Mammalian target of rapamycin;novel insight for management of inflammatory bowel diseases
2022-03-14NaserAldinLashgariNazaninMomeniRoudsariSaeidehMomtazAmirHosseinAbdolghaffari
Naser-Aldin Lashgari,Nazanin Momeni Roudsari,Saeideh Momtaz,Amir Hossein Abdolghaffari
Naser-Aldin Lashgari,Nazanin Momeni Roudsari,Amir Hossein Abdolghaffari,Department of Toxicology and Pharmacology,Faculty of Pharmacy,Tehran Medical Sciences,Islamic Azad University,Tehran 1941933111,Iran
Saeideh Momtaz,Amir Hossein Abdolghaffari,Department of Pharmacology,Medicinal Plants Research Center,Institute of Medicinal Plants,ACECR,Karaj 1417614411,Iran
Saeideh Momtaz,Amir Hossein Abdolghaffari,Toxicology and Diseases Group (TDG),Pharmaceutical Sciences Research Center (PSRC),The Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences(TIPS),Tehran University of Medical Sciences,Tehran 1941933111,Iran
Saeideh Momtaz,Amir Hossein Abdolghaffari,Department of Toxicology and Pharmacology,Faculty of Pharmacy,Tehran University of Medical Sciences,Tehran 1941933111,Iran
Saeideh Momtaz,Amir Hossein Abdolghaffari,Gastrointestinal Pharmacology Interest Group(GPIG),Universal Scientific Education and Research Network (USERN),Tehran 1941933111,Iran
Abstract Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBDs),with blurred etiology,show a rising trend and are of global concern.Of various factors involved in IBD pathogenesis and development,inflammation has been shown to play a major role.Recognition of the molecular and cellular pathways that induce IBD is an emerging subject to develop targeted therapies.Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) is one the most common receptors of many inflammatory pathways,including that of IBD.To this end,we intend to overview the mTOR inhibitors for their possible efficacy in present and future approaches to treatment of IBD.
Key Words:Inflammatory bowel diseases;Inflammation;Mammalian target of rapamycin;Mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors
INTRODUCTION
Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBDs) include two major types:ulcerative colitis (UC)and Crohn’s disease (CD) that mainly progress due to abnormal dysregulation of the immune system[1].Aberrations of the innate and adaptive immune responses and inflammatory processes play crucial roles in IBD pathogenesis[2].Unregulated immune response stimulates Toll-like receptor-4 and the gastrointestinal enteric bacteria flora,thus activating the mucosal T cells and interferon (IFN) production and release.These events initiate the signal transduction cascades such as the nuclear factor (NF)-κB pathway;the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) and transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1) pathway.As a result,the activation of these pathways leads to elevation of inflammatory cytokines and induction of IBD.In the next step,leukocytes are aberrantly activated,leading to enhanced infiltration into the injured colonic site.
Therefore,modulation of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines could be important for IBD treatment.Pharmacological products or surgery are commonly used in IBD patients.Anti-inflammatory drugs (i.e.corticosteroids and aminosalicylates);immunomodulatory treatments (i.e.azathioprine,mercaptopurine,cyclosporine and methotrexate);biologic compounds [i.e.tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α inhibitors];and antimicrobials (i.e.ciprofloxacin and metronidazole) are current therapeutic options for IBD treatment.Among them,mTOR is a serine/threonine protein kinase of the phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase related kinase (PIKK) family,and a critical regulator of the inflammatory pathways[3,4].mTOR has two subtypes of mTORC1 and mTORC2.Structurally,mTORC1 contains SEC13 protein 8 (mLST8)/G-protein b subunit-like protein (GbL),the regulatory-associated protein of mTOR (Raptor),DEPTOR,PRAS40,and a scaffold protein TTI1/TEL2 complex.The composition of mTOR,the mammalian stress-activated protein kinase interacting protein 1 (mSIN1),Tor2 (mTOR ortholog),mLST8/G_L,insensitive drug companion of mTOR (DICTOR),DEPTOR,TTI1,and TEL2 forms the mTORC2[5].Activation of the mTOR pathway in intestinal epithelial cells has been shown to induce inflammation (Figure 1).In addition,mTOR is a downstream molecule of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway that plays a key role in the cellular transduction system and biological processes.Activation of the mTOR signaling pathway in the intestinal epithelial cells induces inflammation events that lead to IBD.In addition,activation of the mTOR/NF-κB pathway results in upregulation of IFN-γ,interleukin (IL)-6,IL-8,IL-1,and TNF-α.Induction of the P13K/AKT/mTOR pathway promotes TNF-α,IL-1β,transforming growth factor(TGF)-β,IL-12 and IL-6 secretion.The TLR/P38MAPK/mTOR pathway increases the serum levels of IL-12,IL-6,IL-8 and TNF-α.All of these pathways together could trigger IBD due to the induction of inflammatory processes.Activation of the mTOR signaling pathway induces immune cells such as macrophages and T cells,which in turn elevates the secretion of IFN-γ,IL-6,IL-8,IL-1 and TNF-α.It has been shown that regulatory T cells (Tregs) improve colitis through immunosuppression and reduction of inflammatory factors such as IL-1β,TNF-α,IL-6,IL-10 and IL-17A[6].
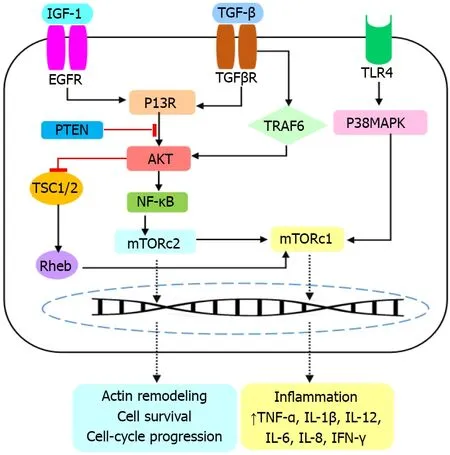
Figure 1 Activation of the mammalian target of rapamycin pathway in intestinal epithelial cells has been shown to induce inflammation.
The myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) are also attributed to the etiology of IBD and have been shown to improve colitisin vivo.It was demonstrated that mTOR inhibitors could suppress MDSCs and improve IBD.MDSCs have shown superior immunosuppressive activities against IBD.mTOR inhibitors increase Tregs but reduce Th1 cells in IBD.These results indicate that some of the mTOR inhibitors attenuate IBDviaTreg expansion promoted by MDSCs[6,7].Inhibition of the mTOR pathway can improve IBD due to suppression of inflammatory processes.Hence,the factors that target the components of this pathway or the mTOR signaling proteins are of interest for drug development.Severe IBD could lead to several dangerous diseases such as colon cancer,irritable bowel syndrome,visceral hypersensitivity,neurodegenerative disease,etc.Induction of proinflammatory and inflammatory cytokines,i.e.,the cytokine storm in conditions such as COVID-19 may affect IBD patients.Therefore,the mTOR inhibitors are important not only to improve IBD,but also to reduce the risk of health-threatening conditions[8,9].
CONCLUSION
Given the high risk of inflammatory diseases and their influence on organ failure,new therapeutic triggers with fewer side effects and more specialization are needed.Clinical evidence demonstrates that inflammatory processes can increase the risk of many diseases.For example,it has been shown that inflammatory factors cause neurodegeneration and increase the risk of neurodegenerative disease such as Alzheimer’s disease,Parkinson’s disease and multiple sclerosis[10,11].IBD could also lead to other gastrointestinal impairments such as colonic cancer.Recently,it has been proposed that IBD induces colonic angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 expression,probably due to the stimulation of cytokines storm,which finally increases susceptibility to COVID-19 and could end in death[12,13].Although the etiopathogenesis of IBD is poorly understood,available evidence suggests that genetic susceptibility and environmental stimuli can predispose to immunological responses,and provoke IBD[14,15].Many inflammatory signaling pathways participate in pathogenesis of IBD [16,17].The severity of IBD relies on the location and extent of the lesions,resulting in numerous extraintestinal manifestations.The mTOR signaling pathway is one of the most important mechanisms that contributes to progression of IBD.In this context,mTOR induces the NF-κB pathway,which together participate in production of several inflammatory mediators such as IFN-γ,IL-6,IL-8,IL-1 and TNF-α[18].The TGF-β/P13K/AKT/mTOR pathway upregulates TNF-α,IL-1β,TGF-β,IL-12 and IL-6 expression.The TLR/P38MAPK/mTOR interaction increases serum levels of IL-12,IL-6,IL-8 and TNF-α[3].Induction of the TLR4,MAPK and NF-κB pathways stimulates autophagy by the regulation of mTOR,thus improving the gut inflammatory responses and IBD[19].These all suggest that inhibition of mTOR and/or the mTORdependent downstream signaling pathways represent promising insight for IBD treatment.To assess such a hypothesis,several biologics such as everolimus,temsirolimus,deforolimus,sunitinib,bevacizumab,vedolizumab,etrolizumab,and the diverse mTOR analogs,AZD-8055,WYE-354,VS-5584,LY3023414,Ku-0063794,PI-103 and SKLB-M8 were analyzed and found to target mTOR and o block inflammatory processes[20,21].Several natural compounds such as resveratrol,curcumin,acacetin,capsaicin,epigallocatechin-3,fisetin,harmine,panduratin A,prodigiosin,sinomenine,honokiol and isoliquiritigenin have shown the ability to inhibit mTOR.Taken together,targeting the mTOR signaling pathway could block secretion of cytokines and chemokines and not only improves IBD but also prevents the risk of other diseases,in which inflammation plays a key pathogenic role[6,22].Future attempts should focus on planning clinical trials to evaluate the therapeutic efficacy of the mTOR inhibitors against IBD.Probable interaction of mTOR signaling with other pathways and effectors of IBD should also be considered to design targeted inhibitors with a broader action.
