Efficacy of short duration versus conventional electroacupuncture in the treatment of obesity: a randomized crossover study
2022-07-28LakkanaRerksuppapholSanguansakRerksuppaphol
Lakkana Rerksuppaphol,Sanguansak Rerksuppaphol
Lakkana Rerksuppaphol,Department of Preventive Medicine,Faculty of Medicine,Srinakharinwirot University,Nakorn Nayok 26120,Thailand
Sanguansak Rerksuppaphol,Department of Pediatrics,Faculty of Medicine,Srinakharinwirot University,Nakorn Nayok 26120,Thailand
Abstract OBJECTIVE:To compare the efficacy of short duration electroacupuncture (EA) with conventional EA to reduce weight and other parameters in obese Thai women.METHODS:A randomized crossover study was conducted in 76 simple obese women.Participants were randomized to undergo either eight weeks of 30-minute EA (EA30) followed by an eight-week washout period,then eight weeks of five-minute EA (EA5),or EA5 followed by a washout period,then EA30.Electroacupuncture was performed at 14 acupoints for two sessions per week.Participants were randomized to undergo either eight weeks of EA30 followed by an eight-week washout period,then eight weeks of EA5,or EA5 followed by a washout period,then EA30.Electroacupuncture was performed using a stainless silver needle at 14 acupoints for two sessions per week.The needle was connected to an electric stimulator that delivered a constant current,40 Hz and 3 mA,for 30 or five minutes according to the assigned treatment period.The primary outcome was the difference in weight reduction between the short-duration and the conventional EA while differences in other anthropometric parameters and biochemical parameters were considered as secondary outcomes.RESULTS:After each treatment period,all anthropometric characteristics of both groups decreased from the baseline regardless of the treatment sequence,including body weight (1.4-1.8 kg;P <0.01),body mass index (0.56-0.70 kg/m2;P < 0.01),waist and hip circumference,skinfold thickness and body fat percentage as well as the improvement in fasting blood glucose and lipid profiles.There were no significant differences of the treatment effects on anthropometric parameters and biomedical chemistries between conventional and short-duration EA.No adverse effects were reported.CONCLUSION:Short duration EA at 14 acupuncture points had comparable efficacy to conventional EA in reduction of weight and other anthropometric parameters as well as to improve biochemistry parameters in obese women.
Keywords:dyslipidemias;electroacupuncture;blood glucose;obesity;weight loss;cross-over studies
1.INTRODUCTION
The prevalence of obesity is rapidly increasing worldwide.World Health Organization estimated that,in 2016,over 650 million or around 13% of world’s adult population were obese and the worldwide prevalence of obesity nearly tripled since 1975.1Obesity is associated with several health problems including type 2 diabetes,mellitus,dyslipidemia,cardiovascular diseases,stroke,sleep apnea and respiratory problems and certain malignancies.2,3The increasing prevalence of obesity is linked to significant rising of healthcare costs.4,5Current conventional treatment strategies for obesity include life style modification,pharmacotherapy and bariatric surgery cannot achieve adequate weight control in all obese patients.Moreover,each of these methods has inherent limitations;e.g.,strict dietary control frequently results in non-compliance for various reasons such as unpalatable taste of food,and pharmacological treatment is losing popularity because of its burdensome cost,long duration of treatment,and potential for serious side effects.6,7Complementary and alternative therapies are becoming more popular management options for weight problems and acupuncture is one of the most widely used.Acupuncture is performed by the insertion of thin metallic needles at specific points that can manipulate by manually or by electrical stimulation.Electroacupuncture (EA) is frequently favored in research because of its readily quantifiable stimulation parameters of frequency,intensity,and duration.8However,the conventional EA is a time-consuming procedure which typically applies electrical stimulation through the needles for at least 15-30 min per session.Manual needle stimulation technique which usually applied for a much shorter duration also showed the effectiveness in obesity treatment.8,9To the best of our knowledge,no studies of short duration of electrical stimulation EA have been published comparing with the efficacy of to conventional EA for treating obesity.Without an evidential study,we cannot conclude that short duration technique is interchangeable with the conventional EA.This study aims to compare the effectiveness of short duration EA with conventional EA to reduce weight and related parameters in obese Thai women.
2.MATERIALS AND METHODS
A randomized,open-label crossover study was conducted in obese women who attended to the acupuncture clinic,Srinakharinwirot University Hospital,Thailand between June 2018 and January 2019.Obese women who had body mass index (BMI)more than 23 kg/m2were invited to participate in the study.The exclusion criteria included women diagnosed with bleeding disorders;heart,liver or renal disorders;neurological diseases;pregnant women;and currently taking anti-obese medication,anti-diabetic medications,or lipid-lowering medications were excluded.The reasons to consider a crossover design for this study are that obesity is a chronic and stable condition and EA has a rapid effect without result in total cure.The advantage of a crossover design is that each participant acts as their own control and thus removed inter-subject variability.
The study was done according to the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki.The study was registered in the Thai Clinical Trials Registry (TCTR20190118002)and the Ethics Committee of Srinakharinwirot University approved the study protocol.Written informed consent was obtained from participants before enrollment to the study.
2.1.Intervention
The participants provided informed consent and were then randomized into 2 groups using computer generated random numbers.Group A → B (hereafter,AB) received the conventional EA,30 min per session(EA30),2 times/week for 8 weeks then 8 weeks of washout period,and then received the short-course EA,5 min per session (EA5),2 times/week for 8 weeks.Group B → A (hereafter,BA) received 8 weeks of short-course EA,8 weeks of washout period and finally 8 weeks of the conventional EA.
Acupuncture in both groups was performed by one acupuncturist (LR) using disposable silver needles(0.25 mm in diameter;Dong Bang DB106 disposable acupuncture needle) at 14 acupuncture points:Guanyuan (CV4),Qihai (CV6),Xiawan (CV10),Zhongwan (CV12),and bilateral Zusanli (ST36),Fenglong (ST40),Sanyinjiao (SP6),Tianshu (ST25)and Shuidao (ST28).To reduce the effect of individualized acupoint selection,the present study used a single standardized set of the main acupoints for all participants.Our previous studies showed that EA at the main acupoints could achieve weight reduction for all types of obesity.11,12An electric stimulator,Hwato SDZ-II model (Suzhou Medical Appliance Factory,Suzhou,China) was connected to the needles and delivered a constant current,40 Hz and 3 mA,for 30 or 5 min according to the assigned treatment period.After each session,the needles were removed.Participants in both groups were asked to maintain their usual pattern of physical activity and dietary intake throughout the study.
2.2.Data collection and monitoring
After enrollment,demographic characteristics and anthropometric data including age,weight,height,waist circumference,hip circumference,mid-upper arm circumference (MUAC),and skinfold thickness were obtained by a blinded investigator.Weight was measured for each participant wearing light clothes to the nearest 100 g using an electronic scale.Standing height was measured using a height rod.Then,BMI was calculated by divided weight by height squared(kg/m2).Waist and hip circumferences were measured by a non-stretch tape to the nearest millimeter.Waist circumference was measured at the midpoint between the lower costal margin and hip circumference was measured at the maximum circumference over the buttocks while the participant was in the standing position.MUAC was measured midway between the tip of left shoulder and the tip of elbow.Triceps skinfold (TSF) thickness,biceps skin fold (BSF)thickness,subscapular skinfold (SSSF) thickness and supra-iliac skinfold (SISF) thickness were measured on the left side using a Lang skinfold caliper.The Deurenberg equation13was used for calculation of body fat percentage (BF%).BF%=1.20 (BMI) +0.23(Age)- 10.8 (Sex)- 5.4 (where age=age in years and Sex=0 in female and=1 in male).Approximately 5 mL venous blood sampling was collected after 12 h of overnight fasting and was measured for total cholesterol (TC),triglycerides (TG),high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C),low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C),and fasting blood glucose (FBG) by using standard hospital laboratory techniques.
All anthropometric data and blood biochemistry parameters were measured at the beginning and at the end of each study period (weeks 0,8,16 and 24).Anthropometric characteristics were measured by the same staff throughout the study.
2.3.Outcome measures
The primary outcome was the difference in efficacy for weight reduction between the short-duration and the conventional EA in treatment for obese women.Secondary outcome measurements were differences in direct treatment effects between the two EA protocols on other obesity parameters and biochemical parameters.Assuming a population variance of 0.7 and the allowable mean difference between the two EA protocols on weight reduction of 0.2 kg,a sample size of 69 participants was needed to achieve an 80% power at alpha error of 0.05 for correctly detecting such difference in a balanced,crossover design.Allowing for a dropout rate of 15%,we planned to enrolled 80 participants into the study.
2.4.Statistical analysis
The data was descriptively presented as means,standard deviations,and percentages.Carryover effect considers whether the effect of the first treatment is still present when the subjects enter the second treatment period.The carryover effect was assessed as the mean(95% confidence interval) difference between the evaluation at the end of the washout period and the evaluation at the baseline using a pairedt-test.The period effect was evaluated by comparing the mean difference between treatments’ change by group of order using an unpairedt-test.The treatment effect considers the benefits of EA30 and EA5,which were estimated as the mean change per post-treatment in the total sample.Treatment effects of EA30 and EA5 were compared by using a pairedt-test and presented as mean difference and 95%CI.For variables with carryover effects from the first treatment into the second,an unpairedt-test was used to analyze the treatment effects of only the data from the first treatment period.Statistical analysis was performed using computer software SPSS 23.0 (SPSS.Inc.,Chicago,IL,USA).APvalue of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3.RESULTS
Of the 86 obese women eligible for consideration,80 were accepted to be enrolled in the study (Figure 1).From 80 participants who were randomly assigned to two groups,4 participants (2 participants from each group) withdrew from the study within the second week due feeling pain during acupuncture and one participant did not return to clinic without giving reason.Therefore,data from 76 participants were included into the final analysis.
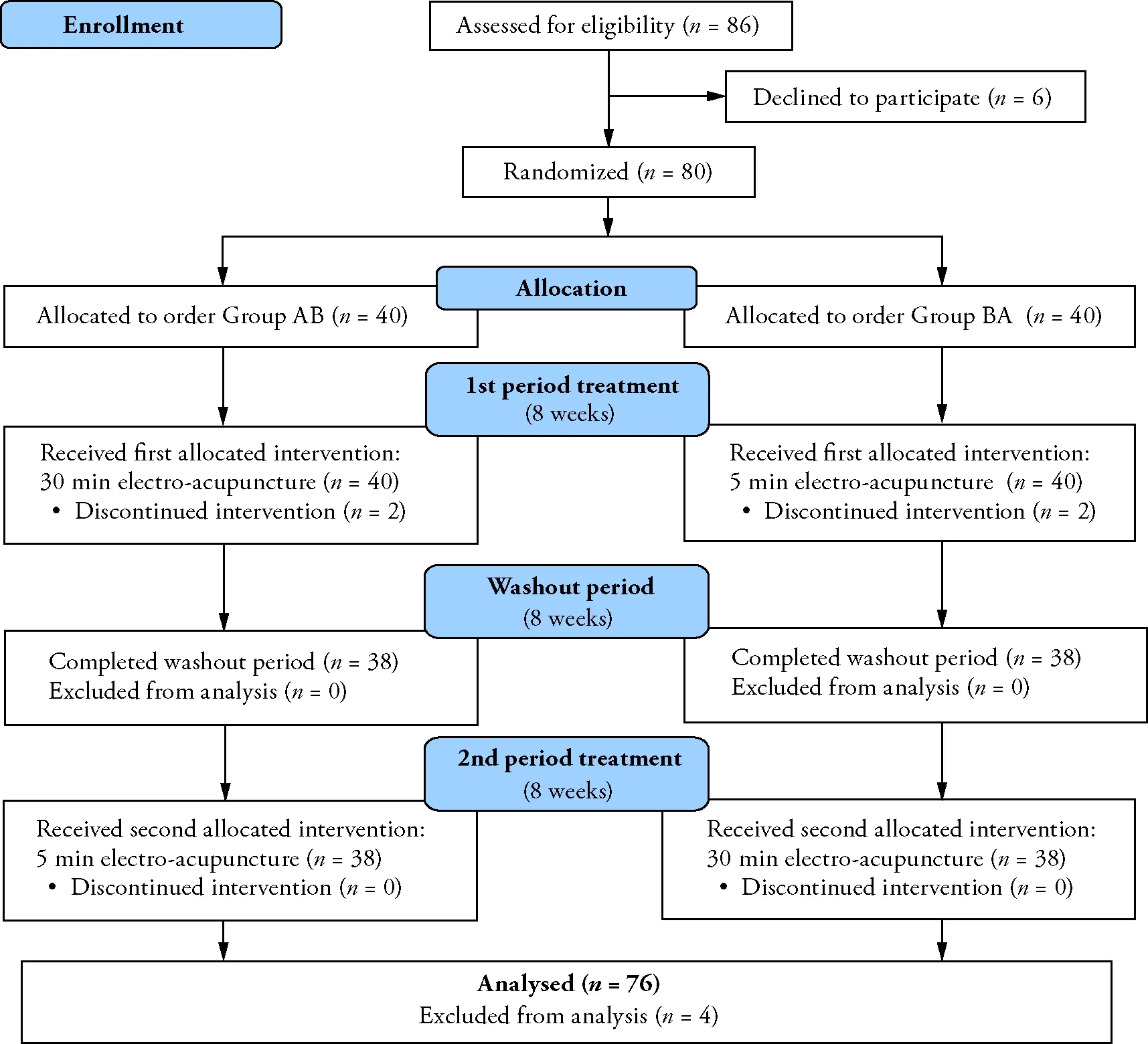
Figure 1 Study flow chart and enrolment
Baseline demographic characteristics are shown in Table 1.The mean age,body weight and BMI of participants at the enrollment were (38 ± 9) years,(73± 11) kg and (29 ± 4) kg/m2,respectively.There was no significant difference in baseline characteristics including age,body weight,BMI,body circumferences,skinfold thickness and biochemistry parameters between the two groups at the enrollment.
Tables 2 and 3 indicates the anthropometric data and biochemistry parameters at the end of each study period as well as the changes during both study sequence.In AB treatment sequence,participants had significant weight reduction of 1.5 kg (P <0.001) from their baseline in the first treatment period (EA30) and after the washout period,they had significant weight reduction of 1.5 kg (P <0.001) from the beginning of the second treatment periods by EA5 treatment protocol.All others anthropometric characteristics including BMI,waist and hip circumferences,skinfold thicknesses and BF% were significant decrease from their baseline in both treatment periods.All biochemistry parameters,except for HDL-C during the EA30 therapy,were significantly improve from their baseline in both periods. In BA treatment sequence,participants had significant weight reduction of 1.4 kg(P <0.001) during the first treatment period (EA5) and of 1.8 kg (P <0.001) during the second treatment period (EA30). All other anthropometric characteristics and biochemistry parameters,except FBS and HDL-C,were also significantly improve from their baseline in both treatment periods of EA5 and EA30.
Table 4 presents the carryover effect,the period effect and the direct treatment effect of each EA treatment.In both BA and BA study sequences,there were no carryover (residual) effects of the first treatment period over the second treatment period in weight,BMI,waist circumference,MUAC,BF%,FBG,TG and HDL-C.The first period treatment of EA30 or EA5 had the residual effects through the second treatment period in the changes of hip circumference,skinfold thicknesses,total cholesterol and LDL-cholesterol.Changing in the sequence of treatment period (AB or BA) had found no significant effects on the therapeutic results of all anthropometric characteristics and biochemical parameters.
Table 1 Baseline characteristics of participants ()

Table 1 Baseline characteristics of participants ()
Notes:LDL:low density lipoprotein;HDL:high density lipoprotein.
Table 2 Anthropometric data and biochemistry parameters at each evaluation of participants allocated to group order AB ()
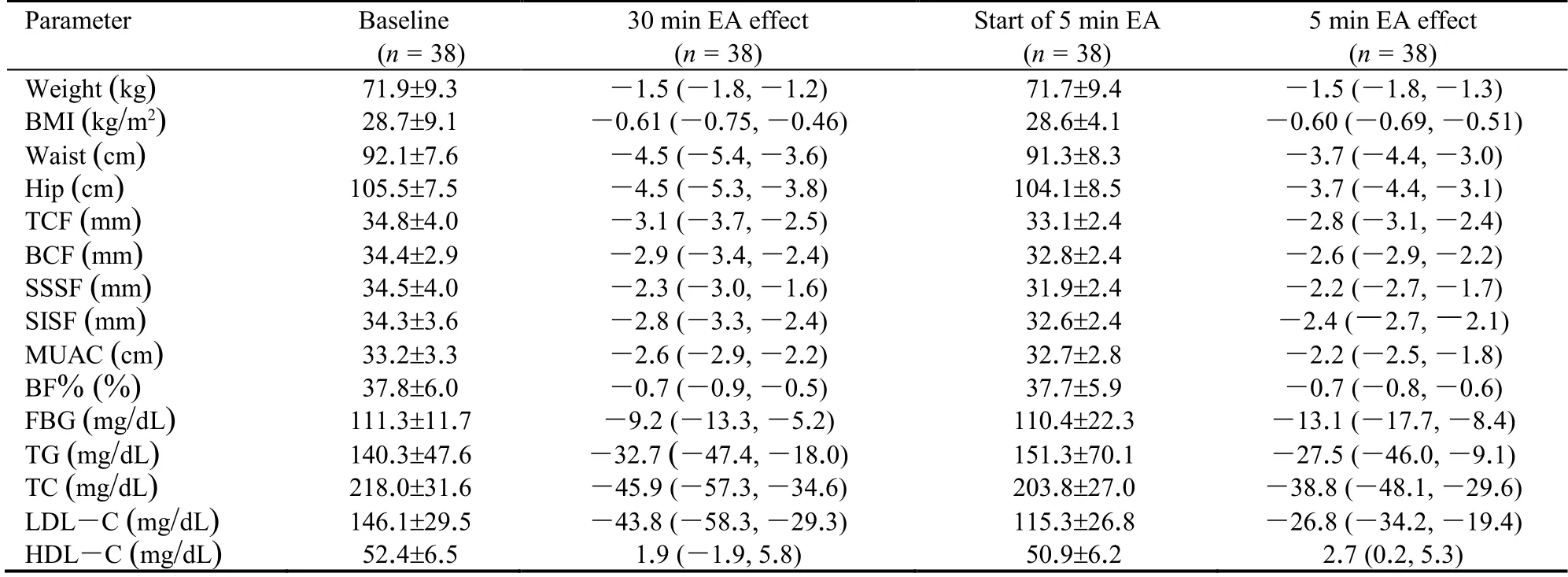
Table 2 Anthropometric data and biochemistry parameters at each evaluation of participants allocated to group order AB ()
Notes: participants received 8 weeks of the 30 min per session electroacupuncture (EA),and then 8 weeks of washout period and finally 8 weeks of the 5 min per session EA.BMI: body mass index;TCF: triceps skinfold;BCF:biceps skinfold;SSSF:subscapular skinfold;SISF:supra-iliac skinfold;MUAC:mid-upper arm circumference;BF%:Body fat percentage;FBG: fasting blood glucose;TG:triglyceride;TC:total cholesterol;LDL-C:low density lipoprotein cholesterol;HDL-C:high density lipoprotein cholesterol;EA:electroacupuncture
Table 3 Anthropometric data and biochemistry parameters at each evaluation of participants allocated to group BA ()
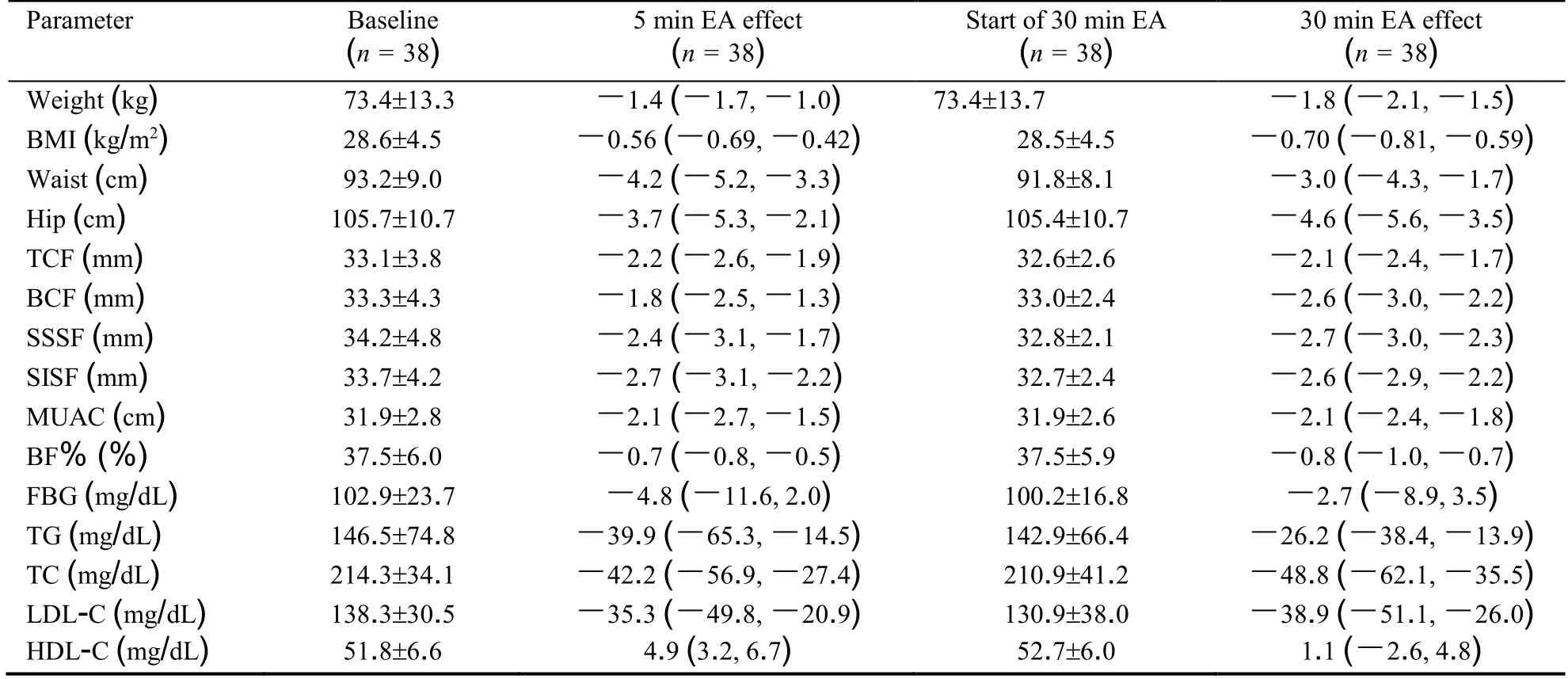
Table 3 Anthropometric data and biochemistry parameters at each evaluation of participants allocated to group BA ()
Notes:participants received 8 weeks of the 5min per session electroacupuncture (EA),and then 8 weeks of washout period and finally 8 weeks of the 30 min per session EA.BMI:body mass index;TCF:triceps skinfold;BCF:biceps skinfold;SSSF:subscapular skinfold;SISF:suprailiac skinfold;MUAC:mid-upper arm circumference;BF%:Body fat percentage;FBG:fasting blood glucose;TG:triglyceride;TC:total cholesterol;LDL-C:low density lipoprotein cholesterol;HDL-C:high density lipoprotein cholesterol;EA:electroacupuncture.
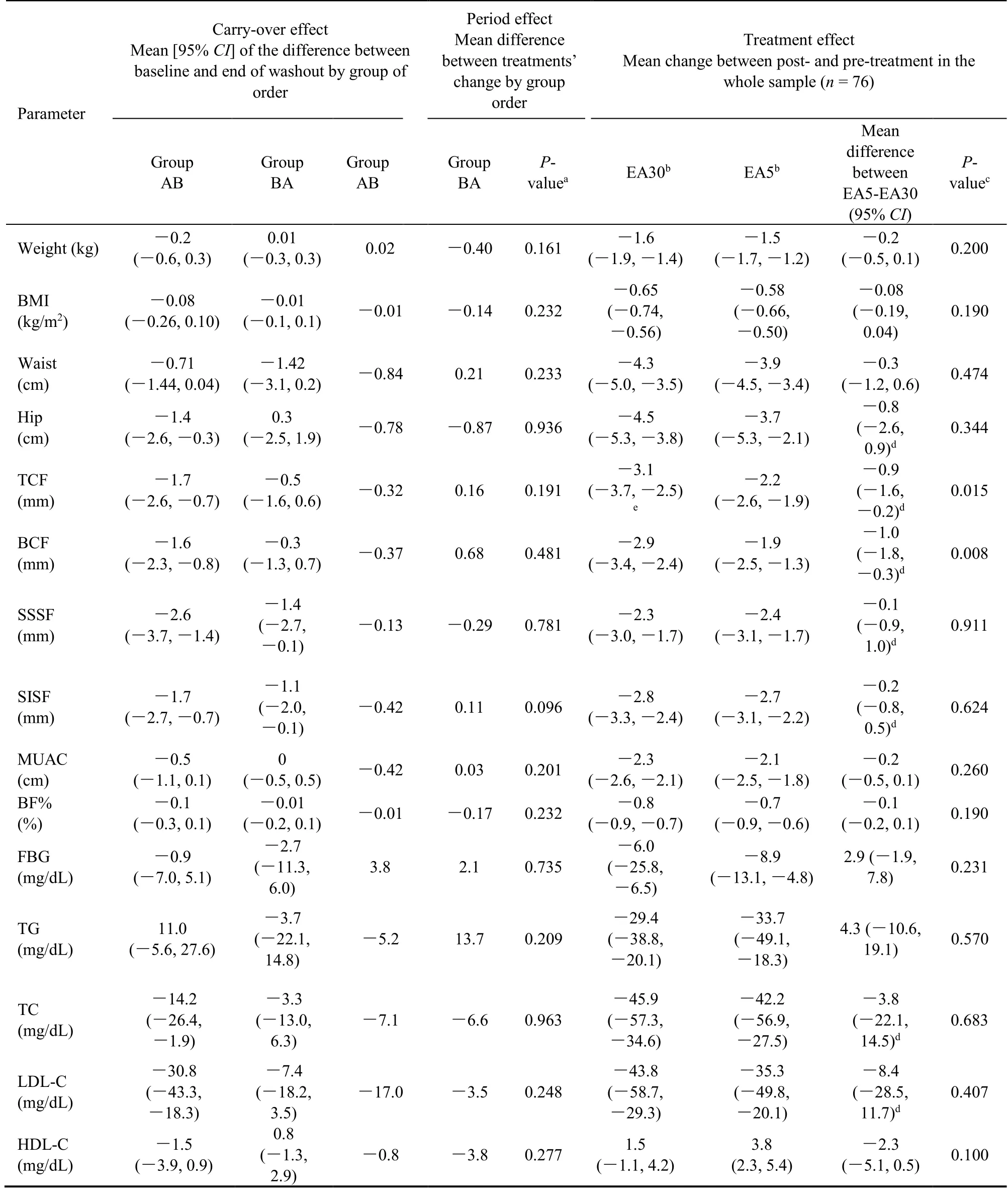
Table 4 Carry-over effect,period effect and treatment effect
At the end of an 8-week EA protocol,participants in both EA treatment protocols had significant weight reduction from their baseline regardless the treatment sequence [weight reduction of 1.6 kg in EA30 (P <0.01) and 1.5 kg in EA5 (P <0.001)].There was no significant difference in weight reduction between these two EA protocols [mean difference-0.2 kg(95%CI:-0.5,0.1);P=0.200].
circumference,MUAC and BF% which were decreased from their baseline;however,there were no significant differences between the two methods.Fasting blood glucose and TG were also significant Both EA methods had significant therapeutic effects on other anthropometric parameters including BMI,waist decrease from their baselines after the end of an 8-week EA of each EA protocol without significant differencebetween EA protocols [FBS decreased 6.0 mg/dL(EA30)vs8.9 mg/dL (EA5);P=0.231;TG decreased 29.4 mg/dL (EA30)vs33.7 mg/dL (EA5);P=0.570].At the end of an 8-week EA protocols,HDL-C levels increased in both EA30 (1.5 mg/dL;P=0.247) and EA5 (3.8 mg/dL;P <0.001) protocols,however,the increasing levels of HDL-C did not significant difference between the two treatment protocols (P=0.100).
After adjusting for the carryover effect of the first treatment period on the following treatment period,it was found that participants in both EA protocols had significant decrease of hip circumference,all skinfold thicknesses,TC and LDL-C levels from their baselines.There were no significant diff-erences in the treatment effects between the two EA protocols except participants in EA30 treatment protocol achieved higher decrease of triceps-and biceps-skinfold thickness than those in EA5 treatment protocol.
There were no reported of adverse events during the study.All participants received two sessions of EA per week as specified by protocol throughout the study protocols.
4.DISCUSSION
The results of this randomized crossover study indicated that electroacupuncture had efficacy to reduce weight,BMI and all others obesity parameters as well as to improve metabolic biochemistry components in Thai obese women.A short,5-minute,duration EA had a comparable efficacy in obesitytreatment to the conventional 30-minute EA.Moreover,some treatment efficacy of EA,especially on the reduction of skinfold thicknesses,hip circumference,total-and LDL-cholesterol levels,had sustain over the 8-week after stop treatment.EA was well tolerated and safe to treat obesity and its related metabolic derangements.
Acupuncture has been regarded as one of an effective treatment for obesity.Several systematic review and Meta-analysis studies reported the positive efficacy for obesity treatment but remaining inconsistent results in some details among studies.This may explain to diversity of study protocols such as acupuncture method (e.g.traditional acupuncture,electroacupuncture,and auricular acupuncture),comparative groups (e.g.no treatment,sham acupuncture,lifestyle modification,placebo or pharmacotherapy) and end results (e.g.weight,BMI,body far mass or body circumference).However,the present study is consistent with the majority of previous studies indicated the great efficacy of EA for reduction of body weight,BMI and other anthropometric parameter including the improvement of lipid profiles and blood glucose in obese patients.Choet al14have reported a systemic review and Meta-analysis that acupuncture on treatment had a significant effects on weight reduction and improvement in obesity compared to placebo,lifestyle control or sham treatments.However,there were some limitations on the interpretation due to the clinical heterogeneity and poor methodological quality of the included studies.There are other systematic review and Meta-analysis studies reporting similar findings.Zanget al15reported that the standard EA or auricular acupuncture either with or without dietary restrictions have efficacy in reduction of BMI,body fat mass and body circumference but have no efficacy in weight reduction compared to sham treatment.Fanget al16also report the efficacy of acupuncture both alone and together with lifestyle modification was more effective than untreated or placebo control group.The 2 most resent Meta-analysis studies report the difference result of the efficacy of EA on obesity therapy.Zhanget al17did a network Meta-analysis which included 34 trials and found that acupuncture and related therapies were superior to lifestyle modification and placebo in reducing weight and BMI.Specifically,EA was associated with a significant improvement in weight and BMI compared to lifestyle modification and significant improvement in BMI compared to placebo.In contrary,Kimet al18reported a systemic review and Meta-analysis which included 27 trials that acupuncture was effective when combined with lifestyle modification.However,acupuncture alone was no superior than sham therapy or no treatment.Differences in these results may explained by the small numbers of RCTs including to the systematic reviews,study selection (inclusion and exclusion criteria) and data sources and searches,heterogeneity of data and outcome measurement.
Acupuncture encompasses various intervention styles and techniques,such as manual acupuncture (MA),electro-acupuncture,auricular acupuncture,catgut embedding acupuncture and laser acupuncture.15-18Moreover,the diversity in treatment frequency and duration and selected acupoints using for treatment make it difficult to compare the efficacy of various acupuncture protocols for the same conditions.For example,it is difficult to compare the efficacy of MA and EA because of the difference in nature and techniques.MA is performed using a short duration of stimulation while EA is usually performed using the longer (15-30 min) duration.From the scientific viewpoint,confounding factors can emerge when efficacy of treatment is compared across two conditions in the presence of another variable.This study showed that short duration EA has comparable efficacy to conventional 30-minute EA for reduction of weight,BMI,BF% and body circumferences as well as improvement of lipid profiles and blood glucose in obese patients.This finding provides additional information for future studies that aim to compare the efficacy of difference intervention styles such as manual acupuncture and electroacupuncture by using the same duration of stimulation for treatment of obesity.Moreover,the shorter duration intervention is more beneficial in terms of reduced time of treatment,cost,and inconvenience to the patients.
The present study has some limitations.Participants were not blinded to the treatment procedures due to the nature of the experimental interventions which may be a potential bias problem.Participants including to the study were only women thus limiting generalizability for explain efficacy for all obese patients.Additionally,the long-term efficacy of EA was not evaluated in this study.The study is designed to determine the immediate effect of 8-week treatment period with no long-term follow-up.It is equally important to mention the carryover effects in some parameters of the first treatment period on the following treatment period in both groups.This means some residual effects of treatment from the previous time period persist into the treatment.This could indicate that EA have longlasting benefit effects over the 8-week after discontinuing treatment.However,when analyzing the data from only the first treatment period,the efficacy of the conventional EA and the short-course EA did not show any significant difference from the total treatment effect.A future study with a longer washout period is recommended to minimize the carryover effect of treatment.
This study has some strengths worth mentioning.The treatment effects for weight reduction and improvement in biochemistry parameters in this study are solely due to EA treatment.We did not give specific recommendations for lifestyle modifications such as diet control or exercise during the study.We advised participants to maintain the usual pattern of physical activity and dietary intake throughout the study.This research is a new approach to electroacupuncture that uses one group of joint acupuncture points to treat all types of obesity.Based on the TCM concept,the cause of obesity has been conceptualized in a variety of ways which need a specific group of acupuncture points for treatment each specific cause of obesity.These variations in treatment require experienced acupuncturists to classify the correct obesity type that make it difficult for the inexperienced acupuncturist for deciding which acupuncture points to use.This new approach will make EA therapy more feasible for any acupuncturist by using this group of acupuncture points,regardless of obesity type,as an effective obesity treatment.A crossover design study can decrease the confounding covariates because each crossover patient serves as her own control.Moreover,this study can be a useful guide for further studies in obesity-related other disorders including fatty liver,polycystic ovarian syndrome,and pro-inflammatory states.
In conclusion,short-duration,5 min,electroacupuncture at a group of 14 acupuncture points had comparable efficacy to the conventional electroacupuncture to reduce weight,BMI,body circumference and fatness as well as to improve biochemistry parameters in obese women.Electroacupuncture is a beneficial,safe,well-tolerate and less expensive mode of treatment for obesity regardless of the duration of electrical stimulation.
5.ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors would like to thank all participants and others who contributed to this research project in different ways.
杂志排行
Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine的其它文章
- Acupoint application therapies for essential hypertension:a systematic review and Meta-analysis
- Biosynthesis of titanium dioxide nanoparticles using Hypericum perforatum and Origanum vulgare extracts and their main components,hypericin and carvacrol as promising antibacterial agents
- Protective effect of resveratrol on rat cardiomyocyte H9C2 cells injured by hypoxia/reoxygenation by regulating mitochondrial autophagy via PTEN-induced putative kinase protein 1/Parkinson disease protein 2 signaling pathway
- Efficacy of aqueous extract of flower of Edgeworthia gardneri (Wall.)Meisn on glucose and lipid metabolism in KK/Upj-Ay/J mice
- Effect of manipulation on cartilage in rats with knee osteoarthritis based on the Rho-associated protein kinase/LIM kinase 1/Cofilin signaling pathways
- Baicalin inhibits inflammation of lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via toll like receptor-4/myeloid differentiation primary response 88/nuclear factor-kappa B signaling pathway
