Effects of Nitrogen Forms on the Growth and Development of Trees
2021-12-31YihanSUZhaoyiYEXiaolinSHENWeixinCHENChengxiangXU
Yihan SU, Zhaoyi YE, Xiaolin SHEN, Weixin CHEN, Chengxiang XU
College of Life Sciences, Zhaoqing University, Zhaoqing 526061, China
Abstract Nitrate nitrogen and ammonium nitrogen are the main nitrogen forms absorbed by trees from soil, and they have significantly different physiological regulation effects on trees; trees can also absorb some soluble organic nitrogen compounds, such as urea and amino acids. Trees supplied with single ammonium nitrogen or nitrate nitrogen will have higher photosynthesis, and the promotion effect of mixed nitrogen sources on tree photosynthesis is stronger. Enzymes play an important role in the metabolism of trees. The key enzymes of nitrogen metabolism include nitrate reductase, etc., which affect the metabolism of trees through different responses of key enzymes to various nitrogen forms. The input of different nitrogen forms changes the content of mineral elements in trees and then affects the growth of trees. Different nitrogen forms have significant differences in the growth and metabolic processes of trees, which in turn have different physiological effects on plants. Several key issues in the future research on nitrogen nutrition and physiology of trees are discussed.
Key words Nitrogen form, Growth, Biomass, Photosynthesis, Nitrogen metabolism
1 Introduction
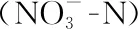
2 Species of trees involved
At present, there are many studies on the effects of nitrogen forms on plants, but most of them are on the effects of crop growth, and there are few studies related to the effects on trees. In recent years, the effects of nitrogen forms on trees have attracted attention, and some progress has been made. In China, the effect of nitrogen forms on the growth of citrus roots was first studied in 1990, which is the beginning of the study on the effect of nitrogen forms on the growth and development of trees. Table 1 shows the changes in the number of Chinese documents on the effects of nitrogen forms on the growth and development of trees. A total of 58 papers have been published so far, of which the number was the largest in 2019, up to 10. The number of documents is currently increasing year by year. At present, the main tree species studied are tea trees, citrange and Pingyi sweet tea, and most of the research objects are economic tree species. Table 2 is a summary of the existing research on the effects of nitrogen forms on the growth and development of different trees. There are 16 tree species. The number of related documents on tea trees and tea-oil trees is the largest, and there are also documents on rare tree species distributed in the north such as ginkgo and red pine.
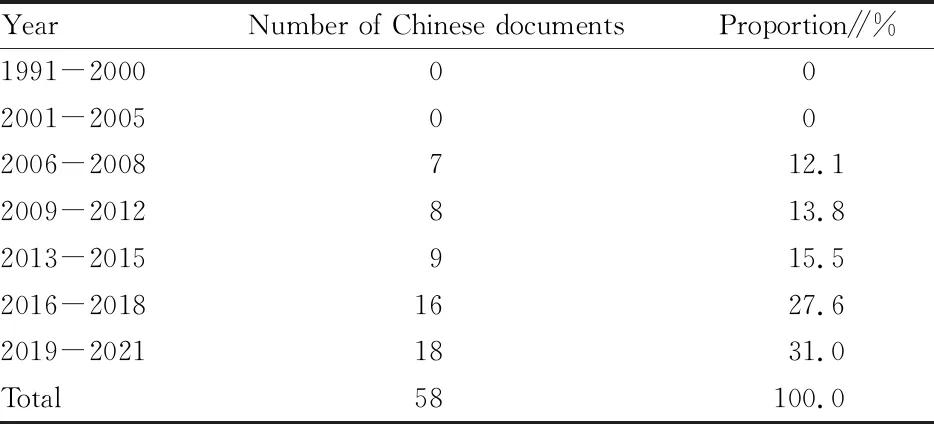
Table 1 Changes in the number of Chinese documents on the effects of nitrogen forms on the growth and development of trees
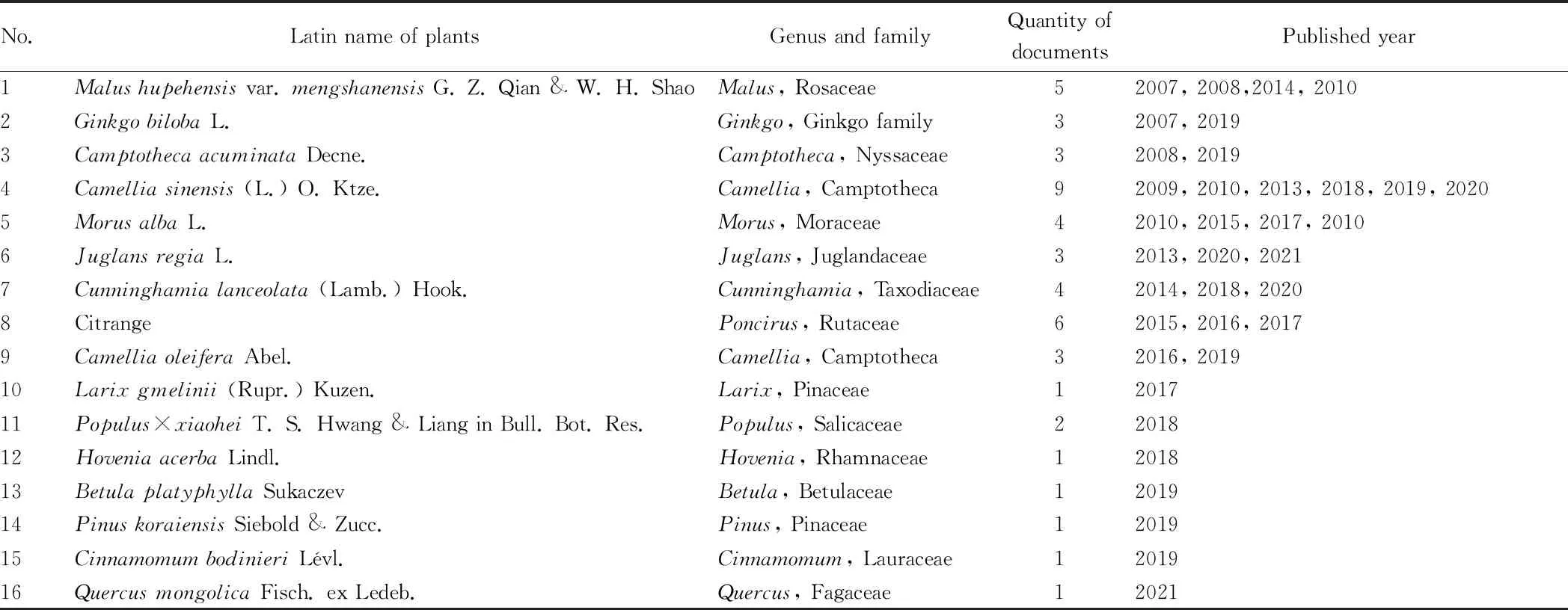
Table 2 Summary of the existing research on the effects of nitrogen forms on the growth and development of different trees
3 Effects on growth and biomass
Nitrate nitrogen and ammonium nitrogen are the main forms of nitrogen absorbed by plants. Plants have different responses to different forms of nitrogen nutrition in the growth environment. Different forms of nitrogen have more significant effects on various morphological indicators of plants. Sun Minhong’s research on citrange shows that total nitrate-nitrogen cultivation is better than total ammonium-nitrogen cultivation, and citrange is a plant that likes nitrate nitrogen. Ma Jianet
al.
found that loquat likes ammonium obviously, and the ammonium nitrogen absorbed by loquat roots is more than nitrate nitrogen.Seen from the mechanism of nitrogen absorption, ammonium nitrogen is more easily absorbed by plants, while absorbing nitrate nitrogen consumes more energy. Compared with a single nitrogen form, when nitrate nitrogen and ammonium nitrogen coexist, its utilization efficiency is higher. Many scholars believe that when ammonium nitrogen and nitrate nitrogen are mixed in a certain proportion, the effect is better than that of single nitrogen application. The application of nitrogen fertilizer at the seedling stage is one of the important measures for cultivating strong seedlings. The suitable nitrogen forms and proportions of different plants are different, and improper fertilization may cause the growth and development of seedlings to be inhibited.
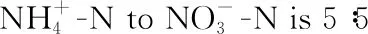
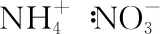
Betula
platyphylla
seedlings, while nitrate nitrogen is conducive to root growth.Since the roots of seedlings growing in a container do not be damaged during the emergence of seedlings, amide nitrogen fertilizer should be the first choice when adding nitrogen toB.
platyphylla
seedlings growing in a container. In the case of single amino acid fertilization, arginine has the best effect on promoting the growth of seedlings, followed by glutamic acid, while glycine is the worst; in the case of combined fertilization of amino acids, the combination of arginine fertilization has good growth of seedlings, and the combination of glycine fertilization has poor growth of seedlings. Different amino acid fertilization treatments have no obvious effect on the nitrogen content in various organs ofPopulus
nigra
seedlings. Guo Yafenet
al.
used a hydroponic experiment and set up different organic nitrogen fertilizers (glycine, glutamic acid, and lysine) to supplyLarix
olgensis
andPinus
koraiensis
. It is found that the growth of seedlings applied with glycine and glutamic acid grow was better than that with lysine.4 Effects on photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the basis of all material metabolism in nature, including a series of complex processes of photophysical, photochemical and biochemical transformations. Studies have shown that nitrogen forms can affect plant photosynthesis, and then affect plant growth and development. Chlorophyll is one of the basic elements of plant physiological metabolism and photosynthetic assimilation.
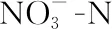
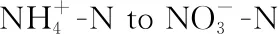
5 Effects on nitrogen metabolism and mineral nutrition
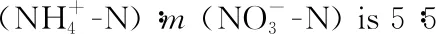
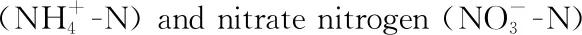
6 Outlook
Nitrate nitrogen and ammonium nitrogen are the main nitrogen forms absorbed by trees from soil, and they have significantly different physiological regulation effects on trees; trees can also absorb some soluble organic nitrogen compounds, such as urea and amino acids. Trees supplied with single ammonium nitrogen or nitrate nitrogen will have higher photosynthesis, and the promotion effect of mixed nitrogen sources on tree photosynthesis is stronger. Enzymes play an important role in the metabolism of trees. The key enzymes of nitrogen metabolism include nitrate reductase,etc.
, which affect the metabolism of trees through different responses of key enzymes to various nitrogen forms. The input of different nitrogen forms changes the content of mineral elements in trees and then affects the growth of trees. The current research on the effects of nitrogen on plants is mainly focused on crops, and there are few related studies on trees, which has attracted attention and has made some progress in recent years. However, the research is not deep enough, and is still concentrated on analysis of the effects of nitrogen forms on trees by conventional physiological methods. The molecular mechanisms of nutrient absorption and transport are less studied, and the understanding of the function of nitrogen transporters is limited. Although many reports have confirmed that the mixed application of ammonium nitrogen and nitrate nitrogen has a positive effect on trees, the coupling mechanism of two forms of nitrogen and the mechanism of how to promote tree growth are still unclear. The characteristics and action rules of two different forms of nitrogen should be deeply analyzed to further clarify their regulation mechanism on trees; the changes in tree-related gene expression caused by different forms of nitrogen should be further clarified, and the gene function should be further analyzed to understand the mechanism of the effects of nitrogen forms on trees; combined with modern omics technology, the molecular basis of nitrogen affecting the growth, development and resistance of trees is analyzed at the protein and metabolism levels, and the physiological and ecological effects of nitrogen are analyzed in depth.杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Nitrogen Metabolism and Curing Characteristics of Flue-cured Tobacco Variety NC71
- Study on Phthalate Esters Pollution in the Soil of Facility Vegetable Base in Yangling District of Xianyang City
- Distribution of Land Increment Income from Marketing Rural Collective Land for Development Purposes: A Case Study of Changyuan City
- Research on the Balance of Urban Benchmark Land Price in Henan Province: A Case Study of Commercial Land
- Enlightenment of EU New Common Agricultural Policy on Protection and Sustainable Utilization of Cultivated Land in China
- Migration of Heavy Metal Elements in Reclaimed Irrigation Water-Soil-Plant System and Potential Risk to Human Health
