Regulation of the mesenchymal stem cell fate by interleukin-17:Implications in osteogenic differentiation
2021-12-24JelenaKrstiSlavkoMojsiloviSonjaMojsiloviJuanSantibanez
Jelena Krstić, Slavko Mojsilović, Sonja S Mojsilović, Juan F Santibanez
Jelena Krstić, Gottfried Schatz Research Center, Medical University of Graz, Graz 8010, Austria
Slavko Mojsilović, Group for Hematology and Stem Cells, Institute for Medical Research, National Institute of Republic of Serbia, University of Belgrade, Belgrade 11129, Serbia
Sonja S Mojsilović, Group for Immunology, Institute for Medical Research, National Institute of Republic of Serbia, Belgrade 11129, Serbia
Juan F Santibanez, Group for Molecular Oncology, Institute for Medical Research, National Institute of Republic of Serbia, University of Belgrade, Belgrade 11000, Serbia
Juan F Santibanez, Centro Integrativo de Biología y Química Aplicada, Universidad Bernardo O’Higgins, Chile 8370993, Chile
Abstract Bone regeneration is a tightly regulated process that ensures proper repair and functionality after injury. The delicate balance between bone formation and resorption is governed by cytokines and signaling molecules released during the inflammatory response. Interleukin (IL)-17A, produced in the early phase of inflammation, influences the fate of osteoprogenitors. Due to their inherent capacity to differentiate into osteoblasts, mesenchymal stem/stromal cells (MSCs) contribute to bone healing and regeneration. This review presents an overview of IL-17A signaling and the leading cellular and molecular mechanisms by which it regulates the osteogenic differentiation of MSCs. The main findings demonstrating IL-17A’s influence on osteoblastogenesis are described. To this end, divergent information exists about the capacity of IL-17A to regulate MSCs’ osteogenic fate, depending on the tissue context and target cell type, along with contradictory findings in the same cell types. Therefore, we summarize the data showing both the pro-osteogenic and anti-osteogenic roles of IL-17, which may help in the understanding of IL-17A function in bone repair and regeneration.
Key Words: Interleukin-17; Mesenchymal stem cells; Osteoblast; Bone; Osteogenesis; Inflammation
INTRODUCTION
The interleukin-17 (IL-17) cytokine was first described in 1993 as a cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 8 (CTLA8) and was, subsequently, in 1995, reported to share 57% of its sequence homology with the herpes virus saimiri gene 13 (HVS13). Both HVS13 and CTLA8 were shown to costimulate T-cell proliferation by binding to a novel cytokine receptor and were named IL-17, vIL-17, and IL-17R, respectively[1,2]. Later on, Parket al[3] defined the cellular requirements for the differentiation of naïve CD4 T-cells into effector T helper cells with the capacity to express and secrete IL-17. This resulted in the discovery of a new subset of T helper cells with proinflammatory functions, referred to as TH17 cells[4]. Today, IL-17 is recognized as a founding member of the IL-17 family that comprises the cytokines IL-17A (initially named IL-17) through IL-17F, which were discoveredviascreening for homologous genes[5]. By producing IL-17A and IL-17F, TH17 cells participate in host protection against external pathogens and recruit macrophages and neutrophils to the infection site[6,7].
The dysfunctional regulation of TH17 may exacerbate the pathogenesis of multiple inflammatory and autoimmune disorders, such as sepsis, pneumonia, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), allograft rejection, and cancer[4,8]. Specifically, the six IL-17 cytokines are secreted glycosylated proteins with molecular weights of about 20-30 kDa and share 20%-50% of their sequence homology with IL-17A. IL-17 family members exhibit a conserved protein C-terminus with two intramolecular disulfide bridges formed by four cysteine residues. Moreover, IL-17s belong to the cystine knot fold superfamily since they dimerize similarly to the nerve growth factor subfamily[8-13]. Furthermore, IL-17A and IL-17F form either homodimers or heterodimers and are co-expressed by linked genes on chromosome 6[6,14,15]. It is well known now that, beyond TH17 cells, many cell types can produce IL-17, including almost all innate and adaptive immune cells[4,6].
IL-17 cytokines exert their actions by binding to the IL-17 receptor (IL-17R) family, composed of five receptor types (IL-17RA to IL-17RE)[5]. Although its expression level varies widely, IL-17R is expressed ubiquitously and is mainly characterized by a shared SEF/IL-17R (SEFIR) motif in the intracellular domain and two fibronectin IIIlike regions (FN1 and FN2) within the extracellular environment[5,16,17]. In addition, all IL-17 isoforms bind to IL-17RA, which forms heterocomplexes with other IL-17R subtypes responsible for ligand-binding specificity[8,18].
IL-17A initiates signaling by binding to an IL-17RA/IL-17RC receptor complex. This binding triggers the multifunctional adaptor Act1, a U-box E3 ubiquitin ligase interaction with IL-17Rviathe SEFIR domain (Figure 1). Next, the IL-17 downstream intracellular signaling is activatedviahomotypic interactions between the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor-associated factor (TRAF)6/transforming growth factor β (TGF-β)-activated kinase 1 (TAK1) complex with Act1. This signaling includes nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) (ERK1,2, p38, and JNK). Similarly, the activated IL-17/IL-17R/Act1 complex can signalviathe TRAF4/MEKK3/MEK5/ERK5 axis. Finally, the noncanonical signaling of IL-17A involves a TRAF2/5-human antigen R (HuR)-alternative splicing factor (ASF or SF2) cascade that results in the control of mRNA stability of IL-17-targeted inflammatory cytokine and chemokine genes[5,18-20].

Figure 1 Overview of interleukin-17A signaling.
Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells (MSCs) are multipotent stromal cells that were first described in the bone marrow (BM) regarding their capacity to support hematopoiesis after heterotopic transplantation in a nude mouse model[21,22]. MSCs display a spindle fibroblast-like shape and are capable of self-renewal. Moreover, when stimulated, bothin vivoandin vitro,they can differentiate into several mesodermal cell types[23,24]. Moreover, it is now well known that MSCs can also differentiate into nonmesodermal lineages, such as hepatocytes, neurons, and pancreatic cells, among others[24].
MSCs are defined by standardized criteria for their identification and characterization. In 2006, the International Society for Cellular Therapy proposed a set of minimum standards to characterize MSCs: fibroblast-like morphology, plastic adherence, three mesodermal lineage differentiation capacities (adipocytes, osteocytes, and chondrocytes), and specific immunophenotype surface markers[25], whereby more than 95% of MSCs should express CD73, CD90, and CD105. Meanwhile, to avoid hematopoietic cell contamination, leukocyte markers CD45, CD34, CD14 or CD11b, CD19 or CD79α, and HLA-DR should be expressed in less than 2% of the cell population. Recently, additional cell surface markers have been identified that ensure the isolation of clonogenic MSCs such as STRO-1, CD29, CD44, CD106, CD146, and CD27 and epidermal growth factor receptor, insulin-like growth factor (IGF) receptor, and nerve growth factor receptor[26].
MSCs are present in almost all adult tissues[27]. Adipose tissue, BM, and dental tissue are the preferred sources for preclinical and clinical research[24,28,29]. Furthermore, the usage of adult MSCs is not compromised by the biological and ethical concerns that surround their embryonic counterparts. Thus, they can be used as autologous transplants, which has opened up new opportunities for tissue regeneration and bioengineering, as well as for cell-based clinical applications[30-32]. Moreover, when transplanted, MSCs do not manifest tumorigenicity, which is an advantage compared to induced pluripotent stem cells[33,34].
Under homeostatic conditions, MSCs are hypoimmunogenic and capable of evading immune system recognition. In addition, they express low class I major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules and lack class II MHC and costimulatory molecule (CD40, CD80, and CD86) expression. These characteristics make MSCs suitable for allogeneic transplantation[35,36]. Likewise, MSCs possess remarkable immunosuppressive, immunomodulatory, and anti-inflammatory functions, accompanied by antimicrobial properties. Thus, MSCs are meaningful candidates to be studied and potentially may be used in therapies for fracture healing and bone regeneration[37-40].
THE BONE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
Bone is a supportive tissue contributing to locomotion, soft tissue and vital organ protection, blood pH regulation, and calcium and phosphate homeostasis. It also provides a functional milieu for blood production in the BM and progenitor cell niche formation. In this regard, the bone contains both mesenchymal and hematopoietic cell compartments[41-43].
Bone tissue is mainly composed of two interrelated compartments: (1) Like connective tissue, bone is rich in the extracellular matrix (ECM) and abundant in organic collagen fibers (comprising about 90% of the matrix proteins) and inorganic hydroxyapatite (a naturally occurring mineral significant for bone reinforcement)[43-46]; and (2) The cellular components of bone mainly encompass osteoprogenitors, osteoblasts, osteocytes, and osteoclasts[45,47,48].
Osteoblasts are differentiated cells originating from BM MSCs. Undifferentiated MSCs reside in the periosteum, which covers the bone surface. The osteogenic process occurs in sequential events, including MSC recruitment to bone remodeling areas, followed by cell proliferation and subsequent lineage commitment[49]. In the beginning, MSCs are committed to generating actively proliferating pre-osteoblasts, which at this early stage do not produce ECM proteins. Next, cells cease proliferation and start to secrete type I collagen, proteoglycans, and other noncollagenous proteins. Afterward, the mineralization process occurs with the phosphates released by osteoblast-associated phosphatases, which combine with calcium to form hydroxyapatite crystals. Once a functional ECM is generated, osteoblasts differentiate into osteocytes, long-lived cells with an average half-life of 25 years, embedded within lacunae[49].
Interestingly, osteocytes encompass approximately 90%-95% of bone cells and are recognized as the principal regulators of bone homeostasis since they contribute to bone formation and resorption during bone remodeling. In addition, osteocytes may act as sensors for organic and inorganic molecules during mechanical stimuli to remodel the environment, thus contributing to the proper maintenance of bone tissue functionality[50-55]. On the other hand, osteoclasts are large multinucleated boneresorbing cells that originate from the fusion of myeloid precursors of the monocyte/ macrophage lineage and participate in bone degradation, bone turnover, and remodeling[56,57].
Bone tissue is created by intramembranous ossification or endochondral ossification. In the first place, direct ossification occurs in the neuro and viscerocranium, flat bones, and in part of the clavicle. It is characterized by MSC-derived osteoblast condensation, which causes mature osteoblasts to evolve into osteocytes. Meanwhile, indirect endochondral ossification occurs in long bones, vertebrae, the skull base, and the posterior skull[58]. This process involves MSCs, which initiate the first round of cartilage differentiation and are later replaced by bone tissue, considerably increasing the ability to withstand mechanical compression[59].
Healthy bone is a dynamic organ with a constant balance of fine-tuned bone resorption and new tissue generation. It confers bone’s ability to repair itself by continuous skeletal adjustment to mechanical forces in varying environmental conditions[41,43]. Therefore, impairment in cell differentiation can result in different bone pathologies. For example, an imbalance in BM MSC differentiation toward the adipocyte lineage, to the detriment of osteoblast/osteocyte generation, may result in bone mass loss and bone diseases such as osteoporosis[60,61].
Mechanistically, early osteogenesis stages include the expression of hedgehog proteins, Wnt/β-catenin signaling, bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs), endocrine hormones, epigenetic regulators, cytokines, and growth factors. These events implicate complex processes of finely regulated and timely orchestrated activation of specific transcription factors to express genes that accurately define the osteoblast phenotype[60,62].
Runt-related transcription factor 2/core-binding factor subunit alpha-1 (Runx2/ Cbfa1) and downstream osterix (OSX) are crucial for osteoblast differentiation. The absence of either Runx2 or OSX results in the impairment of skeleton mineralization. Moreover, Runx2 is essential for MSC commitment toward the osteogenic lineage[63]. Therefore, Runx2 is expressed early during osteogenesis. However, as the differentiation process advances, Runx2 expression is downregulated, accompanied by upregulation of OSX and β-catenin with further osteoblast maturation[60,62].
Namely, Runx2 contains a runt DNA-binding domain harbored by several enhancers and promoters, including those for the genes encoding alkaline phosphatase (ALP), collagen type 1 (COL1), osteocalcin (OC), and osteopontin (OPN). These proteins contribute to bone matrix generation and osteoblast maturation. These genes are also useful as markers for different osteogenesis stages[64-66]. The time course of events indicates that ALP is an early marker of osteogenic differentiation and mineralization in committed osteoprogenitors. In contrast, more advanced osteogenesis stages implicate COL1, osteoprotegerin (OPG), and osteonectin expression, while OC and OPN are confined mainly to the terminal differentiation phase[62,67-69]. OPG, first characterized and named for its protective role in bone remodeling[70,71], functions as a soluble decoy receptor for the cytokine receptor activator of NF-κB-ligand (RANKL) since it prevents the binding of RANKL to the receptor activator of NF-κB (RANK). Therefore, OPG inhibits osteoclastogenesis and protects bone from excessive osteoclast-mediated resorption[72].
In turn, osteonectin is a binding-calcium glycoprotein implicated in mineralization initiation, promoting mineral crystal formation[73]. Furthermore, OC is vital for bone formation and resorption inhibition[74]. Finally, OPN is an integrin-binding glycoprotein expressed at high levels by osteoblasts at the endosteal surface and regulates bone development and bone mass maintenance[75].
Several signaling factors are involved in the activation of Runx2, including wingless-type (Wnt)/β-catenin, BMPs, TGF-β1, hedgehog, and (Nel)-like protein type 1 (NELL-1)[76,77]. The Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway may regulate osteoblastogenesis by modulation of MSC commitment to the osteoblastic lineage. The activated Wnt/β-catenin canonical pathway contributes to the induction of osteogenic regulators Runx2, distal-less homeobox 5, and OSX, which notably induces MSCs’ progression into mature osteoblasts[43,78-80]. Furthermore, Wnt/β-catenin controls bone resorption by increasing the OPG/RANKL ratio[81,82]. Wnt5a induces noncanonical Wnt signaling pathways, such as the co-repressor complex, through calciumcalmodulin-dependent protein kinase II-TAK1-Nemo-like kinase signaling, to regulate MSC differentiation to osteoblasts by Runx2 induction and inhibition of the adipogenic transcription factor PPARγ expression[83,84].
In addition, a large body of experimental evidence unequivocally demonstrates that BMP signaling causes multipotent mesenchymal cells to differentiate into the osteochondral lineage and regulates the maintenance of postnatal bone and cartilage. The abundance of different types of BMPs varies in response to skeletal requirements. BMP-2, -4, -6, -7, and -9 are of particular importance in bone formation, as they activate BMP-associated Smads (Smad-1, -5, and -8) to induce Runx2 and OSX activation axes, while BMP-3 and BMP-13 present exceptions in the subfamily and act as inhibitors of osteogenic differentiation[85,86]. Moreover, inhibitor of differentiation (ID) proteins, especially ID1 and ID3, are critical effectors of BMP-induced osteoblastogenesis[87].
Furthermore, early-response genes that activate downstream BMP signaling in primary BM-MSCs include Dlx2 and 5.In vitrostudies demonstrated that Dlx proteins mediate the expression of several osteoblast lineage genes, including Runx2, OSX[88], and osteoactivin, a positive regulator of bone formation, bothin vitroandin vivo[89].
On the other hand, during osteoblastogenesis, inhibitory Smad6 can intracellularly inhibit BMP receptors. Furthermore, BMP-Smad1–Runx2 regulates Smad6 expression, while Smad6 regulates BMP and Runx2 activity in a negative feedback loop[86,90]. Likewise, Noggin, chordin, gremlin, and follistatin, which sequester BMPs and prevent binding to cell surface receptors, regulate BMP function during bone generation[86,88].
Also, systemic hormones, such as parathyroid hormone, glucocorticoids, estrogens, and local growth factors, such as bone TGF-β1/2, IGF, fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF-2), vascular endothelial growth factor, prostaglandins, and MAPK signaling molecules, regulate MSC osteogenic differentiation[41]. Furthermore, MSC osteoblastogenesis can also be inducedin vitroby adding a combination of dexamethasone, beta-glycerophosphate, and ascorbic acid to the cell culture medium[91].
IL-17A AND MSCS: THE OSTEOGENIC LINK
Bone homeostasis is a finely regulated process relying on the interplay between the immune and musculoskeletal systems[92]. Indeed, the skeletal and immune systems share several regulatory biomolecules, including growth factors, proinflammatory and inflammatory cytokines, and other signaling molecules[93]. Inflammation plays a strategic role in bone homeostasis and turnover in several inflammation-associated diseases and events, such as bone fracture healing, periodontitis, erosive arthritis, osteoarthritis (OA), chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS), and spondyloarthropathy[92,94].
Several immune cell types (e.g., macrophages, neutrophils, and T cells) infiltrate injured bone tissue and regulate new bone formation during normal and dysfunctional bone repair and regeneration. In this sense, cytokines such as IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-17A positively contribute to the healing process. However, the same cytokines can enhance inflammation, triggering dysfunctional bone tissue regeneration and bone-associated inflammatory diseases[92]. Thereby, the immune system interacts closely with the bone system in health and disease.
By regulating bone regeneration and homeostasis, IL-17 also acts on MSCs’ differentiation ability. MSCs express high levels of IL-17RA as well as the other four members of the IL-17R family[95,96], and IL-17A can induce MSC proliferation, migration, and differentiation[97]. For example, in mouse BM-MSCs, IL-17 increases CFU-F (colonyforming unit fibroblasts) average frequency and colony size and cell proliferation, mediated by p38 and ERK1,2 MAPKs[98,99]. Moreover, IL-17A induces the motility and transendothelial migration of peripheral blood MSCsin vitro, suggesting a possible role for IL-17 in the mobilization and recruitment of MSCs to injured tissues[95,100]. Consistently, IL-17A also induces the gene expression of matrix metalloproteases-1 and -13 in MSCs, which potentiates their capacity to degrade collagen and invade the ECM[101].
Moreover, IL-17 promotes the immunosuppressive function of mouse BM-MSCs by inducing nitric oxide (NO) and programmed death-ligand-1[102]. In addition, it enhances human BM-MSC-induced inhibition of T cells, and IL-17A-treated MSCs promote regulatory T cells expansion and function, further increasing their immunosuppressive effect[103,104].
THE PRO-OSTEOGENIC ROLE OF IL-17
One of the first pieces of evidence that IL-17 may regulate MSC osteogenic differentiation was provided by Huanget al[97]. Primary human MSCs under IL-17 treatment responded with increased proliferation and migration alongside activation of the TRAF6-ACT1-NADPH oxidase (NOX)1/reactive oxygen species-MEK-ERK MAPK pathway axis. Furthermore, IL-17 treatment induced ALP expression and activity with subsequent mineralization in cell culture. Moreover, IL-17 induced osteoclastogenesis of mononuclear cells in coculture conditions with primary human MSCs by induction of macrophage colony-stimulating factor and RANKL in primary human MSCs. Thus, IL-17 contributes to bone turnover by modulating osteogenesis and osteoclastogenesis[97].
The effect of IL-17 on MSCs’ osteoblastogenesis can depend on their inflammatory stage or polarization. MSCs display two polarized phenotypes based on the expression of the surface marker Toll-like receptor (TLR): TLR4+MSCs (also called MSC1) and TLR3+MSCs (also called MSC2), with different inflammatory functions[105].In vitro, IL-17 induces MSC2 polarization in mouse-derived MSCs through the WNT10b/Runx2 axis, concomitant with increased mineralization rates. Furthermore, in a mouse model of ankylosing spondylitis (AS), MSC2 polarization was related to new bone formation, and the PBMCs of AS patients with new bone formation expressed significantly higher IL-17A mRNA levels than those of healthy donors[106].
Interestingly, osteocytes may enhance the capacity of IL-17 to induce osteogenic differentiation of murine BM-MSCs. IL-17 triggers osteoblastic differentiationviathe activation of AKT, STAT3, and ERK1,2 along with ALP, Runx2, OCN, and COL-1 expression. The coculture of osteocytes with MSCs under IL-17 treatment leads to an increase in IL-6 and IL-1β secretion by both cell types, which mediates the enhanced osteogenic differentiation of MSCs. Blocking either IL-6 or IL-1β inhibits IL-17-mediated activation of AKT, STAT3, and ERK1/2 in MSC. Therefore, IL-17 may potentiate MSC osteoblastic differentiation within the bone niche by increasing MSCosteocyte interaction, further contributing to osteoblastogenesis[107].
IL-17A has recently emerged as a mediator of extensive inflammation and abnormal bone formation in AS, leading to bony ankylosis. Basal levels of IL-17A in bodily fluids (patient serum and synovial fluid) are elevated in patients with AS. Moreover, IL-17 enhanced ALP activity and mineralization in AS-derived MSC-like primary bonederived cells by activating JAK2/STAT3-mediated both Runx2 and C/EBPβ expression[108,109]. Furthermore, in a biomimetic human periosteum-derived cell (hPDC) model, IL-17 induced osteoblastic differentiation. At the same time, blockage of IL-17 with the humanized monoclonal antibody bimekizumab suppressed serum-induced hPDC osteocommitment in AS patients, as evidenced by Runx2 expression inhibition[110].
IL-17 also plays a role in CRS neo-osteogenesis, a heterogeneous and multifactorial disorder of the paranasal sinus mucosa, which involves bone neo-osteogenesis, especially in recalcitrant CRS patients[111]. Levels of Runx2 and IL-17 were increased in tissue sections from CRS patients with neo-osteogenesis. Furthermore, IL-17Aneutralizing antibodies supported the notion that IL-17 mediates Runx2 expression in mouse mesenchymal precursor C2C12 cells treated with nasal tissue extracts. Thus, these data indicate that Runx2, induced by IL-17A, contributes to new bone formation in CRS patients through its effect on osteoblasts’ activity[112].
Furthermore, Onoet al[113] showed that γδT cells promote bone formation by producing IL-17A and facilitate bone fracture healing in a drill-hole injured femur mouse model. Here, IL-17A was induced in the early phase of bone fracture healing and seems to accelerate bone formation by stimulating the proliferation and osteoblastic differentiation of mesenchymal progenitor cells. Conversely, bone repair impairment inIl17a-/-mice occurs due to decreased osteoblastic-dependent bone formation, while osteoclastic bone resorption is not affected[113]. Furthermore, IL-17 enhancesin vitroBMP-2-induced osteoblastogenesis in injury-associated MSCs.
Similarly, IL-17 synergizes with BMP-2 to induce osteoclastogenesis in human MSCsin vitroandin vivo. IL-17 dramatically increased matrix mineralization mediated by BMP-2 in human MSCs[114]. In a rabbit model, IL-17 enhanced BMP-2-induced ectopic bone formation in ceramic scaffolds coated with bisphosphonate zoledronic acid (ZOL) by suppression of osteoclasts. Doubled bone volume was observed after 12 wk of BMP-2 and IL-17 co-delivery compared to only BMP-2 in subcutaneous ceramic scaffold implantation. IL-17 induces connective tissue ingrowth and restores BMP-2-induced vascularization and connective tissue formation inhibited by the ZOL coating[115].
Dental-derived MSCs, which represent an ideal source for tissue engineering, and regenerative and dental medicine[116], also differentiate toward osteoblasts under IL-17A stimuli. For instance, IL-17 induces the osteogenic-associated proteins Runx2, OC, and ALP and mineralization in MSCs derived from dental pulp[117]. Similarly, IL-17A inducesin vitroosteogenic differentiation in MSCs from human exfoliated deciduous teeth (SHED). IL-17 increases cell proliferation in five days of treatment while inducing ALP expression on day 14 of cultivation. Moreover, stem cell marker c-Myc and Nanog expression were downregulated after IL-17 treatment. This stem cell marker inhibition occurred concomitantly with the upregulation of osteogenesisassociated proteins—such as Runx2, COL1, OPN, OCN, and OPG—along with RANKL downregulation, which increased the OPG/RANKL ratio[118].
IL-17 may regulate RANKL expression in murine primary osteoblasts from the calvaria boneviaJAK2-STAT3 signaling, which depends on cell autophagy in an IL-17 dose-dependent fashion. Low doses of IL-17 induced autophagy, while high doses activated JAK2-STAT 3 signaling, which could be reversed by autophagy induction with the mTOR inhibitor rapamycin[119]. Conversely, autophagy inhibition by the phosphoinositide-3 kinase (PI3K) inhibitor 3-methyladenine greatly enhanced IL-17-induced JAK2-STAT3 signaling. Furthermore, high IL-17 levels promoted ALP induction and mineralization of osteoblast progenitor cells. This treatment also increased the opg and rankl mRNA transcripts levels, and OPG and RANKL proteins were found along with a decreased OPG/RANKL expression ratio. Thus, IL-17A, depending on the dose, may regulate bone turnover,i.e., osteoblastogenesis/osteoclastogenesis balance, by modulating the OPG/RANKL ratio[119].
Furthermore, IL-17A can interact with and potentiate the osteoblastic function of other inflammatory factors such as TNF-α. When used in combination, IL-17A and TNF-α further enhance ALP activity and matrix mineralization. Moreover, this combination synergistically induced the expression of Schnurri-3, a finger protein that plays a critical regulatory role in skeletal remodeling[120] and inhibits RANKL expression associated with osteogenic induction. Furthermore, IL-17A and TNF-α combination increased the type II TNF receptor (TNFRII), which may explain the synergistic effects on the osteoblastic differentiation of MSCs[121]. Similar effects of combined IL-17A and TNF-α are observed on fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) isolated from RA and OA patients, albeit with different potency[122].
Meanwhile, in OA, simultaneous bone destruction and osteophyte formation were observed and related to a reduced joint destruction rate[123]. Namely, FLS are cells of mesenchymal origin and are the dominant nonimmune cells in synovial tissues, vital elements in defining the stromal environment within arthritic bone diseases[124]. Both RA- and OA-derived FLS can perform bone mineralizationin vitroand express Wnt5a under chemical induction, and IL-17A addition further potentiates differentiation. In addition, RA bone explants inex vivoassays showed that IL-17A alone or in combination with TNF-α generates a significant decrease in bone volume over the total volume (BV/TV) ratio, while in OA bone explants, only the combination decreased BV/TV ratio. Besides those specific differences, IL-17A enhances TNF-α-induced osteoblastogenesis in both RA and OA-derived FLS[125].
Interestingly, IL-17A switches the differentiation fate of murine mesenchymal progenitor C2C12 cells. IL-17A strongly promotes osteogenic differentiation in cells cultivated in a myogenic medium mediated by ERK1,2 pathway activation and Runx2 transcriptional activity[112,126]. Moreover, IL-17A strongly inhibits myogenic transcription factor expression and reduces cell migration and urokinase-type plasminogen activator expression[127].
Moreover, IL-17A positively exerts osteogenic induction on murine calvaria progenitor osteoblastic cells under incubation with osteogenic media, since IL-17A further stimulates mineralization, along with mRNA expression of ALP (Alp), OSX (Sp7), bone sialoprotein (Ibsp), and OPN (Spp1). Furthermore, IL-17A significantly enhances healing and bone tissue formation in a mouse calvaria defect model under beta-tricalcium phosphate treatment[128]. Furthermore, IL-17A effectively induces osteogenesis in the spontaneously immortalized murine calvaria pre-osteoblast cell line MC3T3-E1, a widely used model for studying osteoblast biology[129]. For instance, IL-17A, under chemical osteogenic induction, potentiates MC3T3-E1 differentiation towards osteoblastic lineage by activation of PI3K-RAC-β serine/threonineprotein kinase (AKT2). In turn, AKT2 knockdown makes MC3T3 E1 unresponsive to osteogenic induction by IL-17A since Runx2, ALP, OCN, and relative ALP activity and mineralization are almost entirely impaired in these cells[130].
Furthermore, IL-17A synergizes with IL-6 to induce ALP activity on osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 seeded on hydroxyapatite while increasing the expression of OPG and reducing the expression of RANKL, thus increasing the OPG/RANKL ratio and suggesting the potential to reduce osteoclastogenic response[131]. The main aspects of IL-17A-induced osteogenesis are summarized in Table 1.
Other IL-17 family members also have the potential to regulate MC3T3-E1 osteoblastogenesis. Indeed, IL-17F induced osteogenic differentiation by enhancing ERK1,2/C/EBP-β/Runx2 activity[132]. This observation was confirmed by Croeset al[114] in anin vitrostudy where human MSCs increased ALP activity in a dosedependent response to IL-17.
In addition to osteoblastogenesis promotion, IL-17A conversely affects adipogenesis and chondrogenesis in MSCs. Indeed, IL-17A inhibits the adipogenic differentiation of human MSCs and enhances lipolysis of differentiated adipocytesviaupregulation of cyclooxygenase-2 expression and a subsequent increase of anti-adipogenic prostaglandin E2[133]. Noh[134] discovered that IL-17 inhibits human BM-MSC adipogenesis and promotes osteogenesis by upregulating the leptin-JAK/STAT pathway. Also, IL-17A may inhibit adipogenic differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells, a model for adipocyte differentiation, by suppressing pro-adipogenic PPARγ, C/EBPα, and transcription factor Krüppel-like factors (KLF)-15 expression, while enhancing anti-adipogenic KLF2 and KLF3 expression[135].
Moreover, IL-17A inhibits TGF-β3-induced chondrogenic differentiation of human MSCs, mediated by impaired protein kinase A activity with a consequent reduction in SRY-type HMG box9 (SOX9) phosphorylation transcriptional activity. As a consequence, chondrogenesis-associated type II collagen (COL2A1), aggrecan (ACAN), type X collagen (COL10A1), andALPare dose-dependently suppressed by IL-17A[136].
THE ANTI-OSTEOGENIC ROLE OF IL-17A
In contrast to the aforementioned pro-osteogenic function of IL-17A, several studies indicated an anti-osteogenic function of IL-17A (Table 2). IL-17A inhibits proliferation and migration and the osteogenic differentiation of healthy periodontal ligament stem cells through ERK1,2 and JNK MAPK[137]. Similarly, IL-17 suppresses humanperiodontal ligament stem cell osteogenic differentiation (by reducing ALP activity, Runx2, SP7, and OCN expression). However, in that case, inhibition of MAPK activation (ERK1,2, p38, and JNK) was involved[138].
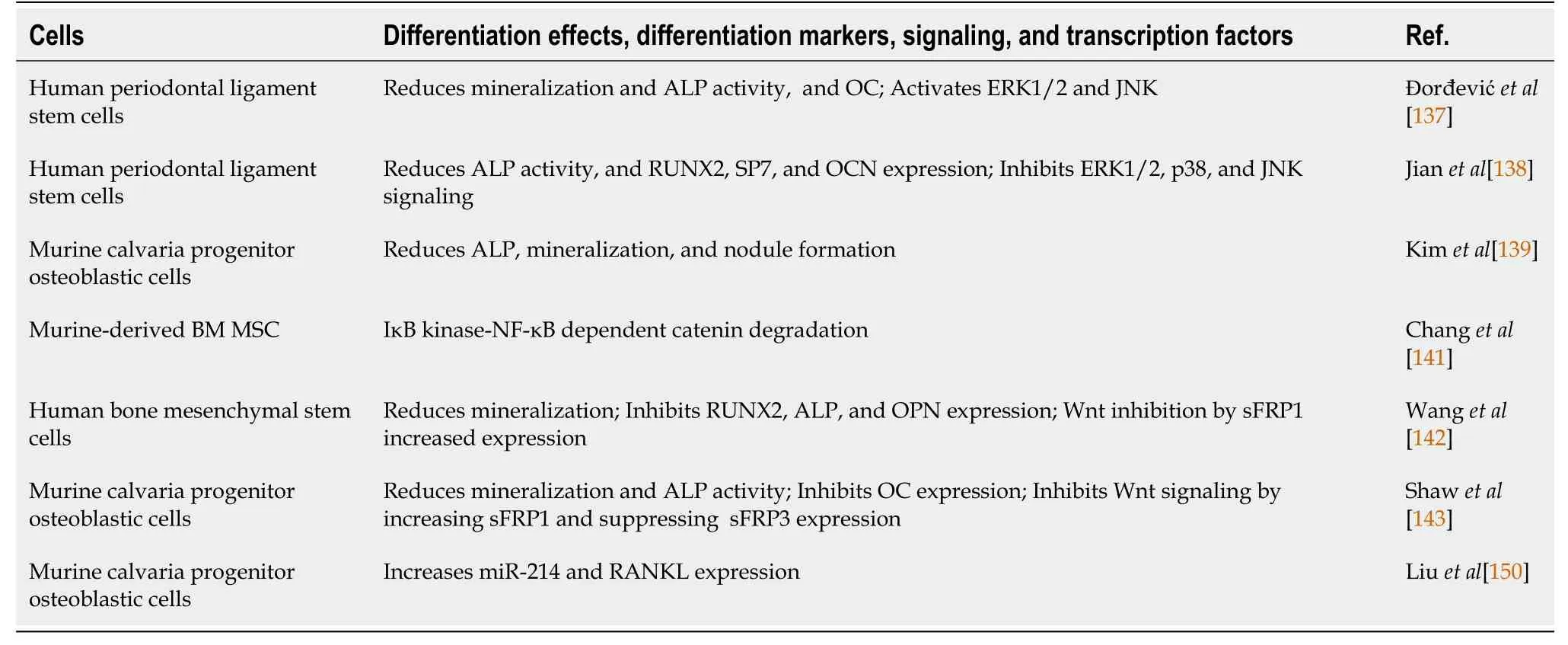
Table 2 Interleukin-17 inhibits osteogenesis: Summary of the main literature data
IL-17A also inhibits osteogenic differentiation of calvaria osteoblast precursor cells upon chemical inductionin vitro, as evidenced by reduced ALP expression, mineralization, and nodule formation. Accordingly, IL-17 significantly delayed thein vivofilling and repairing calvaria defects[113,139]. Furthermore, NF-κB reduces osteoblasts’ capacity forin vivoosteogenic differentiation in a murine periodontal infection model, where IL-17A induced NF-κB transcriptional activity in osteoblasts and osteocytesin vitro[140]. Consistent with this, IL-17A inhibits murine MSC osteogenic differentiationviaIκB kinase (IKK)-NF-κB dependent b-catenin degradation. Moreover, IKK-NF-κB inhibition greatly enhances MSC-mediated bone formationin vivo[141]. Consequently, healthy BM-MSCs treated with IL-17 showed impaired osteogenic differentiation when induced with a chemical osteogenic differentiation medium. In addition, IL-17A inhibits Runx2, ALP, and OPN expression and mineralization.
Besides osteogenic inhibition, IL-17 treatment provoked Wnt factor inhibition and increased the Wnt signaling pathway inhibitor sFRP1, a member of the secreted, frizzled-related protein, which mediates IL-17 effects[142]. Similarly, Shawet al[143] demonstrated that IL-17A inhibits calvaria osteoblastic differentiationin vitroby inducing sFRP1 and suppressing the expression of sFRP3, a decoy Wnt receptor that may stimulate differentiation through a b-catenin-independent pathway[144]. Interestingly, a study in psoriasis patients indicated that bone loss and low bone formation were correlated with increased serum IL-17A levels. Indeed, two mouse models with chronic IL-17A-mediated skin inflammation showed bone loss and impaired osteoblast activity, whereas keratinocytes, γδT cells, and innate lymphoid cells expressed IL-17A, therefore systemically inhibiting both osteoblast and osteocyte function.
Furthermore, IL-17 treatmentin vivoandin vitroinhibited osteoblast differentiation due to Wnt signaling downregulation, while specific IL-17A blocking antibodies ameliorated bone loss and Wnt signaling[145]. Another potential mechanism linking IL-17A to Wnt signaling reduction could be sclerostin (SOST) upregulation. SOST inhibits the Wnt signaling pathway and bone generation[146]. In coculture conditions, SOST overexpression in adipose-derived MSCs (ADSCs) promoted CD4 T cell differentiation toward Th17 cells expressing IL-17A, concomitantly with ADSCs’ impaired osteogenesis and enhanced adipogenic differentiation capacity. Exogenous IL-17A further enhanced ADSCs, overexpressing SOST osteogenic inhibition capacity and promoting adipogenic differentiation[147].
Additionally, IL-17A plays a role in secondary osteoporosis in SLE patients. Human BM-MSCs and SHED transplantation recover bone density and ameliorate structure reduction in MRL/lprmice. The transplantation of human MSCs restores impaired functions and the bone metabolism of recipient mouse BM-MSCs/osteoblasts. The Murine MRL/lprmodel resembles human SLE disorder, with clinical manifestations due to a Faslprmutation that promotes self-reactive lymphocytes’ survival[148]. MSCs’ effects mainly rely on suppressing abnormal BM IL-17A production in recipient MRL/lprmice, as further confirmed by systemic IL-17A blockage by specific antibodies. The authors suggested two potential mechanisms to explain the MSCs’ transplantation effects: MSC integration and differentiation into functional osteoblasts contribute directly to bone regeneration, or proinflammatory cytokines can impair bone regeneration. Therefore, MSCs’ anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects may regulate IL-17A production by immune cells at bone defect sites[149].
It has recently been reported that microRNA mir-214 mediates the capacity of IL-17A to inhibit primary murine calvaria osteoblast differentiationin vitro[150]. MiR-214 inhibits osteogenesisin vivoandin vitro[151], and IL-17A increases osteoblast miR-214 production and RANKL expression, promoting osteoclast differentiation in coculture conditions due to the reduction of the OPG/RANKL ratio. Furthermore, knockout miR-214 in osteoblasts decreasedin vivoosteoclastogenesis. Interestingly, AS patients who manifest bone loss have elevated IL-17A and miR-214 Levels in the serum and synovial fluid, indicating their potential diagnostic value in AS[150].
CONCLUSION
Bone tissue formation and regeneration are highly susceptible to microenvironmental factors that regulate the delicate balance between bone synthesis and resorption. An inflammatory response may influence the proper local cell differentiation after a bone injury to accurately regenerate the tissue. Inflammation precedes bone repair and is crucial for bone healing. As a proinflammatory cytokine, IL-17A is produced at high levels, and its release after bone damage can influence MSCs’ fate into early osteoprogenitor/osteoblast cells, which further contributes to bone regeneration and full functional recovery. Despite IL-17’s capacity to drive the osteogenic commitment of MSCs, it can also function as an anti-osteogenic factor that causes bone loss. Although these divergent IL-17A roles in bone formation are still not well understood, various conditions arising from the local microenvironment, the magnitude of inflammation, and the specific nature and stage of osteoprogenitor cells can influence the directionality of IL-17A’s function, resulting in specific differentiation outcomes.
From a molecular point of view, it is possible to speculate that two mutually antagonistic signaling pathways in osteogenesis may influence the capacity of IL-17 to function as either a pro-osteogenic or anti-osteogenic factor. In this sense, we hypothesize that, depending on the cell source and culture conditions, the activation of the pro-osteogenic Wnt pathway or the anti-osteogenic NF-κB signaling can regulate the cell decision in response to IL-17[84,152]. Thus, if NF-κB prevails, elevated levels of Wnt inhibitors, sFRPs, and SOTS expression are promoted and may trigger b-catenin degradation, whereby IL-17 is acting as an anti-osteogenic factor. Conversely, if cells exhibit low NF-κB activity, the Wnt pathway can freely operate, and IL-17, in cooperation with this signaling, may function as a pro-osteogenic factor. Accordingly, one potential candidate for controlling NF-κB signaling is IL-10[153], also produced by MSCs[154]. The levels of IL-10 in cell culture may influence NF-κB signaling activity[155] and, thereby, drive IL-17’s effect on MSC osteogenic fate. However, this hypothesis needs to be experimentally confirmed.
Moreover, the dual roles of IL-17A might result from species-specific characteristics of MSCs and MSC-derived osteoblasts due to the interplay of various microenvironmental issues that condition IL-17A’s effects or mode of action at the cellular level. Although it is clear that IL-17A profoundly affects osteogenic differentiation, further standardized studies are necessary to determine how osteogenic differentiation is either positively or negatively regulated and when IL-17 acts as a pro-osteogenic or anti-osteogenic cytokine. Finally, a deep understanding of the precise inflammatory and tissue conditions may help design better therapeutic strategies for IL-17Aassociated bone diseases.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We apologize to those colleagues whose work, although relevant to the topic of this review, has not been included due to space limitations. We also thank the support of the visiting professor program of UBO to Santibanez JF.
杂志排行
World Journal of Stem Cells的其它文章
- Priming strategies for controlling stem cell fate: Applications and challenges in dental tissue regeneration
- Epigenetic regulation of dental pulp stem cells and its potential in regenerative endodontics
- Effects of immune cells on mesenchymal stem cells during fracture healing
- Why stem/progenitor cells lose their regenerative potential
- Nanofat: A therapeutic paradigm in regenerative medicine
- Application of adipose-derived stem cells in treating fibrosis
