Application of Six Sigma DMAIC Method in Improving the Good Rate of Blank Value of Cytological Method for Dairy Products
2021-12-31YunxiaWANGShuhuanZHAOLijunLIUXueHUCuizhiLIZhiyongLU
Yunxia WANG, Shuhuan ZHAO*, Lijun LIU, Xue HU, Cuizhi LI, Zhiyong LU
Inner Mongolia Yili Industrial Group Co., Ltd., Hohhot 010110, China
Abstract In this paper, the six Aigma DMAIC method was used to systematically analyze and study the process affecting the good rate of blank value of cytological method for dairy products. Through data collection, analysis and verification in each link, the room for improvement in the experimental process was identified. C&E matrix and FMEA were used to analyze the factors affecting the good rate of blank value. Through the DOE experiment design method and risk analysis, the main influencing factors were optimized and improved. The optimized experimental conditions were: silica gel activation temperature (500±50) ℃, activation time (23±1) h, cells adherent rate (95±1)%, and single-use of 1.5 mL conical flask. Under the above conditions, the good rate of blank value of cytological method was improved from 52.8% to 100%. The improvement of these conditions is of great significance to ensure the accuracy of results, save the testing cost and improve the testing efficiency.
Key words Six Sigma, DMAIC, Dairy product, Good rate
1 Introduction
With the continuous development and deepening of the market economy, the market environment has become more complex and changeable, and the market competition has been transformed from price competition to quality competition. Quality has become the fundamental to enhance the core competitiveness of enterprises, which requires us to continuously improve the quality management level. As a continuous quality improvement method, the six sigma management established by Motorola in the United Statesfocuses on the root cause of defects, improves quality and reduces cost by continuously optimizing the process, and lets the customers be satisfied. It not only provides a clear goal and direction as a compass, but also provides a series of rigorous systematic and scientific methods. Therefore, six sigma method is a method to implement breakthrough quality improvement under the guidance of new quality management concept. DMAICis an important tool for process improvement in six sigma management, which refers to a process improvement method consisting of five stages: define, measure, analyze, improve and control, and each stage is composed of a number of work steps. The process is continuously optimized through systemic application of DMAIC process, which will improve the quality and service, reduce costs, and satisfy customers while enhancing the core competitiveness of the enterprises.
Detection technology and capability are the key factors determining product quality, and the performance of blank value is one of the important indicators determining the accuracy of detection results. Currently, the good rate of blank value of cytological method for dairy products used in the laboratory of Inner Mongolia Yili Industrial Group Co., Ltd. is only 52.8%, which fluctuates greatly and directly affects the accuracy and reproducibility of test results. In order to meet the testing needs, ensure the accuracy of the results, save the testing cost and improve the testing efficiency, six sigma DMAIC method and process were adopted in this paper. With "the good rate of blank value of cytological method for dairy products is low" as the improvement project, the problems were defined. DMAIC system method and six sigma tools such as flow chart, C&E matrix and FMEA analysis method were used to analyze and find the reasons why the good rate of blank value was low. On this basis, the root cause of low good rate of blank value was further determined through DOE method design and risk analysis, and the improvement plan was determined to improve the corresponding influencing factors, improve the good rate of blank value and customer satisfaction, prevent food safety risks, and improve product quality.
2 Application of DMAIC in improving the good rate of blank value of cytological method
2.1 Definition stage
2.1.1
Project topics. Persistent organic pollutants are substances that can enter the body along the food chain and further affect human health. Studies have shown that 90% of human exposure to pollutants comes from diet, especially animal derived food. Therefore, monitoring the content of organic pollutants in dairy products is of great significance to control product quality and reduce human exposure.Because the content of organic pollutants in dairy products is very small, it belongs to ultra-trace analysis and detection, with complex experimental process and large difficulties in detection, the data of cytological biological detection method established by our laboratory fluctuate greatly, and the detection results are unstable, which can not meet the needs of customers. Six sigma DMAIC method was used to find the key quality points by listening to customers’ voices and preliminary analysis. It was found that the low good rate of cell blank value was the main reason affecting the accuracy and stability of detection results. Therefore, "improving the good rate of blank value of cytological method" was selected as the project topics.
2.1.2
Opportunity for improvement. Through statistical analysis of data, it could be found that high blank value was the main reason of data unavailability, accounting for 80.6% of all reasons (Fig.1).
Fig.1 Pareto graph describing the reason of data unavailability
The calculation formula of good rate of blank value is:Y
(good rate of blank value of cytological method)=y
(number of good blank values)/total number×100%. It is regarded as defective specification if the blank value is higher than 1.5. The measured blank values from 2016 to 2018 were analyzed, and the good rate was only 52.8%.2.1.3
Project objective. Since the data were not available and the good rate of blank value was low, the defects were improved through the implementation of six sigma DMAIC method, and the good rate of blank value of cytological method reached 90%. The procedure not only ensured the accuracy and reliability of test results and met customer demands, but also improved the quality of products and prevented food safety risks, making enterprises and customers to achieve a win-win situation.2.2 Measurement stage
The main work in the measurement stage is to collect data objectively and have an objective understanding of problems and improvement schemes based on facts. Correct measurement is always the first step in quality improvement, so it is crucial to evaluate the stability of the measurement system.2.2.1
Measurement systems analysis. Measurement system is the general term of people, measuring tools, measuring objects, measuring methods and the environment related to measurement. In order to ensure the effectiveness and reliability of measurement data, the measurement systems analysis should be done first. MSA (Measurement Systems Analysis)refers to the use of statistical methods to find the source of fluctuations in measurement system and the impact on measurement results, and ultimately determines whether the measurement system meets the requirements of use, or requires further calibration, correction,etc.
The variance of continuously measuring the same characteristic of the same component by the same person using the same measuring instrument is called repeatability. The variance of measuring the same characteristic of the same component by different people using the same measuring instrument is called reproducibility. The capability of a measurement system is usually assessed by measuring capability parameter Gage R&R percentage, which describes the percentage of measurement error in the total error, including repeatability and reproducibility, which are the main factors contributing to the measurement system error. In the experimental process, microplate lumiscence instrument is the main equipment used in blank value detection, which is used to test the absorbance value of sample and calculate the blank value of sample, so microplate lumiscence instrument is used for measurement systems analysis.Two experimenters were appointed to select 10 samples for detection. Each experimenter repeated the test twice for each sample, and recorded the test results respectively. The test data were input into Minitab software for measurement systems analysis. According to the measurement system analysis results in Table 1, it can be concluded that the number of distinct categories was 9. Usually, only when the number of obvious categories was greater than or equal to 5, the measurement data could be used for analysis. The judgment criteria of measurement system ability were as follows: research percentage (P/TV
%)=14.25%, accuracy-tolerance ratio (P/T
%)=21.10%, 10%<P/TV
%<30%, 10%<P/T
%<30%. According to the judgment criteria, <10% was the best condition; 10%-30% was acceptable; > 30% was unacceptable. TheP/TV
% andP/T
% of blank values were both less than 30%. The measurement system detected by the microplate luminescence instrument could be trusted and meet the requirements of the measurement system.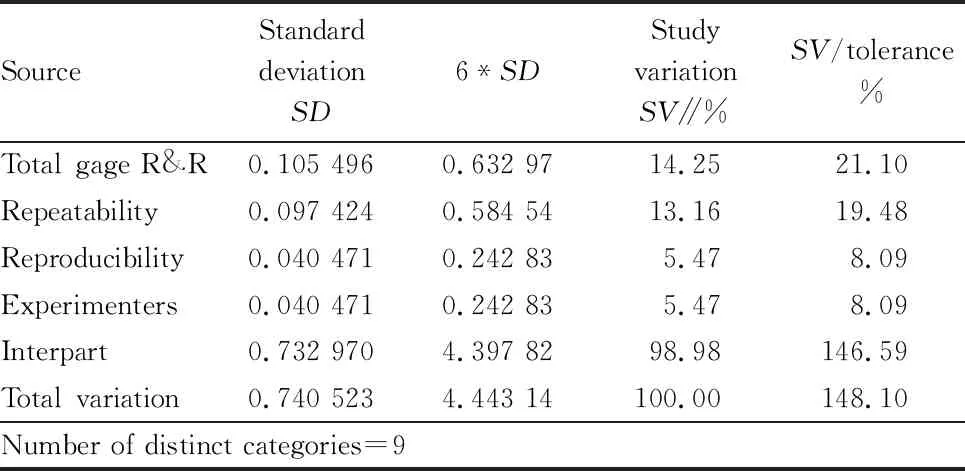
Table 1 Gage R&R analysis results
2.2.2
C&E matrix. Referring to the detailed experimental steps of cytological method, the project members listed the factors causing low good rate of blank value, analyzed each factor one by one, and further screened out five key input factors affecting the blank value of cytological method. In the cleaning process of laboratory supplies, the soaking time of laboratory supplies was short, and it was difficult to clean 1.5 mL conical bottles. In the reagent preparation, the preparation time and temperature of silica gel was unreasonable. In the cytological detection, cell activity was not good during cell planking, resulting in insufficient cell concentration.2.2.3
Failure mode analysis (FMEA). Based on the causality diagram with low good rate of blank values (Fig.3), five key input factors screened out were performed failure mode analysis.Through the field experiment, the glassware were soaked in alkaline rinse for too short time in the cleaning process of experimental supplies, and the impurities were not completely dissolved, which may lead to sample contamination. The bottom of the 1.5 mL conical bottle used in the experiment was pointed. In the cleaning process, the bottom could not be completely cleaned, resulting in pollutant residues that could carry impurities and contaminate the sample extract.
Silica gel was the key reagent for separation and purification in the process of reagent preparation, and it needed to be activated by muffle furnace at high temperature before the experiment. If the activation temperature and time were not reasonable, silica gel activation would be incomplete, and the separation and purification effect of organic pollutants would be poor, thus affecting the accuracy of detection results.
Cytological experiment stage was the key stage of the whole experiment process. The cell activity was evaluated by cell adherent rate, and too high or too low cell adherent rate would affect the experimental results.
2.2.4
Quick win improvement. While analyzing the root cause and seeking a thorough solution, it was found that some problems were obvious, and rapid implementation could effectively improve the problem of low cell good rate. According to the data collected during the measurement phase, it was very difficult to clean the tip bottom of the 1.5 mL conical bottle, which easily caused contaminants to contaminate the sample extract with impurities. The cost of a new 1.5 mL conical bottle was 7 yuan, and the cost of cleaning reagent was 860 yuan per 15 bottles; the soaking lasted 3 d, while the cleaning and drying lasted 1 d. Therefore, the recovery cost was about 57 yuan per bottle, 8 times of the new bottle, and the recovery cost was high. For an individual sample, the use of new bottles would save 50 yuan/bottle. When the 1.5 mL conical bottle was changed to disposable, the good rate of blank value reached 70% as 10 samples were tested, which was nearly 20% higher than 52.8% before improvement, and the fluctuation of blank value decreased.2.3 Analysis stage
The main work in the analysis stage is to summarize the collected data, verify the key factors screened out in the measurement stage, and find out the key influencing factors for improvement in combination with the specific experimental process. In the analysis stage of this project, the tool of variance analysis and hypothesis test were mainly used to verify the four factors screened out in the measurement stage to confirm whether they were necessarily related to the level of blank value.2.3.1
Quick win improvement. According to C&E matrix and FMEA analysis in the measurement stage, the adherent rate of cell resuscitation was low and the cell viability was poor. After planking, the cell died and split to release luciferase, and the fluorescence intensity was enhanced, leading to the increase of blank value. Different adherent rates of cell resuscitation were set for planking experiment, and the experimental data of measured blank value were used to plot Fig.2. As shown in Fig.2,R
-sq
(adj)>90%, with significant correlation, indicating that different adherent rates of cell resuscitation had an impact on blank value. The blank value had a cubic relation with the adherent area (logarithm). As the adherent rate of cell resuscitation increased, the blank value would decrease. Therefore, it was confirmed that the adherent rate of cells reaching 95% was the best condition for planking.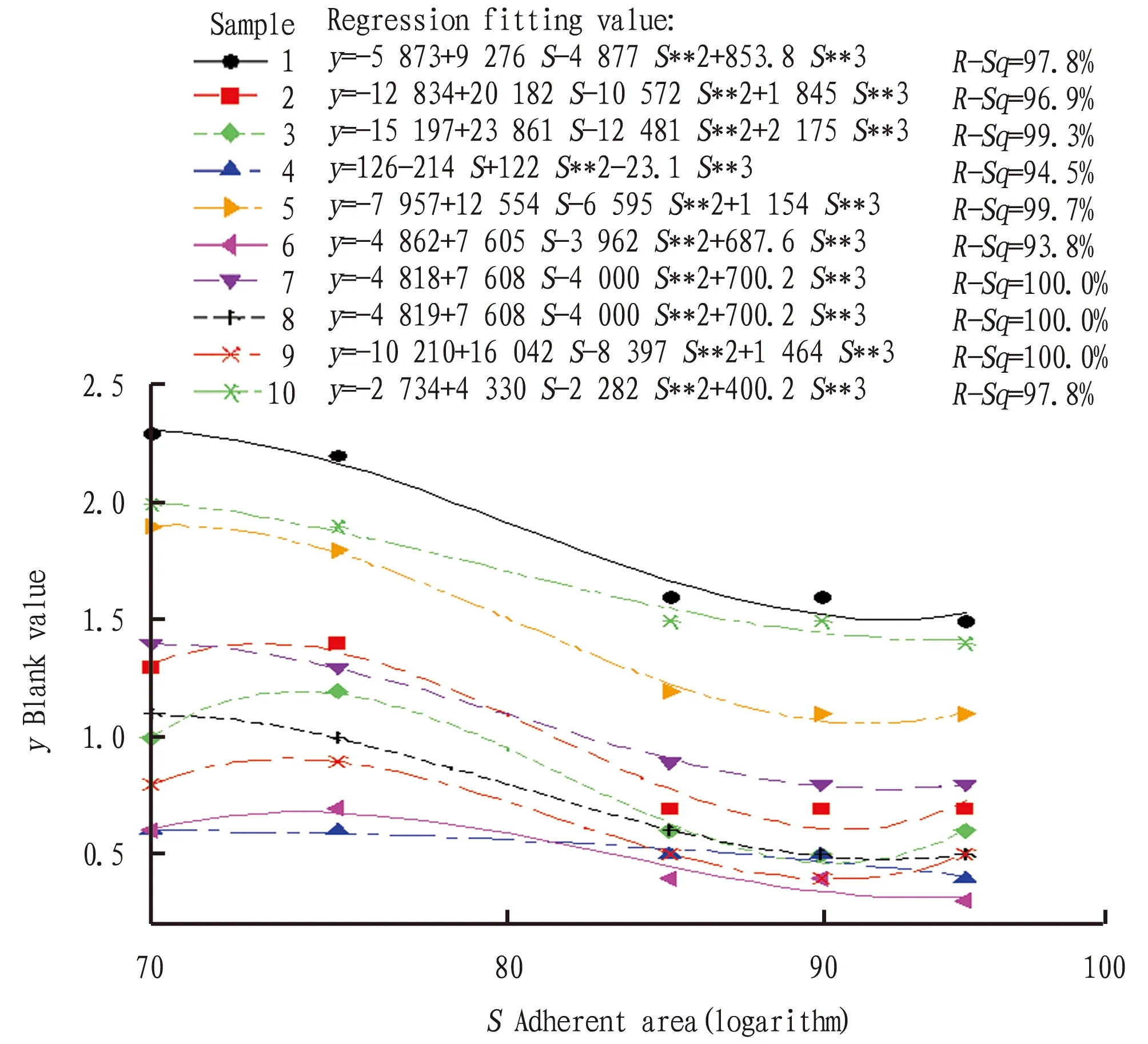
Fig.2 Scatter plot of blank value and adherent area
Planking test was carried out when the cell adherent rate was 95%, and 10 samples were tested. The good rate of blank value reached 90%, which was 20% higher than the last quick win improvement.
2.3.2
Analysis of potential main causes. The remaining three factors were verified by ANOVA and hypothesis test. According to the selection principle of hypothesis testing method, the mean values of the three factors were compared and analyzed by equi-variance test. When establishing the hypothesis, the alternative hypothesis was usually determined first, and then the null hypothesis was established. Finally, the data were collected by calculating various factors via Minitab software. If the calculated valueP
<0.05, the null hypothesis was not established; if the calculated valueP
≥0.05, the null hypothesis was established. The experimental data are shown in Tables 2-4.As shown in Tables 2-4, theP
value of the soaking time of experimental products, was 0.479>0.05, indicating that the null hypothesis was valid. The change of blank value was mainly due to the difference of samples, and soaking time had no effect on blank value. TheP
values of silica gel activation time and temperature were both smaller than 0.05, and their null hypotheses were not valid, indicating that silica gel activation time and temperature were important factors affecting the good rate of blank value. When the silica gel activation time was prolonged and the activation temperature was increased, the blank value would decrease. Therefore, it is necessary to determine the best time and temperature of silica gel activation.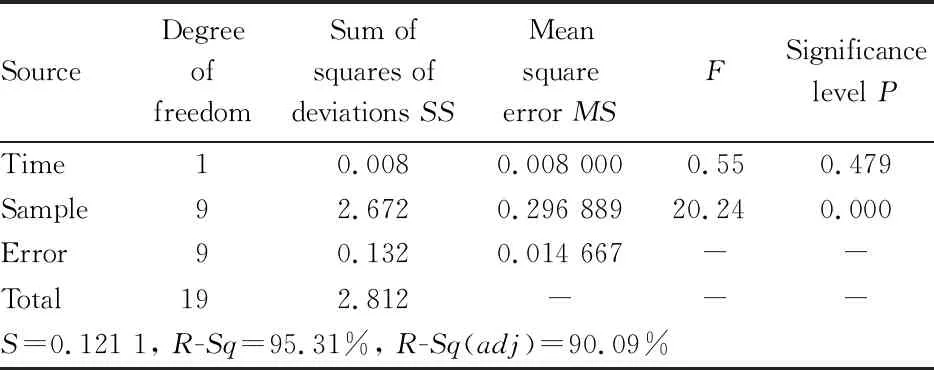
Table 2 Two-factor two-level ANOVA of soaking time and sample
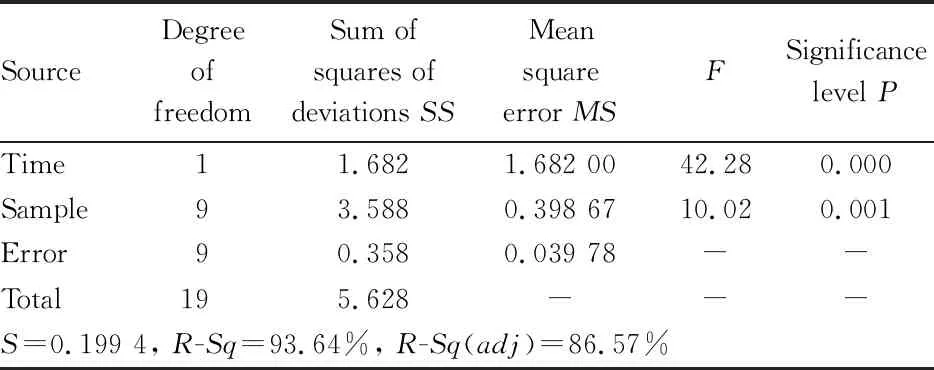
Table 3 Two-factor two-level ANOVA of silica gel activation time and sample
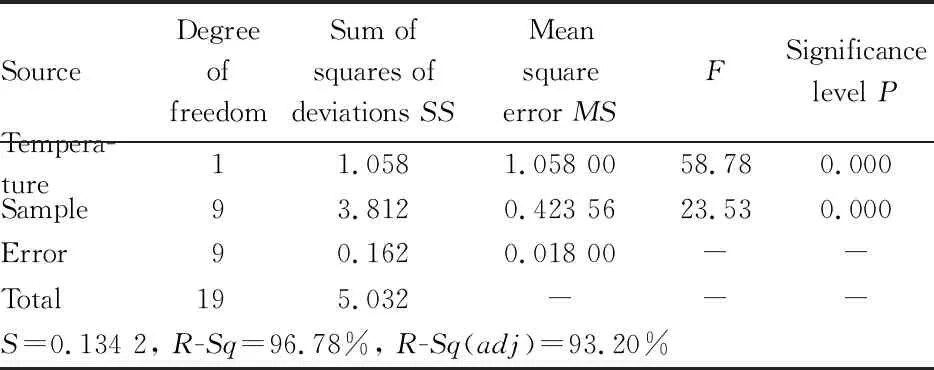
Table 4 Two-factor two-level ANOVA of silica gel activation temperature and sample
2.4 Improvement stage
2.4.1
Design and analysis of DOE full-factor experiment. According to the analysis of the improvement project in the analysis stage, two factors affecting the good rate of blank value were obtained, and the controllable factors and corresponding levels were confirmed. The optimal parameter combination was carried out by the DOE method designed in the experiment.In this DOE experiment, the factor numberF
was 2, two levels were selected for each factor, and the number of full-factor experiments was 8. In order to judge whether the central point was significant, four groups of central point experiments were added. By findingX
that had significant influence onY
, theseX
were improved, and finallyY
reached the target value below 1.5. The full-factor experimental design and results are shown in Table 5.It can be seen from the location of the central point that the model was bent (the central point was far from the straight line). Further variance analysis of the experimental results showed that the bending wasP
=0.004 (less than 0.05), indicating that the model was significantly bent and had a secondary impact. Therefore, it is necessary to conduct the next experiment to add axis points and then optimize the parameters.The experiment was conducted after the central point was added, and the experimental design and results are shown in Table 6. The experimental results were performed regression analysis. Activation time (0.000), activation temperature (0.002), their square term and their interaction regression analysisP
value (0.036) were all less than 0.05, indicating that these four items had significant influence on blank value. ANOVA was further conducted on the regression model. TheP
value of the lack of fit in ANOVA was 0.107, greater than 0.05, indicating that the regression model did not have significant lack of fit and could be used for response optimization of the experimental results (Table 7).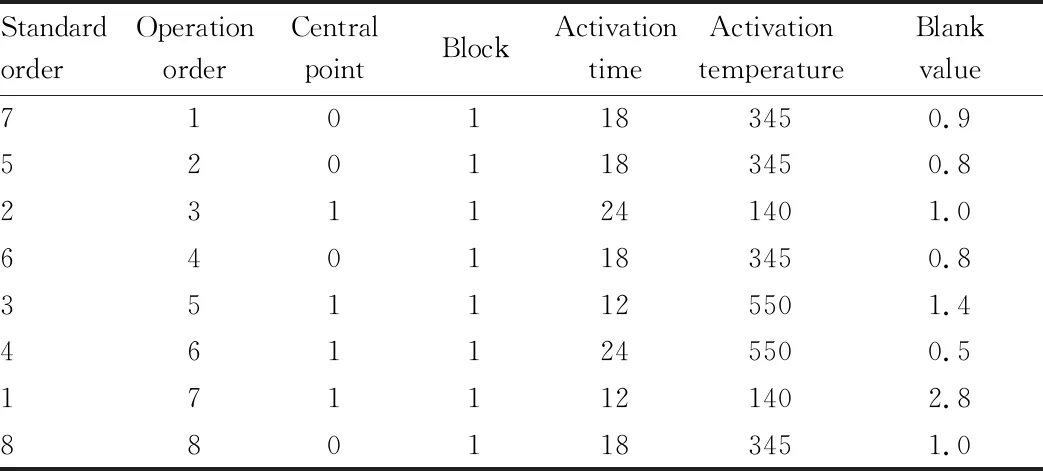
Table 5 DOE full factor experimental schedule and experimental results
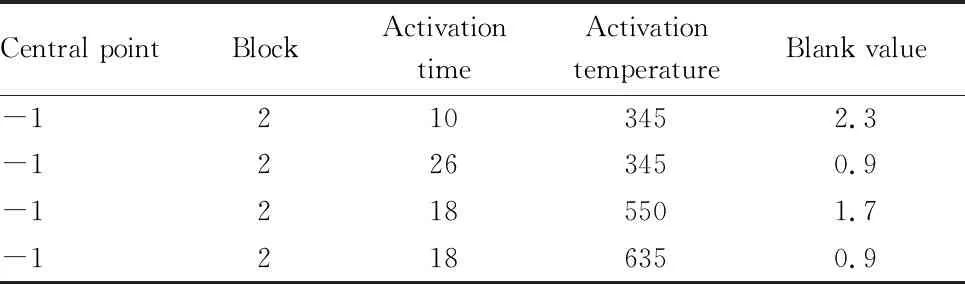
Table 6 Experiment scheme of adding central point and experiment results
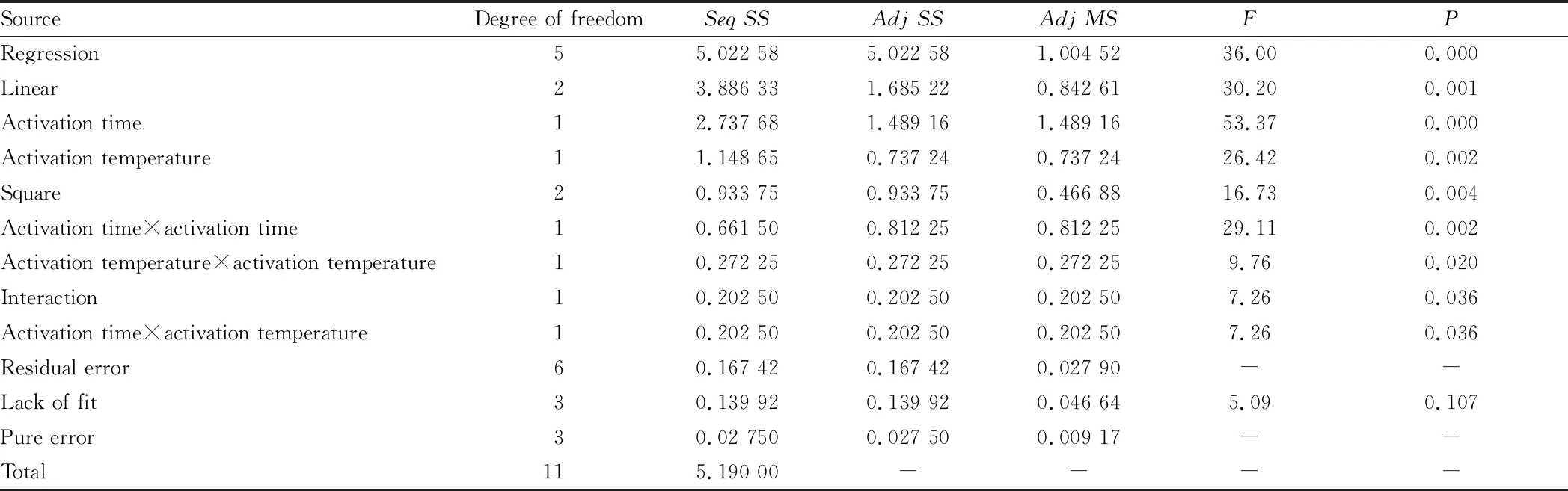
Table 7 ANOVA of DOE experiment
2.4.2
Parameter optimization and verification. According to the regression model, the experimental parameters were optimized. The optimization principle was: optimal activation temperature (save electricity, facilitate operation), shortest activation time (save time cost, improve efficiency), and ensuring that the blank value was reduced from 1.5 to 1.0, superior to the method requirements. The corresponding optimization results are shown in Fig.3. According to the optimization analysis of the model, the optimal parameters were activation temperature around 459.2 ℃ and activation time around 21.8 h. As shown in Fig.4, when the activation time was set at (23±1) h and the activation temperature was set at (550±50) ℃, the predicted blank value could be reduced from 1.5 to less than 1.0.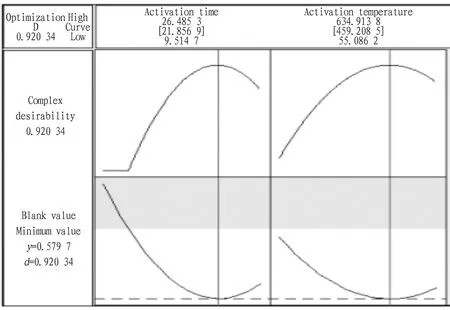
Fig.3 Optimized parameters of DOE experiment
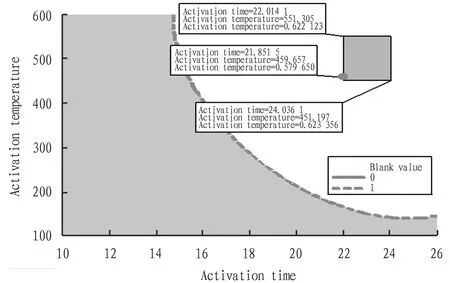
Note: 1. The standard of blank value is reduced from 1.5 to 1.0, superior to the method requirements; 2. In order to save power and facilitate operation, the activation temperature of muffle furnace is selected as 450-550 ℃; 3. In order to save time cost and improve efficiency, the activation time is set to 22-24 h.
According to the optimization results, the optimization parameters were further verified by experiments. Ten batches of sample were tested, and the blank values of the verification results were all below 1.5. The good rate of blank value increased from 52.8% before improvement to 100%, indicating that the parameter optimization was reasonable. Through the optimized experimental parameters, the accuracy of experimental results could be guaranteed to meet customer requirements.
2.5 Control stage
Through the analysis and validation of the above four stages, parameters verified by DOE experiment were used. For the improved experimental conditions, silica gel activation temperature and time were reset to determine the cell planking adherent rate and to determine the use frequency of 1.5 mL conical flask consumables. The new operation instructionDetermination
Method
of
Blank
Value
for
Cytological
Method
was determined, which was incorporated into the laboratory daily control system. The final good rate of blank value increased from 52.8% to 100%, which not only improved the accuracy of test results, but also effectively prevented food safety risks and improved product quality.3 Conclusions
The paper explained the five stages of the six sigma DMAIC method. As the project topics were defined and the key influencing factors were found, the experimental data were analyzed using statistical analysis tools. According to the analysis results, parameters were optimized using DOE experimental design method, and the control plan was eventually made to ensure the improved project results. Experimental analysis results showed that according to the steps of six sigma management DMAIC method, good results had been achieved in improving the good rate of blank value of cytological method, which was increased from 52.8% to 100%, exceeding the target value of 90% and reaching the benchmark value of 95%, exceeding the established goal of the project.
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Nitrogen Metabolism and Curing Characteristics of Flue-cured Tobacco Variety NC71
- Effects of Nitrogen Forms on the Growth and Development of Trees
- Present Situation and Problems of Application of New Media in Rural E-commerce: A Case Study of Anhui Province
- Design and Study of Could Platform Based Sampling Control and Management System
- Formation Mechanism of Heartwood and Research Status
- Research on Evaluation and Development of Industrial Heritage Tourism Resources in Textile Valley
