松材线虫Bx-TIMP克隆及功能研究
2022-04-19杨帆零雅茗舒红姜生伟王佳楠李丹蕾
杨帆 零雅茗 舒红 姜生伟 王佳楠 李丹蕾
摘 要:為探究Bx-TIMP基因在松材线虫(Bursaphelenchus xylophilus)致病过程中的功能,对Bx-TIMP基因进行克隆及分析,并验证基因沉默后松材线虫致病性变化。PCR法克隆Bx-TIMP,应用TMHMM 2.0 server和SignalP 4.1 Server分析该基因编码蛋白质的跨膜结构域和信号肽;应用原位杂交技术确定该基因在松材线虫体内表达部位;应用RNAi技术,分析沉默该基因后松材线虫对红松(Pinus koraiensis)致病性变化。该基因CDS区全长363 bp,编码120个氨基酸,编码蛋白具有跨膜结构域及信号肽。原位杂交表明该基因在松材线虫食道腺中表达。基因沉默后,松材线虫对红松致病性减弱。结果表明,Bx-TIMP为效应因子基因,与松材线虫致病性相关。本研究揭示Bx-TIMP基因是松材线虫危害松树致使其发病的关键基因,为进一步明确松材线虫致病机理提供理论依据,为研发松材线虫的防治技术奠定理论基础。
关键词:松材线虫;致病性;效应因子;红松;基因沉默
中图分类号:S763.18 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1006-8023(2022)02-0014-06
Cloning and Functional Analysis of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus Bx-TIMP
YANG Fan1,2, LING Yaming1,2,5, SHU Hong3, JIANG Shengwei3,4, WANG Jianan1,2, LI Danlei1,2,4*
(1.School of Forestry, Northeast Forestry University, Harbin 150040, China; 2.Key Laboratory of Alien Forest
Pest Monitoring and Control - Heilongjiang Province, Northeast Forestry University, Harbin 150040, China;
3.Liaoning Provincial Station of Forest and Grassland Pest Control and Quarantine, Shenyang
110001, China; 4.Liaoning Provincial Key Laboratory of Dangerous Forest Pest Management
and Control, Shenyang Institute of Technology, Shenyang 113122, China; 5.Shiwandashan
National Nature Reserve Administration, Fangchenggang 535500, China)
Abstract:To explore the function of the gene Bx-TIMP during Bursaphelenchus xylophilus infecting Pinus sp., Bx-TIMP was cloned and analyzed, then the gene was silenced by RNAi and vitrificated. The transmembrane domain and signal peptide of the protein encoded by Bx-TIMP was analyzed by TMHMM 2.0 server and SignalP 4.1 Server. The expression site of the gene in B. ylophilus was determined by in-situ hybridization. By silencing the gene with RNAi, the pathogenicity of B. xylophilus to P. koraiensis was analyzed. The gene had a total length of 363 bp and encoded 120 amino acids. The protein encoded by Bx-TIMP had a transmembrane domain and signal peptide and the results of in-situ hybridization showed that the gene was expressed in the esophageal gland of B. xylophilus, which accorded with the characteristics of effectors. The symptoms of P. koraiensis in Bx-TIMP-RNAi group were significantly weaker than those in the control group. This study showed that Bx-TIMP was an effector gene, which was related to the pathogenicity of B. xylophilus. This study revealed that Bx-TIMP gene is the key gene of B. xylophilus endangering pine trees, which provided a theoretical basis for further clarifying the pathogenesis of B. xylophilus and laying a theoretical foundation for the development of control technology of B. xylophilus.
Keywords:Bursaphelenchus xylophilus; pathogenicity; effect factor; Pinus koraiensis; RNAi
0 引言
与寄主互作时,病原分泌效应因子抑制寄主模式识别受体(pattern recognition receptors,PRRs)识别病原相关分子模式(pathogen-associated molecular patterns,PAMPs)而触发的先天免疫,促进病原成功侵染寄主。植物寄生线虫(plant parasitic nematodes,PPNs)通过口针将食道腺体分泌的效应因子导入寄主细胞中,以完成寄生过程并从寄主细胞中获取营养。效应因子有助于线虫在寄主体内成功取食、繁殖和迁移,促进线虫侵染和寄生。目前,线虫效应因子的研究大都集中在固着性内寄生线虫:胞囊线虫(Heterodera sp.)和根结线虫(Meloidogyne sp.)中。
松材线虫(Bursaphelenchus xylophilus)是引起松树萎蔫病(pine wilt disease,PWD)的一种迁徙性内寄生线虫。松树萎蔫病是对松树极具破坏性的病害之一,导致每年约500万m3的木材损失。在中国,松材线虫最早于1982年在南京中山陵发现。松材线虫与寄主植物的互作是由食道腺分泌的效应因子介导的,一些已知的效应因子可以修饰寄主植物的细胞,促进松材线虫营养物质的摄入以维持生长和发育,还有一些效应因子可以改变寄主植物的信号通路,抑制植物的防御反应。对松材线虫效应因子的研究对了解寄生机制和开发新的松材线虫的防治措施具有重要意义。
根据实验室前期研究结果,通过转录组数据分析筛选到效应因子组织金属蛋白酶抑制剂(tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases,TIMPs)基因Bx-TIMP。TIMPs是一个保守的蛋白家族,是基质蛋白的特异性抑制剂,主要有4种亚型(TIMP-1、TIMP-2、TIMP-3和TIMP-4)。TIMPs整体呈楔形,可直接与MMPs的活性间隙1∶1结合发挥效应,调节MMPs的活性,其N端和C端结构域分别由125和65个氨基酸构成,每个氨基酸都包含3个保守的二硫键,其中N端结构域的单独单元折叠是发挥抑制MMPs效应的主要结构。哺乳动物TIMPs已被证明在体外和器官培养系统中负调控基质金属蛋白酶的活性,也负调控体外聚蛋白多糖酶的活性。目前,尚未见松材线虫TIMPs研究报道。本研究探究Bx-TIMP基因在松材线虫致病过程中的功能,为进一步明确松材线虫致病机理提供理论依据,为研发松材线虫的防治技术奠定理论基础。
1 材料与方法
1.1 Bx-TIMP基因克隆及分析
Trizol法提取松材线虫总RNA,并通过反转录试剂盒获得松材线虫cDNA。根据转录组测序结果设计涵盖Bx-TIMP完整编码蛋白区(coding sequence,CDS)的PCR引物,(Bx-TIMP-F序列:5′-CGCGAAAATCGTCAACCTCG-3′;Bx-TIMP-R序列:5′-GCGGTGCTGTTCAATTCCTC-3′)以植食松材线虫cDNA為模板进行PCR扩增,扩增产物进行TA克隆,克隆后的基因产物送生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司测序。
应用TMHMM 2.0 server对Bx-TIMP编码蛋白质进行跨膜结构域的预测,应用SignalP 4.1 Server进行Bx-TIMP信号肽分析。
1.2 Bx-TIMP原位杂交
提取含有相应目的片段的质粒,应用Roche DIG RNA Labeling Kit (SP6/T7)分别合成正义及反义RNA探针。应用DIG High Prime DNA Labeling and Detection Starter Kit I (Roche)进行杂交及信号检测。将杂交显影后制成的玻片置于Olympus BX51显微镜下拍照。
1.3 Bx-TIMP RNAi及接种验证
用浸泡法对松材线虫进行RNAi干扰。准备10 000条松材线虫(混合虫龄),以Bx-TIMP基因的siRNA(5′-AUAUUCCGCAAAGUCCAUCCUCGGC -3′)浸泡处理后,用M9缓冲液清洗回收线虫,为Bx-TIMP-RNAi组。无靶基因序列siRNA(5′-AGGAGCUGUUCACCGGGGUGGUGCCCAUCCU -3′)处理的线虫为CK组。每组设3个重复。应用GoTaq2-Step RT-qPCR System试剂盒,分别提取Bx-TIMP-RNAi组及CK组线虫总RNA进行Q-PCR扩增(Pri-R:5′-TCTGCCCACTACGGTCTACA-3′;Pri-F:5′-ACCCCCAGTATTTTCATCTCTGA-3′),验证基因沉默效果,两独立样本t检验差异显著性。
用Bx-TIMP-RNAi组线虫、CK组线虫和ddH2O分别接种于红松(Pinus koraiensis)3年生松苗,处理后连续观察症状并拍照记录。
2 结果与分析
2.1 Bx-TIMP基因克隆及结构域分析
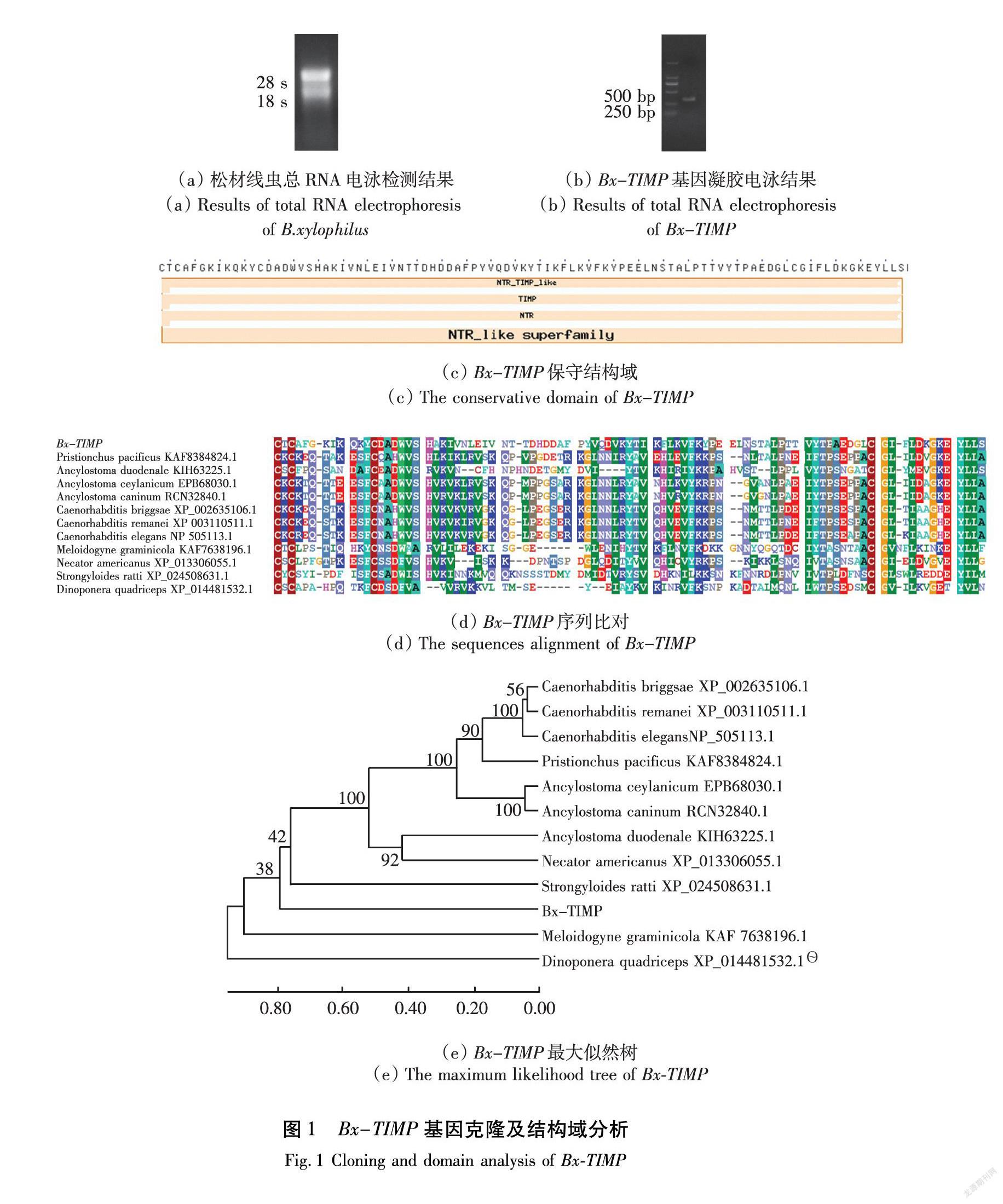
TRIzol法提取松材线虫总RNA,0.8%凝胶电泳检测RNeasy Minikit column(Qiagen, cat. No. 74 104)纯化后的RNA如图1(a)所示,纯度由BioPhotometer D30(Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany)鉴定,OD值(OD260/OD280=1.9,OD260/OD230>1.7)符合要求。
以植食线虫总RNA反转录为cDNA模板进行PCR扩增,扩增产物TA克隆后获得基因产物送由生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司进行测序,测序得到Bx-TIMP基因片段长度363 bp,如图1(b)所示。
在NCBI(National Center for Biotechnology Information)中比對同源序列,如图1(c)所示,筛选到12条同源序列的保守结构域分析均为TIMP结构域,如图1(d)所示。以拟禾本科根结线虫(Meloidogyne graminicola)为内参,方头恐猛蚁(Dinoponera quadriceps)为外参,以这12条同源序列构建系统发育树,如图1(e)所示。
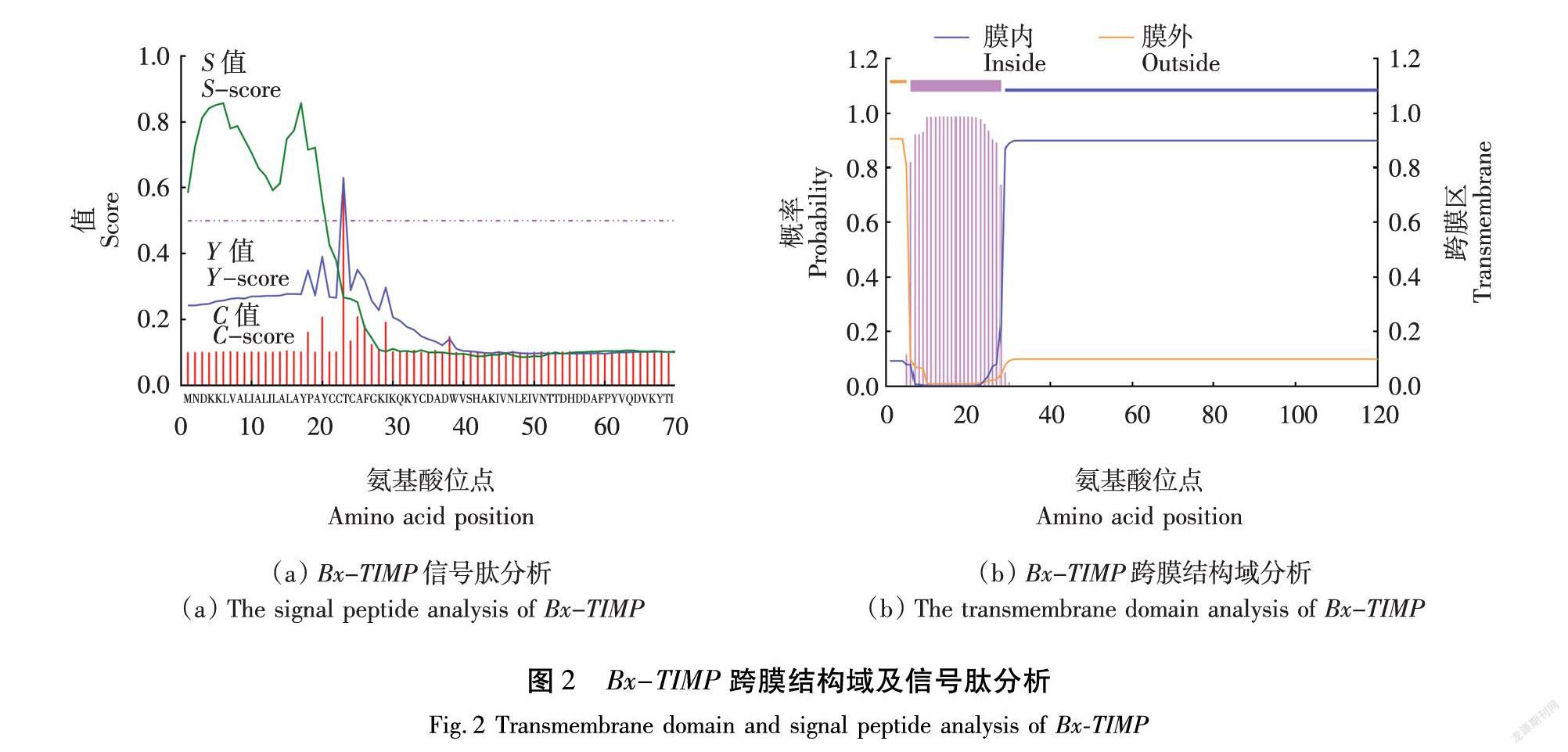
进一步对该基因信号肽及结构域进行验证,结果表明,Bx-TIMP编码的蛋白质具有信号肽(图2(a))和跨膜结构域(图2(b)),均符合效应因子特征。
2.2 Bx-TIMP原位杂交
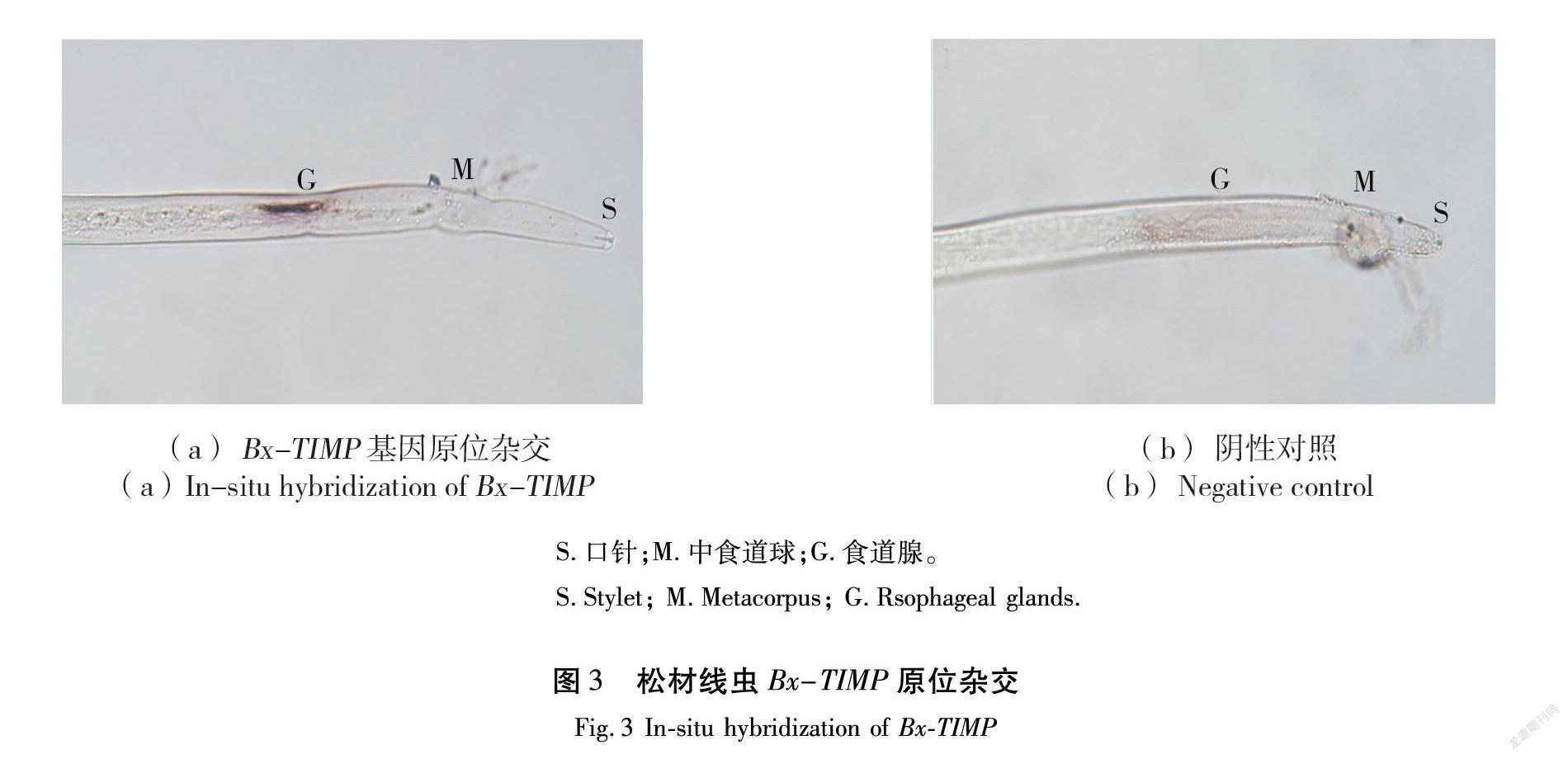
原位杂交结果显示在线虫食道腺上检测到Bx-TIMP基因信号标记(图3)。线虫的食道腺、性腺和侧尾腺是线虫效应因子分泌部位,以食道腺为主, Bx-TIMP原位杂交结果表示该基因符合线虫效应因子基因表达特点。
2.3 Bx-TIMP RNAi及接种验证
使用荧光显微镜检测RNAi组线虫体内由FAM标记的dsRNA,松材线虫通体显示绿色荧光,表明dsRNA已成功进入线虫体内(图4(a))。Q-PCR检测显示,RNAi组Bx-TIMP基因表达下调(图4(b))说明Bx-TIMP基因RNAi效果显著,CK组无明显变化。
根据接种后红松发病情况(图4(c)),连续观察1~33 d,直至33 d观察结束,RNAi组症状为少数松树针叶局部褪绿,病株均仍未完全枯萎死亡。CK组症状为所有针叶黄化。ddH2O处理组红松无症状。
3 结论与讨论
本研究通过克隆TIMPs相关基因Bx-TIMP并进行分析,该基因编码的蛋白质具有跨膜结构域及信号肽,原位杂交试验表明该基因于松材线虫食道腺中表达。将该基因沉默后,松材线虫对红松的致病性降低。因此确定该基因为效应因子基因,该基因编码的效应因子可促进松材线虫侵染松树。
TIMPs除了抑制MMPs活性还有其他作用,如生长因子活性、类固醇生成和细胞形态调节。秀丽线虫(Caenorhabditis elegans)通过TIMP-1调节性腺发育促进其繁殖。Bx-TIMP为组织金属蛋白酶抑制剂(TIMPs)基因,可能通过特异性抑制植物基质金属蛋白酶(MMPs)活性对植物防御反应产生影响,但该基因影响松材线虫致病性的作用机理还需深入研究。本研究通过RNAi技术沉默该基因后接种红松验证其功能,Bx-TIMP基因沉默后松材线虫的致病性降低,表明该基因与松材线虫致病性有关,结合效应因子在松材线虫抑制植物防御反应中的重要作用可知,Bx-TIMP在松材线虫致病性中起关键作用,能够成为松材线虫防治的靶标基因,有效降低松材线虫致病性,为松材线虫的防治提供理论基础。
【参 考 文 献】
HUSSEY R S. Disease-inducing secretions of plant-parasitic nematodes. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 1989, 27: 123-141.
ROSSO M N, HUSSEY R S, DAVIS E L, et al. Effectors in plant-microbe interactions. Oxford, UK: Wiley-Blackwell, 2011.
HAEGEMAN A, MANTELIN S, JONES J T, et al. Functional roles of effectors of plant-parasitic nematodes. Gene, 2012, 492(1): 19-31.
BIRD D M, JONES J T, OPPERMAN C H, et al. Signatures of adaptation to plant parasitism in nematode genomes. Parasitology, 2015, 142(Suppl 1): S71-S84.
王步勇,问荣荣,李秀伟,等.松材线虫谷胱甘肽S转移酶Sigma1基因(BxGSTs1)克隆及表达分析.中南林业科技大学学报,2021,41(4):156-164.
WANG B Y, WEN R R, LI X W, et al. Cloning and expression analysis of glutathione s-transferase gene BxGSTs1 in Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2021,41(4):156-164.
REHMAN S, GUPTA V K, GOYAL A K. Identification and functional analysis of secreted effectors from phytoparasitic nematodes. BMC Microbiology, 2016, 16: 48.
JONES J D G, DANGL J L. The plant immune system. Nature, 2006, 444(7117): 323-329.
HUANG X, HU L J, WU X Q. Identification of a novel effector BxSapB3 that enhances the virulence of pine wood nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Acta Biochimica et Biophysica Sinica, 2019, 51(10): 1071-1078.
许佳瑶,陈俏丽,张瑞芝,等.松材线虫Bx-ubc-3基因克隆及泛素通路鉴定.森林工程,2019,35(5):9-15.
XU J Y, CHEN Q L, ZHANG R Z, et al. Genetic cloning of Bx-ubc-3 and identification of ubiquitin pathway from Bursaphelenchus xylophilus(Aphelenchida: Aphelenchoididae). Forest Engineering, 2019, 35(5): 9-15.
CHEN Q, ZHANG R, LI D, et al. Genetic characteristics of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus third-stage dispersal juveniles. Scientific Reports, 2021, 11(1): 3908.
陶佳慧,肖炜,杨伟,等.计划烧除对松材线虫的影响.中南林业科技大学学报,2021,41(11):65-72.
TAO J H, XIAO W, YANG W, et al. Effects of prescribed burning on Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2021,41(11):65-72.
LIU Q, WEI Y, XU L, et al. Transcriptomic profiling reveals differentially expressed genes associated with pine wood nematode resistance in Masson pine (Pinus massoniana lamb.). Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 4693.
HU L J, WU X Q, LI H Y, et al. An effector, BxSapB1, induces cell death and contributes to virulence in the pine wood nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 2019, 32(4): 452-463.
ESPADA M, DEN AKKER S E V, MAIER T, et al. STATAWAARS: a promoter motif associated with spatial expression in the major effector-producing tissues of the plant-parasitic nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. BMC Genomics, 2018, 19(1): 553.
高景斌,徐六一,葉建仁,等. 马尾松松材线虫病抗性无性系的筛选和遗传多样性分析. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 45(5): 109-118.
GAO J B, XU L Y, YE J R et al. Growth and genetic diversity analysis of clones screened by phenotypical resistant to pine wilt disease inPinus massoniana.Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 45(5): 109-118.
FLINN B S. Plant extracellular matrix metalloproteinases. Functional Plant Biology, 2008, 35(12): 1183-1193.
BREW K, DINAKARPANDIAN D, NAGASE H. Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases: evolution, structure and function. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) -Protein Structure and Molecular Enzymology, 2000, 1477(1/2): 267-283.
FATA J E, HO A T, LECO K J, et al. Cellular turnover and extracellular matrix remodeling in female reproductive tissues: functions of metalloproteinases and their inhibitors. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 2000, 57(1): 77-95.
JACKSON H W, DEFAMIE V, WATERHOUSE P, et al. TIMPs: versatile extracellular regulators in cancer. Nature Reviews Cancer, 2017, 17(1): 38-53.
ISLAM S, CHUENSIRIKULCHAI K, KHUMMUANG S, et al. Accumulation of versican facilitates wound healing: implication of its initial ADAMTS-cleavage site. Matrix Biology, 2020, 87: 77-93.
HASHIMOTO G, AOKI T, NAKAMURA H, et al. Inhibition of ADAMTS4 (aggrecanase-1) by tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMP-1, 2, 3 and 4). FEBS Letters, 2001, 494(3): 192-195.
KASHIWAGI M, TORTORELLA M, NAGASE H, et al. TIMP-3 is a potent inhibitor of aggrecanase 1 (ADAM-TS4) and aggrecanase 2 (ADAM-TS5). Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2001, 276(16): 12501-12504.
WANG W M, GE G X, LIM N H, et al. TIMP-3 inhibits the procollagen N-proteinase ADAMTS-2. The Biochemical Journal, 2006, 398(3): 515-519.
零雅茗.松材線虫3条效应因子基因克隆.哈尔滨:东北林业大学,2018.
LING Y M. The cloning of 3 Bursaphelenchus xylophilus effector genes. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University, 2018.
WOESSNER J F JR. MMPs and TIMPs-an historical perspective. Methods in Molecular Biology (Clifton, N J), 2001, 151: 1-23.
KUBOTA Y, NISHIWAKI K, ITO M, et al. The role of tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in organ development and regulation of ADAMTS family metalloproteinases in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics, 2019, 212(2): 523-535.
