Association of type ll Waardenburg syndrome with hypermetropic amblyopia
2022-04-19SheeWenChuaSafinazMohdKhialdinMushawiahtiMustaphaNorshamsiahMdDinMengHsienYong
We present a case of hypermetropic amblyopia in type II Waardenburg syndrome (WS) to highlight the association. WS is an “oculo-dermato-auditif” dysplasia described in 1947 by Waardenburg and by Klein in 1950. It is distributed worldwide, with no predilection for race or gender.The prevalence is estimated to be 1:42 000 live births in the general population. WS is a genetic disease with autosomal dominant transmission with incomplete penetrance and variable expressivity. Complex network of interaction between six genes have been identified to date. They aregene,primarily responsible for type I and III WS;,, andgenes in type II WS;andgenes in type IV WS.
Patients living with WS can present with telecanthus,broad nasal root, synophrys of eyebrows, white forelock,heterochromia iridis and deaf-mutism. WS is classified into 4 types. Type I presents the full symptomatology with canthorum dystopia while type II has no canthorum dystopia. Type III WS includes type I WS with musculoskeletal abnormalities or ortho-osteo-myo-dysplasia of the upper limbs. Type IV WS (Shah-Waardenburg syndrome) includes type I WS with congenital megacolon.
在课前,教师可以将课程视频、课件以及其他学习资料上传到网络教学平台,发布学习任务和学习通知。由于网络教学平台有对应开发的手机端教师和学生分别使用的APP,这时这些学习资料、学习任务、学习通知也会同时推送给学生。学生可以用手机观看课程视频、课件等资料,也可进行课前测试、参与在线讨论等;教师可以通过手机端随时查看学生的学习情况,批阅学生的测试,参与论坛讨论等。
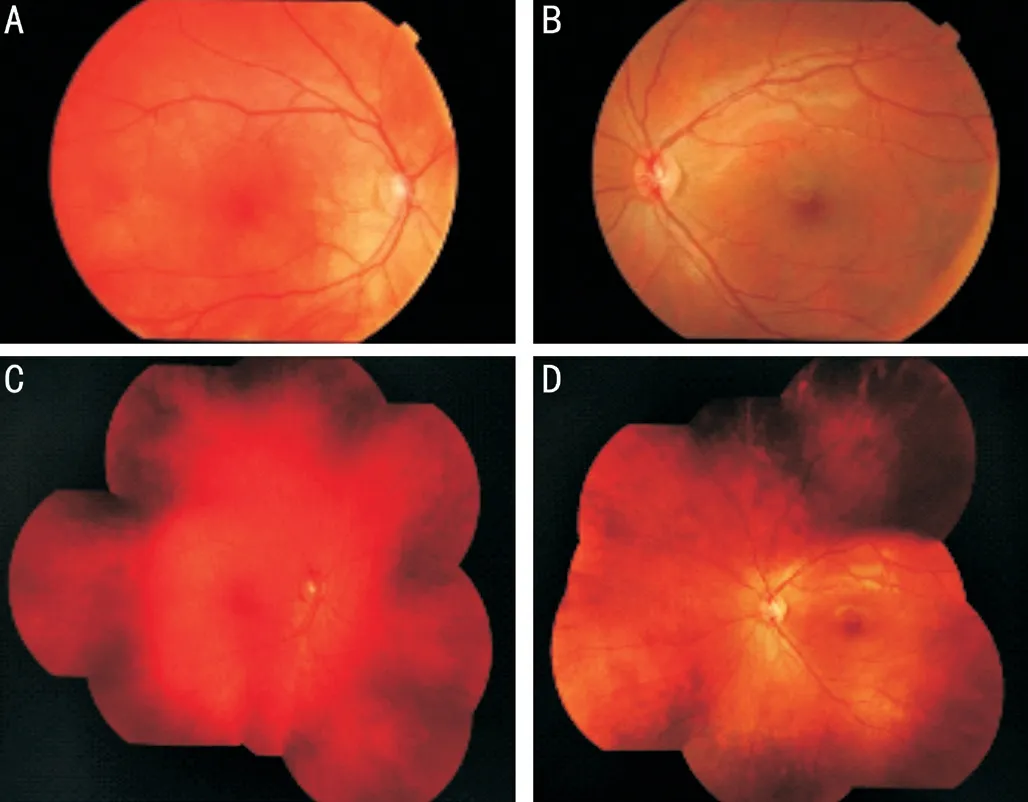
The diagnostic criteria for WS have been proposed by the Waardenburg Consortium in Table 1. It includes at least 2 major criteria or 1 major plus 2 minor criteria.The categorization of WS (I to IV) can be established by clinical features. Molecular genetic analysis can aid in the diagnosis if the clinical features are inconclusive. Our patient has 2 major criteria met without canthorum dystopia and hence classified as type II WS.We obtained the written informed consent from the patient's parent, and this case study is in accordance with the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Our case report revealed an interesting finding of persistent hypermetropia that documented from age of 3 to 11. None of the previous reported cases documented this persistent hypermetropia. The failure of emmetropization showed in this case can be related to the underlying genetic problem in WS.The underlying deranged melanocytic-pigmentary system in WS may lead to disruption of normal emmetropization as suggested by previous studies on ocular albinism,which leads them to the risk of persistent hypermetropia and subsequently development of amblyopia if untreated.
This is a returned case of 11-year-old girl diagnosed with type II WS since the age of five months with bilateral sensorineural hearing loss, heterochromia iridis and a family history of deafness. She underwent a cochlear transplant at three years old. She had her first ophthalmology assessment at three years old with an objective refractive assessment documented as bilateral best corrected visual acuity (BCVA) of 20/30 and hypermetropia of +3.00 spherical diopter (+3.00 D).
Falzonreported that 42% of 141 children who had undergone cochlear implant had ocular abnormalities with refractive errors. Hypermetropia was the most common refractive error (15%) and one of the children was diagnosed with WS.Refractive error and amblyopia are not typically present in WS and are not included in the latest diagnostic criteria of the disease. However, our literature review revealed 12 cases of amblyopia and 7 of them were related to refractive error and all of the 7 cases were hypermetropia. The hypermetropic power ranged from +2.25 D to +6.50 D. None of the reports documented repeated refraction. We believe the true incidence of hypermetropic amblyopia is unknown due to the lack of formal and serial refractive assessment in the previous reports.There were other causes of amblyopia reported from the literature review. Three cases were postulated that amblyopia is related to hypopigmentation of fundus. Six out of 7 cases reported of hypermetropic amblyopia had hypopigmented fundus as well. The remaining 2 cases did not explain the cause of amblyopia. Our patient does have macula hypopigmentation as well. However, patient with hypopigmentation of retinal pigment epithelium without macular hypoplasia may not related to reduced visual acuity.
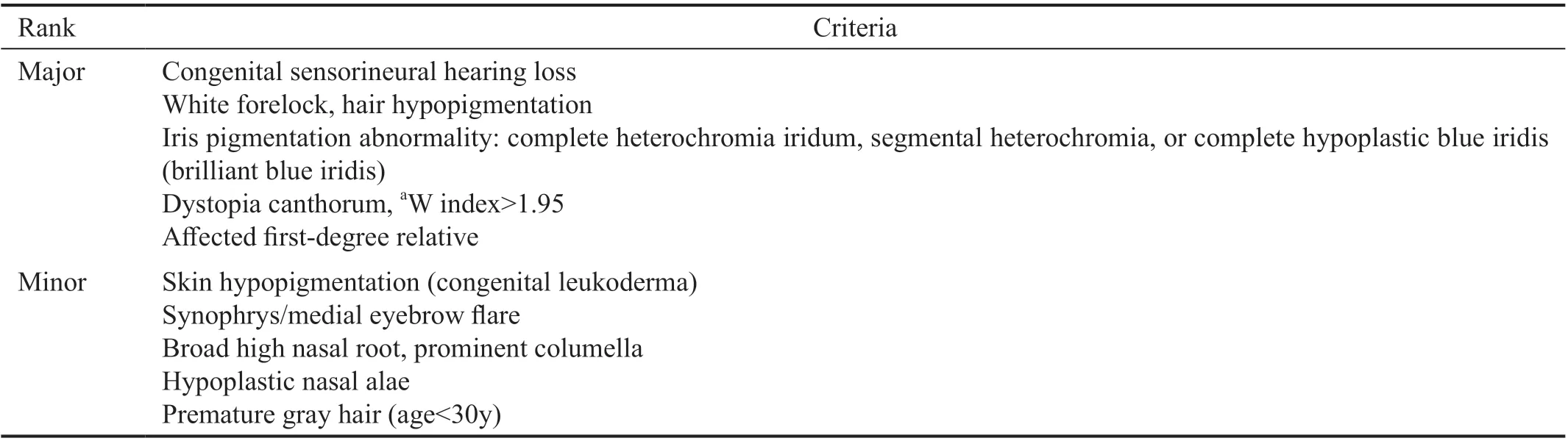
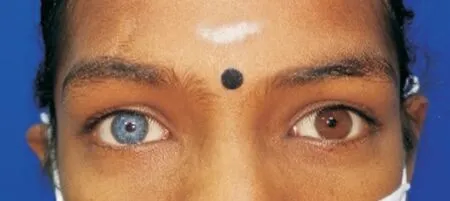
However, she defaulted the ophthalmology follow up until she presented again at the age of 11 years old complaining of bilateral suboptimal vision. A detailed ophthalmic examination revealed both eyes hypermetropic amblyopia with right eye BCVA 20/40, +3.75 D and left eye BCVA 20/40, +3.50 D.Anterior segment examination revealed heterochromia iridis with right eye hypochromia as previously documented (Figure 1).Dilated fundus examination showed bilateral mixed hypo- and hyperpigmentation of the fovea and peripheral retina (Figure 2A, 2B). Other examinations were unremarkable. There was no other feature of WS such as white forelock or telecanthus.She had no squint, anisocoria or reactive afferent pupillary defect. The optic discs were pink with cup-to-disc ratio of 0.3.She was prescribed with glasses with regular follow up for reassessment.
Her BCVA remained 20/40 in the right eye and 20/60 in the left eye after 3y of follow up. There was no other new ocular finding except some further pigmentary changes in the peripheral retina (Figure 2C, 2D).
Similar to Sharma and Arora'sreport, the author reported two cases of type II WS. One of the patients had amblyopia and the author also associated the amblyopia to the fundus depigmentation.
Albarrystudied a Saudi family with eleven members diagnosed with type II WS. Two of the family members had bilateral amblyopia and another two of the family members had unilateral amblyopia. They postulated that amblyopia is related to hypopigmentation of the fundus in the four families as there were no other fundus abnormalities found.
Ohnoreported a cases series involving 11 patients with type II WS and only two patient had a unilateral hypermetropic amblyopia. The rest of the patients had no poor vision or visual field defects.
Akalreported a case of type II WS with anisometropic amblyopia. Reported case had left eye hypermetropia with BCVA 0.3. After occlusion therapy for amblyopia, the left eye BCVA improved to 0.4. The author drew attention for detailed ophthalmology examination in type II WS and amblyopia should be investigated, to avoid delay in diagnosis and treatment of additional pathologies.
Literature search with the words “Waardenburg syndrome”AND “amblyopia” and its related terms using PubMed Medline, EBSCOhost Medline, and Scopus databases revealed seven reports with total of 12 cases, which are summarized in Table 2.
Read and Newtonshowed that there is an association between mutation of thegene with microphthalmia in type II WS.The author explained thatgene, the human homologues of the mouse microphthalmia gene is mapped to the same location. This explained the association of hypermetropic refractive error with reduced AP-AXL in Vianney's report.
Cortés-Gonzálezstudied two unrelated families with WS. The author reported that among all type II WS patients,one had bilateral reduced anteroposterior axial length (APAXL) and a high hypermetropic refractive error corresponding to posterior microphthalmos. The author also reported in the first family, there were 3 patients with hypermetropia and 2 of them had reduced AP-AXL; and in the second family, one patient had hypermetropia with reduced AP-AXL. However,the visual acuities were not reported.
在混合动力系统中利用这种2自由度结构,将不同性质、不同来源的动力相融耦合,并避免了各动力源之间的运动干涉[6].
学术英语智能写作评估的新研究——评《基于语类的二语研究论文智能写作评估:从设计、评估到优化》………………………………………………………………………………………… 钟家宝 钟兰凤(4.108)
社会期望 (social expectation)是指社会或群体根据个体所处的社会地位及其所承担的社会角色所提出的希望或要求,它反映的是社会公认的价值标准或行为规范,对个体而言构成一种社会压力,并成为个体的行为动机[1]。Cradall和Katkovsky认为,社会期望是个人对社会认可的依赖,也是对不认可的回避,是影响个人行为的较为广泛的动机[2]。因此,对个体而言,社会期望会构成一种社会压力,进而成为个体的行为动机。
Refractive hypermetropia is well known to cause amblyopia,but an association between WS and refractive amblyopia due to failure of emmetropization has not been made. This might draw the attention of eye care providers to this association and to be aware that detailed ophthalmic and refractive examinations in patients with WS may prevent refractive amblyopia.
想到那个肇事者胳膊上纹的那个虎头,我隐隐有些担心。那个家伙不会明着报复,但是他要是暗中下手,你老陈死都不知道自己是怎么死的。老陈却无所畏惧,走之前还对我说,光天化日,朗朗乾坤,有什么好怕的。话虽这样说,我还是有些不安,害怕到时他把我说出来。
None;None;None;None;None.
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
International Journal of Ophthalmology的其它文章
- Leptin activates the JAK/STAT pathway to promote angiogenesis in RF/6A cells in vitro
- CCPG1 involved in corneal Aspergillus fumigatus infection
- Anti-scarring effect of sodium hyaluronate at filtration pathway after filtering surgery in rabbits
- Five-in-one: a novel, cost-effective yet simple use of micro needle holder
- CO2 laser-assisted sclerectomy surgery and trabeculectomy combination therapy in Peters’ anomalyrelated glaucoma: a case report
- Congenital fibrovascular pupillary membranes: case series with pathological correlation and surgical treatment
