Evidence and thinking on risk factors of hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage:a meta-analysis
2022-06-28LeiYangJiaLiuZhuangLiangShaoHongLiLiYunHe
Lei Yang,Jia Liu,Zhuang Liang,Shao-Hong Li,Li-Yun He*
1Shaanxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Xianyang 712000, China.2Institute of Clinical Basic Medicine, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences,Beijing 100700,China.
Abstract Background: To explore the related risk factors of hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH)through meta-analysis, and to provide evidence-based medical basis for preventing ICH in hypertensive patients. Methods: The databases of CNKI, Wanfang, VIP, CBM, PubMed, Web of Science and Cochrane Library were searched by computer.Case control study on risk factors for hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage were collected from the database establishment to October 2021.Two reviewers independently screened the literature,extracted the data,and evaluated the bias risk of the included studies.Meta-analysis was conducted on the results of the included studies using RevMan5.3 software. Results: A total of 7 studies were included, including 1512 patients.Meta-analysis results showed that: Smoking history (OR = 6.23, 95%CI (4.32,8.99),P<0.00001), drinking history (OR = 7.24, 95%CI (1.96,26.72), P= 0.003), diabetes mellitus (OR =47.52,95%CI(10.31,219.31), P<0.00001),coronary heart disease(OR=9.90,95%CI(2.96,33.13),P = 0.0002), daily salt intake (OR = 10.21, 95%CI (2.69,38.79), P = 0.0006), failure to take medication regularly on time(OR=10.62, 95%CI(5.40,20.91),P<0.00001),total cholesterol(OR=6.58, 95%CI (2.45,17.65), P = 0.0002), triglyceride (OR = 8.63, 95%CI (6.70,11.12), P<0.00001),body mass index (OR = 6.63, 95%CI (4.56,9.64), P<0.00001) and experiencing severe economic difficulties (OR = 23.97, 95%CI (14.82,38.77), P<0.00001) were risk factors for hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage. Conclusion: Controlling smoking, drinking, reducing daily salt intake,controlling body weight, preventing diabetes and coronary heart disease, low-fat diet, controlling total cholesterol and triglyceride, taking antihypertensive drugs regularly and improving economic status can prevent hypertensive cerebral hemorrhage.
Keywords:hypertensive cerebral hemorrhage;risk factors;Meta-analysis;case-control study
Background
Hypertensive cerebral hemorrhage (HICH) is one of the most serious complications of hypertension [1] the disease mainly occurs in the middle-aged and elderly people, with a high mortality and mortality rate of 70% and 85% respectively [2].In recent years, with the improvement of medical imaging technology and neurosurgery, HICH misdiagnosis rate and mortality declined, but still not seen obviously decreased the disability and mortality rate, high morbidity brings heavy burden to patients families and society [3] therefore understand the risk factors of hypertensive cerebral hemorrhage and prevention and control, to reduce the incidence of hypertension cerebral hemorrhage It is of great significance to improve patients'quality of life and reduce social and family economic burden.
This study conducted a meta-analysis of literatures on the risk factors of hypertensive ich published at home and abroad from the establishment of the database to October 2021, so as to explore the related risk factors of hypertensive ICH and provide evidence-based medical basis for reducing the occurrence of ICH in hypertensive patients.
Data and Methods
Data
The literatures were retrieved from CNKI,Wanfang Database,VIP database,CBM,PubMed,Web of Science and Cochrane Library.
Method
Information retrievalSearch for the literature on the study of risk factors of hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage published in the above database until October 2021; At the same time, references to the included literatures were traced back, and the English keywords were combined with subject words and free words, including hypertension intracerebral pressure, risk factors,and influence factors.Correlation factors, Case-control study, etc.Take CNKI as an example,and see box 1 for the specific retrieval strategy.

Box 1 CNKI search policy
Inclusion and exclusion criteriaInclusion criteria : (1) original literatures on the related risk factors of hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage published till now; (2) Subjects were hypertensive cerebral hemorrhage; (3)Case-control study, the total number of cases with hypertensive cerebral hemorrhage and the number of cases with control group; (4) The data were complete and the statistical method was correct.Analysis indicators include odds ratios (OR) of risk factors and their 95% confidence intervals (CI), OR the OR value and their 95% CI can be calculated; (5) included literature contains at least one exclusion criteria for risk factors : (1) review of systematic evaluation of case report conference papers animal experiments;(2)The subjects were cerebral hemorrhage caused by traumatic vascular malformation and tumor; (3) repeated publication; (4) Poor quality or incomplete data indicators with errors; (5) Literature on non-case control studies.
Literature selection, data collection and quality evaluationTwo researchers independently screened the literature according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria of the literature, and determined the literature to be included in the meta-analysis.The data included in the literature were as follows:the name of the first author,the year of publication,the total number of samples, the number of hypertensive cerebral hemorrhage cases, the number of control cases, risk factors and related factors.The case control study used Newcastle-OttawaThe full score of NOS Scale is 9 stars, and literatures with 6 stars can be included in Meta analysis.In the process of data collection and quality evaluation of literature screening, if conclusions of 2 researchers are inconsistent, the two sides should discuss and solve the problem,or a third researcher should review and assist to solve the problem.
Statistical method
RevMan5.3 software was used for analysis.The odds ratio (OR) and 95%CI were used to represent inter-study heterogeneity.χ2test was used to analyze inter-study heterogeneity(test level α=0.1).0.1 and I2<50%,indicating that there was no heterogeneity among studies, and the fixed-effect model was used for meta-analysis.If P<0.1 or I2>50%,indicating that there was heterogeneity among studies, the source of heterogeneity was further analyzed.After excluding the influence of obvious clinical heterogeneity, a random-effect model was used for Meta analysis to determine P<.0.05 were statistically significant differences in clinical heterogeneity and were treated by subgroup analysis or sensitivity analysis, or only descriptive analysis.
Result
Literature screening process and results
A total of 908 related literatures were retrieved.After eliminating duplicate literatures, 7 [5–11] literatures were included for meta analysis after further careful reading of titles, abstracts and full texts according to inclusion and exclusion criteria.Literature screening process is shown in Figure 1.
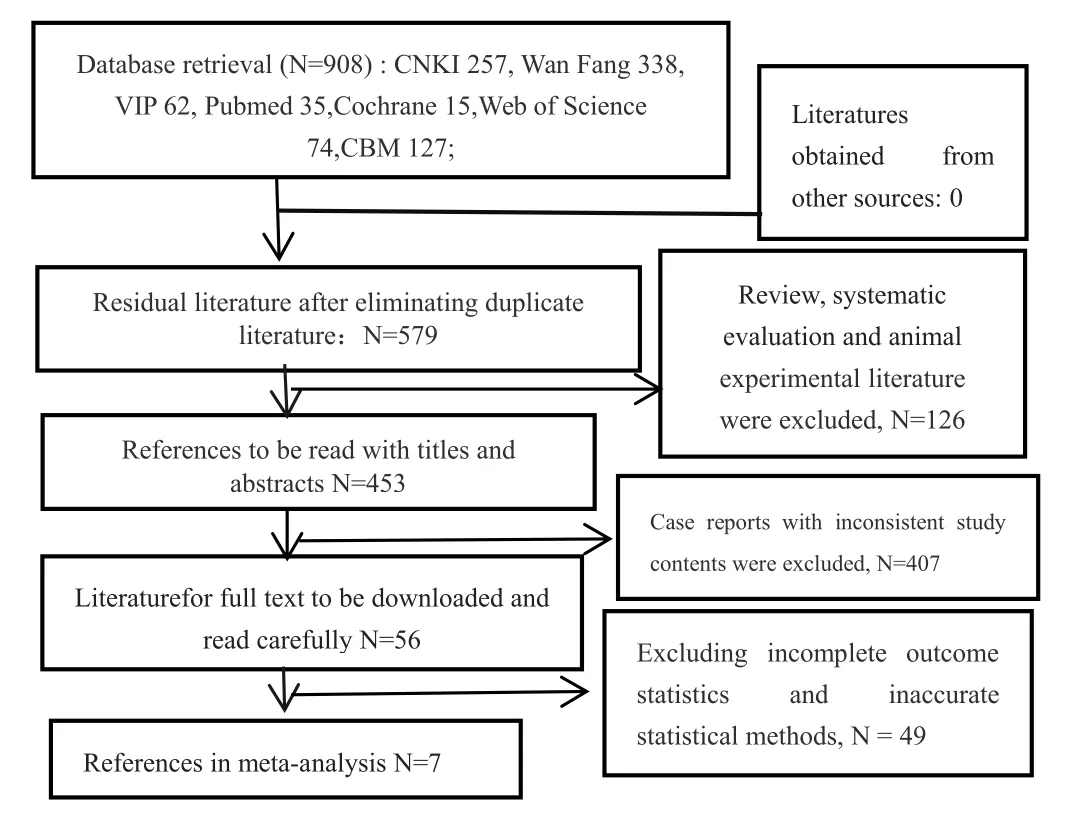
Figure 1 Flow chart of literature screenin
Basic information and quality evaluation of the included literature
The 7 included meta-analysis literatures were all case-control studies,with a total of 1512 patients, including 680 hypertensive cerebral hemorrhage patients and 832 control patients.10 risk factors were included in the analysis, as shown in Table 1.Literature quality was evaluated with NOS scale,and all included literatures were rated 7–8 points,as shown in Table 2.

Table 1 Basic features of the included studies
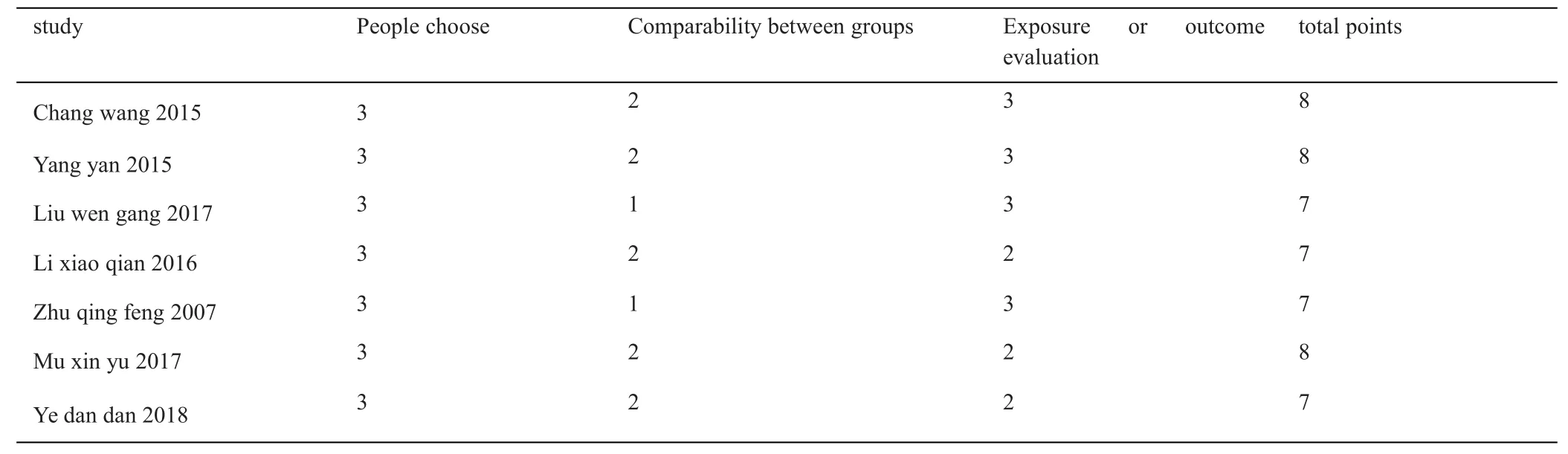
Table 2 Bias risk evaluation results of included case-control studies(score)
The results of meta-analysis showed that smoking history
(OR = 6.23,95%CI(4.32,8.99),P< History (0.00001) drinking OR = 7.24,95% CI (1.96, 26.72),P= 0.003) (with diabetes mellitus OR = 47.52, 95%CI(10.31,219.31),P<0.00001)combined coronary heart disease(CHD)(OR = 9.90, 95% CI (2.96, 33.13),P= 0.0002), salt (OR = 10.21, 95% CI(2.69, 38.79),P= 0.0006) Failure to take medicine regularly on time (OR =10.62,95%CI(5.40,20.91),P< 0.00001) total cholesterol (OR = 6.58, 95%CI(2.45,17.65),P=0.0002)triglycerides(OR=8.63,95%CI(6.70,11.12),P& lt; 0.00001) body-mass index (OR = 6.63, 95% CI (4.56, 9.64), P& lt;0.00001)severe economic difficulties(OR=23.97,95%CI(14.82,38.77),P& lt; All were risk factors for cerebral hemorrhage in hypertensive patients.Results of meta-analysis are shown in Figure 2–11.

Figure 2 Forest map of smoking history analysis
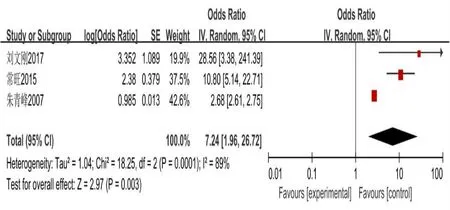
Figure 3 Forest map of drinking history analysis
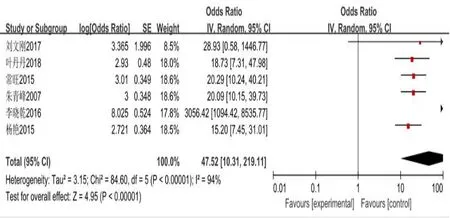
Figure 4 Forest map with diabetes analysis
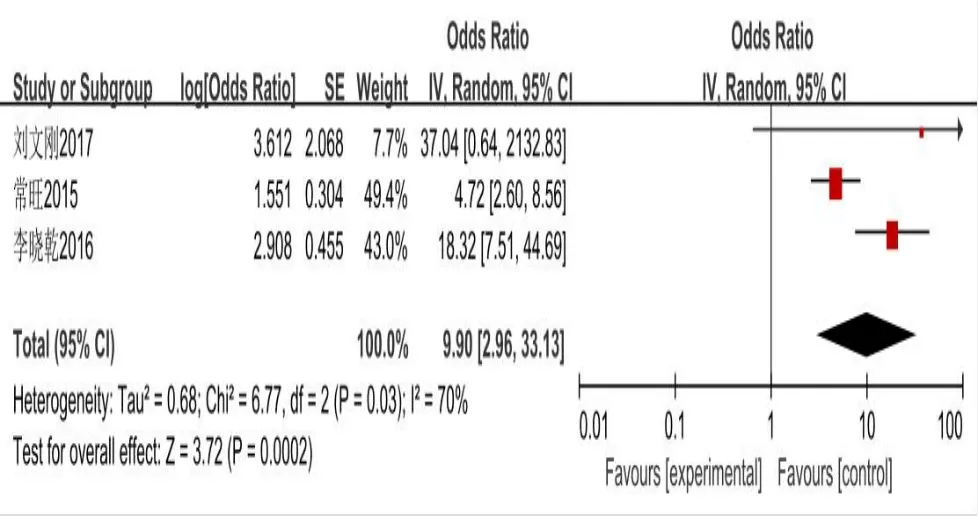
Figure 5 Analysis of forest with coronary heart disease

Figure 6 Forest map of failure to take medicine regularly on time
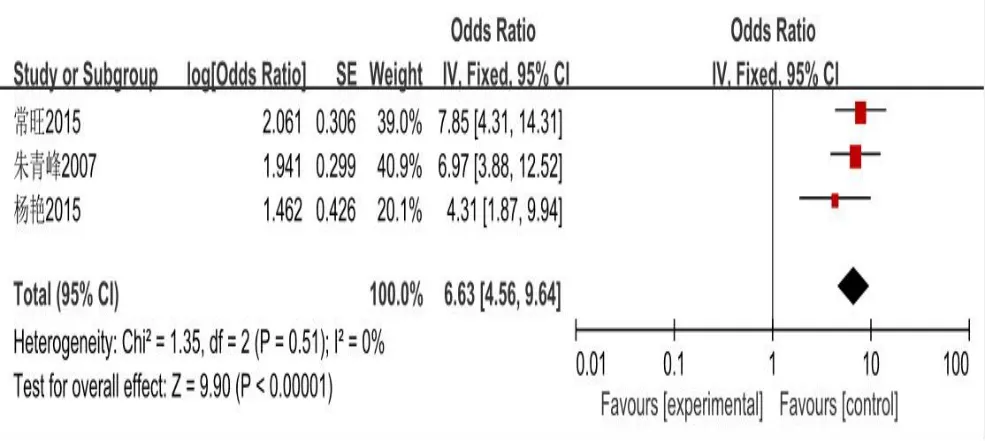
Figure 7 Forest map of bmi analysis
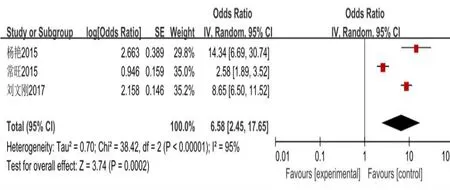
Figure 8 Forest map of total cholesterol analysis

Figure 9 Forest map of triglyceride analysis

Figure 10 Analysis of daily salt intake forest map
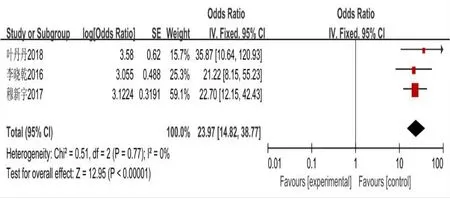
Figure 11 Analysis of forest maps experiencing severe economic hardship
Publish bias analysis
When the number of included literatures was small,potential publication bias already existed.In this study, an inverted funnel plot was drawn for risk factors with the number of included literatures ≥6, and a funnel plot was drawn for the exposure factor of smoking to test publication bias.The results showed that the distribution around each research point was basically symmetric,suggesting no obvious publication bias(Figure 12).
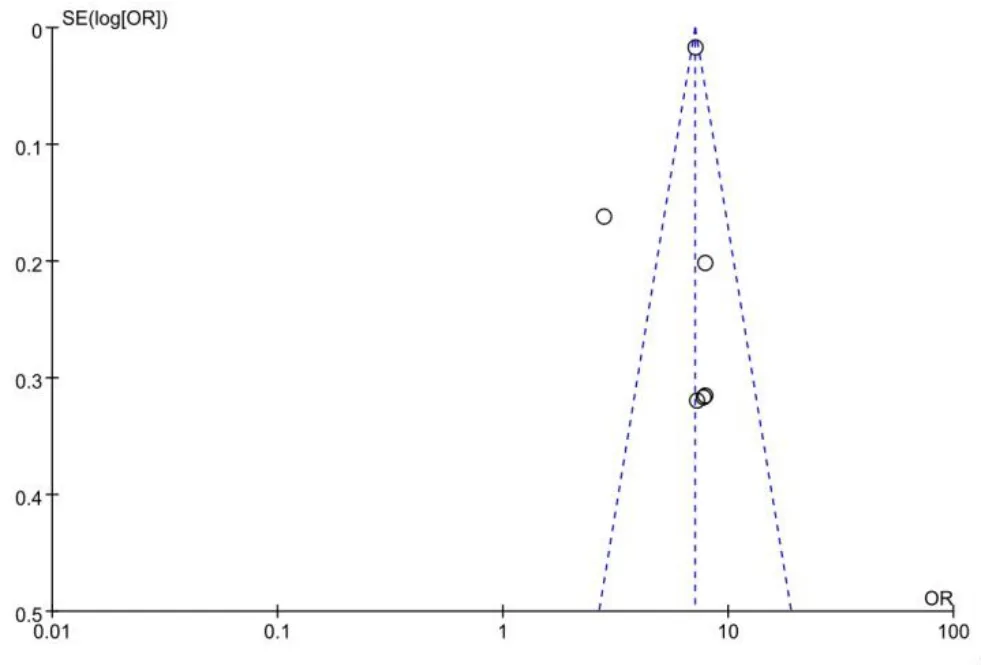
Figure 12 Inverted funnel plot of smoking history analysis
Discussion
Epidemiological studies show that the number of patients with essential hypertension in China has reached more than 100 million,with an increasing trend year by year, and only a small number can be effectively controlled[12, 13].According to statistics, the incidence of CEREBRAL hemorrhage(60–80) people/(100,000 · years), and the majority of cerebral hemorrhage patients with hypertension, in the whole cerebrovascular diseases of cerebral hemorrhage mortality in the first [14].Hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage is one of the most serious complications of hypertension and a serious threat to human life and health due to the dramatic increase in blood pressure caused by emotional agitation, excessive mental and physical labor or other factors, resulting in the rupture and hemorrhage of the damaged cerebrovascular vessels[15].
This study summarized and analyzed 7 case-control studies with a sample size of 1512 cases.The results showed that smoking and drinking,diabetes, coronary heart disease, failure to regularly take antihypertensive drugs, high cholesterol, triglyceride, obesity, excessive daily salt intake, and severe economic difficulties were all risk factors for cerebral hemorrhage in hypertensive patients However, the heterogeneity among different studies is large, mainly due to the different time sample sizes of the population investigated.
Studies have shown that decreased elasticity of cerebrovascular artery wall and long-term hypertension are the internal and external causes of cerebral hemorrhage.Smoking will damage vascular endothelial function,thicken the intima of vascular wall, lead to lipid deposition, cause and gradually aggravate the inflammatory response of vascular endothelium, and eventually lead to accelerated thickening of intima thickness The deterioration of vascular elasticity leads to plaque formation and other pathological changes, which ultimately leads to the increase of blood pressure and vascular fragility, and increases the risk of cerebrovascular hemorrhage [16, 17].Long-term heavy drinking can lead to increased blood pressure, while affecting blood components such as platelet red blood cells and fibrinogen [18], increasing the risk of HICH.Diabetes is a systemic metabolic disorder, not only can affect the metabolism of the sugar, lead to high blood sugar, can also affect the protein and lipid metabolism and lipid metabolism disorders and hyperlipidemia, causing blood vessels injury narrow, induce coronary atherosclerosis, eventually leading to blood vessel brittleness increases, so will increase the risk of hypertension cerebral hemorrhage [19, 20]; Coronary atherosclerosis in patients with coronary heart disease causes changes in hemorheology, which easily leads to thrombosis and increased blood pressure,and then affects cerebrovascular,making it more prone to rupture and cause intracerebral hemorrhage; High triglycerides and total cholesterol levels, namely, hyperlipemia,hyperlipidemia is the damage to the body hidden gradually developed and generalized, such as too many blood lipid, will gradually deposit in arterial blood tube wall, make the artery wall thickening Harden and form a atherosclerosis,increased the risk of vascular rupture bleeding; Patients with high BODY mass index generally have high blood lipids[21],which is also a risk factor for HICH.Irregular taking of antihypertensive drugs is also a risk factor for HICH.Yang Lin [22] investigated the compliance of 302 patients with hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage taking antihypertensive drugs,and found that only 13.60% of patients took drugs regularly and monitored their blood pressure regularly , suggesting that the treatment compliance of hypertension patients is poorer, not regular medication and regular monitoring blood pressure, causing blood pressure fluctuations, lead to HICH This research shows that severe economic hardship is the leading cause of HICH happen risk factors, the author consider emotional instability in patients with economic difficulties, the blood pressure fluctuation is too big,may result in HICH happen.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cultivating and maintaining good living habits, quitting smoking and drinking, controlling body weight, reducing daily salt intake,regularly taking antihypertensive drugs, reducing the occurrence of hypertension, hyperglycemia and hyperlipemia or effectively controlling the development of the disease of hypertension,hyperglycemia and hyperlipemia can significantly improve hypertension and reduce the occurrence of hypertensive cerebral hemorrhage.
