Analysis of the hotspots and trends in traditional Chinese medicine immunomodulation research based on bibliometrics
2022-01-19XIAOLiMANingLAIHnYANJunfengPENGQinghu
XIAO Li, MA Ning, LAI Hn, YAN Junfeng, PENG Qinghu
a. School of Chinese Medicine, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha, Hunan 410208, China
b. Departrment of Pediatrics, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine Third Affiliated Hospital, Beijing 100029, China
c. School of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Sourthern Medical University, Guangzhou, Guangdong 510515, China
d. School of Informatics, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha, Hunan 410208, China
e. The First Hospital of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha, Hunan 410208, China
f. Hunan Provincial Engineering and Technological Research Center for Prevention and Treatment of Ophthalmology and Otolaryngology Diseases with Chinese Medicine and Protecting Visual Function, Changsha, Hunan 410208, China
Keywords Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM)Knowledge graphs Complementary and alternative medicine Bibliometrics Immune regulation Citation bursts
ABSTRACT
1 Introduction
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), which has evolved over thousands of years, is currently the best preserved and most influential traditional medicine with the largest number of users worldwide[1]. With the outbreak of coronavirus disease (COVID-19), a new viral pneumonia declared as a Public Health Emergency of International Concern by the World Health Organization on January 30, 2020, TCM plays an important role in the prevention and treatment of the infectious disease[2]. The empirical therapy of TCM is currently being widely used in Chinese hospitals and may be useful for people all around the world. Regulating the body’s immune system, which can protect from disease, is one of the principles underlying the notion that TCM is effective for COVID-19[3]. Revealing the role of TCMs in immune regulation can open up a promising future in immunomodulatory therapies[4]. However, TCM in immune regulation is very complex and has not yet been fully defined, especially the concrete mechanism, which is one of the major scientific issues described by the China Association for Science and Technology on August 15, 2020. In fact, a large number of relevant studies have been carried out, but they lack systematic and objective organization[5-7].Undoubtedly, it is necessary to effectively track the progress of information in this field. Bibliometrics is an effective way to explore the core authors,institutions and impactive journals and identify the research hotspots and trends in a specific area[8].Therefore, this study aimed to analyze the research structure, research hotspots and trends in this field to provide information for researchers on the beneficial cooperation goals and entry points for in-depth research by means of a scientometric analysis based on Microsoft Excel and CiteSpace, one of the most popular tools for performing bibliometric analysis[8].
2 Methods
2.1 Search strategy
The Web of Science Core Collection (WoSCC),considered the most prominent database of scientific publications on many research topics, was selected for English document mining. The strategy used during the search was Topic Search (TS) = (“Chinese medicine”) AND (Immun*), time = (all years) and language = (English) (Retrieved on August 30, 2020).The database selected for Chinese document mining was China National Knowledge Infrastructure(CNKI). The strategy used during the search was Topic Search (TS) = (traditional Chinese medicine)AND (immunity), time = (up to 2020), language =(Chinese) and type of document = (journal article).
2.2 Eligibility criteria
Original TCM in immune regulation research retrieved from WoSCC and CNKI were included in the study. The time of literature retrieval is up to 2020. Only two document types, review and article,were included. Repeated publications, studies not officially published, unrelated studies and studies conducted by hand and telephone were excluded.
2.3 Study selection
The retrieved publications were screened according to the eligibility criteria. The screened results were verified by two experienced TCM researchers.
2.4 Data analysis
All bibliometric information was exported into text format from the WoSCC database and into refworks format from the CNKI database. CiteSpace 5.7.R1 and Microsoft Excel 2016 software were used for the statistical analysis and bibliometric diagrams,including the co-occurrence network of authors,institutions, countries, keywords, references, dualmap overlays of journals and citation bursts, etc.
3 Results
3.1 Study inclusion
A total of 3 613 English publications related to TCM in immune regulation were obtained from the WoSCC database. Based on the eligibility criteria, 3 549 English publications were included. A total of 8 922 Chinese publications related to TCM in immune regulation were obtained from the CNKI database.Based on the eligibility criteria, 8 721 Chinese publications were included.
3.2 Analysis of the number of publications
Figure 1 shows that the annual number of publications continues to grow, and the growth rate is accelerating overall. In particular, the research entered a stage of rapid development since 2018.
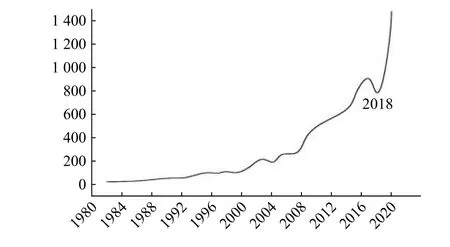
Figure 1 Growth trend of TCM in immune regulation research
3.3 Spatial distribution analysis
The spatial distribution and cooperation network analysis can provide effective information for authors, countries and institutions to find favorable partners using CiteSpace[9].
As shown in Figure 2A, there were 74 countries and 210 lines of cooperation between countries(Density = 0.077 7), showing a close cooperation network with China as the core node has been formed.Four of the top five countries, including China, the United States, Japan, South Korea and India, are located in Asia.
Figure 2B shows 453 institutions and 1 407 lines of cooperation between institutions (Density = 0.013 7),indicating that the cooperation between institutions was relatively close. Through further analysis, it is found that the mechanisms of TCM in regulating immunity mainly include suppressing oxidative stress,modulating gut microbiota and glycolipid metabolism, promoting nerve regeneration, regulating gene expression and suppressing immune inflammatory response.
Figure 2C shows 488 authors and 903 lines of cooperation between authors (Density = 0.007 6),indicating that the cooperation between authors was relatively scattered, forming multiple sub-networks.To measure the core authors in this field, Price’s law was used, which indicates that M = 0.749 (NMax)1/2,where NMax refers to the number of papers of the author with the most publications. Scholars with a publication number above M are considered the core authors in this field[9]. CiteSpace showed that the author with the most publications was LI Yan (with 20 articles) (i.e., NMax = 20). Price’s law states that M =3.35, thereby indicating that authors with over four articles are core authors.
3.4 Knowledge distribution analysis
This study explored the diffusion and evolution of domain knowledge using CiteSpace to construct dual-map overlays of journals with ten years as a time slice[10].
Figure 3A shows that citing journals mainly focused on the disciplinary area labeled Molecular,Biology, Immunology, while the cited journals mainly belonged to the disciplinary areas labeled Molecular,Biology, Genetics and Health, Nursing, Medicine and Chemistry, Materials, Physics from 1982 to 1991.
Figure 3B shows that the core field of citing journals was the same as before, while the marginal area started to expand to other fields, such as the disciplinary areas labeled Medicine, Medical, Clinical and Neurology, Sports, Ophthalmology from 1992 to 2001. In terms of cited journals, its new marginal areas mainly included the disciplinary areas labeled Environmental, Toxicology, Nutrition.
Figure 3C shows that the disciplinary area labeled Medicine, Medical, Clinical expanded and became the core field from 2002 to 2011. Considering the cited journals, its marginal fields increase, mainly including the disciplinary areas labeled Mathematical, Mathematics, Mechanics and Psychology, Education, Social and Sports, Rehabilitation, Sport.

Figure 2 Spatial cooperation network of TCM in immune regulation researchA, distribution of co-operation among countries. B, distribution of co-operation among institutions. C, distribution of co-operation among authors. Each node in the pictures represents a different author, institution or country. The font size of each label and node is proportional to the document counts. The nodes are connected by lines of different colors and different thicknesses, indicating that the nodes are related. The darker the color and the thicker the line, the closer the relationship is.The thickness of the connecting line represents the collaborative intensity. The betweenness centrality of nodes in a network is indicative of the importance of the location of the nodes. The higher the centrality, the more nodes connected with it.

Figure 3 Dual-map overlays of journals of TCM in immune regulation researchA, journals from 1982 to 1991. B, journals from 1992 to 2001. C, journals from 2002 to 2011. D, journals from 2012 to 2020.A base map of cited journals on the left and a base map of cited journals on the right are presented in different colors to depict different journal clusters; journals of the overlay map involved in the citing and cited base maps are marked with circles;the curve depicts a citation link as a spline curve running from the source journal to the target journal of the citation.
Figure 3D shows that the disciplinary area labeled Veterinary, Animal, Science expanded to become one of the core areas from 2012 to 2020. There were three outward citation paths in the disciplinary area labeled Molecular, Biology, Immunology in the citing journals domain, which was the most important area of citing journals. The marginal fields of cited journals increased, mainly including the disciplinary area labeled Systems, Computing, Computer.
What’s more, theJournal of Ethnopharmacologywas marked in the vicinity of the disciplinary area labeled Veterinary, Animal, Science, indicating that this journal frequently published papers relevant to TCM in immune regulation in this area. TheChinese Journal of Integrative Medicinewas the most cited journal in the disciplinary area labeled Medicine,Medical, Clinical. ThePLoS Onewas the cited journal that published the most papers in the disciplinary area labeled Molecular, Biology, Genetics. TheNew England Journal of Medicinewas the most cited in the disciplinary area labeled Health, Nursing, Medicine,and theJournal of Ethnopharmacologywas the most cited in the disciplinary area labeled Environmental,Toxicology, Nutrition.
3.5 Knowledge base analysis
To grasp the core literature and provide a solid foundation for the in-depth study of TCM in immune regulation in the future, this study analyzed the top 10 highly cited research articles[11]. Besides, this study produced a references and keywords co-occurrence network divided into many clusters, representing different directions of research.
As illustrated in Table 1, from 2002 to 2011, there were seven articles in the top 10 highly cited research articles, and three of them were published in 2007.Eight of the top 10 highly cited articles were related to the pharmacological research of Chinese herbs, and the document types were all reviews. These studies showed that Chinese herb regulates inflammatory immune response by influencing inflammatory cytokines, reactive oxygen species and nitric oxide, including Renshen (Ginseng Radix et Rhizoma)[12],Danshen (Salviae Miltiorrhizae Radix et Rhizoma)[13],Wuweizi (Schisandrae Chinensis Fructus)[14], Gancao (Glycyrrhizae Radix et Rhizoma)[15], Bajitian(Morindae Officinalis Radix)[16], Leigongteng (Tripterygium wilfordiiHook.f.)[17]and Gouqizi (Lycii Fructus)[18]. The other two types of studies were clinical randomized controlled trials and epidemiological investigations. A randomized controlled trial showed that short-term meditation training in TCM could improve immunoreactivity and considered that it was achieved by changing the brain network[19].BOON et al.[20]investigated the use of complementary/alternative medicine for breast cancer, and the results showed that it is commonly used among Canadian breast cancer survivors, mainly to boost the immune system. There were two more recent documents[18,21], both published in 2011, which focus on clinical efficacy and application. Clearly, TCM in immune regulation research has shifted from a focus on pharmacological study to clinical efficacy and safety and application.
Figure 4A shows that the most frequent and central keyword in the co-occurrence network is “traditional Chinese medicine”, indicating that a series of studies were conducted around this keyword. RUet al.[22]built a TCM systems pharmacology database and analysis platform to identify drug target networks and drug disease networks, which was the reference with the most frequency and centrality in the co-occurrence network.

Table 1 The top 10 highly cited references relevant to TCM in immune regulation
As shown in Figure 4B and Table 2, it was mainly divided into eight clusters. Cluster #1 and #4 had an average year of publication of 1990 and 1993 respectively, both of which were related to the mechanism.Cluster #2 relevant to the treatment methods of TCM,and cluster #3 relevant to clinical disease research,had an average year of publication of 1995 and 1997,respectively. Cluster #5 and cluster #6, the topics relevant to pharmacological research, had an average year of publication of 1997 and 2000, respectively.Cluster #7 on immunomodulation had an average year of publication of 1999. The recently formed clusters, clusters #8, representing a turning point toward systematization and informatization, had an average year of publication of 2005. Objectively, the integration of multiple disciplines was a research trend.
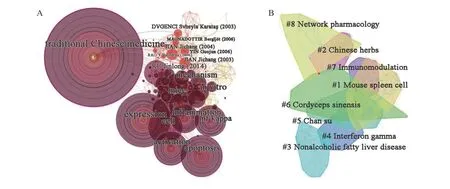
Figure 4 References and keywords co-occurrence network of TCM in immune regulation research A, map of co-occurrence network. The font size of each label and node is proportional to the co-occurrence frequency. The thickness of the connecting line represents the association intensity. B, map of clusters of the co-occurrence network. The convex hulls of different colors represent different clusters; the brighter the convex hull, the more recently it appeared. The number of nodes each convex hull covers is proportional to the number of keywords and references of each cluster. The line thickness of each convex hull cover is proportional to the co-occurrence frequency of each cluster.
3.6 Research fronts
This study used CiteSpace and Microsoft Excel to create the timeline view of references and keywords,citation bursts and frequency change of highfrequency keywords to explore the evolution of research fronts and recent research hotspots and trends[23].
Figure 5A shows that cluster #3 and #8 are the frontier research directions up to now. Metabolism is a recent hotspot in cluster #3. Further analysis of it has shown that rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes mellitus and Alzheimer’s disease were the terms with the highest frequency and high-intensity bursts, suggesting that they are metabolic diseases that have beenconcerned recently. Network pharmacology is a recent hotspot reflected in cluster #8, also shown in Figure 5B. Through further analysis, it was found that it has mainly been used to explore the immunomodulation mechanism of TCM against COVID-19 to mine new TCM formulations and drugs.

Table 2 Major clusters of references and keywords of TCM in immune regulation research
Furthermore, the application of TCM to regulate immunity in cancer has also been a recent research hotspot and trend[24,25](see Figure 5B). Through further analysis, the following information can be obtained. Breast cancer and colorectal cancer were the terms with the highest frequency and high-intensity bursts, suggesting that they were cancer diseases that have received more attention recently. The terms with the highest frequency and high-intensity bursts,including tumor microenvironment, inflammatory response, protein expression and signaling pathway,were the hotspots in anti-tumor mechanism research.

Figure 5 Analysis of references and keywords of TCM in immune regulation A, timeline view of references and keywords co-occurrence network of TCM in immune regulation research. The time is set as the horizontal axis, and the cluster is set as the vertical axis. This view clearly presents the differences in the appearance time point and time span of each cluster. B, the top 10 references with the strongest citation bursts. The green line represents the period from 1982 to 2020, while the periods of each burst reference are plotted by the red line. The strength of burst references represents the sudden growth rate of the references. C, frequency change of keywords with highest frequency and centrality in TCM immunomodulatory research in China.
Figure 5C shows that the keywords with the highest frequency and centrality, including the combination of TCM and western medicine, clinical research, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), rheumatoid arthritis and chemotherapy, have been growing continuously in Chinese publications, reflecting the recent research hotspots and trends in China.
4 Discussi on
In this study, CiteSpace and Microsoft Excel was used to make scientometric analysis on the annual number of publications, authors, institutions,countries, journals, keywords and references of TCM immunomodulation research. Overall, this research has become a subject of growing study worldwide. In particular, the outbreak of COVID-19 triggered a new upsurge in this field.
Based on the co-occurrence analysis of authors,institutions, and countries, it can be concluded that there was close cooperation between countries forming a network with China as the core. It is clear that China plays an important role in promoting the development. Four of the top five countries were located in Asia, explained by the birthplace of TCM and the close cultural exchanges between neighboring countries. The cooperation between institutions was relatively close, but the cooperation between authors was scattered. Therefore, cooperation and exchange among scholars should be strengthened in the future.
Through the analysis of journals, highly cited articles, keywords and references, it can be found that the frontier of research has shifted from animal and cell research for mechanisms to pharmacological research and then to clinical research. In terms of the mechanism, it involves many aspects, including oxidative stress, gut microbiota, immune inflammation response, the interaction between metabolism and immunity, the interaction between nerve and immunity, and epigenetics. In terms of pharmacology research, it has changed from single Chinese herb to compound. Polysaccharides and hydrophobic low molecular weight ingredients, including saponins,terpenoids, flavonoids, organic acids, and phenolic compounds, are major components of Chinese herb with immunomodulatory activities[26-28]. At present,many randomized controlled studies have shown that TCM is safe and effective, and clinical observation has been paid more attention[29,30]. In fact, the treatment principle of TCM in balance adjustment is the same as the essence of immunomodulatory therapies.
Specifically, one of the recent research hotspots is the evaluation of the efficacy and safety of TCM-modulating immunotherapy for clinical diseases, where appropriate evaluation methods are extremely necessary, as clinical observation is the trend in China. In fact, current biomedical research methods for evaluating the efficacy of TCM interventions are often incompatible with TCM theory and clinical practice.Unfortunately, due to cultural differences, the public perception of TCM lagged behind its actual development, and many people saw it as a non-scientific practice. Therefore, it is only possible to understand the theory of TCM, its origins and who said “what”and “why” on the basis of logical arguments. And TCM practitioners should standardize their evaluation systems and study designs guided by TCM theory. Moreover, this work can be combined with big data analysis methods in the real world to produce more suitable and powerful evidence to prove the effectiveness and safety.
The role of TCM with immunomodulatory properties in cancer and metabolic diseases, shown by high-frequency words with high-intensity bursts, is another hotspot in recent research, and may be the focus of future research. At the same time, metabolism is a hotspot and trend in the research on the mechanism of TCM immunomodulatory, especially lipid metabolism[31,32]. TCM is a common treatment for cancer, one of the most serious problems threatening human health and life with morbidity and mortality increasing worldwide. TCM mainly reshapes the immune microenvironment of tumors by enhancing immune surveillance, improving immune suppression, reversing immune escape and regulating immune checkpoints, which are the inhibitory receptors expressed in infiltrating lymphocytes in tumor microenvironments. Breast cancer and colorectal cancer have recently attracted more attention. The research on them has mainly focused on the role of TCM in a variety of oncogenic processes,including anti-metastasis, the inducing of tumor cell apoptosis, and the inhibiting of angiogenesis and proliferation. The immunomodulatory mechanism of TCM in breast cancer and colorectal cancer mainly focuses on inflammation. Besides, studies related to breast cancer paid close attention to gene expression,while colorectal cancer research showed solicitude for regulating the composition of gut microbiota. In China, NSCLC and chemotherapy are also the focus of recent research. Cancer-induced fatigue and myelosuppression are the main concerns of NSCLC research.
Considering the research related to main metabolic diseases in this field, the information obtained was as follows. Articles related to rheumatoid arthritis mainly explored the effect of TCM on its characteristic gene expression and further analyzed its role in pattern-related gene networks, mainly involving the protein transcription process, protein ubiquitination,NF-kappa B regulated gene transcription and apoptosis activated by toll-like receptors, RNA splicing and NF-kappa B signaling. The research on the mechanism of the immunomodulatory effects of TCM on diabetes mellitus and Alzheimer’s disease was focused on oxidative stress, which is their common biological mechanism.
Besides, network pharmacology is a recent research hotspot and trend in this field. Network pharmacology can provide a systematic pharmacological basis and support for TCM immunomodulatory therapy, but there is a lack of basic experiments for verification. In addition, there are many problems to be solved in network pharmacology, including the dosage of Chinese herb, multi-state target and compatibility[33-35]. Faced with massive data and multilayer network analysis, artificial intelligence may be an effective technology[36,37].
In general, there are several strengths in this study. To our best knowledge, no attempt has been made to use CiteSpace to conduct bibliometric research on TCM in immune regulation. It can provide valuable information to locate the core authors, institutions and countries, and further discover the focus of major teams. In addition, it can systematically sort out the intellectual structure and evolution process in this field. And it is very meaningful that it can mine the recent research hotspot. Last but not least, it is valuable for the development to objectively predict the trend of research in this field.
However, there are some limitations of this study.First, the data analyzed in this study is limited, only including data from WoSCC and CNKI. In fact, the different export formats and deduplication make it impossible to analyze the data of multiple databases at the same time, which makes it difficult to ensure the comprehensiveness of the data. But WoSCC and CNKI are representative. Second, bias, including different expressions with the same meaning are difficult to identify and integrate, may also exist. These problems need to be addressed in future.
5 Conclusion
TCM plays a significant role in immune regulation,which has attracted the fast-growing attention of scholars. The research in this field is relatively comprehensive, mainly involving the mechanism of immune regulation, pharmacological research of traditional Chinese medicinal herb, the evaluation of clinical efficacy and safety of TCM. Network pharmacology, metabolism and cancer are the recent research hotspots and trends. Overall, this field will focus on clinical applications in future research and tend toward informatization.
Acknowledgements
We thank for the funding support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81874492),Key Scientific Research Projects of Hunan Provincial Department of Education (No. 18A219), and the Domestic First-Class Discipline Construction Project of Chinese Medicine of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine.
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
杂志排行
Digital Chinese Medicine的其它文章
- Research on classification diagnosis model of psoriasis based on deep residual network
- Novel pyrimidine-benzimidazole hybrids with antibacterial and antifungal properties and potential inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 main protease and spike glycoprotein
- Quality 4.0 technologies to enhance traditional Chinese medicine for overcoming healthcare challenges during COVID-19
- Evaluation of Baishao (Paeoniae Radix Alba) and Chishao(Paeoniae Radix Rubra) from different origins based on characteristic spectra of amino acids
- Network pharmacology research and experimental verification of Huangqi (Astragalus Radix) and Jinyingzi (Rosae Laevigatae Fructus) in treating benign prostatic hyperplasia
- Comparison of mechanisms and efficacies of five formulas for improving blood circulation and removing blood stasis
