半枝莲碱B抑制胶质瘤U251细胞增殖并诱导DNA损伤与凋亡的实验研究*
2022-07-06郝晓杉冯盼盼张云云费洪荣
郝晓杉, 冯盼盼, 张云云, 费洪荣
半枝莲碱B抑制胶质瘤U251细胞增殖并诱导DNA损伤与凋亡的实验研究*
郝晓杉, 冯盼盼, 张云云, 费洪荣△
[山东第一医科大学(山东省医学科学院)药学院,山东 泰安 271016]
探讨半枝莲碱B(SBT-B)对人胶质瘤U251细胞增殖、DNA损伤和凋亡的影响。U251细胞经SBT-B(0.05、0.1和0.2 μmol/L)处理24 h,台盼蓝染色检测细胞活力;参照半数抑制浓度(IC50),将U251细胞分为对照(control)组和SBT-B处理组(处理浓度分别为0.05、0.1和0.2 μmol/L);5-乙炔基-2'-脱氧尿苷(EdU)掺入法检测SBT-B对U251细胞增殖的影响;免疫荧光染色检测DNA损伤; TUNEL细胞凋亡检测试剂盒检测细胞凋亡;同时,SBT-B处理U251细胞24 h,Western blot检测细胞凋亡、DNA损伤修复及丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(MAPK)通路相关蛋白表达水平。SBT-B显著抑制U251细胞活力和增殖(<0.05)。U251细胞经SBT-B作用24 h后,磷酸化组蛋白H2AX(γ-H2AX)灶点形成及表达水平显著增加(<0.05),DNA损伤修复蛋白Rad51的表达水平则下调(<0.05);SBT-B显著诱导U251细胞凋亡(<0.05),同时促进caspase-8、caspase-9和聚(ADP-核糖)聚合酶(PARP)的剪切(<0.05)。SBT-B处理24 h后,细胞外信号调节激酶(ERK)、c-Jun氨基末端激酶(JNK)和p38 MAPK的磷酸化水平显著增加(<0.05)。SBT-B抑制U251细胞增殖,并诱导细胞DNA损伤和凋亡,其可能通过激活MAPK信号通路而对胶质瘤细胞发挥抑制作用。
半枝莲碱B;胶质瘤;DNA损伤;凋亡;丝裂原活化蛋白激酶
神经胶质瘤是一种源于颅内胶质细胞的中枢神经系统恶性肿瘤,约占颅内恶性神经系统肿瘤的80%,具有发病率高、复发率高和高侵袭性等特点[1]。目前,术后联合化疗是治疗脑胶质瘤的主要手段,但化疗药物毒副作用大,易出现耐药性,通常治疗效果不佳。因此,开发新型低毒高效抗肿瘤药物,并阐明其作用机制显得尤为必要。
半枝莲是唇形科植物半枝莲(D. Don)的干燥全草,常与白花蛇舌草配伍治疗肺癌、胃癌等恶性肿瘤[2-4]。二萜类化合物是半枝莲的主要有效部位之一,其中二萜类生物碱能够体外抑制肝癌细胞等多种肿瘤细胞增殖[5-6]。半枝莲碱B(scutebarbatine B, SBT-B)是从半枝莲中分离得到的新克罗型二萜生物碱类化合物,可抑制P-糖蛋白而逆转肿瘤耐药[7-8]。本研究以人胶质瘤U251细胞为实验用细胞株,体外检测SBT-B对U251细胞增殖、DNA损伤及凋亡的影响,并探讨SBT-B抑制胶质瘤细胞活性的内在分子机制。
材料和方法
1 实验材料
SBT-B购自武汉天植生物技术有限公司;胎牛血清和Alexa Fluor®488标记的Ⅱ抗购自Thermo Fisher Scientific;Cell-Light™ EdU细胞增殖检测试剂盒购自锐博生物技术有限公司;TUNEL细胞凋亡检测试剂盒购自Roche;抗caspase-8、caspase-9、聚(ADP-核糖)聚合酶[poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase, PARP]和p-p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinase, MAPK)抗体购自Cell Signaling Technology;抗p38 MAPK抗体购自Sigma Aldrich;抗细胞外信号调节激酶(extracellular signal-regulated kinase, ERK)ERK、p-ERK、c-Jun氨基末端激酶(c-Jun N-terminal kinase, JNK)、GAPDH、Ku70、Ku86和Rad51抗体购自Santa Cruz;抗γ-H2AX抗体购自Abcam;抗p-JNK抗体购自BD Bioscience;HRP偶联Ⅱ抗均购自北京中杉金桥生物技术有限公司;ECL化学发光液购自Merck Millipore。
2 主要方法
2.1细胞培养人胶质瘤U251细胞购自中国科学院典型培养物保藏委员会细胞库,用含10%胎牛血清的DMEM培养液,于5% CO2、37 ℃条件下常规培养。
2.2台盼蓝染色取对数生长期的U251细胞,消化后接种于6孔板中过夜培养。将细胞分为对照组和SBT-B不同剂量处理组。对照组加入含0.1% DMSO的培养液,SBT-B处理组分别加入含0.05、0.1和0.2 μmol/L SBT-B的培养液。药物处理24 h后,胰酶消化并制备单细胞悬液,然后加入终浓度为0.2%的台盼蓝染色,计数活细胞数目,活细胞数=总细胞数-死细胞(着色细胞)数[9]。实验重复3次。采用统计软件SPSS 25.0计算IC50后,后续实验中SBT-B的最大剂量≤1.2×IC50。
2.3EdU检测细胞增殖接种对数生长期的U251细胞于96孔板中培养。待细胞贴壁后,随机分为对照组和SBT-B处理组。对照组加入含0.1% DMSO的培养液,SBT-B处理组分别加入含0.1和 0.2 μmol/L SBT-B的培养液。培养24 h后,按照EdU掺入试剂盒说明书对细胞进行EdU标记和Apollo染色,随机选取3个视野进行EdU阳性率统计。EdU阳性细胞(%)=新增殖细胞数(红色)/总细胞数(蓝色)×100%。
2.4TUNEL检测细胞凋亡接种对数生长期细胞于96孔板中,分组及给药剂量参照2.3。药物处理24 h后,PBS洗涤细胞2次,加入无水甲醇固定细胞1 h,0.1% Triton X-100处理2min。然后按照TUNEL试剂盒说明书对凋亡细胞进行染色;DAPI避光染核15 min后,倒置荧光显微镜观察细胞染色结果,并对结果进行统计分析。
2.5Western blotU251细胞消化后接种于6孔板中继续培养,待细胞贴壁后分组给药,分组及给药剂量参照2.2。药物处理24 h后,用预冷的PBS洗细胞2次,加入RIPA裂解液冰上放置20 min。接着4 ℃、14 000×离心20 min,收集上清并定量。取30 μg总蛋白进行SDS-PAGE,接着将蛋白电转移至硝酸纤维素膜上。膜经5%脱脂奶粉封闭1 h后,加入Ⅰ抗于4 ℃孵育过夜;加入Ⅱ抗室温孵育1 h;最后加入ECL显色液曝光显影。
2.6免疫荧光接种U251细胞于盖玻片上,并过夜培养。分组及给药剂量参照2.3。给药培养24 h后,PBS洗涤细胞2次,无水甲醇固定细胞20 min;用0.1% Triton X-100打孔5 min,山羊血清室温封闭30 min;接着加入γ-H2AX Ⅰ抗室温孵育2 h;PBS洗涤细胞3次,加入荧光标记的Ⅱ抗于37 ℃孵育30 min;DAPI染核15 min后,倒置荧光显微镜观察实验结果[10]。
3 统计学处理
实验结果采用SPSS 25.0软件进行统计分析。各实验独立重复3次,数据结果用均数±标准差(mean±SD)表示。组间比较应用单因素方差分析,组内两两比较采用SNK-检验。以<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
结果
1 SBT-B抑制U251细胞活力
台盼蓝染色实验结果显示,与对照组相比,U251细胞经不同浓度的SBT-B作用24 h后,活细胞数目显著减少(<0.05),表明SBT-B能够抑制胶质瘤细胞活力,且抑制作用呈剂量依赖性(图1),其IC50=0.179 7 μmol/L。
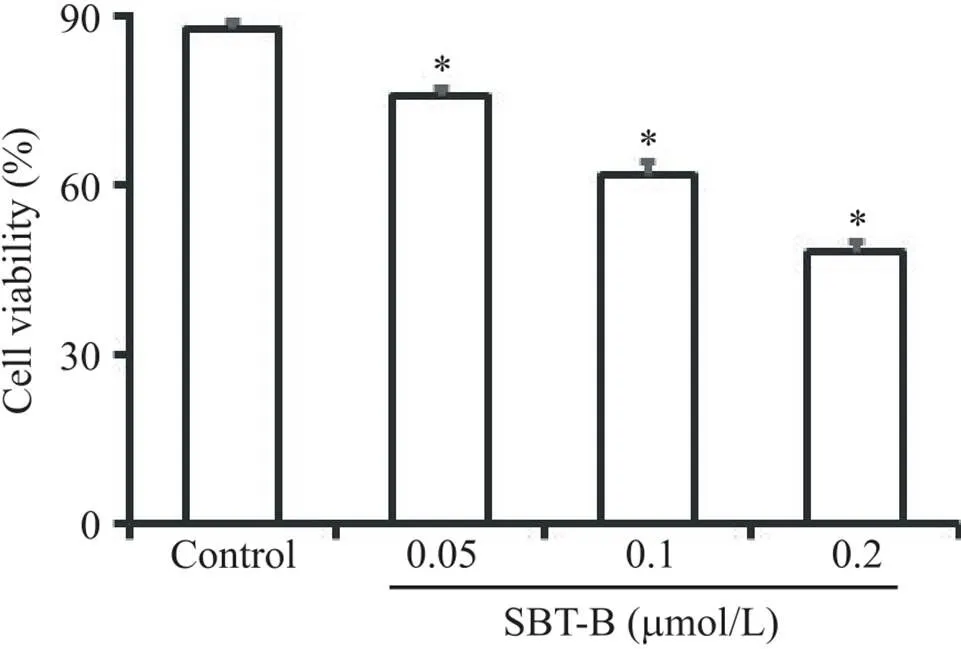
Figure 1. Scutebarbatine B (SBT-B) inhibited the viability of U251 cells. The cells were treated with 0.05, 0.1 and 0.2 μmol/L of SBT-B for 24 h, and the cell viability was determined by Trypan blue exclusion test. Mean±SD. n=3. *P<0.05 vs control group.
2 SBT-B抑制U251细胞增殖
EdU细胞增殖实验结果显示,与对照组比较,SBT-B处理U251细胞24 h后,EdU阳性细胞率显著降低(<0.05),见图2,表明SBT-B能够抑制U251细胞增殖。
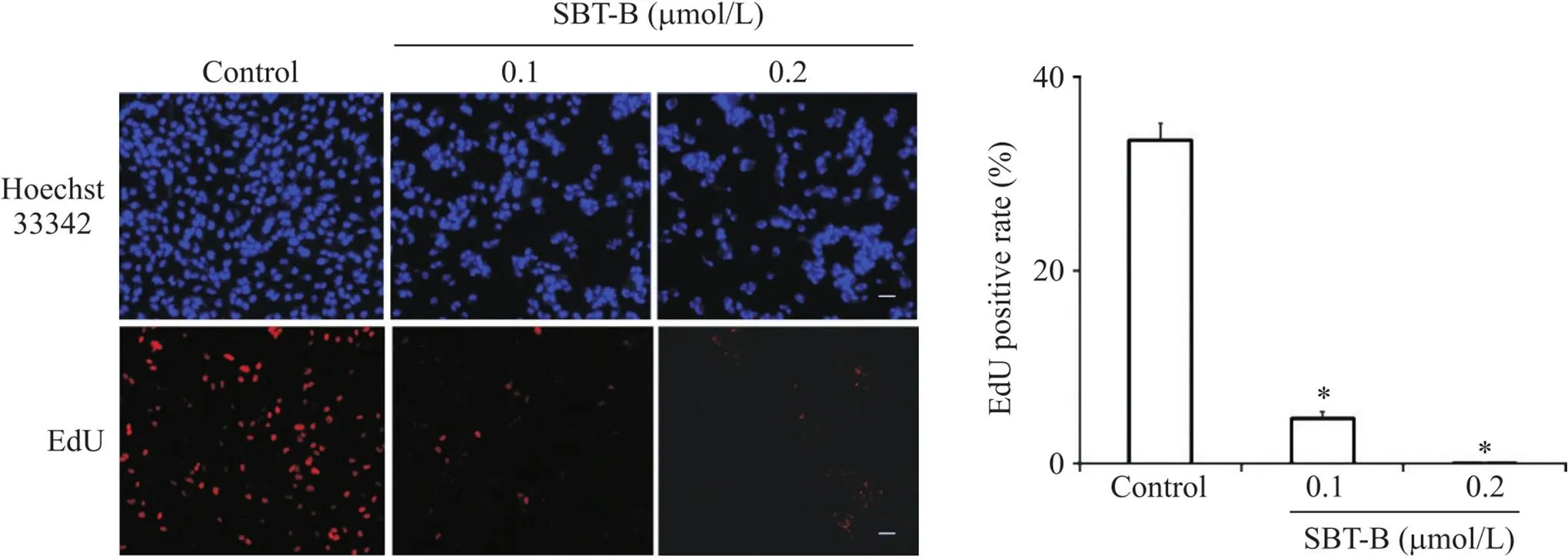
Figure 2. Effect of scutebarbatine B (SBT-B) on the proliferation of U251 cells. The cells were exposed to SBT-B (0.1 and 0.2 μmol/L) for 24 h, and EdU incorporation assay was used to assess the cell proliferation (scale bar=40 μm). Mean±SD. n=3. *P<0.05 vs control group.
3 SBT-B诱导U251细胞DNA双链断裂
免疫荧光结果表明,U251细胞经SBT-B处理24 h后,DNA双链断裂标志分子H2AX的磷酸化(γ-H2AX)灶点数目显著增加(图3)。同时,γ-H2AX的蛋白表达水平显著升高(<0.05),见图4。

Figure 3. Scutebarbatine B (SBT-B) induced γ-H2AX foci formation. The U251 cells were treated with 0.1 and 0.2 μmol/L of SBT-B for 24 h, followed by γ-H2AX staining (scale bar=20 μm). Mean±SD. n=3. *P<0.05 vs control group.

Figure 4. Scutebarbatine B (SBT-B) up-regulated the expression of γ-H2AX. The U251 cells were treated with different concentrations of SBT-B for 24 h, and Western blot analysis was used to detect the expression of γ-H2AX. Mean±SD. n=3. *P<0.05 vs control group.
4 SBT-B对DNA损伤修复蛋白表达影响
Western blot检测了SBT-B对DNA损伤修复相关蛋白表达的影响。图5显示,U251细胞经SBT-B作用24 h后,同源重组修复相关蛋白Rad51的表达水平显著降低(<0.05),而Ku86和Ku70的蛋白表达无显著差异。

Figure 5. Effect of scutebarbatine B (SBT-B) on the expression of Ku70, Ku86 and Rad51. The U251 cells were treated with various concentrations of SBT-B for 24 h, and total cellular extracts were subjected to Western blot analysis with antibodies of Ku70, Ku86 and Rad51. Mean±SD. n=3. *P<0.05 vs control group.
5 SBT-B促进U251细胞凋亡
TUNEL结果显示,SBT-B处理U251细胞24 h后,凋亡细胞数量显著增加(<0.05),见图6。

Figure 6. Scutebarbatine B (SBT-B) induced the apoptosis of U251 cells. The cells were treated with indicated concentrations of SBT-B for 24 h, and the apoptosis was detected by TUNEL staining (scale bar=20 μm). Mean±SD. n=3. *P<0.05 vs control group.
Western blot结果表明,SBT-B显著促进PARP、caspase-8和caspase-9的剪切(<0.05),见图7。

Figure 7. Effect of scutebarbatine B (SBT-B) on the cleavage of capase-8, caspase-9 and PARP. The U251 cells were treated with indicated concentrations of SBT-B for 24 h, and the protein levels of cleaved capase-8, caspase-9 and PARP were detected by Western blot. CF: cleavage fragment. Mean±SD. n=3. *P<0.05 vs control group.
6 SBT-B激活MAPK信号通路
Western blot结果表明,SBT-B作用24 h后,U251细胞中的ERK1/2、p38 MAPK和JNK1/2的磷酸化水平显著升高(图8)。
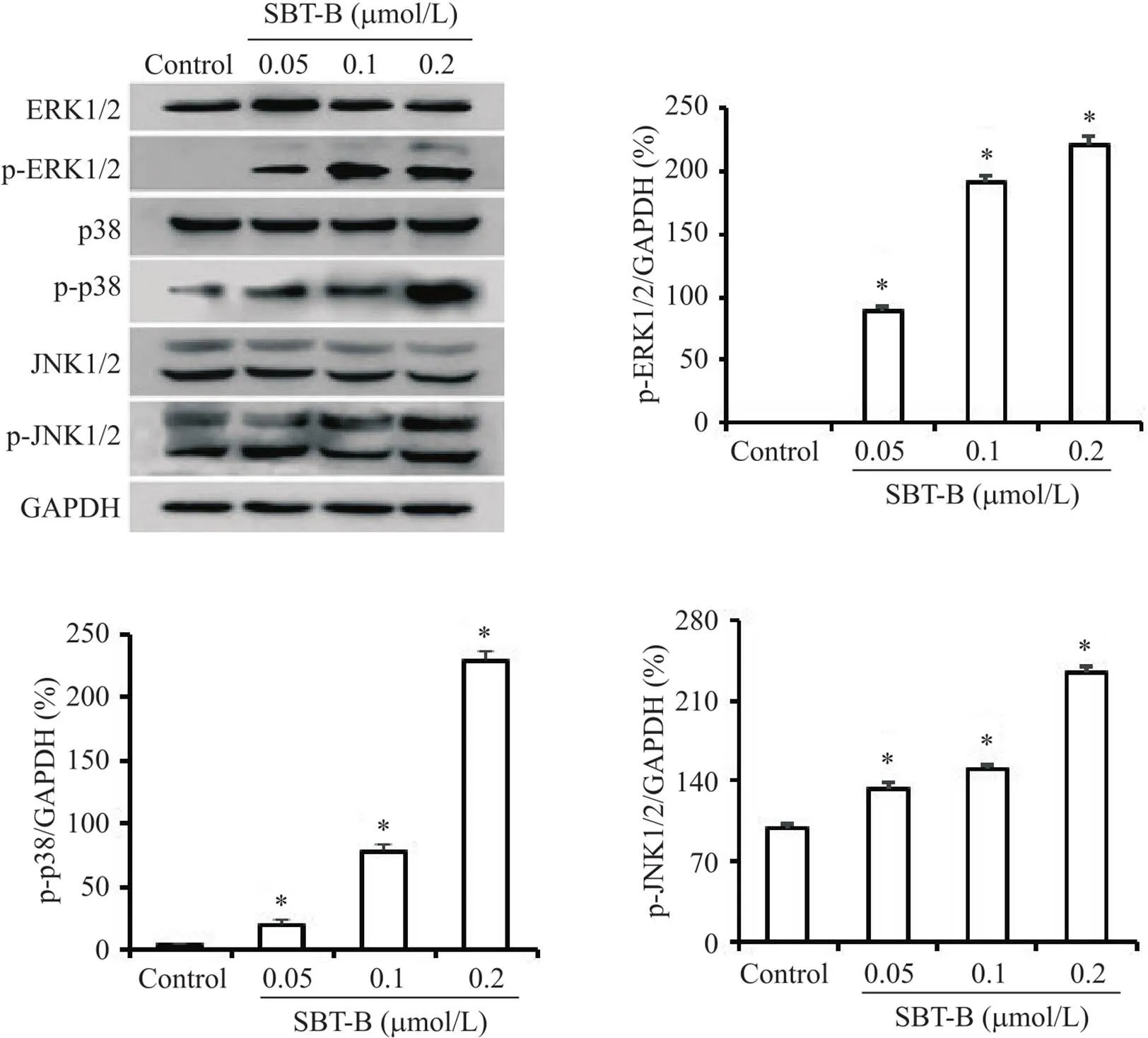
Figure 8. Scutebarbatine B (SBT-B) activated MAPK signaling pathway. The U251 cells were treated with indicated concentrations of SBT-B for 24 h, and the protein levels of p-ERK1/2, p-JNK1/2 and p-p38 MAPK were measured by Western blot. Mean±SD. n=3. *P<0.05 vs control group.
讨论
二萜类生物碱是中草药半枝莲抗肿瘤活性的主要有效成分[6]。本研究探讨了半枝莲中生物碱SBT-B对胶质瘤细胞的体外抑制活性。台盼蓝染色实验结果表明,SBT-B能够剂量依赖性地降低U251细胞活力,EdU掺入法则显示了SBT-B对U251细胞增殖的抑制作用。此外,本研究表明SBT-B能够诱导DNA损伤和细胞凋亡,通过激活MAPK信号通路而对胶质瘤细胞起抑制作用。
诱导细胞DNA损伤是抗肿瘤药物的主要抑癌机制之一[11]。本研究在证实SBT-B抑制胶质瘤细胞增殖的基础上,同时检测了SBT-B对细胞DNA损伤的影响。DNA双链断裂(DNA double-strand break,DSB)是DNA损伤的常见形式,而γ-H2AX灶点数量增多是发生DSB的重要标志[12]。本研究显示U251细胞经SBT-B作用后,γ-H2AX灶点数量及蛋白表达均显著增加,表明SBT-B能够诱导U251细胞DNA发生DSB。当DSB发生后,细胞立即启动DNA修复,如同源重组修复和非同源的末端连接修复等[13],SBT-B下调Rad51的蛋白表达则表明SBT-B抑制DNA同源重组修复。
细胞凋亡是基因组DNA出现严重损伤时所启动的应对措施之一,主要包括外源性途径和内源性途径。外源性途径由死亡受体介导,caspase-8是该凋亡途径的起始因子;内源性途径则是线粒体介导的细胞凋亡,可由caspase-9启动[14]。两条途径均可激活下游caspase-3的活性剪切,诱导底物PARP发生水解,促进细胞凋亡。本研究证实SBT-B促进了casapse-8和caspase-9的活性剪切,表明SBT-B能够通过调控内源性和外源性凋亡途径而诱导胶质瘤细胞凋亡。
MAPK信号通路主要包括ERK、JNK和p38 MAPK三条经典的信号途径,广泛参与调控细胞增殖、凋亡及耐药性等各种生理病理过程[15]。另外,多种天然药物通过调控MAPK信号通路活性而抑制肿瘤的发生发展[16-17]。因此,本研究检测了SBT-B对MAPK家族三个主要成员磷酸化活性的影响,结果显示SBT-B上调ERK、JNK和p38 MAPK的磷酸化水平,表明SBT-B可能通过调控MAPK通路而对U251细胞发挥抑制作用,但该通路是否为SBT-B的直接作用靶点尚需进一步研究。
总之,SBT-B能够抑制U251细胞增殖,并诱导DNA损伤和细胞凋亡,同时下调DNA修复相关蛋白Rad51的表达。此外,SBT-B可能通过激活MAPK信号通路而抑制胶质瘤细胞活性。本研究为阐明半枝莲及其有效成分抗肿瘤作用的分子机制提供了参考。
[1] Barthel L, Hadamitzky M, Dammann P, et al. Glioma: molecular signature and crossroads with tumor microenvironment[J]. Cancer Metastasis Rev, 2022, 41(1):53-75.
[2]吴朗杰,赵春燕,战丽彬. 基于网络药理学和分子对接研究白花蛇舌草和半枝莲药对治疗宫颈癌的作用机制[J]. 中草药, 2021, 52(4):1049-1058.
Wu LJ, Zhao CY, Zhan LB. Mechanism ofandin treatment of cervical cancer based on network pharmacology and molecular docking[J]. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs, 2021, 52(4):1049-1058.
[3]齐卓操,唐德才,尹刚,等. 基于数据挖掘的古今医方辨治消化系统肿瘤用药规律研究[J]. 中草药, 2019, 50(22):5632-5638.
Qi ZC, Tang DC, Yin G, et al. Research on drug use rules of ancient and modern medical prescriptions for differentiation and treatment of digestive system tumors based on data mining[J]. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs, 2019, 50(22):5632-5638.
[4]马婷婷,张甘霖,张博然,等. 半枝莲和白花蛇舌草药对的研究现状[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2021, 36(6):3491-3494.
Ma TT, Zhang GL, Zhang BR, et al. Research status of the couplet medicines Herba Scutellariae Barbatae and Herba Hedyotis[J]. Chin J Tradit Chin Med Pharm, 2021, 36(6):3491-3494.
[5] Feng PP, Qi YK, Li N,et al. Scutebarbatine A induces cytotoxicity in hepatocellular carcinoma via activation of the MAPK and ER stress signaling pathways[J]. J Biochem Mol Toxicol, 2021, 35(5):e22731.
[6] Chen Q, Rahman K, Wang SJ, et al.: a review on chemical constituents, pharmacological activities and clinical applications[J]. Curr Pharm Des, 2020, 26(1):160-175.
[7] Zhu F, Di YT, Li XY, et al. Neoclerodane diterpenoids from[J]. Planta Med, 2011, 77(13):1536-1541.
[8]李锦梅,李丹丹,严威,等. 半枝莲新克罗烷型二萜成分逆转肿瘤多药耐药活性研究[J]. 天然产物研究与开发,2020,32(3):365-372.
Li JM, Li DD, Yan W, et al. Reversal of multi-drug resistance in HepG2/ADR cells by neo-clerodane diterpenoids from[J]. Nat Prod Res Dev, 2020, 32(3):365-372.
[9] Sargazi S, Saravani R, Zavar Reza J, et al. Induction of apoptosis and modulation of homologous recombination DNA repair pathway in prostate cancer cells by the combination of AZD2461 and valproic acid[J]. EXCLI J, 2019, 18:485-498.
[10] Li ZJ, Hou YJ, Hao GP, et al. CUDC-907 enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis through upregulation of DR5 in breast cancer cells [J]. J Cell Commun Signal, 2020, 14(4):377-387.
[11] 焦鹏,黄振州,张晓静,等. CUDC-907诱导胶质瘤细胞DNA损伤与自噬的实验研究[J]. 中国病理生理杂志, 2019, 35(2):260-266.
Jiao P, Huang ZZ, Zhang XJ, et al. CUDC-907 induces DNA damage and autophagy in glioma cells[J]. Chin J Pathophysiol, 2019,35(2):260-266.
[12] Zhao Y, Chen S. Targeting DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair to counteract tumor radio-resistance[J]. Curr Drug Targets, 2019, 20(9):891-902.
[13] 姚德山,张振刚,龚开政. PIKK调控DNA双链断裂修复的研究进展[J]. 中国病理生理杂志, 2020, 36(4):741-746.
Yao DS, Zhang ZG, Gong KZ. Progress in DNA double-strand break repair regulated by PIKK[J]. Chin J Pathophysiol, 2020, 36(4):741-746.
[14] Shi Y. Mechanisms of caspase activation and inhibition during apoptosis[J]. Mol Cell, 2002, 9(3):459-470.
[15] Fang JY, Richardson BC. The MAPK signalling pathways and colorectal cancer[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2005, 6(5):322-327.
[16] Zhao J, Li P, Zhu H, et al. 7,8-Dihydroxyflavone suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis of human osteosarcoma cells[J]. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai), 2021, 53(7):903-911.
[17] Ye XS, Tian WJ, Zhou M, et al. Prenylated flavonoids frominduces HeLa cells apoptosis via MAPK and AKT signaling pathways[J]. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 2021, 38:127859.
Scutebarbatine B suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis of human glioma U251 cells
HAO Xiao-shan, FENG Pan-pan, ZHANG Yun-yun, FEI Hong-rong△
(,,271016,)
To investigate the effect of scutebarbatine B (SBT-B) on the proliferation, DNA damage and apoptosis of human glioma U251 cells.The U251 cells were treated with various concentrations (0.05, 0.1 and 0.2 μmol/L) of SBT-B for 24 h, and the cell viability was detected by Trypan blue staining assay. The U251 cells were divided into control group, 0.05 μmol/L SBT-B group, 0.1 μmol/L SBT-B group and 0.2 μmol/L SBT-B group according to the value of IC50. EdU incorporation assay was used to determine the inhibitory effect of SBT-B (0.1 and 0.2 μmol/L) on the cell proliferation. DNA damage was measured by immunofluorescence assay. Apoptosis was detected by TUNEL method. The expression levels of apoptosis-related proteins, DNA damage repair-related proteins and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway-related proteins were detected by Western blot.Treatment with SBT-B inhibited the viability and proliferation of U251cells (<0.05). Treatment with SBT-B for 24 h significantly increased γ-H2AX foci formation and protein levels, wihile the expression of Rad51 was down-regulated (<0.05). Treatment with SBT-B induced cell apoptosis and cleavage of caspase-8, caspase-9 and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) in U251 cells (<0.05). In addition, SBT-B increased the phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and p38 MAPK (<0.05).Treatment with SBT-B inhibits cell proliferation and triggers DNA damage and apoptosis through MAPK signaling pathway in U251 cells.
Scutebarbatine B; Glioma; DNA damage; Apoptosis; Mitogen-activated protein kinase
R739.4; R285.5
A
10.3969/j.issn.1000-4718.2022.06.006
1000-4718(2022)06-1001-07
2022-02-21
2022-05-20
国家自然科学基金资助项目(No. 81703039);山东省中医药科技项目(No. 2020M062);山东第一医科大学学术提升计划(No. 2019LJ003)
Tel: 15662099068; E-mail: hrfei@sdfmu.edu.cn
(责任编辑:李淑媛,罗森)
