1.5T下高介电材料几何结构对发射场影响的仿真研究
2022-06-14唐德港李红闯刘小玲李海东叶朝辉
唐德港,李红闯,刘小玲,石 磊,李海东,叶朝辉,周 欣*
1.5T下高介电材料几何结构对发射场影响的仿真研究
唐德港1,2,李红闯1,2,刘小玲1,2,石 磊1,2,李海东1,2,叶朝辉1,2,周 欣1,2*
1. 波谱与原子分子物理国家重点实验室,武汉磁共振中心(中国科学院精密测量科学与技术创新研究院),湖北 武汉 430071;2. 中国科学院大学,北京 100049

引 言


1 HPMs几何结构对发射场影响的仿真研究
1.1 HPMs提高射频线圈发射效率的原理



将HPMs放置在成像物体ROI附近,在射频脉冲激励下,根据麦克斯韦全电流定律:
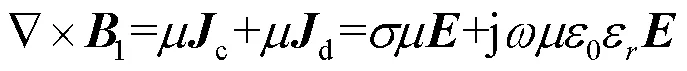
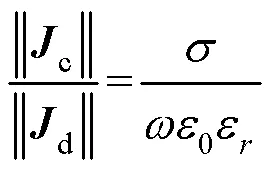
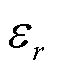

1.2 仿真模型及参数设置

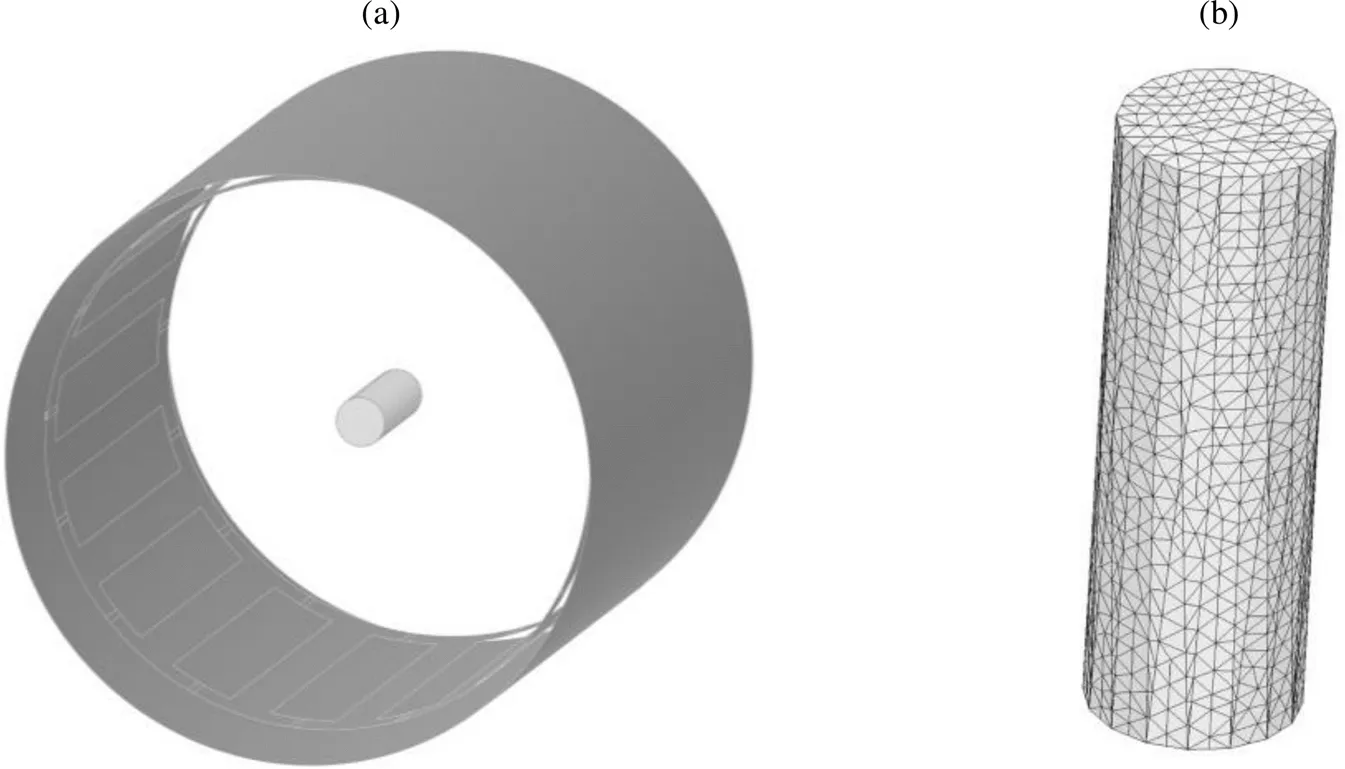
图1 带有水模负载的鸟笼线圈仿真模型(对照组).(a)仿真模型示意图;(b)水模内有限元网格剖分结果
在水模附近加入四种文献报道过的不同几何结构的高介电衬垫作为实验组,包括:(1)四等分圆筒状衬垫[30];(2)对称环绕水模的四块方形衬垫[20];(3)同侧三块方形衬垫[31];(4)120°扇环柱状衬垫[32].采用的HPMs厚度均为13 mm、长度均为71 mm.其中四等分圆筒状衬垫相邻单元间隙为3 mm;环绕四方块衬垫宽58 mm;同侧三方块衬垫宽34 mm,相邻两单元中心成60°夹角.衬垫材料为掺杂镐和铈的钛酸钡,首先将钛酸钡(Ba/Ti比为0.996)和高纯度的ZrO2、CeO2研磨混合,再在1 340°下高温烧结为陶瓷衬垫.衬垫相对介电常数设为4 500[20],电导率为0.44 S/m.实验组水模均采用和对照组相同的网格剖分,以保证参数和电磁场的精确度和一致性,实验组水模仿真模型示意图如图2所示.

图2 不同几何结构的高介电衬垫(深灰色)的仿真模型示意图(隐藏线圈).(a)无衬垫;(b)四等分圆筒状衬垫;(c)四块方形衬垫对称环绕水模;(d)同侧三块方形衬垫;(e) 120°扇环柱状衬垫


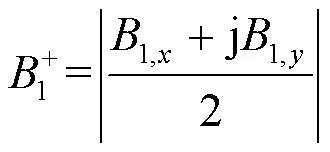
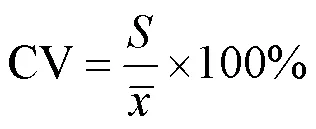

2 结果与讨论
2.1 HPMs几何结构对发射场的影响


图3 不同几何结构的高介电衬垫仿真模型水模中心横断面的发射效率h分布.(a)无衬垫;(b)四等分圆筒状衬垫;(c)四块方形衬垫对称环绕水模;(d)同侧三块方形衬垫;(e) 120°扇环柱状衬垫

表1 不同几何结构的高介电衬垫仿真模型ROI内的发射效率h均值与不均匀度(CV)


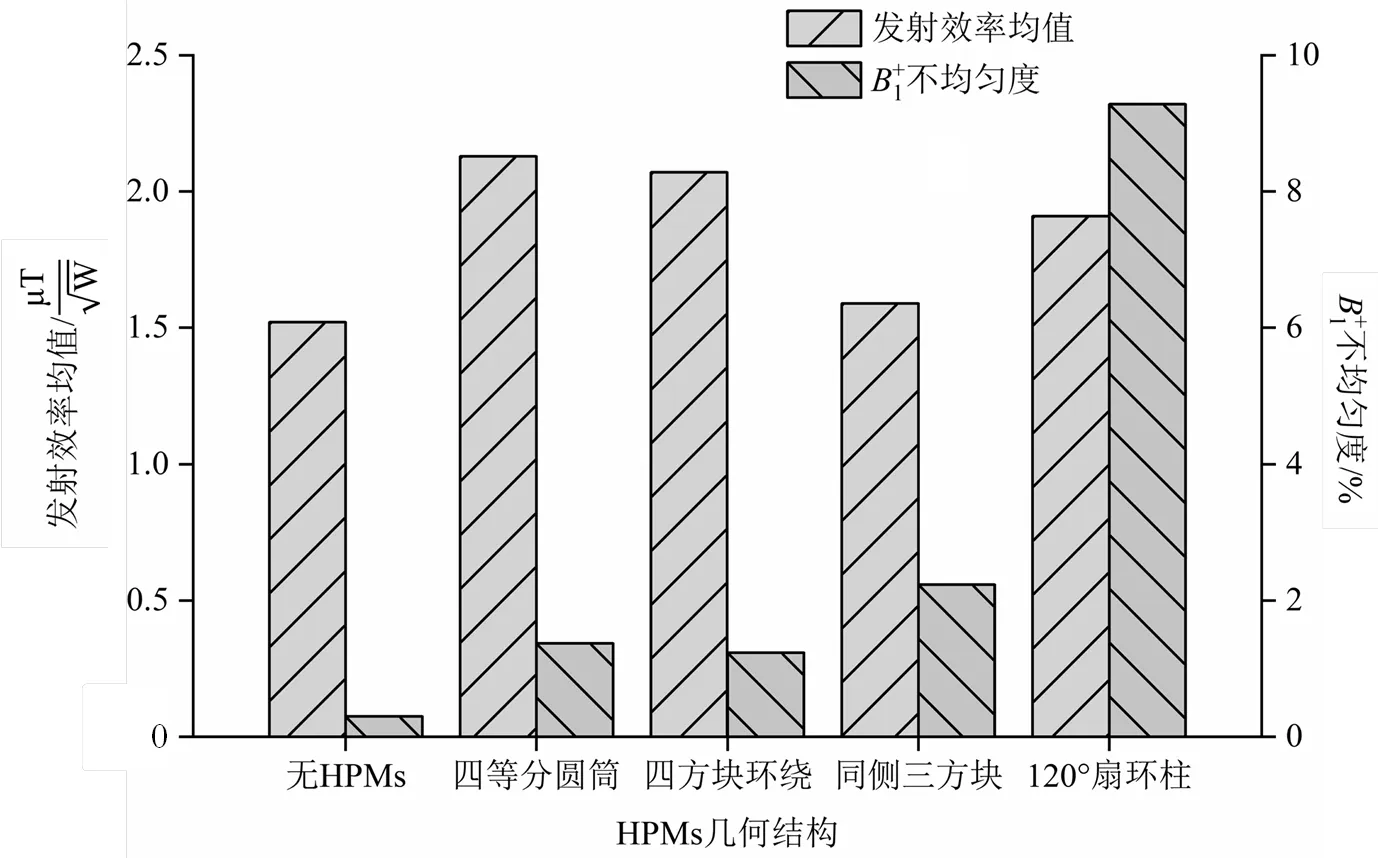
图4 不同几何结构的高介电衬垫仿真模型ROI内发射效率均值和不均匀度分析
2.2 理论分析
不同模型水模中心横断面沿轴方向中心线的发射效率分布如图5所示,可以看出,加入四等分圆筒状、环绕四方块、同侧三方块衬垫后,发射效率沿轴方向中心线分布都较为均匀.
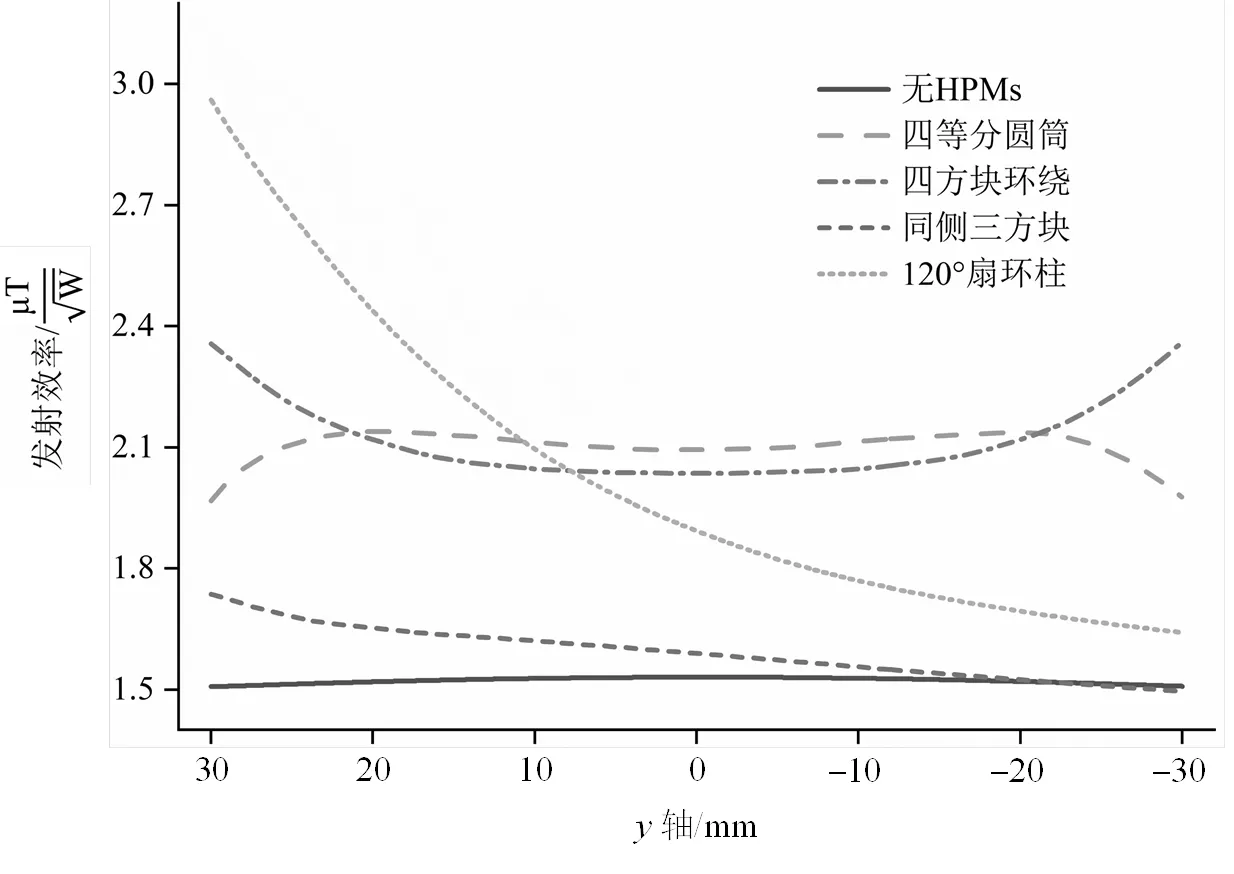
图5 不同仿真模型水模中心横断面沿y轴方向中心线的发射效率分布(以中心为原点)



3 结论
无
[1] UGURBIL K. Imaging at ultrahigh magnetic fields: history, challenges, and solutions[J]. Neuroimage, 2018, 168: 7-32.
[2] YANG Q X, WANG J, ZHANG X, et al. Analysis of wave behavior in lossy dielectric samples at high field[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2002, 47(5): 982-989.
[3] SCHICK F. Whole-body MRI at high field: technical limits and clinical potential[J]. Eur Radiol, 2005, 15(5): 946-959.
[4] DIETRICH O, REISER M F, SCHOENBERG S O. Artifacts in 3-T MRI: Physical background and reduction strategies[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2008, 65(1): 29-35.
[5] KANGARLU A, BAERTLEIN B A, LEE R, et al. Dielectric resonance phenomena in ultra high field MRI[J]. J Comput Assist Tomogr, 1999, 23(6): 821-831.
[6] HUANG Q H, GAO Y, XIN X G. Study on the law of B1field homogeneity and SAR inside human body varying with field strength at high and ultra-high field MR[J]. Chin J Biological Eng, 2013, 32(1): 21-27.
黄绮华, 高勇, 辛学刚. 高场和超高场MR下人体内B1场均匀性及SAR随场强变化规律的研究[J]. 中国生物医学工程学报, 2013, 32(1): 21-27.
[7] OSCH M J P V, WEBB A G. Safety of ultra-high field MRI: What are the specific risks?[J]. Curr Radiol Rep, 2014, 2(8): 1-8.
[8] DOTY F D, ENTZMINGER G, KULKARNI J, et al. Radio frequency coil technology for small-animal MRI[J]. NMR Biomed, 2007, 20(3): 304-325.
[9] GULSEN G, MUFTULER L T, NALCIOGLU O. A double end-cap birdcage RF coil for small animal whole body imaging[J]. J Magn Reson, 2002, 156(2): 309-312.
[10] DARDZINSKI B J, LI S H, COLLINS C M, et al. A birdcage coil tuned by RF shielding for application at 9.4 T[J]. J Magn Reson, 1998, 131(1): 32-38.
[11] LEE K H, CHENG M C, CHAN K C, et al. Performance of large-size superconducting coil in 0.21 T MRI system[J]. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng, 2004, 51(11): 2024-2030.
[12] LIN I T, YANG H C, HSIEH C W, et al. Human hand imaging using a 20 cm high-temperature superconducting coil in a 3 T magnetic resonance imaging system[J]. J Appl Phys, 2010, 107(12): 124701.
[13] LIAO Z W, CHEN J F, YANG C S, et al. A design scheme for1H/31P dual-nuclear parallel MRI coil[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2020, 37(3): 273-282.
廖志文, 陈俊飞, 杨春升, 等.1H/31P双核并行磁共振成像线圈的研究与设计[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2020, 37(3): 273-282.
[14] FENG T, CHEN J F, ZHANG Z, et al. A design of short dead-time RF coil and RF switch for low-field NMR[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2021, 38(1): 1-11.
冯涛, 陈俊飞, 张震, 等. 低场核磁共振短死时间射频线圈与射频开关的设计[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2021, 38(1): 1-11.
[15] WEBB A G, VAN DE MOORTELE P F. The technological future of 7 T MRI hardware[J]. NMR Biomed, 2016, 29(9): 1305-1315.
[16] ANDREYCHENKO A, BLUEMINK J J, RAAIJMAKERS A J E, et al. Improved RF performance of travelling wave MR with a high permittivity dielectric lining of the bore[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2013, 70(3): 885-894.
[17] YANG Q X, MAO W, WANG J, et al. Manipulation of image intensity distribution at 7.0 T: Passive RF shimming and focusing with dielectric materials[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2006, 24(1): 197-202.
[18] FRANKLIN K M, DALE B M, MERKLE E M. Improvement in B1-inhomogeneity artifacts in the abdomen at 3 T MR imaging using a radiofrequency cushion[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2008, 27(6): 1443-1447.
[19] DE HEER P, BRINK W M, KOOIJ B J, et al. Increasing signal homogeneity and image quality in abdominal imaging at 3 T with very high permittivity materials[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2012, 68(4): 1317-1324.
[20] ZIVKOVIC I, TEEUWISSE W, SLOBOZHANYUK A, et al. High permittivity ceramics improve the transmit field and receive efficiency of a commercial extremity coil at 1.5 tesla[J]. J Magn Reson, 2019, 299: 59-65.
[21] SICA C T, RUPPRECHT S, HOU R J, et al. Toward whole-cortex enhancement with a ultrahigh dielectric constant helmet at 3 T[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2020, 83(3): 1123-1134.
[22] LEE B Y, ZHU X H, RUPPRECHT S, et al. Large improvement of RF transmission efficiency and reception sensitivity for human in vivo P-31 MRS imaging using ultrahigh dielectric constant materials at 7 T[J]. Magn Reson Imaging, 2017, 42: 158-163.
[23] RUPPRECHT S, SICA C T, CHEN W, et al. Improvements of transmit efficiency and receive sensitivity with ultrahigh dielectric constant (uHDC) ceramics at 1.5 T and 3 T[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2018, 79(5): 2842-2851.
[24] VAN GEMERT J, BRINK W, REMIS R, et al. A simulation study on the effect of optimized high permittivity materials on fetal imaging at 3 T[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2019, 82(5): 1822-1831.
[25] BRINK W M, WEBB A G. High permittivity pads reduce specific absorption rate, improve B-1 homogeneity, and increase contrast-to-noise ratio for functional cardiac MRI at 3 T[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2014, 71(4): 1632-1640.
[26] SCHMIDT R, WEBB A. A new approach for electrical properties estimation using a global integral equation and improvements using high permittivity materials[J]. J Magn Reson, 2016, 262: 814.
[27] VAN GEMERT J, BRINK W, WEBB A, et al. High-permittivity pad design tool for 7 T neuroimaging and 3 T body imaging[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2019, 81(5): 3370-3378.
[28] BRINK W M, REMIS R F, WEBB A G. A theoretical approach based on electromagnetic scattering for analysing dielectric shimming in high-field MRI[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2016, 75(5): 2185-2194.
[29] LUO M, HU C, ZHUANG Y, et al. Numerical assessment of the reduction of specific absorption rate by adding high dielectric materials for fetus MRI at 3 T[J]. Biomed Eng-Biomed Tech, 2016, 61(4): 455-461.
[30] SEO J H, HAN S D, KIM K N. Improvements in magnetic field intensity and uniformity for small-animal MRI through a high-permittivity material attachment[J]. Electron Lett, 2016, 52(11): 898-899.
[31] RUYTENBERG T, O’REILLY T P, WEBB A G. Design and characterization of receive-only surface coil arrays at 3 T with integrated solid high permittivity materials[J]. J Magn Reson, 2020, 311: 106681.
[32] CHEN W, LEE B Y, ZHU X H, et al. Tunable ultrahigh dielectric constant (TuHDC) ceramic technique to largely improve RF coil efficiency and MR imaging performance[J]. IEEE Trans Med Imaging, 2020, 39(10): 3187-3197.
[33] 方俊鑫, 殷之文. 电介质物理学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1989.
[34] WEBB A G. Dielectric materials in magnetic resonance[J]. Concepts Magn Reson Part A, 2011, 38A(4): 148-184.
[35] HOULT D I. The principle of reciprocity in signal strength calculations—A mathematical guide[J]. Concepts Magn Reson, 2000, 12(4): 173-187.
[36] 罗超. 基于超材料的3 T磁共振射频接收线圈性能研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆理工大学, 2016.
[37] 张巍巍. 基于1.5 T磁共振系统体线圈电磁参数分析及共振频率算法实现[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2016.
[38] XIN S X, HUANG Q, GAO Y, et al. Fetus MRI at 7 T: B1shimming strategy and SAR safety implications[J]. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech, 2013, 61(5): 2146-2152.
1,2,1,2,1,2,1,2,1,2,1,2,1,2*
1. State Key Laboratory of Magnetic Resonance and Atomic and Molecular Physics, National Center for Magnetic Resonance in Wuhan, Innovation Academy for Precision Measurement Science and Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wuhan 430071, China; 2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China


O482.53
A
10.11938/cjmr20212904
2021-04-01;
2021-05-15
国家重点研发计划(2016YFC1304702);国家自然科学基金资助项目(82127802,81227902);中国科学院战略性先导科技专项(XDB25000000);广东省重点领域研发计划(2018B030333001);湖北省科技重大专项(2021ACA013);中国科学院磁共振技术联盟资助项目(2020GZL002).
* Tel: 027-87198802, E-mail: xinzhou@wipm.ac.cn.
