Vancomycin dosing in an obese patient with acute renal failure: A case report and review of literature
2022-06-27KunYanXuDanLiZhenJieHuCongCongZhaoJingBaiWenLiDu
lNTRODUCTlON
Since 1980, the prevalence of obesity has more than doubled worldwide. It is estimated that by 2030,60% of the world's adult population will be classified as obesity[1]. In the United States from 2013 to 2014, the prevalence of obesity was 35.0% for male and 40.4% for female adults, and there was a significant linear increasing trend among women in the prevalence of obesity from 2005 through 2014[2]. Obesity has also become a major public health burden in China. Over the past 40 years, the prevalence of obesity has increased significantly. The nationally representative survey showed that more than half of the Chinese adults are obese according to the Chinese standards[3]. The increased prevalence of obesity poses a challenge for clinicians to deliver optimized doses of antimicrobial drugs in the intensive care unit. Obesity is a key risk factor for community and hospital-acquired infections[4],and increases risks of incidence and mortality compared to non-obese individuals[5]. It may affect the pharmacokinetics of antimicrobial agents, particularly in patients requiring high-dose antimicrobial therapy[6], and can also influence the immune response and increase susceptibility to infections[7],resulting in a high risk of infection in obese patients[8]. As a consequence, clinicians are increasingly facing severely obese patients requiring antibiotic treatment. However, few studies have summarised the published data and provided clinical guidance for effective dosing in these patients.
A Summary of the Research Achievements of Mongolian Folk Songs Published
The treatment produced significant improvement in the patient’s respiratory status and the infection.Vancomycin and CRRT treatment were subsequently discontinued on December 24. Two days later, the patient was transferred out of the ICU to continue treatment. He was well with no further complaints at the routine 1-mo follow-up.
Although the pharmacokinetics of vancomycin in the general population is well-described, to the best of our knowledge, only a few studies have investigated the effect of vancomycin dose in the obese population. This study reports the medical records of dose adjustment of vancomycin in an obese patient weighing up to 240 kg, including the dose adjustment protocol in the acute renal injury. This article also reviews the current literature on the application of vancomycin in the obese population and provides recommendations on how to make dose adjustments based on the available evidence.
今天的花卉供应市场面向大众消费,常有新品种花卉吸引顾客,古典园林自然可以基于市场供应丰富花卉种类。当然,花卉的选择范围应当谨慎推敲,尤其是园林厅堂摆花的位置、品种都应与特定的园林意境要求和室内风格特点呼应,这也是苏州古典园林造园技艺的一个部分。清代李渔在《闲情偶寄》中明确指出选择厅堂摆设花卉的标准主要集中于芳香、姿态和花期3个方面[3]。
CASE PRESENTATlON
Chief complaints
A 40-year-old man was referred to our intensive care unit (ICU), with the complaints of chest tightness and shortness of breath with no obvious cause for 3 mo.
History of present illness
In November 2020, the patient reported chest tightness and shortness of breath with no obvious cause.Three days later, the patient’s symptoms aggravated with abdominal distension and edema of both lower limbs. He was admitted to the ICU of a local hospital for acute respiratory failure. After 2 wk of treatment, the patient still had persistent fever and was transferred to the ICU of our hospital on November 18, 2020.
History of past illness
The patient had suffered from hypertension for 3 years and erysipelas of the right lower extremity for 2 years.
Personal and family history
The patient had no specific personal or family history.
Physical examination
In summary, we report a case of adjusting the blood concentration of vancomycin with enhanced effectiveness in an obese patient. The initial TBW of the patient with normal renal function was 240 kg.Thus, the patient should receive an initial TBW-based load of 6 to 7.2 g of vancomycin every day.However, the dose of vancomycin is greater than 4 g/d, which increases the risk of nephrotoxicity[51].Following the recommended dose limit of 3 g, the patient received an initial TBW-based loading dose of 2 g and a maintenance dose of 1 g of vancomycin every 8 h. The initial serum concentration of 11.7 μg/mL was obtained, after the patient had received three doses of vancomycin. The serum concentration demonstrated that the dosing regimen is reasonable. Due to acute renal failure with reduced urine output or even anuria, intravenous injection of vancomycin at 3 g/d led to a blood concentration of vancomycin that was higher than 20 μg/mL. We immediately reduced the dose of vancomycin and monitored the blood concentration of the drug. On the 29day, the patient was treated with CRRT, the dosage regimen of vancomycin was 1 g every 12 h considering the clearance of vancomycin by CRRT,and the blood concentration was 13.3 μg/mL. The final blood concentration of vancomycin was maintained in the range of 10 to 20 mg/L.
Laboratory examinations
The culture of secretion revealedat a local hospital.
Imaging examinations
Case 2.The two sources exhibit both Gaussian distribution.
抽象执行的本质是在抽象域将程序变量的抽象表示形式作为程序变量本身带入程序进行计算。首先要对程序的变量和程序中的函数操作进行抽象表示,然后抽象域中执行程序的运行过程。
FlNAL DlAGNOSlS
The final diagnoses were: (1) Sepsis; (2) Acute respiratory distress syndrome; (3) Pneumonia; (4) Heart failure; (5) Necrotizing fasciitis of the scrotum and left lower extremity; and (6) Severe obesity.
近年来,玉米幼苗矮小细弱,叶窄叶薄发黄,心叶扭曲不舒展,轻者生长缓慢,重者幼苗枯死。也有的玉米地块叶片发紫逐渐枯死。因此,造成不少地块玉米参差不齐缺苗断条,导致部分农民对个别厂家的肥料质量产生质疑。
TREATMENT
The patient had pulmonary infection andwas detected in his secretion at the local hospital. His initial serum creatinine was 63.3 μmol/L and creatinine clearance (CrCl) was greater than 90 mL/min. Based on the patient's history and drug sensitivity testing results, intravenous levofloxacin 0.75 g/d and tigecycline 0.2 g/d were started empirically for anti-infection treatment. Then,linezolid 0.6 g intravenous injection every 12 h was prescribed to replace levofloxacin, and the patient's temperature decreased to normal after 3 d of treatment. On November 27, the patient developed a high fever (temperature up to 40.2 °C), and his high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) rose to 183.51 mg/L (Table 1). Considering the infection from the lower extremity and the scrotum, the patient received enhanced drainage and dressing change. Meanwhile, the culture of sputum and scrotal revealed. The linezolid was subsequently discontinued and intravenous infusion of vancomycin was started. Because the patient was severely obese, after reviewing the literature, we determined the dosing regimen of a loading dose (vancomycin administered as continuous infusion of 2 g over 2 h) and a maintenance dose (vancomycin 1 g infused over 60 min every 8 h). The vancomycin blood trough concentration was 11.7 μg/mL after the patient had received three doses of vancomycin.The patient developed acute renal failure due to the aggravation of infection, the serum creatinine levels showed a gradual increase, and the vancomycin trough concentration was greater than 20 μg/mL (up to 34.3 μg/mL). We then adjusted the vancomycin administration dose according to the blood drug concentration monitoring. On December 16, continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT) was used because of anuria of the patient. Given using continuous veno-venous hemodiafiltration mode, we adjusted the vancomycin administration dose to 1 g every 12 h, during which vancomycin blood drug concentration fluctuated between 10 and 20 μg/mL.
近些年来我国的公路里程不断创下历史新高,公路建设规模不断扩大,这就对公路工程建设提出了新的挑战。面对日益复杂的公路工程建设环境,只有严格做好公路工程质量的管理工作,才能够确保良好的工程质量。
OUTCOME AND FOLLOW-UP
Since the early 1980s, as the number of methicillin-resistant(MRSA) infections began to increase, vancomycin has become the drug of first choice for this microbial infection[9].Vancomycin belongs to glycopeptide antibiotic which acts by inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis[10].It is the most widely used antibiotic worldwide for the treatment of severe Gram-positive bacterial infections[11]. The binding of vancomycin to protein is approximately 50% to 55%[10]. The volume of distribution is 0.4-1 L/kg[9]. Vancomycin is primarily clearedrenal excretion[12]. The actual body weight of obese subjects increases the chance of vancomycin exposure and the incidence of vancomycinassociated nephrotoxicity[13]. Therefore, dose adjustment is required when vancomycin is used in obese patients, because of the effect of obesity on vancomycin pharmacokinetic parameters. One study shows that therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) significantly improves the clinical curative effect and reduces the incidence of nephrotoxicity in patients treated with vancomycin[14].
随着我校招生门槛的降低,学生人数逐年增加,现每班均超过50人,甚至达到110人。在健康评估实训教学中,一个班最多配备两位教师,各负责一半学生的教学与指导,很难保证教学质量,也会导致部分监管不到的学生无事可做,出现闲聊、玩手机及其他违纪行为,课堂纪律混乱。因此,师资力量不足,教师力不从心,已经成为健康评估实训教学急需解决的问题。
DlSCUSSlON
Vancomycin is a time-dependent antibiotic and a number of factors influence its clinical activity,including variable tissue distribution, dose size, and clearance rate[17]. One study showed that total body weight (TBW) influenced the Vand clearance (CL) of vancomycin (Table 2)[18]. As expected,obesity is a known factor affecting drug pharmacokinetics[19]. Vancomycin, as a hydrophilic drug, is able to penetrate and distribute, to a certain extent, in adipose tissues, thereby increasing the V[20]. A large retrospective study by Ducharme[21] showed that the Vwas greater in obese subjects than in normal subjects by examining pharmacokinetics of vancomycin in 704 patients. Blouin and his colleagues[22] also demonstrated statistically significant differences in weight-indexed Vbetween two groups of subjects. A recent study suggests that Vchanges in obese patients can be ascribed to the physicochemical properties of the drugs in most cases[23]. In addition, the degree of the Vdepends on the lipophilicity, hydrophilicity, protein binding, and molecular weight of the antibiotic[24]. In the obese population, higher cardiac output and blood volume may increase blood flow, and lead to larger V[25].Edema combined with fluid resuscitation can increase the Vof different antibacterial agents in obese,critically ill patients[26].


In recent years, body mass index (BMI) is a world-accepted grading method to assess the degree ofobesity. According to the criteria of the guideline, obesity is defined as a BMI of 30.0 kg/mor higher[15]. Based on the body weight and height of this patient, his BMI was calculated to be 78.4 kg/m,which met the threshold for obesity. Numerous physiopathological changes occur in obese individuals,including changes in distribution (V) and renal excretion[16].
Previous studies indicated that CL of vancomycin was much higher in the obese population,especially in young obese patients, and they required high doses to obtain adequate trough concentrations[9]. Han[27] demonstrated that obese adults exhibited higher drug clearance rates than nonobese ones. Unlike V, the physicochemical properties of drugs have little effect on CL, which is largely controlled by physiological processes[23]. The change in clearance was mainly attributed to an increase in kidney mass and renal blood flow in obese subjects[28]. Greater glomerular filtration rate and renal perfusion in obese individuals increase the CL of vancomycin[29]. At the same time, greater renal volume, hypertrophy of the renal unit, and hydrostatic pressure of the glomerulus were also associated with greater CL of vancomycin in the obese group[30]. Vancomycin is a hydrophilic drug with predominant renal excretion. Furthermore, augmented renal clearance (ARC), defined as a creatinine clearance more than or equal to 130 mL/min/1.73 m, refers to enhanced elimination of hydrophilic solutes by the kidneys[31]. The results indicate that ARC has been described in the obese, non-critically ill patient[32], and is a common finding in critically ill patients with normal plasma creatinine concentrations[33].
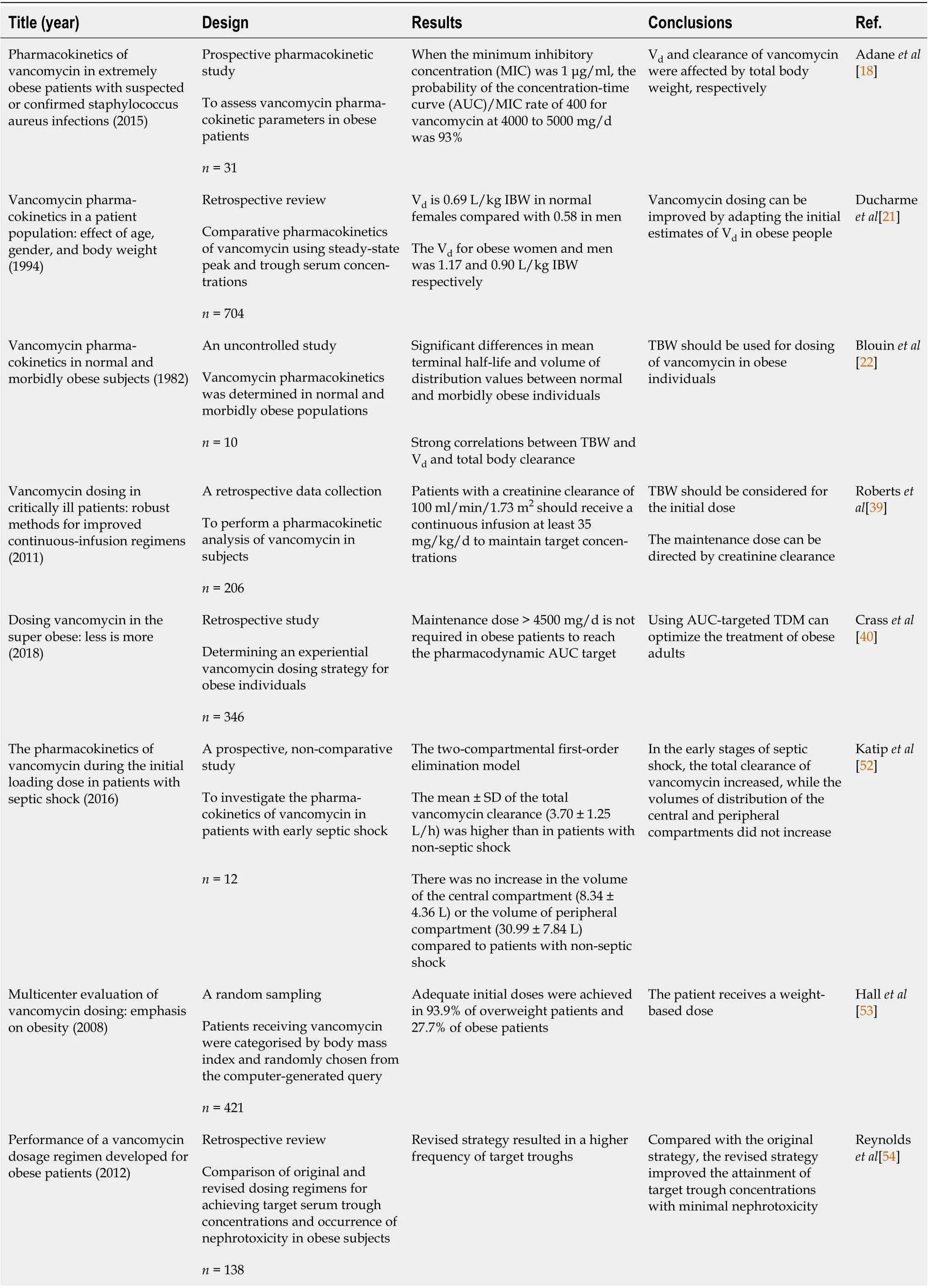
The option of vancomycin loading doses is dependent on the estimate of the V. Pharmacokinetic research had demonstrated that vancomycin Vincreases with increasing TBW[34]. The physicochemical properties of drugs lead us not to define a universal body-size parameter for the distribution and clearance of drugs. As a consequence, the body weight was used in dose selection for drug administration[35]. One guideline states that a reasonable approach to the initial dose of vancomycin in obese individuals is to increase the loading dose to 20 to 25 mg/kg TBW and to decrease the maintenance dose, then adjust the dose according to TDM[36]. The 2020 Infectious Diseases Society of America(IDSA) consensus recommends the use of a TBW-based loading dose of 20 to 25 mg/kg in obese adults with severe infections, and considers capping doses of 3000 mg as the most practical dosing regimen[37].
Data have shown an excellent correlation between TBW and CL[38]. Thus, the empirical maintenance dose of vancomycin is dependent on the estimated CL[39]. The initial maintenance doses of vancomycin can be calculated by vancomycin CL and target AUC for obese population[18,40]. The 2020 IDSA consensus points out that the mean vancomycin CL in obese patients is approximately 6 L/h, which corresponds to an AUC of approximately 500 mg·h/L at a daily dose of 3000 mg. The empirical vancomycin maintenance dose for obese adults should not exceed 4500 mg/d because vancomycin CL rarely goes beyond 9 L/h[37].
There were no abnormal imaging data findings.
The pharmacodynamic parameter that best predicts the efficacy of vancomycin is the ratio of the area under the curve (AUC) to the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC)[9]. In adult patients with suspected or definitive serious MRSA infection, the AUC/MIC ratio (assuming a vancomycin MIC of 1 mg/L) with targets between 400 and 600 was recommended in the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP) 2020 guideline[37]. Based on the historical difficulty of AUC estimation in clinical practice, previous expert guidelines recommended monitoring trough concentrations as a surrogate marker for the AUC/MIC ratio[41]. The 2020 Evidence-based Guideline for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Vancomycin recommends maintaining vancomycin steady-state trough concentrations at 10-20 mg/L to achieve clinical efficacy and improve patient safety[42].
多角度写——既从参与者(自己)的角度来写所见、所闻、所感,也从旁观者(他人)的角度来写;既从面上来写集体的表现,也从点上来写有特点的个体表现。
The patient’s height and body weight were 175 cm and 240 kg, respectively. The patient had necrotizing fasciitis of the scrotum and left lower extremity, and large brown skin pigmentation of the left calf, and two approximately 2-cm surgical incisions with built-in gauze drainage and cloudiness drainage fluid were visible in the left thigh and the middle of the left calf (Figure 1).
CONCLUSlON
The clinical dose of drugs administered is generally determined based on the results of pharmacokinetic studies and clinical trial studies in non-obese patients, which may not be optimal in obese individuals.Hence, the difference in pharmacokinetics of different drugs between obese and non-obese patients must be considered during drug treatment. Obesity is also associated with physiological changes that can alter the pharmacokinetics of vancomycin, and the selection of the dose of vancomycin administered needs to take into account the effect of the body weight of patients. Furthermore, both the loading dose and the maintenance dose are different from non-obese patients. During treatment, we should make appropriate dose adjustments based on the patient's therapeutic drug monitoring and renal function. At the same time, altered pharmacokinetics of antibacterial drugs may require dose individualization to achieve target concentrations. Adjustment of loading dose and maintenance dose is critical for the antibiotic treatment in obese patients using vancomycin. Unfortunately, limited data are available analyzing vancomycin concentrations in obese patients.
在重组方案选择时,应该综合考虑重组形式、支付方式以及所得税相关优惠条款等内容进行纳税筹划。首先,企业应该对比分析不同形式的重组方式,结合企业战略定位,优先选择税负低的方案。其次,企业可以采取现金支付、固定资产、股权支付等支付方式,其中,非股权支付方式容易产生较高的税收成本,而股权支付可以避免一部分税收,且能享受税收递延带来的收益,因此,企业应该选择最有利的支付方式。最后,企业在重组前应该认真研究所得税相关优惠条款,为减少税收做充分的准备。
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We thank the intensive care unit multidisciplinary team of the Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University for their treatment support.
FOOTNOTES
Bai J and Du WL conceived the manuscript; Xu KY drafted the manuscript; Li D monitored blood vancomycin concentrations; Hu ZJ was involved in drug therapy; Zhao CC was responsible for the patient.
CRRT is a common treatment for critically ill patients with acute renal injury[43]. With advances in hemodialysis membrane technology, vancomycin is cleared substantially by effective and high-flux dialyzers[44]. Therefore, vancomycin dosing regimens for CRRT need to be changed, but there is no mention of CRRT dosing recommendations in the latest FDA-approved vancomycin package insert[45].Vmay be increased in CRRT patients compared to healthy individuals with normal kidney function[46]. During CRRT treatment, vancomycin CL remains a near-steady-state condition over the dosing interval, although vancomycin CL may decline over time as a result of hemodialysis filter plugging[46].Vancomycin CL is closely related to the flow rate of ultrafiltration/dialysis solution[47]. The recommended loading dose for patients receiving CRRT is based on the actual TBW, at the dose of 20 to 25 mg/kg[48]. In order to achieve the generation of steady-state concentrations between 15 and 20 mg/L, a maintenance dose of 400 to 650 mg/12 h of vancomycin at an ultrafiltration flow rate of 30-40 mg/kg/h is recommended for most critically ill patients[49]. Due to the unstable clinical situation,vancomycin concentration must be strictly monitored in critical patients[50].
the Hebei Natural Science Foundation of China, No. H2019206614.
Informed written consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this report and any accompanying images.
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest to disclose.
戴菲儿完全按照他的要求完成——身材,肤色,口音,性格,文化程度,童年记忆……他本想让她完全变成妻子的模样,可是最终,他放弃了这种打算。他认为这样只会增加他的思念和悲伤。他认为,或许,一位看起来完全陌生的女孩更能够让他找到一点“从相识到相知”的感觉。后来他发现自己似乎爱上了戴菲儿,那一刻,他没有幸福,只有恐惧。
The authors have read the CARE Checklist (2016), and the manuscript was prepared and revised according to the CARE Checklist (2016).
This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers. It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial (CC BYNC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is noncommercial. See: https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by-nc/4.0/
China
Kun-Yan Xu 0000-0002-5416-9288; Dan Li 0000-0002-5863-6234; Zhen-Jie Hu 0000-0002-9528-8371;Cong-Cong Zhao 0000-0002-1298-6351; Jing Bai 0000-0002-2717-6458; Wen-Li Du 0000-0002-4208-0008.
Xing YX
Wang TQ
Xing YX
杂志排行
World Journal of Clinical Cases的其它文章
- Stem cells as an option for the treatment of COVID-19
- Development of clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats/CRISPR-associated technology for potential clinical applications
- Prostate sclerosing adenopathy: A clinicopathological and immunohistochemical study of twelve patients
- Effectiveness and postoperative rehabilitation of one-stage combined anterior-posterior surgery for severe thoracolumbar fractures with spinal cord injury
- Construction and validation of a novel prediction system for detection of overall survival in lung cancer patients
- Identification of potential key molecules and signaling pathways for psoriasis based on weighted gene coexpression network analysis
