Effects of Concentration of(3-Aminopropyl)Triethoxysilane on Waterborne Polyurethane
2022-08-08GUOHengyi郭恒义LIUYanPENGXiaoxiao彭晓晓YUYunge于运歌XINBinjie辛斌杰
GUO Hengyi(郭恒义), LIU Yan(刘 岩)*, PENG Xiaoxiao(彭晓晓), YU Yunge(于运歌), XIN Binjie(辛斌杰)
1 School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Shanghai University of Engineering Science, Shanghai 201620, China 2 School of Textiles and Fashion, Shanghai University of Engineering Science, Shanghai 201620, China
Abstract: As a coupling agent,(3-aminopropyl)triethoxysilane(APTES)was used to synthesize a series of silanized waterborne polyurethanes(Si-WPUs)through the acetone process. The Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy(FTIR)together with the X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy(XPS)was utilized to measure both elements and structures of these samples. The scanning electron microscope(SEM)results explained that APTES would be agglomerate on the surface of WPU films when the mass fraction of the agent concentration was more than 8%. Besides, the contact angle of water(CAW)can be improved from 56.5° to 90.0° by adjusting APTES concentration in Si-WPU. The decomposition temperature of films was also improved with the increase of APTES, and a significant increase could be seen in the glass temperature from 51.00 ℃ to 85.74 ℃.
Key words: waterborne polyurethanes;(3-aminopropyl)trirthoxysilane(APTES); agglomeration; modified; water resistant
Introduction
Exhibiting excellent flexibility and remarkable abrasion resistance, such as high strength and elasticity, superior water and solvent resistance, the polyurethane was synthesized by Otto Bayer[1].It has been successfully applied in plenty of areas with the development of technology, such as leather, coating, bio-medicine, and military[2-5].Nowadays, environment questions have become an important issue when people want to use or choose some materials.In this background, as an environmentally-friendly material, the waterborne polyurethane(WPU)has gradually replaced solvent polyurethane which contains volatile organic compounds(VOCs)[6].
As a kind of superior material, WPU has many striking properties.The WPU coating has good adhesion on some substrate’s surface, and the coating is excellent in abrasion resistance and impact resistance.Besides, through the cross-linking reaction, other materials can be easily modified by WPU, such as acrylic and alkyd resins.Unfortunately, the extensive use of WPU is still limited by its certain unexpected disadvantage.(1)In the process of synthesising WPU, ionic groups or water-soluble chain ends are introduced, which is harmful water resistance of WPU films.(2)Unlike solvent polyurethane, WPU is not able to form cross-linking network easily by—NCO.Hence, mechanical properties and solvent resistance will become worse[7].(3)Due to higher specific heat capacity of water, WPU has a slower drying speed.In recent years, a great many researchers have devoted themselves to modifying the properties of WPU through many different methods[6].
Geetal.[8]used polytertramethylene glycol(PTMG), isophorone diisocyanate(IPDI), dimethylol propionic acid(DMPA), and terminated polydimethylsiloxane(DHPDMS)as the main materials, to synthesis a novel ultraviolet(UV)crosslinking waterborne siloxane-polyurethane, which was coped with by UV.The contact angle of the UV-WPU films was increased significantly in the surface of the glass piece and polyester cotton.The result might prove that UV and siloxane can improve the water resistance of WPU films.Yang and Sun[9]prepared a kind of supramolecular WPU, which is based on quadruple hydrogen bonds(4H-WPU), using 5-(2-hydroxyethyl)-6-methyl-2-aminouracil(HMA)to synthesis the UPy-functionalized monomer.The result showed that the stress of 4H-WPU films was improved from 0.54 MPa to 5.47 MPa with the HMA increasing.
The WPU synthesis, in nature, is the step-growth addition polymerization reaction which is different from other normal polymerizations that usually create some by-products(e.g., H2O in the esterification).However, the stepwise addition polymerization is a kind of exothermic reaction; hence there will be no measurements that can be taken for the sake of the improvement in case of product gelation[10].Apart from this, pure polyurethane is hydrophobic.Due to diisocyanate or polyisocyanate highly sensitising to water, it is hard to directly synthesize polyurethane in water, so using hydrophilic chain extenders helping PU to disperse in water is necessary[11].During the past decades, many researchers used 2, 2-dimethylol propionic acid(DMPA)to synthesize the WPU[12-16].The 2, 2-dimethylolbutyric acid(DMBA), requiring lower reactive temperature and shorter reaction time, was adopted in this research as well[17].Moreover, the acetone process made the experiment much easier in such aspects as figuring out the problem of high viscosity in the process[10].
Possessing multiple excellent properties such as splendid thermal stability and the superior oxidation resistance, the silicone resin stands out among a lot of materials[7, 18].Comparing with others, silicon resin has superior strengths.(1)Due to the special structure of the silane coupling agent, grafting it to other polymers can improve the affinity between organic and inorganic compounds, and can enhance some physical and chemical properties of the material, such as strength, water resistance, and thermal stability.(2)It can also improve the anti-ageing properties of the material and the disintegration of the bonding on the interface during use, in other words, the agent is able to combine two surfaces that are not easily bonded together more stably.(3)The material can also be used as a cross-linking agent to achieve non-cross-linking system polymers at normal temperature and pressure cross-linking; for some composite materials, the selection of appropriate silane coupling agent can enhance the bonding strength of the coating and adhesive while improving the resistance to humidity and certain harsh environments.
For these reasons, silicone, especially(3-aminopropyl)triethoxysilane(APTES), is used to modify WPU[1, 5-6, 19-20].In this work, APTES, as a coupling agent, reacts with—NCO and forms hard segment in WPU.
In previously-performed researches, other materials were used to strengthen hydrophobicity and APTES is only used as the hydrophilic chain extender.Hossainetal.[21]found contact angle of water(CAW)of coating which modified by APTES only was just 40°.Wangetal.[22]reported that polyvinylidene fluoride(PVDF)film could be transformed from high hydrophobicity into super hydrophilicity when the material was treated by tannic acid(TA)and APTES.However, it was found that adjusting the APTES concentration to an appropriate degree contributes to the improvement in water resistance of WPU, not requiring other materials.What was more, we researched the states of silicon in WPU films and how APTES influenced the thermal properties for WPU.
1 Experiments
1.1 Materials
The polycaprolactone glycol(PCL-1000)was purchased from Jining Huakai Resin Co., Ltd., China.DMBA and IPDI were acquired from Shanghai Titan Scientific Co., Ltd., China.Dibutyltin dilaurate(DBTDL)and triethylamine(TEA)were obtained from Shanghai Lingfeng Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., China.APTES and acetone were provided by Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., China.Molecular sieves type 4A was offered by Hengye Molecular Sieve Co., Ltd., China.1, 4-butanediol(BDO)was supplied by Shanghai Aladdin Bio-Chem Technology Co., Ltd., China.
1.2 Preparation of Si-WPU dispersions
Initially, the PCL-1000 and DMBA were dried for 8.0 h in a vacuum environment(80 ℃).Subsequently, they were mixed in a 250 ml three-necked flask which is equipped with a mechanical stirrer(200-350 r/min), a drying tube and a nitrogen inlet.Afterwards, the flask was placed in an oil bath with 80 ℃, then the IPDI and DBTDL were added into the system and reacted for 2.5 h, and the BDO was fed into the reactor for 1.0 h.when the situation of oil bath cooled down to 40 ℃, the TEA was added into the flask.After obtaining the alkaline liquid(about 0.5 h), the APTES was utilized and reacted about 1 h.Ultimately, in the event of the system cooled down to 25 ℃, distilled water was added at a low stirring rate(200-350 r/min), drop by drop.After that, the liquid was stirred for 1.0 h at high speed(1 800-2 000 r/min).Aimed at decreasing the viscosity, the acetone(absorbing water with molecular sieves type 4A)was adopted during the whole process.Once completed all reactions, the dispersions were placed in a vacuum environment(40 ℃, 1.0 h)in order to remove acetone.Figure 1 displays the reaction process and Table 1 shows all reagents used in different reactions.

Table 1 Weights of materials used for synthesizing Si-WPU
1.3 Preparation of Si-WPU films
The Si-WPU films were prepared by casting the dispersions onto teflon surfaces, then followed by placing them at room temperature for 5 d and then at 50 ℃ for 2 h.
1.4 Instrumentations
Designed and developed with the function of qualitatively analysing the elements and structures of Si-WPU, a Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy(FTIR, PerkinElmer Spectrum Two, USA)was adopted.Dropping 1 or 2 drops Si-WPU dispersions on the sample stage, controlling the pressure at 100, the instrument can generate results automatically.

Fig.1 Flow chart of Si-WPU synthesis
An X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy(XPS, ThermoFisher Escalab 250Xi, China)was employed, to reach the goals of quantitatively illustrating the content of silicon and the element existing states in Si-WPU films.The samples are cut into a long strip of 1.5 cm×3.0 cm and put them into the sample chamber.When the vacuum degree is better than 5.0×10-5Pa, the V1 valve should be opened and the samples are transferred into the analysis chamber.After the vacuum degree better than 2.0×10-5Pa, the tests can be started.
A scanning electron microscope(SEM, SU8010, Hitachi, Japan)was used to observe the film surfaces and the APTES dispersions.After the signals are collected by the collector, the amplifier will amplify these signals in proportion and order, and then messages will be sent to the grid of the kinescope.Meanwhile, the electron beam intensity of the kinescope can be used to modulate synchronously.In this way, a screen corresponding to the characteristics of the sample, that is, the SEM image of the samples, can be obtained on the fluorescent screen.
The CAW tester(Jinshengxin PCA-315, China)was used with the objective of measuring the hydrophilicity of the films.During the test, the samples are cut into suitable strips and attached to the slide with double-sided tape, and the slide is placed on the platform, adjusting the brightness, the height of the instrument and the vertical needle.The computer software is used to control the needle to drop the water onto the surface of the sample, and then the CAW is measured after taking the picture.
Be capable of explaining the weights of samples decreasing with temperature increasing, a thermogravimetric(TGA, PerkinElmer TGA4000, USA)was utilized.Films with weights within the range of 6-8 mg were heated from 30-700 ℃(10 ℃/min), in the N2atmosphere(20 mL/min).
A differential scanning calorimeter(DSC, PerkinElmer DSC4000, USA)was used to measure thermal properties, especially glass transition temperature.Each sample(6-8 mg)was placed in a testing pan, with the temperature within the range of-60-400 ℃(20 ℃/min)and in the N2atmosphere(20 mL/min).
2 Results and Discussion
2.1 Elements and structures analysis
Six different dispersions were characterized by using FTIR spectroscopy, as shown in Fig.2.The absorption peak, indicating both the CH2and CH, can be viewed at 2 954 cm-1.Associated with the—CO—bond of the—CO—O—, a peak can be observed at 1 691 cm-1.These peaks show—NCO reacts with—OH.As well as, all samples have similar absorption intensity in these positions, because every reaction used the same amount of PCL-1000 and DMBA.It can be found from the figure that the C—N bond appears at 1 234 cm-1.There are no any stretching peaks at 2 263 cm-1, which means the—NCO is completely reacted.Based on these observation results, a conclusion can be drawn that the WPU was synthesized successfully.Figure 2(b)shows the presence of APTES can be confirmed by the presence of a new bond appearing at 1 066 cm-1, which relates to the—Si—O—Si—of the alkoxy group stretching vibrations.Hence, it is verified that the amino in APTES reacts with—NCO of WPU successfully.
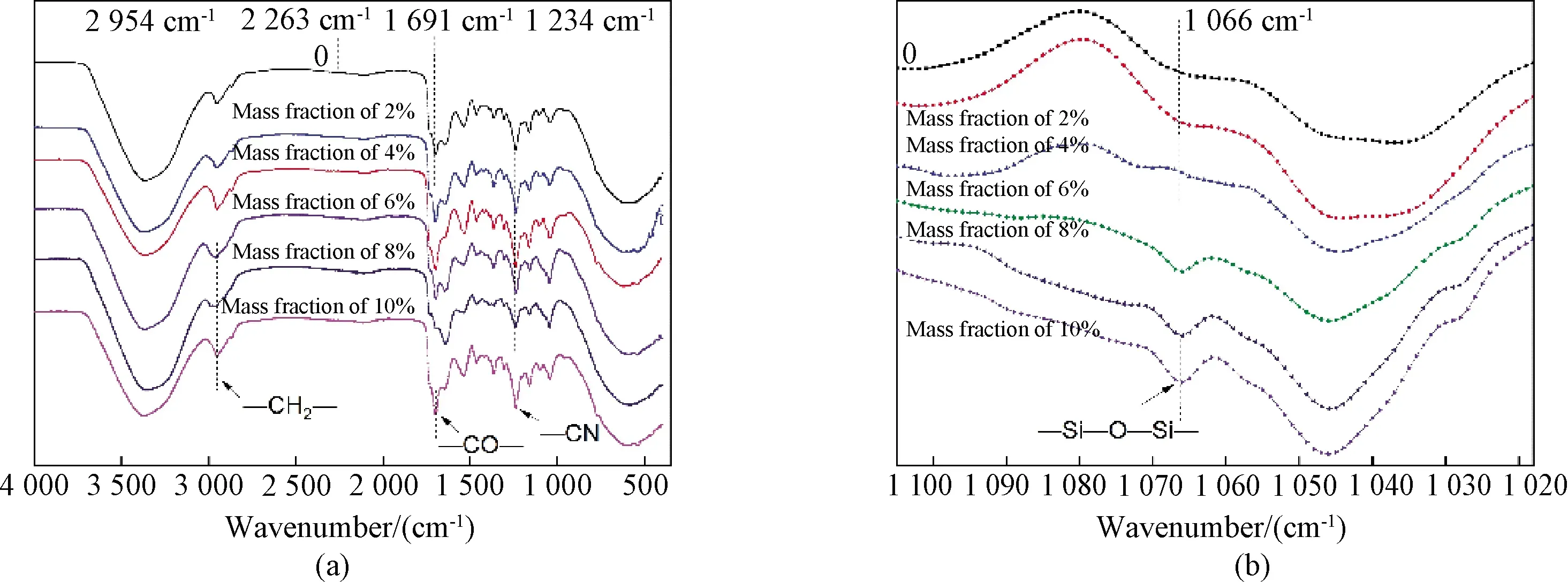
Fig.2 Spectrograms of(a)Si-WPU dispersions and(b)partially-enlarged images
It can be found from Table 2 that, the mass fraction of APTES increases from 0 to 6%, and the Si concentration measured in the experiment is close to that in theory, which confirms all APTES reacts in this reaction.However, specific differences still existed in other samples(the mass fraction of APTES is more than 6%).Similar phenomena can be found in the FTIR.When the mass fraction of APTES is over 6%, the peak in 1 066 cm-1has merely less change, even after adding more APTES.The reason is possible that the amino in APTES reacting with—NCO need more time.Furthermore, analysing the two Si-WPU films adding mass fraction of APTES with 8% and 10%, respectively(shown in Fig.3), there are three different chemically bound states for Si: Si—O—Si(101.2 eV), Si—O—H(101.8 eV), and Si—O—C(102.5 eV).Two of these bonds, Si—O—H and Si—O—Si, can be obtained by hydrolysis and condensation reactions, respectively.However, the Si—O—C, belonging to the APTES molecule, can be found, and it means a certain part of methoxysilyl without reacting.It may be related that some APTES agglomerate in Si—WPU so that it is not able to react with other molecules.
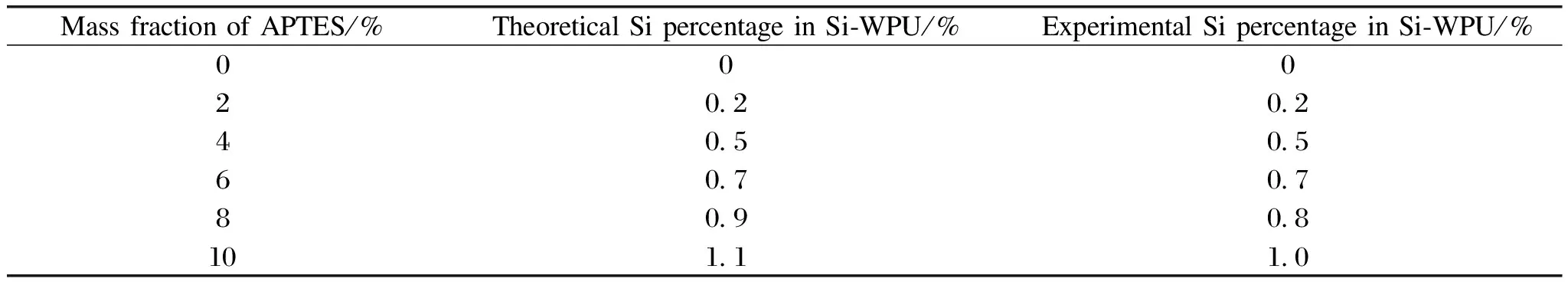
Table 2 XPS results of the Si-WPU films
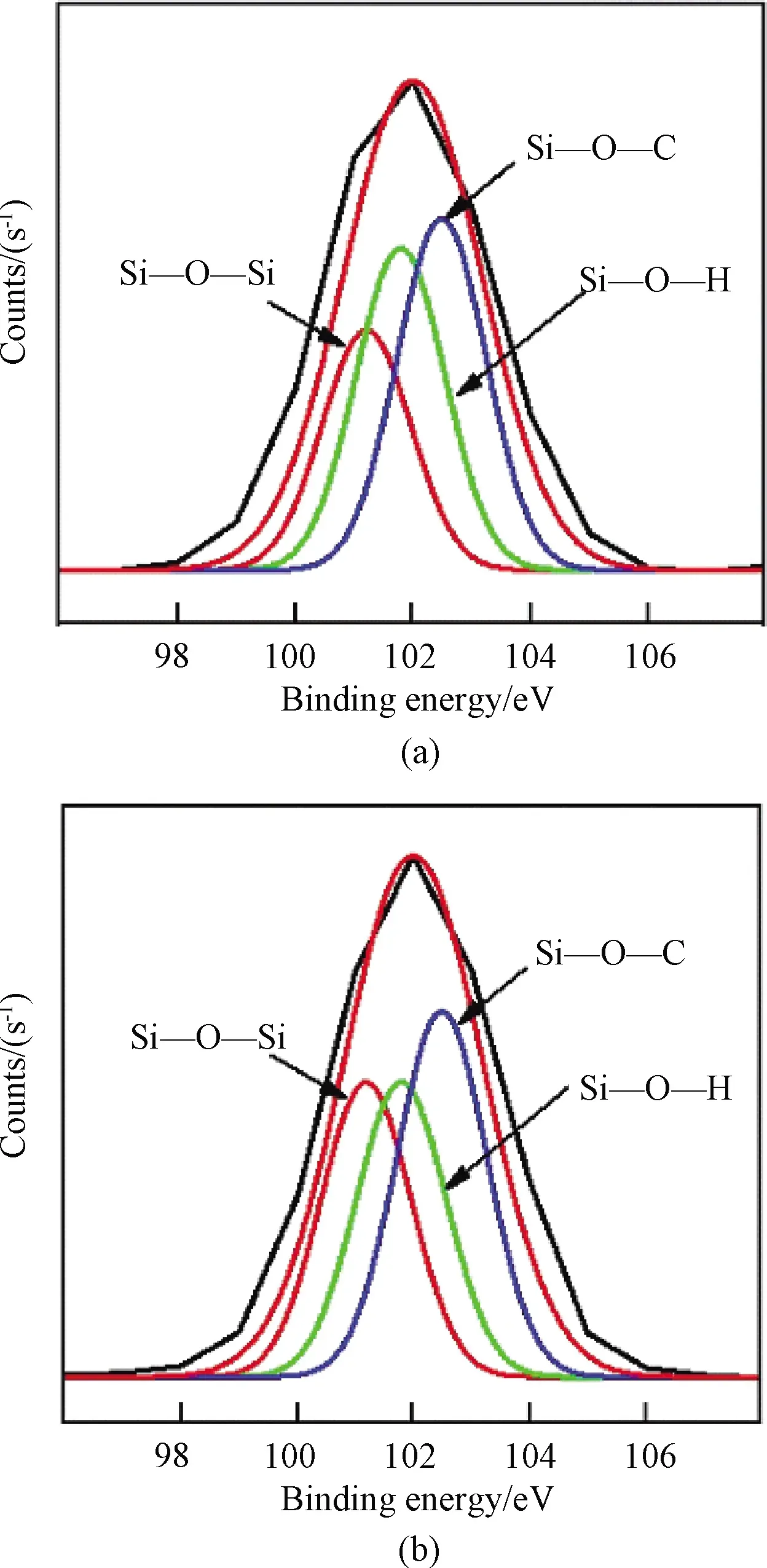
Fig.3 XPS spectrum of films with(a)8% APTES and(b)10% APTES
2.2 Surface analysis
As depicted in Fig.4, the images of polyurethane with different APTES concentrations are displayed.In the samples with the mass fraction of APTES increases from 0 to 6%, no particles can be distinctly observed; on the contrary, in Fig.4(b), large particles can be detected.It is possible that the APTES can react with WPU comfortably when the mass fraction of APTES is below 6%, but it will be agglomerate or insufficient after the mass fraction is over 8%, which is consistent with the XPS results.What is more, surface tension will increase after adding more APTES.The force is beneficial to groups containing silicon migrating to the surface of the latex film, so the agglomeration is clearer in the membrane when the mass fraction of APTES is up to 10%.
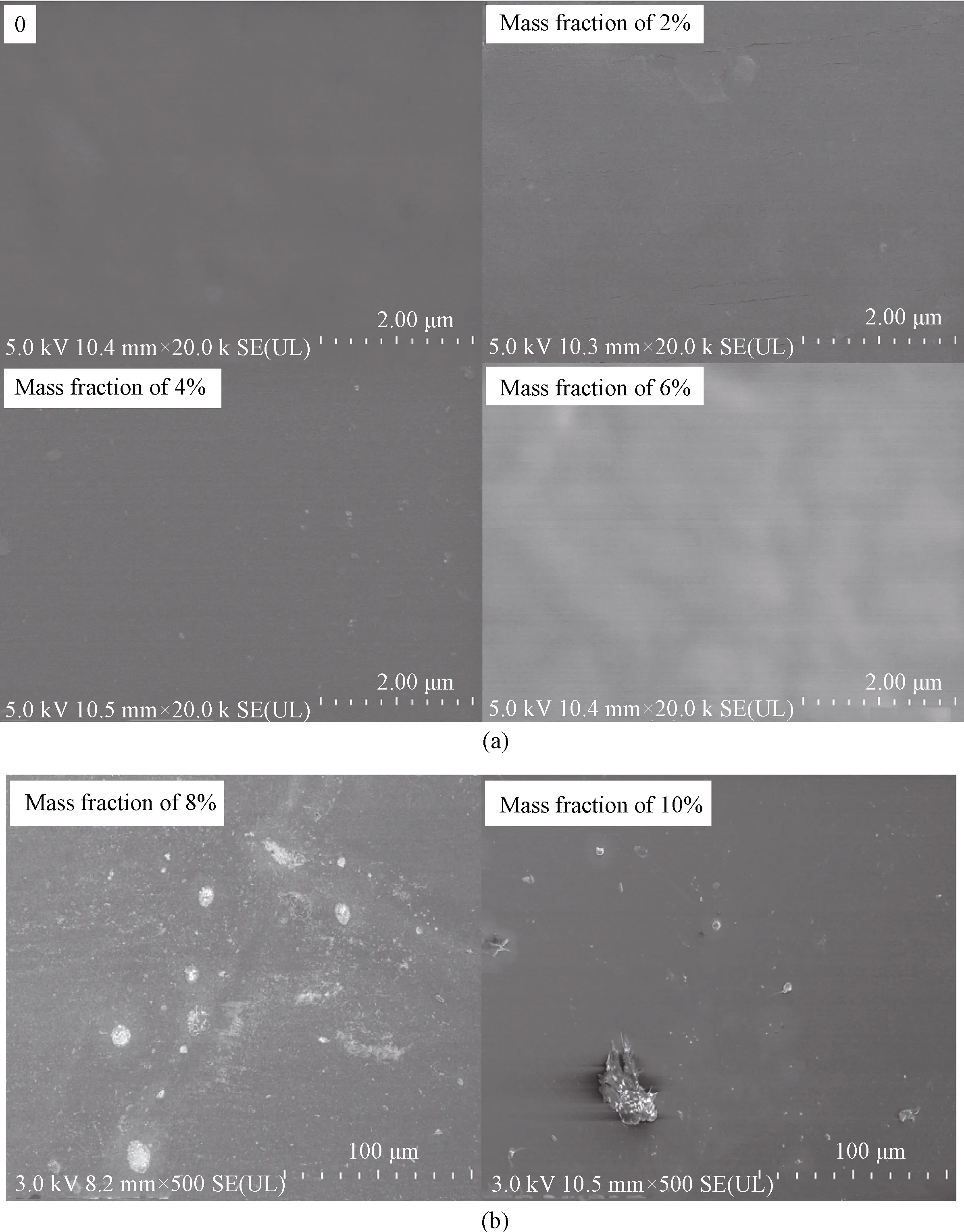
Fig.4 SEM images of Si-WPU films with(a)mass fraction of APTES from 0 to 6% and(b)mass fraction of APTES with 8% and 10%
However, the water resistance of these films is still in good condition without decline.As the mass fraction of APTES increases from 0 to 10%, the contact angle of the film increases from 56.5° to 90.0°(shown in Fig.5).It seems that this result is due to certain coatings formed by the APTES on the surface of Si-WPU films[21].Affected by the same reason, the colours of films change from white to brown and from light to dark(shown in Fig.6).What is more, comparing these films, a significant colour transition can be seen when the mass fraction of APTES is improved from 6% to 8%.It may be the unreacted APTES influenced the films’ colour.Based on these considerations, a conclusion can be drawn that a hydrophobic film can be produced through the application of APTES with appropriate concentration.
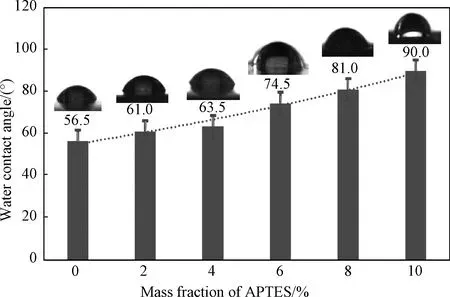
Fig.5 CAW of Si-WPU films with different APTES concentrations
2.3 Thermodynamic analysis
From Fig.7, the thermal weight loss curves of modified WPU films can be divided into three stages to a considerable degree.At the first stage(30.00-301.77 ℃), due to the small unreacted particles and other small molecules, like H2O, the decomposition temperature was almost unchanged in the period.Then, the decomposition rate of the samples is greatly accelerated at 301.77-336.37 ℃, but they are basically in the same range.The phenomenon may be because the stage is mainly the decomposition of these WPU soft segments and each film contains soft segments composed of similar content PCL-1000.The final stage(over 336.37 ℃), with the increase of APTES, the films decomposition rate starts to decrease gradually.The films with the mass fraction of APTES are 8% and 10% respectively still do not be decomposed entirely, even the temperature up to 700 ℃.The reason is possible that the crosslinked network is formed by these modified samples.It may result in those bubbles(spots in Fig.6)were found in the two sample films(even measures were taken, it was still hard to remove these bubbles).Besides, the Si—O bond in Si-WPU possesses higher energy than the C—O band[1].Another result also can be observed that the decomposition process of the film with the mass fraction of 2% APTES is like the unmodified sample.It may be that fewer APTES cannot form enough Si—O bond to improve the thermal stability of Si-WPU.

Fig.6 Colours of Si-WPU films with different APTES concentrations

Fig.7 TGA thermograms of Si-WPU films
At the end of this paper, DSC studies were carried out to determine the thermodynamic properties of Si-WPU.In Fig.8, when the mass fraction of APTES is below 6% in Si-WPU films, there are melting peak in DSC curves, and the breadth is narrowing gradually with APTES adding.After the mass fraction of agent is more than 6%, there are no melting peaks in any curves.It may be that the degree of crystallization in films decreases because the addition of APTES could form more branching or side groups in the linear polyurethane system.Meanwhile, when the crosslinking density increases to a certain degree, soft segments in WPU will lose crystallinity, and the polyurethane system will change from a harder crystalline state to an amorphous state with better elasticity.

Fig.8 DSC curves of Si-WPU films
In Table 3, the glass transition temperature(Tg)of films is improved with the concentration of APTES increasing.However, when the mass fraction of agent is more than 6% in WPU,Tgwill decrease.The possible reason is that the films crosslinked network structure is strengthened with adding APTES, then theTgof films is influenced.Meanwhile, the amount of hydrogen bond in WPU system is improved because of adding BDO.Hence the distance of molecules becomes smaller, intermolecular forces also increasing.These factors are helpful for higher glass transition temperature.It should be mentioned that small amount of APTES may not react with WPU after the agent exceeding 6%(mass fraction), and these rest agents are harmful to highTg.
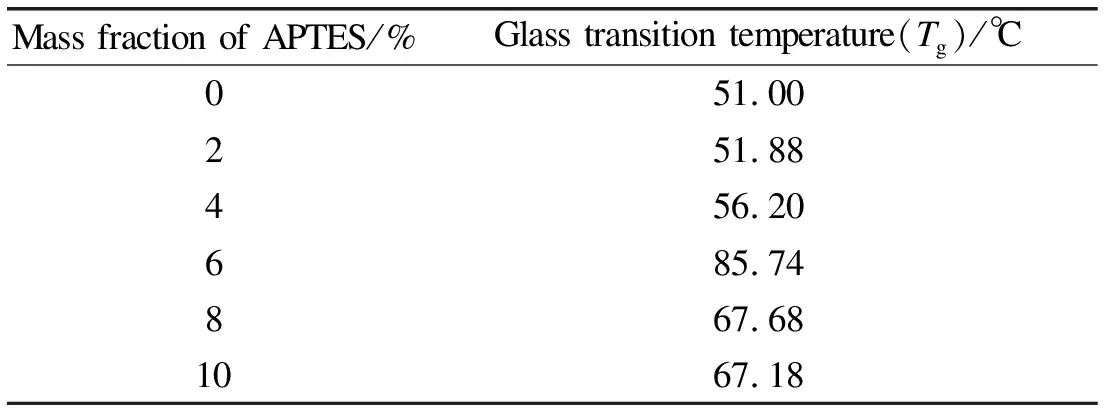
Table 3 Glass transition temperatures of Si-WPU films with different APTES concentrations
3 Conclusions
In this study, WPU was prepared and modified with adding APTES.Through the FTIR,—NCO failed to be found.However, new bond peaks were observed.Based on this, it was verified that the—NH2of APTES could react with—NCO at 40 ℃.Meanwhile, the results obtained from the FTIR, XPS, SEM, CAW, TGA, and DSC illustrate these conclusions.In the experimental environment, the APTES with low concentration(the mass fraction is lower than 2%)has non-significant effects on modified WPU, but adding more APTES(the mass fraction is more than 8%)may resist for the synthesising process because of some agent agglomerating in the surface of WPU films.Since the crosslinked network and certain coatings can be formed by the APTES, Si-WPU exhibits superior thermodynamic stability and outstanding water resistance.
杂志排行
Journal of Donghua University(English Edition)的其它文章
- Design of Creative Incentive Contract of Cultural and Creative Industry Chain from Dual Perspective
- Design and Synthesis of Acceptor-Donor-Acceptor Type Non-Fullerene Acceptors Using Oxindole-Based Bridge for Polymer Solar Cells Applications
- PbI2/Pb5S2I6 van der Waals Heterojunction Photodetector
- Health Monitoring of Induction Motor Using Electrical Signature Analysis
- Acquisition, Pointing and Tracking System for Shipborne Space Laser Communication without Prior Information
- Students’ Feedback on Integrating Engineering Practice Cases into Lecture Task in Course of Built Environment
