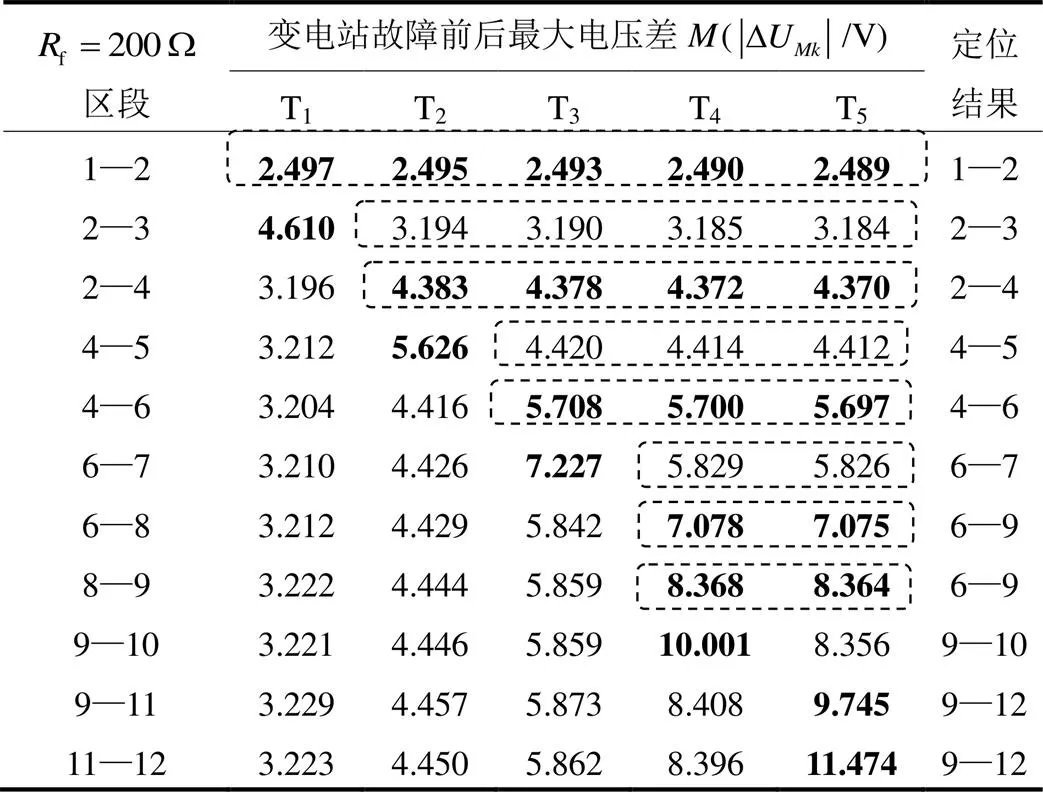
表1 A相接地故障仿真结果
Table 1 Simulation results of A-phase grounding fault
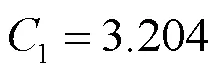

3.1 不同故障类型对定位的影响
表2 AB两相接地故障电阻为200W时仿真结果
Table 2 Simulation result when AB phase-to-ground fault resistance is 200W
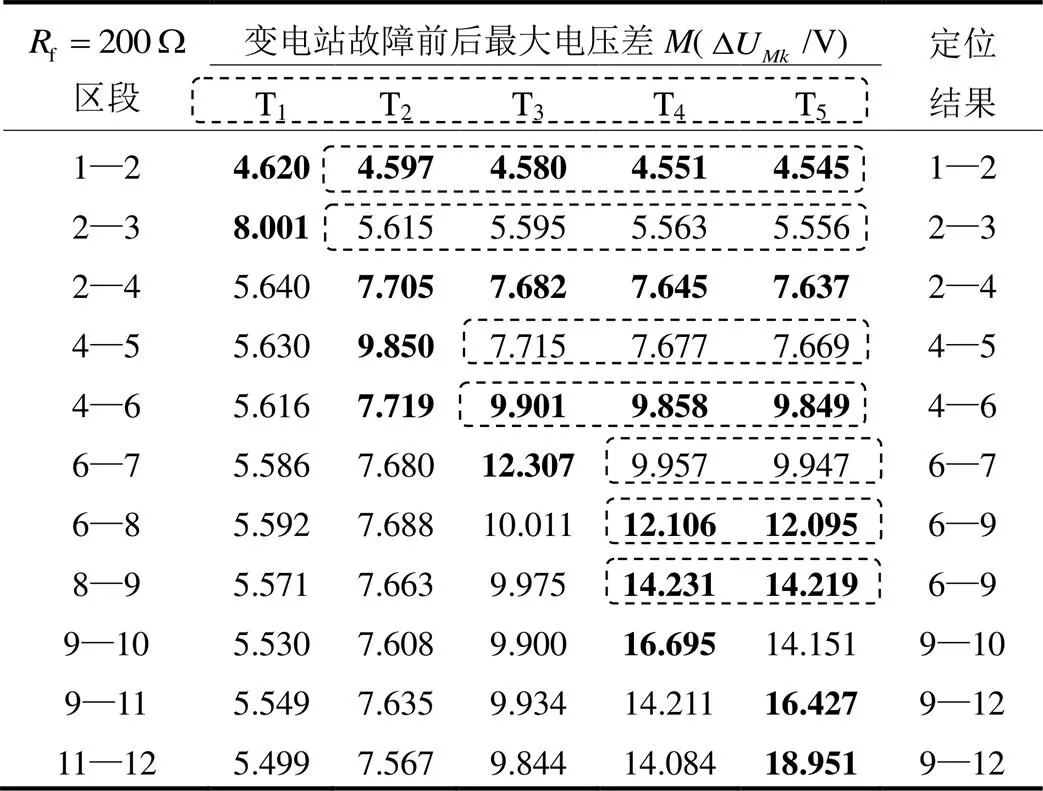
表3 AB两相故障电阻为200W时仿真结果
Table 3 Simulation result when AB phase-to-phase fault resistance is 200W
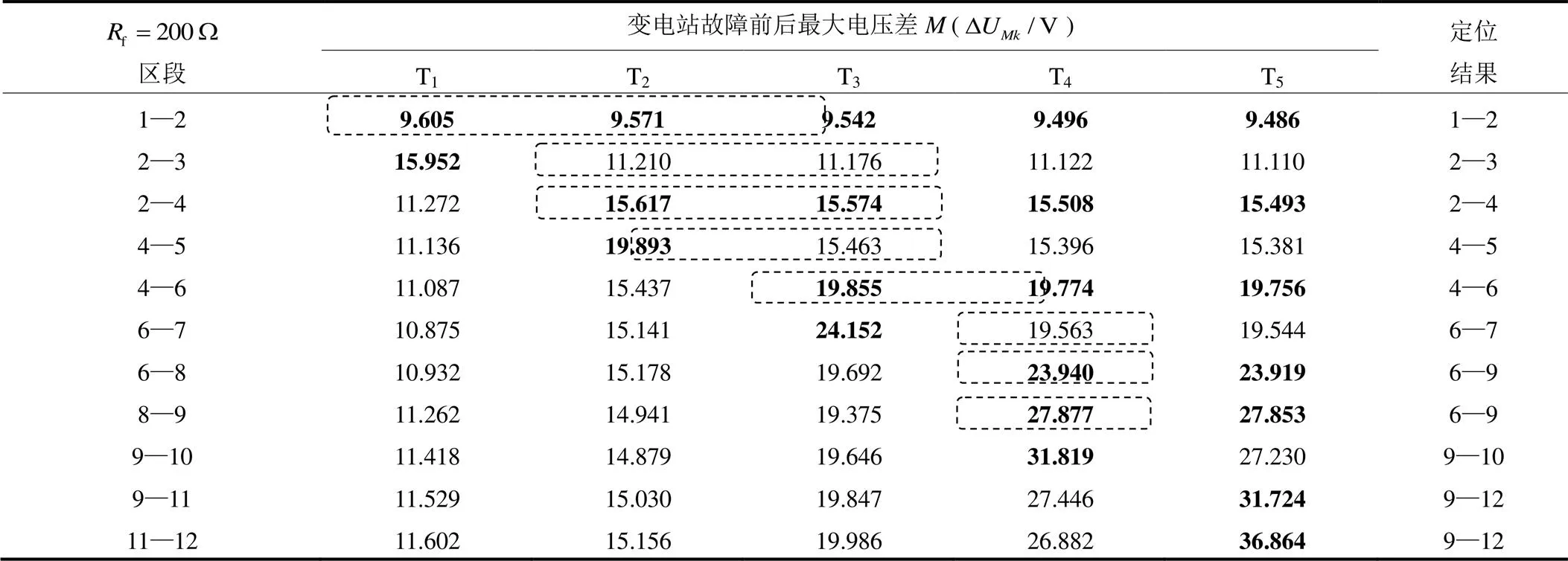
表4 ABC三相故障电阻为200W时仿真结果
Table 4 Simulation result when ABC three phase fault resistance is 200W
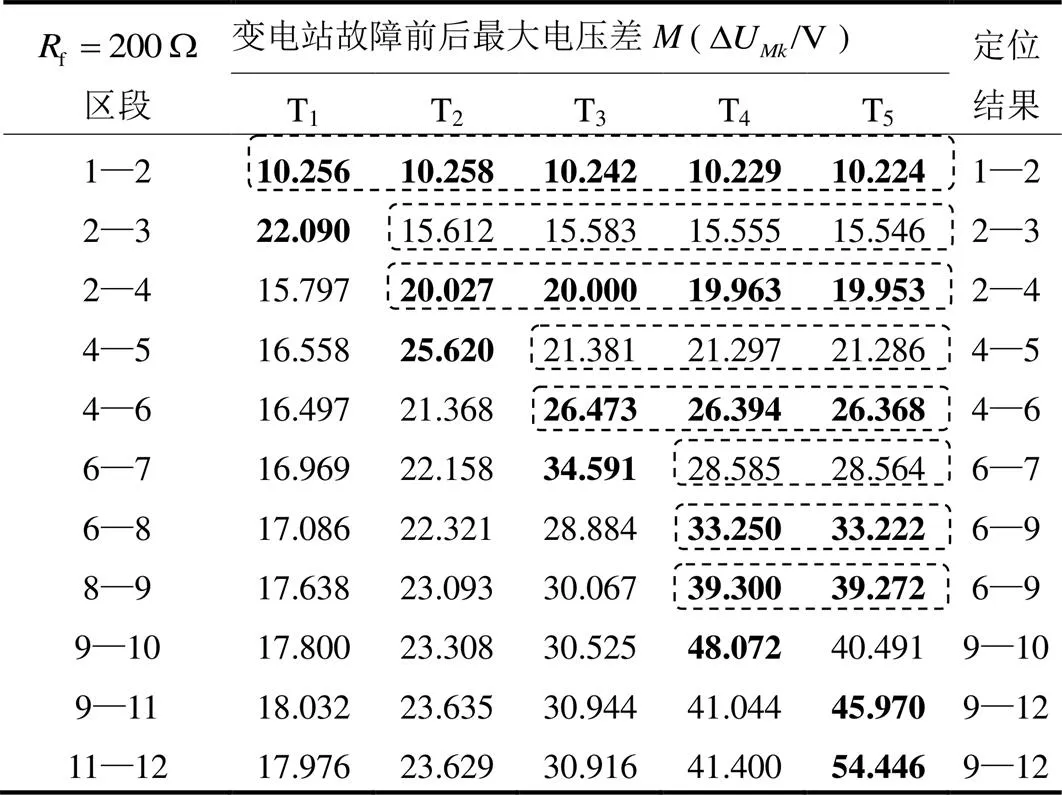
表2—表4表明,该定位方法能够较好地适应不同的故障类型。
3.2 不同故障电阻对定位的影响
通过仿真验证可得,在不同的故障电阻条件下,本文的故障定位方法均能够判别出正确的故障区段。
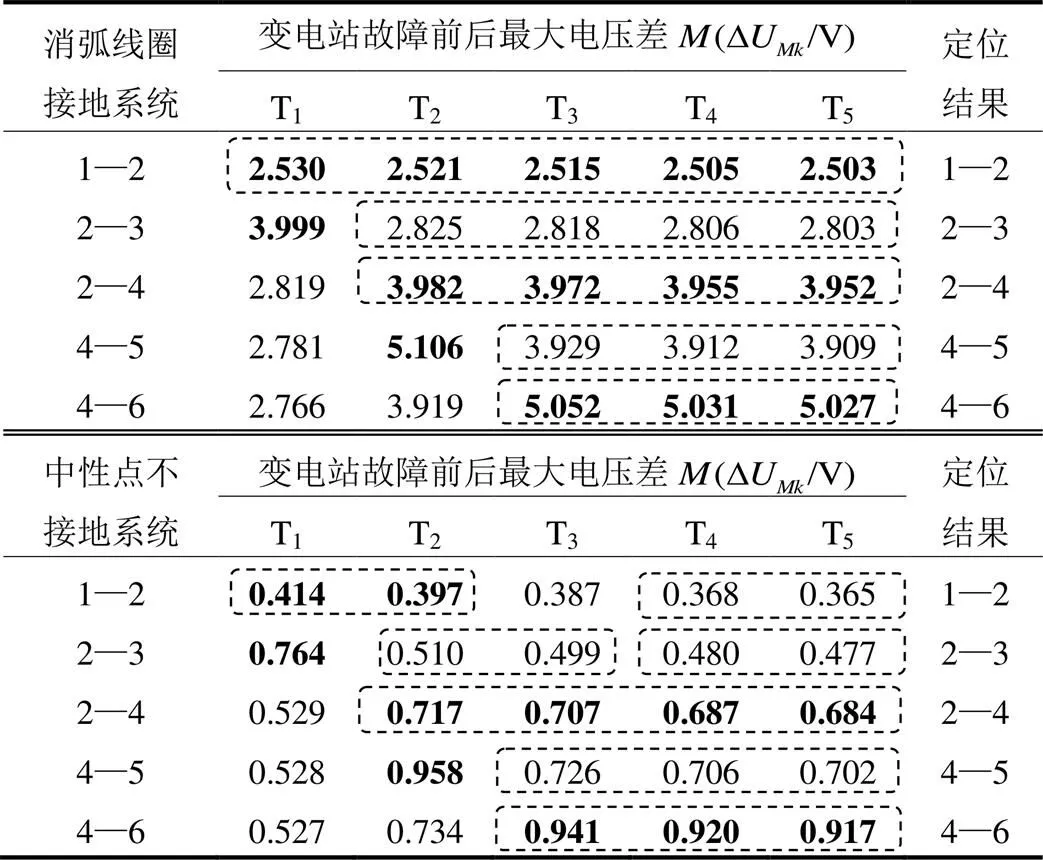
3.3 中性点不同接地方式对定位的影响
由表6可以看到,相对经消弧线圈接地系统而言,中性点不接地系统电压变化非常小,导致在区段1—2和区段2—3上聚类效果有偏差,但是依据定位判据还是可以准确识别出故障区段。
表5 AB两相接地故障不同故障电阻仿真结果
Table 5 Different fault resistance simulation result of AB phase-to-ground fault
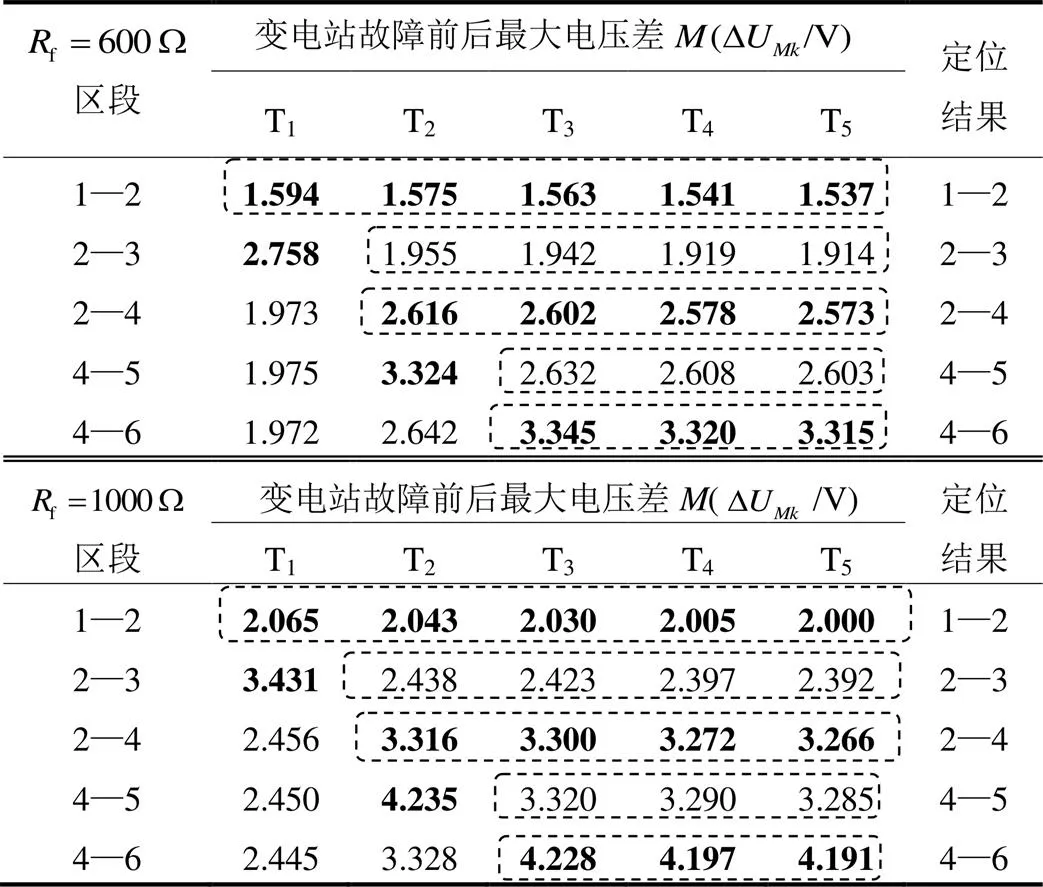
表6 中性点经消弧线圈接地系统
Table 6 Neutral point via arc suppression coil grounding system
3.4 电压监测装置延时对定位的影响
表7 装置延时仿真结果
Table 7 Simulation results of device delay
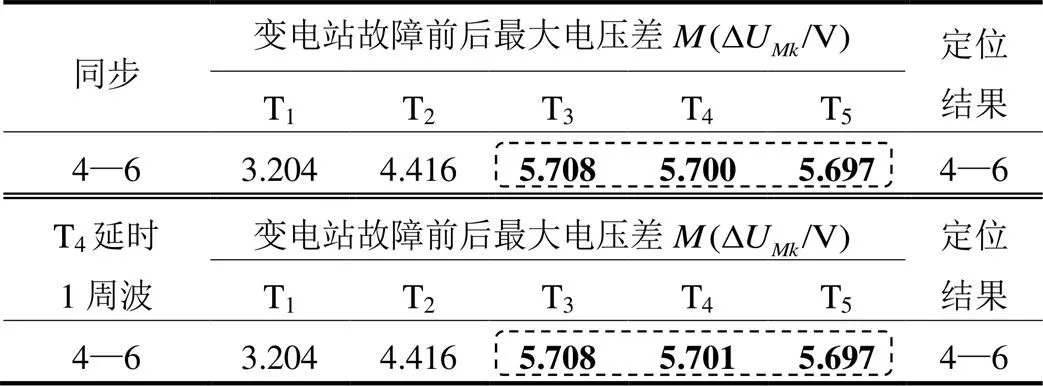
由表7可知,对于T4装置延时,数据虽然有变动但是变化不大,依然可以实现准确的区段定位,说明该方法不受台区变压器监测装置时间延迟的影响。
4 结论
本文提出了一种基于低压变压器二次侧电压变化的配电网故障区段定位方法。该方法利用台区变压器二次侧故障前后的电压变化幅值构成判据,通过改进的邻近聚类法快速分类故障上下游区段,大量仿真表明:
(1) 配电网低压变压器二次侧的电压变化满足故障上游沿着故障路径依次增加,故障下游电压变化相似的特点。
(2) 改进的邻近聚类法能够对监测点的电压变化进行快速分类,识别出故障路径和非故障路径监测点集合。
(3) 利用低压变压器二次侧电压变化的故障区段定位方法能够在不同的中性点接地系统,不同的故障类型、故障电阻等工况下准确判定故障区段,同时对监测数据的同步性要求不高,具有较好的适应性。
相较于利用中压侧电气量的定位方法,本文所提出的区段定位不需要电流信息,同时仅需要配电变压器低压侧的电压幅值,监测信息容易获取,监测装置安装和维护也更加便捷。同时,区段定位流程中不需要复杂的迭代过程,通过引入改进的邻近聚类法能够准确地辨识出故障路径和非故障路径监测点集合,为配网自动化水平不高地区的故障检测提供了技术思路。
发生BC两相短路故障的序网络如附图1所示。
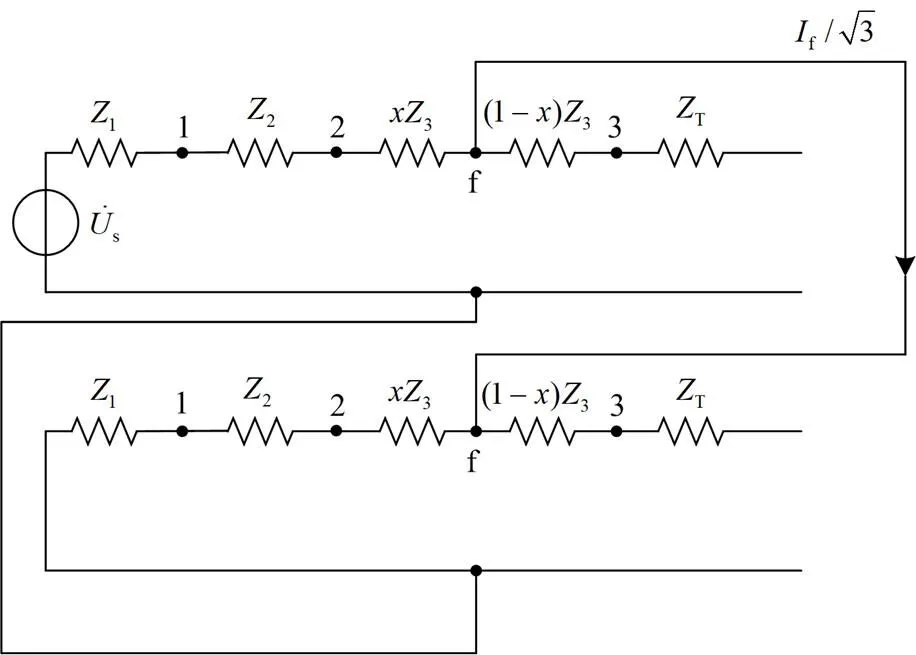
附图1 两相短路复合序网
Attached Fig. 1 Two-phase short circuit compound sequence network
故障点的正负零序电压则可以表示为
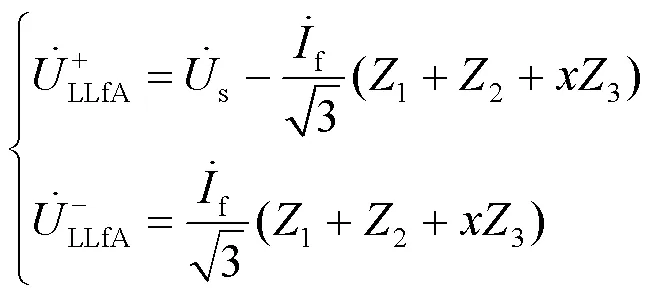
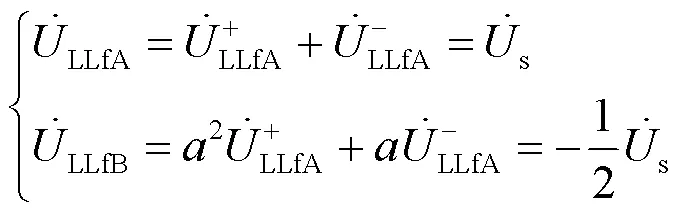
将式(18)代入式(5)可得故障点的低压侧相电压为
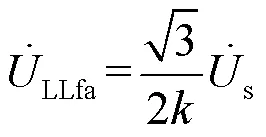
由式(19)和式(8),可获得变压器T低压侧监测点的电压变化为,如式(20)所示。

同理可得出节点2和节点1处低压侧的电压变化分别如式(21)和式(22)所示。
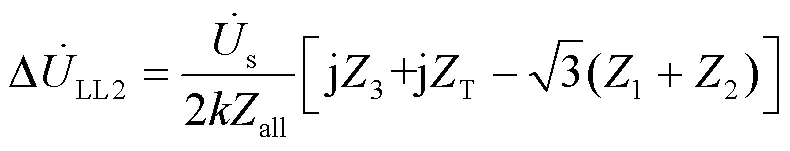

分别用式(20)减去式(21),用式(21)减去式(22)可得:
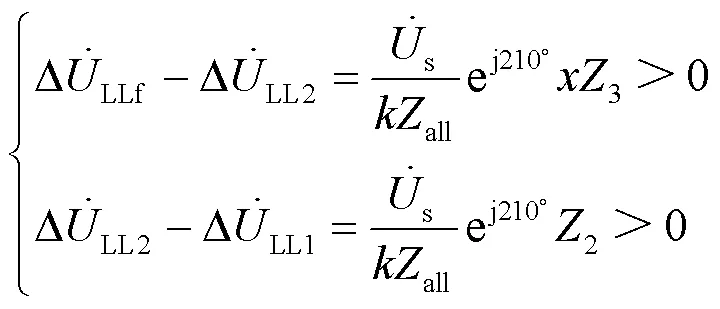
则有:
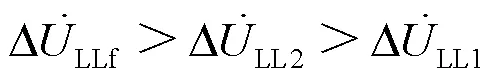
发生BC两相短路接地故障的边界条件是:
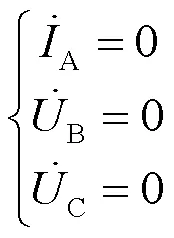
代入式(5)可得故障点的低压侧相电压:
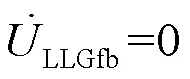
由式(26)和式(8),可获得变压器T低压侧监测点的电压变化如式(27)所示。
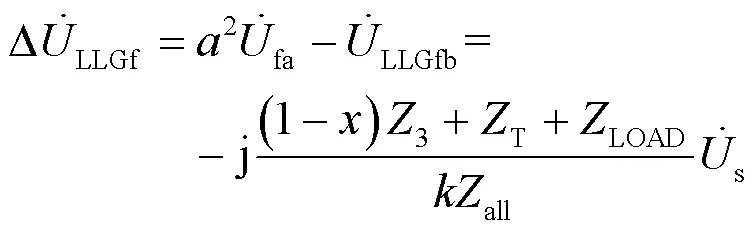
同理可得出节点2和节点1处低压侧的电压变化分别如式(28)和式(29)所示。
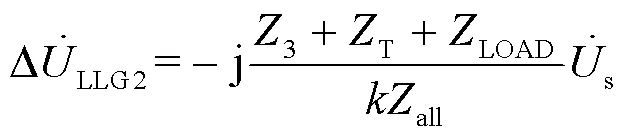
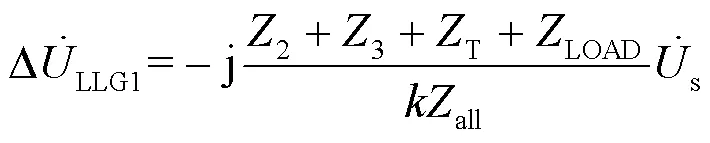
同理有:
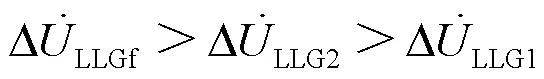
发生ABC三相短路故障的单相等效图如附图2所示。
附图2 单相等效图
Attached Fig. 2 Single phase equivalent diagram
由基尔霍夫电压定律(KVL)和正文式(6)可得故障点的低压侧相电压:
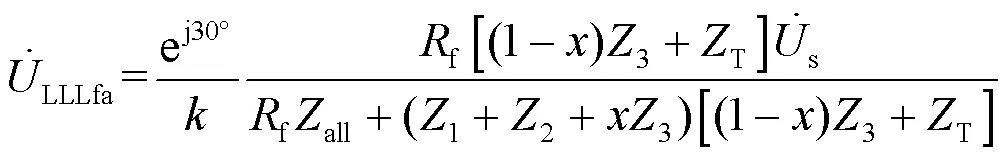
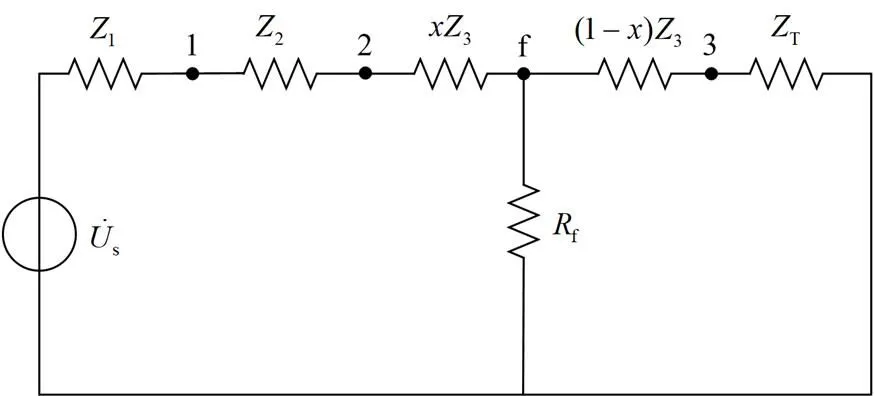
由式(31)和式(8),可获得变压器T低压侧监测点的电压变化如式(32)所示。

同理可得出节点2和节点1处低压侧的电压变化分别如式(33)和式(34)所示。
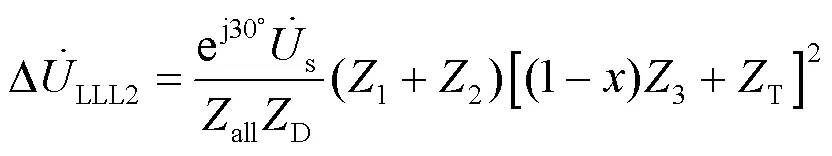
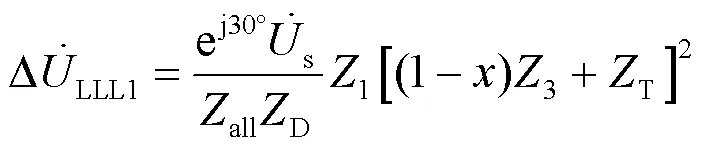
则有:
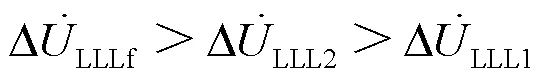
[1] 刘广一, 朱文东, 陈金祥, 等. 智能电网大数据的特点、应用场景与分析平台[J]. 南方电网技术, 2016, 10(5): 102-110.
LIU Guangyi, ZHU Wendong, CHEN Jinxiang, et al. Characteristics, application scenarios and analysis platform of smart grid big data[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2016, 10(5): 102-110.
[2] 唐金锐, 尹项根, 张哲, 等. 配电网故障自动定位技术研究综述[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2013, 33(5): 7-13.
TANG Jinrui, YIN Xianggen, ZHANG Zhe, et al. Survey of fault location technology for distribution networks[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2013, 33(5): 7-13.
[3] KUMAR D S, SAVIER J S, BIJU S S. Micro-synchrophasor based special protection scheme for distribution system automation in a smart city[J]. Protection and Control of Modern Power Systems, 2020, 5(1): 97-110.
[4] 蒋原, 李擎, 冯茜, 等. 基于BP神经网络的直流电网故障定位与保护方法[J]. 高压电器, 2020, 56(8): 23-28.
JIANG Yuan, LI Qing, FENG Qian, et al. Fault location and protection method for DC power grid based on BP neural network[J]. High Voltage Apparatus, 2020, 56(8): 23-28.
[5] 王玲, 邓志, 马明, 等. 基于状态估计残差比较的配电网故障区段定位方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2021, 49(14): 132-139.
WANG Ling, DENG Zhi, MA Ming, et al. A method for locating fault sections in distribution networks based on the comparison of state estimation residual errors[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2021, 49(14): 132-139.
[6] 张林利, 曹丽丽, 李立生, 等. 不接地系统单相断线故障分析及区段定位[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2018, 46(16): 1-7.
ZHANG Linli, CAO Lili, LI Lisheng, et al. Analysis and fault section location of single-phase open fault for ungrounding system[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2018, 46(16): 1-7.
[7] 潘本仁, 宋华茂, 张秋凤, 等. 小电流接地故障无功功率分析及选线新方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2017, 45(14): 51-56.
PAN Benren, SONG Huamao, ZHANG Qiufeng, et al. Reactive power analysis and novel faulty selection method in resonant grounding system[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2017, 45(14): 51-56.
[8] 郑一斌, 王慧芳, 张磊, 等. 基于LightGBM算法的配电网单相接地故障区段定位方法[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2021, 41(12): 54-61.
ZHENG Yibin, WANG Huifang, ZHANG Lei, et al. Single-phase grounding fault section location in distribution network based on LightGBM algorithm[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2021, 41(12): 54-61.
[9] 杨睿, 高红均, 李海波, 等. 基于稀疏表示的配电网故障区段定位研究[J]. 智慧电力, 2021, 49(10): 8-15, 96.
YANG Rui, GAO Hongjun, LI Haibo, et al. Fault section location in distribution network based on sparse representation[J]. Smart Power, 2021, 49(10): 8-15, 96.
[10] 宫璇, 任欣旭, 王秋杰, 等. 具有高容错稳定性的含DG配电网区段定位方法[J]. 高电压技术, 2021, 47(11): 3992-4006.
GONG Xuan, REN Xinxu, WANG Qiujie, et al. Section location method with high fault tolerance stability for distribution network with distributed generation[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2021, 47(11): 3992-4006.
[11] 姚永峰, 王启哲, 王慧萍, 等. 基于邻接矩阵的低压配电网故障区段定位方法[J]. 中国电力, 2021, 54(11): 91-96, 114.
YAO Yongfeng, WANG Qizhe, WANG Huiping, et al. Faulted line segment location method for low-voltage distribution network based on adjacency matrix[J]. Electric Power, 2021, 54(11): 91-96, 114.
[12] 黄佳乐, 杨冠鲁. 配电网故障区间定位的改进矩阵算法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2014, 42(11): 41-45.
HUANG Jiale, YANG Guanlu. Modified matrix algorithm for fault section location of distribution network[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2014, 42(11): 41-45.
[13] 李卫国, 许文文, 乔振宇, 等. 基于暂态零序电流凹凸特征的配电网故障区段定位方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2020, 48(10): 164-173.
LI Weiguo, XU Wenwen, QIAO Zhenyu, et al. Fault section location method for a distribution network based on concave and convex characteristics of transient zero sequence current[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2020, 48(10): 164-173.
[14] 万信书, 方连航, 梁钰, 等. 基于三相电流幅值分析的小电流单相接地故障区段定位方法[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2020, 35(4): 49-57.
WAN Xinshu, FANG Lianhang, LIANG Yu, et al. Method of fault section location for the small current single-phase-to-ground fault based on the amplitude analysis of three-phase current[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2020, 35(4): 49-57.
[15] 马腾飞, 高亮. 含多微网的主动配电网故障区段定位算法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2017, 45(7): 64-68.
MA Tengfei, GAO Liang. Fault location algorithm for active distribution network with multi micro-grids[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2017, 45(7): 64-68.
[16] 丛伟, 荀堂生, 肖静, 等. 包含多微网的配电系统故障检测算法[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2010, 30(7): 50-53.
CONG Wei, XUN Tangsheng, XIAO Jing, et al. Faulty section detection algorithm for distribution system with multi micro-grids[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2010, 30(7): 50-53.
[17] 郭壮志, 陈涛, 徐其兴, 等. 配电网故障区段定位的互补松弛约束新模型与算法[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2020, 40(5): 129-137.
GUO Zhuangzhi, CHEN Tao, XU Qixing, et al. Novel fault section location model for distribution network with complementary relaxation constraints and its algorithm[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2020, 40(5): 129-137.
[18] LI Y, YE H, CHEN Z. Binary particle swarm optimization algorithm with gene translocation for distribution network fault location[C] // 2012 Spring Congress on Engineering and Technology, May 27-30, 2012, Xi'an, China: 1-4.
[19] 张林利, 徐丙垠, 薛永端, 等. 基于线电压和零模电流的小电流接地故障暂态定位方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2012, 32(13): 110-115, 198.
ZHANG Linli, XU Bingyin, XUE Yongduan, et al. Transient fault locating method based on line voltage and zero-mode current in non-solidly earthed network[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2012, 32(13): 110-115, 198.
[20] ZHAO J W, MA N B, HOU H, et al. A fault section location method for small current grounding system based on HHT[C] // 2018 China International Conference on Electricity Distribution (CICED), September 17-19, 2018, Tianjin, China: 1769-1773.
[21] 贾清泉, 郑旭然, 刘楚, 等. 基于故障方向测度的配电网故障区段定位方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2017, 37(20): 5933-5941.
JIA Qingquan, ZHENG Xuran, LIU Chu, et al. A method of fault section location in distribution networks based on fault direction measures[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2017, 37(20): 5933-5941.
[22] 刘斯琪, 喻锟, 曾祥君, 等. 基于零序电流幅值连调的小电流接地系统故障区段定位方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2021, 49(9): 48-56.
LIU Siqi, YU Kun, ZENG Xiangjun, et al. Fault location method of a non-effective earthed system based on zero sequence current amplitude continuous regulation[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2021, 49(9): 48-56.
[23] LI Zhenxing, WAN Jialing, WANG Pengfei, et al. A novel fault section locating method based on distance matching degree in distribution network[J]. Protection and Control of Modern Power Systems, 2021, 6(2): 253-263.
[24] 李卫国, 王旭光, 卢广旗, 等. 基于DOST 能量相似度的有源配电网故障区间定位方法[J]. 电测与仪表, 2019, 56(6): 50-55.
LI Weiguo, WANG Xuguang, LU Guangqi, et al. A fault section location method for active distribution network based on discrete orthogonal S-transform and energy similarity[J]. Electrical Measurement & Instrumentation, 2019, 56(6): 50-55.
[25] 马士聪, 徐丙垠, 高厚磊, 等. 检测暂态零模电流相关性的小电流接地故障定位方法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2008, 32(7): 48-52.
MA Shicong, XU Bingyin, GAO Houlei, et al. An earth fault locating method in feeder automation system by examining correlation of transient zero mode currents[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2008, 32(7): 48-52.
[26] JIA K, REN Z, BI T, et al. Ground fault location usingthe low-voltage-side recorded data in distribution systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2015, 51(6): 4994-5001.
[27] TOPOLANEK D, LEHTONEN M, ADZMAN M R, et al. Earth fault location based on evaluation of voltage sag at secondary side of medium voltage/low voltage transformers[J]. IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution, 2015, 9(14): 1-9.
Fault section location of a distribution network based on voltage variation of the secondary side of a transformer in the station area
ZHANG Yunhao, ZHANG Shu, ZHANG Wenhai, XIAO Xianyong
(College of Electrical Engineering, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610065, China)
With the construction of high-quality distribution network stations, more and more monitoring devices are extended to the low-voltage side of the distribution network, providing new ideas for fault location on the distribution network. This paper presents a method for locating fault sections of a distribution network based on voltage changes on the secondary side of transformers in the station area. It analyzes the voltage change law on the transformer side of the distribution network after a fault occurs, and uses the difference between the three-phase voltage amplitude changes at the monitoring point under the fault path and the non-fault path to identify the faulty section. It uses an improved nearest neighbor clustering method to identify the set of monitoring points at different locations from the fault in the voltage monitoring set. This can quickly partition the monitoring information. This method does not require 10 kV line monitoring data, but only needs 10/0.4 kV transformer low-voltage side voltage amplitude change information in the distribution station area. The monitoring collection device is easy to install and maintain. A large number of simulations show that the method can adapt to different neutral grounding methods, fault types and transition resistances, and has strong applicability.
distribution network; voltage monitoring device; fault section location; secondary side of substation; nearest neighbor clustering algorithm
10.19783/j.cnki.pspc.211438
2021-10-26;
2021-12-23
张耘浩(1995—),男,硕士研究生,研究方向为电力系统继电保护;E-mail: 1010575530@qq.com
张 姝(1988—),女,通信作者,博士,硕士生导师,研究方向为电力系统继电保护。E-mail: ZS20061621@163.com
国家重点研发计划项目资助(2020YFF0305800);四川大学专职博士后研发基金项目资助(2019SCU12003)
This work is supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2020YFF0305800).
(编辑 魏小丽)
