Investigation of coronoid process hyperplasia using Levandoski analysis on panoramic radiographs
2022-06-01SuleErdemSuhedaErdem
INTRODUCTION
Coronoid process hyperplasia (CPH) was first described by the German surgeon Bernhard Von Langenbeck in 1853[1]. CPH is an abnormal bone elongation that commonly occurs bilaterally. As it a rare condition, no epidemiological studies have been reported[2]. It is predominantly seen during the second decade of life, mostly among the male population[3] and may develop asymptomatically, presenting with late symptoms[4]. However, CPH is usually noticed with a progressive mouth opening limitation, which is thought to be caused by interference with the zygomatic bone[3]. Thus, it becomes necessary to explain the morphometric relationship between the coronoid processes and condyles because limited mouth opening is not always caused by CPH. Additionally, visual diagnosis of CPH without using an analysis system is not an accurate and reproducible way[5].
Computed tomography (CT) and cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) have been reported to be useful methods, providing three-dimensional images in the diagnosis of CPH[6]. However, CT and CBCT are not used in routine radiological examinations. Panoramic radiography is the simplest radiological method that can be used in the diagnosis of CPH and has a low radiation dose[5]. In addition, the majority of CPH cases reported to date have used panoramic graphy as a diagnostic method[3].
26.Godmother:The godmother did not become a common and well-known character in the Cinderella tale until Perrault incorporated her into his version of the story. Other versions of Cinderella in different cultures often have the heroine receive assistance from the deceased mother. The fairy godmother versions are the best known in Western culture thanks to Perrault and later versions from Disney and other sources.
To date, no morphometric or prevalence study has been performed on a large sample group using Levandoski analysis. The purpose of this article is to investigate the coronoid process morphometrically and determine the prevalence of CPH in a sample subpopulation using Levandoski analysis with panoramic radiographs.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The present study followed the principles of the Helsinki Declaration. Approval was granted by the Ethics Committee of University Ordu (No: 2021/231).
The images of the participants who underwent panoramic graphy were analysed retrospectively. The study was performed on images without artefacts that could adversely affect the evaluation. The participants included in this study were in the second decade and older. The participants with trauma, pathological formations and anomalies in condyle or coronoid process regions, musculoskeletal anomalies and congenital bone dysplasia were not included. In addition, the images where the condyle and coronoid tips and the gonion point could not be clearly distinguished, and the images with any artifacts were not included. The patients gave their consent for their radiographic images and information to be used in scientific studies.
Image analysis
The images were obtained with a panoramic X-ray unit (Orthopos XG 3, Sirona Dental Systems, Bensheim, Germany) operating at 60-90 kVp and 3-16 mAs. When the scans were being taken, the patients were in an upright position, with their heads and necks in a neutral position and the Frankfort plane parallel to the floor. All examinations and measurements were performed on a 27-inch colour LCD screen (BE27AQLB, Asus Computer GmBH, Ratingen, Germany) with a resolution of 2560 × 1440 pixels.
SHE did not know how to sew or make clothes, and she was sure to die of starvation into the bargain if her brother Ironhead did not come soon and bring her some raw meat and bones, for she really could eat nothing else
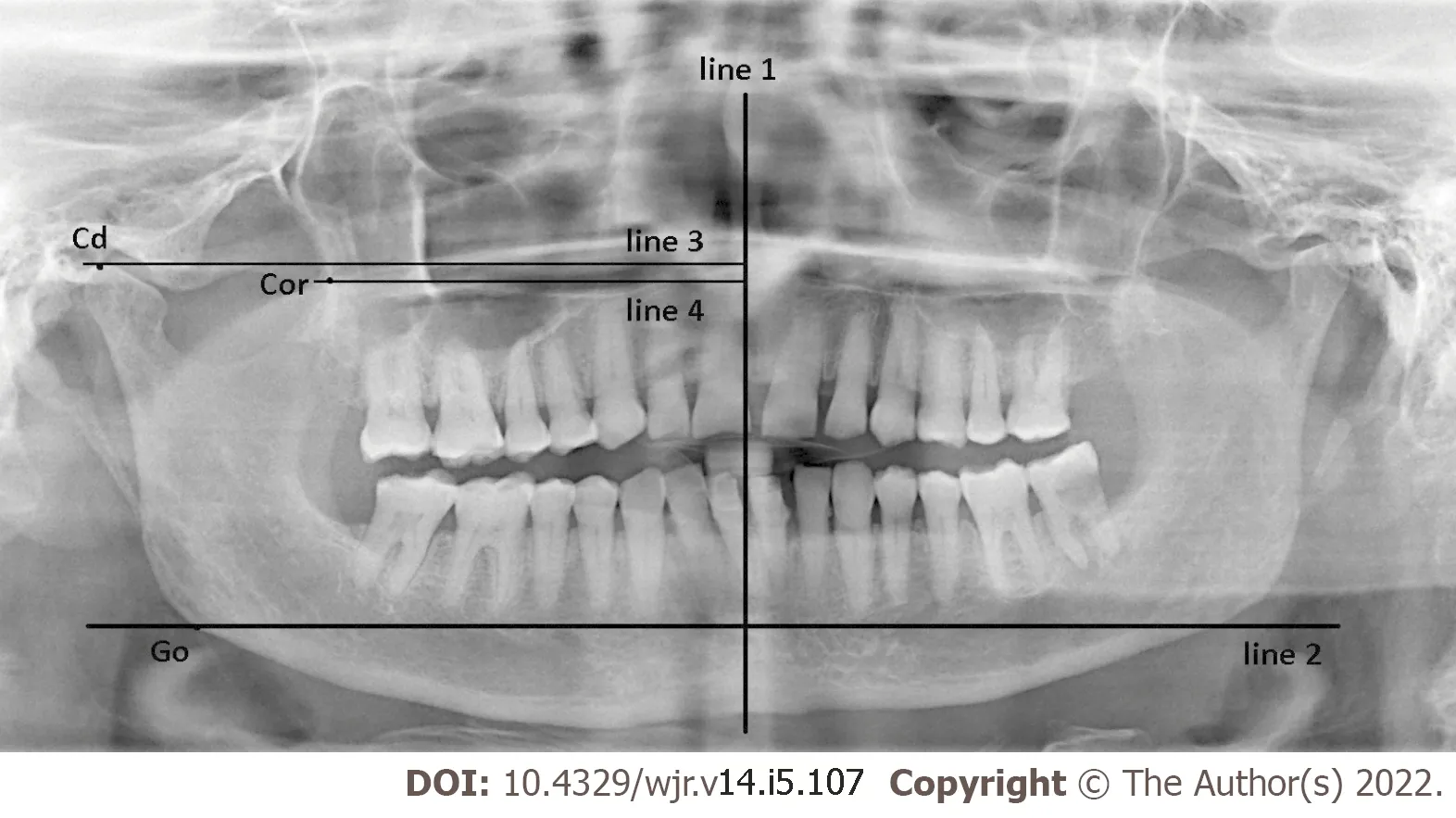
A total of 300 panoramic graphs (600 coronoid processes) were examined using Levandoski analysis by a maxillofacial radiologist with five years of experience in a dimly-lit room. The ages and genders of participants were recorded using to the software database system. When Condyle (Cd)-Gonion (Go) and Coronoid (Cor)-Go distances were measured, the Cor-Go: Cd-Go ratio was calculated for the left and right side of each image (Figure 1). Line 1 is the maxillary vertical midline, which passes through the nasal septum. Lines 2, 3 and 4 are perpendicular to line 1 and are tangent to the lower border of the symphysis mandible, the tip of the condyle and the tip of the coronoid process, respectively.
The colored lanterns had been extinguished, no more rockets rose in the air, and the cannon47 had ceased firing; but the sea became restless, and a moaning, grumbling48 sound could be heard beneath the waves: still the little mermaid remained by the cabin window, rocking up and down on the water, which enabled her to look in
To examine the intra-observer agreement, the images were reassessed by the same observer two weeks later.
CPH was detected in only one patient. The measurements of the patient were as follows: Cor-Go/Cd-Go 76.6/63.6 mm for the right side, 69.1/54.8 mm for the left side, Cor-Go:Cd-Go 1.20 for the right side and 1.26 for the left side.
Cd: Tip of the condyle.
The whole castle was surrounded by a deep moat, and the drawbridge and the gates, and even the water in the moat, were all of the same sombre hue46 as the walls and towers
The present study was performed retrospectively using 300 panoramic radiographs (126 males and 174 females). CPH was encountered in only one female out of 300 participants; the prevalence of CPH was found to be 0.3% in the sample subpopulation.
Cd-Go: Distances between the Cd and Go points.
Cor-Go: Distances between the Cor and Go points.
I wish with all my heart that I could put a delicate ribbon on a gayly wrapped package and give you a something to express my appreciation18 and affection. But I have nothing to give you that would surpass the most precious gift I have ever had to offer and which you already so graciously accepted months ago-the one you have held close to your heart, laughed with and probably cried with, applauded and scolded, lifted and encouraged, molded and shaped-my child.
Cor-Go: Cd-Go: Ratio diagnosed of CPH when above 1.15 (Kubota
[5]).
Statistical analysis
The data were transferred to the Statistical Package for Social Sciences 20.0 for Windows. Mann-Whitney U test was used for the variables with two categories that do not have a normal distribution. The Student t-test was used to compare the means of the data in two independent groups with normal distribution.
Since the relationship between two continuous variables without normal distribution was examined, the Spearman's rho correlation test was used to evaluate the intra-observer agreement.
All statistical tests were conducted at the 95% confidence level; the findings were considered statistically significant at the significance level of 0.05.
And outside the house was a large courtyard with horse and cow stables and a coach-house--all fine buildings; and a splendid garden with most beautiful flowers and fruit, and in a park quite a league long were deer and roe10 and hares, and everything one could wish for
RESULTS
Go: The most outward point of the mandibular angle.
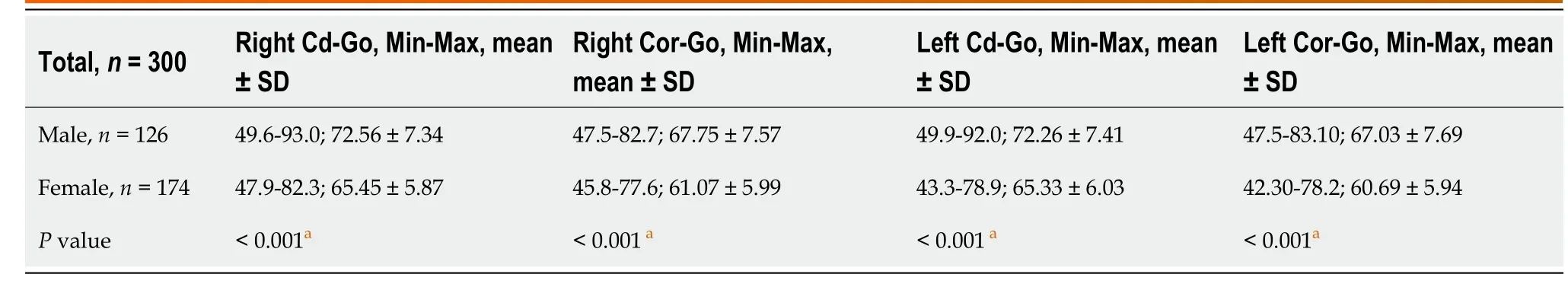
The Cd-Go and Cor-Go distances by gender are displayed in Table 1. There was a statistically significant difference in the Cd-Go and Cor-Go distances between male and female participants (
0.001). The Cd-Go and Cor-Go distances are statistically significantly increased in males on both left and right sides. Table 2 displays the Cor-Go: Cd-Go ratios according to gender. There was no statistically significant relationship between the Cor-Go: Cd-Go ratios and gender (
0.05).

Kubota
[5] used Levandoski analysis on panoramic radiographs for the diagnosis of CPH. They compared three patients with CT-confirmed CPH and a control group of 56 participants to verify the reliability of the analysis in the diagnosis of CPH. They reported that the Cor-Go and Cor-Go: Cd-Go values were significantly higher in the patients than in the control group. They reported the Cor-Go: Cd-Go value as the maximum of 1.07 for the control group and the minimum of 1.15 for the patient group. At the same time, they compared the Cor-Go: Cd-Go value with cephalometric and panoramic radiographs only for the right side in all participants (
= 59) and found a stable correlation. They did not report a statistically significant difference in the Cor-Go: Cd-Go values based on gender. In the current study consisting of 300 participants, there was no significant difference in the Cor-Go:Cd-Go values between males and females, similar to the study of Kubota
However, the Cd-Go and Cor-Go distances for both left and right sides increased statistically significantly in males (
0.001).
It doesn t matter when. I m sure the Addisons are nice people, but I m not going to waste an evening socializing with people who don t have any eligible3 daughters.
Although CPH is known to be a rare condition, its prevalence is unknown. Izumi
[18] encountered CPH in 17 of 1665 patients whose data had been examined. However, this is not a prevalence study but a case-control study conducted with database records of a clinic where only patients with temporomandibular joint findings were admitted. In the present study, the Cor-Go:Cd-Go ratio was measured applying Levandoski analysis, which is a useful and reproducible way to diagnose CPH, on the panoramic radiographs of each participant. CPH was encountered in only one out of 300 participants, and the prevalence of CPH was found to be 0.3% in the sample subpopulation.
DISCUSSION
CPH, also known as an elongated mandibular coronoid process, is a rare condition characterised by elongation of the process. In the case of clinical suspicion of CPH, the diagnosis can be made radiologically. The cephalometric analysis has been reported to be a reliable method in the diagnosis of CPH[5]. However, based on this method, only the measurements and evaluations of the right coronoid process can be made, leaving the left side of the radiograph unclear. Therefore, a simple radiographic method, such as panoramic radiography that allows bilateral examination, is required[5]. Displaying anatomical structures in true dimensions without magnification and superimposition, CT is a useful diagnostic method in CPH[7,8]. However, CT is an imaging method involving a high radiation dose; therefore, it cannot be used for routine examination. Four-dimensional CT (4DCT) is a new imaging method that can display the mandibular movement as well as the surrounding soft tissue mobility. The 4DCT assessment has the potential to understand the mechanisms underlying the symptoms in CPH patients[9]. Panoramic radiography is a simple and useful method to diagnose patients with CPH[5]; therefore, it is the most frequently used imaging method to diagnose CPH[3].
The etiology of CPH is not well described, and many theories have been put forward, such as genetic inheritance[10], hormonal stimulus[11], facial injuries and trauma[12] and temporal muscle activity[13]. According to a review that included 115 cases and was published by Goh
[3] in 2020, CPH is predominantly seen bilaterally, mostly in males, during the second decade of life. In the present study of 300 patients, bilateral CPH was found in a 50-year-old female patient.
Two men walked slowly, one after the other, through the shallow1 water of a stream. All they could see were stones and earth. The stream ran cold over their feet. They had blanket packs on their backs. They had guns, but no bullets2; matches, but no food.
At eleven o’clock in the morning, the most of the staff of garden centre they took the break and have a nice cup of tea or coffee in the staff tea room.
Levandoski developed his analysis for examining panoramic radiographs and adapted it for temporomandibular joint evaluation[14]. This analysis has been used in the diagnosis of facial and dental asymmetries and CPH in later years. There has been reported a good correlation between standard face photographs and Levandoski analysis[15]. Various studies have supported the applicability of the analysis in diagnosing facial and dental asymmetries[15,16].
Based on the Spearman’s rho analysis, the statistically significant (
0.01) perfect agreement was found between the Cor-Go:Cd-Go ratios calculated at two-week intervals (the rho value for the left side equals 0.987, for the right side 0.978).
Cor: Tip of the coronoid process.
An Anatolian skull with CPH was examined by Çorumlu
using Levandoski analysis on panoramic radiographs[17]. They reported that the Cor-Go and Cd-Go measurements were 95.10 mm and 79.03 mm on the right side and 97.53 mm and 87.80 mm on the left side; the Cor-Go: Cd-Go value was 1.20 on the right side. In the case they reported, the Cor-Go: Cd-Go value for the left side was below the 1.15 required for CPH but above the normal value of 1.07. For this reason, they interpreted their case bilaterally. In the present study, CPH was detected in only one patient. The measurements of the patient were as follows: Cor-Go and Cd-Go are 76.6 and 63.6 mm, respectively, for the right side and 69.1 and 54.8 mm for the left side; the Cor-Go: Cd-Go ratio is 1.20 for the right side and 1.26 for the left side.
Izumi
[18] retrospectively analysed the data of 1,665 patients who visited the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) centre to contribute to a case-control study. They determined criteria to rule out the conditions other than CPH that cause limitation in mouth opening: (1) Limitation of the mouth opening that does not heal for a year or more; (2) The impossibility of forced mouth opening; (3) The absence of any symptoms, such as pain or sound, when opening the mouth in the TMJ area; (4) The absence of abnormal disc position and osteoarthritic condylar changes on magnetic resonance images; and (5) The absence of a history of mandibular trauma and inflammation. Seventeen of the 18 patients who satisfied the criteria agreed to undergo CT and participate in the study. CPH without interference with the zygomatic bone was detected in 13 out of 17 patients, and CPH with interference with the zygomatic bone was diagnosed in four patients. Moreover, the configurations and height levels of coronoid processes were examined. An angular shape was seen in only four cases with the zygomatic bone interference. The height of the coronoid process was reported to be significantly higher in the case group than in the control group.
In another study in which 16 patients with CPH (eight congenital, eight induced) were examined with cephalometric graphs together with a control group of 16 participants, no difference in the height of the condylar process was reported between the groups; however, the height of the coronoid process was reported to be significantly greater in the patient group[19].
Stopa
[20] used the coronoid-condylar index (CCI) on CT images to diagnose CPH. They included in their study 13 participants with CPH and 13 participants without mandibular disease and reported that the CCI value, obtained using the measurement method they recommended, in the patients without CPH was approximately 1. They claimed that in the presence of CPH, the CCI increased to 1.25 and supposed that if the value rose above 1.15, there was a coronoid-condylar derangement.
In the study conducted by Tavassol
[21], CT images of 41 patients, consisting of 40 healthy individuals and 1 with CPH, were examined. The condyle and coronoid lengths and Cor: Cd ratio were measured with reference to the tangent point that passed through the sigmoid notch. The mean ratio for the healthy group of the participants was 0.78. The values were calculated for only one patient with bilateral CPH: the ratio was 2.1 for the left side and 1.87 for the right side. The accuracy of the results of this study is questionable, as the reference tangent line is determined arbitrarily.
CONCLUSION
The Cd-Go and Cor-Go distances were statistically significantly increased in males on both the left and right sides. The evidence that these values were predominant in males may be related to the fact that the anatomical dimensions of males are larger than those of females. Although the Cd-Go and Cor-Go distances were higher in males, the ratio of Cor-Go: Cd-Go was preserved for both genders.
According to the results of this study using the Levandoski analysis, the prevalence of CPH was found to be 0.3%. In the present study, the images were re-evaluated after two weeks, and intraobserver agreement was found perfect. According to this result, can be say that Levandoski analysis is a reproducible method for diagnosis of CPH. This method is very simple and can be used in the diagnosis of CPH by measuring with any radiology software.
Present study was not conducted with a large sample group and only one case of CPH was found. in order to reliably obtain the prevalence of CPH, studies with larger sample groups and different ethnic populations are necessary.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
The images of the participants who underwent panoramic graphy were analysed retrospectively. The radiographs taken in the last 1 year retrospectively from the date of the study were used.
Research motivation
The fact that there are few studies on Coronoid Process Hyperplasia was the main motivation of this research.
Soon after he died the king set forth1 a proclamation through the whole country that whoever could build a ship that should float both on land and sea should have his daughter to wife
Research objectives
To detect coronoid process hyperplasia by making repeatable measurements on panoramic radiographs.
Research methods
When Condyle (Cd)-Gonion (Go) and Coronoid (Cor)-Go distances were measured, the Cor-Go:Cd-Go ratio was calculated for the left and right side of each image. Line 1 is the maxillary vertical midline,which passes through the nasal septum. Lines 2, 3 and 4 are perpendicular to line 1 and are tangent to the lower border of the symphysis mandible, the tip of the condyle and the tip of the coronoid process,respectively.
Research results
Coronoid Process Hyperplasia was encountered in only one female out of 300 participants; the prevalence of CPH was found to be 0.3% in the sample subpopulation.
When my friend asked me What will make this love last? I ran through all the obvious reasons: commitment, shared interests, unselfishness, physical attraction, communication. Yet there s more. We still have fun. Spontaneous good times. Yesterday, after slipping the rubber band off the rolled up newspaper, Scott flipped4 it playfully at me: this led to an all-out war. Last Saturday at the grocery, we split the list and raced each other to see who could make it to the checkout5 first. Even washing dishes can be a blast. We enjoy simply being together.
Research conclusions
The Cd-Go and Cor-Go distances were statistically significantly increased in males on both the left and right sides. The evidence that these values were predominant in males may be related to the fact that the anatomical dimensions of males are larger than those of females. Although the Cd-Go and Cor-Go distances were higher in males, the ratio of Cor-Go:Cd-Go was preserved for both genders.
Research perspectives
Present study was not conducted with a large sample group and only one case of CPH was found. in order to reliably obtain the prevalence of CPH, studies with larger sample groups and different ethnic populations are necessary.
FOOTNOTES
Erdem S developed the protocol and wrote manuscript, collected data and edited manuscript; both authors analysed data, have read and approve the final manuscript.
Approval was granted by the Ethics Committee of University Ordu (No: 2021/231).
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Since the retrospective study was conducted, informed consent was not obtained from the patients. No data other than age and gender were recorded.
This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers. It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial (CC BYNC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is noncommercial. See: https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by-nc/4.0/
When she wished to get on her horse Falada again, the waiting- maid called out: I mean to ride Falada: you must mount my beast ; and this too she had to submit to
Turkey
Sule Erdem 0000-0002-8670-9947; Suheda Erdem 0000-0002-3214-7272.
Wang LL
A
Unfortunately, the Fairy found this out, and just as I was falling into a sweet slumber114, she made me get up once more, but even then I managed to escape her vigilance, and only took off my upper robe
Wang LL
1 Von Langenbeck B. Angeborene kleinheit der unterkiefer.
1861; 1: 451-455
2 Mulder CH, Kalaykova SI, Gortzak RA. Coronoid process hyperplasia: a systematic review of the literature from 1995.
2012; 41: 1483-1489 [PMID: 22608198 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijom.2012.03.029]
3 Goh YC, Tan CC, Lim D. Coronoid hyperplasia: A review.
2020; 121: 397-403 [PMID:31904534 DOI: 10.1016/j.jormas.2019.12.019]
4 Farronato M, Lucchina AG, Mortellaro C, Fama A, Galbiati G, Farronato G, Maspero C. Bilateral Hyperplasia of the Coronoid Process in Pediatric Patients: What is the Gold Standard for Treatment?
2019; 30: 1058-1063[PMID: 30339589 DOI: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000004768]
5 Kubota Y, Takenoshita Y, Takamori K, Kanamoto M, Shirasuna K. Levandoski panographic analysis in the diagnosis of hyperplasia of the coronoid process.
1999; 37: 409-411 [PMID: 10577758 DOI:10.1054/bjom.1999.0159]
6 Ghazizadeh M, Sheikhi M, Salehi MM, Khaleghi A. Bilateral coronoid hyperplasia causing painless limitation of mandibular movement.
2018; 13: 112-117 [PMID: 29487645 DOI: 10.1016/j.radcr.2017.11.001]
7 Alias A, Ibrahim ANM, Bakar SNA. Morphometric Analysis of Coronoid Process of Mandible by CT in the Malaysian Population: An Important Step for Determination of Sex.
2018; 5: 1-8 [DOI:10.29199/2637-7055/dsrt.101015]
8 Fukumori T, Tagawa T, Inui M. Bilateral coronoid process hyperplasia and short stature. A case report.
1993; 22: 139-144 [PMID: 8340622 DOI: 10.1016/s0901-5027(05)80237-1]
9 Huang W, Akashi M, Nishio T, Negi N, Kimoto A, Hasegawa T. Can four-dimensional computed tomography support diagnosis and treatment planning?
2020; 24: 515-520 [PMID: 32621034 DOI:10.1007/s10006-020-00876-1]
10 Leonardi R, Caltabiano M, Lo Muzio L, Gorlin RJ, Bucci P, Pannone G, Canfora M, Sorge G. Bilateral hyperplasia of the mandibular coronoid processes in patients with nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome: an undescribed sign.
2002; 110: 400-403 [PMID: 12116218 DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.10432]
11 Rowe NL. Bilateral developmental hyperplasia of the mandibular coronoid process. a report of two cases.
1963; 1: 90-104 [PMID: 14089492 DOI: 10.1016/s0007-117x(63)80056-6]
12 Bayar GR, Akcam T, Gulses A, Sencimen M, Gunhan O. An excessive coronoid hyperplasia with suspected traumatic etiology resulting in mandibular hypomobility.
2012; 30: 144-149 [PMID: 22606859 DOI: 10.1179/crn.2012.021]
13 Sarnat BG, Engel MB. A serial study of mandibular growth after removal of the condyle in the Macaca rhesus monkey.
1951; 7: 364-380 [PMID: 14833933 DOI: 10.1097/00006534-195105000-00002]
14 Levandoski RR. Mandibular whiplash. Part II. An extension flexion injury of the temporomandibular joints.
1993; 10: 45-51 [PMID: 8359749]
15 Piedra I. The Levandoski Panoramic Analysis in the diagnosis of facial and dental asymmetries.
1995;20: 15-21 [PMID: 8634190]
16 Biagi R, Craparo A, Trovato F, Butti AC, Salvato A. Diagnosis of dental and mandibular asymmetries in children according to Levandoski Panoramic Analysis.
2012; 13: 297-300 [PMID: 23270287]
17 Lee JC. Retraction notice to "Therapeutic effect of prostaglandin E1 in monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension rats" by Lee JC (Anat Cell Biol 2017;50:60-8).
2017; 50: 245 [PMID: 29043105 DOI:10.5115/acb.2017.50.3.245]
18 Izumi M, Isobe M, Toyama M, Ariji Y, Gotoh M, Naitoh M, Kurita K, Ariji E. Computed tomographic features of bilateral coronoid process hyperplasia with special emphasis on patients without interference between the process and the zygomatic bone.
2005; 99: 93-100 [PMID: 15599354 DOI:10.1016/j.tripleo.2004.04.013]
19 Isberg A, Eliasson S. A cephalometric analysis of patients with coronoid process enlargement and locking.
1990; 97: 35-40 [PMID: 2296941 DOI: 10.1016/S0889-5406(05)81706-8]
20 Stopa Z, Wanyura H, Kowalczyk P. Coronoid-condylar index in assessing of mandibular coronoid hyperplasia. Preliminary results.
2013; 58: 429-433 [PMID: 24327533 DOI: 10.2478/ams-2013-0005]
21 Tavassol F, Spalthoff S, Essig H, Bredt M, Gellrich NC, Kokemüller H. Elongated coronoid process: CT-based quantitative analysis of the coronoid process and review of literature.
2012; 41: 331-338 [PMID:22192388 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijom.2011.10.033]
