Robust H∞state estimation for a class of complex networks with dynamic event-triggered scheme against hybrid attacks
2022-02-24YahanDeng邓雅瀚ZhongkaiMo莫中凯andHongqianLu陆宏谦
Yahan Deng(邓雅瀚), Zhongkai Mo(莫中凯), and Hongqian Lu(陆宏谦)
School of Intelligent Systems Engineering,Guangxi City Vocational University,Chongzuo 532200,China
We investigate the dynamic event-triggered state estimation for uncertain complex networks with hybrid delays suffering from both deception attacks and denial-of-service attacks.Firstly, the effects of time-varying delays and finitedistributed delays are considered during data transmission between nodes.Secondly, a dynamic event-triggered scheme(ETS)is introduced to reduce the frequency of data transmission between sensors and estimators.Thirdly,by considering the discussed plant, dynamic ETS, state estimator, and hybrid attacks into a unified framework, this framework is transferred into a novel dynamical model.Furthermore,with the help of Lyapunov stability theory and linear matrix inequality techniques, sufficient condition to ensure that the system is exponentially stable and satisfies H∞performance constraints is obtained,and the design algorithm for estimator gains is given.Finally,two numerical examples verify the effectiveness of the proposed method.
Keywords: dynamic event-triggered scheme,hybrid attacks,complex networks,state estimation
1.Introduction
Complex networks (CNs) can be seen as a class of generalized mathematical models abstracted from certain actual complex systems and introduced as an important tool in related cross-disciplines.A CN model can describe a large number of complex systems that exist in practice,and it usually consists of nodes,edges and topologies.[1]Nodes are used to represent different individuals in an actual system.The relationship between individuals is represented by edges, and the dynamic structure of the network is influenced by the topology.[2]Neural systems,computer networks, power networks,social relationship networks,and transportation systems are typical CNs,for example, in a nervous system, each nerve cell connected by nerve fibers can be regarded as a node,and a nervous system can be regarded as a CN.[3]Due to many advantages of CNs,they have been widely used in fields such as the Internet,sociology, communication security and image processing.[4]In recent years, research on complex networks has become a hot topic in theory and practice,for example,synchronization,consensus and state estimation.[5,6,8–11]Specifically, the authors of Ref.[9] proposed synchronization approach for delay CNs with nonlinearity and deception attacks.Based on an event-triggered scheme(ETS),the authors of Ref.[10]discussed the state estimation problem for nonlinearly coupled CNs with finite-distributed delays and discrete delay.Considering incomplete measurements and uncertain inner-coupling,a design method ofH∞state estimator was proposed for discrete CNs in Ref.[11].In this paper, we discuss the state estimation problem of complex networks with respect to both network security and resource constraint.
Generally, for the traditional data transmission strategy,the measurement signal of the estimator is updated with equal cycles.[12]Due to the limited network bandwidth resources,how to ensure the system has a certain performance,while effectively reducing the waste of network resources has been one of the key issues for networked systems.[13,14]Among many data transmission scheduling schemes, the event-triggered scheme stands out.[15]The core idea of ETS is to determine whether the current packet can meet the preset triggering conditions, and if so, the packet will be transmitted to the remote destination through the communication network.[16]As the problem of networked systems becomes more complex,more and more improved ETSs are proposed for reaping superior results, such as dynamic ETS,[17]adaptive ETS,[18]selftriggered scheme,[19]distributed ETS,[20]and hybrid ETS.[21]Specifically,a dynamic event-driven state estimation issue was investigated in Ref.[22] for discrete CNs with probabilistic sensor saturation.By utilizing an adaptive ETS,an state estimation problem was conducted for fractional-order CNs with probabilistic nonlinearities against cyber attacks in Ref.[23].In this paper, the design scheme of dynamic event-driven estimator is discussed in order to reduce the frequency of data exchange between sensors and estimators.
The application of networked systems has brought us a lot of convenience, but in the open network environment, the system faces security issues that cannot be ignored.[24]In recent years, malicious attacks against the networked systems of government agencies and enterprises have been increasing.For examples, on January 10, 2021, the Central Bank of New Zealand’s third-party hosting provider suffered a cyber attack that resulted in a data breach;on January 15,2021,the Scottish Environment Protection Agency disclosed a ransom attack that caused a serious network outage and theft of some data.[25]Based on the above-mentioned attaches, many security strategies for defending against cyber attacks[denialof-service (DoS) attacks, deception attacks, replay attacks,etc.] have been proposed.[26–28]Specifically, the authors of Ref.[29] proposed an improved recursive filtering algorithm for a class of CNs with state saturation and deception attacks.In Ref.[30],the problem of partial-nodes-based state estimation was studied for a class of uncertain CNs against deception attacks.Given that the impact of deception and DoS attacks on complex networks will be considered in this paper.The characteristics of the attacks are as follows: Deception attacks replace real data in a communication network by fake data.DoS attacks prevent the transmission of data in a communication network to a remote destination in order to destabilize the system.Note that the hybrid attacks mentioned subsequently in this paper refer to the attack model consisting of the deception attacks and the DoS attacks.
Currently, many scholars have studied the security of complex networks from the perspective of state estimation.However, the literature related to state estimation of complex networks under cyber attacks and network resource constraints is very limited,which is the main motivation of this paper.The other two motivations are as follows: on the one hand,the introduction of dynamic event triggering scheme to avoid bandwidth resource redundancy under high sampling frequency;on the other hand,the development of appropriate security strategies to deal with potential threats in an open network environment.Based on the above three points, this paper aims to meet the system performance requirements while improving the utilization of network resources and effectively resisting cyber attacks.
In this paper,the problem of security state estimation for a class of uncertain CNs with mixed delays and hybrid attacks is studied with the help of a dynamic ETS.To avoid the transmission of redundant data in the communication network, a dynamic ETS is introduced to reduce the need for estimators to perform unnecessary updates of measurement information.Also,a class of complex networks under cyber attacks and dynamic ETS is modeled as a dynamic system by considering unknown deception attacks and DoS attacks in the communication network.Then,sufficient conditions to ensure that this system is stable and satisfies theH∞performance constraint are obtained by using Lyapunov stability theory and linear matrix inequality(LMI).Based on the above stability criterion,a dynamic event-triggered estimator is designed to estimate the plant state.Finally,the validity of the designed dynamic eventtriggered estimator is verified by two examples.The main contributions of this paper are as follows:
A novel dynamics model is developed to describe the delay phenomenon among nodes, data transmission scheduling strategies and hybrid attack behaviors in CNs.
Considering the complexity of physical networks, the form of cyber attacks is extended from the universal single attack to the hybrid attacks consisting of many different attack behaviors.
Two sets of Bernoulli random variables are utilized to depict the random occurrence sequences of deception attacks and DoS attacks,respectively.
Based on the above dynamics model,uncertainties in the system parameters are further considered and robust stability analysis is also developed.
Notations: Rn×mmeansn×mreal matrix; Rndenotesn-dimensional Euclidean space;A> 0 (A≥0) implies positive definite (positive semi-definite) symmetric matrix; E {A} represents mathematical expectation of random variableA; colN{Xi} and diagN{Yi} stand for the blockcolumn matrix col{X1,X2,...,XN}and the block-diagonal matrix col{Y1,Y2,...,YN},respectively.
2.Preliminaries
Consider the following CNs withNcoupled nodes:

wherexi(k)∈Rn,yi(k)∈Rmandzi(k)∈Rrare,respectively,the state vector, the ideal measurement output and the output to be estimated of thei-th node; η(k) is the discrete timevarying delay and satisfies ηm≤η(k)≤ηM;is the finite-distributed delay and satisfies 1

whereNi,Mai,Mbi,Mdi,NΓandMΓare known matrices.F(k)is a uncertain matrix and satisfiesFT(k)F(k)≤I.

Fig.1.The systematic structure.
It is well known that the limited network bandwidth is insufficient to support the transmission of high frequency sampled signals in communication networks.For this reason,we need to introduce a suitable data transmission scheduling scheme to reduce the amount of data transmission in the communication network.In addition for open network environments,we have to take into account the potential risk of cyber attacks.Specifically, the main work of this paper is devoted to study a co-design method for robust state estimation and dynamic event-triggered schemes against hybrid attacks.In Eq.(1),the uncertain complex networks with time-varying delay and finite-distributed delay are given.As shown in Fig.1,we model the dynamic event-triggered scheme,hybrid attacks as well as the system under consideration uniformly,and transform them into an estimation error dynamic model.Details are as follows:
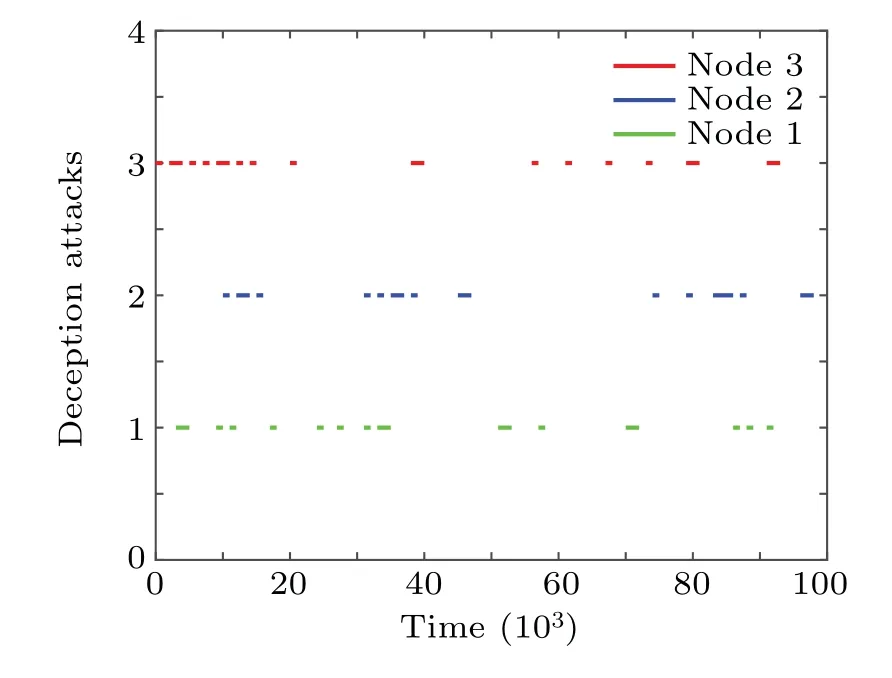
Firstly,without dynamic event-triggered scheme and hybrid attacks, the ideal measurement output can be expressed asyi(k)=Cixi(k).Secondly, we introduce a dynamic eventtriggered scheme in the communication network between sensors and estimators.For each node, the next release instantof thei-th node(1 where πiand σiare given constants,and ξi(k)=yi(k)−;is the last released data-packet.Moreover,φi(k)is a dynamic function and satisfies where 0<τi<1,and φi(0)is a given initial condition. For ξi(k)=yi(k)−,the measurement output applied to the above scheme can be represented as Then, since an open network environment may be exposed to multiple potential security risks, we discuss the impact of two types of cyber attacks on the complex networks.As a result,the data-packet transmitted to the estimator under the hybrid attacks can be expressed as where αi(k) and βi(k) are Bernoulli distributed white sequences. Assumption 1The nonlinear functionf(xi(k)) represents the deception attack signal and satisfies the following condition: withFbeing a real constant matrix. Assumption 2αi(k)and βi(k)satisfy the following statistical properties: From this,we have Remark 1In Eq.(6),andf(xi(k)) are introduced to model the transmission data under hybrid cyber attacks.When αi(k)=0 and βi(k)=0,the data transmission in the communication network is normal.When αi(k)=1 and βi(k)=0,the real data is replaced by false signal from deception attack.When αi(k)=0 and βi(k)=1,DoS attacks block all data transmission in the communication network. Remark 2If∈(0,1)and∈(0,1),data transmission in the communication network is affected by both types of cyber attacks.The Bernoulli distributed white sequence used to describe the occurrence or non-occurrence of different cyber attacks is unlikely to be identical.DoS attack and deception attack may occur alternately or simultaneously.The DoS attack is characterized by preventing any data from being transmitted through the communication network to its destination,and the false signal generated by the deception attack is no exception.Therefore, we default the DoS attack to enjoy priority in the actual numerical simulation,that is,the deception attack is not considered when both types of cyber attacks are released at the same time. Construct the following state estimator for nodei: Denote thatei(k)=xi(k)−,and. For natational convenience,we further denote Then, through Kronecker product,in Eqs.(1) and (10) can be rewritten as.From Eqs.(1)–(10),we obtain By setting ζ(k)=,we obtain the following augmented system: where For convenience of follow-on work,we require some necessary processing of Eq.(12)according to Assumption 2,and Eq.(12)can be rewritten as where Lemma 1For a real constant ρi>0, and matrixR>0,the following inequality holds: The following definition will play an important role in the stability analysis of dynamic system(12)and the design of the corresponding estimator(10). Definition 1[10]For real constants ˆa>0 and 0<<1,dynamic system(12)withw(k)=0 is said to be exponentially mean-square stable(EMSS),so that In this section,we design the estimator gain for a class of complex networks under the premise of ensuring the stability of the augmented system.First,we give a sufficient condition to ensure that the system is exponentially mean-square stable and that theH∞performance constraint is satisfied.Then,based on the above theorem,a design method for the estimator gain is given.The main content of this section will be presented as the following theorems. Theorem 1Given,γ,τi,πi,σi(i=1,2,...,N),and the estimator gainL, system (12) is EMSS, and satisfies theH∞performance constraint for all nonzero ω(k),if there exist matricesP>0,Q>0,R>0,and scalar δ1>0,the following LMI will hold: where ProofChoose the following Lyapunov functional candidate: where Taking the difference and mathematical expectation ofV(k)along the system(12)yields Taking consideration of triggering condition(3)and nonlinear constraint(7),the following inequalities hold: Then,it follows from Lemma 1 that where Σµ=.Notice that the following zero equality holds: Denote where C,F,M,Λ3,Λ4,Λ5,Π1,Π2,Π3and Π4are defined in Eq.(15). Under the zero initial condition,we can obtain the following inequality by summing both sides of Eq.(26)from 0 toTand lettingT→∞: which implies that theH∞performance constraint is ensured.Then,with the help of Schur complement,we can obtain From Definition 1 and Eq.(27), when LMI (14) holds,augmented system(12)is EMSS and satisfiesH∞performance constraint.This completes the proof. Next,a design method of the desired estimator in form of Eq.(10)for the augmented system(12)can be presented in the following theorem. Theorem 2Given,,γ,τi,πi,σi(i=1,2,...,N),the estimator in form of Eq.(10) for the augmented system (12)can be designed if there exist matricesP=diag{P1,P2}>0(P1=diagN{P1i},P2=diagN{P2i}),Q>0,R>0, and scalar δ1>0,ε >0,such that the following LMI holds: where and Ξ is defined in Eq.(15).Moreover,the designed estimator gains can be obtained by ProofRecalling Eq.(14),one has where Then,it follows from the S-procedure Lemma: Through the Schur complement Lemma, Eq.(34) can be rewritten as ConsideringP2L=X, we can obtain that Eq.(35) is equivalent to Eq.(29).This completes the proof. In this section, two numerical examples are provided to verify the effectiveness of the proposed design scheme. Example 1Consider CNs(1)withN=3, and the relevant parameters as follows: The noise signal and the deception attack signal are chosen as ω(k) = 0.2cos(k)e−0.1kandf(y(k)) =−tanh(0.18y(k)), respectively.Set other parameters to ηm=2, ηM=4,h=0.1,d=3, µs=2−(s+1),F=0.18, πi=0.2,σi=0.5, τi=0.7,i=0.2,i=0.2 and γi=2(i=1,2,3).Then, the estimator gain matrices can be obtained by Theorem 2: In simulation, the initial conditions of CNs and internal dynamic variable of dynamic event-triggered scheme(DETS)are assumed thatxi(0) =[0.1 −0.1]T, and φi(0) = 0 (i=1,2,3). Fig.2.Output estimation error of node 1. Fig.3.Output estimation error of node 2. For nodei(i= 1,2,3), the estimation errorsare shown in Figs.2–4; the occurrence of the deception attacks and the DoS attacks are illustrated in Figs.5 and 6. Fig.4.Output estimation error of node 3. Fig.5.Occurrence of the deception attacks. Fig.6.Occurrence of the DoS attacks. Fig.7.Output estimation errors of node 1,node 2,and node 3. Fig.8.Dynamic event-triggered release instants and intervals in node 1. Fig.9.Dynamic event-triggered release instants and intervals in node 2. Example 2Consider that CNs (1) are composed of 3 nodes with Other parameters are set as the same as in Example 1.Next,the gains of the designed estimator are given by Theorem 2: Fig.10.Dynamic event-triggered release instants and intervals in node 3. Simulation time isT=20 s,and sampling period selectsh=0.1 s.For nodei(i=1,2,3),the estimation errorsare shown in Fig.7.The dynamic event-triggered release instants and intervals in nodes 1, 2, and 3 are shown in Figs.8–10.The average period,maximum release interval,and transmission rate by DETS and time-triggered scheme are listed in Table 1.According to Table 1,it is easily found that the results simulated by DETS are better than those of the time-triggered scheme.From Figs.8–10 and Table 1, with the help of the dynamic event-triggered scheme(DETS),a higher communication efficiency is obtained against the hybrid attacks while ensuring the desired system performance,which shows the effectiveness of the proposed method. Table 1.The average period,maximum release interval and transmission rate for different schemes in the examples. In summary, the problem of robustH∞state estimation for a class of uncertain CNs with mixed delays and hybrid attacks has been studied by introducing a dynamic ETS.The hybrid attacks have been modeled with the help of two sets of Bernoulli random variables.A dynamic ETS has been introduced to improve the utilization of network resources.A structural framework containing CNs,dynamic ETS,state estimators, and hybrid attacks has been developed.The stability criterion for dynamic systems of this framework has been obtained.A dynamic event-triggered estimator has been designed for CNs under hybrid attacks.Finally, two examples have been given to illustrate the effectiveness of the proposed method.In the future,the problem of synchronization and pinning control for CNs under cyber attacks will be investigated.



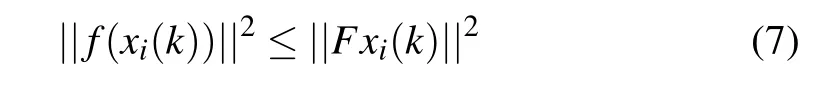
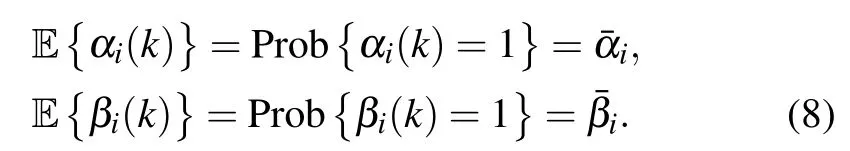




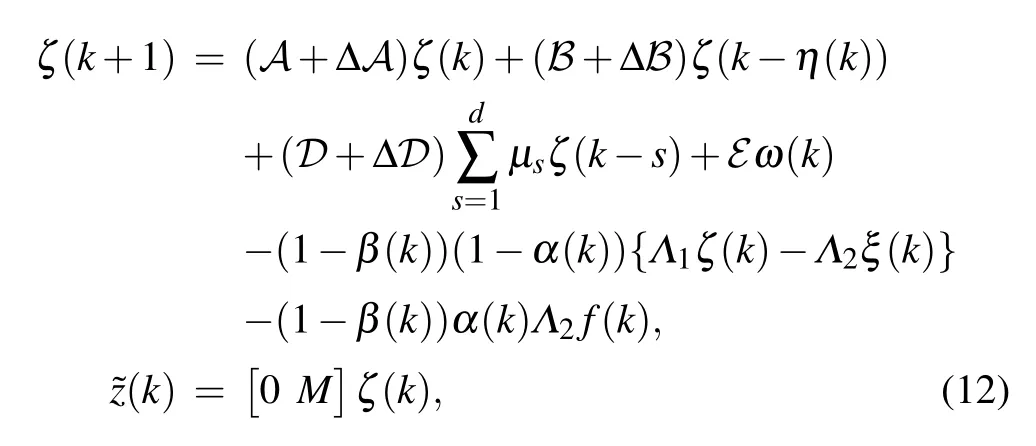





3.Main results



















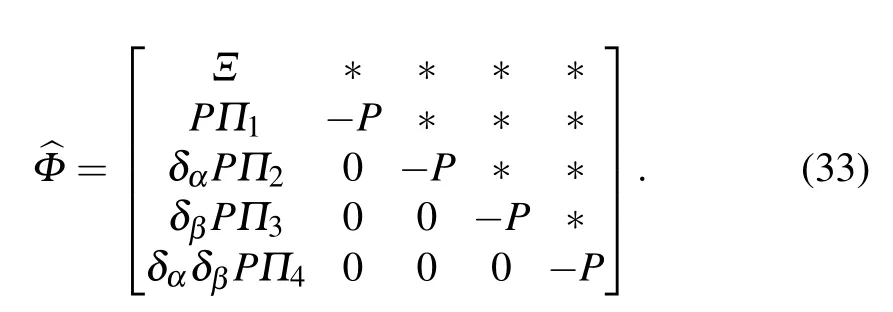


4.Examples and simulations











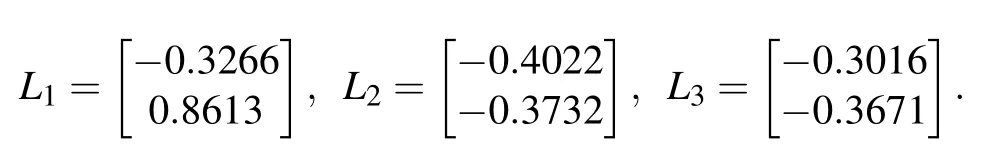


5.Conclusion
杂志排行
Chinese Physics B的其它文章
- High sensitivity plasmonic temperature sensor based on a side-polished photonic crystal fiber
- Digital synthesis of programmable photonic integrated circuits
- Non-Rayleigh photon statistics of superbunching pseudothermal light
- Refractive index sensing of double Fano resonance excited by nano-cube array coupled with multilayer all-dielectric film
- A novel polarization converter based on the band-stop frequency selective surface
- Effects of pulse energy ratios on plasma characteristics of dual-pulse fiber-optic laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy