PLA/胶丝交织弹性带阻燃整理工艺研究
2022-02-14陈军武王其卢雨正
陈军武 王其 卢雨正





摘要:
针对PLA纤维阻燃性差的问题,文章采用环磷酸酯阻燃剂对PLA/胶丝机织弹性带进行阻燃改性整理,探讨了阻燃剂质量浓度、浸渍温度和浸渍时间对弹性带阻燃性能的影响,并设计了正交试验和单因素优化试验对阻燃浸渍工艺进行优化。结果表明:最优的阻燃浸渍工艺条件为阻燃剂质量浓度250 g/L、浸渍温度50 ℃、浸渍时间2 h。经该工艺处理后,机织弹性带的阻燃性能达到FAR 25.853—1995美国航空材料防火检测标准,表现出良好的阻燃效果。
关键词:
PLA纤维;机织弹性带;阻燃整理;正交试验;单因素试验;阻燃性能
中图分类号: TS195.5
文献标志码: A
文章编号: 10017003(2022)02001205
引用页码: 021102
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7003.2022.02.002(篇序)
收稿日期: 20210601;
修回日期: 20211213
基金项目:
作者简介: 陈军武(1996),男,硕士研究生,研究方向为纺织品的开发与功能整理。通信作者:卢雨正,副研究员,LuYz@jiangnan.edu.cn。
弹性带又称松紧带、游泳带,是含橡胶丝或乳胶丝的弹性织物,通常作为纺织辅料中的紧固性产品广泛应用于服装、家具、医疗、器械、玩具、汽车安全带等领域,属于织带行业生产的大类品种之一[1]。机织弹性带的经纬纱一般选用棉或涤纶,在经向搭配一定的橡胶丝提高弹性后,可以通过设计平纹、斜纹、提花等不同的组织结构扩展使用范围[2]。
近年来,纺织品的阻燃性和环保性越发受到行业和消费者的重视,织带产品被要求有一定的阻燃和环保作用,但是目前弹性带在这方面的研究相对较少。聚乳酸纤维(Polylactic Acid,PLA)因其原料可再生和可生物降解等特点被称为21世纪的绿色环保纤维,其制品废弃后在自然条件下可降解成乳酸、二氧化碳和水,不污染环境[3]。此外,PLA纤维的物理机械性能与涤纶、锦纶相似,结构稳定且加工性能良好。PLA纤维的极限氧指数(LOI)有26%,比棉和涤纶高,但只是在一段时间内起到自熄的效果,并不具备良好的阻燃性,若用在阻燃防火产品上则需要进行额外的阻燃处理[4]。磷系阻燃剂具有低毒、低烟和阻燃效率高的特点,是取代传统卤系阻燃剂的重
点研究对象[5-6]。国内外学者在磷系阻燃PLA方面做了大量研究,Chen Yajun等[7]和刘婷[8]研究发现,不同分子结构的磷酸酯阻燃剂通过改变PLA材料燃烧时的成炭速率和形态,从而影响其阻燃性能。Liao[9]等制备出一种含磷-氮-硅元素的阻燃PLA复合材料,分析其阻燃机理发现,硅元素的存在形成了石墨残炭结构,有效阻止了材料的燃烧。
根据PLA纤维和胶丝的特性,本文采用环磷酸酯阻燃剂,通过浸渍方式对PLA/胶丝弹性带进行阻燃整理,根据正交试验和单因素优化试验得到最佳的阻燃浸渍整理工艺。
1 试 验
1.1 试样准备
经纱为333.33 dtex/288 f PLA与40号阻燃胶丝(常州振华服饰材料有限公司)按照2︰1配合使用,纬纱采用333.33 dtex/288 f PLA纱线。通过万利达窄幅织物机织成纬密为172.4根/10 cm的PLA/胶丝机织弹性带,用于阻燃性能测试。弹性带的基本物理机械性能如表1所示。
1.2 试 剂
环磷酸酯阻燃剂(上海享金化工有限公司),异丙醇(分析纯,江苏彤晟化学试剂有限公司),片状NaOH(分析纯,无锡新叶临化工贸易有限公司)。
1.3 設 备
HH-6数显恒温水浴锅(上海力辰邦西仪器科技有限公司),881-TG型热风循环干燥箱(吴江市创新烘箱制造有限公司),AI-7000S拉力强度试验机(高铁检测仪器(东莞)有限公司),XJ830等速伸长CRE拉伸试验仪(上海湘杰仪器仪表科技有限公司),YG815垂直法织物阻燃性能测试仪(山东安丘江北纺织仪器有限公司),V5M6/50万利达窄幅织物机(万利达集团有限公司)。
1.4 阻燃整理工艺
阻燃整理液由环磷酸酯阻燃剂、异丙醇和水经NaOH调节pH值至6.5配制而成,其中织物平方米质量与水的用量比为1︰10。把PLA/胶丝机织弹性带放入配制好的阻燃整理液中进行浸渍处理,浸渍结束后,在100 ℃烘干3 min,冷却后在165 ℃焙烘30 s。
1.5 测 试
采用YG815垂直法织物阻燃性能测试仪对织带的阻燃性能进行测试,试验标准参照标准FAR 25.853(a)—1995《航空材料防火检测标准》。测试要求:弹性带长度300 mm,用试样夹固定好后点燃试样,燃烧12 s后离开火焰,待试样燃烧停止后,量取并记录织带的燃烧长度、余焰时间和滴焰时间,每组样品测试5次取平均值。考虑到余焰时间和滴焰时间的测试精度问题,本文采用平均燃烧长度作为指标来评价弹性带的阻燃性能,当平均燃烧长度<20.3 cm[10]时认为织带具有阻燃效果。
2 结果与分析
2.1 正交试验
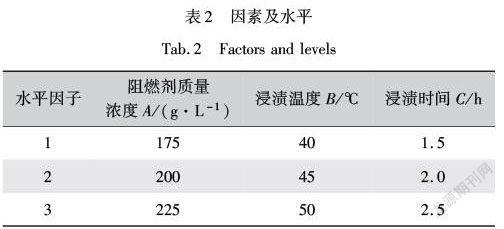
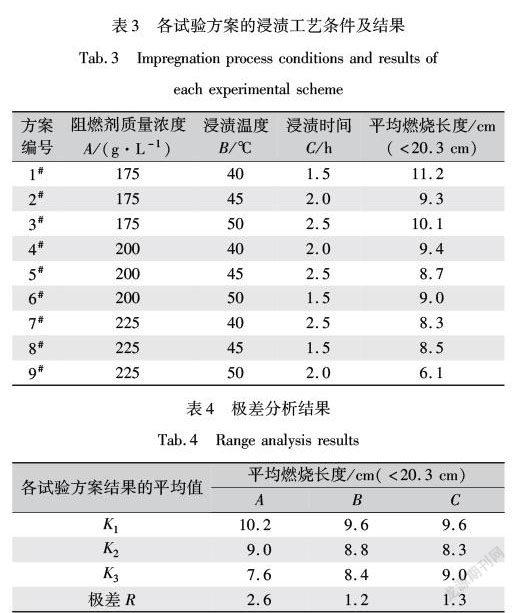
通过设计正交试验,探究阻燃剂质量浓度、浸渍温度和浸渍时间对弹性带阻燃性能的影响。由于异丙醇在试验中仅作为增强剂,并不起阻燃作用,因此在本试验中,把阻燃剂和异丙醇的质量浓度看作是一个因素,异丙醇相对阻燃剂质量分数为12%,恒定不变。采用L9(33)正交表进行试验,因素及水平见表2,各试验方案工艺条件及结果见表3,极差分析结果见表4。
从表4的极差分析可知,影响PLA/胶丝机织弹性带平均燃烧长度指标的主次因素分别为:阻燃剂质量浓度>浸渍时间>浸渍温度,对应的较优阻燃浸渍工艺为A3B3C2,即阻燃剂质量浓度225 g/L、浸渍温度50 ℃、浸渍时间2 h。
2.2 单因素优化试验
从正交试验结果可知,因素A和因素B都是在最高点处获得较好的阻燃效果,而因素C在中间2 h处取得较优的阻燃效果。因此,固定因素C,单独对因素A和因素B进行优化实验。
2.2.1 阻燃剂质量浓度对阻燃性能的影响
在浸渍温度为50 ℃、浸渍时间为2 h的条件下,通过改变阻燃剂质量浓度进行优化试验,结果如图1所示。
由图1可知,阻燃剂质量浓度对PLA/胶丝弹性带的阻燃性能有显著影响。当阻燃剂质量浓度在200~250 g/L时,阻燃效果明显。随着阻燃剂质量浓度的增加,与织带结合的阻燃剂越多,这些阻燃剂受热时会生成含氧酸和偏磷酸聚合物覆盖在纤维表面,起到减少放热量和隔氧作用,从而有效抑制燃烧反应的进行;当阻燃剂质量浓度超过250 g/L后,阻燃效果降低,这是因为织带与阻燃剂之间已经达到动态吸附平衡,即使继续增加阻燃剂质量浓度,新结合的阻燃剂也只能附着在纤维表面,燃烧时阻燃剂分解的热量会加速纤维的熔融分解,从而降低织带的阻燃性能[11]。根据单因素试验结果,阻燃剂的最优质量浓度为250 g/L。
2.2.2 浸渍温度对阻燃性能的影响
在阻燃剂质量浓度为250 g/L、浸渍时间为2 h的条件下改变浸渍温度进行优化试验,结果如图2所示。
由图2可知,浸渍温度为50 ℃时织带的阻燃效果最好,超过此温度后,织带的阻燃性能有所下降。这是因为高温破坏了阻燃剂的结构,导致与织带结合的部分阻燃剂没有发挥作用,甚至加速了燃烧过程,最终阻燃效果降低。
结合图3可知,胶丝的力学性能受温度影响很大[12]。在55 ℃时,弹性带的强力损失超过了5%,考虑到高温焙烘后其强力损失会进一步增加,优选最佳浸渍温度为50 ℃。
2.3 阻燃性能分析
根据正交试验和单因素试验结果得到最优的阻燃工艺为:阻燃剂质量浓度250 g/L、浸渍温度50 ℃、浸渍时间2 h。在该工艺条件下,测试PLA/胶丝弹性带的阻燃性能,结果如表5所示。
从表5可知,原PLA弹性带在垂直燃烧测试时,三项指标均不能通过;最优工艺整理的PLA弹性带平均燃烧长度只有3.9 cm,余焰时间0.7 s,表明弹性带在离开火源时能迅速自熄且无熔滴产生,能够通过美国航空材料防火检测标准FAR 25.853—1995的阻燃测试。
3 结 论
本文以PLA纤维和阻燃胶丝为原料织造了纬密为172.4根/10 cm的机织弹性带。采用浸渍方法对织带进行阻燃整理,并通过正交试验和单因素优化试验获得最优的阻燃浸渍工艺:阻燃剂质量浓度250 g/L、浸渍温度50 ℃和浸渍时间2 h。经上述工艺整理后,PLA/胶丝机织弹性带的阻燃指标能够达到FAR 25.853美国航空材料防火检测标准,表现出良好的阻燃效果。
《丝绸》官网下载
中国知网下载
参考文献:
[1]奚志根. 松紧带生产新技术及其效益[J]. 上海纺织科技, 1984(6): 20-22.
XI Zhigen. New technology of elastic band production and its benefits[J]. Shanghai Textile Science & Technology, 1984(6): 20-22.
[2]雒芳林, 沈兰萍, 凌子超. 新型弹性纤维在松紧带行业应用中的可行性分析[J]. 合成纤维, 2018, 47(8): 29-33.
LUO Fanglin, SHEN Lanping, LING Zichao. Feasibility analysis of new elastic fiber in elastic band industry application[J]. Synthetic Fiber in China, 2018, 47(8): 29-33.
[3]刘丽, 李红霞. 聚乳酸纤维的结构性能和应用前景[J]. 天津纺织科技, 2009(1): 4-7.
LIU Li, LI Hongxia. The structure, properties and usages of the PLA fiber[J]. Tianjin Textile Science & Technology, 2009(1): 4-7.
[4]齐悦, 杨博, 马慧玲, 等. 生物可降解聚乳酸纤维的发展现状及其改性研究[J]. 北京服装学院学报(自然科学版), 2019, 39(1): 85-93.
QI Yue, YANG Bo, MA Huiling, et al. Development and modification of polylactic acid fibers[J]. Journal of Beijing Institute of Fashion Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 39(1): 85-93.
[5]劉天祎, 龙佳朋, 梁兵. 聚合型无卤阻燃剂研究进展[J]. 化工新型材料, 2021, 49(2): 43-47.
LIU Tianyi, LONG Jiapeng, LIANG Bing. Research progress on polymerized halogen-free flame retardant[J]. New Chemical Materials, 2021, 49(2): 43-47.
[6]辛海亮, 梁兵. 新型磷系阻燃剂合成及其在聚丙烯中的应用[J]. 塑料, 2019, 48(4): 6-10.
XIN Hailiang, LIANG Bing. Synthesis of a novel phosphorus flame retardant and application for polypropylene[J]. Plastics, 2019, 48(4): 6-10.
[7]CHEN Y J, WANG W, QIU Y, et al. Terminal group effects of phosphazene-triazine bi-group flame retardant additives in flame retardant polylactic acid composites[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 2017, 140: 166-175.
[8]劉婷. 聚磷酸酯阻燃剂的合成及其在聚乳酸中的应用[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2018.
LIU Ting. Synthesis of A Novel Polyphosphate and Its Application for Flame Retardant PLA[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2018.
[9]LIAO F H, ZHOU L, JU Y Q, et al. Synthesis of a novel phosphorus-nitrogen-silicon polymeric flame retardant and its application in poly(lactic acid)[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2014, 53(24): 10015-10023.
[10]张天祥, 王其, 刘昌杰, 等. PLA阻燃粘扣带的开发[J]. 国际纺织导报, 2017, 45(8): 28-30, 32-34.
ZHANG Tianxiang, WANG Qi, LIU Changjie, et al. The development of PLA flame-retardant velcro[J]. Melliand China, 2017, 45(8): 28-30, 32-34.
[11]谷志旗. 涤纶/锦纶交织粘扣带无卤素耐洗涤阻燃整理工艺研究[D]. 上海: 东华大学, 2014.
GU Zhiqi. The Study on Flame Retardant Finishing Technology of Polyester/Nylon Interlaced Hook and Loop Fastener with Properties of Halogen-Free and Wash-Resistant[D]. Shanghai: Donghua University, 2014.
[12]张倩云, 崔继文, 刘盼, 等. 不同温度下天然橡胶/聚酯纤维界面的黏结失效[J]. 高分子材料科学与工程, 2019, 35(11): 62-66.
ZHANG Qianyun, CUI Jiwen, LIU Pan, et al. Interfacial adhesion failure of natural rubber/polyester fibers at different temperatures[J]. Polymer Materials Science & Engineering, 2019, 35(11): 62-66.
Abstract:
Elastic belt, also known as elastic band, is a high-elasticity fabric usually made of polyester, polyamide and rubber silk, and belongs to one of the major categories of ribbon industry production. It is widely used as a necessary auxiliary material for sewing traditional sports goods, industrial goods and household goods and is also mainly used as a fastening material for cuffs, shoe linings, leg openings, hat linings, collars, waistbands and other places close to the human body. At present, most of the functional elastic belt products on the market are wet permeable, antibacterial, comfortable, UV resistant and yellowing resistant, etc. However, such products are used in some high-temperature operations, transportation tools, medical and health environment and laboratories, etc., which may easily cause fire accidents. Polylactic acid (PLA) is a green and environmentally friendly fiber. Despite its poor flame retardancy, it has the characteristics of renewable and biodegradable raw materials. It can be made into elastic belt products for flame-retardant modification, which can not only improve its use security, but also can be degraded into lactic acid, CO2 and water under natural conditions after being discarded, without pollution to the environment.
In order to improve the flame retardancy of environmentally friendly polylactic acid (PLA) elastic belt, the biodegradable characteristics of PLA fiber were studied to interweave woven elastic belt with flame retardant rubber silk. Firstly, a cyclic phosphate ester flame retardant with low toxicity, low smoke and high flame retardant efficiency was used to conduct flame retardant modification and finishing of PLA/plastic silk woven elastic belt by impregnation baking process. On this basis, the effects of the concentration of flame retardant, impregnation temperature and impregnation time on the flame retardancy of elastic belt were discussed. Among them, a three-level three-factor orthogonal test was designed with the average burning length as the evaluation index through range analysis method. It was found that the primary and secondary factors affecting the flame retardant performance of the elastic belt were: flame retardant concentration>impregnation time>impregnation temperature. The flame retardant effect was good when flame retardant concentration and impregnation temperature were at level 3, while the flame retardant effect was the optimal when the impregnation time was at level 2. Based on this, a single factor optimization experiment was performed to explore the influence of the separate change of flame retardant concentration on the average burning length of the elastic belt, then to discuss the variation rules of the average burning length and strength loss of the elastic belt at different impregnation temperatures, and finally to obtain the optimal process conditions of flame retardant impregnation and finishing. On this basis, the article adopted orthogonal experiment, range analysis and single factor experiment to optimize the impregnation, baking and flame-retardant finishing process of PLA/plastic silk woven elastic belt. The study found that the optimal flame retardant impregnation process conditions are: flame retardant concentration 250 g/L, impregnation temperature 50 ℃, impregnation time 2 h. Through the above process finishing, the flame retardant index of PLA/plastic silk woven elastic belt reached FAR 25.853-1995 American aviation material fire test standard, and exhibited excellent flame retardant effect.
The relationship between the impregnation and baking finishing process conditions and the flame retardant performance of PLA/plastic silk woven elastic belt can provide revelations for the R&D of flame-retardant elastic belt products. From the perspective of product application, when used in transportation vehicles, sitting bedding, fire-fighting clothing, and software fasteners such as equipment, experimental clothing and equipment, and medical clothing and equipment, it is expected to effectively reduce potential safety hazards, without pollutions to the environment after being discarded. The research results can provide referential suggestions for the design and development of flame-retardant and environmentally friendly elastic belt products.
Key words:
PLA fiber; woven elastic band; flame retardant finishing; orthogonal test; single factor experiment; flame retardant performance
