Two⁃Dimensional Coordination Polymer[Tb(1,4⁃bdc)1.5(phen)(H2O)]n:Synthesis,Crystal Structure and Luminescent Detection of Fe3+
2022-03-16WANGZiWeiWUHaoDongMuhammadYaseenLIANGAiLinLIUHeNINGZiAngWANGShuaiWANGGangQUANWeiWANGHao
WANG Zi-WeiWU Hao-DongMuhammad YaseenLIANG Ai-LinLIU He NING Zi-AngWANG ShuaiWANG GangQUAN WeiWANG Hao*,
(1Beijing Key Lab of Special Elastomer Composite Materials,College of New Materials and Chemical Engineering,Beijing Institute of Petrochemical Technology,Beijing 102617,China)
(2Institute of Chemical Sciences,University of Peshawar,Peshawar 25120,Pakistan)
Abstract:Two-dimensional coordination polymer of[Tb(1,4-bdc)1.5(phen)(H2O)]n(1)(1,4-H2bdc=terephthalic acid,phen=1,10-phenanthroline)was synthesized by solvothermal approach.Complex 1 was characterized by single-crystal X-ray diffraction,powder X-ray diffraction,FT-IR spectroscopy,elemental analysis,and fluorescence spectra.X-ray diffraction crystallographic analyses show that complex 1 crystallizes in the triclinic crystal system P1 space group;two adjacent Tb(Ⅲ) ions are bridged by—O—C—O—from four 1,4-bdc2-into a binuclear unit,and further bridged by 1,4-bdc2-into an infinite 2D layered structure.The fluorescence experiment proved that the complex 1 can detect Fe3+through the fluorescence quenching mechanism with Ksv=8.39×103L·mol-1and limit of detection of 0.017µmol·L-1.CCDC:2095406.
Keywords:coordination polymer;crystal structure;luminescence sensing
0 Introduction
The uncontrolled release of iron ions into air and water sources leading to several types of environmental pollutions are human health hazards[1-3].Therefore,it is important to develop a simple and efficient method for the detection of Fe3+.Among many reported sensing approaches,fluorescence sensing has received extensive attention attributed to its high sensitivity,low detection limit,and fast detection speed[4-5].Therefore,a fluorescence sensor can be developed to detect lowconcentration of Fe3+[6-9].
Coordination polymers(CPs)are fascinating materials that are both fundamentally important and technologically relevant[10-11]and have been extensively studied,not only because of their diverse structures,but also for their wide application prospects in the fields of molecular storage,luminescence,and magnetism[12-14].Currently,luminescent coordination polymers(LCPs)as fluorescent probes have become one of the research hotspots,which can effectively monitor the presence of iron ions based on the fluorescence quenching mechanism[15].
The application of the mixed ligands strategy has been proved an effective method to construct a variety of CPs[16-21].In this work,a new Tb3+CP with terephthalic acid(1,4-bdc)and 1,10-phenanthroline(phen),[Tb(1,4-bdc)1.5(phen)(H2O)]n(1),was synthesized and structurally determined using mixed ligands strategy.The resulting CP exhibited high luminescence sensing performance for Fe3+with a fluorescence quenching mechanism.
1 Experimental
1.1 Reagents and characterization
Terbium nitrate hexahydrate,1,10-phenanthroline,and terephthalic acid were of commercial grade and used without further purification.Powder X-ray diffraction(PXRD)patterns were recorded on a Rigaku D/Max-2500 diffractometer(Cu Kα,λ=0.154 06 nm,2θ=5°-50°,U=40 kV,I=40 mA),having a graphite monochromator.Simulation of the PXRD pattern was carried out by the single-crystal data and diffraction-crystal module of the Mercury program version 1.4.2.Elemental analyses for C,H,and N were performed on a Perkin-Elemer240C analyzer.FT-IR spectra of the powder samples were collected on a Nicolet IS10 infrared spectrum radiometer in a wavenumber range of 4 000-400 cm-1using the KBr pellets.The luminescence spectra and luminescence lifetimes properties were measured with the FS5 fluorescence spectrometer(Edinburgh Instruments).
1.2 Synthesis of the title complex
1,4-H2bdc(8 mg,0.05 mmol),Tb(NO3)3·6H2O(21 mg,0.05 mmol),phen(9 mg,0.05 mmol)and H2O/DMAC/EtOH(5 mL,1∶1∶1,V/V)were sealed in a clear glass vial(10 mL),heated at 95℃for 72 h,and then cooled slowly to room temperature.The colorless and sticklike crystals were obtained and washed with ethanol with a yield of 20%(based on Tb3+).Anal.Calcd.for C24H16N2O7Tb(%):C,47.77;H,2.65;N,4.64.Found(%):C,47.81;H,2.77;N,4.83.IR(KBr pellet,cm-1):2 819(w),2 671(w),2 545(w),1 678(s),1 396(s),1 390(s),1387(s),1286(s),1020(m),933(m),781(m),728(vs).
1.3 XRD structural determination
Diffraction data of 1 were collected on a Bruker D8 venture diffractometer with graphite-monochromator at 293(2)K with Mo Kα radiation(λ =0.071 073 nm).The crystal data was solved by direct methods using the SHELXS-2014 program and refined by fullmatrix least-squares methods on F2using the program SHELXL-2014.Metal atoms in the complex were located from the E-maps while non-hydrogen atoms were located in successive difference Fourier syntheses and refined with anisotropic thermal parameters on F2.Hydrogen atoms of the ligands were generated theoretically onto the specific atoms and refined with fixed thermal factors.The crystallographic data and experimental details for structural analyses are summarized in Table 1.Selected bond lengths for the complex are listed in Table 2.
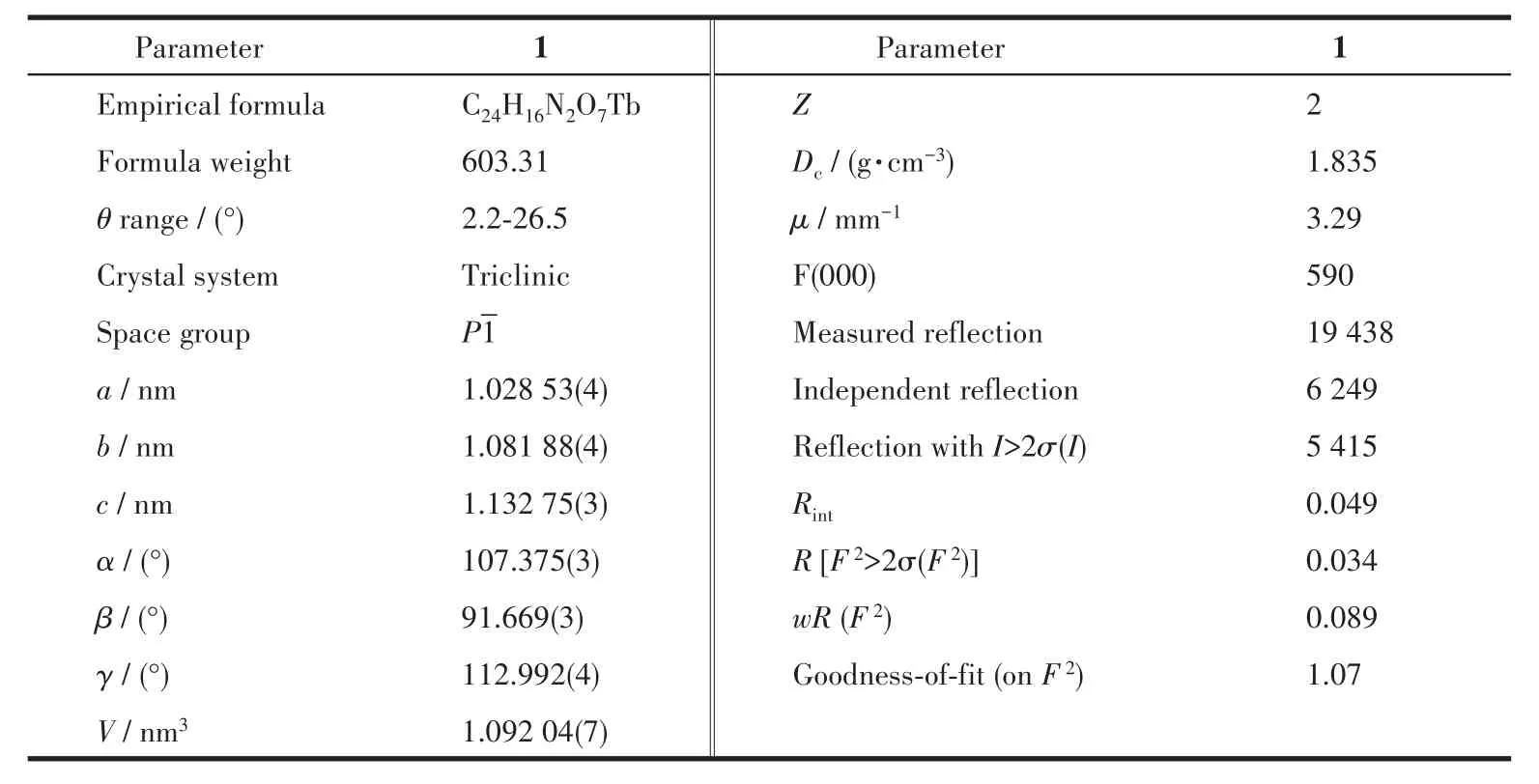
Table 1 Crystallographic data and structural refinements of complex 1
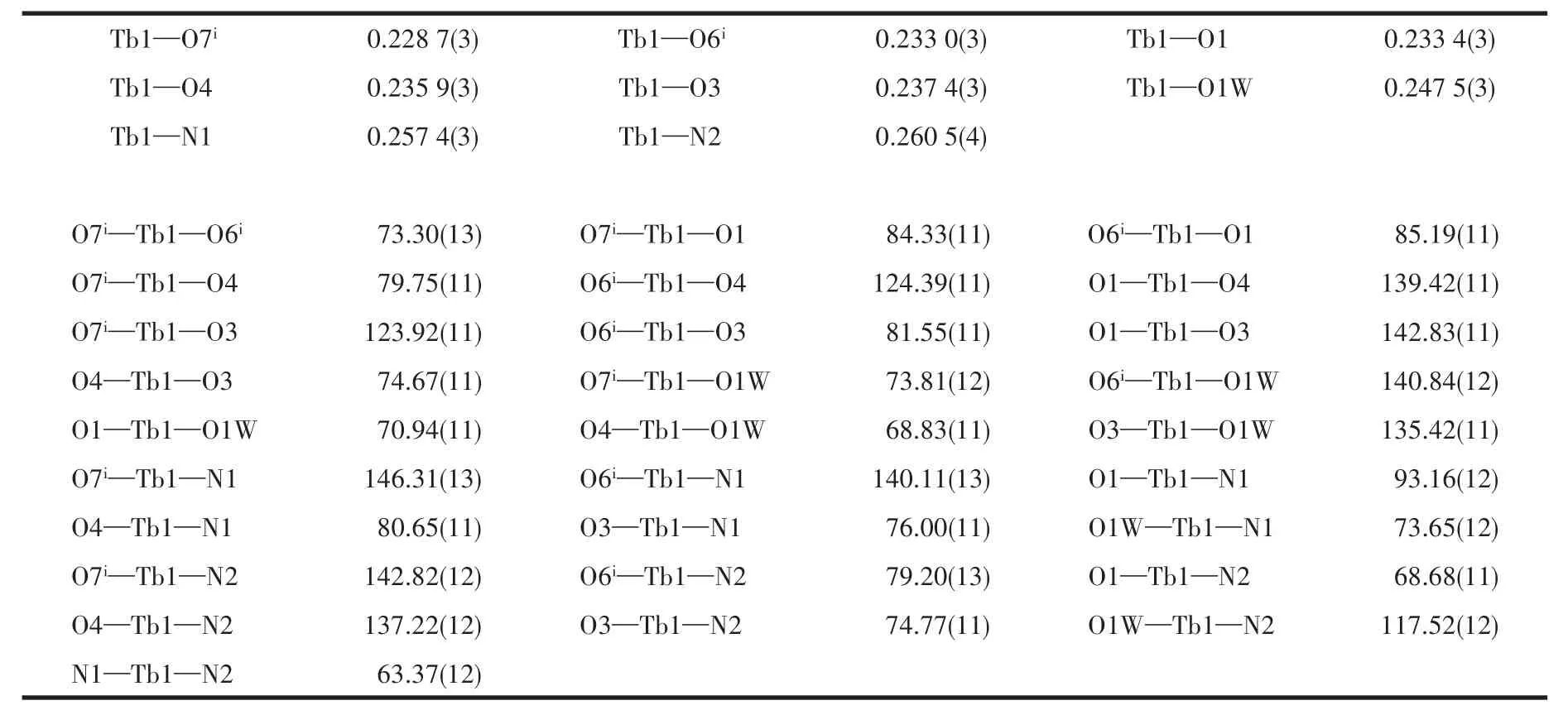
Table 2 Selected bond lengths(nm)and bond angles(°)of 1
CCDC:2095406.
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Structural description of 1
X-ray single-crystal analysis reveals that complex 1 crystallizes in the triclinic space groupThe asym-metric unit of 1 is composed of one Tb3+ion,one and a half 1,4-bdc2-ligands,one phen ligand,and one coordinated water molecule.Tb3+ion is eight-coordinate and surrounded by five oxygen atoms from five 1,4-bdc2-,one oxygen atom from the water molecule,and two nitrogen atoms from one chelating phen molecule(Fig.1a).As expected,the average distance of Tb—O(0.255 6 nm)is shorter than that of Tb—N(0.257 4 nm).1,4-bdc2-adopt two kinds of coordination modes to bridge three Tb3+ions and four Tb3+ions(Fig.1b).Neighboring Tb3+ions are bridged by—O—C—O—links from four 1,4-bdc2-into a binuclear unit with Tb…Tb distance of 0.432 1 nm(Fig.1c).Such units are further bridged by 1,4-bdc2-into an infinite 2D plane(Fig.1d).
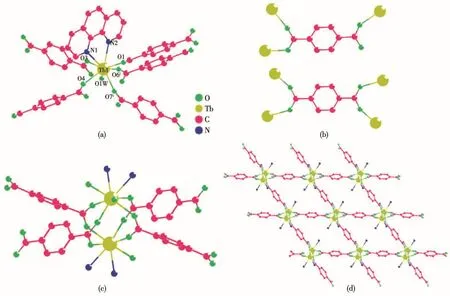
Fig.1 Crystal structure of complex 1:(a)coordination environment;(b)two kinds of coordination mode of 1,4-bdc2-;(c)binuclear unit;(d)2D plane where phen molecules are omitted for clarity
2.2 PXRD analysis and stability in organic solvents
The purity of the crystalline samples of 1 was confirmed by PXRD and the results shown in Fig.2a confirm that the PXRD pattern of the as-synthesized complex matched well with the simulated one based on the single-crystal diffraction data.To explore its stability in different solvents,crystal samples of 1 were immersed in several common organic solvents,which were ethylene glycol (EG), N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP),MeOH,EtOH,dimethyl sulfoxide(DMSO),N,N-dimethylformamide(DMF),N,N-dimethylacetamide(DMAC),N,N-diethylformamide(DEF),and CH2Cl2,for 24 h.As shown in Fig.2b,the peak positions of the sample after soaking in different organic solvents and experimental patterns were in good agreement with each other,proving that 1 has good stability in the above organic solvents.
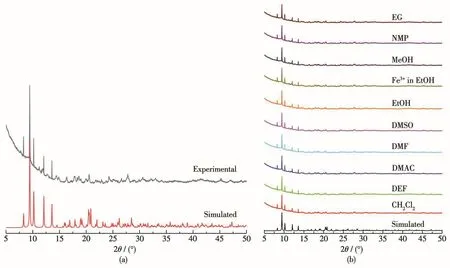
Fig.2 (a)View of simulated and experimental PXRD patterns of 1;(b)PXRD patterns of 1 soaked in different solvents
2.3 Fluorescence spectra and sensing performance
2.3.1 Luminescent properties
The solid-state luminescence performance of 1 was studied at room temperature and the results are shown in Fig.3.As shown in Fig.3a,the luminescence spectrum of 1 showed a characteristic emission of Tb(Ⅲ)with an excitation wavelength of 310 nm.The emission peaks located at 489,544,585,613 nm are ascribed to the5D4→7Fj(j=6,5,4,3)transition of Tb3+.To better understand its luminescent properties,the luminescence lifetime was also studied.Under 310 nm excita-tion wavelength,the luminescence lifetime was studied by monitoring the most intense peak in the whole spectrum of 1(5D4→7F5).The observed luminescent lifetime determined from Fig.3b was 708µs.
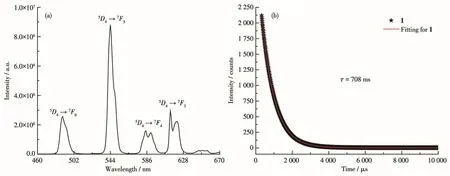
Fig.3 (a)Emission spectra of 1 in solid-state;(b)Decay curve of 1 at room temperature
2.3.2 Sensing performance for metal ions
To investigate the sensing ability of different metal ions,the ground powder of complex 1(3 mg)was introduced into an ethanol solution(3 mL)of M(NO3)m(Mm+=Ni2+,Mn2+,Zn2+,K+,Cd2+,Ca2+,Mg2+,Fe3+,1 mmol·L-1).The resulting solution was homogenized under ultrasonication for 5 min,and then the fluorescence responses were recorded at room temperature(Fig.4a).The luminescence intensity at 544 nm showed a slight decrease with the addition of Ni2+,Mn2+,Zn2+,K+,Cd2+,Ca2+,and Mg2+.On the contrary,the addition of Fe3+prominently decreased the luminescence intensity(almost 0),indicating that complex 1 can selectively detect Fe3+by fluorescence“turn-off”,which also can even be observed by naked eyes(Fig.4b).
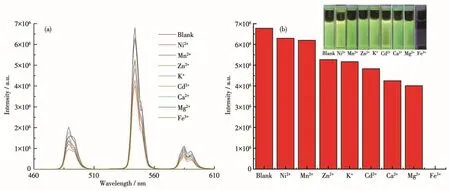
Fig.4 (a)Emission spectra of 1 in ethanol solutions with different metal ions;(b)Luminescence intensity at 544 nm of 1 in different ethanol solutions of various metal ions
To better understand the sensitivity to Fe3+ions of complex 1,a luminescence quantitative titration experiment was carried out.The luminescence intensity of complex 1 descended gradually with increasing the concentration of Fe3+ions(Fig.5).Quantitatively,the calculated value of Ksvwas 8.39 × 103L·mol-1using the Stern-Volmer equation at low concentration with a linear correlation coefficient value(R2)of 0.995[22-26](Fig.6).According to LOD=3σ/k[27-30],the calculated detection limit was 0.017 µmol·L-1.The limit of detection of compound 1 was much superior to those CPsbased sensor materials reported in the literature(Table 3).
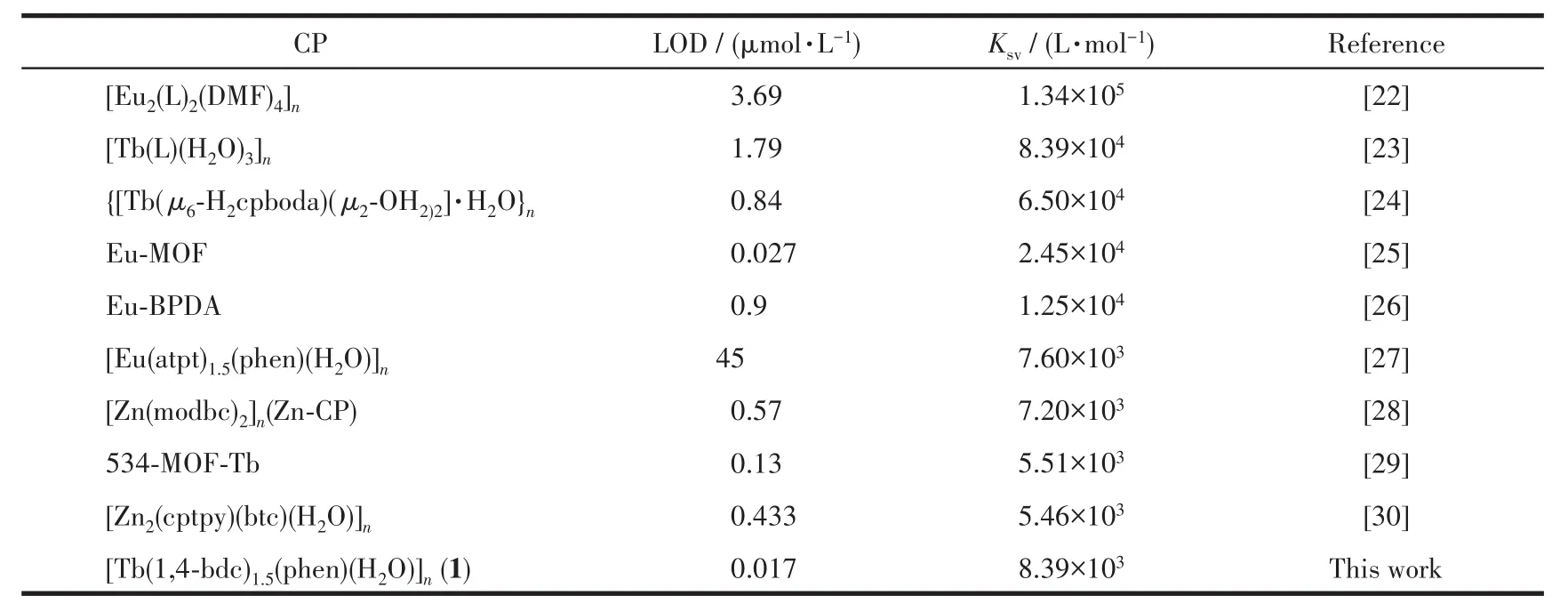
Table 3 Comparison of sensing performance of compounds 1 for Fe3+ions with other reported CPs
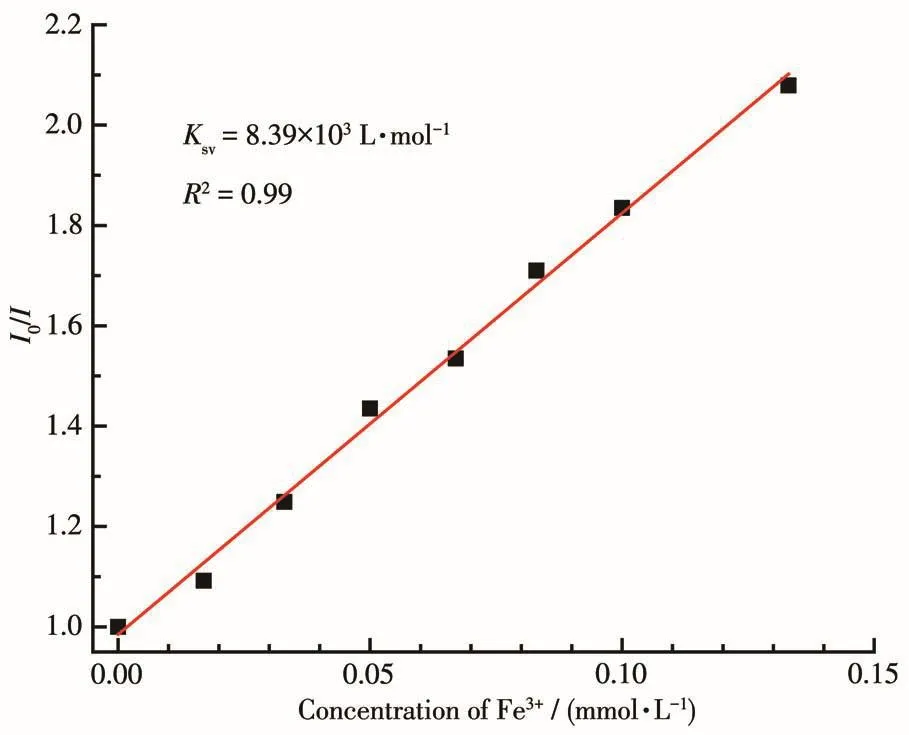
Fig.6 Stern-Volmer plot of 1 in Fe3+solution with various concentrations
The PXRD patterns of 1 before and after the Fe3+treatment proved that the crystal structure of 1 remained stable(Fig.2b),so the luminescence quenching was not caused by the decomposition of the framework.We further obtained the UV-Vis spectra of all the identified metal ions(1 mmol·L-1in ethanol).In Fig.7,it can be seen that the absorption band of Fe3+was in 300-400 nm region,which overlaps with the excitation wavelength of 1(310 nm),indicating that there may be a competitive energy absorption progress.And other metal ions had negligible absorption on 310 nm.So,the quenching mechanism of 1 for Fe3+may be attributed to competitive energy absorption,which is a common quenching mechanism in CPs sensing for Fe3+[31-32].
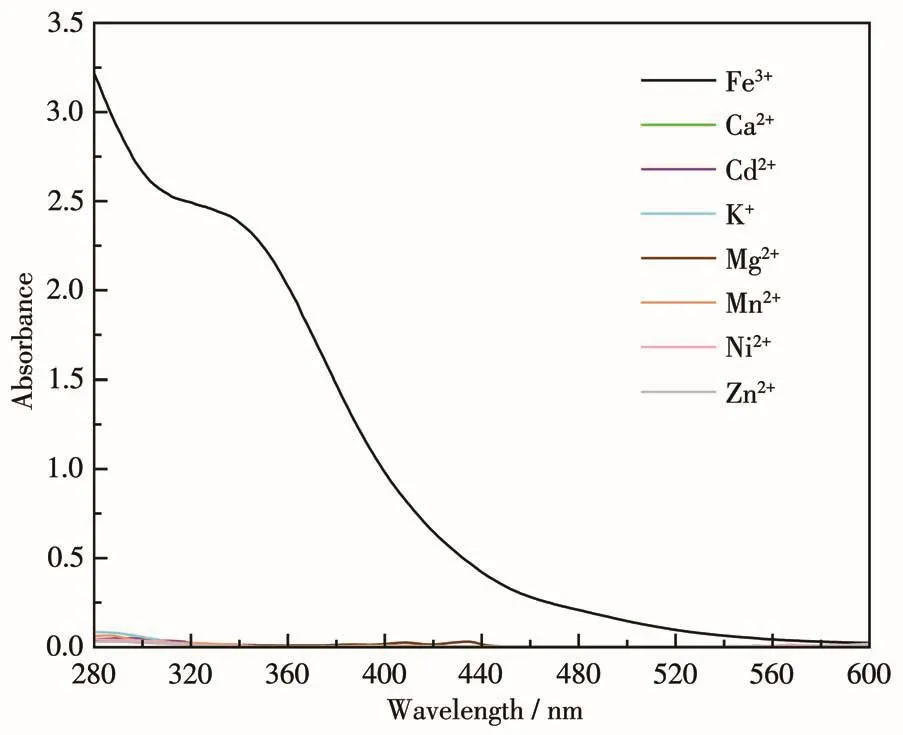
Fig.7 UV-Vis spectra of different metal ions used for the detection experiments
Seven kinds of interference substances were used to selectively detect the identified iron ions.As shown in Fig.8,initially,with the addition of other metal ions,the fluorescence intensity of 1 showed a negligible change(left column).However,with the addition of Fe3+,the fluorescence intensity decreased rapidly(right column).The decrease in fluorescence intensity indicates that it can detect Fe3+ions even in the presence of other metal ions.
3 Conclusions
A 2D coordination polymer,[Tb(1,4-bdc)1.5(phen)(H2O)]n(1),was synthesized by the solvothermal method and the luminescent emission spectrum and luminescence lifetime were investigated.Compound 1 exhibited good sensitivity and selectivity for detecting Fe3+ions by fluorescence quenching mechanism with Ksv=8.39×103L·mol-1and limit of detection of 0.017 µmol·L-1.
杂志排行
无机化学学报的其它文章
- Barium Complex In Situ Synthesized from 1,4,5,8⁃Naphthalene Tetracarboxylic Acid:Structure,Detection of Aromatic Amines,and Use as a Precursor of Nano BaCO3
- Synthesis,Crystal Structure and Magnetic Properties of Dinuclear Dy(Ⅲ)Complex Based on Multidentate Schiff Base
- 石墨烯吸附TiCl4分子的条件控制及光电性能的理论研究
- 亚铁金属有机层的合成、结构及其超快仿生催化性能
- 一维TiO2锐钛矿/金红石异相结的制备及光催化降解甲醛性能
- 源于铋玻璃的富氧空位BiOCl光催化材料的原位合成及性能
