The protective effect of icariin on glucocorticoid-damaged BMECs explored by microfluidic organ chip
2022-07-11TngqiLiQingyuZhangFuqiangGaoYaiLiuWiSunaYiyangDong
Tngqi Li,Qingyu Zhang,Fuqiang Gao,Yai Liu,Wi Suna,,∗,Yiyang Dong
a Department of Orthopedics,Peking University China-Japan Friendship School of Clinical Medicine,Beijing 100029,China
b Department of Orthopedics,Peking University Shougang Hospital,Beijing 100144,China
c Department of Orthopedics,Shandong Provincial Hospital Affiliated to Shandong First Medical University,Ji’nan 250021,China
d Department of Orthopedics,China-Japan Friendship Hospital,Beijing 100029,China
e Office of Academic Affairs,Beijing University of Chemical Technology,Beijing 100029,China
f Department of Pharmaceutical Analysis,College of Life Science and Technology,Beijing University of Chemical Technology,Beijing 100029,China
Keywords:Osteonecrosis of the femoral head Bone microvascular endothelial cells Glucocorticoid Microfluidic chip Bioinformatic analysis
ABSTRACT Osteonecrosis of the femoral head (ONFH) is a devastating musculoskeletal disease characterized by the impaired circulation of bone.The purpose of this study was to explore the underlying mechanisms of the protective effect of icariin on the glucocorticoid-induced injury of bone microvascular endothelial cells(BMECs).Normal BMECs were extracted from the femoral heads by enzymatic isolation and magneticactivated cell sorting methods.Dexamethasone and icariin were used to intervene BMECs in microfluidic organ chips,and phalloidin staining was conducted to observe the cell morphology and viability.Then next-generation transcriptome sequencing and real-time quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) were performed to identify the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in different groups.Through the microfluidic organ chip,it can be observed that after dexamethasone intervention,the filamentous structure in cell fibers disappeared and the cell morphology changed from spindle to round until death.Icariin could relieve these changes and showed a protective effect on glucocorticoiddamaged BMECs.In addition,201 DEGs were detected between the icariin protection group and the dexamethasone group,which were significantly enriched in 17 signaling pathways.8 of the top ten selected hub genes (IL6,PTGS2,VEGFA, etc.) were confirmed by qRT-PCR.Transcription factors (TFs)-gene network showed 63 connections between 18 TFs and 12 DEGs.For instance,GATA2 could regulate 5 DEGs.The associations between 92 miRNA and 12 DEGs were visualized in a miRNA-gene network.The hub miRNA,has-mir-335–5p was predicted to interact with 8 DEGs (PTGS2,VEGFA, etc.).Microfluidic organ chips could provide excellent morphological results for cell experiments,by which it could be observed that icariin showed a protective effect on the glucocorticoid-induced injury of BMECs.Beside,these DEGs,possible regulatory TF (GATA2,FOXC1, etc.) and miRNA (has-mir-335–5p) might be dysregulated in the initiation of ONFH and have prospective importance in ONFH diagnosis and therapy.
Osteonecrosis of the femoral head (ONFH) is a common musculoskeletal disease with rapid progression and a high disability rate [1].It imposes a heavy economic burden on individual families and society.As its pathogenesis remains unclear,treatment choice is challenging to be exact [2].In the early stage of ONFH,patients normally have no obvious clinical symptoms,and when there are pain and mobility problems,the course of the disease is often severe,and the femoral head often has collapsed [3,4].At present,more and more scholars believe that the disruption of blood supply around the femoral head is closely related to the occurrence of ONFH (Fig.S1 in Supporting information) [5,6].Therefore,the study of bone microvascular endothelial cells (BMECs) that constitute bone microvessels may help to further reveal the pathogenesis of ONFH and provide alternatives for treatment.Icariin is the main active ingredient of epimedium brevicornum,a traditional Chinese herb known for “strengthening bone and tonifying kidney”[7].Icariin could decrease the risk of glucocorticoid-induced ONFH by promoting the proliferation and mineralization of osteoblasts and decreasing the activity of osteoblasts but efforts to understand the underlying mechanisms are still ongoing [7,8].
In recent years,multidisciplinary and cross-professional collaboration has become the trend of clinical investigation.The continuous development of microfluidic technology is bound to drive the growth of biological medicine and other industries.Many sophisticated microfluidic devices can be used to simulate tissues and organs,and provide physiological microenvironments for cells [9–11].More advanced microfluidic models have been used for diseases investigation and drug screening [12–14].Sinhaet al.[15]reported a single-cell analysis using microfluidic technology,which provided development platforms for novel therapies and rapid diagnostics.Mature organ chips can even replace animal experiments in biomedical,pharmaceutical,and toxicology applications,showing excellent development potential.Jo and Lee [16]used microfluidic technology to produce polymeric microparticles (MPs) with designed structure and composition by precise control of multiphase flow on a micro-scale.These MPs can be used in curative effect observation,3D cell culture,and biomolecular sensing.The application prospects of microfluidics technology,from simple cell culture chip to organ chip,are unlimited.
The dysregulation of various RNAs,such as circRNA,miRNA,and mRNA,has been used to study the pathogenesis of orthopedic disorders such as osteoarthritis and osteonecrosis [17,18].Xianget al.[19]extracted synovial samples of knee osteoarthritis and compared them with controls.They found that 122 circRNAs were differentially expressed between two groups,suggesting that these circRNAs might be related to the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis.Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a type of single-stranded ribonucleic acid transcribed from a strand of DNA and detecting the change of mRNA expression level can help to understand the change of cell protein synthesis.Leijtenet al.[20]found some mRNAs such as GREM1,FRZB and DKK1 in articular cartilage were inversely associated with osteoarthritis disease.Udomsinprasertet al.[21]demonstrated that the level of interleukin-34 mRNA expression could predict the severity of synovitis in knee osteoarthritis.It can be seen that in the pathogenesis of many diseases,changes at the cellular level,such as various protein indicators and different RNA expression levels,tend to appear earlier in comparison with clinical symptoms,and identification of these differences may facilitate the early detection and diagnosis of these diseases.
In the present study,to explore the pathogenesis of glucocorticoid-induced ONFH and the protective effect of icariin,BMECs were extracted and inoculated in microfluidic organ chips,and treated with glucocorticoids and icariin to observe the changes in cell morphology.Next,the mRNA differential expression of cells after different interventions was detected by next-generation transcriptome sequencing technology.The differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were further explored to predict the hub genes by using bioinformatics analysis.Finally,the screened hub genes were verified by quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR).We hope these findings will help us to further explore the pathogenesis of ONFH and guide a more accurate early diagnosis and treatment.
As a result,a live view and schematic diagram of the chip are shown in Fig.1.There are four channels with precisely the same parameters.Fig.2 shows the isolated cells were almost 100% positive in CD31 and vWF and 100% negative in CD133,indicating that these cells were BMECs.Under the transmission electron microscope,these cells showed polygonal shape with large ovular nuclei and the cell surface was covered with microvilli formed by cytoplasm bulge.
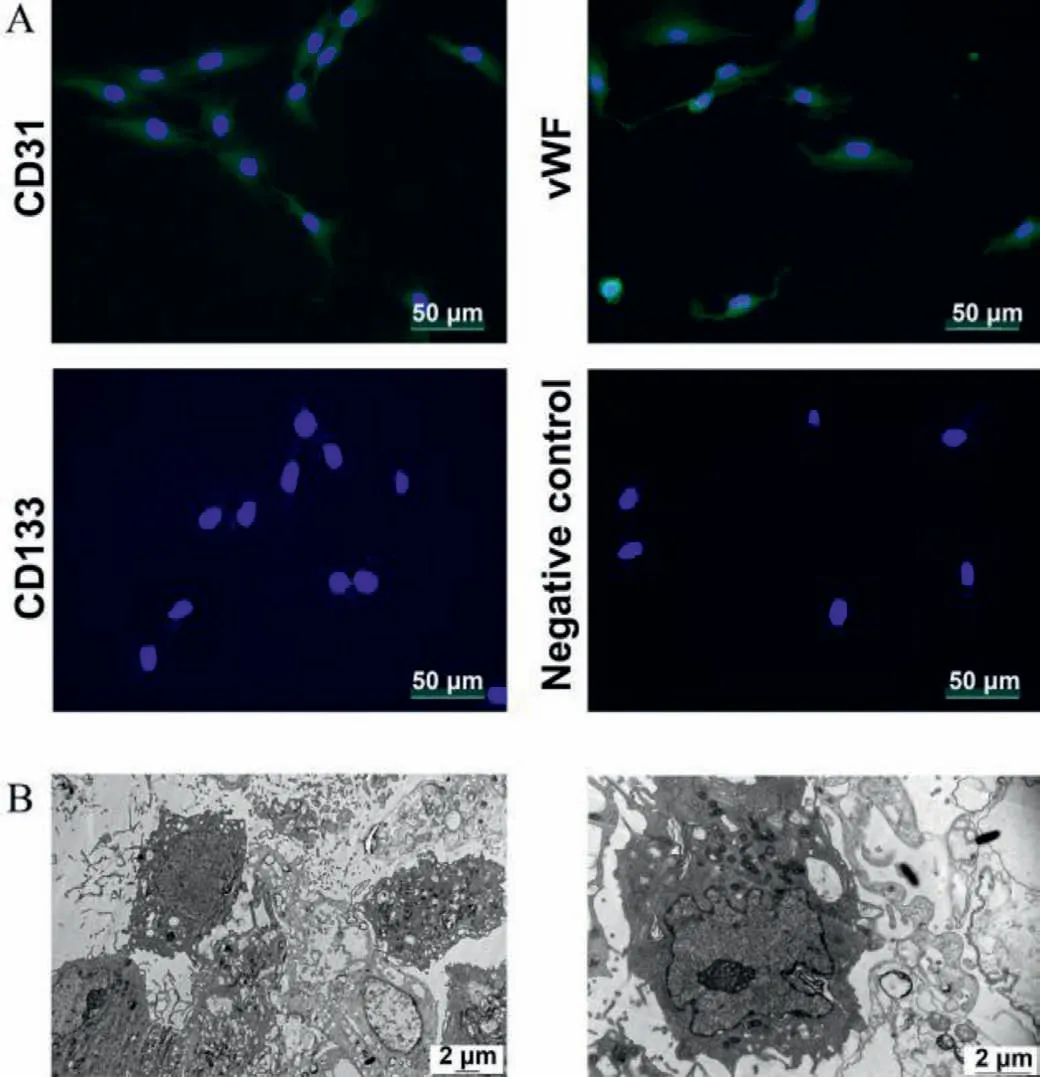
Fig.2.(A) Immunofluorescence staining of endothelial cell markers.(B) Observation under transmission electron microscope observation.
Through image acquisition and data analysis (Fig.3),we can find that the number of surviving cells in group C (34.7±10.3) is significantly less than that in group A (73.3±6.7,P=0.015).The cytoskeleton area coverage percentage in group B (26.3% ± 3.9%,P=0.003) and C (18.4% ± 4.2%,P<0.001) is significantly less than that in group A (43.5% ± 3.1%).In addition,the comparison of fiber length showed that group B (6906.62±1721.75,P=0.001) and C(7961.69±1891.98,P=0.001) is significantly shorter than the control group (16,708.15±1181.78).As shown in group C (Fig.3A),the skeleton fiber length of individual cells recovered somewhat.However,due to the small number of cells,the overall fiber length showed no significant difference between groups B and C(P=0.72).In addition to data analysis,we can also see from morphology that the normal morphology of cells disappeared after dexamethasone (DXMS) injury,and the cells were deformed from spindle to ellipse or even round.When these connections between cells were broken,blood vessel structures were damaged.After icariin intervention,the morphology of single cells recovered to some extent,but there was still a difference compared with the blank group.
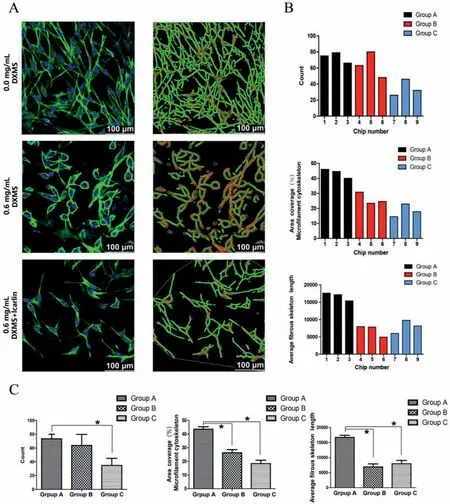
Fig.3.Microfluidic experiment part results.(A) The left is confocal microscopy image of BMECs in the three groups (40-fold oil lens;scale bars,100 μm).The right is diagram of fiber length analysis.(B) Data statistics of all the chips conducted by ImageJ software.(C) Comparison of statistical differences between the three groups.∗P < 0.05 vs.group A.Group A,0.0 mg/mL dexamethasone;Group B,0.6 mg/mL dexamethasone;Group C,0.6 mg/mL dexamethasone+icariin.
Unlike former literature,in this study,the protective drug icariin was used for post-intervention rather than pre-protection.The primary purpose of this study was to investigate whether icariin could still protect BMECs 24 h after glucocorticoid injury.Microfluidics chip experiments showed that after icariin intervention,the morphology of BMECs was improved,and the filamentous structure of some cells was restored,but the morphology and length of BMECs were still different compared with the blank group.In addition,the number of cells was also significantly reduced,indicating that after the intervention of a high concentration of glucocorticoid,the cells would gradually undergo morphological changes and develop to cell death.Although the highconcentration glucocorticoid intervenes stopped after 24 h and some cell morphology recovered after icariin protection,the fact that a large number of cells died could not be changed.
Data normalization was performed to confirm the crosscomparability of biological variability between different samples(Fig.S2A in Supporting information).In total,143 DEGs were identified between the DXMS group and the control group,including 102 upregulated and 41 downregulated genes listed in Table S2(Supporting information).Meanwhile,201 DEGs were detected between the icariin protection group and the DXMS group,including 143 upregulated and 58 downregulated genes (Table S3 in Supporting information).In addition,a volcano plot and a heatmap of all DEGs between three groups were generated using the R ggplot2 package (Figs.S2B and S3 in Supporting information).
Baiet al.[22]found that in patients with ONFH,the alteration of bone trabecular tissue structure was preceded by discovering alteration of mRNA profile through gene sequencing.Liet al.[23]studied the difference of serum miRNAs in patients with both systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and ONFH,and those with SLE alone.They found 42 differentially abundant miRNAs (14 upregulated and 28 downregulated) between the two groups.These could also be targets for future treatments.Beside,the mRNA of cells also changed considerably after icariin treatment.These upregulated or downregulated genes provide a reference for the study of its mechanism.Yuet al.[24]conducted a similar experiment using glucocorticoid intervention with BMECs and finally found 239 differentially expressed long noncoding RNAs.Xieet al.[25]established the model of rabbit ONFH by methylprednisolone.After the intervention with icariin,it was found that the repairability of bone defect in the icariin group was significantly higher than that in the control group,and the expression of VEGF was also considerably elevated.Yuet al.[26]found that icariin could significantly promote the migration of BMECs and the expression of factors related to tubular and angiogenesis.However,no one has previously studied the molecular mechanism by which icariin affects BMECs,and our study provides an essential reference for the study of its molecular mechanism.
Gene ontology (GO) enrichment analysis of 143 DEGs between the DXMS group and the control group was performed to identify the most relevant biological processes (BPs),molecular functions (MFs),and cellular components (CCs).The top ten enriched terms in BP,CC,and MF were presented in Figs.S4A–C (Supporting information).Meanwhile,based on the KEGG pathway analysis,the DEGs were significantly enriched in 8 signaling pathways,such as cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction (7 DEGs) and PI3KAkt signaling pathway (7 DEGs) (Fig.S4D in Supporting information).There is also extensive literature investigating the functions of these pathways,such as inhibition of glycogen synthesis and promotion of glycolysis [27].Inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway could promote autophagy in mouse articular cartilage[28].
Meanwhile,GO enrichment analysis of 201 DEGs between the icariin protection group and the DXMS group was performed and the top ten enriched terms in BP,CC,and MF are presented in Fig.S5A–C (Supporting information).Meanwhile,based on KEGG pathway analysis,the DEGs were significantly enriched in 17 signaling pathways,such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) signaling pathway (12 DEGs),PI3K-Akt signaling pathway (12 DEGs) and pathways in cancer (11 DEGs) (Fig.S5D in Supporting information).This suggested that the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway plays an important role in both the deleterious effect of DMXS and the protective effect of icariin on BMECs.The top 20 terms associated with 201 DEGs,enriched in BP,CC and MF as well as various KEGG pathways are presented in Table S4 (Supporting information).
The interactions between the proteins expressed from DEGs between the icariin protection group and the DXMS group consisted of 139 nodes and 404 edges (Fig.S6A in Supporting information).In addition,11 of the DEGs revealed connectivity degrees>15:IL6 (Degree=47),VEGFA (Degree=38),FOS (Degree=30),PTGS2(Degree=26),ATF4 (Degree=22),CXCR4 (Degree=17),ATF3 (Degree=17),ICAM1 (Degree=17),DDIT3 (Degree=17),CXCL12 (Degree=16),and NOS3 (Degree=16).In addition to connectivity degrees,top 10 hub genes were also selected by CytoHubba based on the maximal clique centrality (MCC) and maximum neighborhood component (MNC) classification methods (Table S5,Fig.S7 in Supporting information),showing overlapping genes with different priority.Seven significant modules (Fig.S6B in Supporting information) were obtained by module analysis using MCODE from Cytoscape.
The top ten selected hub genes by MCC were further determined by qRT-PCR analysis,the expression of eight genes (IL6,PTGS2,VEGFA,CXCR4,ICAM1,CXCL12,MMP3,and FOS) between the icariin protection group and the DXMS group showed a statistical difference (P <0.05,Fig.4).IL6 can promote the development of blood cells [29];the expression of IL6 was significantly decreased in the DXMS group,and significantly increased in the icariin protection group.COX-2 encoded by PTGS2 can promote cell proliferation,inhibit cell apoptosis,and promote angiogenesis [30].CXCR4,ICAM1,and other genes could also regulate angiogenesis[31,32].Compared with the DXMS group,the expression of these genes was significantly increased in the icariin protection group.These results indicated that icariin can effectively reduce the damage of BMECs induced by DXMS.This is similar to the research conclusions in many related orthopedic diseases.For example,icariin can relieve knee osteoarthritis in mice [33]and effectively prevent postmenopausal osteoporosis in women through inhibiting NLRP3 mediated pyroptosis [34].
According to the binding site and genetic coordinate position provided on ENCODE,the potential TFs targeting DEGs between the icariin protection group and the DXMS group were predicted.Eventually,a total of 63 associations between 18 TFs and 12 DEGs were obtained (Fig.S8 in Supporting information).The miRNAgene pairs were identified through network analysis of 201 DEGs between the icariin protection group and the DXMS group using the TarBase and miRTarBase databases.Finally,a total of 128 associations between 92 microRNAs and 12 DEGs were identified (Fig.S9 in Supporting information).Therefore,the TF-gene-miRNA interaction involved 12 genes,18 TFs,and 92 microRNAs (Fig.5,Table S6 in Supporting information).For instance,GATA2 regulated 5 DEGs (e.g.,VEGFA and CXCR4),IRF1 regulated 5 DEGs (e.g.,ICAM1 and VEGFA) and TFDP1 regulated 5 DEGs (e.g.,ICAM1 and VEGFA).VEGFA was regulated by 50 interacting microRNAs,while a hub microRNA,hsa-mir-335–5p,was predicted to interact with 8 genes(PTGS2,VEGFA,ICAM1,NOS3,KLF4,CXCL2,IL6,and FOS).Has-miR-335–5p,as an essential regulator of bone homeostasis,has also been demonstrated in other orthopedic diseases.Tornero-Estebanet al.[35]found that the expression of ha-miR-335–5p was significantly down-regulated during induced osteogenesis of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells.In the pathogenesis of ONFH,we believe that has-miR-335–5p also plays a particular regulatory role,which needs to be further confirmed in the future.
Different from traditional culture methods,microfluidic chips provide a new environment for cells to live in.The main feature of microfluidic platform is fluidity.Cells can be fused with rat tail collagen,suspended in it,and can move around slightly.Meanwhile,cell mobility can be increased by installing microfluidic pumps.In this way,different from ordinary Petri dishes,cells are no longer limited by plant growth and can grow to the surrounding space,which increases the chance of contact between cells and makes it easier to form tubular and vascular structures.Another feature of this platform is the independent operation.Four channels can be operated independently.Affected by liquid surface tension,the material exchange can only be realized when liquid exists in adjacent channels simultaneously,so the four channels are both independent and interconnected.Our previous research [36]has confirmed that microfluidic chips can provide high-definition morphological results for cell experiments,which is significantly better than the images collected in ordinary Petri dishes.As a cell culture device,this microfluidic chip can also be used to culture other vascular endothelial cells,such as human umbilical venous endothelial cells.We will further verify the possibility for culturing non-vascular cell culture in this chip.However,the feature of disposability should not be neglected.The matrix cured in channels cannot be removed,and therefore after cell intervention and dyeing,the chip will be scrapped.
Through a microfluidic organ chip investigation,we intuitively saw the damage of dexamethasone to BMECs and the protective effect of icariin.Beside,for the first time we summarized the effect of dexamethasone and icariin on mRNA expression of BMECs and the RNA network map was constructed by bioinformatic analysis.The GO and KEGG pathways analysis revealed that PI3K-Akt signaling pathway was one of the enrichment pathways of DEGs that may be involved in the intervention of dexamethasone and icariin on BMECs.These identified DEGs,possible regulatory TF (GATA2,FOXC1,etc.) and miRNA (has-mir-335–5p) might be dysregulated in the initiation of ONFH and have prospective importance in ONFH diagnosis and therapy.
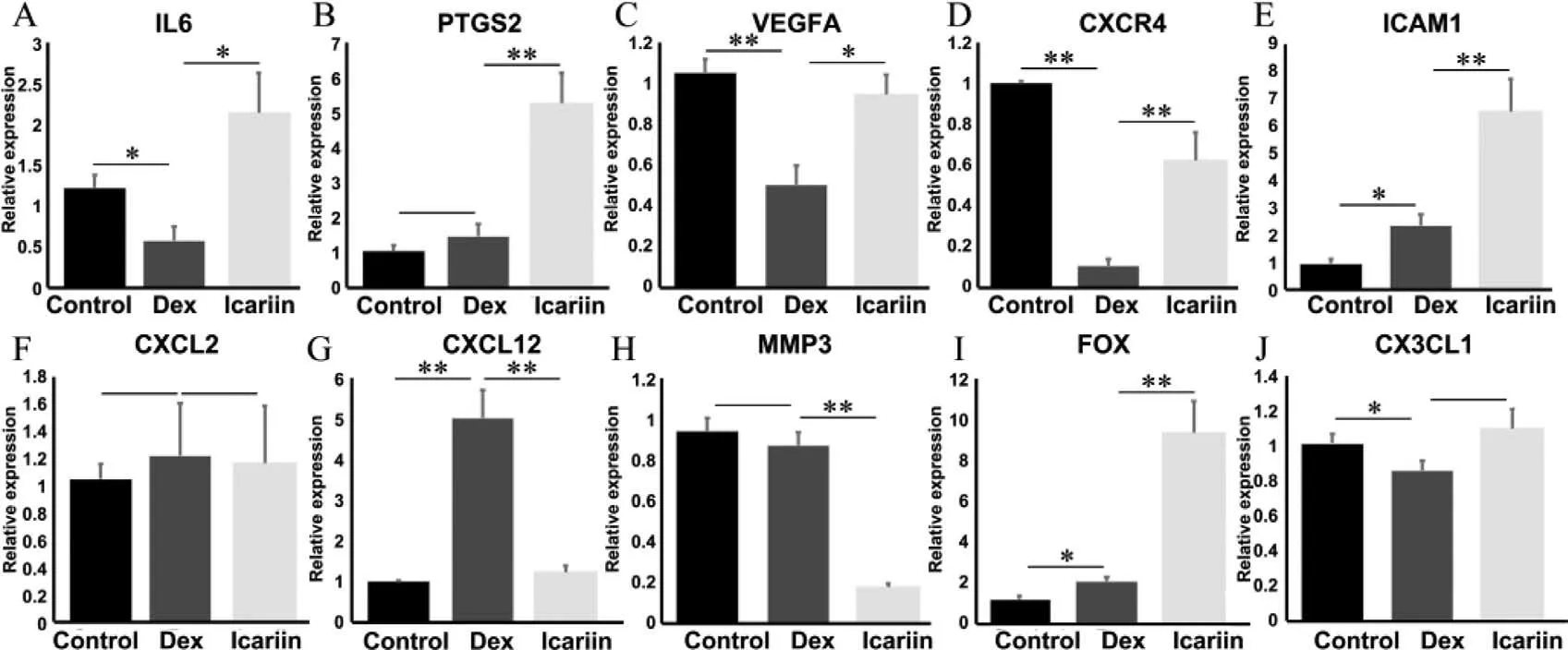
Fig.4.Validation of the top ten differentially expressed mRNAs between the icariin protection group and the DXMS group by qRT-PCR.(A) IL6,(B) PTGS2,(C) VEGFA,(D)CXCR4,(E) ICAM1,(F) CXCL2,(G) CXCL12,(H) MMP3,(I) FOS,(J) CX3CL1.∗P < 0.05,∗∗P < 0.01.
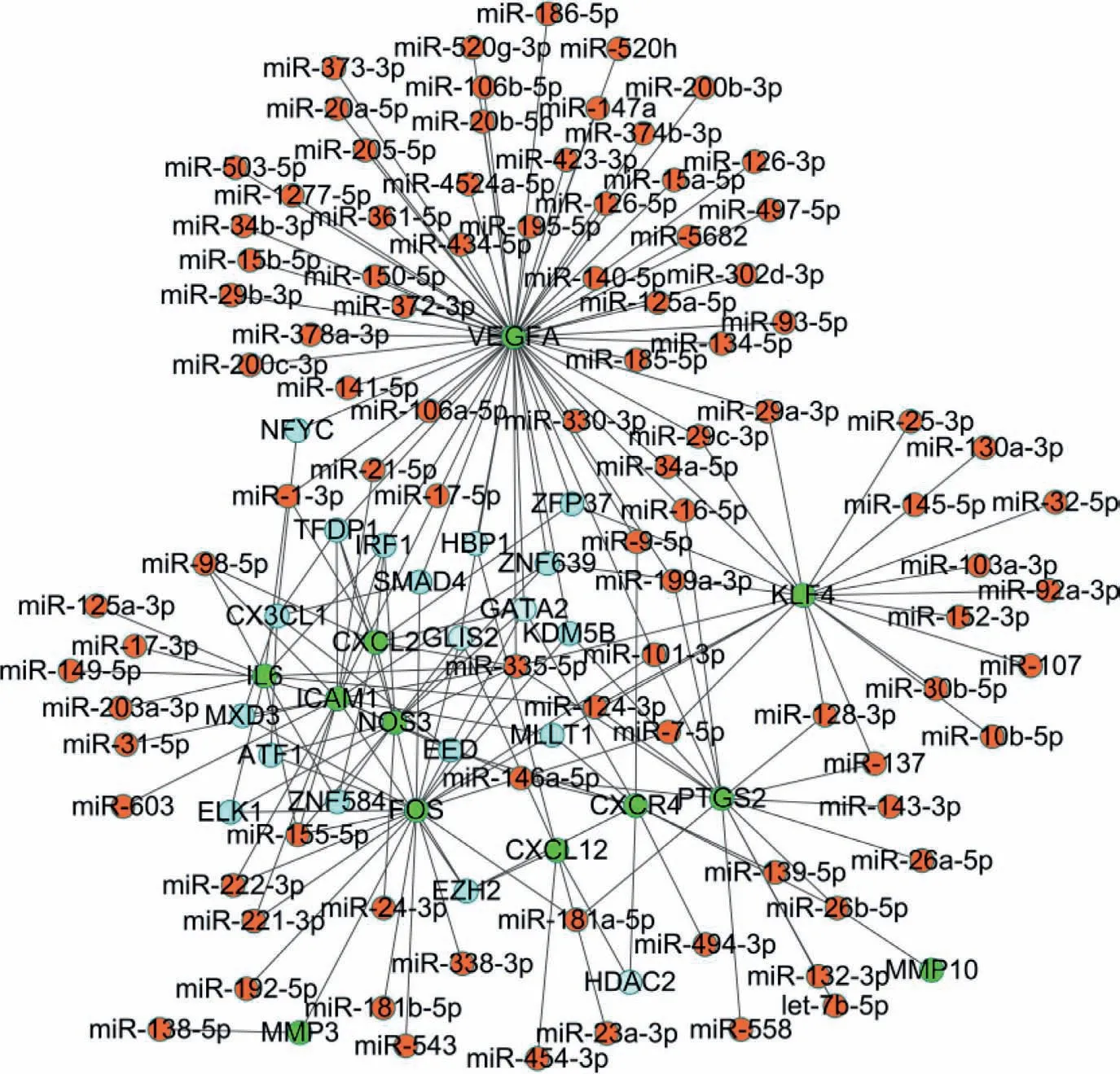
Fig.5.The TF-gene-microRNA interaction network between the icariin protection group and the DXMS group.
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Beijing Natural Science Foundation (No.7182146),the Biomedical Translational Engineering Research Center of BUCT-CJFH (No.RZ2020–02),the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.82072524),the Young Taishan Scholars Program of Shandong Province (No.tsqn201909183),the Academic promotion program of Shandong First Medical University(No.2020RC008) and the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (No.ZR201911090016).
Supplementary materials
Supplementary material associated with this article can be found,in the online version,at doi:10.1016/j.cclet.2021.11.093.
杂志排行
Chinese Chemical Letters的其它文章
- Photochemical defluorinative functionalization of α-polyfluorinated carbonyls via spin-center shift
- Methods of screening,monitoring and management of cardiac toxicity induced by chemotherapeutics
- Light-guided tumor diagnosis and therapeutics: From nanoclusters to polyoxometalates
- Nanofluidics for sub-single cellular studies:Nascent progress,critical technologies,and future perspectives
- Effective purification of oily wastewater using lignocellulosic biomass:A review
- Recent advances in microchip-based methods for the detection of pathogenic bacteria
